Posterior Pituitary Hormones
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Mechanism of Bromocriptine
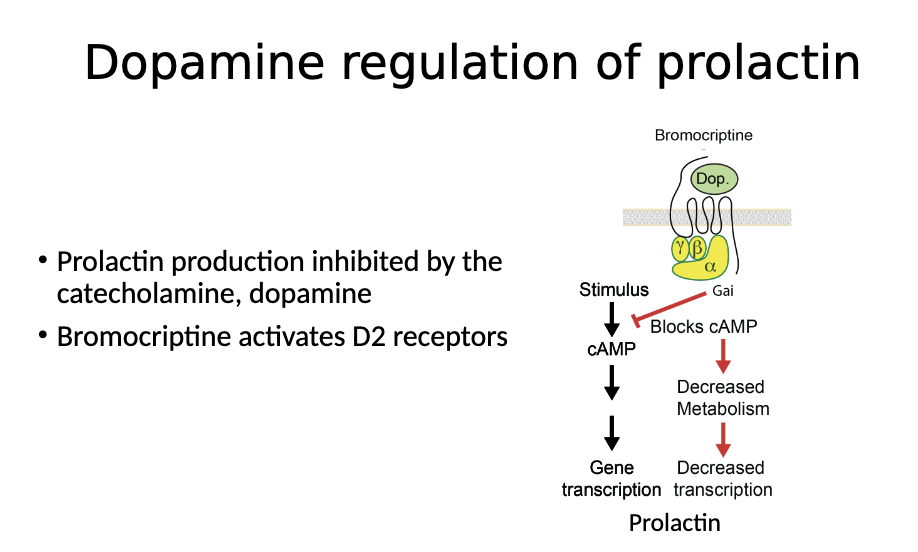
Dopamine agonist —> stops cAMP and decreases transcription of prolactin
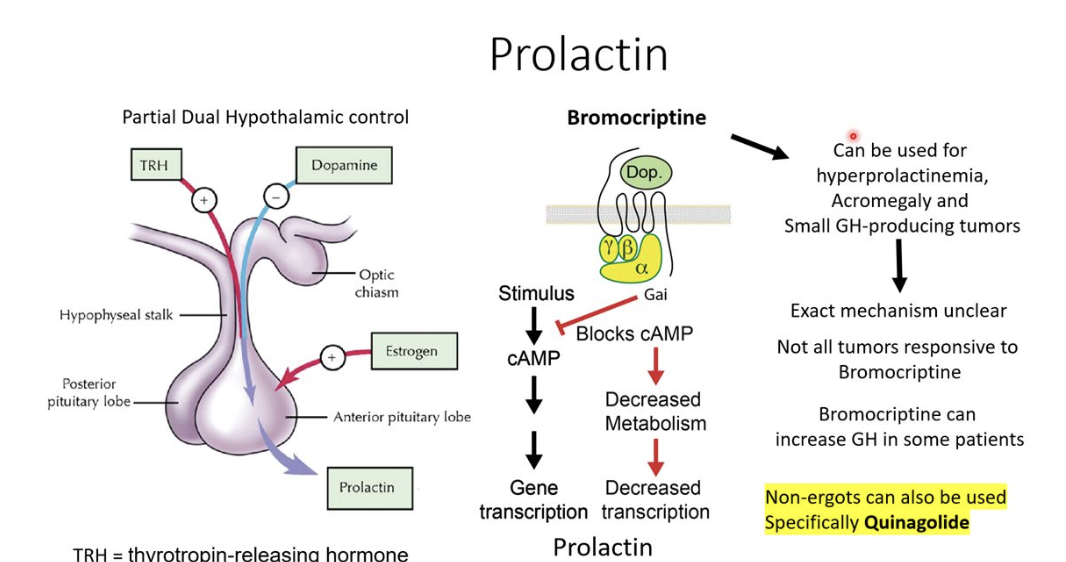
Use of bromocriptine
Used for hyperprolactinemia
Acromegaly
Small GH producing tumors
How does prolactin modulate GnRH and Estrogen
Prolactin can negatively affect GnRH, which will in turn decrease FSH and LH production, which can decrease estrogen production
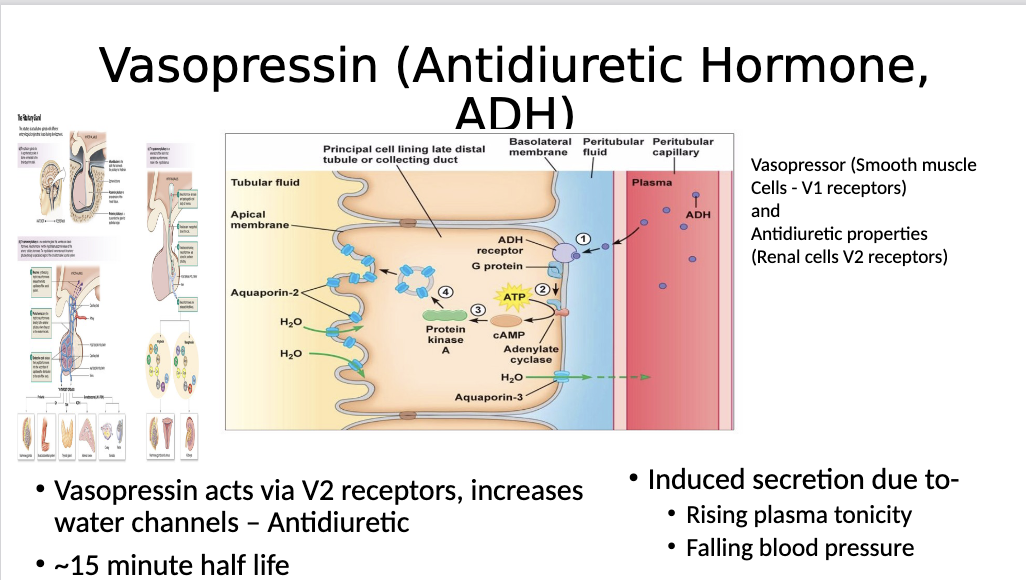
Does vasopressin induce water retention or water elimination?
