BIO 101-Chapter 1: The Scientific Study of Life
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
the five characteristics of life
(1) Organization, (2) energy use, (3) maintenance of internal constancy, (4) reproduction, growth, and development, (5) evolution

organization
Atoms make up molecules, which make up cells, which make up tissues, and so on. One of the five characteristics of life.

energy use
A kitten uses the energy from its mother's milk to fuel its own growth. One of the five characteristics of life.

maintenance of internal constancy
Your kidneys regulate your body's water balance by adjusting the concentration of your urine. One of the five characteristics of life.

reproduction, growth and development
An acorn germinates, develops into an oak seedling, and, at maturity, reproduces sexually to produce its own acorns. One of the five characteristics of life.

evolution
A change in the genetic makeup of a population over multiple generations. Increasing numbers of bacteria survive treatment with antibiotic drugs. One of the five characteristics of life.

atom
The smallest chemical unit of a type of pure substance (element).

molecule
A group of joined atoms.
organelle
A membrane-bounded structure that has a specific function within a cell.
cell
The fundamental unit of life.

tissue
A collection of specialized cells that function in a coordinated fashion.
organ
A structure consisting of tissues organized to interact and carry out specific functions.

organ system
Organs connected physically or chemically that function together.

organism
A single living individual.

population
A group of the same species of organism living in the same place and time.

community
All populations that occupy the same region.

ecosystem
The living and nonliving components of an area.

biosphere
The global ecosystem; the part of the planet and its atmosphere where life is possible.

emergent properties
arise from interactions among the parts that make up an organism.
producers
Make their own food by extracting energy and nutrients from the nonliving environment. Also called autotrophs.

consumers
Obtain energy and nutrients by eating other organisms, living or dead. Also called heterotrophs.

decomposers
are consumers that obtain nutrients from dead organisms and organic wastes.
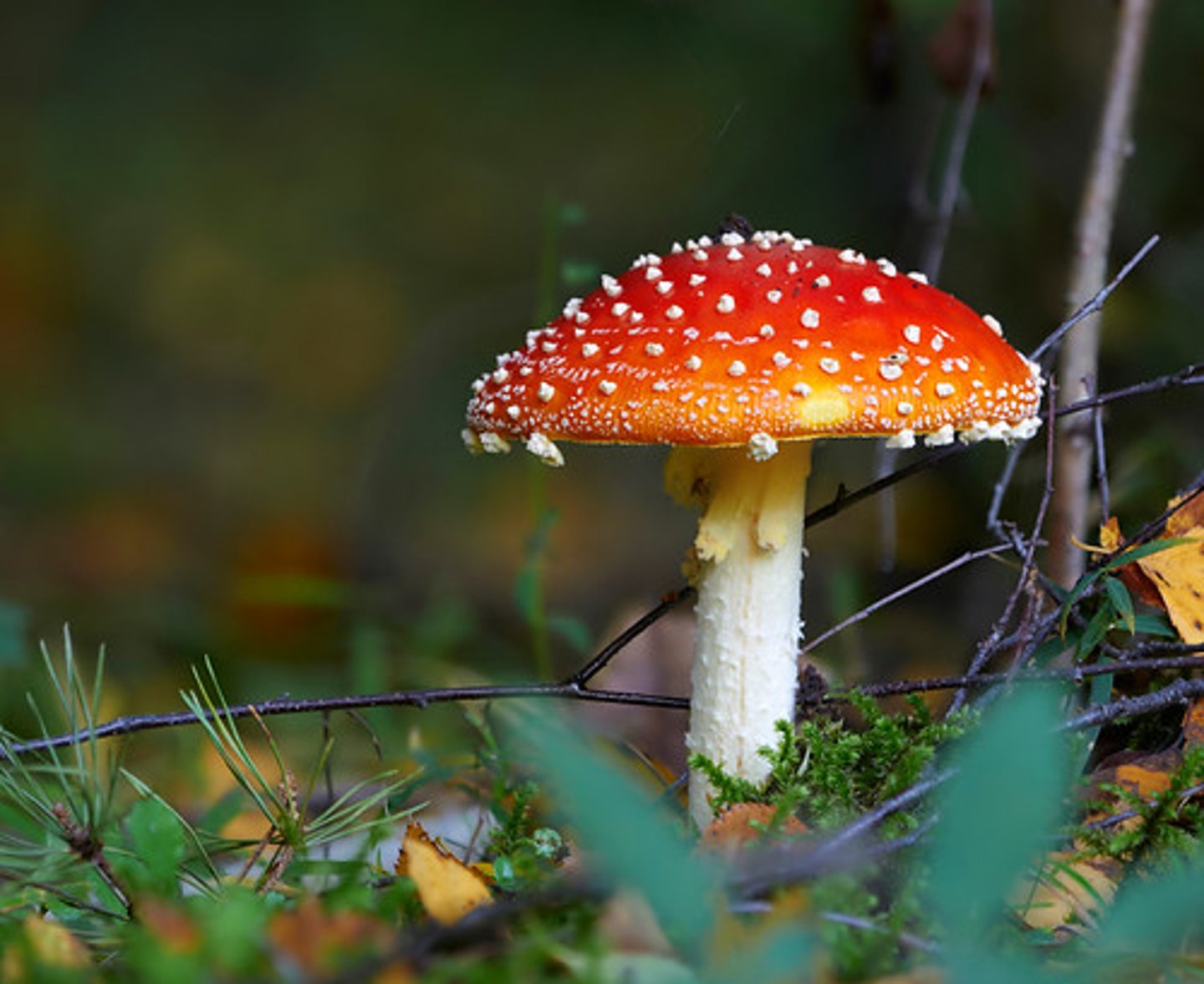

homeostasis
process by which a cell or organism maintains a state of internal constancy or equilibrium.

