Praxis 5624 Principles of Learning and Teaching: Grades 7-12
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
Bandura
Social Learning Theory/Observational Learning Theory-people can learn new information and behaviors by watching other people.
Bruner
Constructivist Theory- learning is an active process; learners construct new ideas or concepts based on their current/past knowledge.
Dewey
Learning by Doing- Learning occurs through experience.
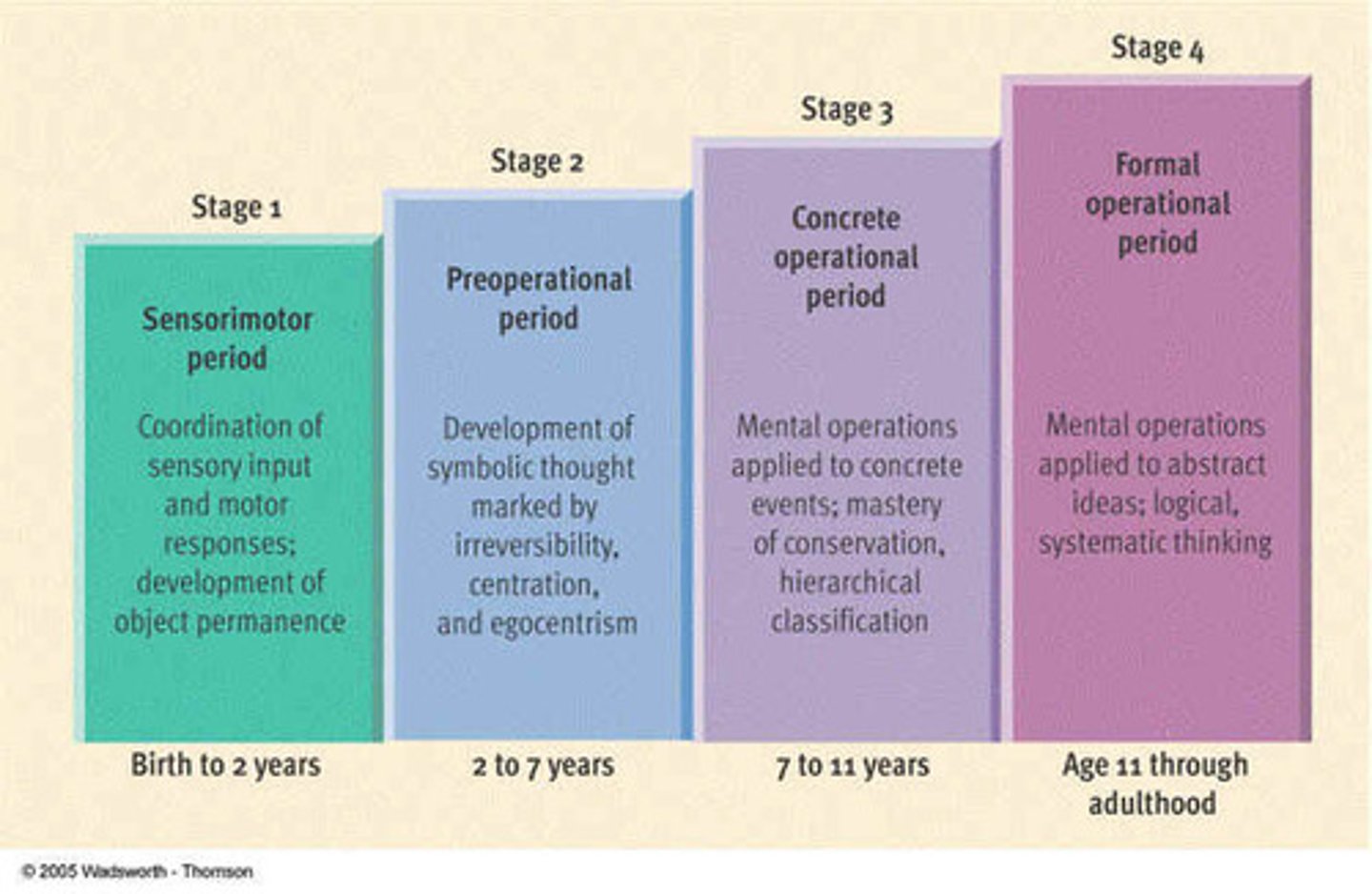
Piaget
Genetic Epistemology- Developmental Stages of Child Development:
0-2 years: "sensorimotor"- motor development
3-7 years: "preoperation"- intuitive
8-11 years: "concrete operational"- logical, but non-abstract
12-15 years: "formal operations"- abstract thinking
Vygotsky
Social Development Theory & ZPD: Social interaction=critical for cognitive development; Zone of Proximal Development: theoretical basis for scaffolding
