metabolic stress, inflammation, and cancer
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
lecture 2, prof zani
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
adipocytes
fat cells
white adipose tissue (WATs) are most common
WAT function
release signals into blood for communication
eg leptin is secreted to tell you ur full
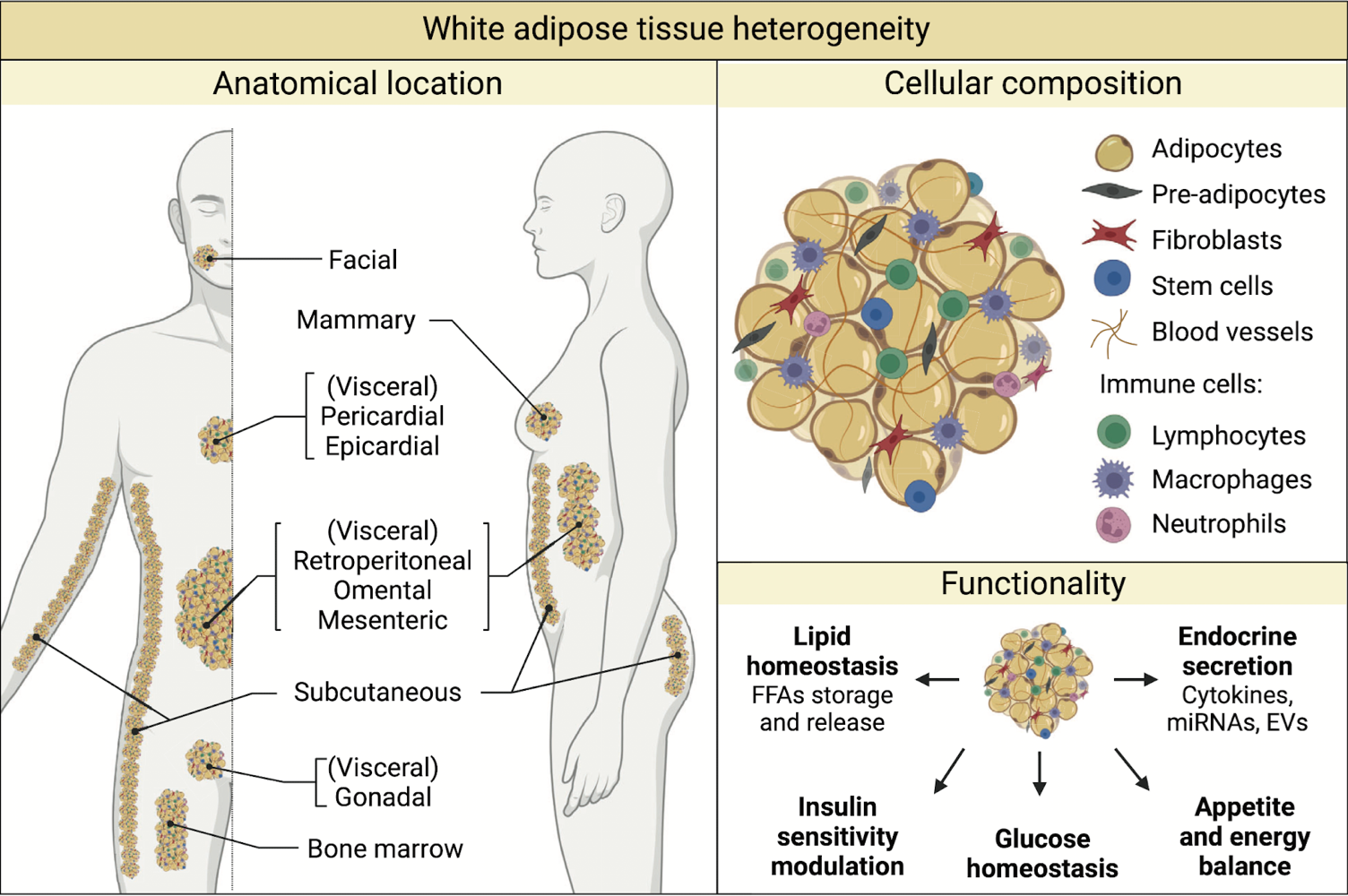
where are WATs found in body?
all over
face
mamary
visceral in chest and abdomen
subcutaneous areas
bone marrow
obesity
excessive fat accumulation that presents a health risk
35% rate in canada
BMI vs alternatives
very convenient but not an accurate indication of health
mass/height squared
dexa scans and waist-hip ratios are more accurate
what does obesity increase the risk of
inflammation
cardiovasuclar disease
diabetes
13 types of cancer
obesity impact on adipose tissue function
inflammation makes it hard for WAT to store energy well
can develop fatty liver
size and quanittiy of adipocytes increases
cancer cells impact on adipocytes
corrupt adipocytes and convince them to release lipids and endocrine factors to be used for metastisizing and prolifeeration
why is prof zani choosing to look at pancreatic cancer
PC invades WAT
adipocytes can infiltrate the pancreas
PC is linked to obesity
what are KVAT
genetically engineered mice
how are KVAT being studied for PC and adipocyte interaciton?
isolated PC tissue cells from KVAT are given tissue calcium feed
there was sufficient growth w/o adipocytes
now given poor feed with access to adipocytes
PC cells proliferate more than before
what impact does an adipocyte conditioned medium have on PC cell growth? why?
promotes cell growth
could be
cancer cells corrupting adipocytes
adipocytes release endocrine factors on their own that can be taken advantage of
which adipocyte secreted factors help the cancerous cells?
metabolites such as polar sugars and amino acids were identified in the adipocyte conditioned medium
does obesity increase the amount of metabolies secreted by adipocytes
we’re looking into it
how do artifical sweeteners work?
they activate the sweet taste receptor but we cannnot digest them
have sucralose which is 600 more times sweet than sucrose
0 caloried
sweet taste receptor
key receptor is a 2 unit G-coupled protein receptor
T1R2 and T1R3
present in many cells, not just mouth
what do sweeteners increase risk of?
cancer
cerebrovascular events
coronary heart disease
sucralose impact on T cells
dampens T cell (CD4+ and CD8+) proliferation
delays tumour rejection (autoimmunity)
how did Zani confirm that sucralose is really whats impacting T cell function?
test tumour growth in 2 mice: one immunodeficient (no t cells) and one immunocompetent
in the tcell lacking mouse, the tumour growth was the same with our without sucralose
in the immunocompetent mouse, tumour growth increased with sucralose