REG CPA EXAM STUDY GUIDE: R1
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
138 Terms
Filing Requirements: Who
Who - Must file if income is equal to or greater than the sum of the:
- Regular Standard Deduction Amount
- Additional Standard Deduction Amount
*must also file if self-employment income is $400+
Filing Requirements: When
When - Taxpayers must file by April 15th
*Extension to file is for 6 months to October 15th
- Extension to file, not pay taxes; must pay taxes by April 15th still
- Fill out Form 4868
Filing Status: Single
- On the last day of the tax year, they are unmarried or legally separated
*Based on end of year status
Filing Status: Joint Returns
Must be:
A) Married at Year-end
B) Living together in a common law marriage
C) Married and living apart (but not legally separated)
*Based on end of year status
*If divorced during the year -> Joint Return may NOT be filed
*If spouse dies during the year -> Joint Return may be filed
Filing Status: Married Filing Separately
- In a separate property state -> Separately report own incomes
- In a community property state -> Most incomes are split 50.50
Filing Status: Qualifying Widow(er) with Dependent Child
- Taxpayer who may use the joint tax deduction for two years following death
- Spouse must pay over half of support and lives for the WHOLE year
- Dependent child must be a child (adopted but not fostered) or stepchild
Filing Status: Head of Household
Single but takes care of dependent
Must be:
A) Person is unmarried, legally separated, or married living away for 6 months
B) Individual is not a "qualifying widower"
C) Person is not a nonresident alien
D) Maintains a home for more than HALF the taxable year
Qualifying Child - child, stepchild, legally adopted, foster, sibling, or descendent
Parents - dependent parent is not required to live with taxpayer, but taxpayer must contribute to at least half of their costs
Dependent Relatives - must live with taxpayer (grandpa, siblings, aunts)
* Cousins, foster parents and unrelated dependents do not qualify
Taxable Interest Income (Gross Income)
- Interest from federal, industrial development, and corporate bonds
- Part of the proceeds from an installment sale
- Interest paid by government for late payment of a tax refund
- Bond premium -> reduction to interest received and bond basis
- Bond discount -> addition to interest received and bond basis
- Gifts given by banks for opening an account are taxable @FMV
Tax-Exempt Interest Income (Gross Income - Reportable but not taxable)
- State and Local Governments Bonds/Obligations
- Bonds of US Possession (Guam or Puerto Rico)
- *US Series EE Savings Bonds (Educational Expenses)
* is tax-exempt when issued after 1989 and:
1) Is used to pay for higher education of taxpayer and dependents
2) The taxpayer is over age 25 when the bond is issued
3) Married taxpayer files a joint return
4) The taxpayer meets certain income requirements
5) Purchases of the bonds must be the sole owner of the bonds
* is Phased out when modified AGI reaches a certain level
Single/HOH: $96,800-$111,800 || MFJ: $145,200-$175,200
IRA Distributions (Gross Income): Traditional Deductible IRA
Principal -> Taxable
Earnings ->Taxable
IRA Distributions (Gross Income): Traditional Nondeductible IRA
Principal -> Nontaxable
Earnings -> Taxable
IRA Distributions (Gross Income): Qualified Roth IRA
Principal -> Nontaxable
Earnings -> Nontaxable
IRA Distributions (Gross Income): Nonqualified Roth IRA
Principal -> Nontaxable
Earnings -> Taxable
Qualified Rother IRAs Distributions
Must be:
1) Distribution is made after at least 5 years of first contribution
2) One of the following other requirements:
a) Taxpayer is age 59.5 to older
b) Taxpayer is disabled
c) Taxpayer is a first-time home-buyer and is using the funds to buy a house
d) Distribution is made after taxpayer's death
* Premature distribution is subject to a 10% penalty tax
Exception to IRA Penalty Tax (Still subject to ordinary taxes)
H - Homebuyer (first-time) distribution used for home purchases ($10k max)
I - Insurance (medical) if unemployed with 12 weeks of compensation
M - Medical Expenses in excess of % of AGI floor
D - Disability (only permanent or indefinite)
E - Education (books, fees, tuition)
A - Adoption/Child Birth (made within one year $5k max exclusion)
D - Disasters qualified natural disasters ($22k max per event)
T - Terminal illness or death of account owner
E - Emergency expense (up to $1k per year)
D - Domestic abuse victims (lesser of $10k or 50% of retirement)
Payments for Divorce (Gross Income)
*Payments made pursuant to a divorce before Dec 2018
- Included in gross income and deductible by payor spouse
Payments made pursuant to a divorce after Dec 2018
- Alimony received is not included in gross income and payment is not deducted
Payments for Divorce (Gross Income) Cont.
