OPT 311 Pupil Exam
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What are the 5 steps of the pupil exam?
1. is there anisocoria and is it greater in light or dark?
2. what are the eyelid positions?
3. what is the direct response to light?
4. is there a RAPD?
5. is the near response greater than the direct response?
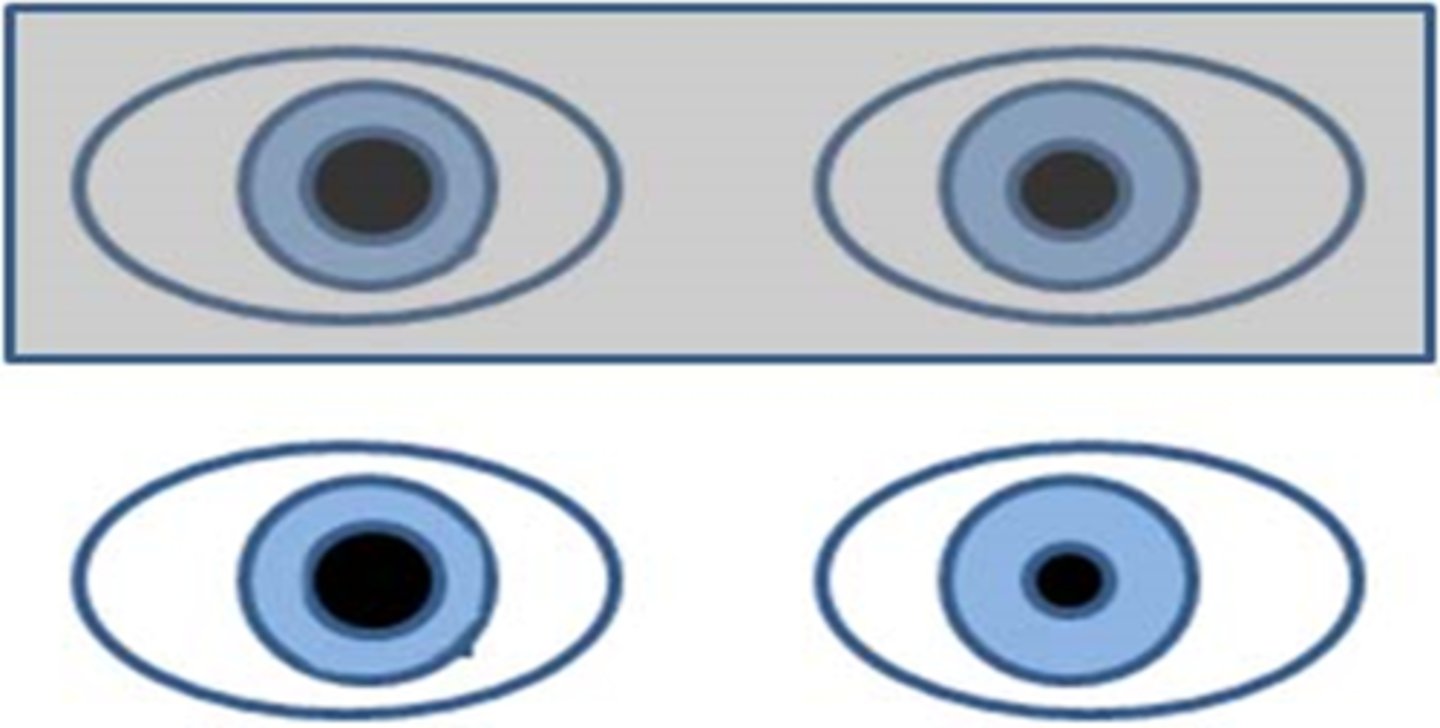
What does it mean if the anisocoria is greater in the dark?
iris cannot dilate = sympathetic issue
ex) Horner's syndrome
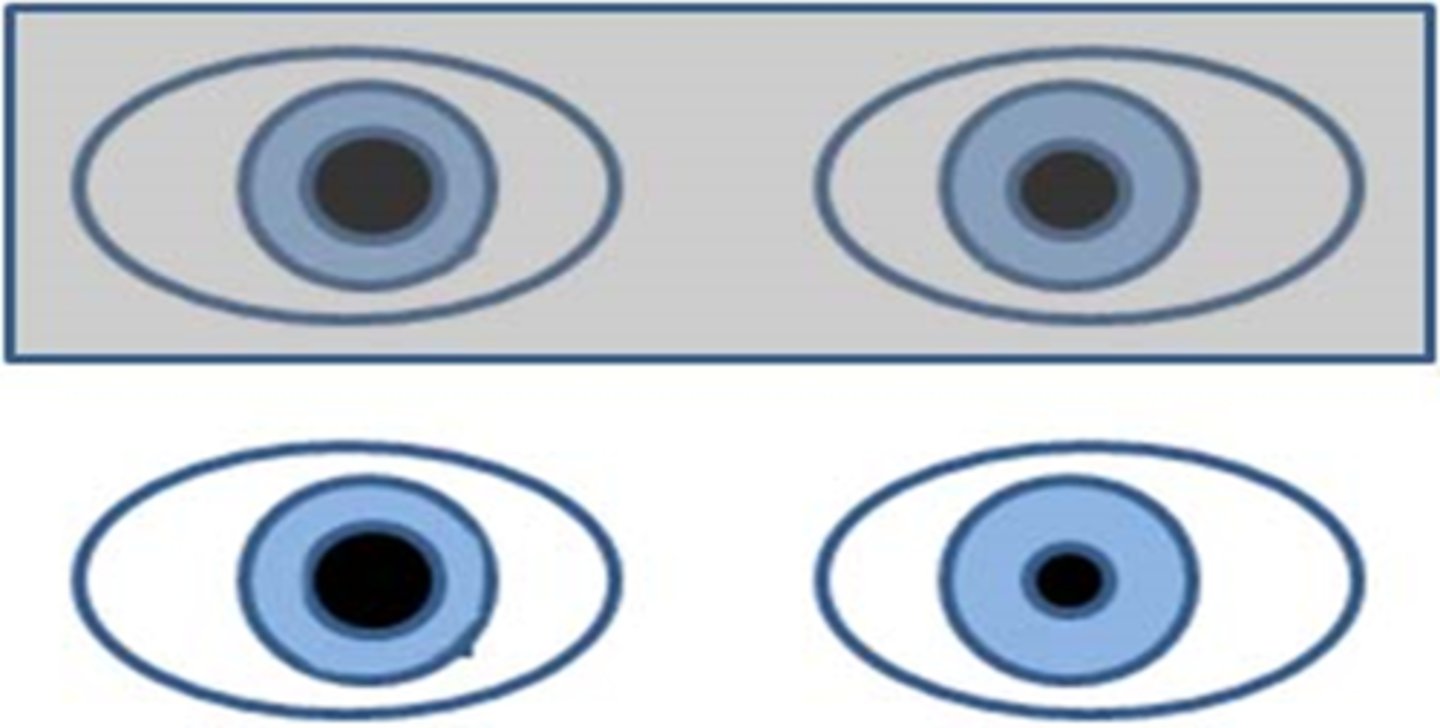
What does it mean if the anisocoria is greater in the light?
iris cannot constrict = parasympathetic issue
ex) internal ophthalmoplegia
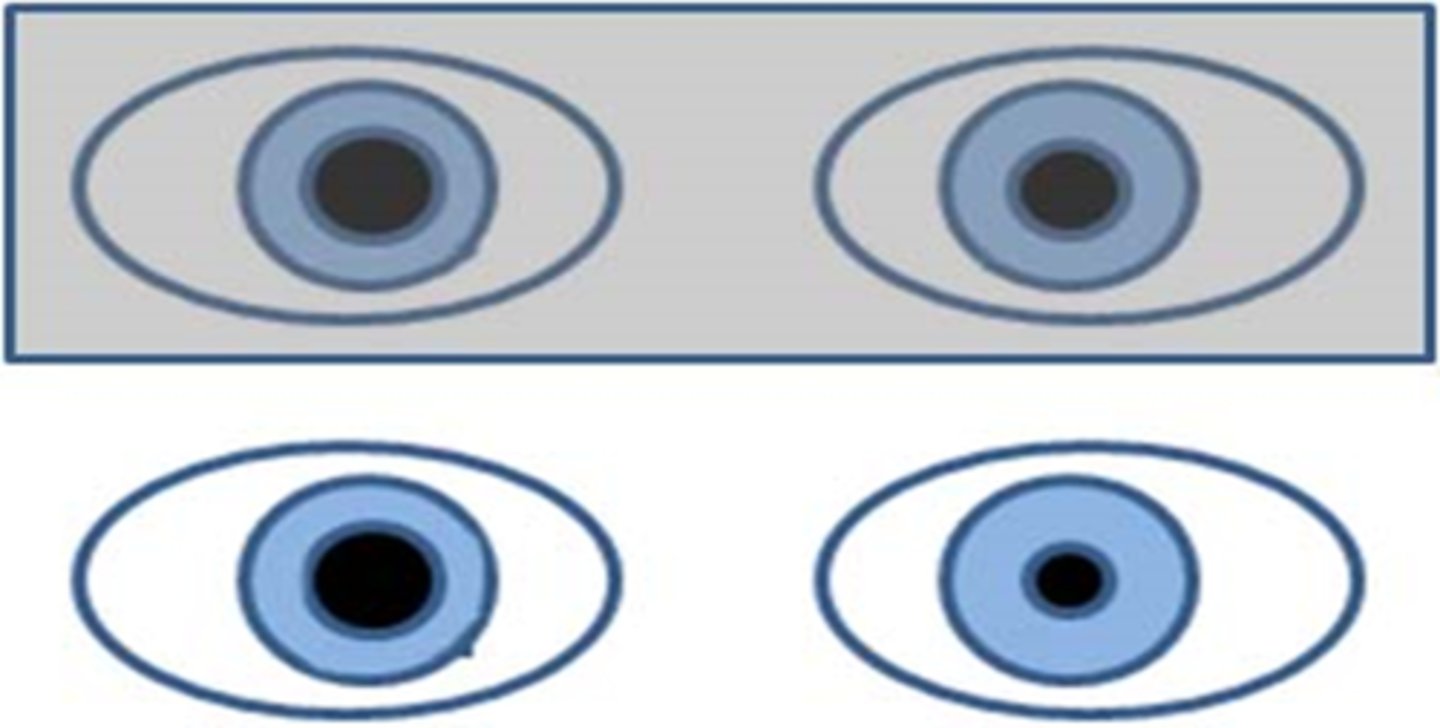
What does it mean if the anisocoria is the same in the light and the dark?
physiologic aka benign anisocoria
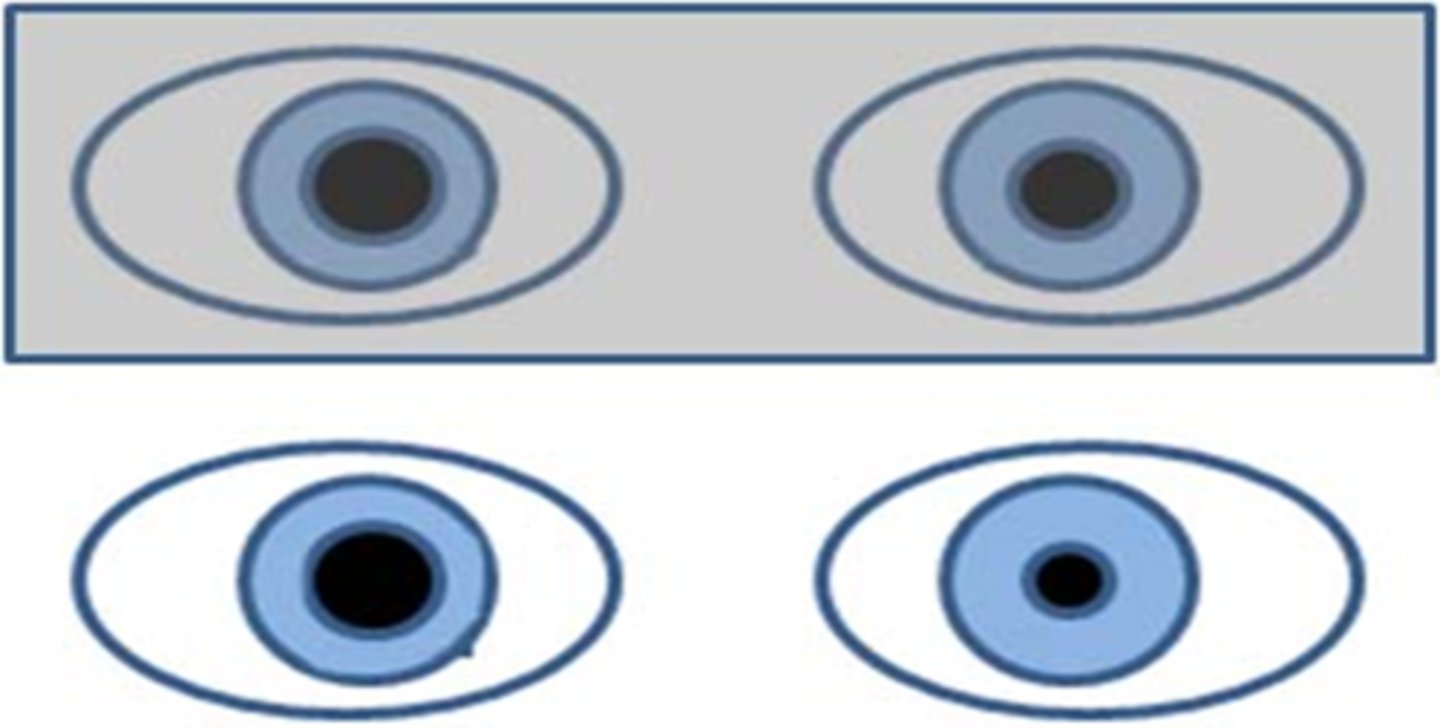
What does it mean if the anisocoria will switch in the dark vs light?
iris is not changing/moving at all = tonic pupil
What amount of change between anisocoria difference in the light and dark (or between years ago vs today) is considered clinically significant?
