Joints and movements
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
skeletal framework of the body
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Joint
An area where 2 or more bones meet
Join other name
articulation
functions of joints
hold bones together, allow for mobility, classified according to structure
Classification of joints
fibrous/fixed, cartilaginous, synovial
fibrous joints
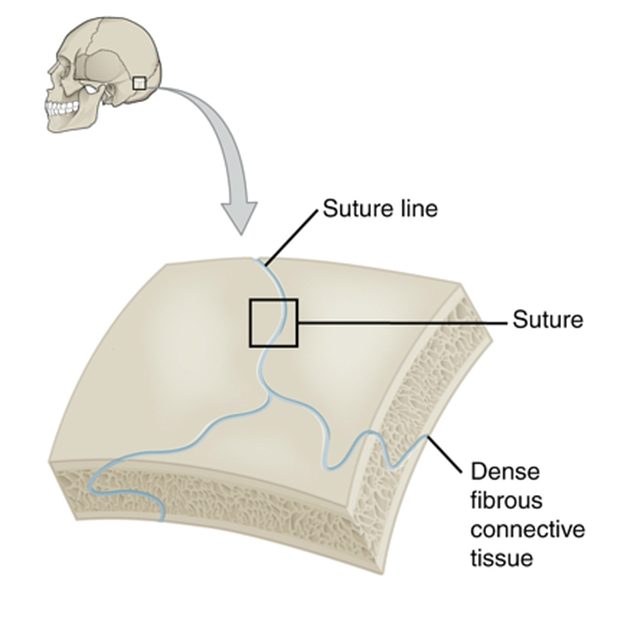
immovable, held together by connective tissue, strong
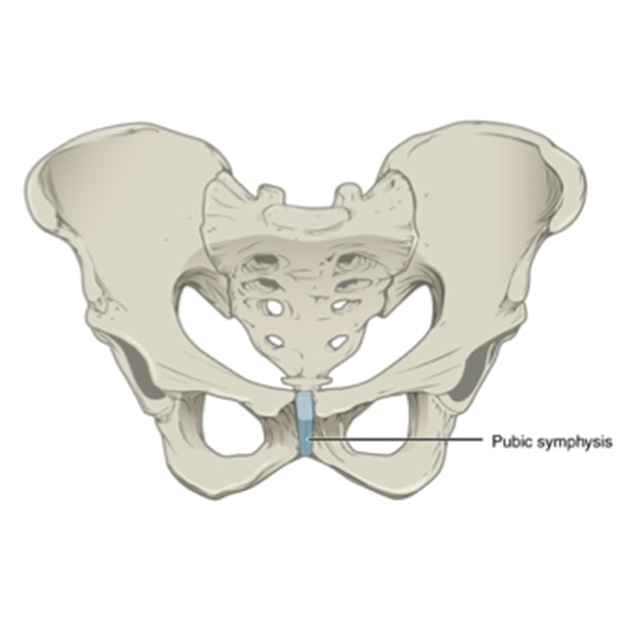
cartilaginous joints
slightly moveable, held in place by cartilage, stronger than synovial
cartilaginous examples
pubic, symphysis, intervertebral discs
fibrous examples
sutures of skull, teeth and jaw
synovial
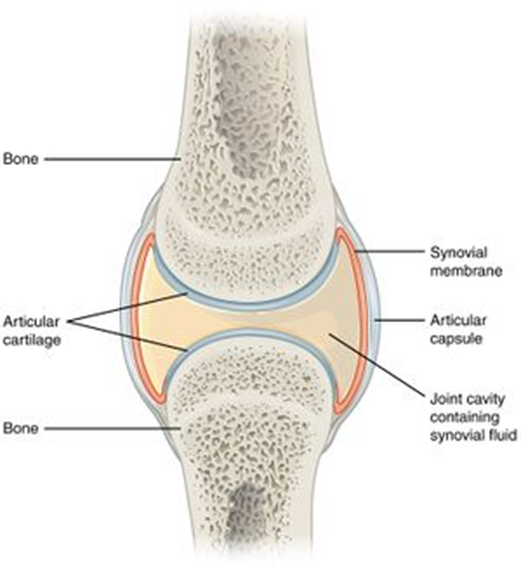
freely movable, ligaments, muscles and tendons control movement, more easily damaged
