2.1.6 - Cell division, cell diversity and cellular organisation
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
State what the cell cycle is and outline its stages
Regulated cycle of division with intermediate growth periods
interphase
mitosis or meiosis (nuclear division)
cytokinesis (cytoplasmic division)
Outline what happens during interphase
G1: cell synthesises proteins for replication e.g. tubulin for spindle fibres & cell size doubles
S: DNA replicates = chromosomes consist of 2 sister chromatids joined at a centromere
G2: Organelles divide
What is the purpose of mitosis?
Produces 2 genetically identical daughter cells for:
growth
cell replacement/ tissue repair
asexual reproduction
Name the stages of mitosis
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase
Outline what happens during prophase
Chromosomes condense, becoming visible. (X-shaped: 2 sister chromatids joined at centromere)
Centrioles move to opposite poles of cell (animal cells) & mitotic spindle fibres form
Nuclear envelope & nucleolus break down = chromosomes free in cytoplasm
Outline what happens during metaphase
Sister chromatids line up at cell equator, attached to the mitotic spindle by their centromeres
Outline what happens during anaphase
Requires energy from ATP hydrolysis
Spindle fibres contract = centromeres divide
Sister chromatids separate into 2 distinct chromosomes & are pulled to opposite poles of cell. (looks like ‘V’ shapes facing each other)
Spindle fibres break down
Outline what happens during telophase
Chromosomes decondense, becoming invisible again
New nuclear envelopes form around each set of chromosomes = 2 new nuclei each with 1 copy of each chromosome
What happens during cytokinesis
Cell membrane cleavage furrow forms
Contractile division of cytoplasm
How is the cell cycle regulated
Checkpoints regulated by cell-signalling proteins ensure damaged cells do not progress to next stage of cycle
Cyclin-dependent kinase enzymes phosphorylate proteins that initiate next phase of reactions
Describe what happens at each key checkpoint in the cell cycle
Between G1 & S, cell checks for DNA damage (e.g. via action of p53). After restriction point, cell enters cycle
Between G2 & M, cell checks chromosome replication
At metaphase checkpoint, cell checks that sister chromatids have attached to spindle correctly
What is meiosis?
A form of cell division that produces four genetically different haploid cells (cells with half the number of chromosomes found in the parent cell) known as gametes
What happens during meiosis I?
Homologous chromosomes pair to form bivalents
Crossing over (exchange of sections of genetic material) occurs at chiasmata
Cell divides into two. Homologous chromosomes separate randomly. Each cell contains either maternal or paternal copy
What are homologous chromosomes?
Pair of chromosomes with genes at the same locus. 1 maternal & paternal
Some alleles may be the same while others are different
What happens during meiosis II?
Independent segregation of sister chromatids
Each cell divides again, producing 4 haploid cells
How does meiosis produce genetic variation
Crossing over during meiosis I
Independent assortment (random segregation) of homologous chromosomes & sister chromatids
Result in new combinations of alleles
How do cells become specialised?
Some genes are expressed while others are silenced due to cell differentiation mediated by transcription factors. Cells produce proteins that determine their structure and function
What is a transcription factor?
A protein that controls the transcription of genes so that only certain parts of the DNA are expressed, e.g. in order to allow a cell to specialise
How do transcription factors work?
Move from the cytoplasm into the nucleus
Bind to promoter region upstream of target gene
Makes it easier or more difficult for RNA polymerase to bind to gene. This increases or decreases rate of transcription
What is a stem cell?
Undifferentiated cells that can divide indefinitely and turn into other specific cell types
Name and define the 4 types of stem cell
Totipotent: can develop into any cell type including the placenta and embryo
Pluripotent: can develop into any cell type excluding placenta and embryo
Multipotent: can only develop into a few types of cell
Unipotent: can only develop into one type of cell
Suggest some uses of stem cells
Repair of damaged tissue e.g. cardiomyocytes after myocardial infarction
Drug testing on artificially grown tissues
Treating neurological diseases e.g. Alzheimer’s & Parkinson’s
Researching developmental biology e.g. formation of organs, embryos
Describe the 2 groups of specialised cells in the blood
Erythrocytes (red blood cells): biconcave, no nucleus, lots of haemoglobin to carry oxygen
Leucocytes (white blood cells): lymphocytes, eosinophils, neutrophils to engulf foreign material, monocytes
How do specialised cells in blood form?