1) Alimony/Spousal Support Payments (for agreements before Dec 2018)
- Payments must be legally required under written divorce agreement
- Payments must be in cash or equivalent
- Payments cannot extend beyond the death of the payee
- Payments cannot be made to members of the same household
- Payments must not be designated as anything other than alimony
- Fillers can not file a joint tax return
2) Child Support is nontaxable
3) Property Settlements are nontaxable
Business Income/Loss, Schedule C (Gross Income)
Profit or Loss = Gross Business Income - Business Expenses
Gross Income
Includes cash received, property @FMV, and cancellation of debt
Business Expenses
Are items that are expected to be found to businesses
- COGS, Wages, Legal, Suppliers, Automobile Expenses, 50% of meals
- Depreciation of Business Assets, Employee Benefits, State/Local Taxes
- Interest Expenses on Business Loans is limited to the sum of:
1) Business interest income
2) 30% of adjusted taxable income
3) floor plan (debt is secured for inventory) interest income
* Limitation does not apply if average gross receipts are less than $30 million
Nondeductible Expenses
- Salaries paid to the sole proprietor (considered withdrawal)
- Federal income tax
- Personal portion of auto/meal expense, interest, taxes, and insurance
- Bad debt of a cash-basis taxpayer
- Charitable contributions and entertainment expenses
Two federal taxes on Net Business Income
1) Income Taxes
2) Self-employment Taxes
Calculation of Self-employment Taxes
Net Earnings from SE = (Earnings * 92.35%)
Self Employment Taxes = (Earnings * 92.35%) * 15.3%
Medical Expenses (Itemized Deductions)
- Only for payments on behalf of taxpayer, spouse, or depended with half support
- Includes amounts paid during the year in cash or charged to credit card
Qualified Medical Expenses
- Medications and prescriptions, doctors, medical insurance premiums
- Medically necessary surgery, transport to medical facility
Nondeductible Medical Expensess
- Anything elective
- Illegal drugs
- OTC/Vitamins
- Funerals
State, Local, and Foreign Taxes (Itemized Deductions)
- SALT itemized deductions are limited to $10k in aggregate
* for cash method taxpayers -> taxes are deductible in the year period
* for accrual method taxpayers -> taxes are deductible in the year accrued
Nondeductible Taxes
- Federal taxes, inheritance taxes, business on Sch C, rental property taxes
Interest (Itemized Deductions)
There is no AGI limitation on Deductibility of Qualified Interest
Home Mortgage Interest (Itemized Deductions)
* Only for 1st/2nd home
- Interest up to $750k of home-related indebtedness is deductible
- The excess is treated as personal interest and not deductible
* points to purchase -> Deductible
* points to refinance -> capitalized and amortzed
Investment Interest (Itemized Deductions)
- Deduction is limited to net taxable investment income
Personal Interest
Not deductible
Prepaid Interest (Itemized Deductions)
- Allocate over the period of the loan
- If it is received: it's taxable in year received
Education Loan Interest
- Is an adjustment to AGI and not a deduction
Charity (Itemized Deductions)
- Individual taxpayers may deduct the FMV of property donated to charity
- Can carry excess of charitable contributions forwards 5 years
Charity (Itemized Deductions): Cash
Public/Private Ops: 60% of AGI
Private Non-Ops: 30% of AGI
Charity (Itemized Deductions): Ordinary Income Property
Public/Private Ops: 50% of AGI
Private Non-Ops: 30% of AGI
Charity (Itemized Deductions): Long Term Capital Gains Property
Public/Private Ops: 30% of AGI
Private Non-Ops: 20% of AGI
For Ordinary Income (less than a year)
Lesser of:
a) FMV
b) Purchase Price
Private Non-Operating
- Distributes funds to other charitable organizations
Private Operating
- Conducts charitable activities and distributes to its own programs
Charity (Itemized Deductions): Services
- No deductions for contributions of services except for travel
Charity (Itemized Deductions): Students Living in Taxpayers Home
- Gets $50 a month while student in school
Refundable Tax Credits: Child Tax Credit
- Payers may claim a $2k credit for each qualified child under 17
- Phase Out: Must reduce credit by $50 for each $1k over AGI limit
- Refundable Amount is the lesser of:
a) Excess of child tax credit over tax liability
b) Earned income in excess of $2,500 * 15%
c) 1,600 per qualified child
* Can claim $500 for non-child dependents
Refundable Tax Credits: Earned Income Credit
Eligibility Requirements
a) Live in the US for more than half of the taxable year
b) Meet certain earned low income thresholds
c) Not have more than specified amount of disqualified income
d) If there are no children, must be over 25 and under 65
e) File a joint return with ones spouse
Individual Income Tax Formula
Gross Income
(Adjustments)
Adjusted Gross Income (AGI)
(Standard or Itemized Deductions)
Taxable Income before QBI deduction
(QBI Deduction)
Taxable Income
Federal Income Tax
(Tax Credits)
Other Taxes
(Payments)
Tax Due or Refund
Children of Divorced Parents
- Parent who has custody of the child for the greater part of the year qualifies to use them as a dependent, not about money.