Kohlberg
Stages of Moral Development:
Pre-conventional- based on self-centered interests
Conventional- based on conformity to local expectations
Post-Conventional- based on higher principles
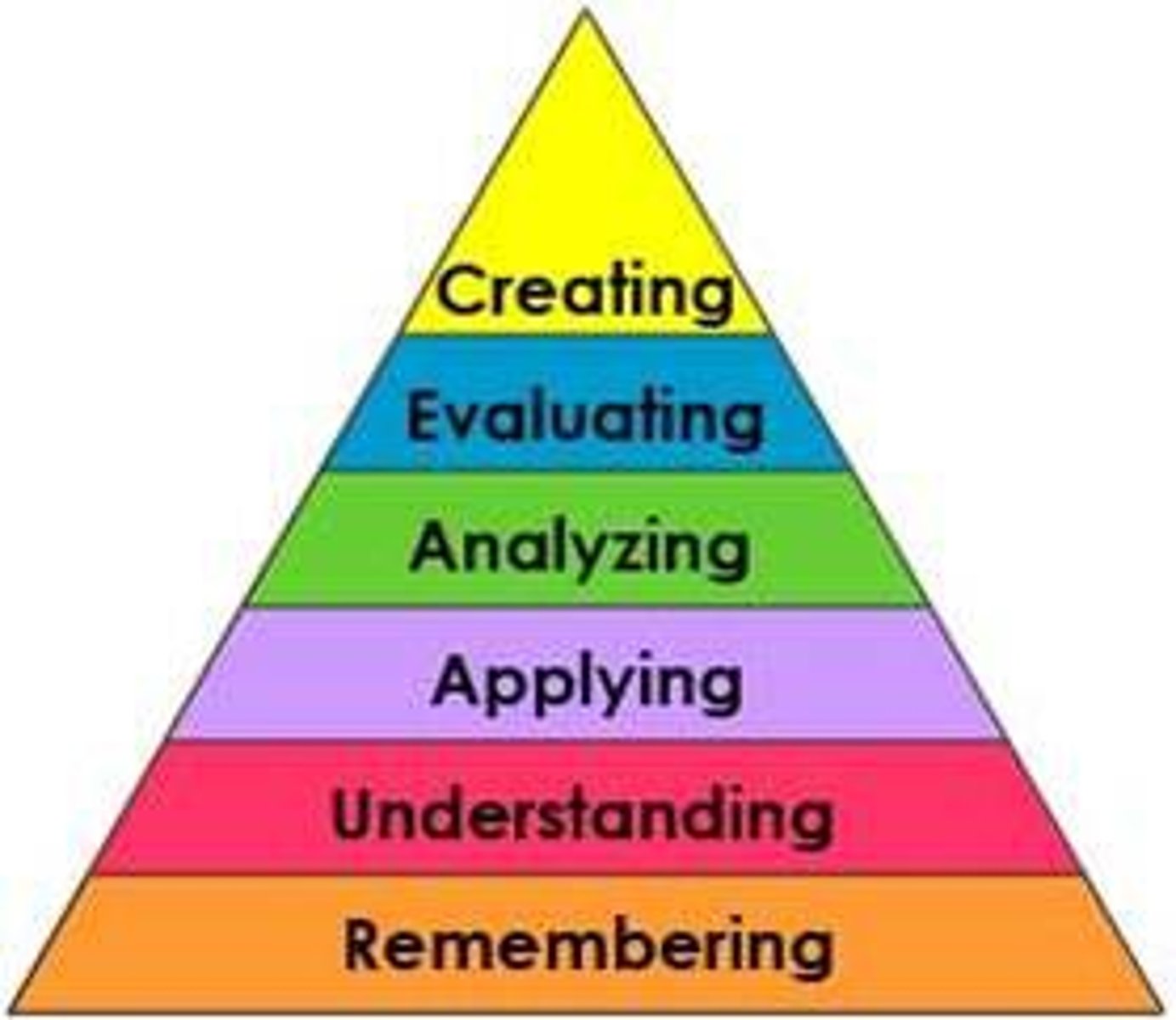
Bloom
Taxonomy- a hierarchy model; way to classify thinking according to six cognitive levels of complexity
Metacognition
awareness and understanding of one's own thought process
Schema
A schema is both the category of knowledge as well as the process of acquiring that knowledge. As experiences happen and new information is presented, new schemas are developed and old schemas are changed or modified.
Transfer
Information or skills related to one topic can sometimes either help or hinder the acquisition of information or skills related to another topic.
