Marketing
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
For what strategy is marketing more important, overall cost leadership or differentiation?
Differentiation
In which two ways can marketing be looked at?
Functional view: the marketing department which is traditionally responsible for communication, advertising, sales support…
Strategic view: An organizational mindset that aims at creating competitive advantage through unique selling points (UPS). In this sense marketing spans different departments and processes of the company, and it is tightly integrated with the company’s strategy.
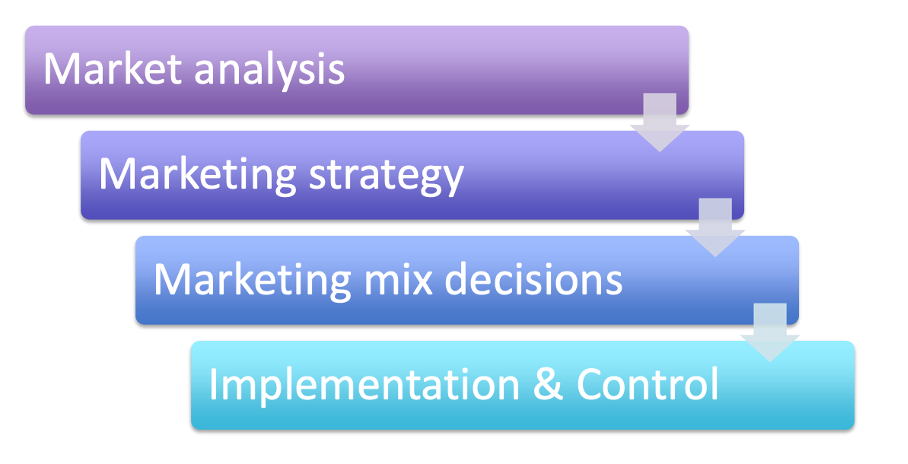
What are 4 different steps in the marketing process?
Market analysis
Market strategy
Marketing mix decisions
Implementation and control
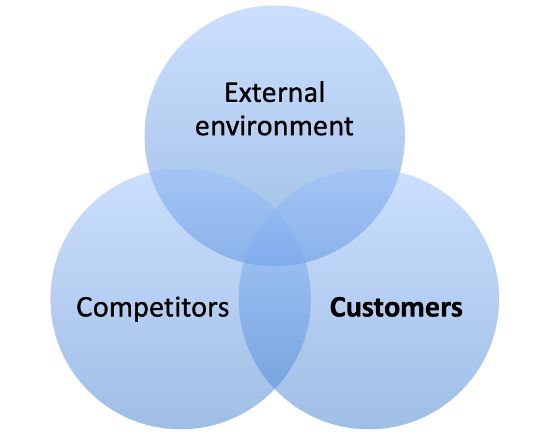
What is included in the market analysis?
The market analysis is related to the market so you have to understand the business area you are competing in. This includes analysis of external environment, competitors and customers.
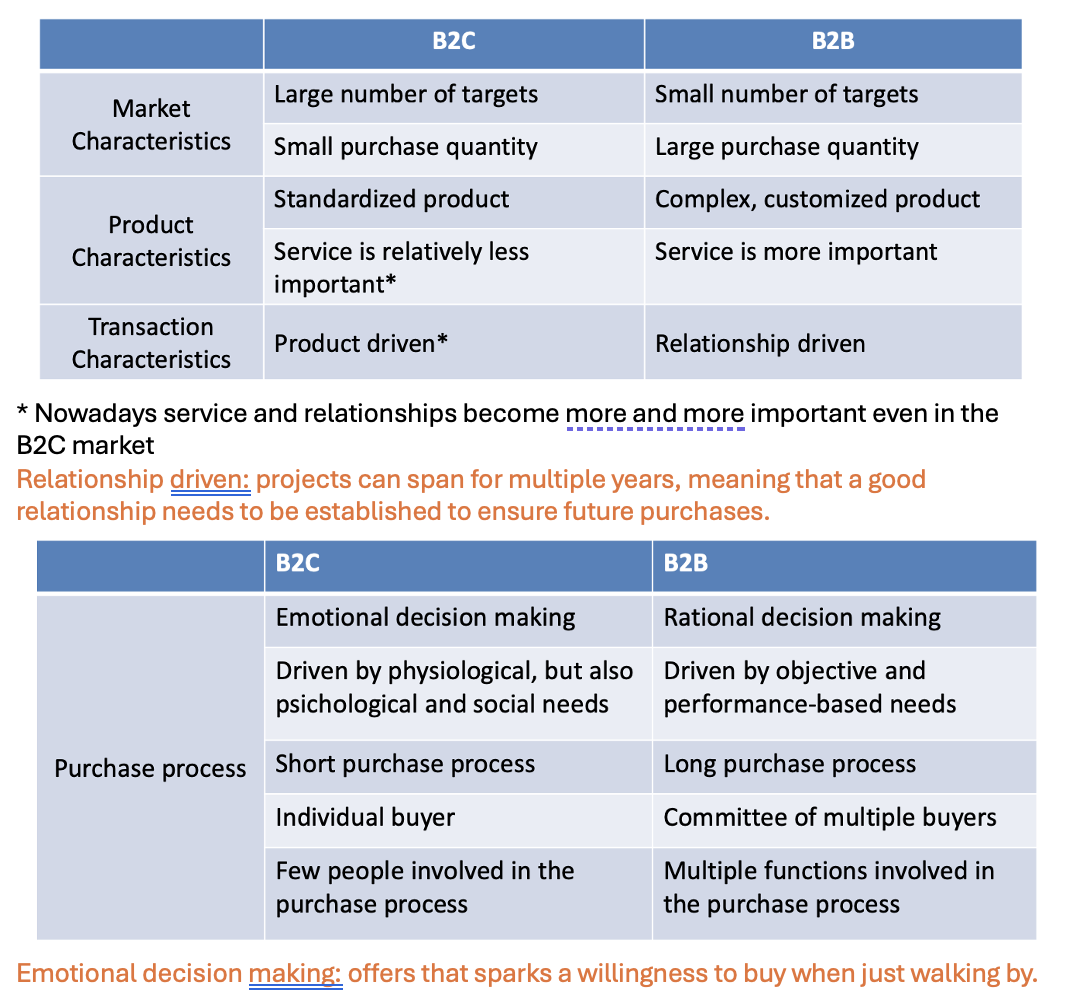
What are main characteristics if you choose B2B or B2C?
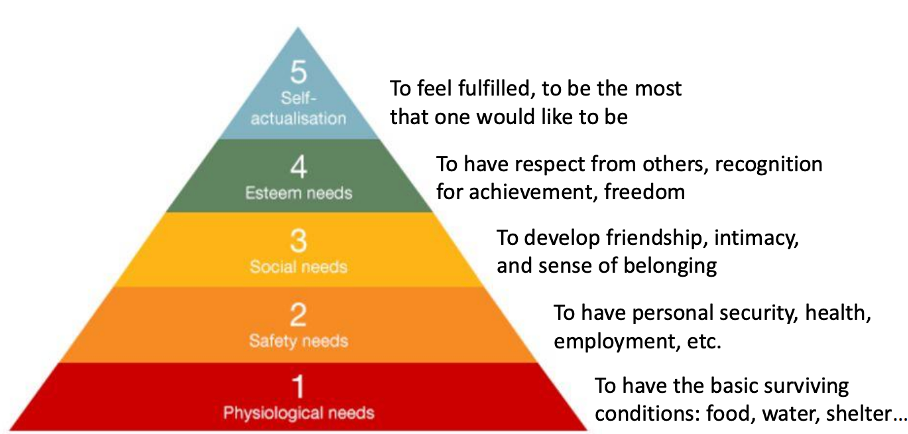
What is Maslow’s hierarchy of needs?
A need is a lack of something that, in a specific moment, causes a sense of less than full satisfaction. Every individual has a different need.
How is Maslow’s hierarchy of needs for businesses?

How do you meet the different kinds of needs?
Lower levels of needs are satisfied through tangible and functional values: what does the product do, the performance, price
Higher levels of needs are satisfied through intangible and emotional values. What appeal to one’s emotional needs can be highly diverse.
