AWS Machine Learning Associate
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
Machine Learning (ML)
Field of study in AI concerned with the development and study of statistical algorithms that can learn from data and generalize from unseen data and thus perform tasks without explicit instructions
ML models can be deterministic or probablistic or a mix of both.
Types: Supervised, Unsupervised and Deep Learning.
*Note: At the start of a ML project, Identify the business goal, and frame the problem*
Types of Data
Structured: Data that is organized in a defined manner or schema. Typically found in relational databases (database tables, excel spreadsheets) (RDS, Aurora)
Unstructured: Data that does not have a pre-defined structure or schema (videos, images, emails) (DynamoDB)
Semi-structured: Data that is not as organized as structured data but has some form of structure (tags, hierarchies) (XML, JSON)
Supervised vs. Unsupervised learning
Supervised learning: relies on two variables: labeled input and output training data.
Unsupervised learning: processes unlabelled/ raw data.
Mean/Median/Mode
Mean: (average) normal distributions where the mean represents the average of the cumulative data set.
Median: (middle number): better option when outliers are present. Only works on columnar datasets and can not be used on categorical features. Not very accurate.
Mode: (most frequent): used with categorical values.
Data Repositories
Data Warehouses: Centralized repository optimized for querying and analysis with structured data where data is injested from different sources. (Redshift)
Data Lakes: Storage repository that holds vast amounts of raw data in its native format, including structured, unstructured and semi-structured data. (S3)
Data Lakehouse: Hybrid of DW and DL. Primarily used in ML/AI. Combines the flexibility/cost effectiveness of a DL and the performance of a DW. (AWS Lake Formation w/S3, Redshift Spectrum)
Data Processing Frameworks
Python (Pandas): for SMBs. Perfect for local, in-memory merge tasks. Used with small amount of structured data.
PySpark (Python API for Apache Spark): for large-scale distributed machines and datasets stored in cloud environments such as S3, RDS (Recommended)
Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)
Scans image for specific features by passing an image through a series of hierarchical filters/layers
Image classification, object detection regardless of placement.
Includes: LeNet (handwriting), AlexNet (image recognition), GoogLeNet (deeper, better performance), ResNet (deepest)
*NOTE: CNNs are difficult to administer: resource intensive, lots of hyperparameters, getting training data (as well as storing and accessing)
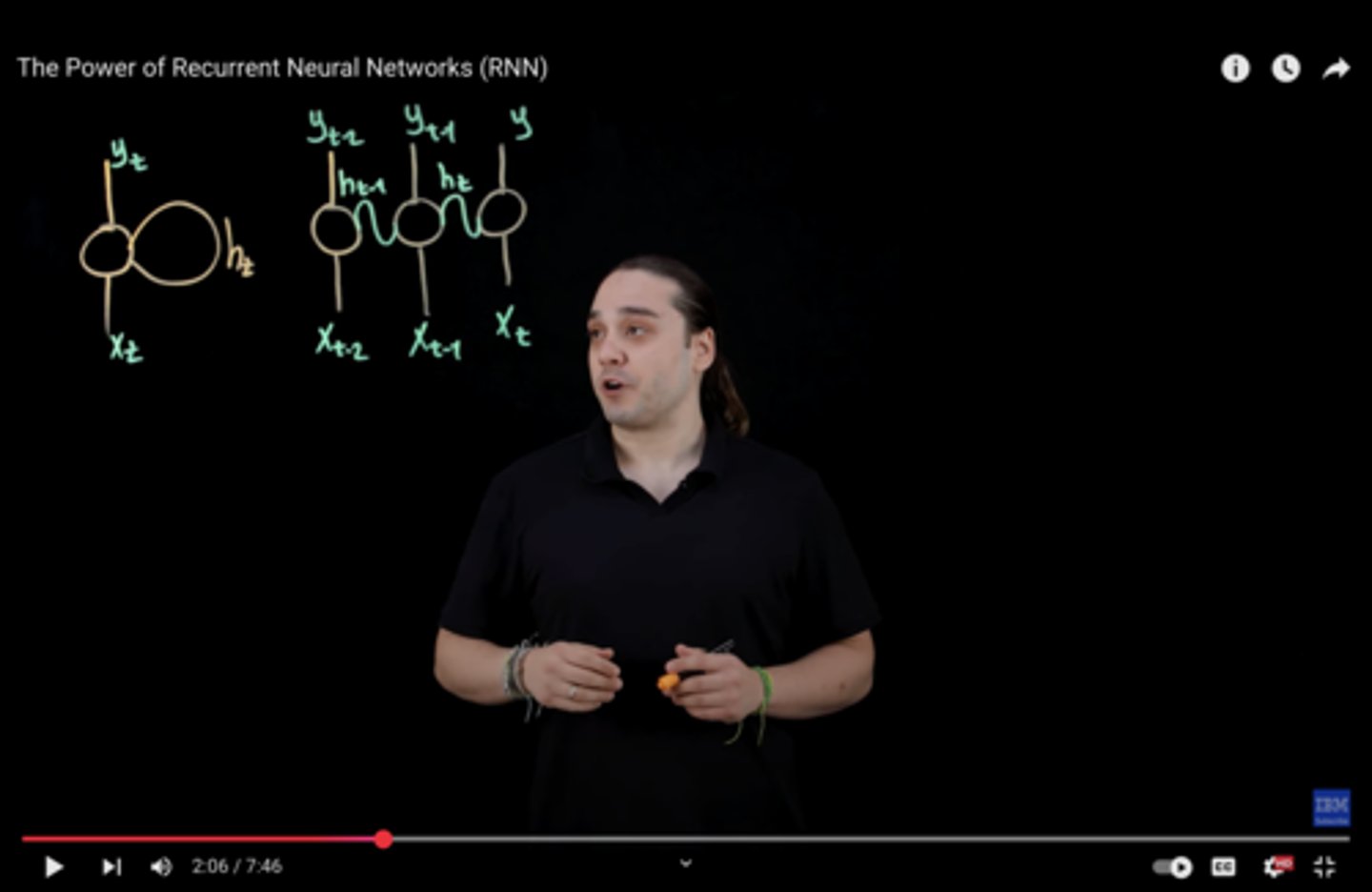
Recurrent Neural Network (RNN)
Designed for sequential data such as text, time series and speech.