0.5mm
When doing pharmacologic testing of the pupil, when should we record pupil size?
before and after instilling the drugs

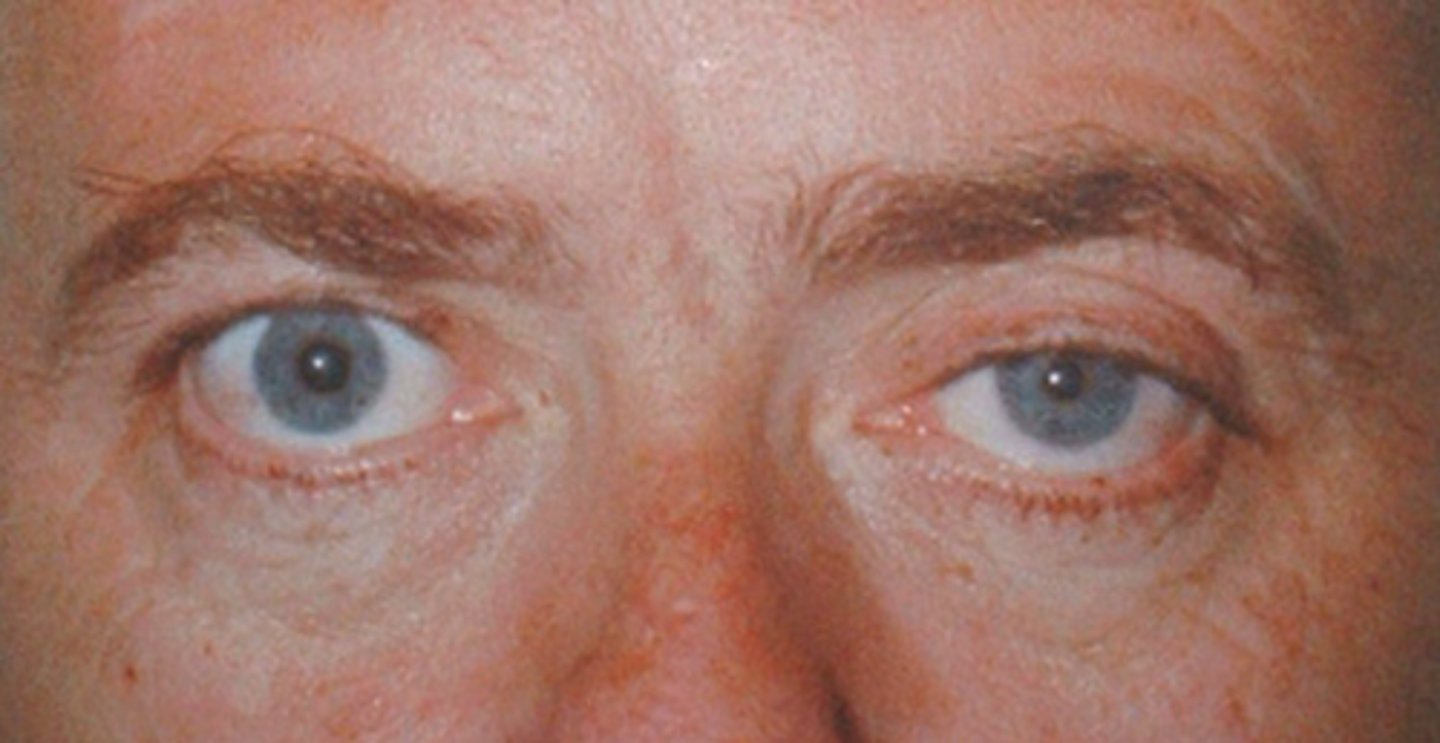
When seen with a large pupil, what might a ptosis indicate?
CN 3 palsy (parasymp issue) will show...
ptotis
eye is "down and out"
large pupil

When seen with a small pupil, what might a ptosis indicate?
Horner's syndrome (symp issue) will show...
ptosis due to Muller's affected
small pupil = miosis
anhydrosis
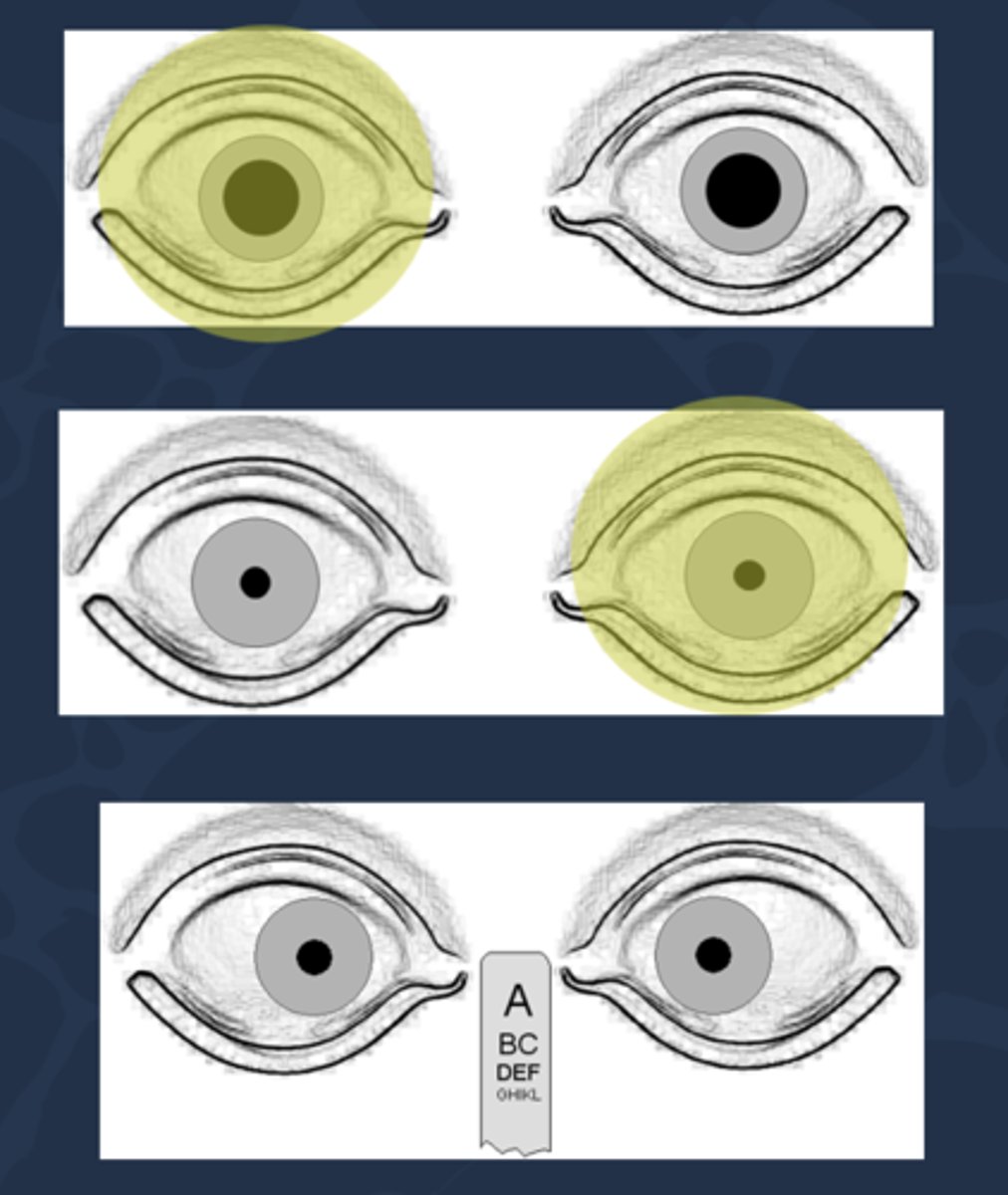
What does it mean when the direct response to light is inhibited?
amaurotic pupil reaction = total blindness in the eye that has no direct response...
no direct response in bad eye
no consensual response in good eye
direct response in good eye
consensual response in bad eye
near response intact OU
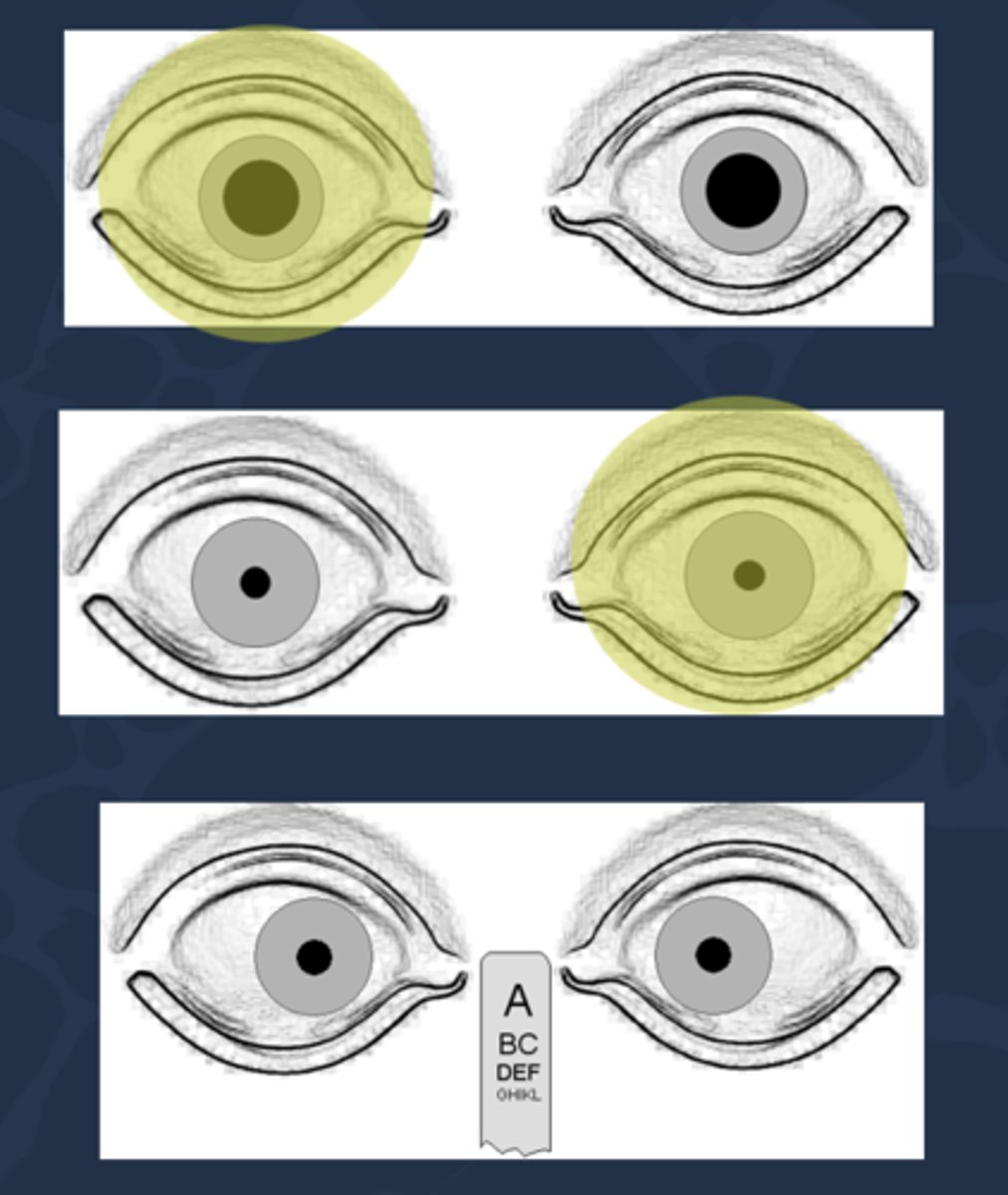
In what conditions may the direct response to light be absent?
severe head trauma
cardiac arrest
medical coma
brain death
Aside: what are 3 possible tests for malingerers?