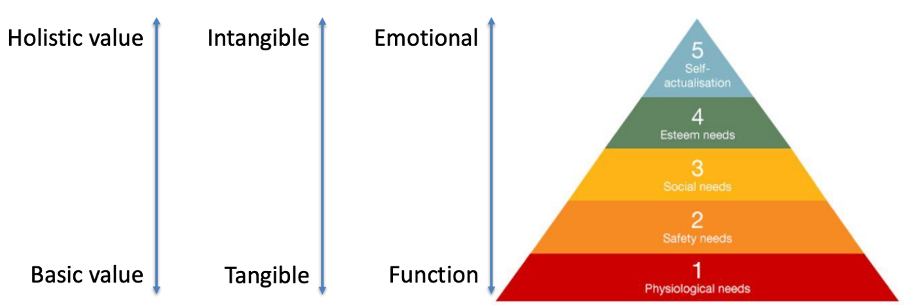
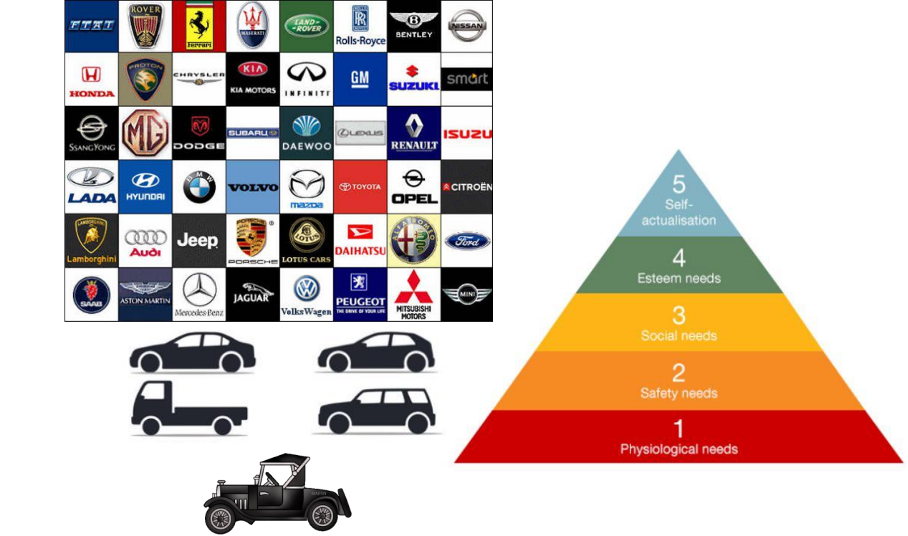
How can the car market be reflected in the pyramid of needs?
Ferrari does not satisfy physiological needs - that is more fiat.
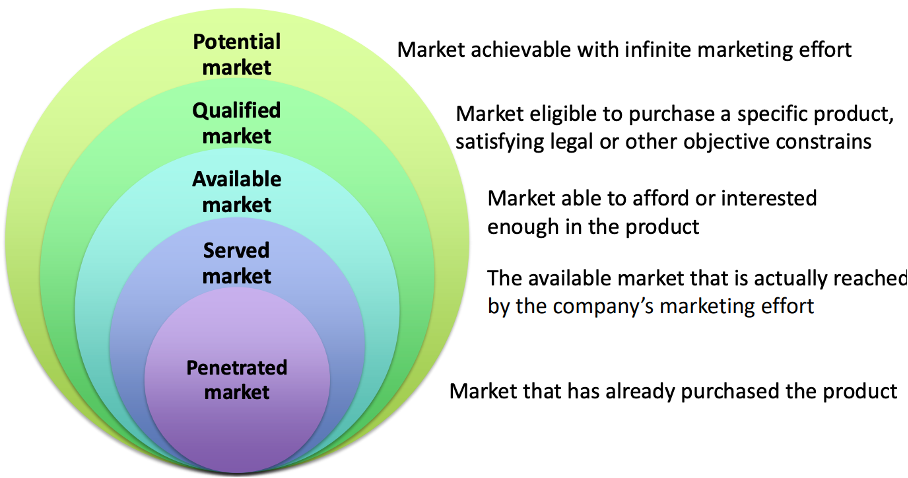
How can you divide the market for marketing?
Potential market: If i sell bread, everyone can buy it except people allergic.
Qualified market: selling a car, everyone can buy a car but only people with driver’s license and the right age will buy it.
Available market: People with the right amount of money and those who have the interest of buying it
Served market: The ones who know what the company offers and have seen the marketing
Penetrated market: Those who have purchased it before.
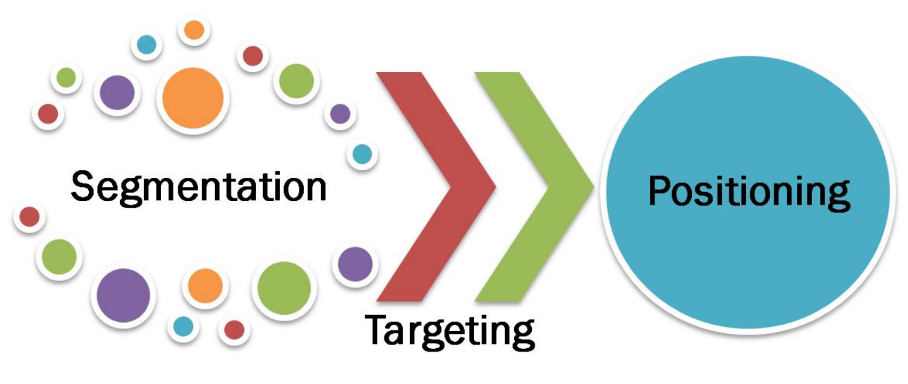
In what three phases can marketing strategy be divided into?
Segmentation, Targeting, Positioning
Why do we have to segment the market?
Needed to offer a better value for our customer. We can’t sell to everyone. Need to reduce the complexity of the market and instead segment the market since everyone have different ideas, preferences etc…
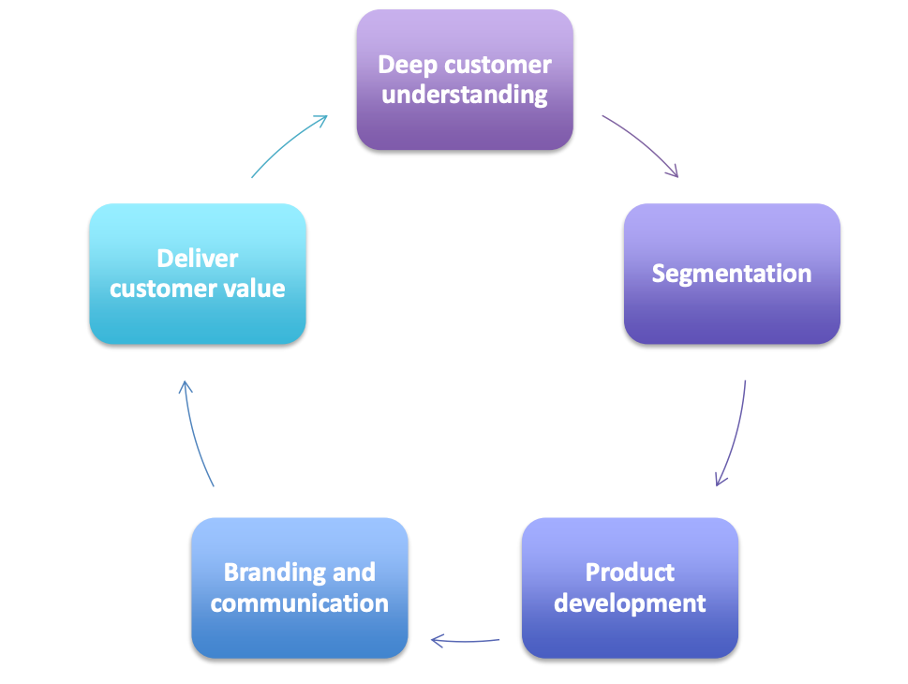
Get deep customer understanding
Segment based on the information
Develop product to the segmented market
Brand and communication: is constructed based on the segmentation, not everyone will know about the bran but the targeted will know.
Deliver customer value.
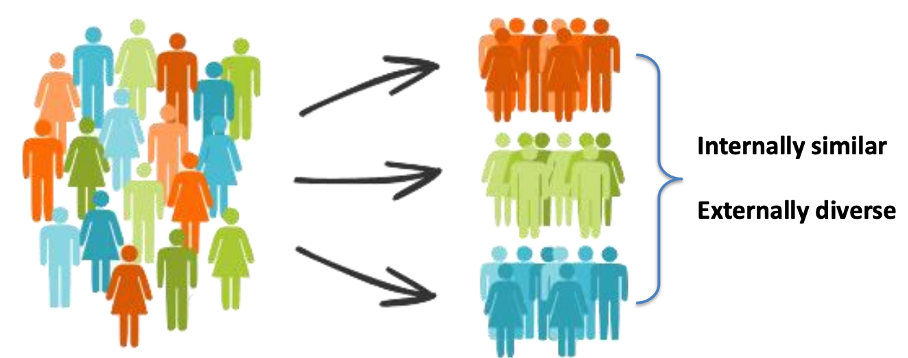
What is market segmentation?
Reducing the market complexity by dividing the customers into groups that share commonalities that are relevant to a company’s marketing needs.
