Textiles & Fiber-Dye Interactions
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
What is a bicomponent fiber?
A fiber made of two polymers with different chemical or physical properties, spun from the same filament.
What are the advantages of bicomponent fibers?
They provide suitability for end products, such as creating thermally bonded non-woven fabrics or mimicking animal hair structures.
What is the function of a spinneret in fiber manufacturing?
A spinneret is a metal plate with tiny holes that shapes extruded fibers into specific cross-sectional forms.
What is the significance of fiber cross-section in forensic analysis?
The shape of a fiber when cut along its length is used to identify fiber type and manufacturing origin.
What are mordants in dyeing?
Mordants are substances that form coordination complexes with metal ions, which then bind to fibers, making dyes insoluble.
Azo dyes
(R-N=N-R) Form H-bonds between N and H in OH groups in fiber
-Ex: cotton
Ionic dyes
Fiber= + (cation/basic) dye= - (anionic/acidic)
- Ex: Nylon
Weft knitting
knitting forms loops in a horizontal manner using adjacent needles
Warp knitting
forms loops in a vertical manner with needles knitting a series of warp yarns.
yarn
Yarn is a continuous strand of textile fibers, filaments, or material suitable for weaving, knitting, or entangling to form a textile fabric.
fabric
A fabric is a textile structure produced by interlacing fibers with a substantial surface area in relation to its thickness.
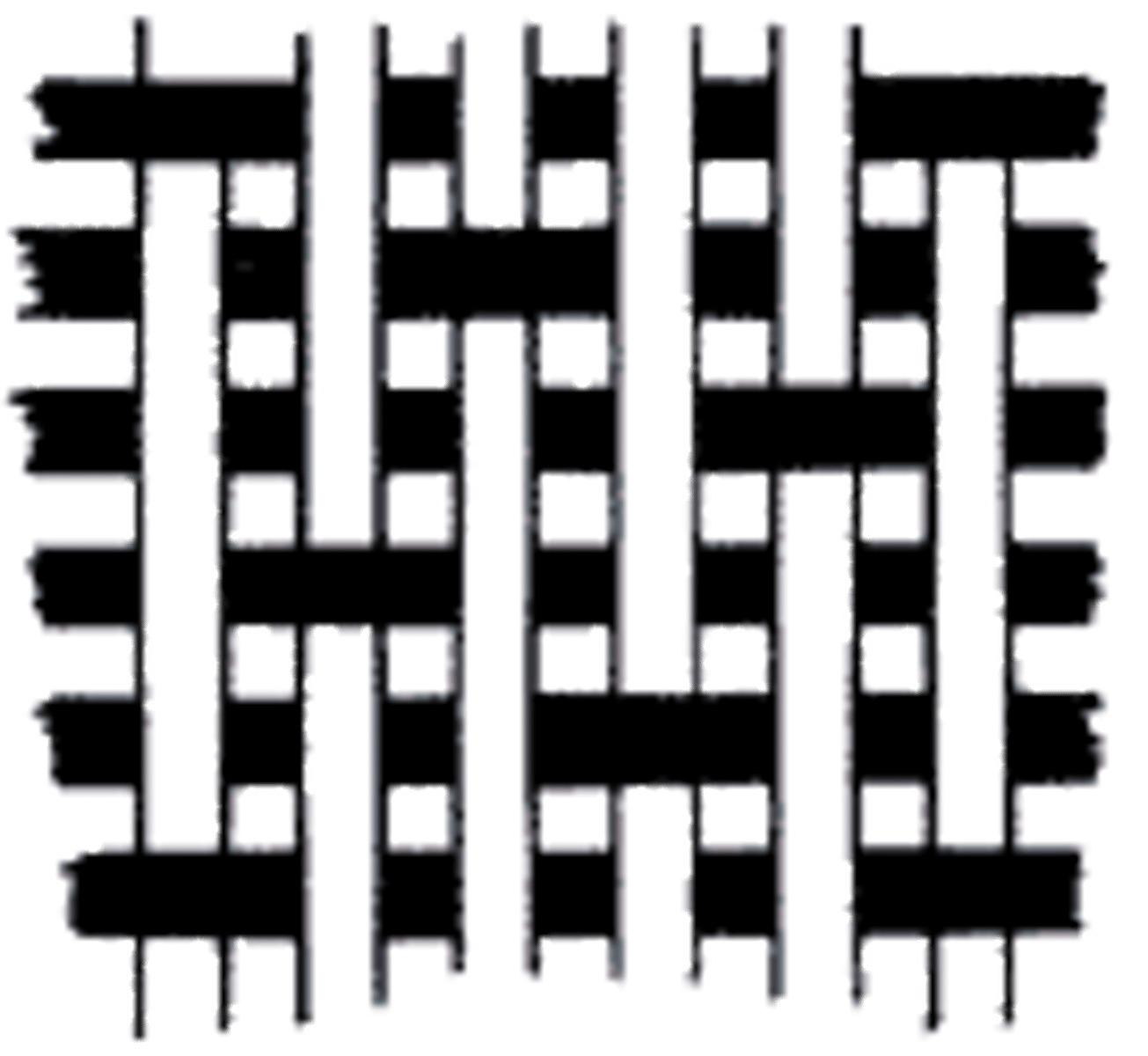
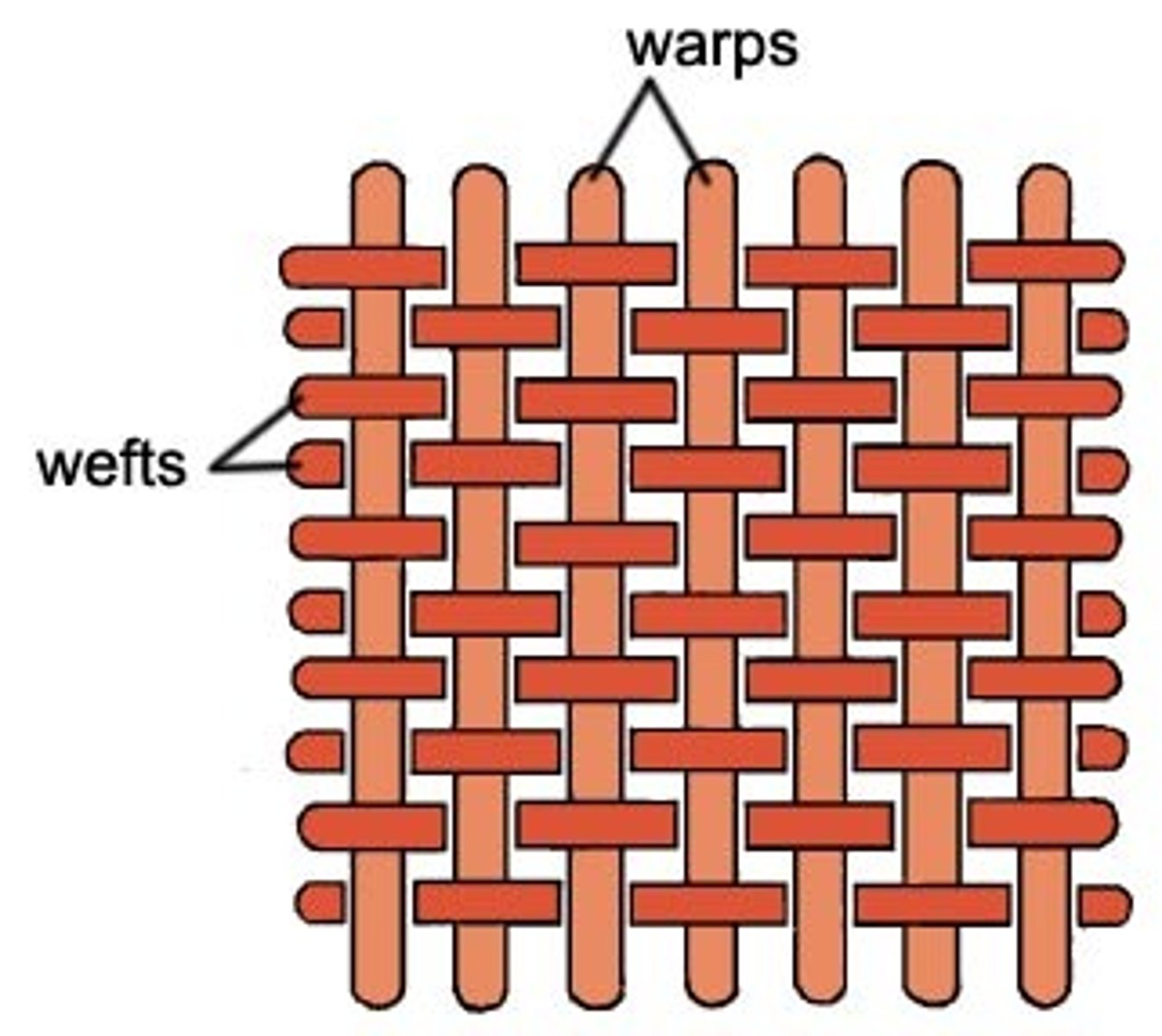
What is the basic principle of weaving?