Self-Efficacy
The extent or strength of one's belief in one's own ability to complete tasks and reach goals
Self-Regulation
Ability to monitor and control our own behavior, emotions, or thoughts, altering them in accordance with the demands of the situation.
Classical Conditioning
Pavlov; altering another's behavior (dogs and bells)
Operant Conditioning
Rewards and punishments to teach proper behavior
Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA)
Prohibits discrimination against people with disabilities
Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA)
Protect rights of students with disabilities by ensuring everyone receives a free appropriate public education, regardless of ability.
Section 504, Rehabilitation Act
Protect rights of those with disabilities in programs and activities that receive federal financial assistance, including federal funds
Thorndike
Connectionism (Behaviorism): Learners form associations or connections between a stimulus and a response. Through trial and error, rewarded responses would be strengthened.
Watson
Behaviorism: Proposed that most human learning and behavior was controlled by experience (not genetically predetermined). Believed the only behaviors that should be studied are the "observable" ones.
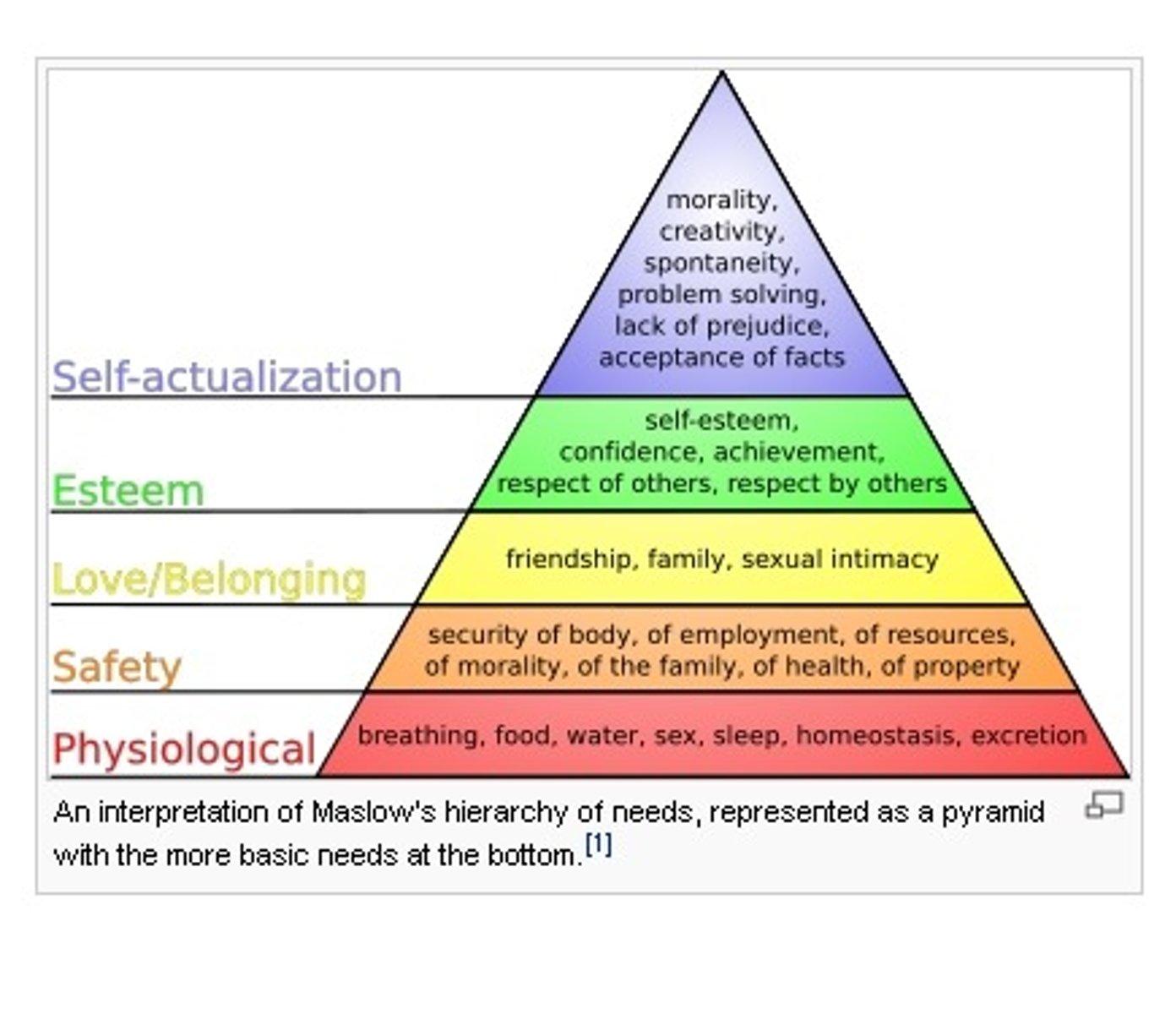
Maslow
Hierarchy of Needs: Humans naturally strive to satisfy needs. Lower levels must be satisfied before the individual can move on to satisfy higher level needs.
Skinner
Operant Conditioning: Learning is the result of changes in behavior. As stimulus-response cycles are reinforced, individuals are "conditioned" to respond. Individuals can initiate responses, not mearely respond to stimuli.