Skincare: dry skin, normal skin, oily skin can be categories of the same customers. They have the same basic needs (internally similar) but are still externally diverse.
What are characteristics of a good market segment?
Measurability: it must be possible to measure the size and buying power of the segments. Numbers provides evidence.
Accessibility: Real possibility of addressing the segment using marketing actions, you can reach the segment you want.
Homogeneity: Within the segment as regards one or more characteristics. One or more characteristics must be shared (Ferrari: have a lot of money, want’s to show it off). Heterogeneity compared to other segments.
Importance: A segment large enough to justify a targeted marketing action. Better to develop a drug that can be used by a whole population than a very rare decease.
Duration: Possibility of exploiting the segment for a particular period of time. Things developed for covid cannot be exploited when the pandemic is over.
What are the advantages of segmentation?
The strategic objectives of segmentation are to create competitive advantage through:
Reduction in diversity: Not having sushi, burgers, fish in the same restaurant
More focus of resources & professionals: You can focus more on good resources if you don’t have multiple dishes.
Possible creation of entry barriers: Making it harder for others to entry
Improvement in customer satisfaction: Trying to fit everyone will result in not satisfying anyone.
Market share defense during maturity: If you are more focused to your customers, you will stand better against competitors during the market maturity.
Higher control on marketing decisions
Risk hedging: Reduce risk since the probability of two segments performing positive/negative at the same time is low. (Healthcare vs automotive can be two segments. )
What are some challenges of segmentation?
The challenges faced by a company approaching the market through segmentation include:
• Different products for different segments (R&D, engineering)
• Increased production costs
• Increased stocks
• Fragmentation of advertising/promotion costs
• Increased market research costs
• Higher distribution costs: create different channels for the products.
• Inefficient resource exploitation (e.g. duplication): In a car dealer shop; if you where to sell every brand, the staff would be occupied a lot but if you sell only Ferrari, people would not enter the store as frequent.
Higher complexity, inefficiency and higher costs caused by segmentation
What is targeting in market strategy?
You want to target the segment that is most attractive to you. Some factors to consider:
Is the segment large enough?
What is its growth potential?
How is the competition in this segment?
Do we have the right skills, knowledge and competences to serve this segment?
Is pursuing this segment consistent with our strategic mission?
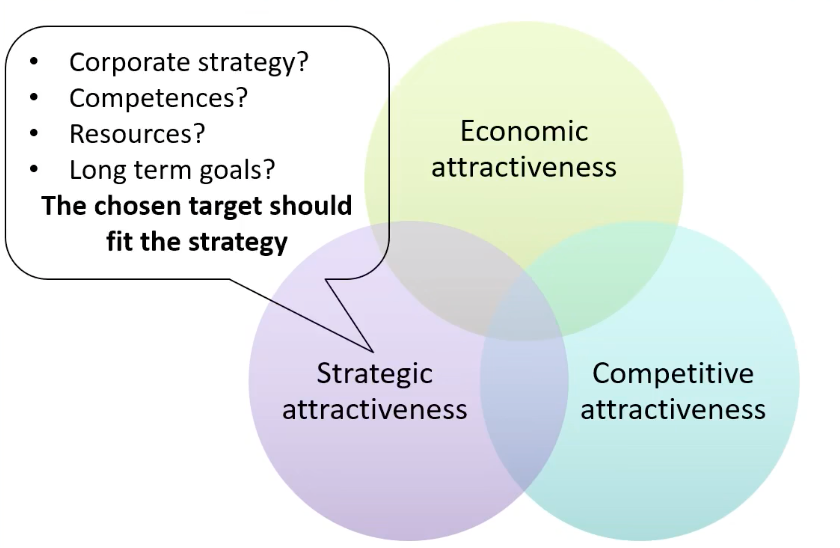
What is target attractiveness?
The attractiveness can be viewed in three ways:
Economic attractiveness: sales volume, sales value, growth trends (how will the company evolve in 3-5 years)
Competitive attractiveness: Consider the intensity of the competition
Strategic attractiveness: The chosen target should fit the strategy: corporate strategy? competences? resources? long term goals?
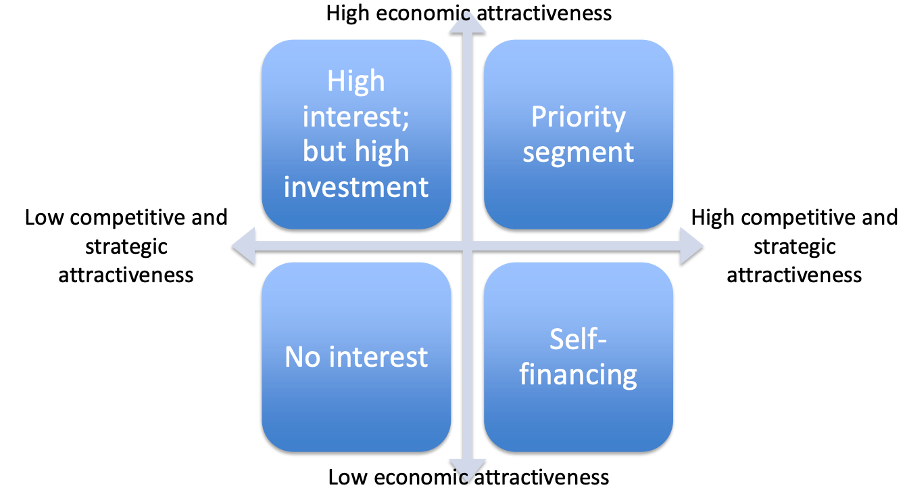
How do you choose your target segments with the different attractivenesses in mind?
Priority segment: you want to invest in this segment. High economic attractiveness and high competitive and strategic attractiveness.
No interest: No attractiveness so do not invest.
Self-financing: not very large market but can be high competitive advantage, can invest to be in line with strategy but no economic interest.
High interest but high investment: not coherent with strategy, plenty of competitors, can invest.
What is undifferentiated targeting strategy?
Use a single product to serve the whole market
Suitable for product with low possibility of differentiation and low importance
Suitable when market competition is limited
Advantage: lower production and marketing costs
Disadvantage: if in the market there are other products which could satisfy more precisely the consumers’ needs, it is hard for undifferentiated strategy to be successful. Possibility of substitutes.
The competition is about price

What is differentiated targeting strategy?
While satisfying the same basic needs, it uses different products to satisfy different preferences that the customers have.
Advantage:lower risk; customers are willing to pay more for a product that better satisfies their needs; customers are more loyal to brands/products which understand their needs better
Disadvantage: increased R&D, production, logistics, and marketing costs

What is concentrated targeting strategy?
Use a small set of highly customizable products to serve a market niche
Advantage: customer knowledge and intimacy, potentially extremely high profit
Disadvantage: difficult to gain competitive advantage in such market

What are the 5 approaches for market coverage?
Single segment
Market specialization
Product specialization
Selective specialization
Full coverage
Describe the single segment approach
Highly focused resources and competencies. Deep understanding and strong relationship with its customers. Highly related to concentrated strategy. High-end.

Describe market specialization approach
Deep understanding and strong relationship with its customers. Synergizing resources and competencies to provide different product lines to satisfy different needs of the same customers. Different electronic products but only offers to someone who like apple/tech.
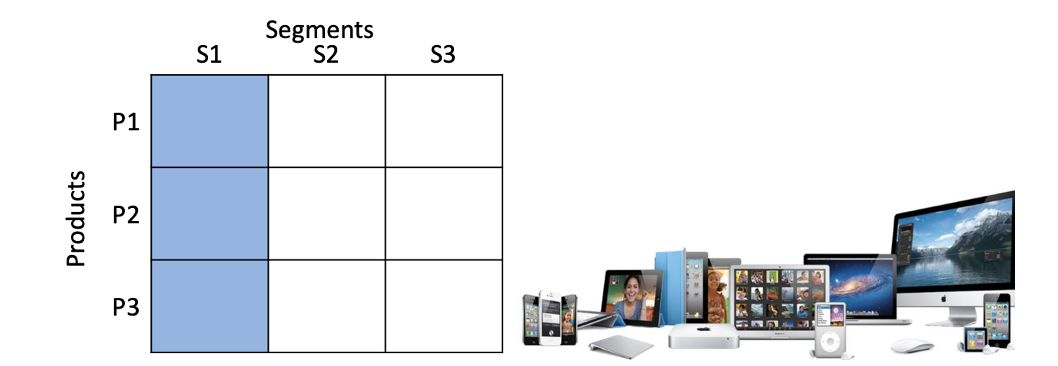
Describe the product specialization approach
Strong competitive advantage in product knowhow and strong brand reputation in its industry. Selling to
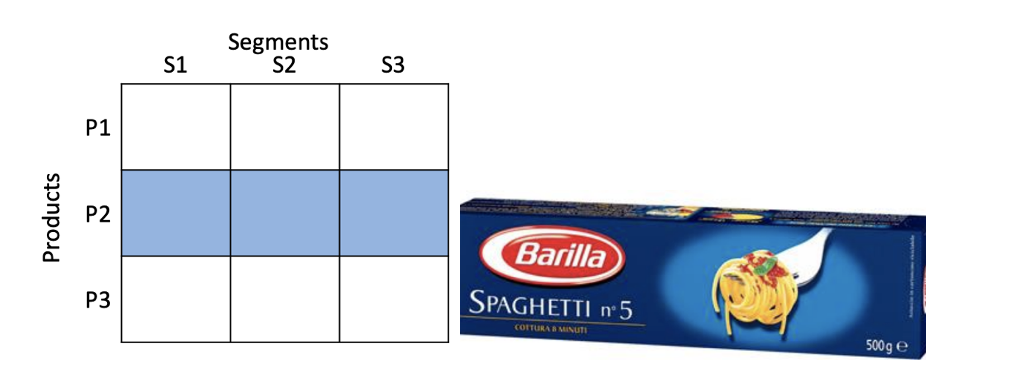
mass market. Sell pasta to distributors, customers, restaurants…
Describe selective specialization approach
Different strategies in different markets. Potential synergies in terms of corporate brand image and operations. Offer different products to different segments. They do completely different things. Virgin Atlantic: airplanes, virgin active: gyms.