Goal of vasopressin is to increase BV:
Therefore, we would increase water retention via
Controls aquaporin tubes via GPCR cAMP
ADH binds to its receptor in the collecting ducts. When the blood delivers vasopressin -> triggers cAMP - moves tubes to the membrane and water is reabsorbed into the body
A 7-year-old boy underwent successful chemotherapy and cranial radiation for Treatment of acute lymphocytic leukemia. One month after the completion of therapy, the patient presented with excessive thirst and urination plus hypernatremia. Laboratory testing revealed pituitary diabetes insipidus. To correct these problems, this patient is likely to be treated with which of the following?
A. Corticotropin
B. Desmopresin
C. hCG
D. Menotropins
E. Thyrotropin
HYPERnatremia = high salt
We want to reabsorb water yes? How do we do that? Vasopressin analogue IE increase water reabsorption via desmopressin
Vasopressin antagonists
Conviaptan and Tovaptan
What 2 hormones are released by the posterior pituitary
Oxytocin and Vasopressin
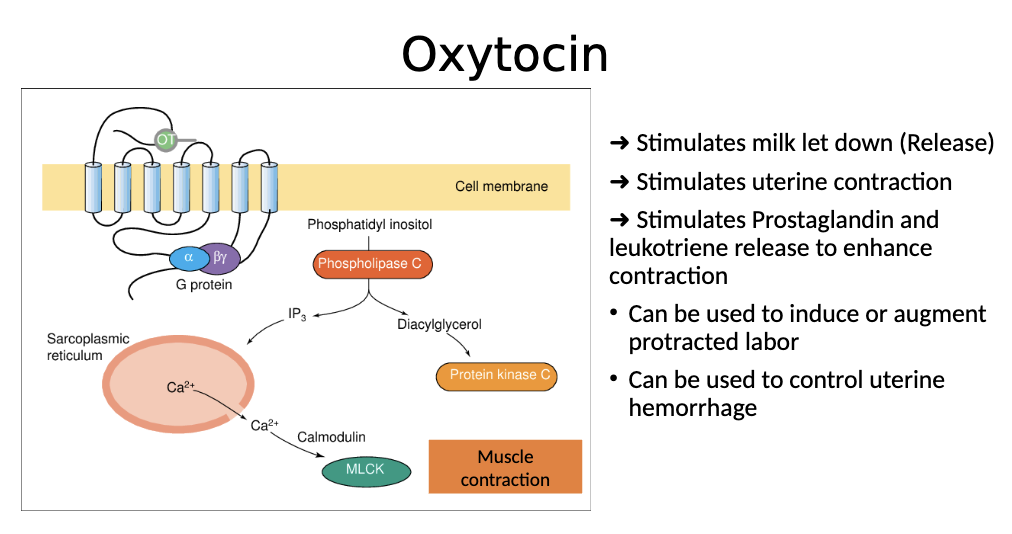
Oxytocin receptors activate:
GPCR, triggers IP3 and phospholipase C —> increase influx of calcium —> stimulates muscle contraction
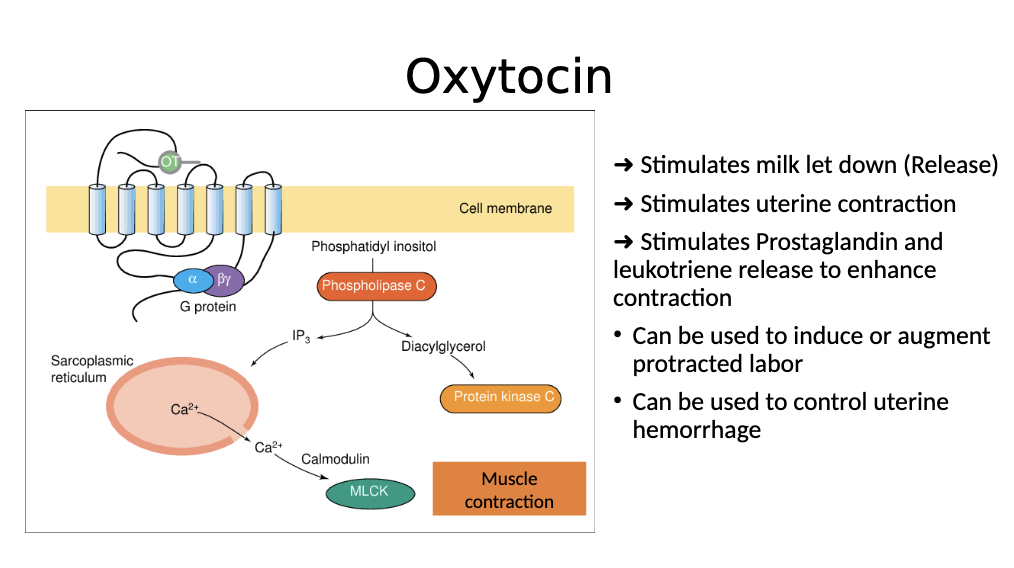
Oxytocin leads to
Milk stimulation, uterine contraction
Prostaglandin and leukotriene release
Induce labor
Oxytocin antagonist
Atisoban
Nifendipine is a CCB used for this purpose but is controversial
Vasopressin MOA?