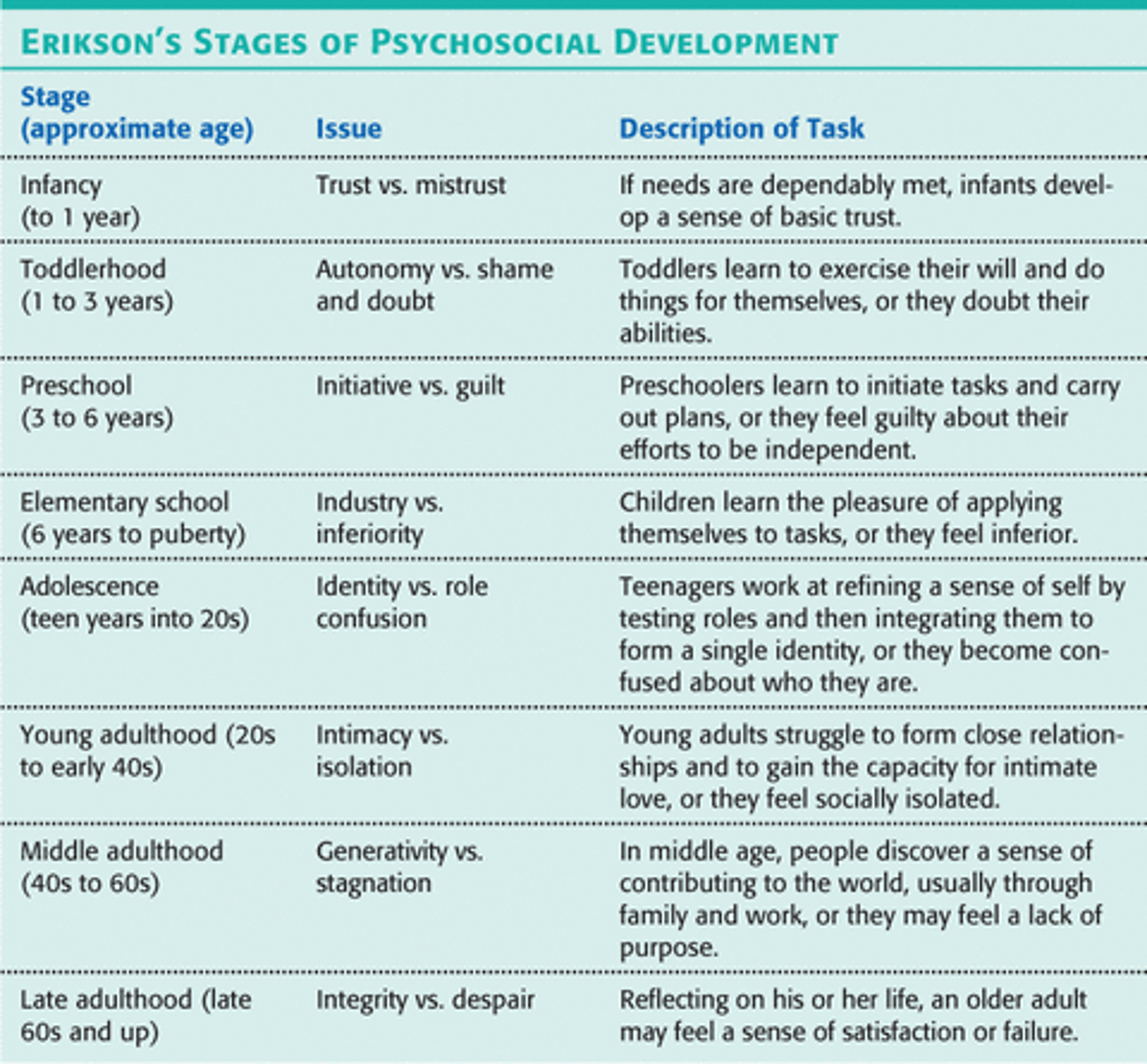
Erikson
Socioemotional Development: "Eight Stages of Man;" describes series of crises individuals pass through at different ages.
Cognitive Dissonance
Discomfort felt at a mismatch between what you already know or believe and new information or interpretation.
Strategies to Develop Self-Motivation (4)
-Assigning valuable tasks
-Providing frequent positive feedback
-Including students in instructional decisions
-De-emphasizing grades
Cognitivism (3)
Basic Concepts:
Schema,
Information Processing,
Mapping
Social Learning Theory (3)
Basic Concepts:
Modeling,
Reciprocal Determinism,
Vicarious Learning
Constructivism (5)
Basic Concepts:
Learning as experience
Problem-based learning
Zone of Proximal Development
Scaffolding
Inquiry/discovery learning
Behaviorism (4)
Basic Concepts:
Conditioning
Intrinsic and extrinsic rewards
Reinforcement
Punishment
Scope
The breadth and depth of content to be covered in a curriculum at any one time. All that you do in a given period.