asexual reproduction
genetic information comes from only one parent and all offspring are virtually identical.

sexual reproduction
genetic material from two parent individuals unites to form an offspring, which has a new combination of inherited traits. By mixing genes at each generation, this results in tremendous diversity in population.

adaptation
An inherited characteristic or behavior that enables an organism to survive and reproduce successfully in it's environment.

natural selection
The enhanced reproductive success of certain individuals from a population based on inherited characteristics.

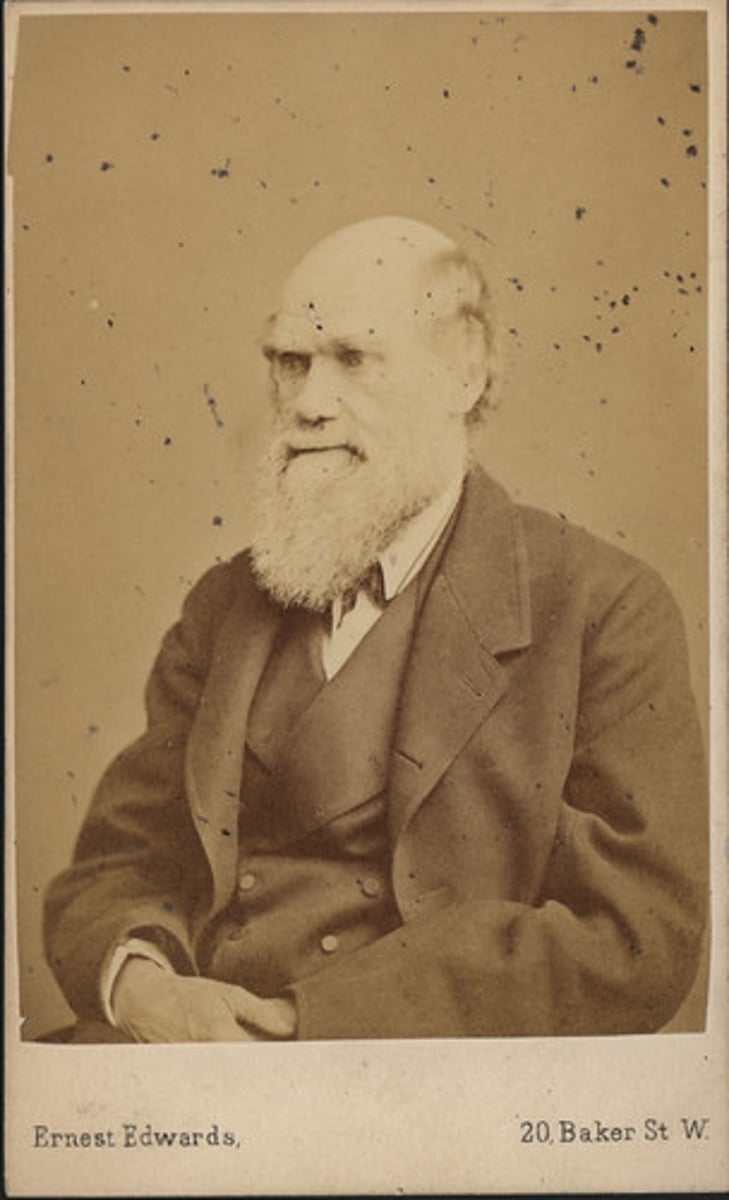
Charles Darwin
1809-1882 English naturalist and scientist whose theory of evolution through natural selection was first published in 'On The Origin of the Species" in 1859.

Alfred Russel Wallace
(1823-1913) English naturalist who proposed, independently of Charles Darwin, the concept of natural selection as a mechanism for evolution and as a way to explain the great variety of living things.

On the Origin of Species
Darwin's book published in 1859 that presented evidence and proposed a mechanism for evolution that he called natural selection.

taxonomy
The biological science of naming and classifying organisms.

species
The basic unit of classification which designates a distinctive "type" of organisms.

genus
A group of closely related species.

domains
The broadest taxonomic category consisting of: Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya.
kingdoms
A subdivision of domains.

the scientific method
A general way of using evidence to answer questions and test ideas.
hypothesis
A tentative explanation for one or more observations.

peer review
Evaluation of scientific results by experts before publication in a journal.

experiment
An investigation carried out in controlled conditions.

sample size
The number of individuals that the scientist will study in an experiment.

variable
A changeable element of an experiment.
independent variable
The variable in an experiment that is manipulated by the investigator to determine whether it influences some other phenomenon.
dependent variable
The response that the investigator measures.
standardized variable
Anything that the investigator holds constant for all subjects in the experiment, ensuring the best chance of detecting the effect of the independent variable.

control
Untreated group used as a basis for comparison with a treated group in an experiment.

placebo
An inert substance that resembles the treatment given to the experimental group.

double-blind
Type of experiment in which neither participants nor researchers know which subjects received a placebo and which receive the treatment being evaluated.

statistical significance
The probability that the results arose purely by chance.
theory
Well supported scientific explanation.
