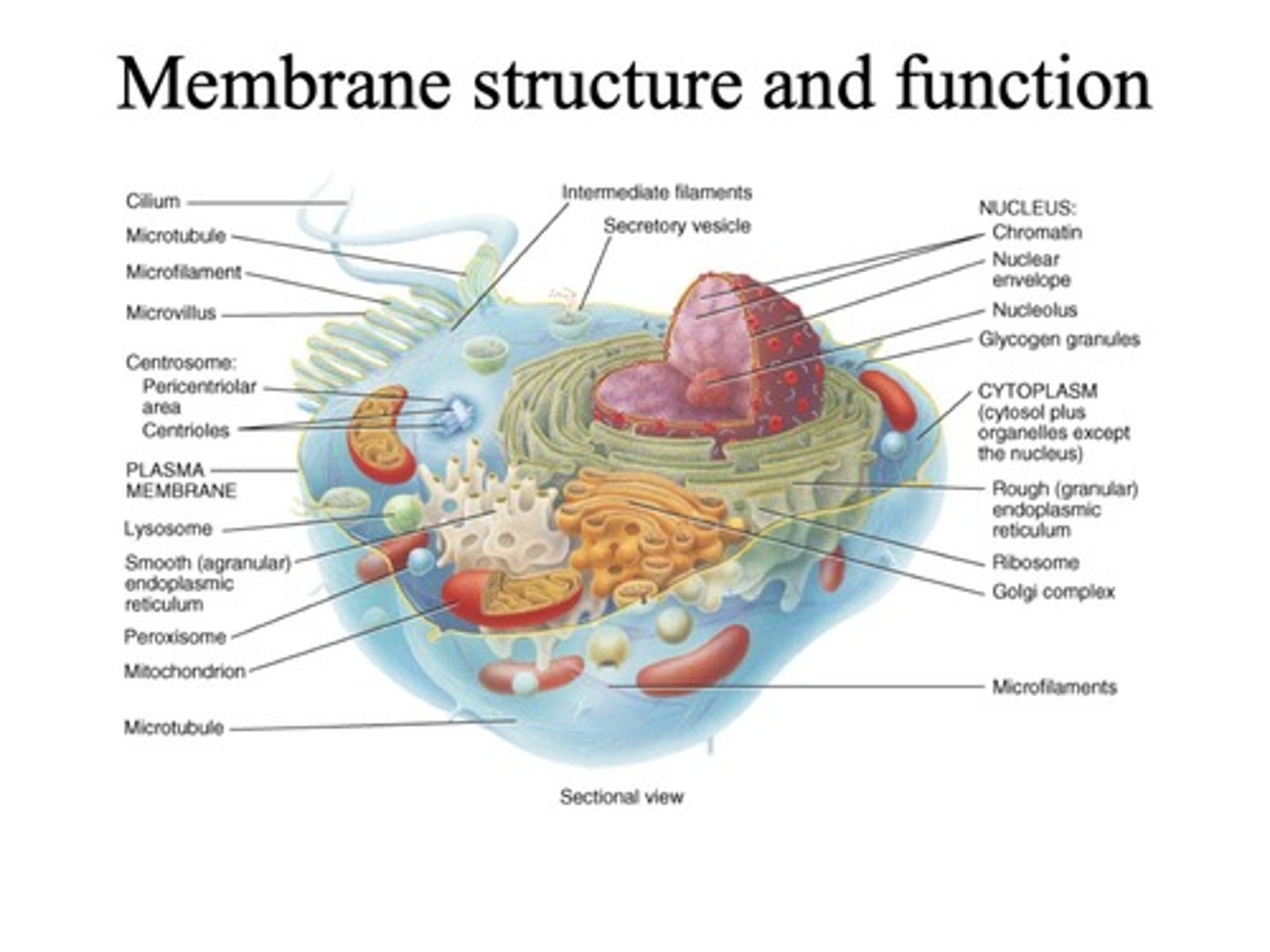
Cell Membrane Structure and Function in Biosci107
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Fluid Mosaic Model
Membrane structure described as lipids and proteins.
Selective Permeability
Membrane allows certain substances to cross.
Phospholipids
Comprise 75% of membrane lipids.
Phospholipid Bilayer
Two parallel layers of phospholipids.