- If parents have equal custody, the parents with the higher adjusted gross income, will claim the dependent.
Gross Income Basis: Accrual Method
Recognition occurs when earned similar to GAAP (with exceptions)
Gross Income Basis: Cash Method
Recognition occurs in the period the revenue is actually/constructively received
Realization
What really happened
Recognition
What's recorded on the records
Dividend Income (Gross Income)
Distribution of Company's Earnings and Profits:
From E&P -> Taxable Dividend
No E&P but no basis -> Nontaxable and lowers basis
No E&P and no basis -> Taxable capital gain income
Qualified Dividends
Those paid by domestic or certain qualified foreign corporations
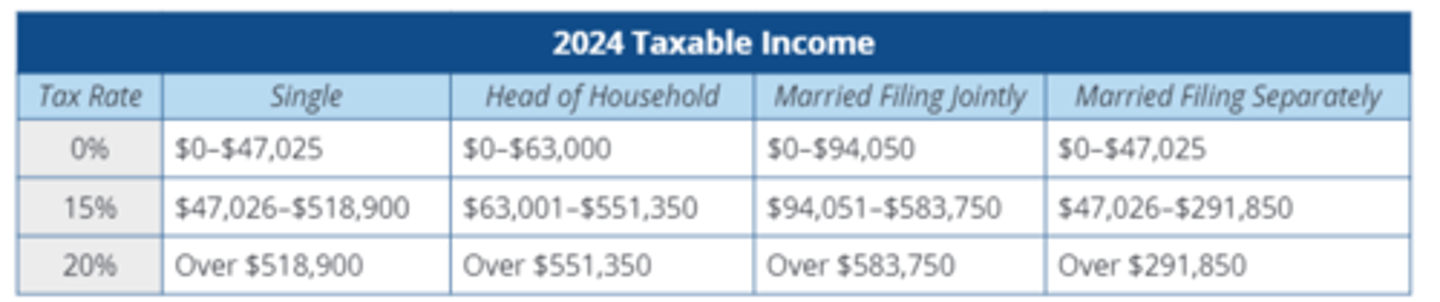
Qualified Holding Period
Stock must be held for more than 60 days before the dividend date
Nonqualified Dividends
- Employer stock held in stock ownership plan
- Amount taken into account as investment income
- Short sale positions
- Certain foreign corporations
- Paid by credit unions, mutual savings ect.