Weaving involves interlacing one warp yarn over one weft yarn and then passing it under the next weft yarn.
What characterizes a satin weave?
In a satin weave, the warp yarn floats over multiple weft yarns before passing under one.
What is the role of fibers in forensic examinations?
Fibers provide evidence that can associate suspects with a crime scene and can be individualized if reference fibers match those collected.
regenerated cellulose
A fiber made from cellulose through a regeneration process, such as rayon and viscose, which involves dissolving the polymer and reforming it.
What is the purpose of regenerated cellulose?
to produce continuous fibers and separate unwanted chemicals present in the raw cotton
What are some examples of natural fibers?
Natural fibers include cellulose fibers like cotton and animal fibers like silk and wool.
What is the process of acetylation in fiber production?
Acetylation is a chemical modification process that alters hydroxyl groups in cellulose to produce Cellulose acetate fibers
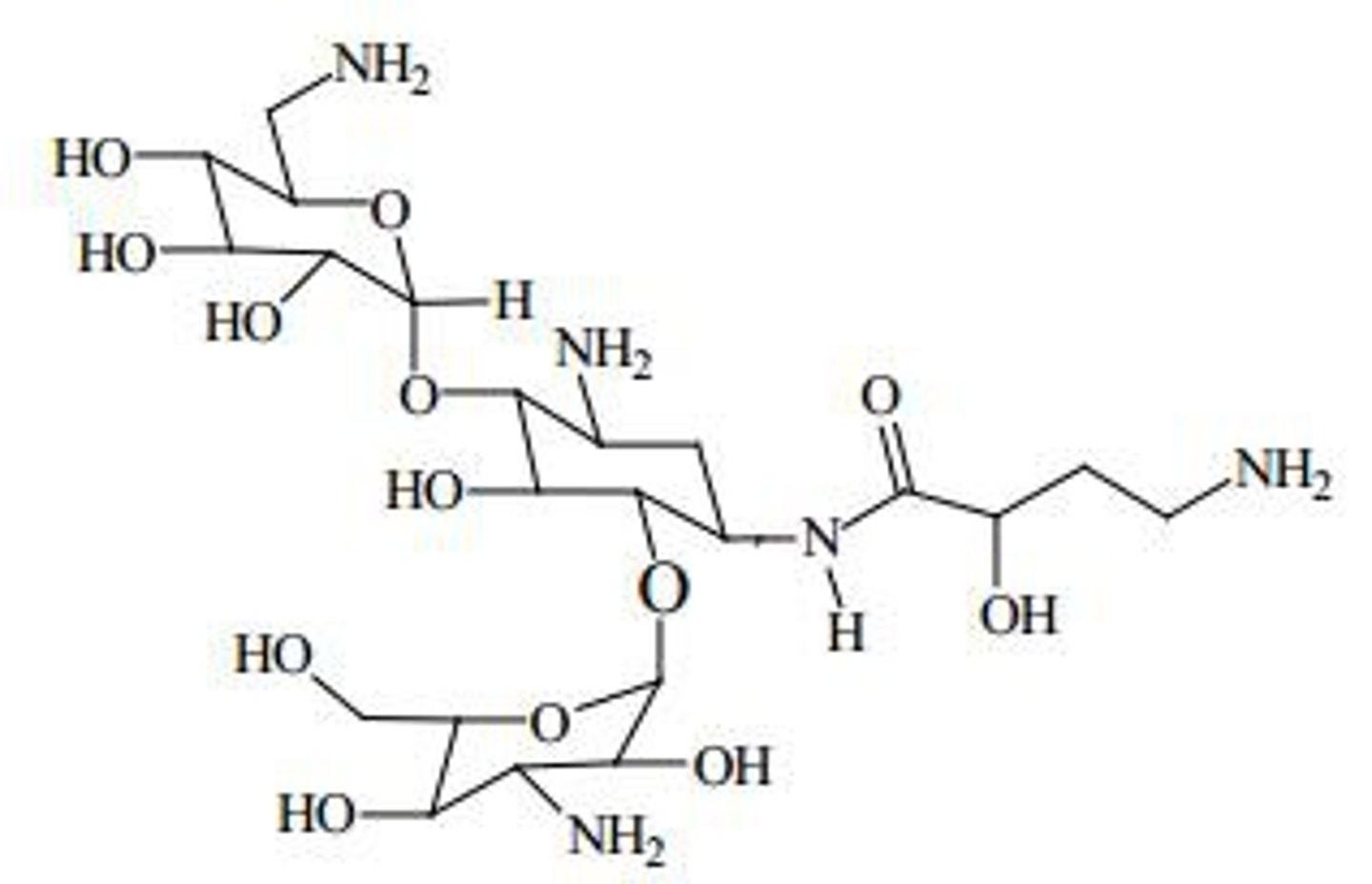
triacetate
Cellulose polymer where all the oh groups are acetylated
Acetate
Cellulose polymer where some of the OH groups are acetylated (2.5/repeat unit)
What are synthetic fibers?
Polymeric fibers produced from simple starting materials, such as polyesters and polyamides
What is the significance of fiber uniformity?
Fiber uniformity affects the properties and quality of the final textile product.
What is the difference between natural and synthetic fibers?
Natural fibers are derived from plants or animals, while synthetic fibers are man-made from chemical processes.
What is the purpose of using azo dyes in textiles?
Azo dyes are used for coloring fibers and form complexes with metal ions to enhance dye stability.
What is the role of cellulose in fiber production?