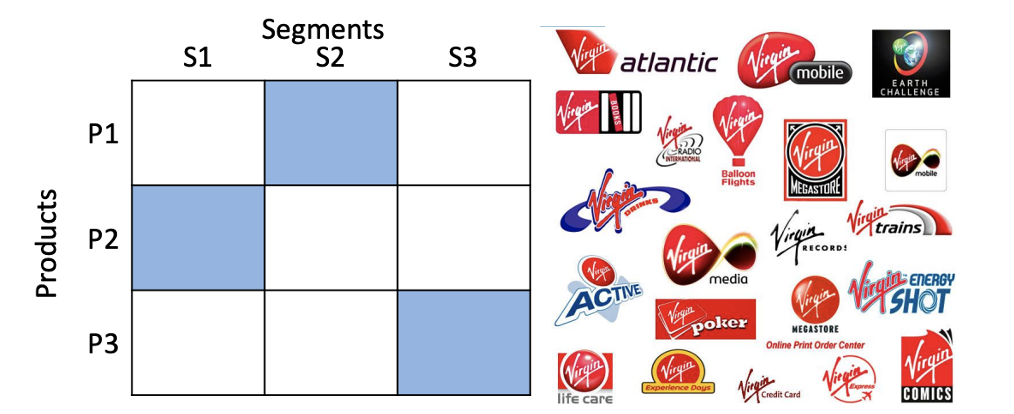
Describe the full coverage approach
Use a rich product portfolio to address different mar
kets and different segments. Enjoy operational synergies.
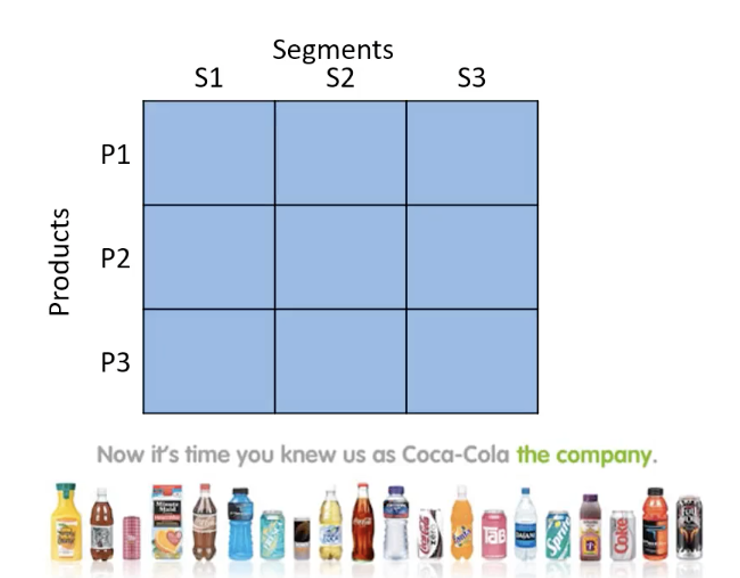
What are the criteria for targeting?
When a company chooses its target segment(s), it should consider:
1. The size of the segment(s)
2. Expected growth
3. The company’s competitiveness in the segment(s)
4. Costs of reaching the segment(s) Customers can be in different countries, hard to reach out to.
5. Compatibility with the organization’s objectives and resources
What is positioning in marketing?
Positioning means how we are perceived by the customers in comparison to our competitors.
The key of positioning lies in the creation of differentiation, of unique selling points, which are valuable for the market.
The differentiation has to be realized not only through products and services, but also through marketing communication to build awareness and a consistent perception in customers’ mind.
What are the two sources of differentiation for positioning?
Physical positioning;
The physical attributes of the product
Other elements that compose the offering
Essentially, the 4Ps
Psychographic positioning:
7Ps model - added three
The customer’s perception about the offering
The “mental image“ of our offer compared to the competitor’s one
Essentially, the practice of branding and communication
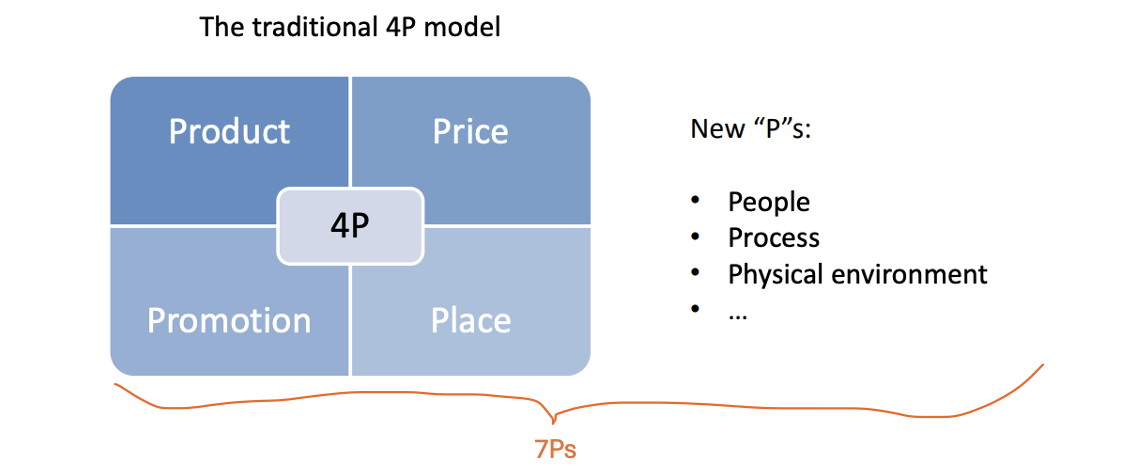
What are the 4Ps?
Product, Price, Place, Promotion
What are the 7Ps?
Product, Price, Place, Promotion, People, Process, Physical environment
What are the steps of positioning?
understanding which are the most important factors evaluated by customers when deciding what to buy, and their relative importance
evaluating how customers perceive the competitors’ offer as far as the most important factors are concerned
finding “free spaces” allowing a unique and distinctive positioning. Look at the market, what exists and where can we do changes to be different than existing companies?
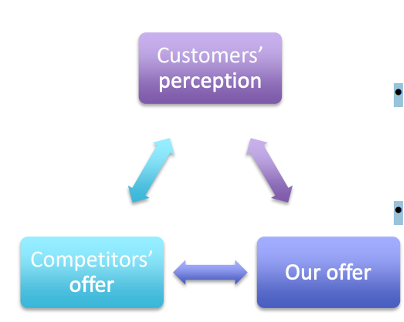
Why is it important to monitor the current positioning?
To evaluate how customers perceive competitors offer and our offer
To identify our strengths and weaknesses compared to the competitors ones
To understand our unique selling points that can effectively persuade the customers
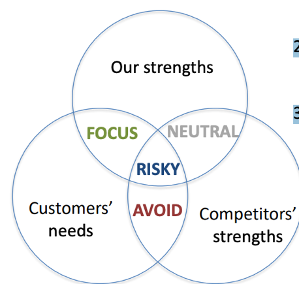
Focus: on the field where our strengths and customers needs collide but where competitors strengths do not collide.
Risky zone: a zone where we head to head compete with the competitors.
Avoid: do not compete in fields where you do not have strengths.