Has a Memory mechanism: Remembers previous inputs to determine future outputs using time-series data.
Uses a "hidden state" to loop info from previous trainings. Helps carry info forward.
Vanishing gradient problem: Simple RNNs have "short-term memory." Major flaw in RNN architecture
Sequential, can not handle parallel learning.
*NOTE: Build upon previous research when creating since they are very resource intensive.
Activation Functions
Takes the weighted input signals for a node and determines its final output (or "activation") in a neural network
Activation functions introduce non-linearity in neural networks, allowing for increased complexity.
Popular tools: Sigmoid function, ReLU
Loss Function (*)
Aggregates the residuals of all data points in a model and provides a single output to calculate overall error rate.
Quantifies how well a model's overall predictions align with the actual, correct data.
Unbalanced Data
When there is a large discrepancy between what you are/are not testing for.
*Common issue when dealing with ML algorithms*
To resolve:
1) Correctly identify the minority group in data sample
2) Use Oversampling and Undersampling to increase accuracy
Oversampling: increase the number of what you are testing for, matching with the majority class
Undersampling: decrease the majority of samples you are not testing for, matching with the majority class
Tools Used:
Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique (SMOTE): Generating wide variety of newly, artificial samples of minority classes (*advanced form of oversampling based on KNN)
Common Data Formats (*)
CSV (Simplicity): simple text file, used for spreadsheets; separated by commas/semicolons.
(Data Import from Spreadsheets)
JSON (Compatability): simple, schema-less, key-value pair, text format used to structure data.
Parquet (Performance): structured, binary data is stored in columns, not rows. Excellent compression and performance. Broad ecosystem support.
*Gold standard for big data analytics*
(Hadoop, Apache Spark, Redshift Spectrum)
NOTE: Does not work well with unsorted data
Apache ORC (Optimized Row Columnar) (Data Volume): Specialized, columnar database used with Apache Hive. Fast performance for tasks that require a lot of reading. Used when dealing with large amounts of data.
(Apache Hive)
Apache AVRO (Streaming, Storage, Schema Evolution) Compact, fast, binary, row-based data. Great for schema evolution (adding/deleting/renaming features/columns), allowing it to change over time.
RecordIO (Deep Learning): Combines multiple data sets into a single file. Stores and moves big datasets. Common use case is AWS Sagemaker.
Feature Engineering
The art of selecting, modifying or creating new features from raw data to improve a model's performance.
Includes:
-Feature Creation from Missing Data
-Combining and splitting features
-Feature Scaling
-Encoding Categorical Variables
Watch for the Curse of Dimensionality: the more features you have, the sparser your data.
*Choose the features that are most relevant to the problem.*
Inputting Missing Feature Data: taking the mean of the column and replacing all missing values with that value. (limited with outliers and categories). Not an overall best practice.
Other Options:
KNN: find most similar row, average their values
Deep Learning model: great for categorical values
Regression: find linear or non-linear relationships
Regression Analysis (*)
Method for modeling relationships between variables.
*Primary benefit in Machine Learning is to predict future values.*
Simple Linear: one independent variable is used
Multiple Linear: multiple variables is used
Logistics: categorical variables
Binary Logistics: (yes/no) categorical variables
Epoch/Batches/Steps
Epoch: One complete pass-through of entire training dataset by the ML algorithm. Multiple epochs are needed for the model to learn the underlying patterns in the data.
Batches: Small, manageable chunk of training data. Primary reason is memory efficiency, allowing for quicker iterations of the model in a single step.
Steps/Iterations: Process of training a model on one batch. After the step ends, updates are made to the model's parameters.
Batch Sizes/Learning Rate
In hyperparameter tuning: how many examples the model "sees" before it updates its internal parameters.
Small batch: "bumpy, noisy" learning process. tends not to get stuck in local minima -a point that looks like the best solution but really isn't
Large batch: "smoother, faster" learning process. can get stuck in local minima
Small learning rates: increased learning over time. slower process but does not "overshoot" the optimal solution.
Large learning rates: "large steps, faster process". can overshoot the optimal solution and cause performance to diverge.
*NOTE: Watch for too high or low of a learning rate.
Underfitting(*)
Responses are too simplistic to capture the underlying patterns in the data
Responds poorly both to existing data and new, unseen data
Fails to capture the specific nuances, correlations or details of the query. High bias.