Multipotent stem cells in the bone marrow differentiate into:
Erythrocytes, which have a short lifespan & cannot undergo mitosis since they have no nucleus
Leucocytes, including neutrophils
State the relationship between a system and specialised cells
specialised cells → tissues that perform specific function → organs made of several tissue types → organ systems
Describe the structure of squamous and ciliated epithelia
Simple squamous epithelium: single smooth layer of squamous cells (thin & flat with round nucleus) fixed in place by basement membrane
Ciliated epithelium: made of ciliated epithelial cells (column-shaped with surface projections called cilia that move in a synchronised pattern)
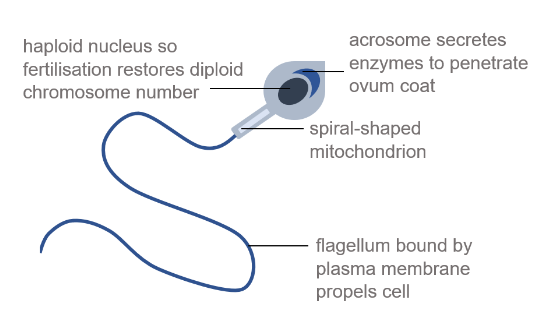
Describe the specialised structure of a spermatozoon
Specialised to fertilise an ovum during sexual reproduction in mammals
Describe the structure and function of palisade cells and guard cells in plants
palisade cells: Specialised to absorb light energy for photosynthesis, so contain many chloroplasts. Pack closely together
guard cells: Form stoma. When turgid, stoma opens; when flaccid, stoma closes. Walls are thickened by spirals of cellulose
Describe the function and structure of root hair cells
Specialised to absorb water and low-concentration minerals from soil
Hair-like projections increase surface area for osmosis / carrier proteins for active transport
Many mitochondria produce ATP for active transport
What are meristems?
Totipotent undifferentiated plant cells that can develop into various types of plant cell, including xylem vessels & phloem sieve tubes
Classified as apical (at root and shoot tips), intercalary (stem) or lateral (in vascular areas)
Define the structure of a vascular bundle
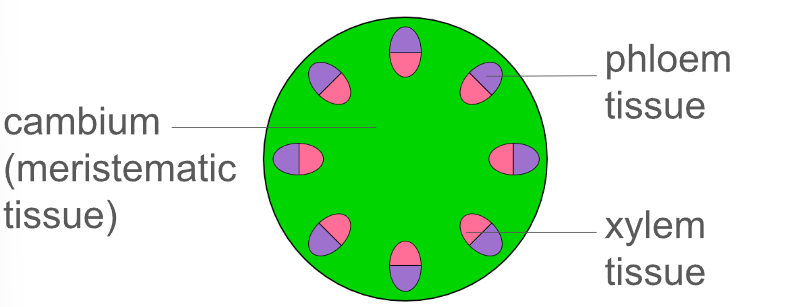
Describe the structure of phloem tissue
Sieve tube elements: form a tube to transport sucrose in the dissolved form of sap
Companion cells: involved in ATP production for active loading of sucrose into sieve tubes
Plasmodesmata: gaps between cell walls where the cytoplasm links, allowing substances to flow
Describe the structure of xylem tissue
Vessel elements: lignified secondary walls for mechanical strength & waterproofing; perforated end walls for rapid water flow
Tracheids: tapered ends for close packing; pits for lateral water movement; no cytoplasm or nucleus
Describe the additional cell types in xylem tissue
xylem parenchyma: packing tissue with thin walls transmit turgidity
sclereids
sclerenchyma fibres: heavily lignified to withstand negative pressure
Describe the function of cartilage
Avascular smooth elastic tissue made of chondrocytes, which produce extensive extracellular matrix (ECM)
ECM mainly contains collagen & proteoglycan
3 categories: hyaline, yellow elastic, white fibrous (depends on ratio of cells: ECM)
Name the 3 types of muscle in the body and where they are located
Cardiac: exclusively found in heart
Smooth: walls of blood vessels and intestines
Skeletal: attached to incompressible skeleton by tendons
Describe the gross structure of skeletal muscle
Muscle cells are fused together to form bundles of parallel muscle fibres (myofibrils)
Arrangement ensures there is no point of weakness between cells
Each bundle is surrounded by endomysium: loose connective tissue with many capillaries