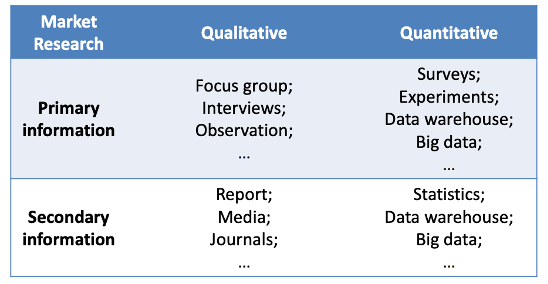
How do you perform step 1 in positioning: relevant factors?
In order to understand which are the most important factors evaluated by customers in order to choose what to buy, and their relative importance it is necessary to develop a market research.
Quantitative: numbers
Qualitative: emotions, perceptions
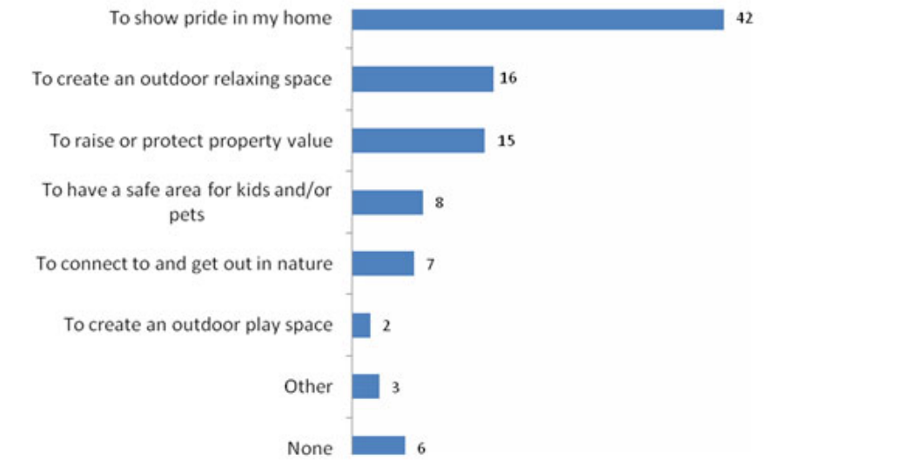
What are relevant factors?
Ex: When you maintain or renovate your front yard, what is the main motivation?
How do you perform step 2&3 in positioning with a perceptual map?
In order to identify our strengths and weaknesses compared to the competitors’ ones and to understand our unique selling points it is suggested to create a Perceptual Map. The Perceptual Map could incorporate two relevant factors. The two axes represent bi-polar values of these two factors.
Note that:
Bi-polar doesn’t simply mean “good” and “bad”.
Go beyond the absolute quality, discover true insight under each factor
You can prefer a car that goes faster, has sport performance but also one that has low fuel consumption, that is safe.
So what is good for a person is subjective and hence you can fall in both good and bad.
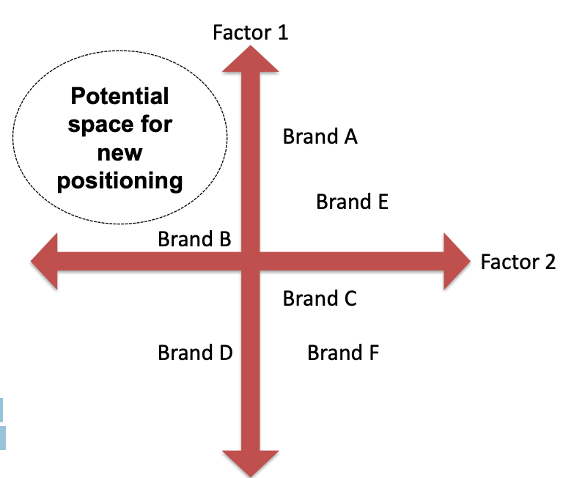
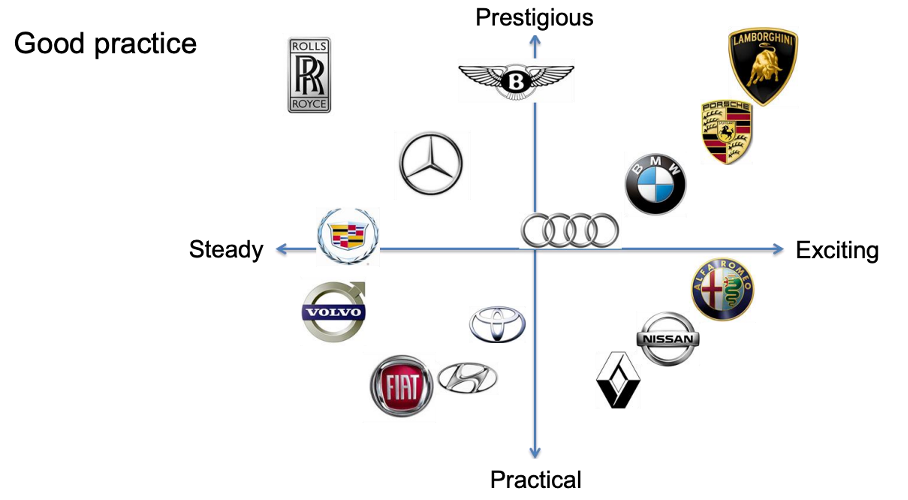
What could be a good example of a perceptual map?
Here it is not clear what is good and what is bad – but it depends on the perspective of the customer. In this map you can find empty spaces and sometimes it is the fact that the space is not interesting but sometimes it can also be where the opportunity lies.
What are critical success factors in positioning?
Positioning should address precise market segment(s)
Positioning should be clear and simple – easy to understand for the target segment
Positioning should create a sustainable competitive advantage
Positioning should be consistent with the company’s longterm objectives and capabilities
What is red ocean vs blue ocean?
Red oceans represent all the existing industries (the known market space). In red ocean industry boundaries are defined and accepted, and the competitive rules of the game are well understood. Here, companies try to outperform their rivals in order to grab a greater share of existing demand. Red for competition – blood. Fierce competition, war. Field competition. Not a good ocean because even if you win you still loose in some way. Like wars, you will loose some and win some.
Blue oceans denote all the industries that do not exist today (the unknown market space, untainted by competition). In blue oceans, demand is created rather than fought over. There is ample opportunity for growth, that is both profitable and rapid.
Introducing something unique, completely different where there are no competitors. Apple was a blue ocean. We had mobile phones but not smartphones. Today we only have smartphones so they completely changed the market. Want to be in blue oceans, avoid competition.
Explain the marketing mix (or 4Ps and 7Ps)
The marketing strategy needs to be translated into a clear and well-defined offer that has to be delivered to the market
People: people wearing the brand and representing it instead of wearing regular clothes
Physical environment: all Esselunga stores look the same inside
What can 7P - product be?
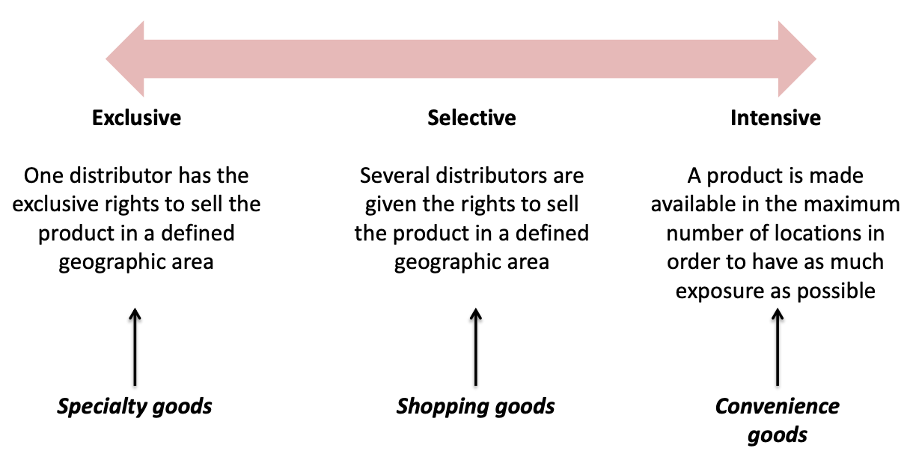
Physical object, service, person, place, organization. There are three categories of products:
Convenient goods
Shopping goods
Specialty goods
Important to understand which category you are in since they have different characteristic and needs to be managed in different ways.
What are convenient goods?
Ex: toothpaste, food, coffee at a bar
Buying behavior: frequent purchase; little planning; low involvement; minimum effort
Staples; Impulse purchase; emergency purchase (You are thirsty and see someone sell water)
Marketing consideration
Need a widespread distribution for these goods (when someone wants water they need to be quickly able to shop it)
Stock availability (Bad reaction if the water is out of stock – then customers will go elsewhere.)
Competitive price (Plenty of competitors on the market so have to compete with price.)
Mass market awareness
Sales promotion (Points, sales)

What are shopping goods?
Ex: Smart watches, glasses, phones. Think twice before buying.