synovial examples
shoulder and knee joint
structure of synovial joints
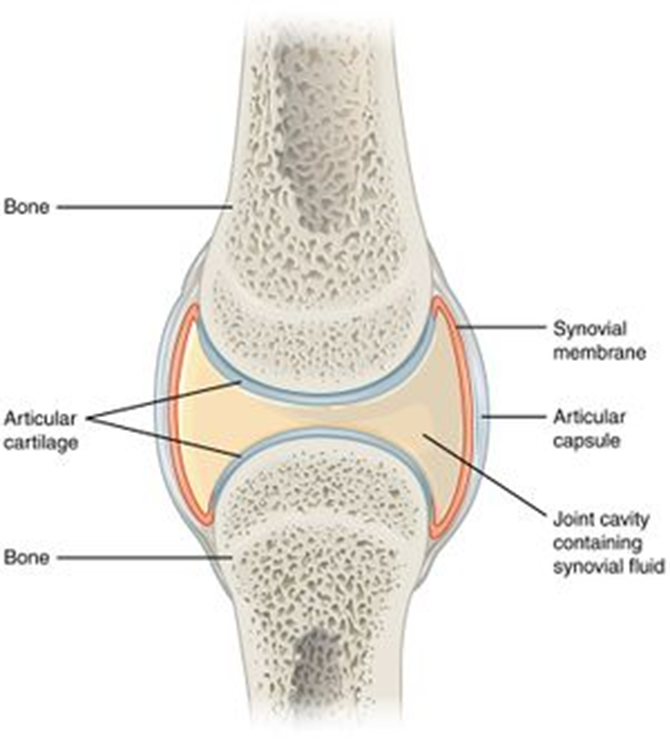
articular capsule made of fibrous capsule, synovial membrane, articular cartilage, articular discs, bursae, ligaments
articular capsule
surrounds entire joint and made of fibrous capsule and synovial membrane
fibrous capsule
outer layer, dense connective tissue attached to bones. flexible enough, allowing movement but strong enough for no dislocation
synovial membrane
inner layer or capsule, loose connective tissue. Lines the entire cavity, well supplied with blood vessels
articular capsule
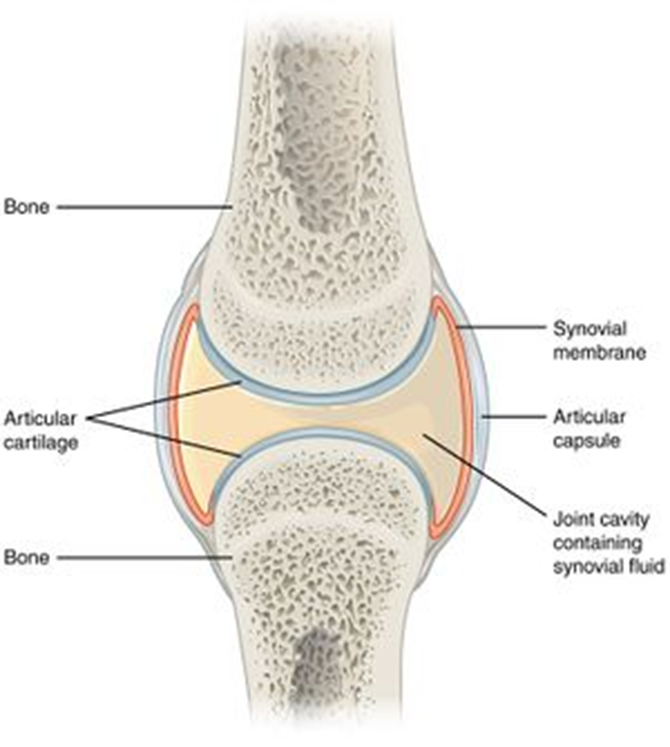
covers surfaces of bones to reduce friction on surfaces
articular discs (meniscus in knee)
direct synovial fluid into areas of greates need, like articulating surfaces
bursae
sacs of synovial fluid preventing friction between features like tendons/joints/skin and bones