1. have pt cover good eye, then throw a tennis ball to see if pt reacts
2. Troost's test = have pt cover good eye, pass a mirror in front of their face to see if there is an OKN movement
3. pass an offensive word written on a card in front of the pt to see if there is any facial expression/pupil dilation

What is the Au sign test for assessing consensual response, often used in determining whether or not pt has anterior segment inflam or malingering?
pt occludes light sensitive, painful eye and shine light in normal eye = if consensual response is intact, the bad eye pupil will constrict and will increase the pain
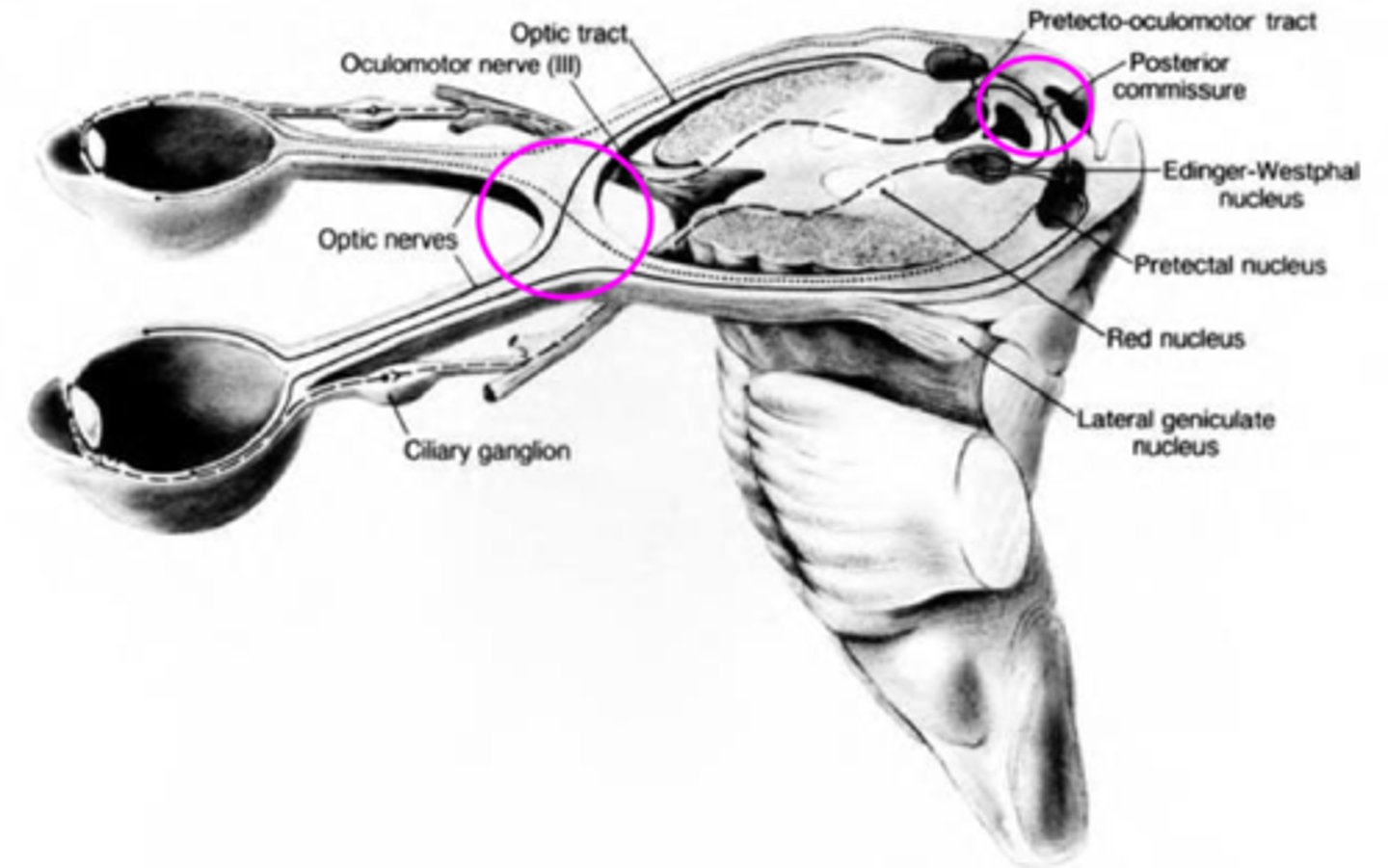
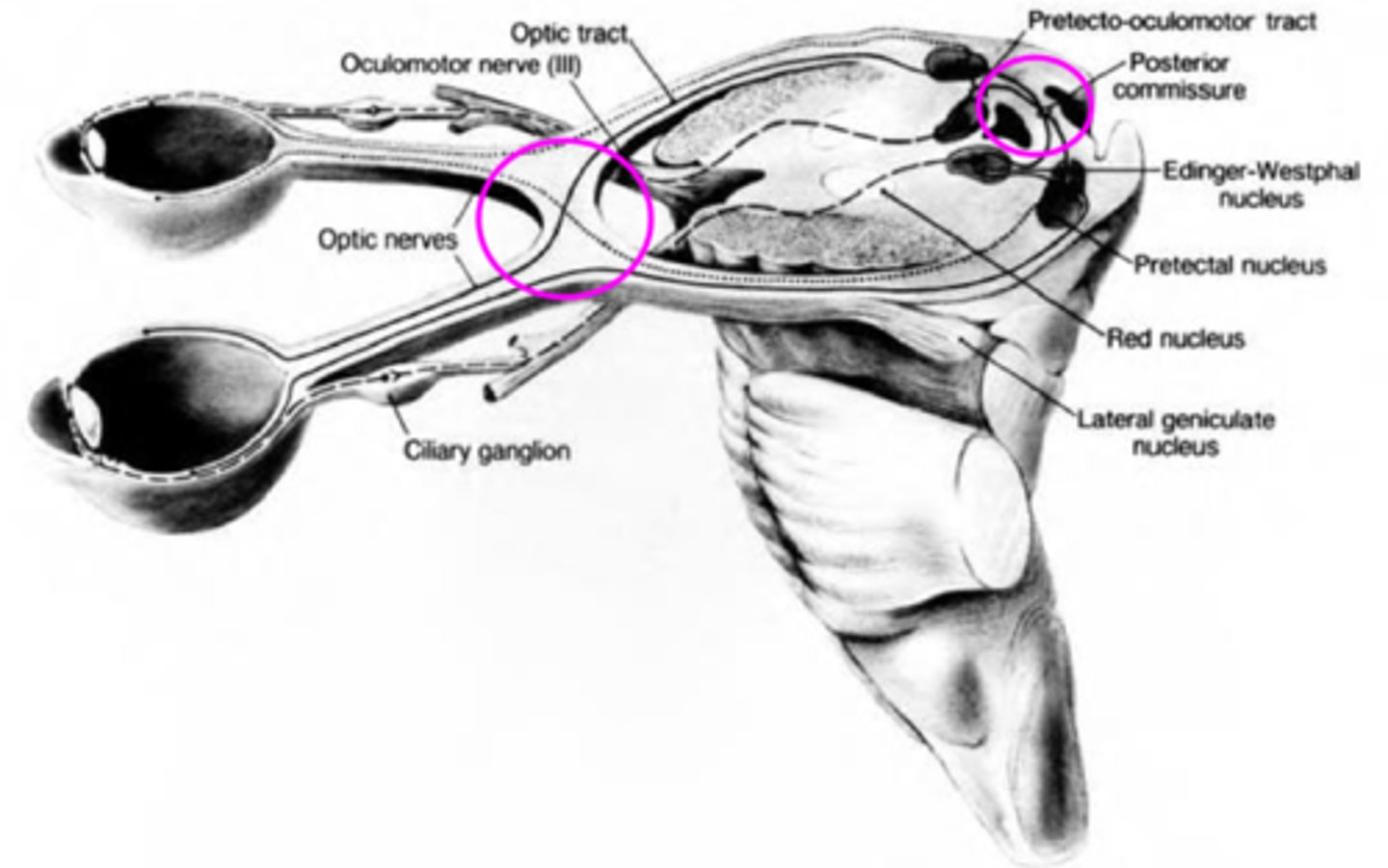
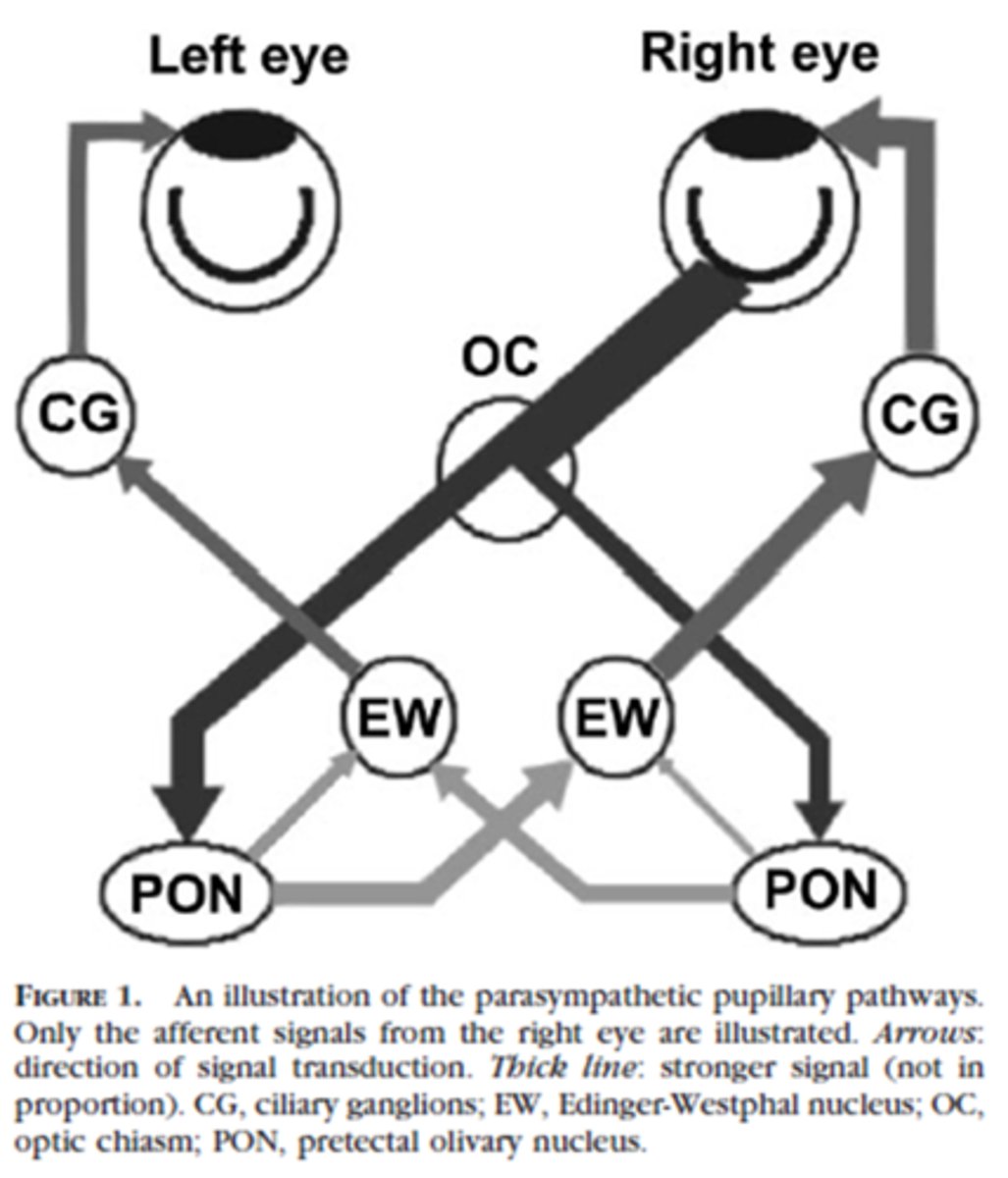
Explain the pathway of neural signals that is responsible for the pupil response.
RGC fibers travel to optic tract = some fibers separate and synapse in midbrain pretectal nucleus (superior colliculus) before reaching LGN = some of these fibers go to the ipsilateral E-W nucleus and others cross at the posterior commissure to the contralateral E-W nucleus.
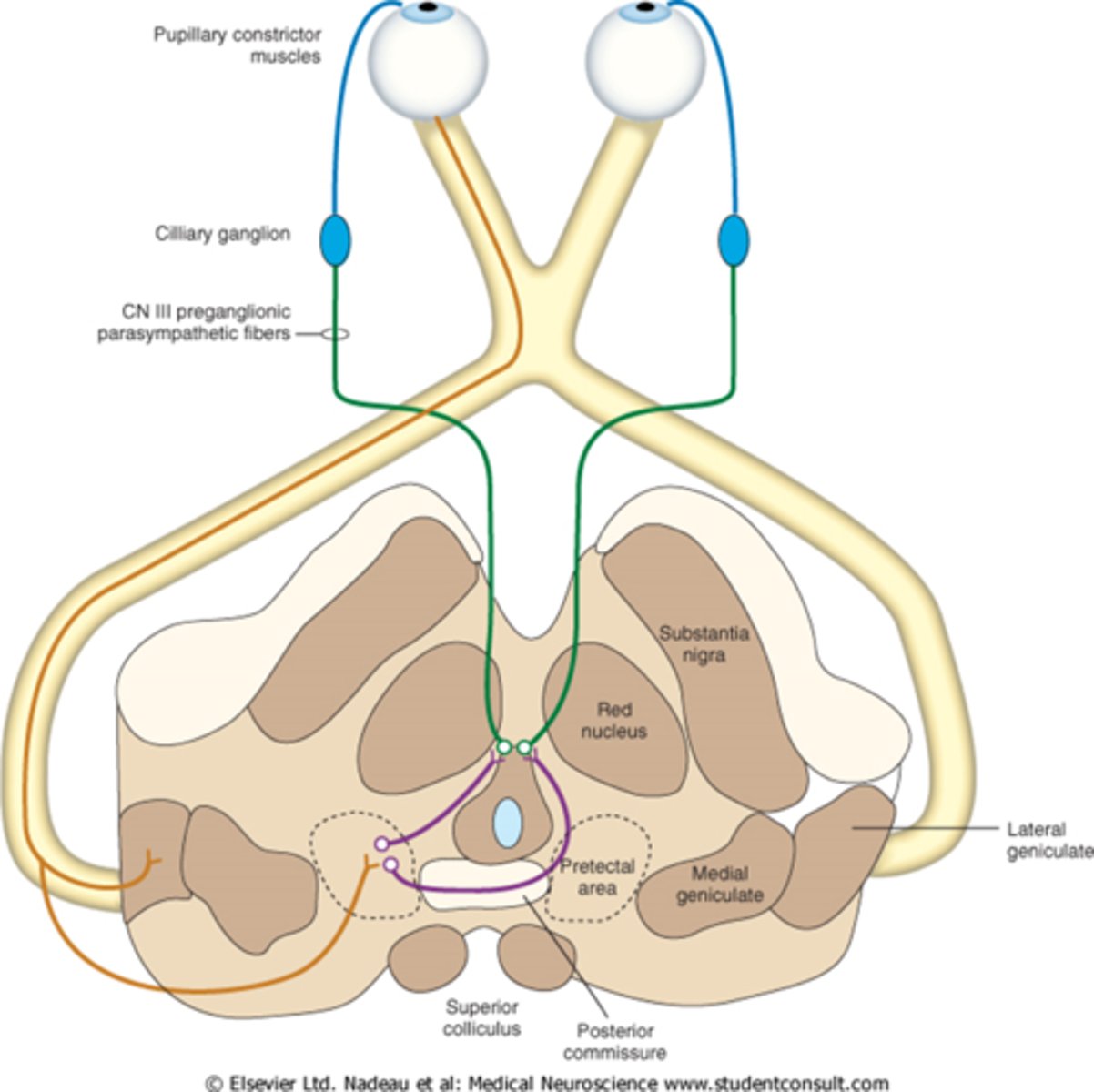
Where are the 2 decussations of fibers involved in the pupil response?