*Typically occurs when the model is not trained on enough relevant data or does not understand the context.
How to resolve:
increase model complexity
Add epochs
Add more features
Overfitting (*)
Excels at training data but fails to predict results correctly from new, unseen data.
When the model learns the data too well. including noise and outliers.
*Typically occurs when the model is trained too heavily on a specific set of data or is overly reliant on memorization rather than understanding.
How to resolve: (LEEDCP)
L1/L2 Regularization: adds specific penalties when coefficients become too large. Prevents a model from becoming overly complex.
L1: Reduces the features to zero
L2: Reduces the features evenly (but not to zero)
Early stopping: pauses the data before too much noise is introduced. Timing is essential.
Ensembling: averaging predictions over multiple models for more robust predictions.
Data Augmentation: changes the data set slightly each time the model processes it. Keeps data fresh and reduces rote memorization.
Cross-validation: data is split into equal-sized subsets. One fold is held as for test/validation and the others used for training/evaluation. Repeated with each fold getting at least one turn as test/validation set. Performance metric is calculated.
Pruning/Feature Selection: identifies most important features and removes unnecessary ones.
Binning/Encoding/Decoding
Binning: Converting continuous data into "bins" based on category. (think of school grades (100-90: "A", 89-80 "B", etc)
Encoding: Transforming data into some numerical format that the model can understand.
Decoding: Taking the numerical format and converting it back into meaningful data.
Encoding techniques
One-hot encoding: Used for data pre-processing. converts each category into a binary vector representation (where there is no inherent order) that neural networks can process.
Binary encoding: A compact method that first assigns a unique integer to each category, then converts that integer into its binary code.
Label encoding: Used when categorical variables have a "meaningful rank" to their categories.

Confusion Matrix
Model evaluation tool used to compare predicted outcome vs actual outcome in simple, binary response (ie. is the picture a fish? a: yes/no) (TP/FP/TN/FN)
Helps provide precision/accuracy of the model.

Classification(*)
Accuracy: How many predictions the model got right overall.
*Not suitable for imbalanced datasets*
Precision: (Positive Predictions Pct) What pct of positive identifications were actually correct? The higher the better (TP/TP+FP)
"Of these 10 patients we flagged, how many actually were sick?"
*Important when the cost of a false positive is high*
(Being right when you say yes)
Recall: What proportion of actual positives were identified correctly? The higher the better. (TP/TP+FN)
"Of these 100 sick patients, how many did our test successfully identify?"
(Not missing any yes's)
Specification: (Recall's Counterpart) What proportion of actual negatives were identified correctly? (TN/TN+FP)
(Not missing any no's)
F1 Score: Overall performance of Precision and Recall.
2*(precision*recall/precision+recall)
AUC-ROC curve: A performance measurement for binary classification model across all classification thresholds
(=1.0, perfect model, =0.5, random guessing)
Precision/Recall Curve (PR Curve): *Similar to AUC-ROC* Good for zooming in on specific use cases. Better for imbalanced datasets.
Measuring/evaluating regression models:
Mean Absolute Error (MAE): Calculates diff betw actual value and predicted value. Used with simple metrics, measuring outliers and weighting all errors equally.
Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE): common metric to assess the performance of a regression model (lower the better). Used in prediction of large model errors.
NOTE: Both MAE and RMSE are used to evaluate performance of regression models. Key difference is how they handle errors/outliers.
CPU vs GPU
CPU: low cost, generalized processor, designed for basic ML tasks, cleans data, handles small jobs. Used with training sets (AWS: T3, M5, C5)
GPU: specialized processing unit for real-time, computationally heavy tasks (deep learning). Ideal for computer graphics, vectors, multiple high-thoughput, time-sensitive ML tasks (P-series NVDIA)
ML Instance Types
Utilizes C-series, G-series, R-series, P-series, Inf-series and Trainium instances
C-series: Optimized for intensive Compute tasks. Ideal for model training plus big simulations. Cost-effective compute power.
G-series: Graphic optimized instances. Image recognition, object detection and video analysis
P-series: Performance optimized for Deep Learning. Heavily computational, large scale model training.
R-series/X1e: Provides superior memory capacity.
Inf-series: Optimized for faster prediction or model inference tasks. Real-time suggestions, chatbots
AWS Trainium instances: meets sustainability goals when training ultra-large models. Not used for inference.
Amazon Titan Models
Amazon Titan Text Embeddings: natural language converted converted to numerical representations called "embeddings" or "vectors"
Use case: real-time, low-latency applications via the InvokeModel API and for large-scale processing tasks using batch jobs, which are optimized for high throughput.
Amazon Titan Image Generator G1: text to image with simple language prompts.
Use case: Advertising, marketing, design, architecture
Amazon Titan Text: text related tasks for Enterprise use cases.
Use case: Open-ended text generation, conversational chat, summarization, RAG
Amazon Titan Multimodal Embeddings G1 model: multi-modal model (both image and text), converting to embeddings/vectors.
Use case: Perform searches across various data types
SageMaker AI
Fully managed, one-click, comprehensive and scalable solution for building, training, and deploying high-quality models at scale for data scientists and developers.

Sagemaker Studio
Visual IDE for teams used for end-to-end ML collaboration and development
AWS SSO/IAM based access; Used with a single domain
ie. CodeEditor, JupyterLab, RStudio, Canvas
Sagemaker Notebooks
Fully managed, Jupyter environment
Comes with: pre-installed libraries, easy set-up, automatic saving and scalability.