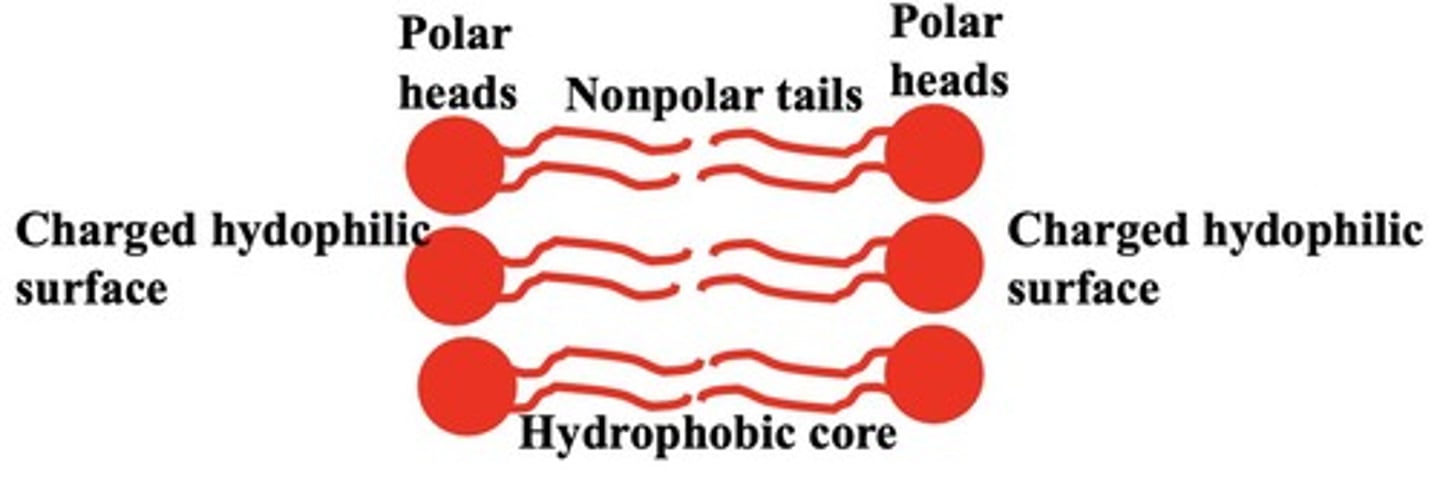
Amphipathic Molecules
Molecules with both polar and nonpolar regions.
Membrane Fluidity
Ability of lipids to move within membrane.
Lipid Tail Length
Longer tails decrease membrane fluidity.
Double Bonds in Lipids
More double bonds increase membrane fluidity.
Cholesterol's Role
Increases membrane stability, decreases fluidity.