Buying behavior: less frequent purchase; much higher involvement and effort to compare various aspects of the alternative products
Marketing consideration:
Marketing communication with the target segment to create awareness and desirability (you need to communicate that you have new models and updates so that people will keep buying from you.)
Selective distribution with higher service level (You don’t have a specific car dealer everywhere but when you go you can get more service on the goods than in a supermarket)
Higher price level as well as larger price range

What are special goods?
Ex: House, luxury car, diamond ring
Buying behavior: strong brand preference and loyalty; willing to make extra purchase effort; low sensitivity to price
Marketing consideration:
High importance in branding (you basically buy the brand, even if it theoretically is the same you will choose the one with known brand); creating awareness and admirableness by mass market yet highly targeted communication
Exclusive distribution with exceptional service level
High price

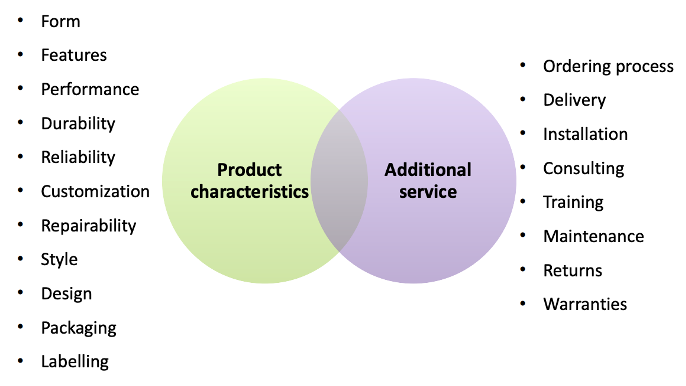
What does Product mix mean?
Need to define the product characteristics as well as the additional service. However need to choose - can’t be good at everything
What does 7Ps - price mean?
Need to distinguish between cost and price. Price is your decision but you cant have something with a lower price than what the cost is.
Price is a fundamental tool in the marketing mix
It is one of the most important and powerful communication tools about a product or service (If you see something nice – the price will also sometimes tell you about quality)
It is one of the most significant impacting factors on a company’s performance (directly and indirectly)
Price decisions for today have a strong impact on the future. Not simple to change the price policy later when it has entered the market. If you sell it cheaper people might think the quality is lacking.
It could be flexible, but also easily imitable. Supermarkets can fluctuate a bit. However, they are being watched by each other. If Ica lowers their price, Coop will immediately be able to do the same.
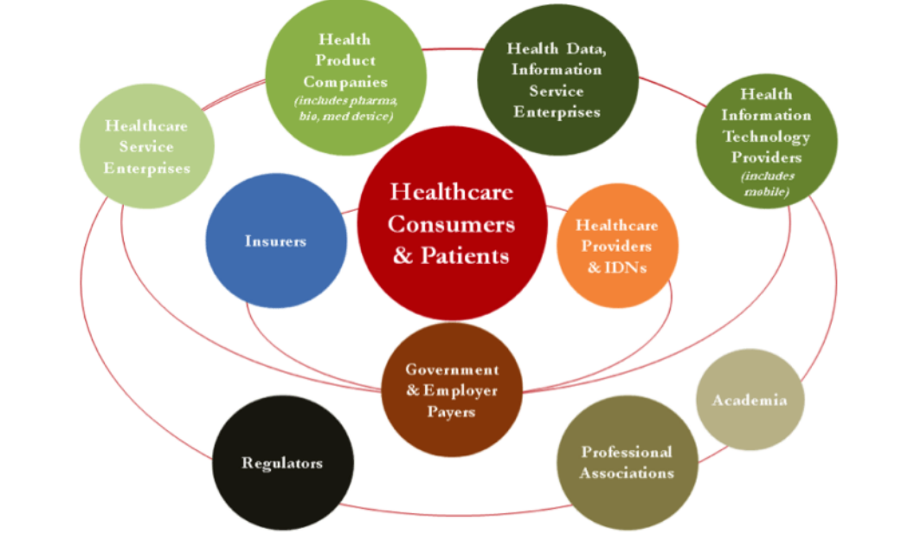
What are the different players in the healthcare industry?
To define the «Retail» pricing in healthcare industry could be extremely complicated and the way it is defined is rather peculiar of this industry.
The «retail» price of healthcare paid by the consumers or patients is a result of a negotiation among insurers, governments, employers, and wholesalers and healthcare providers. It can change largely from country to country, due to different policies and regulations.
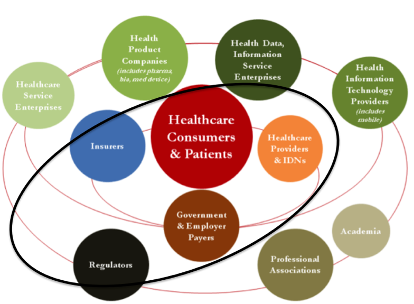
Why can it be easier to define price for research and development, device and supply manufacturing etc?
Not as many players are in that field. Often B2B context.
What are some factors influencing the price?
General economic situation: is bargaining power from customers increasing/decreasing? Inflation?
Laws and norms: Labour law, safety regulations, norms about level of pollution, tax policy
Competition: High level of competition pushes the average price level down and at the same time, lowers the difference between competitors prices
Cost structure: Where do the costs lie and how can I change it?
Product lifecycle: Mature products become less expensive since technology evolves
Business and marketing strategy: price is a marketing lever, it is not a source of competitive advantage (the cost is a source of competitive advantage)
What does pricing policy mean?
The pricing policy defines criteria and guidelines for setting the price. Strategic decisions made by pricing policy may include:
• General level of prices for the company and/or the specific product categories
• Variability of prices in response to external factors
• Management of price along product lifecycle
What does pricing process mean?
It could be an iterative process (what is the right price for the market and what is the right cost for that cost)
1. Define pricing objective
2. Forecast demand
3. Estimate costs
4. Analyze competitors
5. Select pricing method (Cost-based, Demand-based, Competitionbased, Value-based)
6. Decide price
What does 7Ps - place (distribution channel) mean?
The importance of the distribution channel is related to different factors:
• It is an essential step to eventually fulfill the market demand
• It is a key factor to achieve company’s profitability
• It could create and maintain a company’s competitive advantage
• It is complex
• It could change over time
Example:
Publisher can sell the book through amazon, salesperson who can sell to universities, digital platform
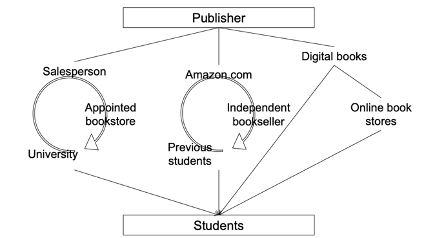
Why do different distribution channels exist?
Geographic and demographic development of the markets: A company can’t sell everywhere by themselves
Specialization: Going to a bookstore to buy a book will have more specialized books than going to a supermarket
Economies of scale & economies of learning
Lack of financial resource to serve the market directly
Consolidation of contacts and transactions
Reduction of disparities in supply and demand (in terms of lot size, time, seasonality, place, etc.)
Why is the distribution channel important?
Distribution channels simplifies the chain from production to customers so that we can focus on the product. However, sometimes it adds value to have these factors yourself.
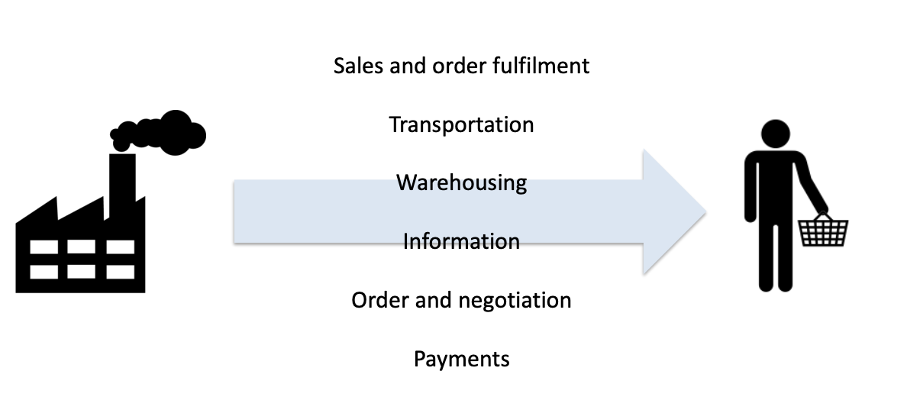
What different distribution options are there?
Wholesalers, Distributors, Retailers:
• Buy and resell the products
• Usually supported by substantial infrastructure and network
• Manage the inventory and take the risk of obsolescence: During Christmas they might buy more than they sell and they have to sell before a specific date. This problem is on the retailer and not the company.