Audience: Individual data scientists (simple, focused environment)
Sagemaker Domain
Dedicated, collaborative workspace for your data scientist teams, streamlining administration, enhancing security and seemlessly integrates with Sagemaker Studio.
Centralized management hub for your Machine learning environments.
Provides: Shared spaces, Shared EFS volumes, 2 default VPCs
SageMaker Canvas
Perform visual data preparation and feature engineering, create and compare models, and generate predictions by simply interacting with the data via a visual, no-code, point-and-click interface.
Perfect for non-technical users (part of Sagemaker Studio)
Sagemaker Jumpstart
Open-source, hub for pre-trained models with full control and customization to jump-start the modeling process.
Provides blogs, videos and training.
SageMaker Data Wrangler (*)
Prepares data using a simple visual interface for modeling/ML deployment (ETL Pipeline)
Verify data quality and anomoly detection
Balance "class imbalance" issues (over/under sampling)
Can use preconfigured templates
Quick ML accuracy estimates
Can be automated
Works with a variety ot tools: SageMaker Studio, Sagemaker Pipelines and Sagemaker Feature Store
(*)Types of splits: Randomized, Ordered, Split-by-key, Stratified
Support features such as binning, scaling and one-hot encoding
SageMaker Feature Store
Central repository to share, store, update and retrieve feature definitions for your models from multiple sources.
On-line/off-line repositories:
On-line: real-time inference, low latency access
Off-line: model training/batch inference/historical data
Works with streaming data (Kinesis), CI/CD pipelines and batch data
SageMaker Processing
Highly flexible, managed service that assists with pre-processing/post-processing and model evaluation, before model deployment.
*Used by developers and data scientists for complex, custom code-based workloads.
SageMaker Training Compiler
Accelerate the process of deep learning models by making the code run faster on the GPU.
Resources:
Warm Pools: retrain/re-use provisioned infrastructure
Checkpointing: Creates snapshots during your training
Distributed Training: Allow multiple jobs to run in parallel
Cluster Healthchecks: monitoring system for computer cluster.
Automatic Restarts: recovery mechanism when a job fails
Sagemaker Automatic Model Tuning (AMT)(*)
Automatically fine tunes hyper-parameter ranges based on objective metrics which you pre-define.
Set performance metric and training algorithm to start tuning job.
Uses Baysesian Optimizer to choose the optimal hyper-parameter.
Features: Parallel training, Cost-effective, Automated, Fully-customizable
"It learns as it goes" so it doesn't have to try every possible combination of the parameters.
Automated Hyperparameter Tuning
Early stopping
Warm start
Resource Limits
Transfer Learning
*NOTE: Similar to Canvas. The key difference is that Canvas is a graphical user interface, whereas Autopilot uses SageMaker API or SDK, giving developers and data scientists more programmatic control
Sagemaker Debugger
Automated quality control as your ML models learn.
Automatically monitors and analyzes your training data in real-time, catching issues early in the process.
Define rules for detecting unwanted conditions while training
Auto-generated performance reports and insights dashboard.
Sagemaker Profiler (*)
Provides detailed information about the resource utilization of your training job, including CPU, GPU, memory, and I/O operations
Identify bottlenecks and optimize training process
Bias vs Variance (*)
Bias: error due to overly simplistic assumptions in the model not allowiing it to capture underlying patterns in the data (underfitting)
Variance: error due to the model being too complex and sensitive to small fluctuations in the training data (overfitting)
Augmented vs Synthetic Data
Augmented: data is augmented from existing data set
Synthetic: new data set is created
SageMaker Clarify (*)
Provides greater insight into fairness, explainability and biases of your models
Increase transparency to your stakeholders, informs human decision making, and tracks whether a model is performing as intended.
Explains how input features effects the output of your model by importance.
Provides a comprehensive suite of tools to help developers build more transparent and less biased machine learning models.
Uses continuous monitoring for detecting changes in feature/bias attribution drift after model is deployed.
*NOTE: Can also use SHAP (local and global) and LIME (local) for model explainability.
*Integrated with SageMaker Studio and SageMaker Model Monitor
SageMaker Autopilot (ie. AutoML)(*)
Fully managed, end-to-end ML service.
Automates algorithm selection, data preprocessing, model tuning, "trial and error" testing, and incorporates all associated infrastructure.
*Provides a model leaderboard that shows which ML model works best.*
Three Training modes to Choose From:
Ensemble: trains several base models (XGBoost, RandomForest) to provide predictions.
Hyperparameter Optimization (HPO): precision tuning one, single best algorithm.
Auto: Let's Autopilot choose the most appropriate strategy.
(if dataset <100mb = Ensembling, if > 100mb = HPO)
NOTE: Integrates with Sagemaker Clarify
Sagemaker Model Optimizer
Automatically lessens the model's complexity while maintaining accuracy.
When low latency and high throughput are essential.
Sagemaker Neo
Optimize machine learning with Edge devices.
Key Features: Model Optimization, Increased Speed and Efficiency (smaller, less complex), Cross-Platform Deployment
Used with AWS IoT Greengrass
Sagemaker Model Parallel Library
Trains very large deep learning models that are too big to fit into the memory of a single CPU.