Integral Membrane Proteins
Proteins that span the lipid bilayer.
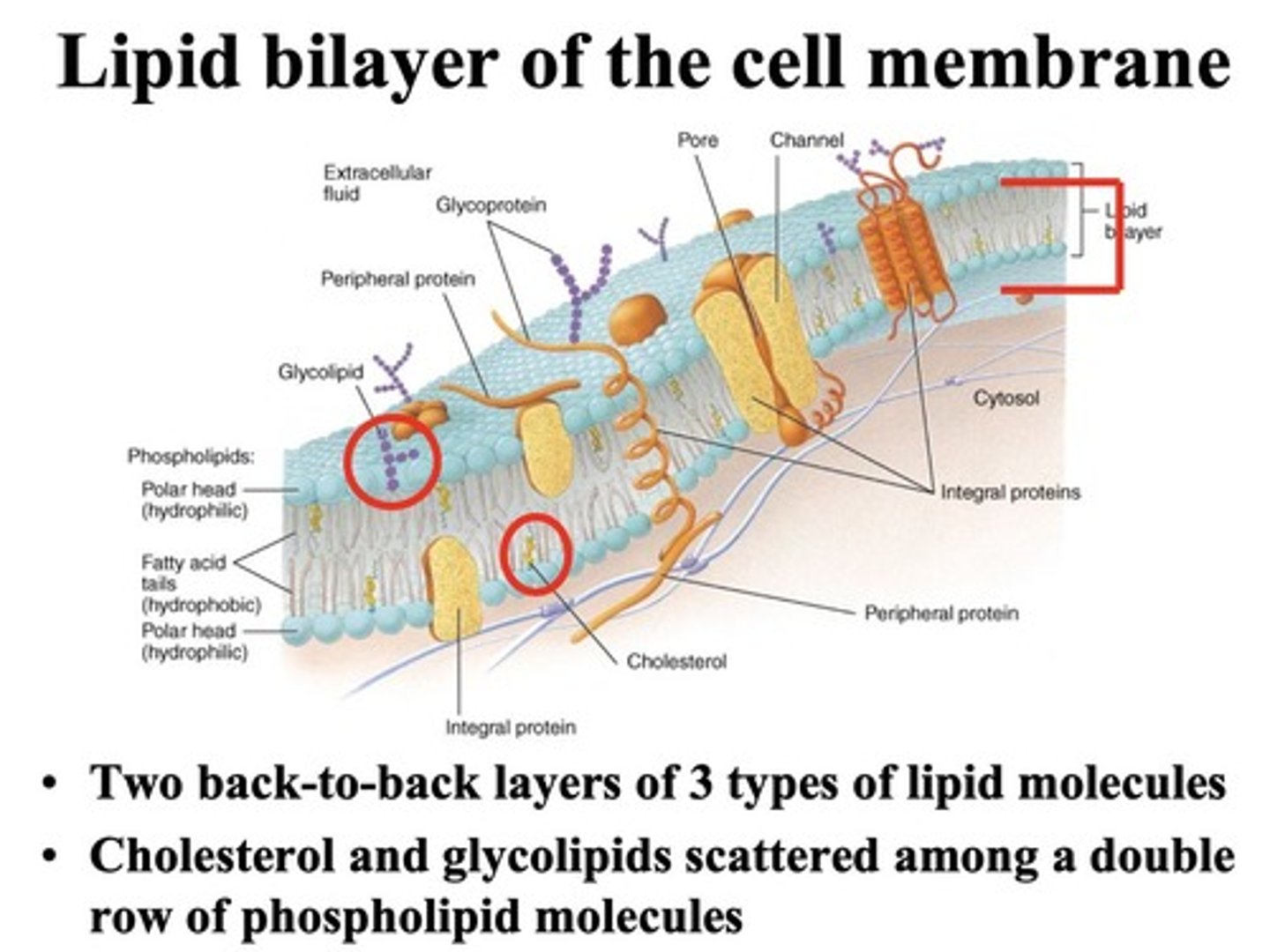
Peripheral Membrane Proteins
Proteins attached to membrane surface.
Receptor Proteins
Proteins that receive chemical signals.
Transporter Proteins
Proteins that facilitate substance movement.
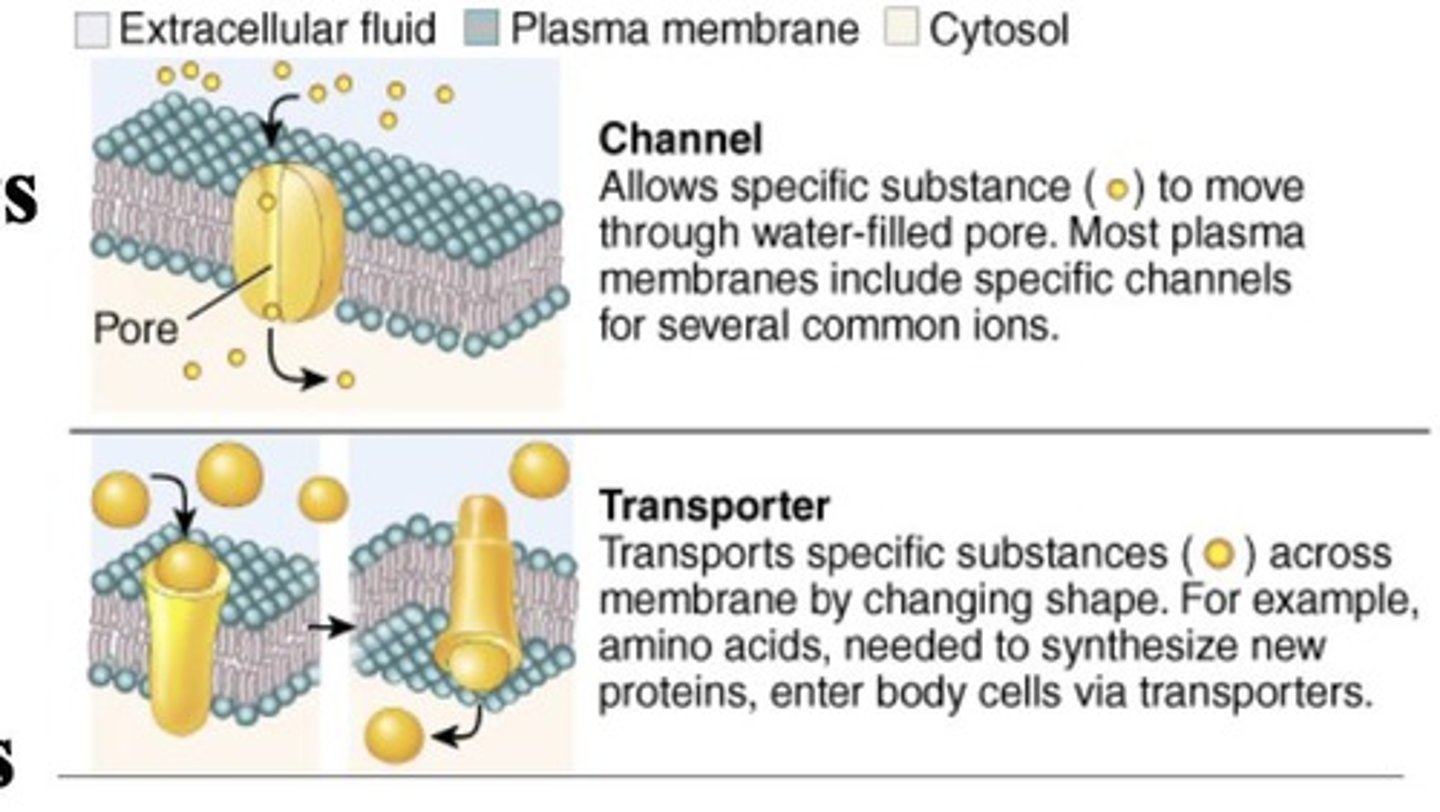
Ion Channels
Proteins that allow ion passage through membranes.