Dividend Income (Gross Income): Stock Spits
Are nontaxable:
- Allocate the original basis over new shares held
Dividend Income (Gross Income): Stock Dividends
Are nontaxable:
- Unless there is the option for cash or property
Annuities (Gross Income)
Each annuity payment received consists of:
a) Contributions -> nontaxable
b) Earnings -> Taxed as ordinary income
Fixed Period Annuity Payments
Taxable Portion = ( 1 - (Original Investment/Expected Value)) + Monthly Payment
Life Annuity Payments
- Use the IRS life expectancy tables
* If lives longer -> all is taxable income
* If dies earlier -> remaining investment is deducted
State/Local Tax Refunds (Gross Income)
* Interest paid by the state on late refund is taxable
Refund in subsequent year is not taxable if no benefit:
* Itemized deduction -> refund is taxable
* Standard deduction -> refund is nontaxable
Rental Income - Passive (Gross Income)
- Net amount is calculated on SCH E on form 1040
Net Amount - Rental Income - Total rental expenses
Unemployment Compensation (Gross Income)
All of unemployment compensation is taxable
Social Security Income (Gross Income)
Low Income (Single MAGI < 25k | MFJ < 32k):
- No SS benefits are taxable
Middle Income (Single MAGI 25-34k | MFJ 32-44k):
- Up to 50% of SS benefits are taxable
Upper Income (Single MAGI > 34k | MFJ > 44k)
- Up to 85% of SS benefits are taxable
Modified Adjusted Gross Income (AEIOU)
A - Adoption Exclusion
E - EE bond Income
I - IRA
O - Out of US Income
U - University Student Loan Interest
Rental Income - (Gross Income)
- Gross Rental Income
- Prepaid Rental Income
- Rent Cancellation Payment
- Improvements -in-lieu of rent
- (Rental Expenses)
Net Rent Income/Loss: Rental of Residence
Rented < 15 days:
- Treated as a personal residence
- Rental income is excluded from income
- Mortgage interest/Real Estate taxes = itemized deductions
- Can't deduct utilities, repairs, and depreciation
Rented > 15 days:
- Must be used for personally for 14 days or 10% of rental days
- expenses must be prorated between personal/rent
Net Rent Income/Loss: Non-Residence Rentals
- Included income in gross income and use Sch E
- Can deduct all expenses allocated to the rental property on Sch E
Standard Deduction
- Those who do not itemize receive a standard deduction with the amount determined based on filing status

Standard Deduction: Additional Deduction
Additional Deduction for those 65+ or Blind
- Married: $1,550 per issue per taxpayer
- Unmarried: $1,950 per issue per taxpayer

Calculation of Deductible Medical Expenses
Qualified Medical Expenses
(Insurance Reimbursement)
Qualified Medical Expenses "Paid"
(7.5% of AGI)
Deductible Medical Expenses
Casualty Loss
Only for areas in a declared disaster area
Smaller of:
1) Lost cost/Adjusted Basis
2) Decreased FMV
(Insurance Recovery
Taxpayer Loss
($100)
Eligible Loss
(10% of AGI)
Deductible Loss
Qualified Business Income: Basics
Must be in USA
Specified Service Trade or Business (SSTB):
- Health, Law, Accounting, Actuarial Science
- Performing Arts, Consulting, Athletics, Financial Services/Brokerage
- Engineering and architectural services are specifically excluded from the definition of SSTB
Qualified Trade or Business (QTB):
- Any business other than SSTB
Max Deduction: 20% of QBI
Qualified Business Income: Under Beginning Threshold (Category 1)
Single - $191.9k or MFJ $383.9k
- Same rule for both QTBs and SSTBs
1) Tentative QBI Deduction = QBI * 20%
2) Overall Limit = Lesser of (Taxable Income before QBI - Net Capital Gains) * 20% or;
Combined QBI deductions for all qualifying businesses
3) Section 199A QBI deduction is the lesser of the two
Qualified Business Income: Above Upper Threshold (Category 2)
Single - $241k or MFJ $483k
For SSTBs = No QBI Deduction allowed
For QTBs = Apply full W-2 wage and property limitation