SageMaker Ground Truth
Fully managed, crowd-sourced data labeling service for image classification and object detection.
A combination of machine learning and human feedback where human workers only intervene in complex tasks, improving labeling efficiency.
*Focuses on preparing data before model training*
Reinforcement learning through machine or human feedback (internal employees, 3rd party contractors, Amazon Turk)
*Ground Truth Plus: AWS fully managed, turn-key solution.
Use cases: build high quality data training sets for MLs reducing time and cost
Sagemaker Pipelines
CI/CD service dedicated to the automation of ML Workflow.
Manages raw data preparation to model release along with performance tracking.
Supports manual approval workflows
*Includes retraining based on data/concept drift detected by Sagemaker Model Monitor*
SageMaker Model Registry
Organize, catalog and track versioning of models, metadata and approval status.
Manages approval status of models and deploys models.
Sagemaker Experiments
Organize, compare, and search experiment trials and historical ML training jobs.
Provides a structured way to manage the inputs, parameters, configurations, and results of your training runs, making it easier to analyze performance and reproduce results.
Deeply woven into the fabric of Sagemaker.
Sagemaker Endpoints /Inference Endpoints
Fully managed service, creating a dedicated secure web address for real-time inferences of your trained model.
Key Features in ML:
Autoscaling: The system changes the number of servers based on request count or delay goals.
Multi-Model Endpoints: It places several models at one address, sharing resources/cutting costs.
Production Variants: deploy multiple models behind a single endpoint. Primarily used for testing and comparing models.
Traffic Shifting: It sends part of the traffic to a new model during an initial run.
Secure Access: It works with VPC, uses SSL encryption plus IAM-based entry.
SageMaker Serverless Inference
Fully managed, serverless, cost-effective inference tool used when the model has idle time and uneven traffic.
Ideal for workloads that can handle idle time/cold starts.
*NOTE: Specify container, memory and concurrency req.
Sagemaker Serverless Inference Recommender
Recommends best instance type/configuration for your model, automates load testing model tuning and deploys to optimal endpoint.
Good for cost-optimization.
*NOTE: Use for pre-deployment. Use Cost Optimizer after free trials are complete.
Shapley vs PDP models
Shapley: Provides local, individualized explanation each feature makes to model prediction.
PDP: Provides global explanation to understand overall relationship between a feature and the model behavior across a dataset.
Inference Pipeline
Combines pre-processing, predictions, and post-processing.
Linear sequence of containers.
SageMaker Tensorboard
Helps ML engineers visualize, understand and debug during model training/development.
Used for manual inspection rather than real-time monitoring.
Problem it solves: helps you understand if your model is learning effectively, if its architecture is correct, and how different hyperparameters are affecting performance
SageMaker Model Monitor
Continuous monitoring system used to detect deviations in data quality and model quality after a model has been deployed.
Assesses quality of the models in production on a scheduled basis.
Can be used to configure alerts for anomalies, outliers, data drift and new features.
*Integrated with Cloudwatch*
Supervised vs Unsupervised training
Supervised: Learns from labeled datasets
Unsupervised: raw, unstructured data
Sagemaker Built-in Algorithms (part I)(*)
*Different models/algorithms serve different purposes*
*First understand the use case
Linear Learner: determines simple linear relationship between variables. Baseline for classification and regression tasks. (supervised)
Use Cases: Predicting house prices based on age
Seq2Seq: Sequence of tokenized text files (encoder/decoder) (supervised)
Use case: Speech-to-text (AWS Transcribe)
XGBoost/LightGBM: Boosted group of decision trees used to sequentially learn from/correct errors/update from previous versions. Highly accurate, interpretable with emphasis on features. (supervised)
Use case: Sales forecasting, Customer churn
Image Classification: Assigns labels to the objects within an image.
Use Case: Classifying images
Object Detection: Detects, identifies and categorizes all objects in an image with bounding boxes. Provides confidence scores.
Use case: AWS Rekognition, Self-driving cars
Semantic Segmentation: High-precision, image analysis. More specialized than object detection.
Use case: Medical
Sagemaker Built-in Algorithms (part II)(*)
BlazingText/Word2Vec/Doc2Vec:
(BT) High-performance, word embeddings and text classification for large datasets. Customized for your environment (compared to AWS Comprehend)
(W2V) Vector embeddings for words. Smaller datasets
(O2V) Similar to W2V but used with many object types.
Use case: Sentiment analysis, Genre predictions
K-Nearest Neighbor (KNN): returns most common classification nearest neighbor in latent space based on proximity to labeled data . (supervised)
K-Means Clustering: large scale clustering of data points into groups in latent space (unsupervised)
DeepAR: Time-series forecasting. Finds frequencies and seasonality. (supervised using RNN)
Use case: Demand forecasting, Financial predictions
Factorization Machines: Extension of linear learning, dealing with features and high-dimensionality, sparse data (both supervised and unsupervised)
Use case: Recommendation engines where user has rated very few items.