chiasm where all nasal retinal fibers cross
posterior commissure where some fibers go to the ipsilateral E-W and others to the contralateral E-W
In a normally functioning system, pupil reactions are always __________________ when light is directed into either eye.
grossly equal
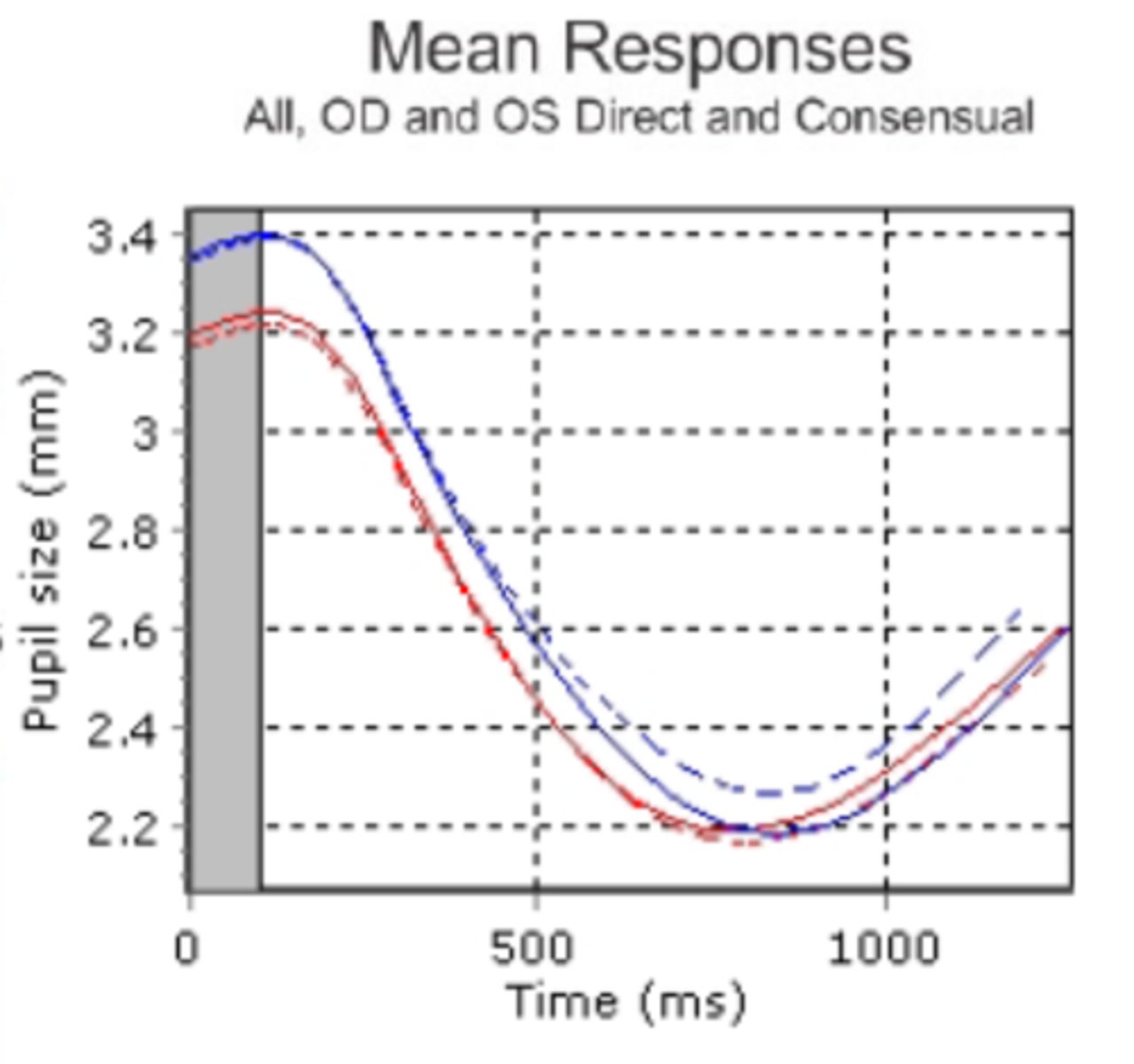
Is there an anisocoria and/or an APD shown here?
anisocoria is present bc of unequal pupil sizes, but both pupils show the same latency and velocities so there is no APD
What is contraction anisocoria?
pupil size obtained when shining light into direct eye is different than the consensual response obtained in the other eye (even if you didn't see aniso before this)
can be bilateral (doesn't matter which eye) or unilateral (ony occurs in one eye)
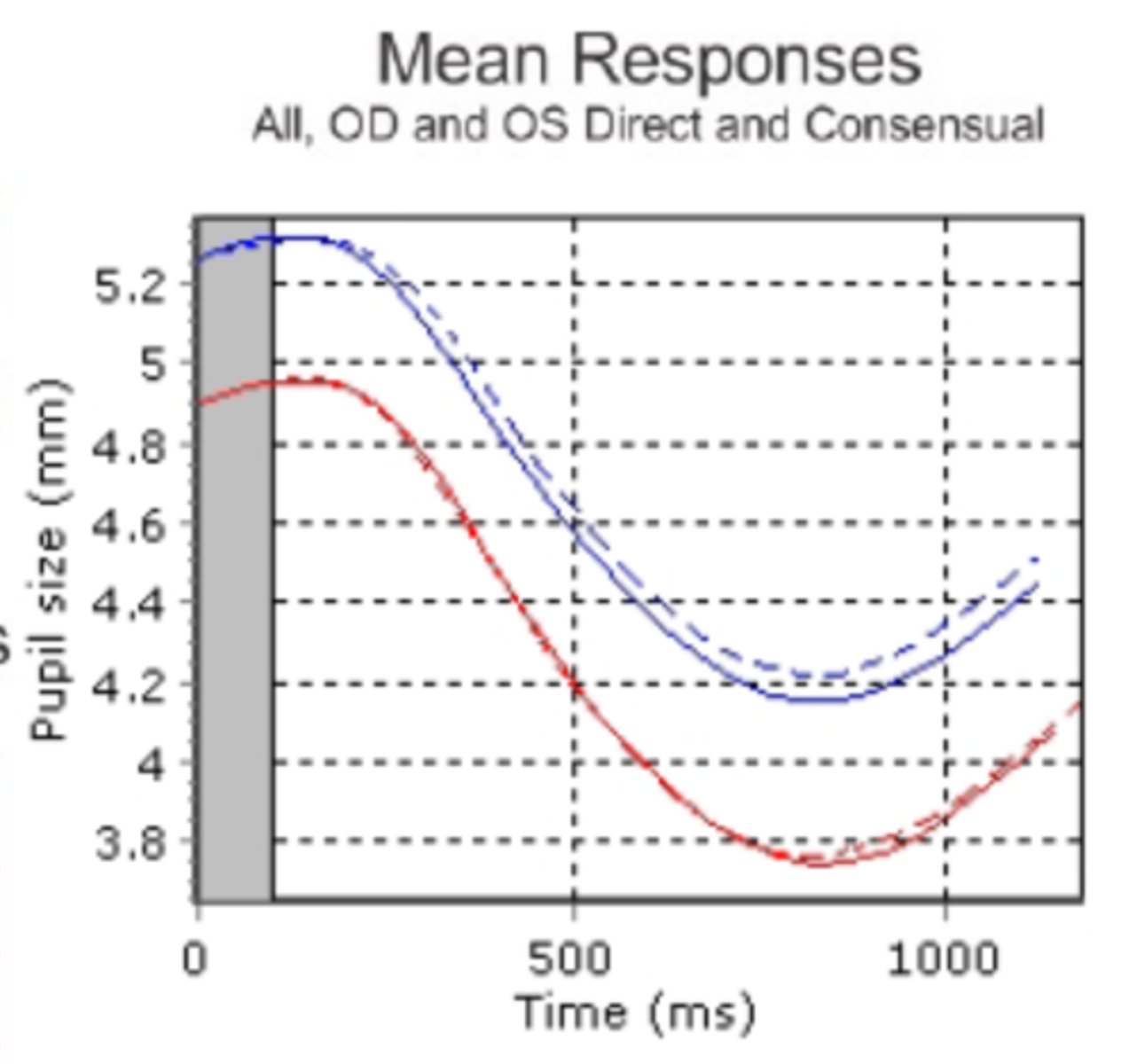
What is shown here?
OD consensual is slightly smaller than the OD direct response, but this is a normal variation!
What does a positive RAPD (aka Marcus Gunn pupil) look like?
direct response is less than the consensual response in the same eye
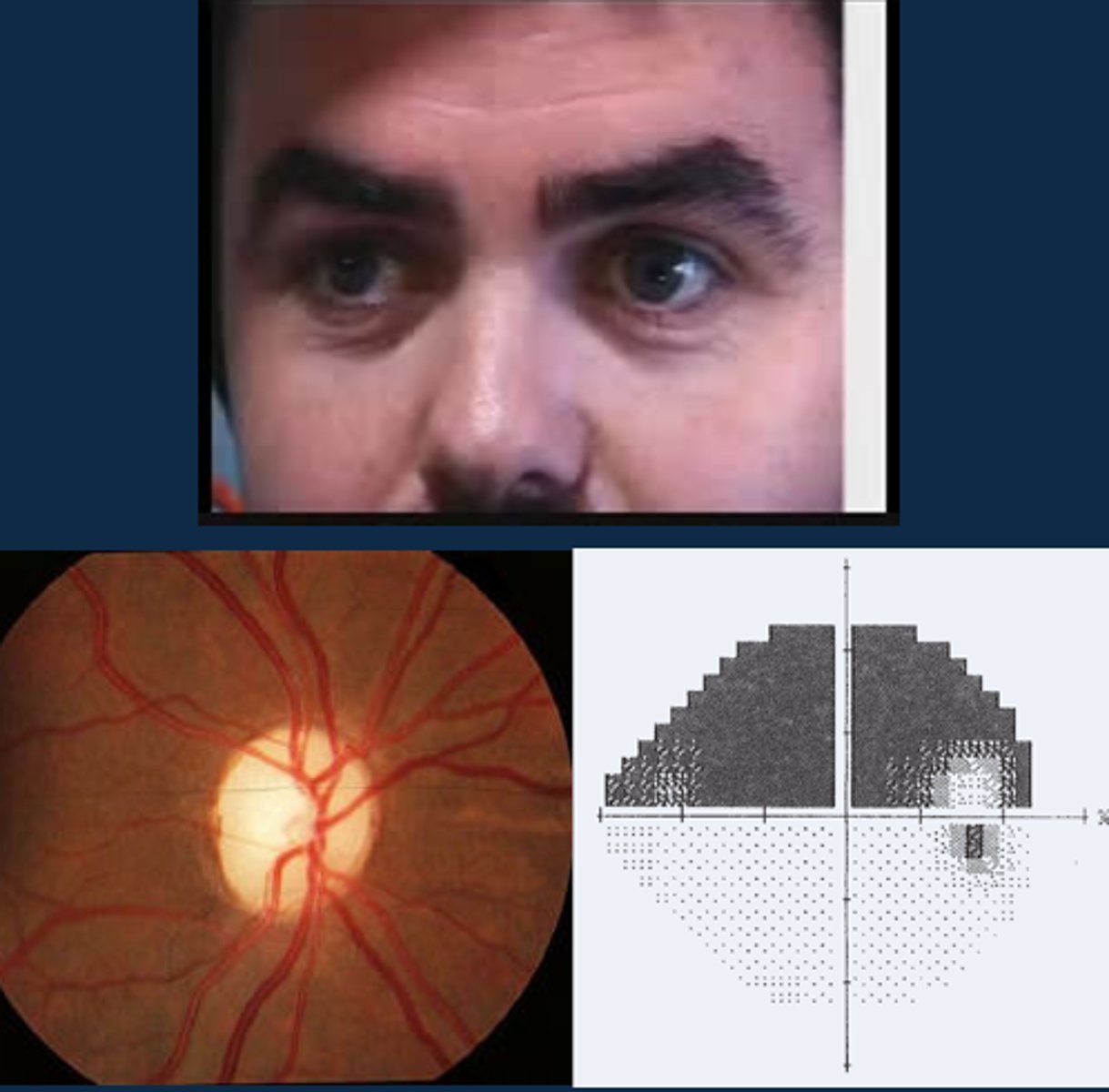
What does a positive RAPD (aka Marcus Gunn pupil) mean?