1) Tentative QBI Deduction = QBI * 20%
2) Full W-2 Wage and Property Limit = Greater of:
A) W-2 Wages * 50%
B) W-2 Wages * 25% + UBIA of Qualified Property * 2.5%
3) Take the lesser of Step 1 and Step 2
4) Overall Limit = (Taxable Income before QBI - Net Capital Gains) * 20%
5) Section 199A QBI deduction is the lesser of 3 and 4
Income Tax Calculation
Individual Tax Rates are in a progressive tax rate
- Tax rate is applied to each incremental income
Tax Credit Basics
Reduce Tax Liability dollar for dollar:
- Nonrefundable Tax Credits -> reduce tax, no refund
- Refundable Tax Credits -> reduce tax, refund
Estimated Minimum Taxes
Taxpayer's withholding is the lesser of:
a) 90% of the current year's tax
b) 100% of the prior year's tax
Exception: Taxpayer had AGI > 150k in the prior year
b) 110% of the prior year's tax
Net Investment Income Tax
Applies a rate of 3.8% to certain investments
Threshold: MFJ: $250k
Used on the lesser of:
a) Net Investment Income
b) The excess of AGI over the threshold
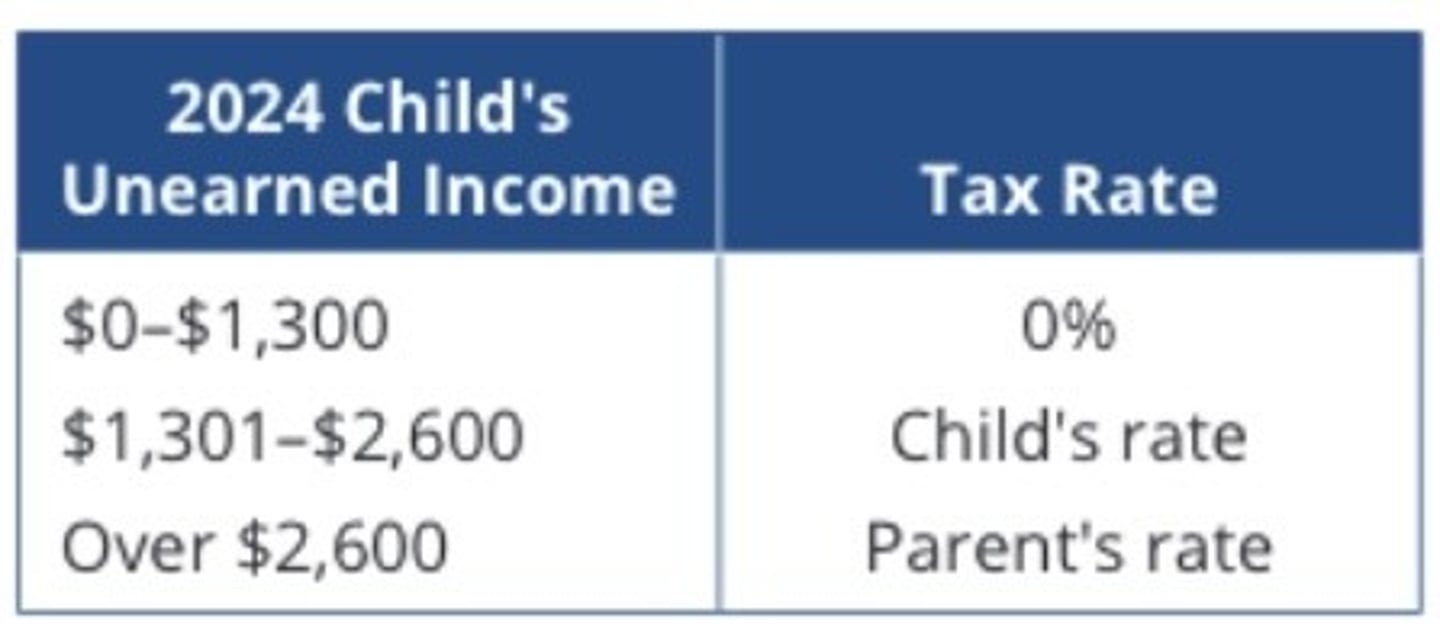
Kiddie Tax
Net unearned income (passive forms) of dependent is taxed at the parents marginal rate
Net Unearned = Income - $2,600
Qualifying Child (CARES)
C - Close Relative:
- Must be taxpayers son, daughter, stepchild, siblings, step-siblings, and descendants of them
- Also includes legally adopted Children or Foster Children
A - Age Limit:
- Child must be younger than taxpayer and under 19 (or 24 for full time students)
- Full Time Student must attend an educational institution for at least part of 5 months of the taxable year
R - Residency and Filing Requirements
- Child must have the same principal place of abode as taxpayer for month than half of the year
- Child must be a citizen of the US or a resident of the US, Canada, or Mexico
E - Eliminate Gross Income Tess
- Gross income test does not apply to a qualifying child
S - Support Test
- Qualifying child must not have contributed more than half of their own support
- Does not include scholarships of the dependents
Qualifying Relative (SUPORT)
S - Support Test
- Taxpayers have supplied more than half of the support of a person in order to claim as a relative
U - Under Gross Income Limitation
- May not be claimed as a qualifying relative unless the gross income is less than $5,050
- Only income that is taxable is included (doesn't include social security, tax-exempt interest, or scholarships)
P - Precludes Dependent Filing a Joint Return
- Not a dependent if they are a married dependent filing a joint return
O - Only Citizens of the US or Residents of the US, Canada, or Mexico
R - Relative
- Children, grandchildren, parents, grandparents, siblings, aunts, nieces, stepsiblings, stepparents, and in-laws
- Children include legally adopted children, foster children, and stepchildren
- Foster parents and cousins are not considered relatives
T - Taxpayer lives with Individual (for non-relatives) for the whole year
- Includes cousins or foster parents because they are not technically relatives
Salaries and Wages (Gross Income)
Money: All money received, credited, or available
Property: FMV of all property is included in gross income
Bargain Purchases: If an employer sells property for less than FMV -> the difference is income to employee
Guaranteed Payments to Partners: Treated as self-employment tax
Taxable Fringe Benefits: FMV of fringe benefits is included in employee's income
Employer Contributions to Roth 401k: Contributions made by the employer are included in income
Portion of Life Insurance Premiums: Not income up to the first $50k; are taxable above that
Nontaxable Fringe Benefits (Gross Income): Employer Paid Health Insurance
- Premiums are excludable from employee's income
- Amount paid to the employee are includable in income unless:
A) Reimbursement for medical expenses actually incurred
B) Compensation for permanent loss, or loss of use, of a member or function of body
Nontaxable Fringe Benefits (Gross Income): De Minimis Fringe Benefits
Benefits so small to account for; excluded from income
Nontaxable Fringe Benefits (Gross Income): Meals and Lodging
Not included if used because of the convince of the employer
Nontaxable Fringe Benefits (Gross Income): Employer Payment of Employee's Educational Expenses
- Up to $5,250 may be excluded from gross income for payments on behalf of student loans
Nontaxable Fringe Benefits (Gross Income): Employee Adoption Assistance Program
- Taxpayer can exclude $16,810 from taxable income of qualified adoption expenses paid by employer
- Exclusion is phased out for taxpayers with MAGI of $252,150 - $292,150
Nontaxable Fringe Benefits (Gross Income): Dependent Care Assistance
- Employees can exclude $5,000 of benefits for dependent care expenses from gross income
Qualifying Dependents Include:
a) Dependent children under age 13
b) Spouse or other dependent physically or mentally incapable of self-care
Nontaxable Fringe Benefits (Gross Income): Qualified Tuition Reduction
- Undergraduate level tuition reduction may be excluded from income
- Graduate level tuition reduction may be excluded from income if both:
a) Engaged in teaching or research activities
b) Tuition reduction is in addition to the pay for teaching/research
Nontaxable Fringe Benefits (Gross Income): Merchandise Discount
Excludable discount is limited to employer's gross profit percentage
Nontaxable Fringe Benefits (Gross Income): Service Discount
Excludable discount is limited to 20% of the FMV of the services
Nontaxable Fringe Benefits (Gross Income): Employer-Provided Parking
Value of parking up to $315 per month can be excluded
Nontaxable Fringe Benefits (Gross Income): Transit Passes
Value of employer-provided passes up to $315 per month can be excluded
Nontaxable Fringe Benefits (Gross Income): Qualified Non-Roth Retirement Plans
- Contributions made by Employer are not income at the time of contribution
- Contributions made by Employee are not income at the time of contribution
- Earnings on amounts contributed are not taxable income to the employee until distributed
- Benefits received are ordinary income the year the amount was made available
Nontaxable Fringe Benefits (Gross Income): Flexible Spending Arrangements (FSAs)
- Stems from Section 125 employee flexible benefit plan; allows a pretax reimbursement of certain expenses
- Can elect to have part of salary (up to $3,200) deposited to pay for certain expenses
- Must be used within the plan year; forfeited if not used within 2.5 months after year end
Taxable Miscellaneous Income (Gross Income): Prizes and Awards
- FMV of prizes and awards is taxable UNLESS selected without entering contest and assigns prize to charity
Taxable Miscellaneous Income (Gross Income): Gambling Winnings and Losses
- Winnings are included in gross income
- Losses are deductible on Sch A as an itemized deduction only to the extent of winnings
Taxable Miscellaneous Income (Gross Income): Damage Awards
If award is compensation for lost profit -> the award is income
Taxable Miscellaneous Income (Gross Income): Punitive Damages
- Are fully taxable if received in a business context or for loss of personal reputation
- Includes personal injury but not wrongful death cases
Taxable Miscellaneous Income (Gross Income): Cancellation of Debt
Is taxable
Partially Taxable Miscellaneous Income (Gross Income)
Degree Seeking Students - Scholarships are excludable only up to amounts spent on tuition, and fees (not room and board)
Non-Degree Seeking Students - Scholarships are fully taxable at FMV
Tuition Reductions - Only included in taxes if it is their only form of compensation