Cellulose serves as a primary raw material for producing regenerated fibers like rayon.
What does the term 'heat setting' refer to in fiber processing?
Heat setting is a process that stabilizes the shape and properties of fibers, often used in thermally bonded fabrics.
What is the importance of understanding fiber interactions in textiles?
Understanding fiber interactions is crucial for dyeing processes and achieving desired fabric properties.
Extrusion
A manufacturing process that forces polymer solution through a spinneret to form a synthetic fiber, affecting the uniformity nd properties
single ply
One strand of twisted fibers
Plied yarn
multiple yarn strands twisted together
plain weave
A basic weave in which each filling strand goes over and under each warp strand once.
twill weave
A weave in which the weft yarn is passed over and 2-3 warp yarns
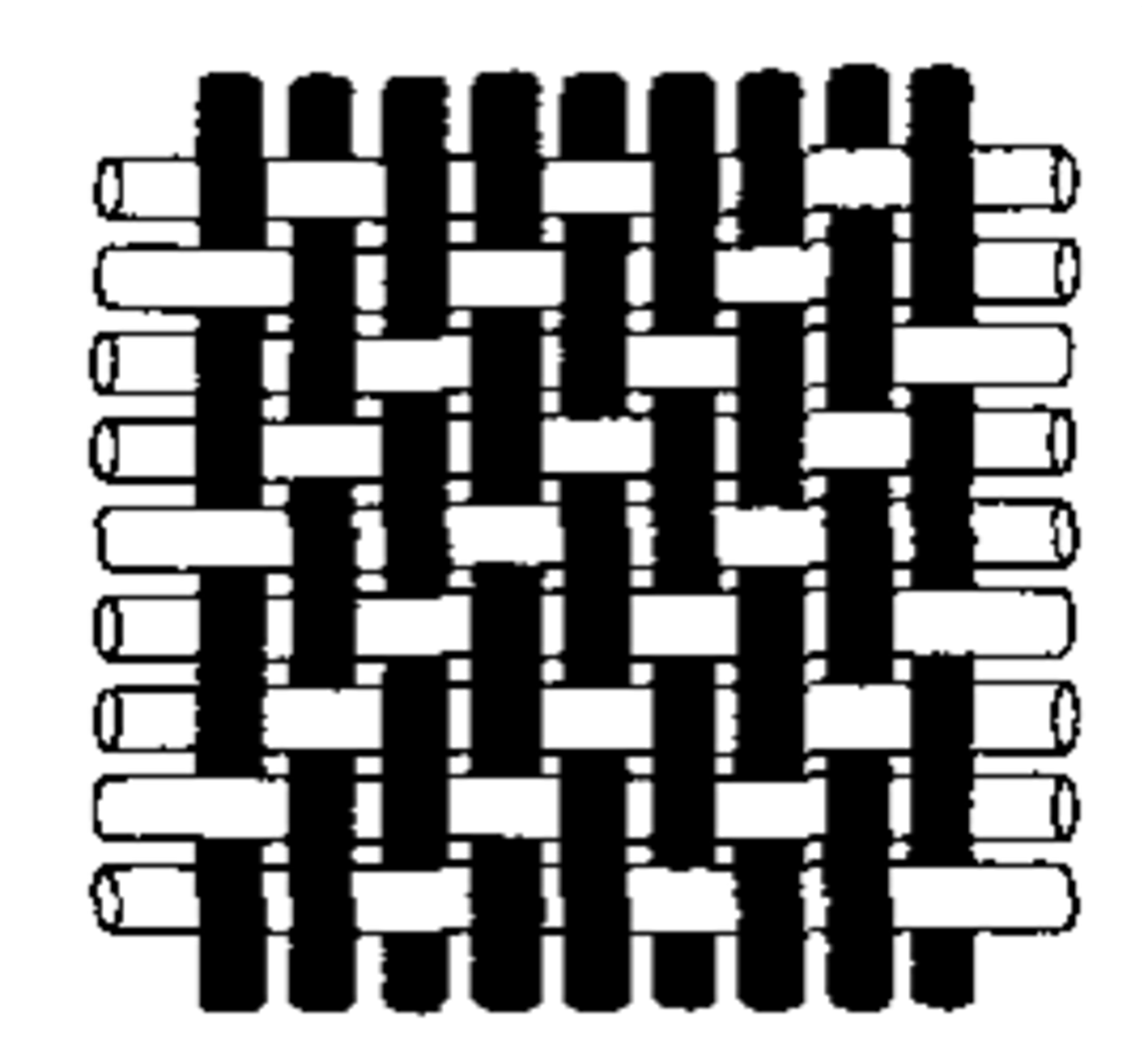
knitted fabrics