ADH binds to the receptor and activates adenylyl cyclase → cyclic AMP → protein kinase a → movement of aquaporins to the apical membrane (the side with the pee). This allows for more water to move out of the collecting duct back into the blood for reabsorption. (Diuretics block this and make us pee to lower BP)
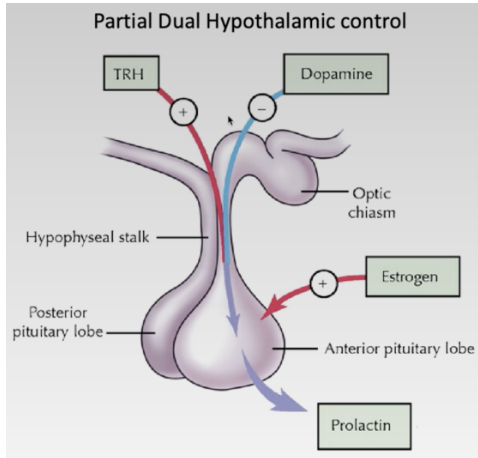
Role of prolactin?
Principle hormone for lactation, stimulated by circulating estrogen, progestin, corticosteroids, and insulin
Mediators of prolactin
Prolactin does not have a direct hypothalamic releasing hormone, but it can be regulated by other hormones
TRH can increase prolactin
Estrogen can increase prolactin
Dopamine can block prolactin
Excess prolactin leads to:
Fertility problems (alters feedback mechanism of estrogen and can alter ovulation, as estrogen excess can lead to GnRH inhibition)
Loss of libido
Causes of prolactin secretion:
PRL stimulation in primary hypothyroidism or adrenal insufficiency
Increase PRL production can occur via pituitary tumors or PCOS
Pregnancy
Hepatic insufficiency or renal failure (reduced clearing of prolactin)
Effect of opiates and neuroleptics on dopamine:
These typically inhibit dopamine release. If dopamine typically negatively affects prolactin release, then removing the inhibitor allows for less downregulation of dopamine and thus increase dopamine levels. (hyperprolactinemia is a side effect of antipsychotics)
Effect of bromocriptine on prolactin?
Bromocriptine is a dopamine agonist
Dopamine activates gai to block cAMP production. This decreases the transcription of prolactin and suppresses prolactin release
This reduces prolactin expression
Therapeutic use of bromocriptine
Dopamine receptor agonists reduce PRL
Can shrink pituitary prolactin secreting tumors
Examples of dopamine agonists:
Bromocriptine, cabergoline (ergot derivative)
Quinagolide, pramipexole, ropinirole (nonergot) ← antiparkinson treatment, give them dopamine and anticholinergics
What neurohormone is released in the anterior pituitary but acts directly on its target organs?
Prolactin
How is oxytocin activated?
Activates GPCR, which activates Phospholipase C → IP3 pathway → , which results in release of calcium, which leads to muscle contraction. This releases milk and stimulates uterine contraction and stimulates prostaglandin and leukotriene release
Therapeutic use of oxytocin
Release milk, induce labor
Can be used to control uterine hemorrhage
What is a physiological trigger that will release vasopressin
Release is triggered by rising tonicity (high salt in the blood will trigger the reabsorption of water) or falling BP
Released by the kidney to increase water retention
ADH activates a GPCR adh receptor. This enhances cAMP to activate PKA, which triggers the movement of aquaporins (water channels) to move to the apical membrane. This induces water reabsorption to increase BP
Modified vasopressin analogue:
Desmopressin, long lasting analog and more selective to V2
Desmopressin therapeutic use:
Can be used to treat mild hemophilia A
Diabetes Insipidus (inability to control water levels in the blood due to pituitary insufficiency)
Use for vasopressin antagonists
Used in hyponatremia, antagonize the binding of add to the receptor and block the reabsorption of water. This increases excretion and increases the tonicity of the blood by removing the water volume to concentrate the blood with more salt