issue with the afferent pathway of information getting to brain = ONH disease like optic atrophy, optic neuritis, optic neuropathy, glaucoma, OR pt already bleached
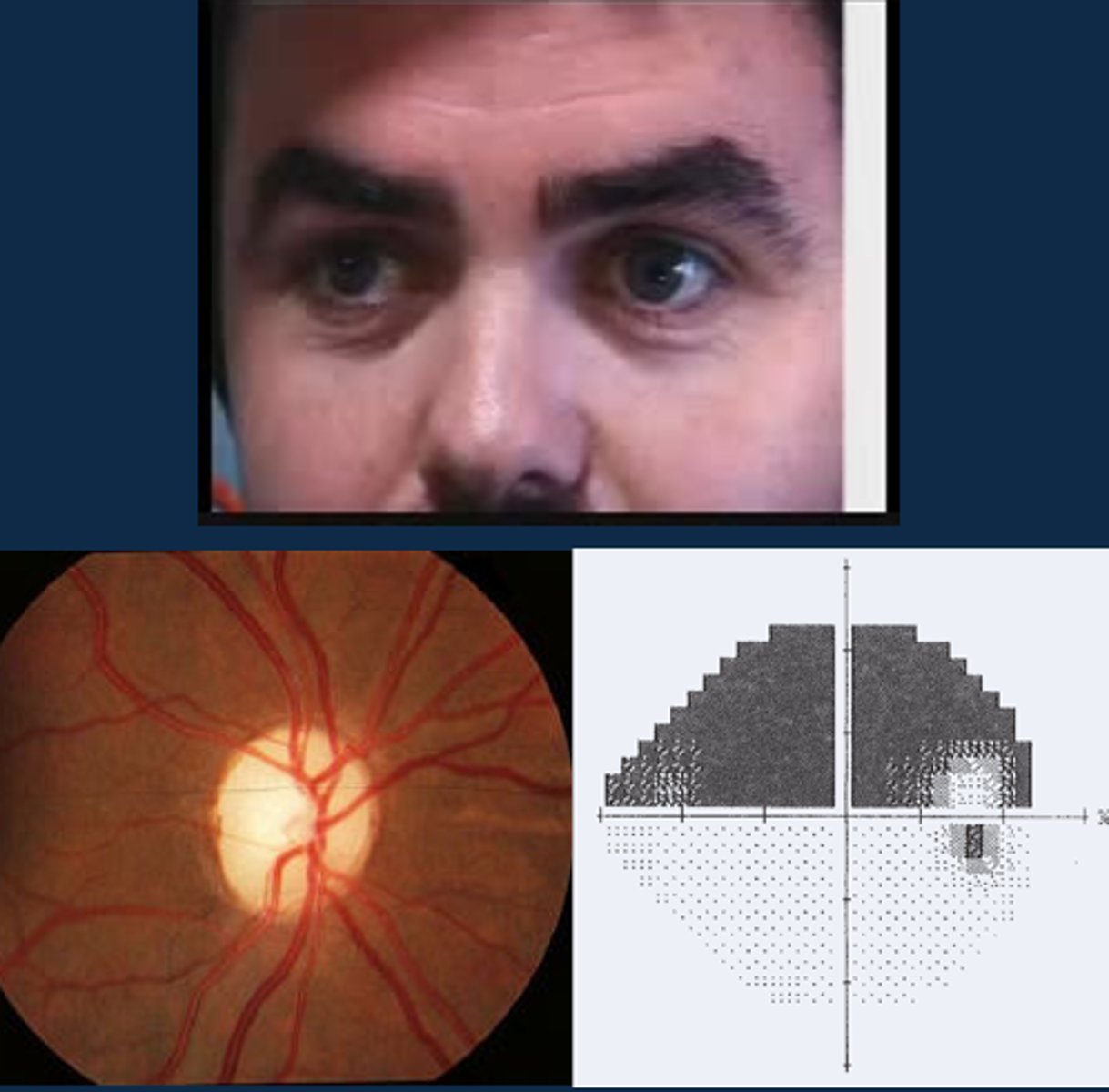
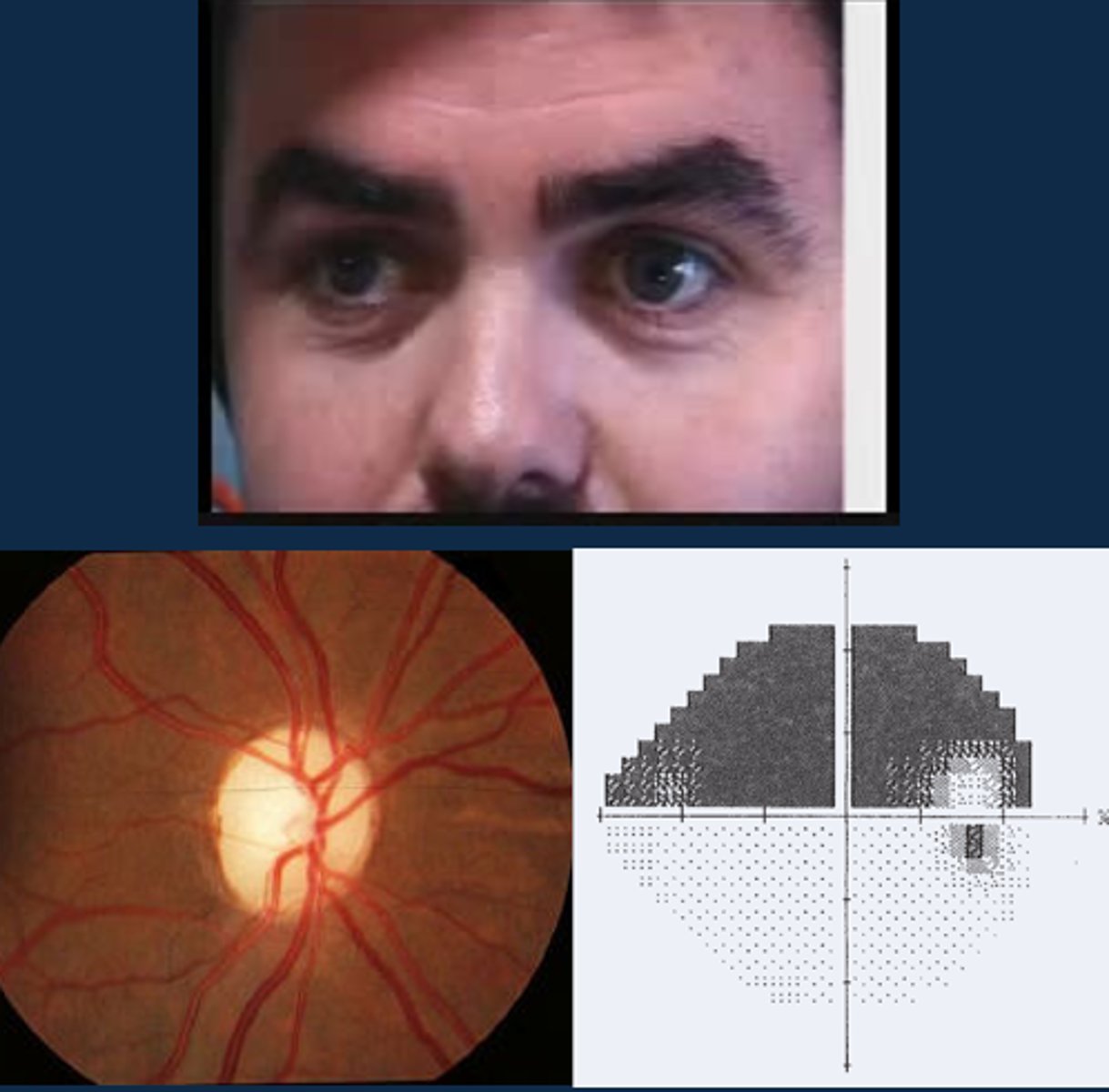
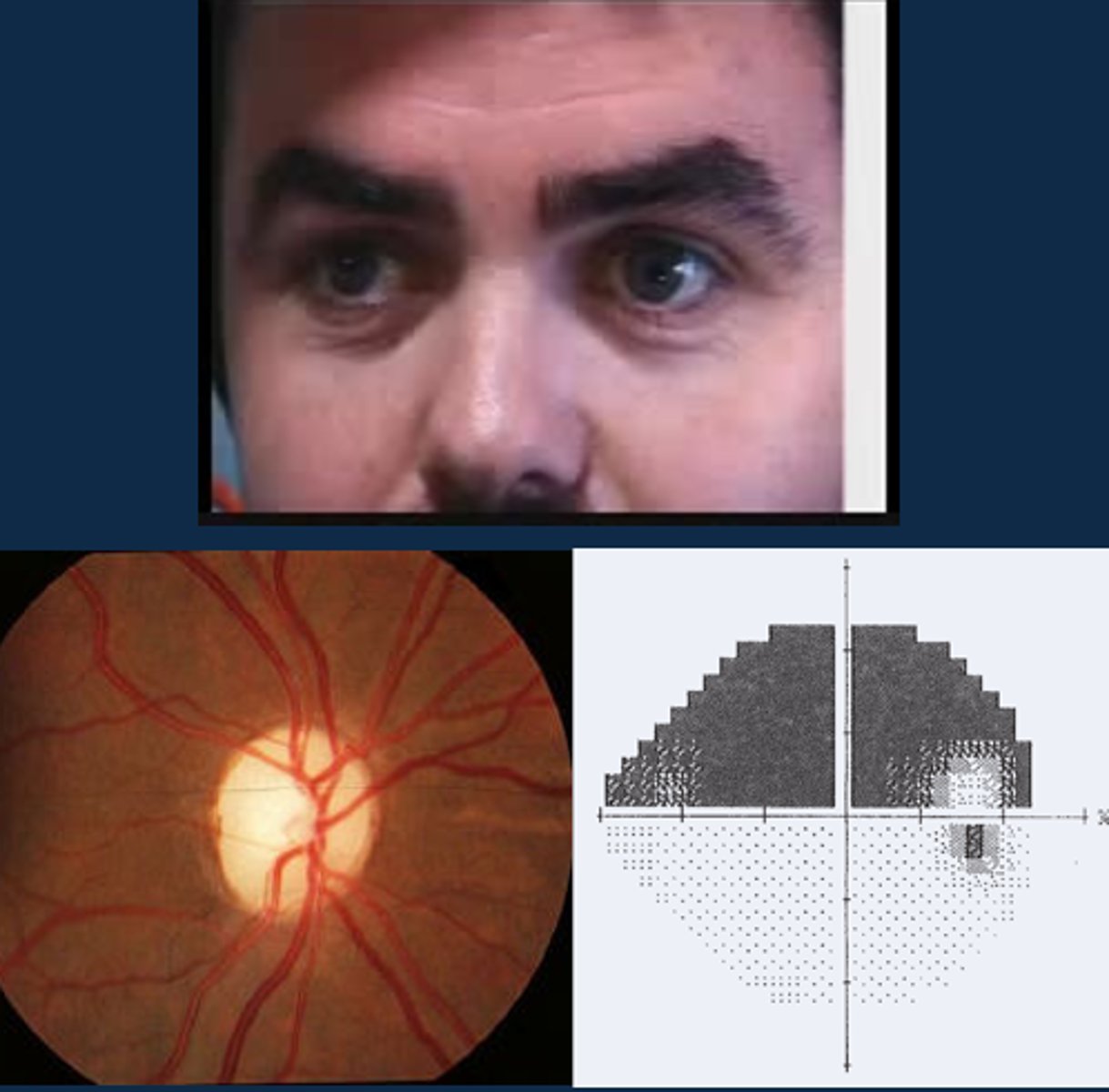
Aside from a positive RAPD, what other signs might indicate optic atrophy?
ONH pallour
dyschromatopsia
altitudinal VF defect
ONH NFL dropout
What are some tips for performing an APD test?
pt should fixate across the room
perform in dim illumination
use a bright, cool light
check for aniso first
don't bleach eye beforehand
avoid eyedrops beforehand
What is the subjective luminosity test to verify an APD?
ask pt "if this penlight is worth $100 of brightness with your good eye, what is it now worth looking with the bad eye?"
similar to red-cap test

What should we expect to see on the subjective luminosity test if there is an APD?
bad eye should see things more dimly by a difference of at least $15 due to a slower, less intense AP in that diseased eye
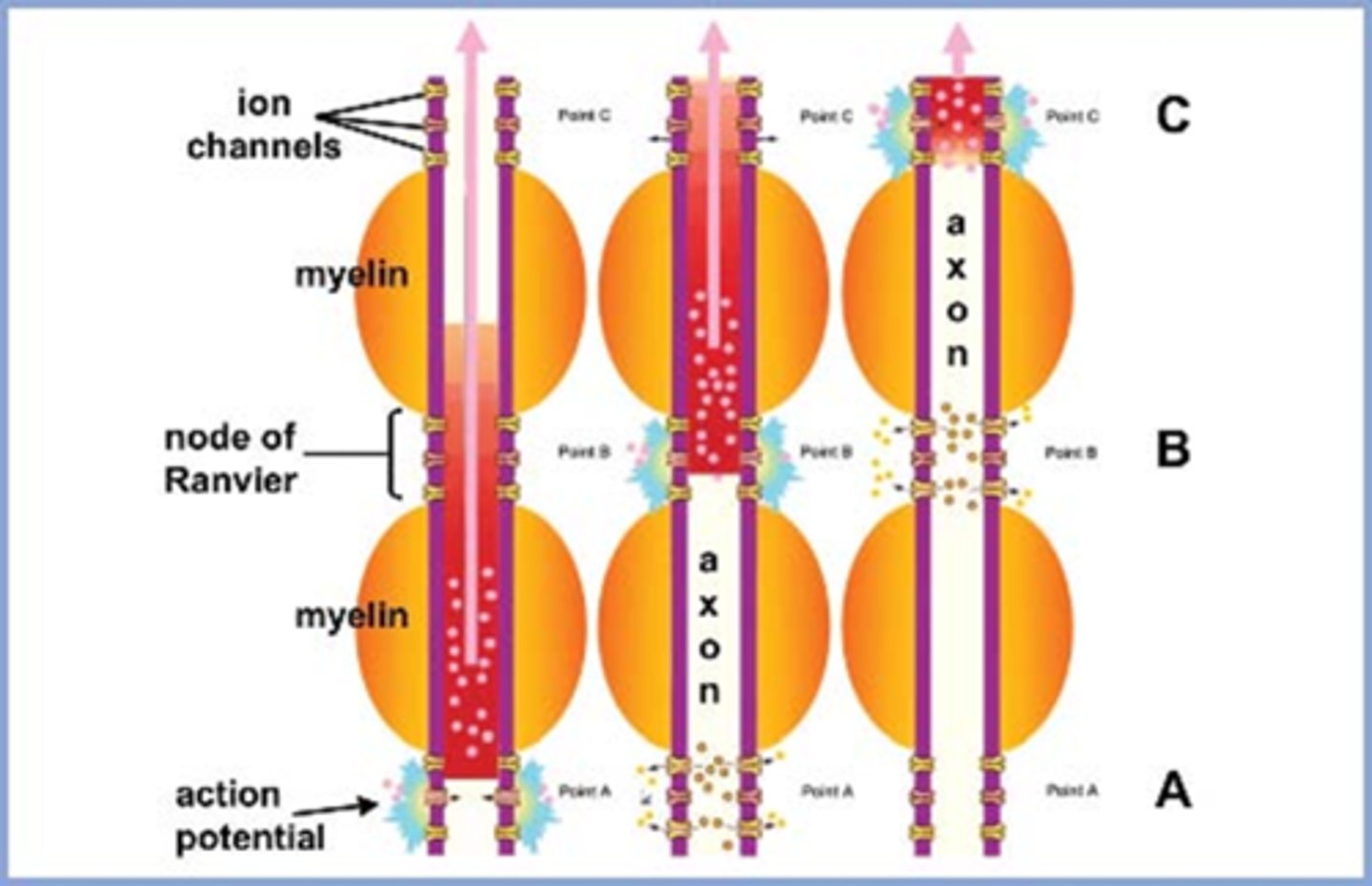
What is the indirect APD test?