fabric made by looping yarns together
Each yarn series in a knitted fabric is called a ________
stitch
Woven fabrics
Made by interlacing warp (longer) and weft (shorter) yarns together to produce a planar fabric
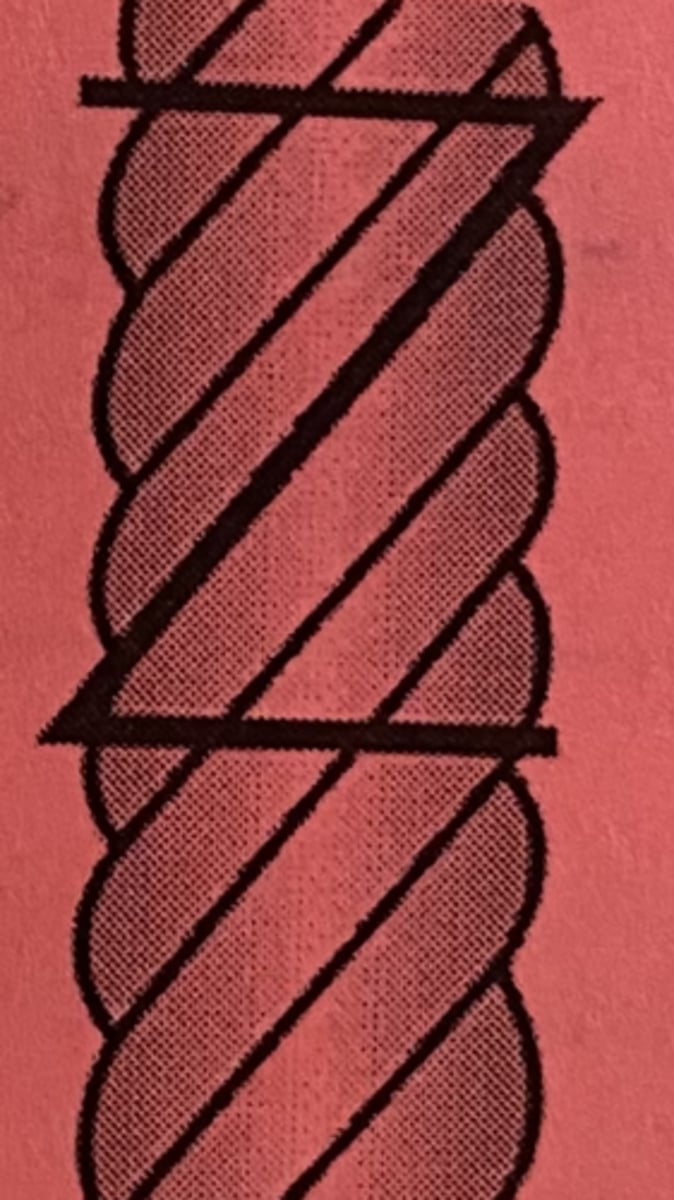
Z-twist yarn
a twisted yarn with the direction of twist conforming to the center bar of the letter "Z" (up to the right)

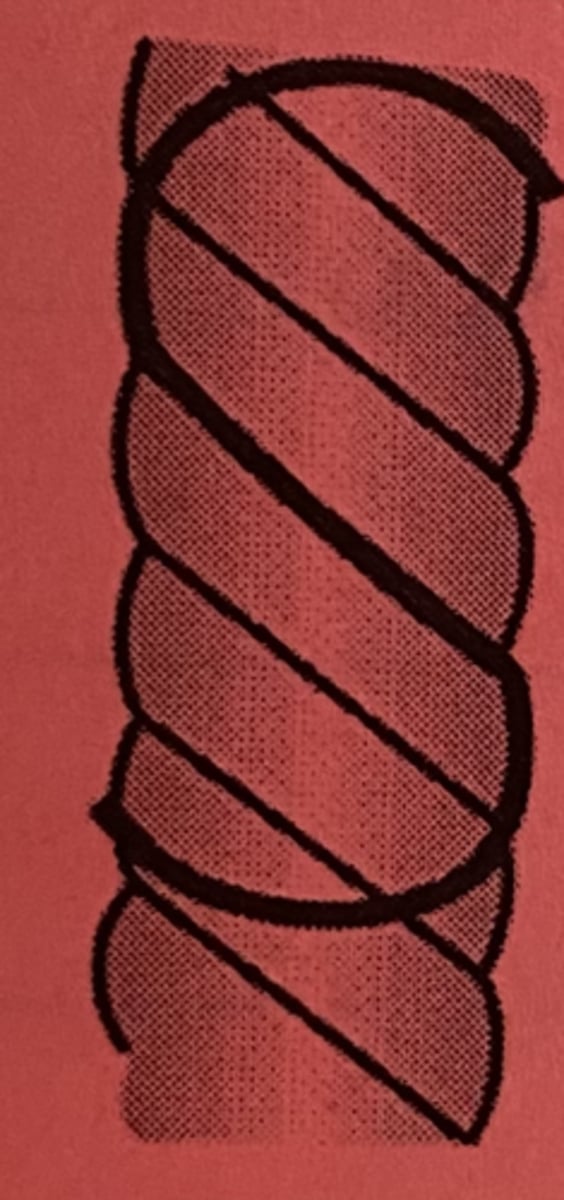
S-twist Yarn
a twisted yarn with the direction of twist conforming to the center bar of the letter "S" (up to the left)

Forensic Analyses for general classification of fibers
Polarized light microscopy, FTIR, Pyrolysis-gas chromatography, Microscopic properties, solubility, thermal analysis
Forensic Analyses for physical characteristics of fibers
Stereomicroscopy, light microscopy, scanning electron microscopy
Forensic Analyses for color of fibers
microspectrophotometry, thin layer chromatography, fluorescence