Random Cut Forest: Anomaly detection (unsupervised)
Use case: Unstructured, streaming data
Neural Topic Model: Neural-network topic model. Organizes documents into topics. Expensive and computationally heavy. (unsupervised)
Use case: Nuanced sentiment analysis
LDA: Another topic model (not using neural networks). More general purpose. Cheaper, efficient and more widely used. (unsupervised)
Use case: Discovering research trends
PCA: dimensionality reduction (unsupervised)
IP Insights: Security tool. Finds suspicious behavior. (unsupervised)
Use case: Security teams
Sagemaker Input Modes (*)
S3 File Mode: copies training data from S3 to local directory in Docker container. Good for a small amt of data.
S3 Fast File Mode: streaming from S3 source. Speeds up training time. Can do random access or sequential. (recommended)
Pipe Mode: streaming from S3 sequentially, continuous, forward-moving. Used for streaming high throughput, large datasets.
S3 Express One-Zone: High performance in One-zone.
FSx for Lustre: High performance, parallel distributed shared file server for compute heavy workloads.
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)
A technique which allows a Foundational Model (FM) to retrieve an external data source outside of its training data (called an augumented prompt).
With RAG, language models can go beyond their original training data to use up-to-date, real-world information.
Use Case Examples: Customer Service Chatbots, Legal Research and Analysis, Healthcare Q/A
Products: Amazon Bedrock, AWS Kendra, AWS Sagemaker Jumpstart
Note: One of the challenges in question answering is a limited number of tokens in the context. It is resolved by using RAG. The architecture pattern for personalized and specific use cases results in reliable and accurate responses.
Note2: Does not change the weights of the model (unlike fine-tuning)
Note3: Very sensitive to the prompt templates.
Amazon Bedrock
Serverless, fully managed service that makes pre-trained FMs from Amazon and leading AI startups, available via an API
Keep control of all data used to train the model (data does not leave your account)
Security, Privacy and Governance and responsible AI features included.
Pricing: On-demand/Batch, Provisioned Throughput/Custom (provison throughput for performance requirements in exchange for time-based term commitment)
*Charged by the number of input tokens received and the number of output tokens that are generated // or image generated*
NOTE: Custom models can only use Provisioned Throughput (time-based commitment)
Fine-tuning Amazon Bedrock
Instruction-based Fine tuning: adapting a pre-trained model to follow instructions and perform specific tasks
Continuous Pre-training: continually updating model with the latest data using unlabeled data.
Single-turn messaging: single interaction between user and LLM (chatbots)
Multi-turn messaging.: conversation between user and LLM, maintaining conversation and understanding.
Usage: chat bots, training with exclusive data, targeted use cases, training with more up to date data.
Higher accuracy and lower latency. Loses generalization.
Fine tuning will change the weighting of the base foundational model (FM). Requires a higher budget and prepared data.
Training data: must adhere to a specific format and be stored in S3.
Use VPC with Privatelink to ensure secure data transfer during fine-tuning.
Note: not all models can be fine tuned.
Amazon Bedrock - Agents
Fully managed, securely connected and stateful piece of software that manage and carries out multi-step tasks, automatically.
Agents orchestrate multiple, complex interactions between foundation models (FMs), data sources, software applications, and user conversations.
Agents help users execute steps by calling appropriate tools, APIs and services.
Agents are proactive and autonomous, using a reasoning engine to plan and decide what to do.
*Note: Can automate data analysis, provide actionable insights, trace through chain-of-thought reasoning, gather external information, and enable proactive decision making within the enterprise.
Amazon Bedrock - Guardrails
Control the interaction between users and the FMs and for monitoring model outputs.
Filter any undesirable and harmful content or key words/topics
Remove Personable Identification Identification (PII)
Reduce hallucinations
Use only internal vs external information
Amazon Bedrock Studio
Web-based IDE environment for developers to quickly build and iterate GenAI applications using existing foundation models (FMs).
Specialized workshop where you take powerful, pre-built engines (the FMs) and quickly assemble them into applications.
Amazon Bedrock - Action Groups
Define the tools available to the LLM and guide it on when to use each based on the user's query
Amazon Augmented AI (A2I)
Combines ML automation (for easy tasks) and human review workflow (for tougher problems) in ML models
Used for analysis and predictions.
Amazon Q Business
Fully managed, Enterprise AI-powered solution trained on your internal data that answers questions, generates content, creates summaries, routine tasks, and automates tasks
Built with Amazon Bedrock (you can not define the FM model)
Third party plug-ins for data source integrations (Slack, MS Teams, etc)
Delivered using a built-in web experience or through APIs.
Admin controls are available; similar to guardrails.
Customizable security. User logins with IAM Identity Center
Amazon Q Apps
Create Gen-AI apps (without coding) by using natual language.
Amazon Q Developer
AI coding companion which helps increase productivity by developing code directly within the developers IDE, tracking dependencies, and ensuring compliance with open-source licenses
Broader tool which helps you understand your AI environment (compared to Code Whisperer)
Answers questions about AWS documentation and AWS service selection.
Features include: assisting with developer onboarding, writing boilerplate code (AI Code Companion), using unfamiliar languages, and detecting security vulnerabilities
AWS Glue
Fully managed, serverless, extract, transform, and load service (ETL) from multiple sources allowing for fast data integration.
Primarily for data warehouse & data lake integration
Easy for customers to prepare and load their data for analytics into a Redshift database
Use case:
Transform data from one format to another (.CSV to Parquet),
Migrate data from one system to another,
Prepare data for analytics/ML,
Improve data quality (error correcting),
Visualize data for BI
Works with Lambda function for Eventbridge
AWS Glue Data Catalog
A central repository to store structural and operational metadata for all your data assets.