when we compare the consensual response and the direct response in the normal eye

When might we use the indirect APD test?
to check for an APD in an eye where the pupil doesn't work/is fixed in position due to posterior synechiae, CN III palsy
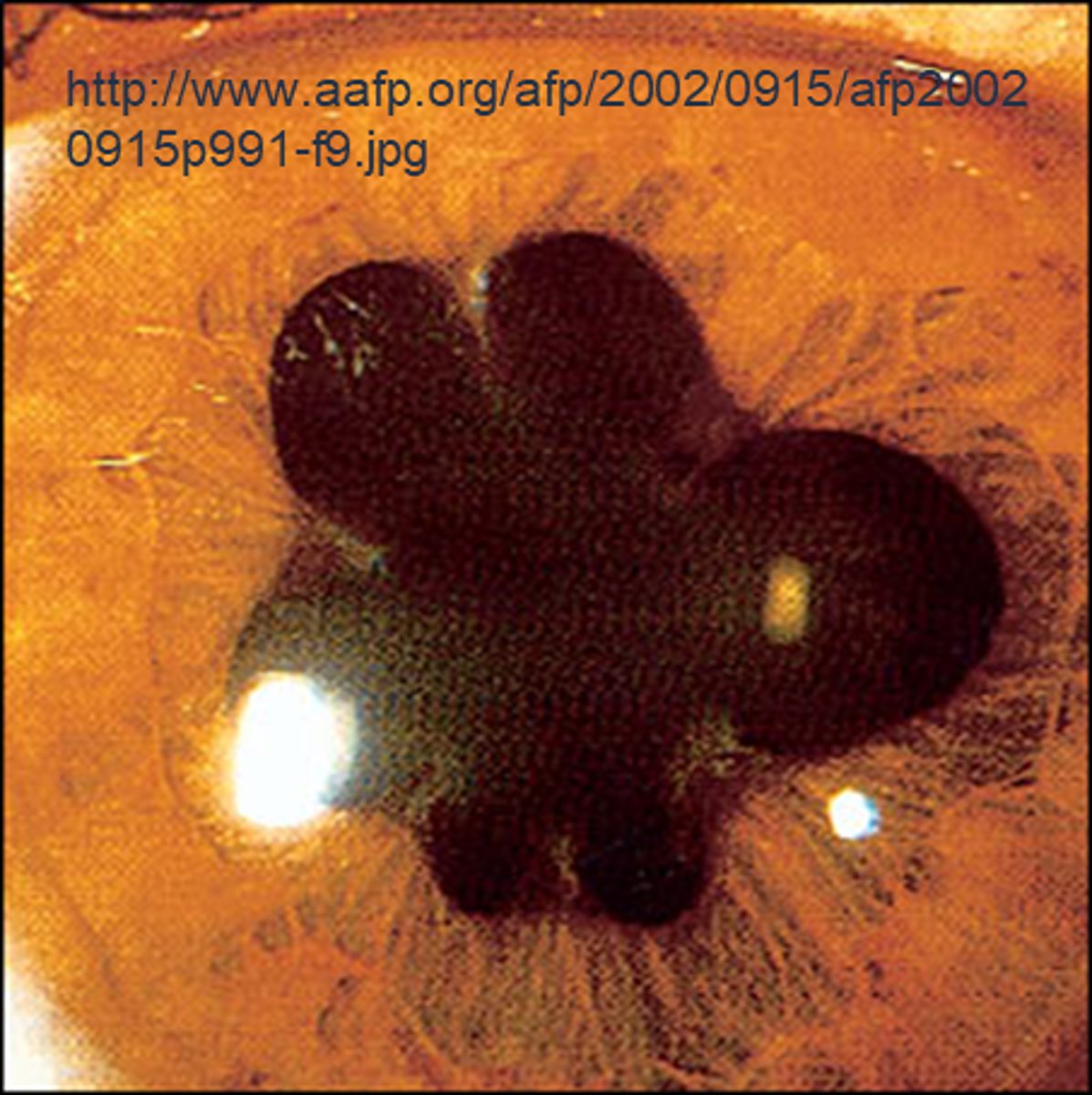
Ex) Your pt has a Hx of trauma causing an OD efferent pupil defect. How would you perform the indirect APD test here?
OD does not react directly or consensually = look at OS direct and consensual responses = if OS constricts when pupil is shined into either eye, then there is NO APD in either eye
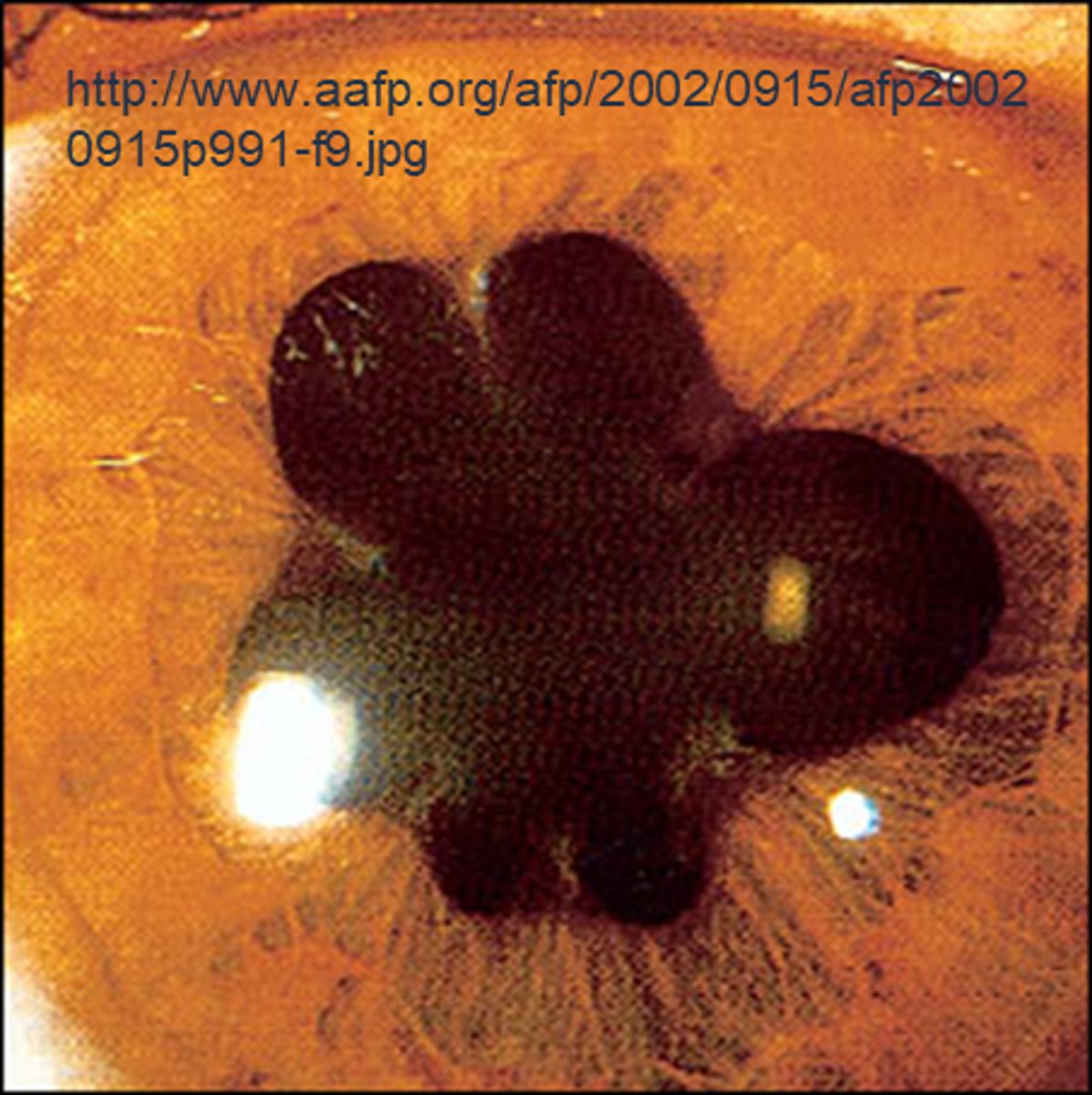
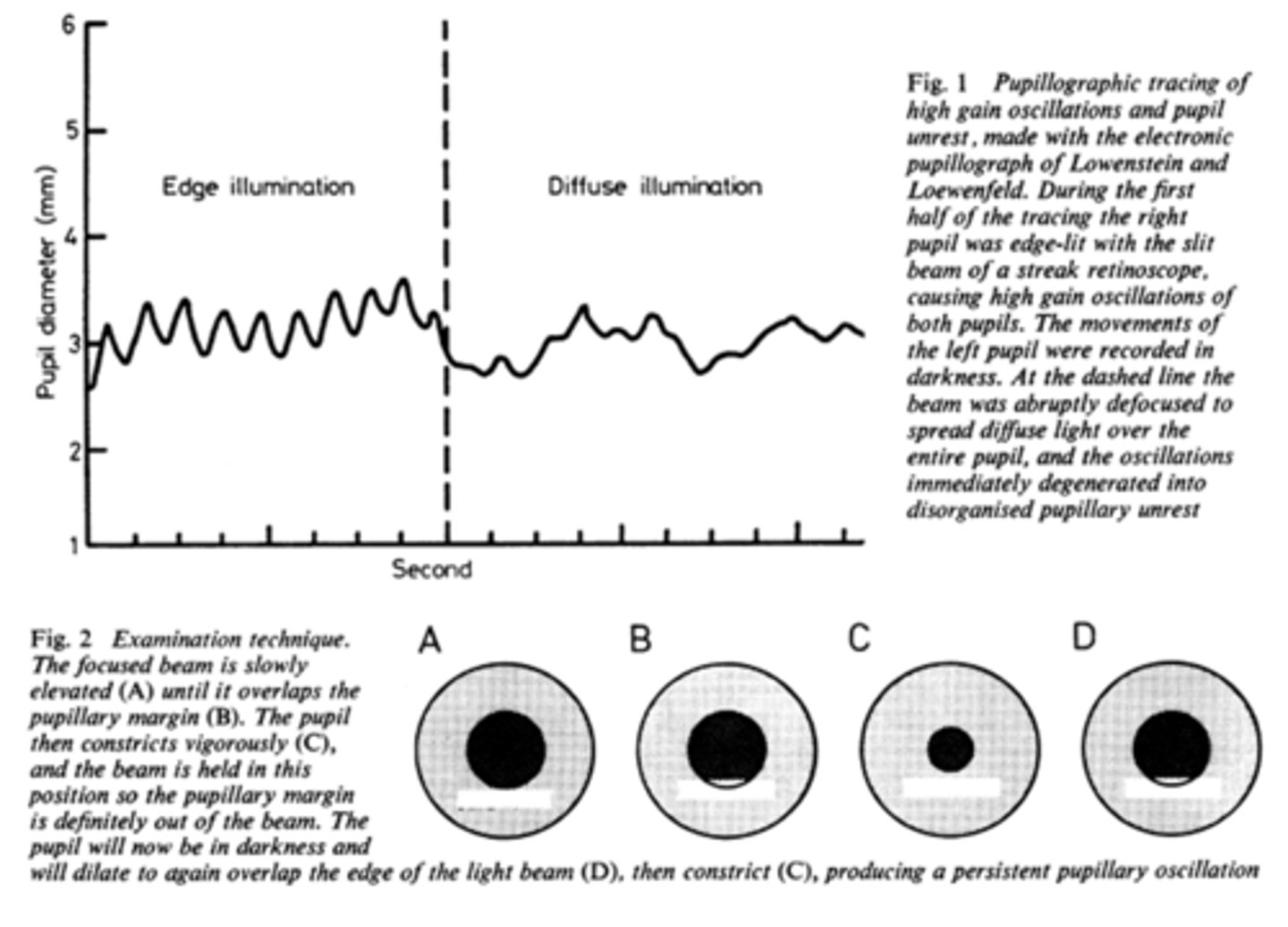
What is pupil cycle time?