Diffusion
Movement from high to low concentration.
Equilibrium in Diffusion
Even distribution of particles in a solution.
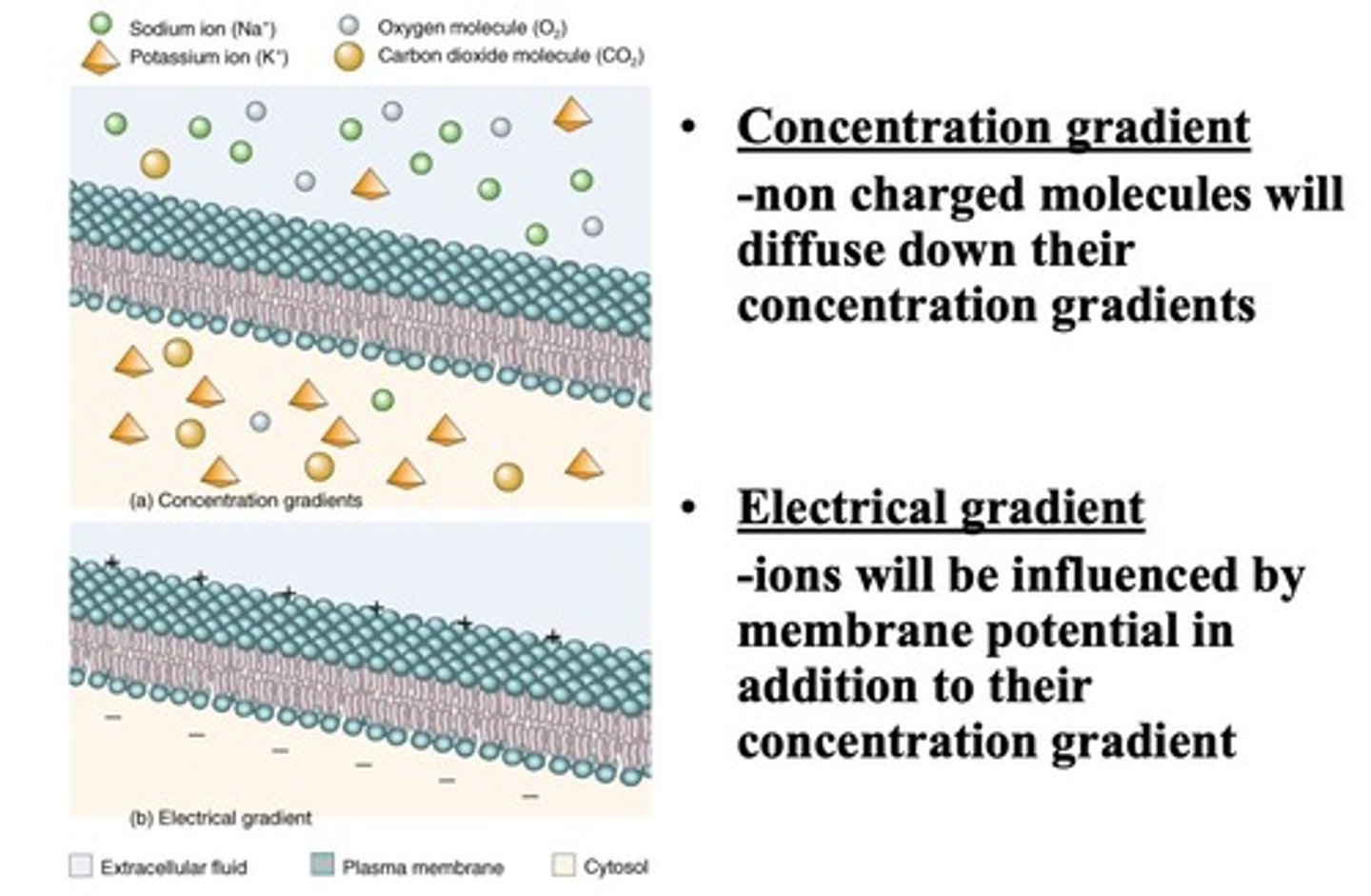
Concentration Gradient
Difference in concentration across a membrane.
Osmosis
Water movement across a selectively permeable membrane.
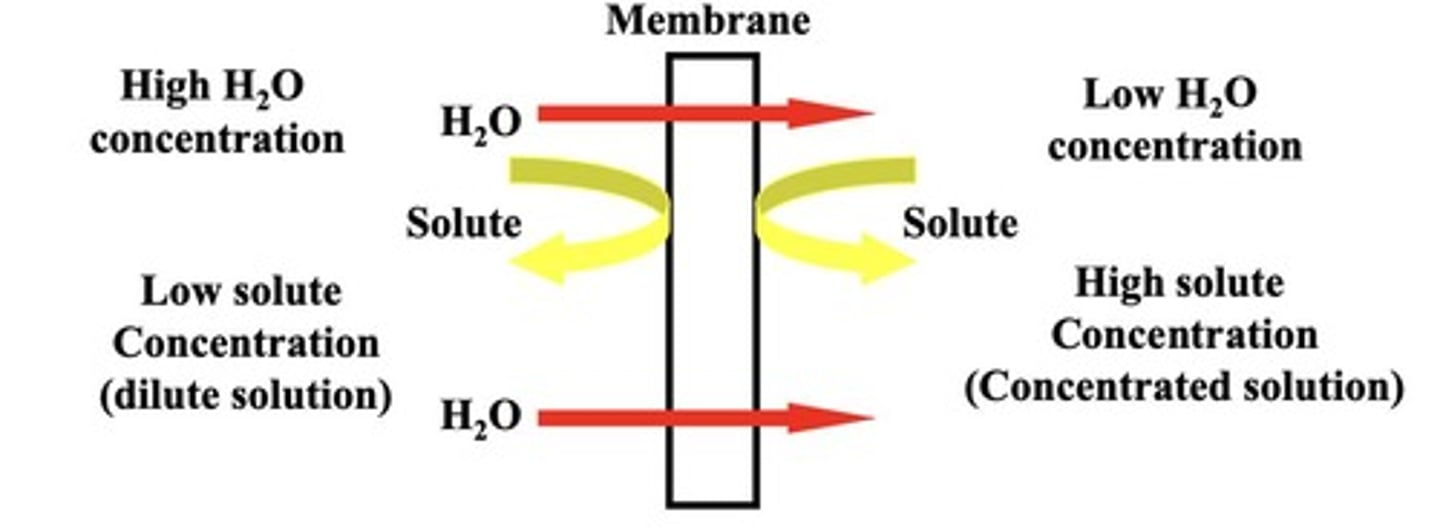
Aquaporins
Proteins that facilitate water transport.

Osmotic Pressure
Pressure preventing water flow across a membrane.
Membrane Potential
Electrical gradient across the cell membrane.
Electrochemical Gradient
Influence of charge and concentration on ion movement.
Diffusion Distance
Greater distance slows the rate of diffusion.
Cell Size Limit
Rate of diffusion limits cell size to 20 µm.