AWS Glue Crawler
1) Scans/analyzes data,
2) Extracts schema info
3) Creates metadata tables in the AWS Glue Data Catalog.
AWS Glue Studio
Visual interface for defining and creating complex ETL workflows in an integrated development environment (IDE).
AWS Glue Jobs
Where the ETL is executed.
ie. AWS Glue FindMatches transform: identifies and merges duplicate records within a dataset.
AWS Glue Data Quality
Rules that allow you to assess and monitor the quality of your data, which is crucial for making informed business decisions.
AWS Glue DataBrew (*)
Visual UI for cleaning and pre-processing large data sets.
Over 250 ready-made transformations.
Handles PII information and automatic outlier detection.
Good for non-technical users.
EMR (Elastic MapReduce)/ EMR Serverless
Big data cloud platform for large scale, complex data processing using open source tools (Hadoop/Spark) running on EC2.
Help you to analyze, transform and move large amounts of data, identify patterns, and make predictions.
Highly flexible and customizable
Consists of a master node (manages the cluster), core node (hosts HDFS data) and task node (runs tasks).
Can be used on transient and long-running clusters.
EMR Serverless: pre-initialized capacity, fully automated solution
*NOTE: EMR is the platform and Spark is the engine that runs on EMR
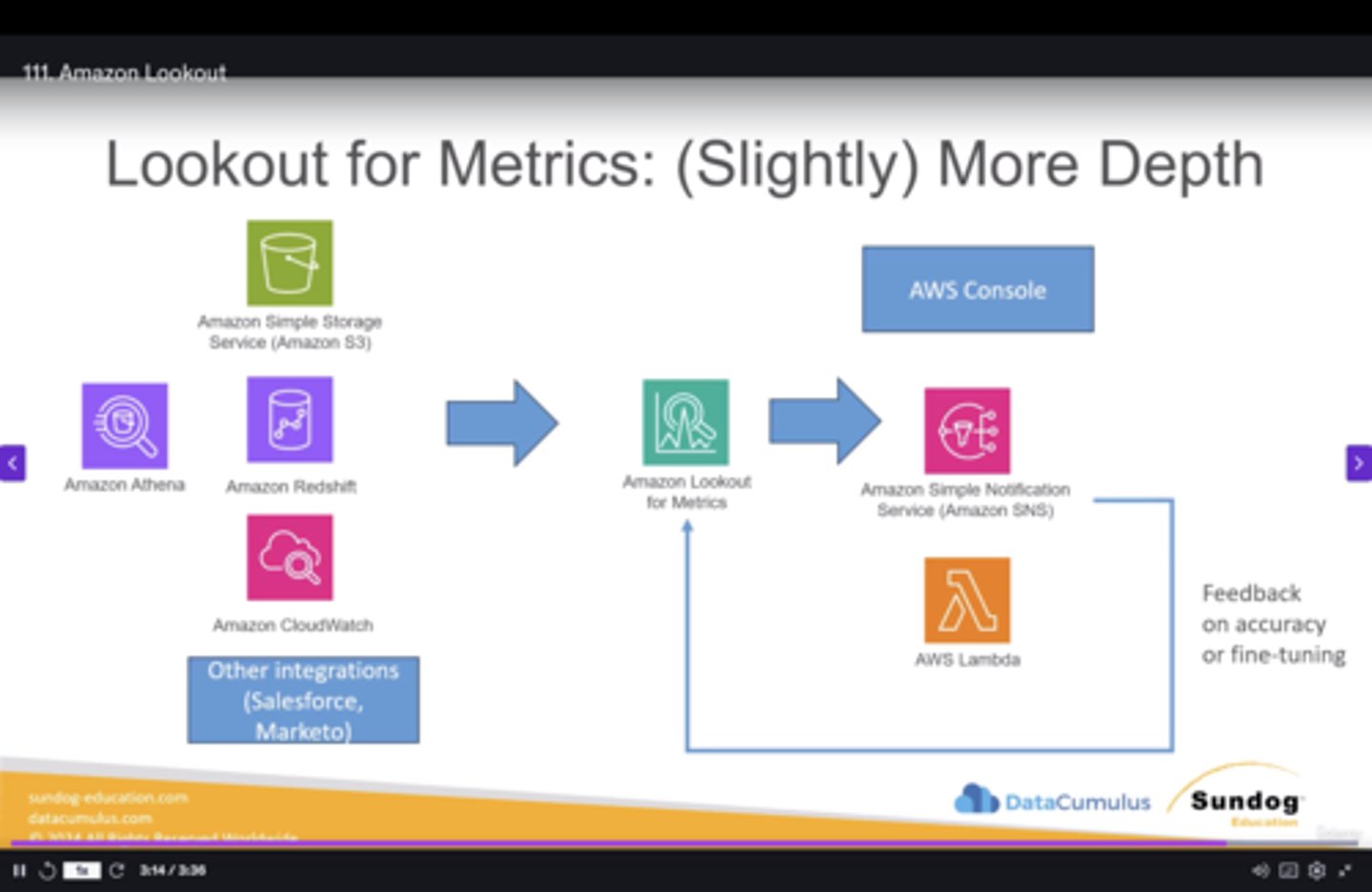
Amazon Lookout (*)
Uses ML (Detectors) to detect and diagnose anomalies in datasets.