playing peek-a-boo with the pupil = position slit lamp bream on edge of iris causing pupil to oscillate between constrict, dilate, constrict, dilate
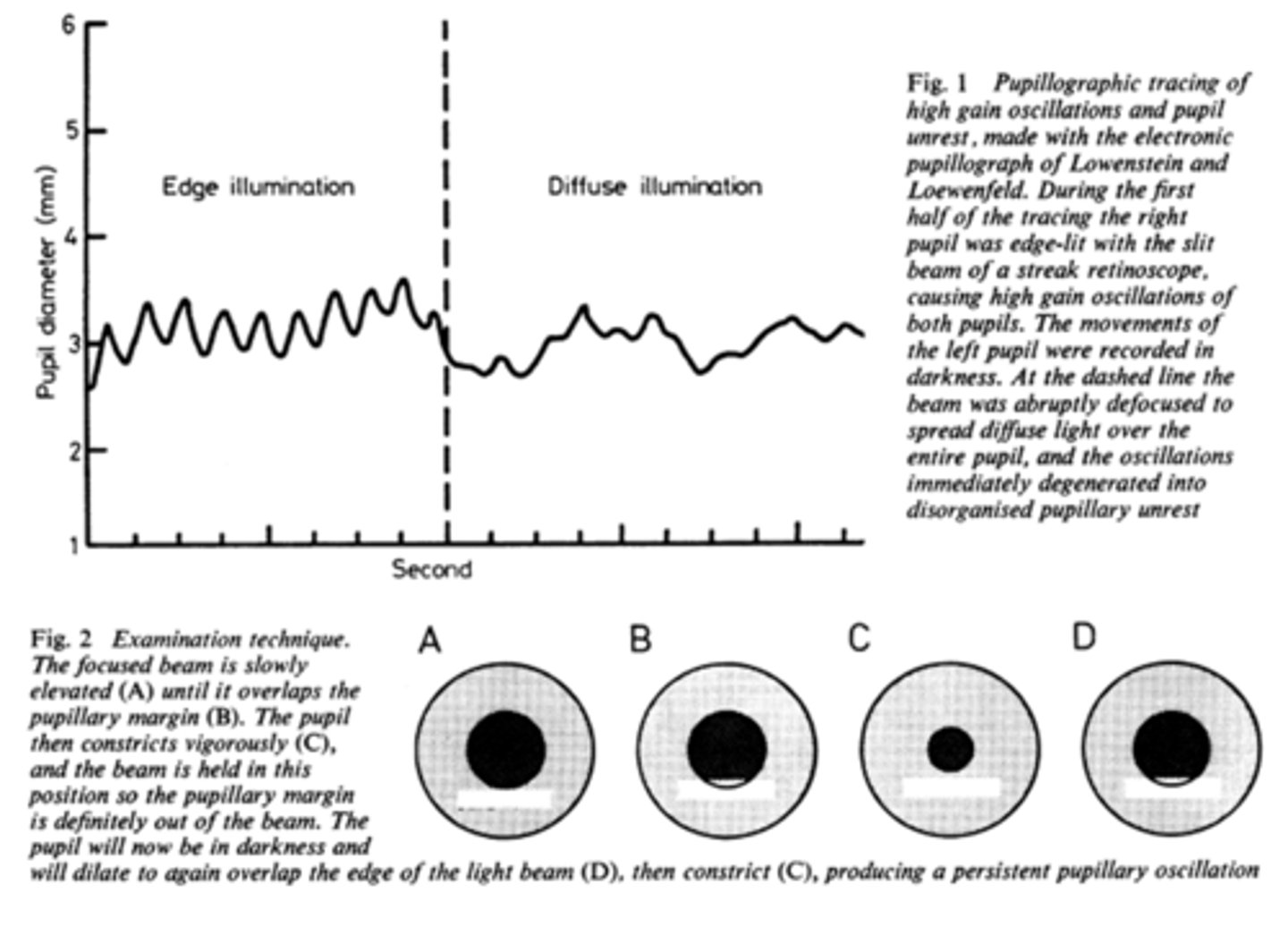
How do we obtain/measure a pupil cycle time?
time 100 cycles of oscillations and convert time to msec = this tells us how many msec per cycle
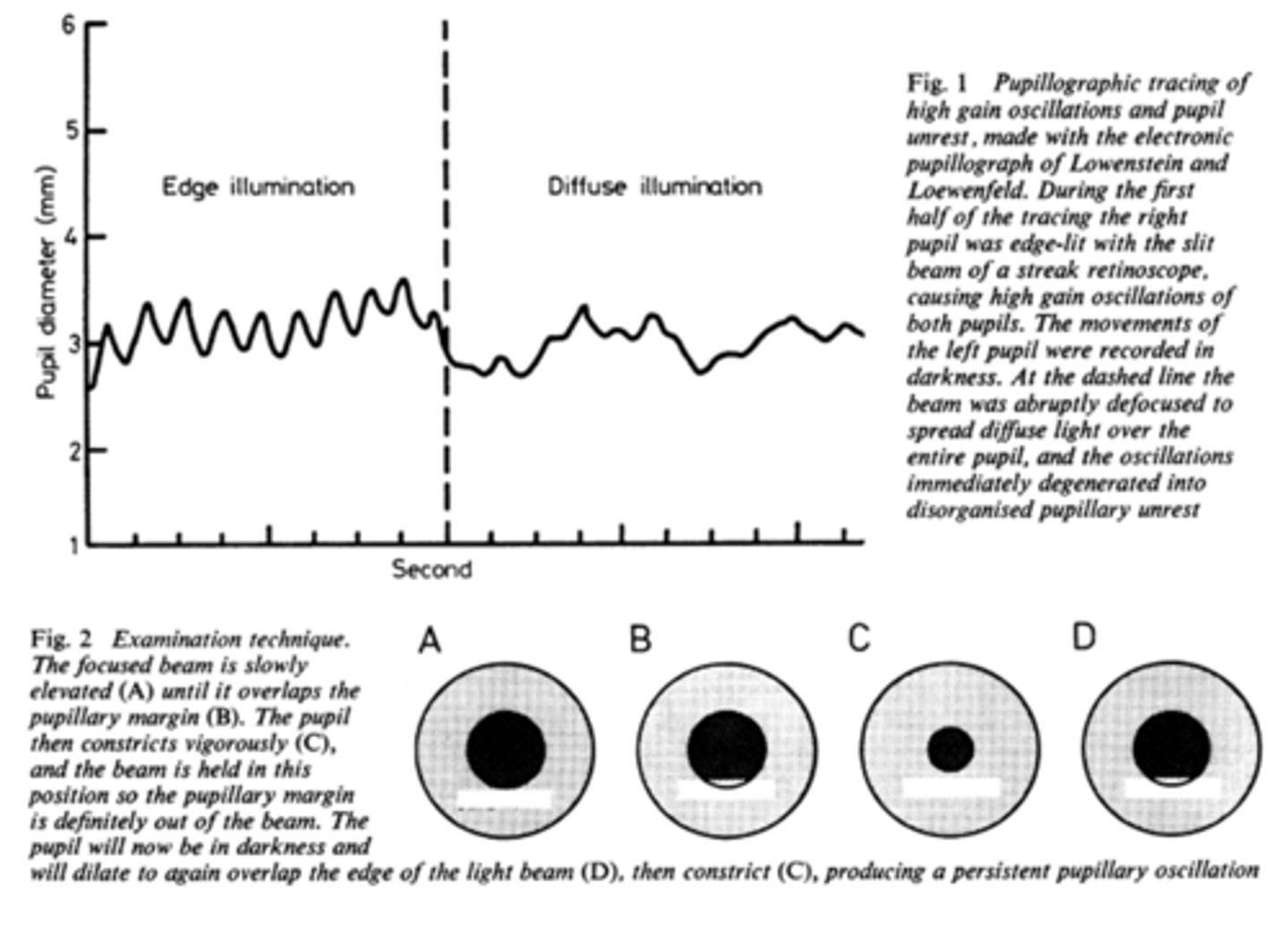
What does pupil cycle time tell us?
tells us how much impulse is getting to the E-W nucleus = another indicator of ONH function
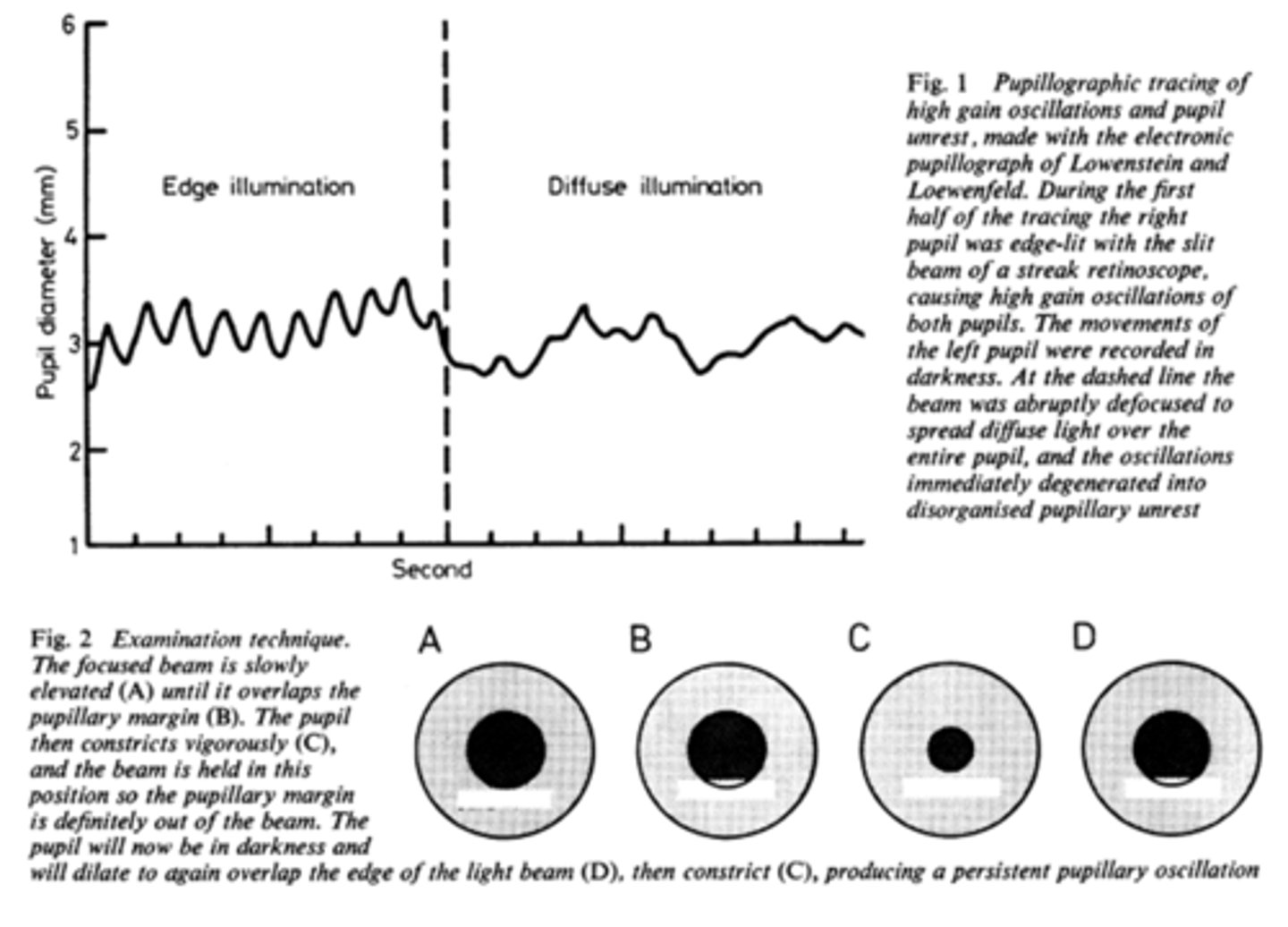
What is a normal pupil cycle time?
954 msec
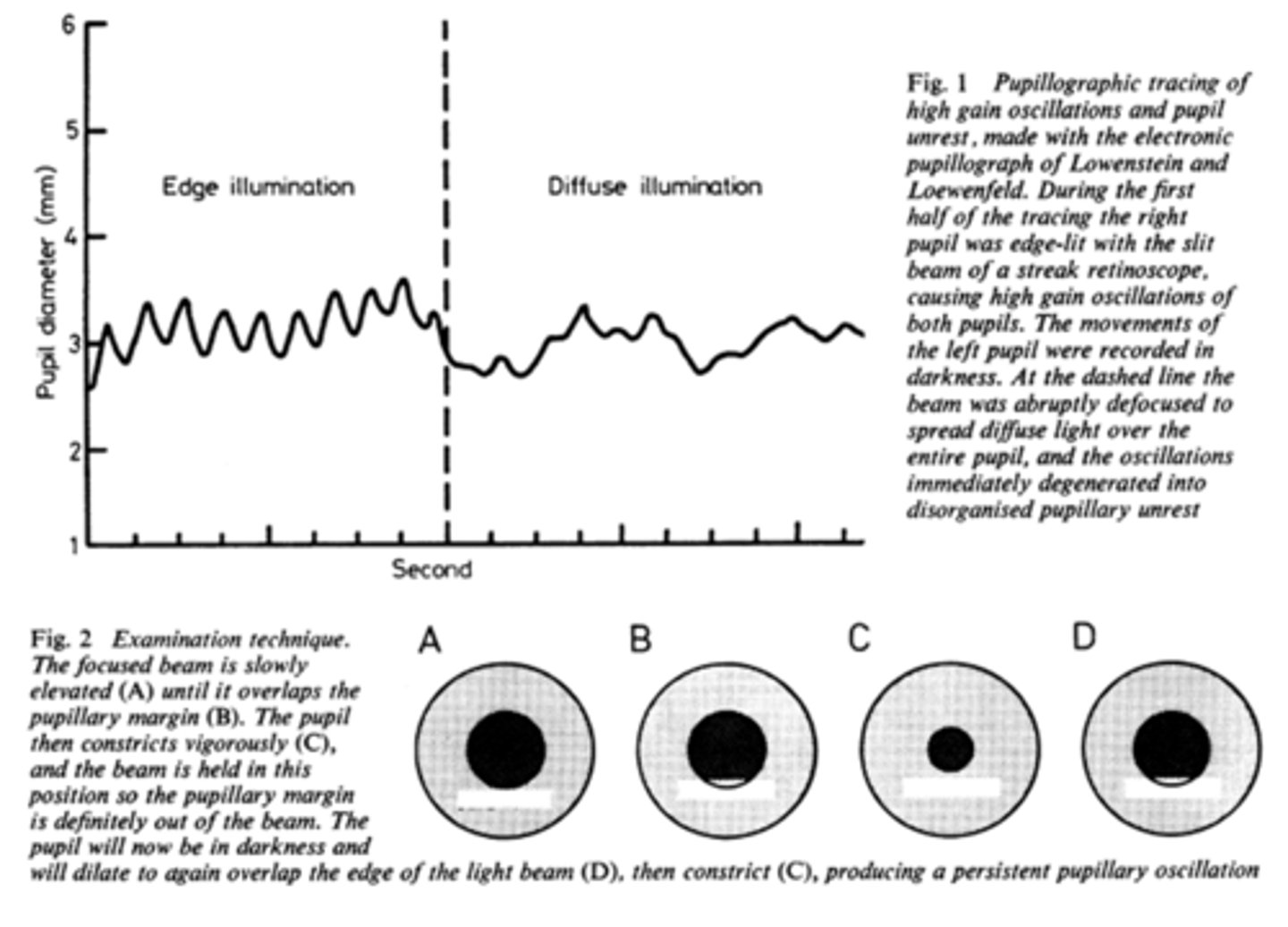
What does a prolonged pupil cycle time tell us?