Sequence
The order in which content is presented to learners over time. The order in which you do it.
Learning Domains (3)
Cognitive: mental skills (knowledge)
Affective: growth in feelings or emotional areas (attitude or self)
Psychomotor: manual or physical skills (skills)
Remediation
Giving students extra instruction to help increase proficiency in a particular skill area
Enrichment
Directed to creative and critical thinking skills; student shows exceptional performance and responsibility in the classroom. Find material to still challenge students who may be gifted and talented to keep them engaged and motivated.
Components of Thematic Units (4)
-Selecting a theme
-Designing integrated learning activities
-Selecting resources
-Designing assessments
Components of Interdisciplinary Units(6)
-Collaborating
-Generating applicable topics
-Developing an integrative framework
-Planning instruction for each discipline
-Designing integrative assessment
-Recognizes their role in collaborating with instructional partners in instructional planning
Instructional Planning Partners (5)
-Special Education Teachers
-Library Media Specialists
-Teachers of the Gifted and Talented
-IEP Team Members
-Para Educators
Deductive Reasoning
Top-down approach; work from more general information to more specific
Ex: Every day, I leave for work in my car at eight o'clock. Every day, the drive to work takes 45 minutes I arrive to work on time. Therefore, if I leave for work at eight o'clock today, I will be on time.
Inductive Reasoning
Bottom-up approach; work from more specific observations to broader generalizations and theories
Ex: Today, I left for work at eight o'clock and I arrived on time. Therefore, every day that I leave the house at eight o'clock, I will arrive to work on time.
Direct Instruction Strategies (5)
-Explicit teaching
-Drill and practice
-Lecture
-Demonstrations
-Guides for reading, listening, viewing
Indirect Instruction Strategies (6)
-Problem solving
-Inquiry
-Case studies
-Concept mapping
-Reading for meaning
-Cloze procedures
Independent Instruction Strategies (5)
-Learning contracts
-Research projects
-Learning centers
-Computer mediated instruction
-Distance learning
Experiential and Virtual Instruction Strategies (6)
-Field trips
-Experiments
-Simulations
-Role play
-Games
-Observations
Interactive Instruction Strategies (6)
-Brainstorming
-Cooperative learning groups
-Interviews
-Discussion
-Peer Practice
-Debates
Complex Cognitive Processes (5)
-Concept Learning
-Problem Solving
-Metacognition
-Critical thinking
-Transfer
Complex Cognitive Processes Instructional Activities (13)
-Distinguishing fact from opinion
-Comparing and contrasting
-Detecting bias
-Predicting
-Categorizing
-Analyzing
-Sequencing
-Summarizing
-Inferring
-Decision making
-Evaluating
-Synthesizing
-Generalizing
Supporting Student Learning Strategies (6)
-Modeling
-Developing self-regulation skills
-Scaffolding
-Differentiating Instruction
-Guided practice
-Coaching
Students' Self-Regulatory Skills (7)
-Setting Goals
-Managing Time
-Organizing Information
-Monitoring Progress
-Reflecting on Outcomes
-Establishing a Productive Work Environment
-Understands the Design of Different Group Configurations for Learning
Group Configurations (5)
-Whole Class
-Small Group
-Independent Learning
-One on one
-Pair/Share
Grouping Techniques (6)
-Cooperative Learning
-Collaborative Learning
-Heterogeneous Grouping
-Homogeneous Grouping
-Multi-Age Grouping
-Grouping by Gender
Components of Effective Questioning (8)
-Allowing think/wait time
-Helping students articulate their ideas
-Respecting students' answers
-Handling incorrect answers
-Encouraging participation
-Establishing a non-critical classroom environment
-Promoting active listening
-Varying the types of questions
Purposes of Questioning (12)
-Developing interest and motivating students
-Evaluating students' preparation
-Reviewing previous lessons
-Helping students set realistic expectations
-Engaging students in discussion
-Determining prior knowledge
-Preparing students for what is to be learned
-Guided thinking