Tailored for business users rather than data scientists (Sagemaker Model Monitor)
Uses: S3, Athena, Redshift, Cloudwatch, third-party (Salesforce)
Amazon Fraud Detector
Fully managed fraud detection, customized to your data.
Provides insights into which model feature variables are relevant when detecting fraud.
Ingests data from S3 or API
Apache Spark
Lightning fast, open source engine used for the maintenance of large scale data processing, query optimization and analytics.
Uses in-memory caching for optimized query execution.
Composed of large, heterogeneous data sets.
Breaks streams into micro-batches for processing.
Supports code reuse across batch processing, queries, Machine Learning.
Spark Streaming: integrates with Kinesis, Kafka, Redshift and EMR.
Can be integrated with Athena.
*NOTE: Used as a better alternative to MapReduce
Apache Flink(*)
Stateful, fully managed, open-source tool used with big data flows for quick event-time processing and minimal delays.
Can handle out-of order events using "event timestamps" (rather than processing time)
Ideal for fast processing: streaming ETL, continuous metric generation, real-time analytics, fraud detection, and monitoring
Apache Kafka / Amazon Managed Streaming for Apache Kafka (MSK)
Apache Kafka: Open-Source platform for building real-time streaming data pipelines and applications.
Fully managed Apache Kafka on AWS - *Alternative to Kinesis*
Can create custom configurations for your cluster (unlike Kinesis)
Authentication and Authorization allows you to determine who can read/write to specific topics.
Monitoring through Cloudwatch and Prometheus
Apache Airflow(*)
Open-source tool for scheduling, defining and monitoring complex workflows.
DAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) is a key component used for providing the sequence/dependencies for how the tasks should be executed
Provides flexibility, version control, and collaboration benefits.
Training Parameter Datasets
Small dataset: You can use a smaller batch size with more epochs to make the model more accurate.
Large dataset: You can use a larger batch size with fewer epochs for faster model training.
Complex models: You should use more epochs and be careful with batch size tuning if your model is complex.
Transformers
Giant neural networks enabling parallel computation
ie. Chat, Question and Answer, Sentiment Analysis, GPT (OpenAI)
Self Attention
Learns the contextual meaning of words
Masked Self Attention
A mask is used to prevent tokens from "peeking" into the future tokens (words)
BERT & ROUGE Score (*)
Measures for semantic similarity between generated and reference text.
*Used for predicting missing words from texts, filling in gaps in transcripts.*
Less reliable for short texts
Tokenization
Converting raw text into a sequence of tokens
Tokens can be words, phrases, or individual characters (like a period).
Each token has an ID which is easier for LLMs to process.
1000 tokens is approx 750 words
Token Embeddings
Captures semantic relationship between tokens
Inference Parameters (*)
System Prompts: describes how the model should behave and reply
Temperature (0 to 1): creativity and randomness of the output.
Lower values = more consistent, predictable
High values = more random and creative
Top P (0 to 1) cuts off low probability word choices based on cumulative probability. It tightens overall response distribution.
Top K (amount:#): how many words are to be considered for choosing the next word. Higher K increases sample size.
Maximum token count/Length: maximum length of the answer (response length, length penalty, stop sequences)
Stop Sequence: tokens that signal the model to stop generating output. (ie. ".", "?")
Prompt Latency: how fast the model responds.
Image-to-Image Prompt: inputting one image to get variations
Inpainting: reconstructing the missing parts of an image
Outpainting: constructing a seemless extension of an existing image.
Prompt Strength: Determines variability between prompt and output of the picture
Generation Step: Sequential process of predicting and
Hyperparameter tuning strategies (*)
In model training, used as a final step in ML workflow to fine-tune configuration settings to achieve the optimal performance
Hyperband: Multi-fidelity based tuning strategy which dynamically reallocates resources. Highly efficient and fast. Used for early stopping when resources are under-performing.
Grid search: Defines all possible values. Exhaustive and computationally heavy, yet provides best performance.
Random search: Samples a fixed number of random combinations. Addresses complexity of grid search
Transfer Learning
Fine-tunes a pre-trained model for a new task, such as feature extraction.
Embedding vectors
The ML algorithm that creates the vector embeddings
Transforms text, images or audio into numerical embeddings, capturing the semantic meaning and relationship between data points
Uses visualization to plot the embedding relationship.
Use cases: Q&A, Personalized recommendations
Chunking/Clustering
Used with longer text, dividing text into smaller groups, ensuring the model can process the text efficiently.
Helps manage the limitations of how many tokens can be processed at one time.
ML Deployments
Blue/green: two separate, production environments. Traffic is changed using a binary switch. Allows for near-instantaneous switching/rollback, minimizing risks.
Canary: small subset of users exposed to new environment
Shadow Testing: Simulates a copy of the production model under real-world conditions without affecting live traffic/users.
VPC Endpoints
Keeps traffic within a private network and connects to other VPCs and services without going through public internet
Provisions an ENI with a Private IP in the subnet
Can be associated with security groups to allow/deny traffic
Utilizes PrivateLink for connectivity
Connect to Amazon Bedrock privately.
*VPC endpoints are a security tool first, and then a connectivity device*
Private Link
Securely connect your VPC to AWS services/marketplace and other VPCs
Note: Does not support IPv6