APD or afferent lesion of ONH
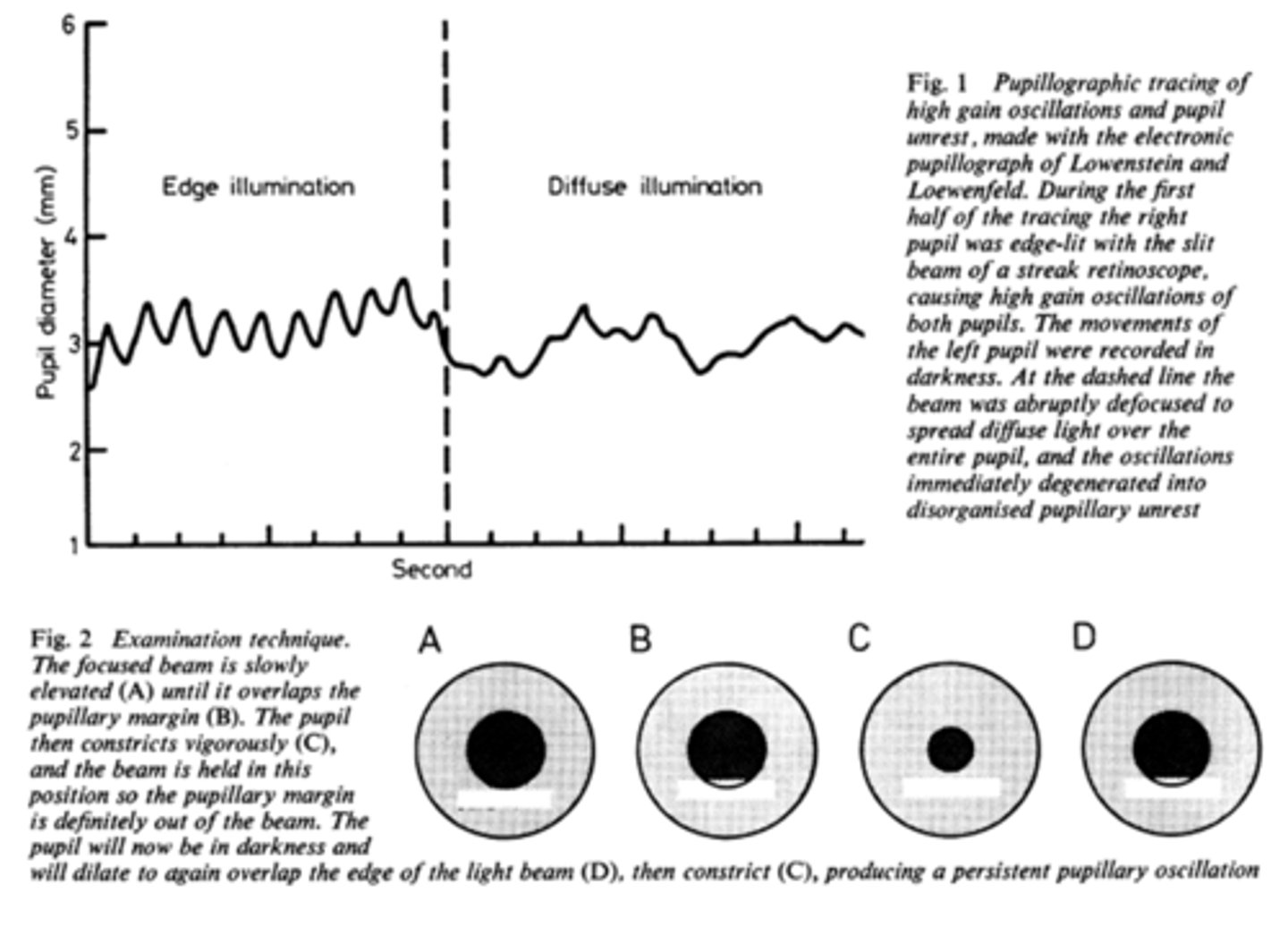
What does an asymmetric (40 msec difference between eyes) pupil cycle time tell us?
prolonged cycle time = APD or afferent lesion of ONH
Is it more likely to have a poorer near repsonse or direct response when assessing pupils in a normal pt?
near reponse is typically worse than direct response in a normal pt
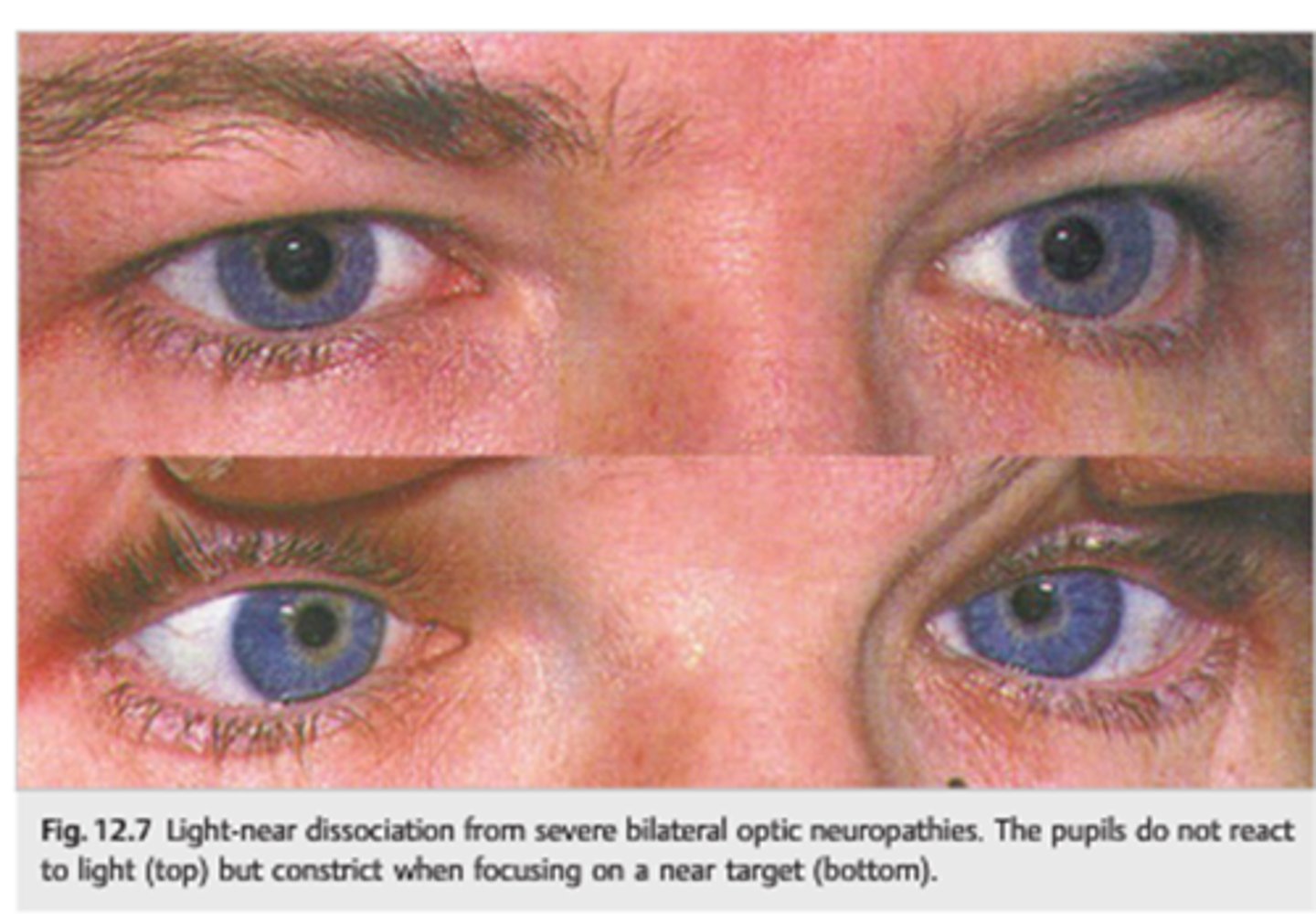
What is a light-near dissociation pupil?
pupil that does NOT respond to light, but does have a near response
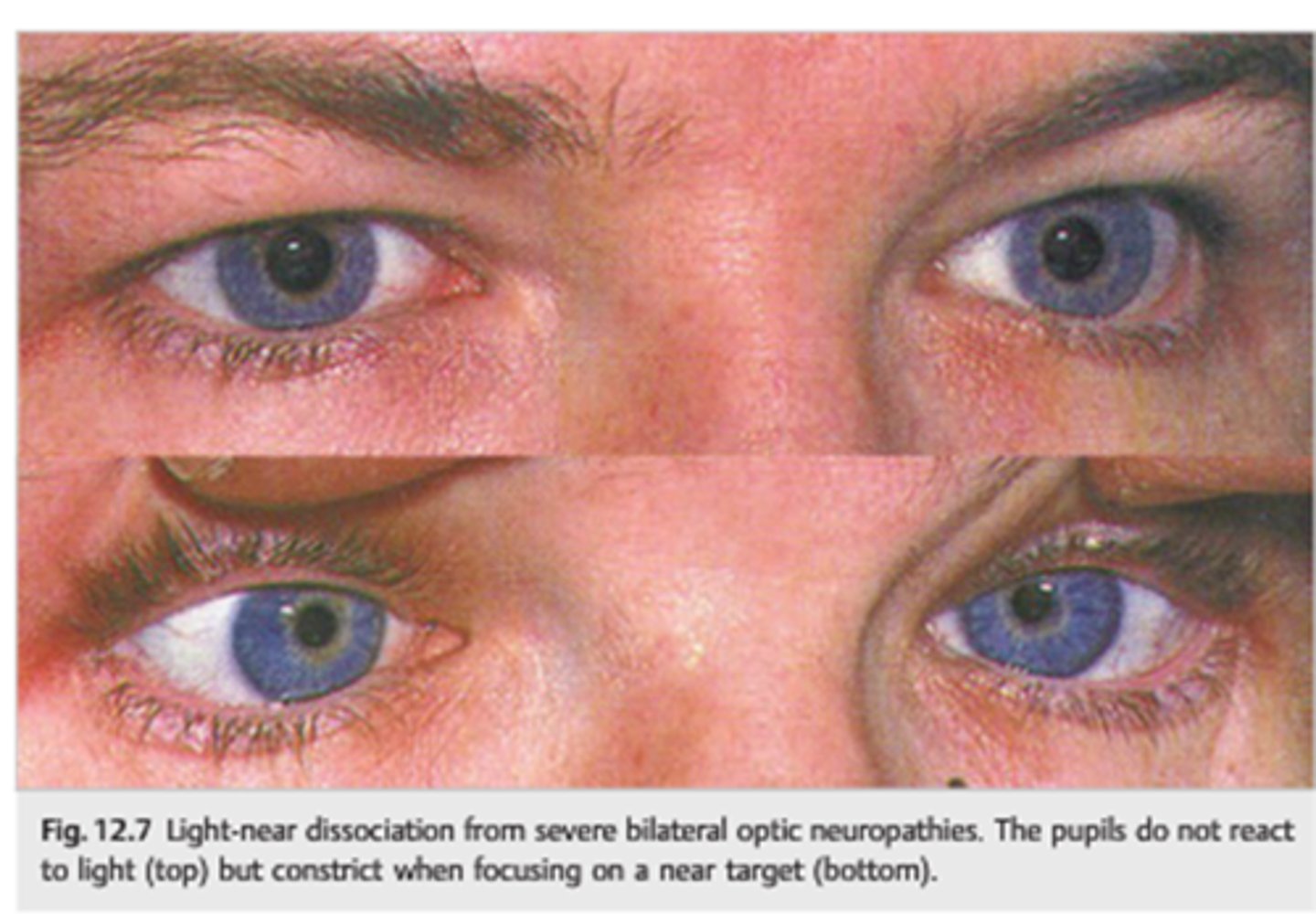
What can cause a light-near dissociation pupil?
Argyll-Robertson (CNS syphillis)
amaurotic pupil
aberrant regeneration of CN III
tonic pupil
tectal pupils (upper midbrain)
tabes diabetica (posterior spinal columns in DM)