-Developing critical and creative thinking skills
-Checking for comprehension or level of understanding
-Summarizing information
-Stimulating students to pursue knowledge on their own
Support Students in Articulating their Ideas (4)
-Verbal and non-verbal prompting
-Restatement
-Reflective listening statements
-Wait time
Higher Level Thinking Guides Students to...(7)
-Reflect
-Challenging assumptions
-Find relationships
-Determine relevancy and validity of information
-Design alternate solutions
-Draw conclusions
-Transfer knowledge
Basic Techniques for Establishing/Maintaining Standards of Conduct for Discussions (4)
-Engaging all learners
-Creating a collaborative environment
-Respecting diverse opinions
-Supporting risk taking
Verbal and Nonverbal Communication Modes (6)
-Body language
-Gesture
-Tone, stress, and inflection
-Eye contact
-Facial expression
-Personal space
Active Listening Strategies (6)
-Attending to the speaker
-Restating key points
-Asking questions
-Interpreting Information
-Providing supportive feedback
-Being respectful
Diagnostic Assessment
Gathering and carefully evaluating detailed data using students' knowledge and skills in a given learning area to diagnose strengths and areas of need in all students; use data to plan appropriate pedagogy and targeted learning
Assists teachers to gain...
1. understanding of current situation
2. knowledge about how to improve
3. required resources
Leads to action and improved learning outcomes
Assessment Tools (5)
-Rubrics
-Analytical checklists
-Scoring guides
-Anecdotal notes
-Continuums
Assessment Formats (6)
-Essay
-Selected response
-Portfolio
-Conference
-Observation
-Performance
Types and Purposes of Standardized Tests (3)
-Achievement
-Aptitude
-Ability
Norm-referenced Scoring
Designed to compare and rank test takers in relation to one another; whether test takers performed better or worse than a hypothetical average student
Criterion-referenced Scoring
Designed to measure student performance against a fixed set of predetermined criteria or learning standards
Testing and Scoring Terms (9)
-Validity
-Reliability
-Raw score
-Scaled score
-Percentile
-Standard deviation
-Mean, mode, and median
-Grade-equivalent scores
-Age-equivalent scores
Holistic Scoring
Single scale; All factors are to be evaluated are identified together for each level of performance; a checklist, description of each attainable level of performance, etc.; Quicker to develop, learn, score, and find agreement among various evaluators

Analytical Scoring
Consists of multiple, separate scales, and therefore provides a set of scores rather than just one; lets students know exactly which areas to improve on; takes longer to learn well and longer to score
Professional Development Practices and Resources (10)
-Professional literature
-Professional associations
-Workshops
-Conferences
-Learning communities
-Graduate courses
-Independent research
-Internships
-Mentors
-Study groups
Reflective Practice
Continuous cycle of self-observation and self-evaluation; thinking to benefit of the individuals and communities being served; how to improve or knowing what works well
Support Reflective Practice Activities (6)
-Reflective journal
-Self and peer assessment
-Incident Analysis
-Portfolio
-Peer observation
-Critical friend
Student Support Personnel (7)
-Guidance counselors
-IEP team members
-Special education teachers
-Speech, physical, and occupational therapists
-Library media specialists
-Teachers of the gifted and talented
-Para educators
Elements of Successful Collaboration (5)
-Developing an action plan
-Identifying the stakeholders
-Identifying the purpose of the collaboration
-Supporting effective communication
-Seeking support
Equal Access
Prohibits public secondary schools that receive federal assistance and that maintain a limited open forum from denying equal access to students who wish to meet within the forum on the basis of the religious, political, philosophical, or other content of the speech at such meetings.
Due Process
No state shall deprive any person of life, liberty, or property, without due process of law