• Could be multi-brand or mono-brand (franchising)
Sales agents & Brokers:
• Both do not buy the product and keep the stock; the transaction takes place directly between the seller and the buyer
• Both are paid through commissions on what they sell
• Sales agents act on behalf of the selling company
• Brokers match sellers and buyers helping them to find each other and completing the transaction. For this reason, brokers may receive payments from both the seller and the buyer
OEMs & VARs:
• Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) produce and sell parts or subsystems to other companies that may hence produce their end product
• Value-Added Resellers (VARs) produce and sell end products using supplies from OEMs
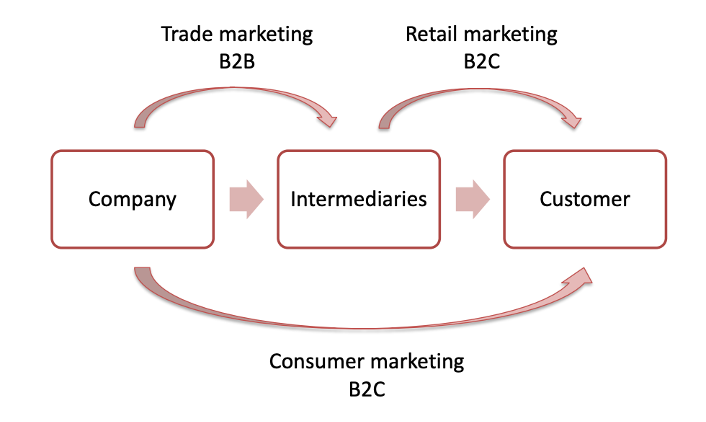
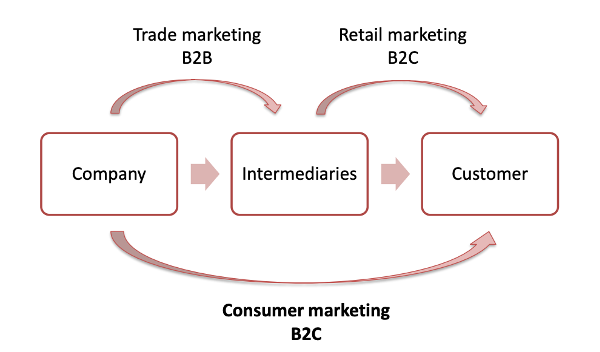
What is the difference between consumer marketing, trade marketing and retail marketing??
Consumer marketing: B2C (marketing should be towards the final customer). Barilla tries to convince people to buy from barilla and no other brands.
Trade marketing: B2B (convince distributers to push your product more than others.). Shells in the store are at different heights, and it is more effective to have brands in eye-sight. You want to push the retailers to have your products in larger spaces and better places.
Retail marketing: B2C (when intermediaries convince customers). When a supermarket have discounts or persons give out samples in the supermarket
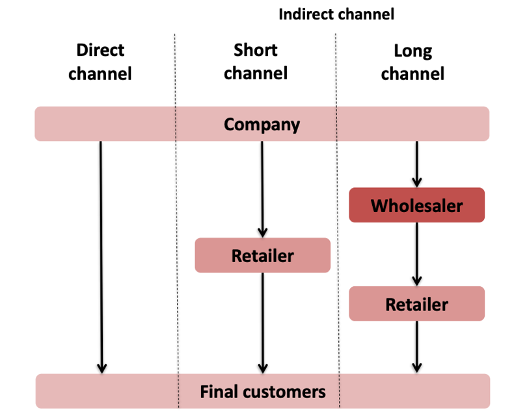
What different channel lengths are there in distribution channels?
Direct channel: directly to customers (through brand website for example)
Short channel: Only one intermediary (shop parfum through Douglas)
Long channel: multiple intermediaries (other countries can’t buy through a short channel so you first sell to a wholesaler that sells through retailers in that country).
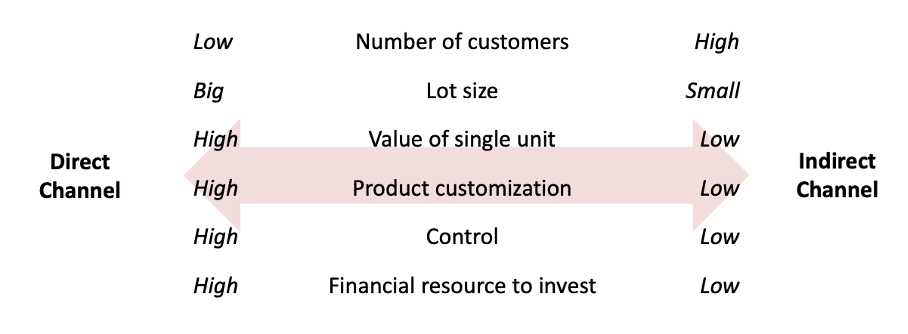
What should you choose? Direct or indirect channels?
A company may exploit simultaneously direct and indirect channels in order to achieve different objectives.
Can buy directly from apple or from distributors as MediaWorld.
Not good or bad. Have different advantages. Need to specify what is good for a specific target.
How are channels related to type of product?
Different categories of goods often have different channels.
What does 7Ps - promotion (communication) mean?
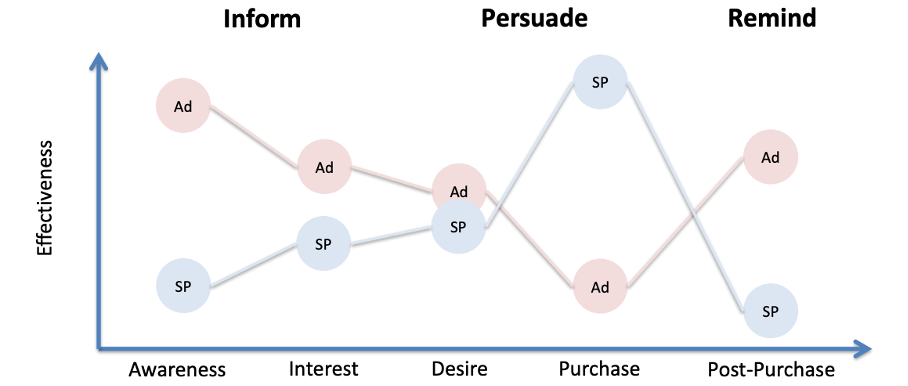
Companies leverage on communication to inform, to persuade, and to remind customers, directly or indirectly, of their products and brands.
Different communication based on which way you decide to go.
How does the communication process look like?
Define the target (what is the target of your communication, need to focus)
Define the objectives of communication (what do you want to say)
Develop the message to convey (make sure you really say what you mean to say)
Define the communication mix and select the channel (how should you communicate)
Define the communication budget (how much can we afford on the communication)
Assess performance (Has the objective been achieved or not?)
How do you define the target?
Who are the targets of the communication?
• Prospects
• Current customers: Once you have obtained a customer it is also necessary to maintain the customer, so convince them to keep buying from you.
• Influencers or decision makers: Can make other people buy from you
• Stakeholders
• …
The target of communication could influence:
• The core message of communication
• The format of communication
• The channel of communication
• The time of communication (can’t communicate in the middle of the night since most people sleep then)
What is brand, product and instituonial communication?
Communication could have different objectives:
Brand communication: aims to raise awareness, spread information, and build a positive image of the brand
Product communication: aims to raise awareness, spread information, and create interests in a product
Institutional communication: building and managing company image towards public, stakeholders, policy makers, supply chain partners, etc.
What does AIDA mean in the purchase process?
Attention: A product can’t be sold if the market is not aware of its existence, the first step is to attract the attention of potential customers
Interest: Attention is not sufficient, companies need to spark customers’ interest in the product by demonstrating its features, uses, and benefits
Desire: Companies need to further stimulate customers’ desire by convincing them of the product’s superiority and ability to satisfy specific needs
Action: After convincing the potential customers of the benefits they may achieve buying the product, promotion should then push them to actually purchase it
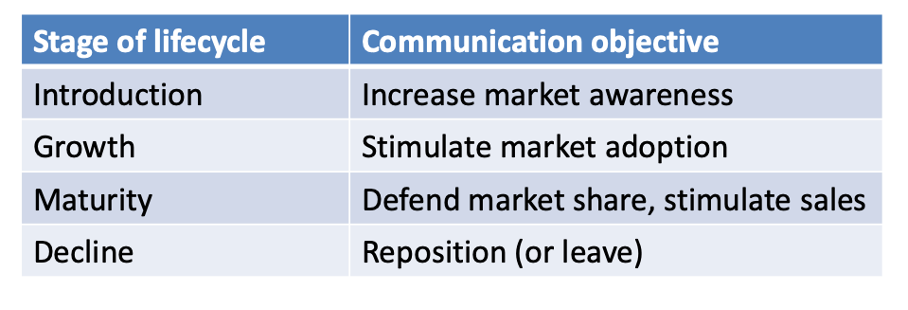
How do you define the objective - product lifecycle?
Products at different stages of the lifecycle have different objectives as far as marketing communication is concerned.
Decline: most dangerous faze since market is declining. Need to change something in the communication to increase people buying it.
How do you develop the message?
Need to use different languages based on the target (age, company/people)
Sometimes you don’t deliver the right message due to noise in the communication.
If the right message is not delivered it is your fault and not the receiver.

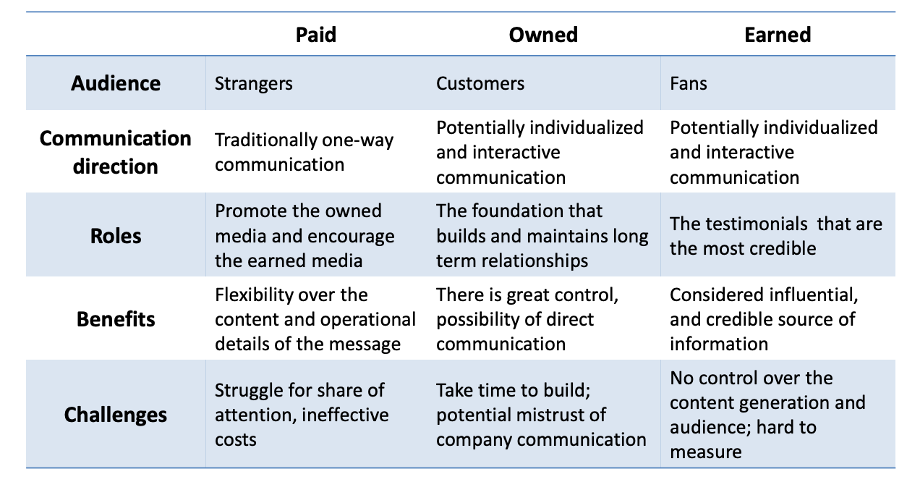
What is the difference between paid, owned and earned media`?
Paid media: pay for advertisement
Owned media: your own media, where you can communicate whatever you want
Earned media: 50% of students to business school comes from word of mouth.
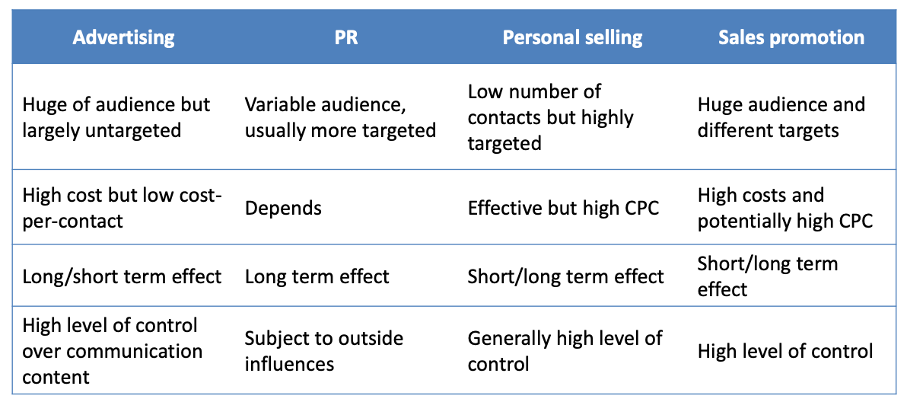
What is advertising (mass communication)?
Mass communication is heavily used to raise awareness and interest due to its efficiency in reaching large numbers of potential customers
Most commonly seen mass communication mix include TV advertising, radio, outdoor billboard, sponsorship, and so on.
Advertising is paid, non-personal communication, transmitted through media such as television, radio, magazines, newspapers, outdoor billboards, direct mail, as well as internet, mobile devices, and so on.
It is the most commonly applied marketing communication program.
Advertising through mass media such as television, radio and outdoor billboards could reach an extremely large, although not specifically targeted, audience group.

What are advantages and disadvantages about internet advertising?
With internet and increasingly powerful databases, companies are allowed to make specifically targeted communication through direct mail, internet, and mobile communication
Internet advertising provides a much more economic, and more targeted alternative
However, internet advertising is still struggling to more effectively convert the impression into click-through and into further action
What are public relations?
The goal of Public Relations is to track public attitudes, identify issues that may elicit public concern, and develop programs to create and maintain positive relationships between a firm and its stakeholders
Public relations can be used to promote the company, its people, its culture, its ideas, its image, and so on.
Public relations could improve the general awareness of a company and create specific image which gives the company a competitive advantage.

What are some examples of public relation platforms?
News releases: a written communication which draws attention of company’s stakeholders to the company’s event
Press conference: a meeting with news media to announce or to respond to major events
Featured articles/white paper: elaborated communications (possibly with technical details) about company’s products or initiatives and their potential impacts, directed at specific stakeholders
Event sponsorship: sponsoring events such as charity, exhibition, sports, and so on, from local to global
Product placement: placing a product in the hand of movie or television characters, especially the highly identifiable brands

What is personal selling?
Some communication mix could also target individuals and be more directly related to actions.
Interactive Personal selling, or consultation from salesperson at the Point of Sale (POS) could enhance the effectiveness of communication, stimulate customers’ desire and move them to a purchase action. Other sales promotion activities such as coupons, trial packages, special offers, and so on, could help to push the purchase action as well.
Personal selling is done through paid personal that attempts to inform customers about products and persuade them to purchase those products. Personal selling could take many forms, for example:
A salesperson of a home appliances retailer explains to customers the features and benefits of an electric oven
Pharmaceutical salesperson visits doctors and physicians to introduce their products
Business development team of construction equipment meet governmental officials of urban planning for their construction projects
Some types of Personal selling (especially in B2B market) are complex and involve long term relations.
It could be the most precise and effective form of communication.
However, Personal selling could have an extremely high cost per contact.
Salespersons must possess selling skills, but, quite often, they are also required to be familiar with the technical details (e.g. pharmaceutical reps).
What is sales promotion?
Sales promotion involves activities that create incentives for customers to purchase a product, or that add value for customers or distributors
Sales promotion often accounts for a large portion (up to 70%) of a company’s promotional budget, especially commonly seen in FMCG (Fast Moving Consumers Goods)
Sales promotion could be a stand-alone activity, but it could also support advertisement, sponsorship, public relation initiatives, and so on.

What are some examples of sales promotion?
Coupons: effective way to increase sales volume, attract repeat purchase or induce first trials
Samples: stimulate first trials, especially in the early stage of product lifecycle
Loyalty program: rewards loyal customers for repeat purchases
Premium: a bonus is offered for free or at minimum cost with the purchase of a product
What sales promotion is used for B2B?
Quantity discount
Free merchandise
Training assistance
Cooperative advertising
Selling incentives
How do you define communication mix and select the channel?
How can the communication mix and channels change over time?
To achieve different objectives along the purchase process
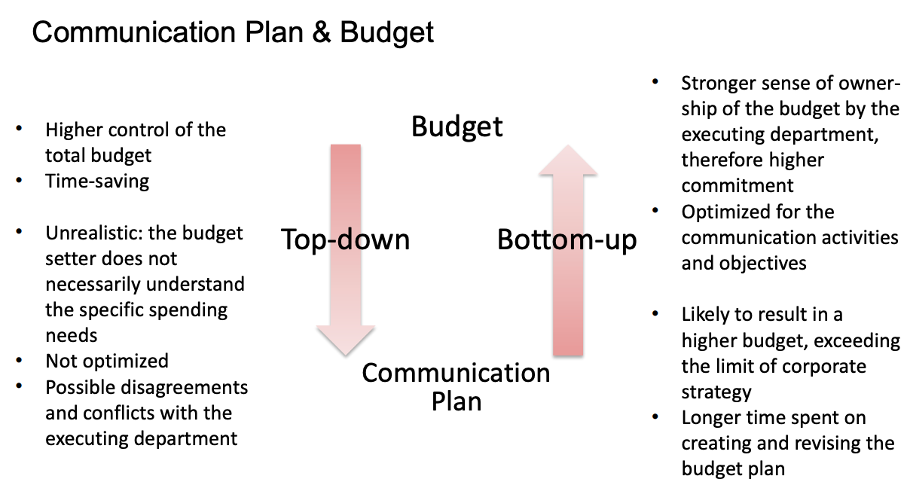
How do you define the communication budget?
Factors that can influence the communication budget:
Stage of product lifecycle
Desired market share
General market size
Level of competition (direct and indirect)
Resources available to be invested
Communication accountability
How do you asses performance?
Define Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
What are the objectives of the communication campaign and which KPIs measure these objectives?
The following KPIs can be used for different objectives.