ligaments
join bone to bone, adds strength to joints
structure and function of synovial fluid
synovial fluid, functions: lubricates, provides nourishment, contains phagocytes
synovial fluid
secreted by synovial membrane and fills synovial cavity
function of synovial fluidm (lubricates, nourishment, phagocytes)
lubricates joints and keeps two surfaces of bones from rubbing eachother, provides nourishment for cartilage cells, contains phagocytes to destroy any pathogens/debris from wear nd tear
function of synovial fluid
lubricates, nourishment, phagocytes
injury to a synovial joint
increase the synovial fluid leading to inflammation
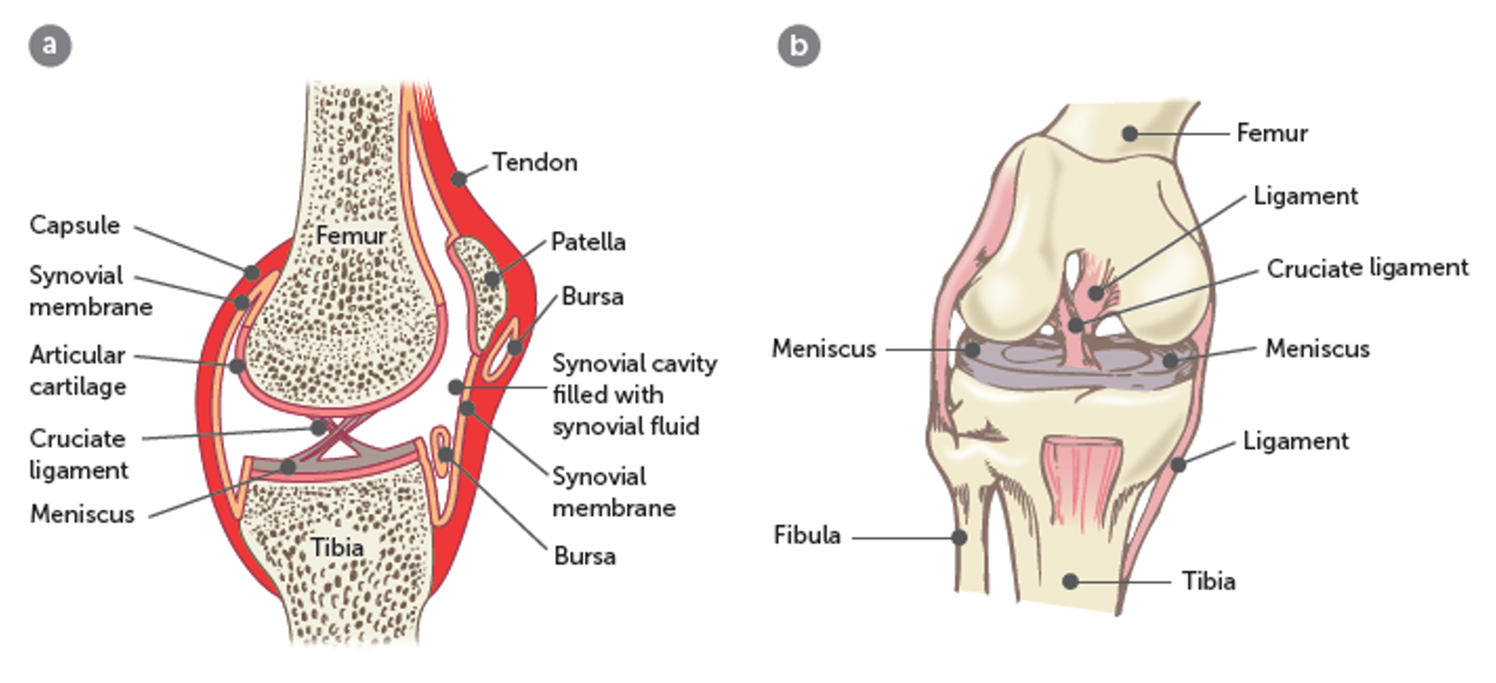
structure of synovial joint
types of synovial joints 6
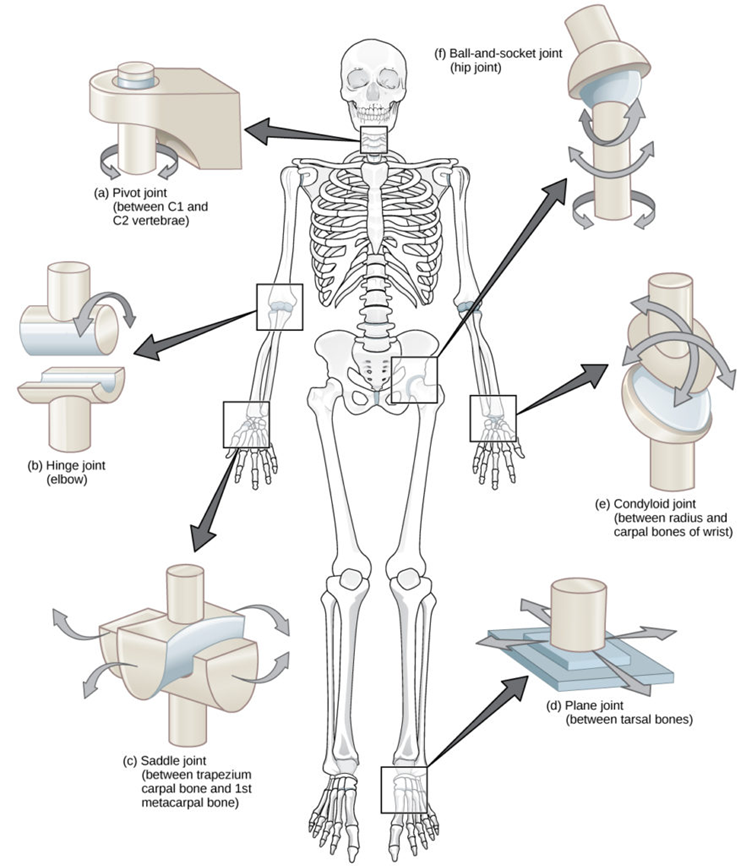
ball and socket, hinge, pivot, gliding, saddle, condyloid
ball and socket joint
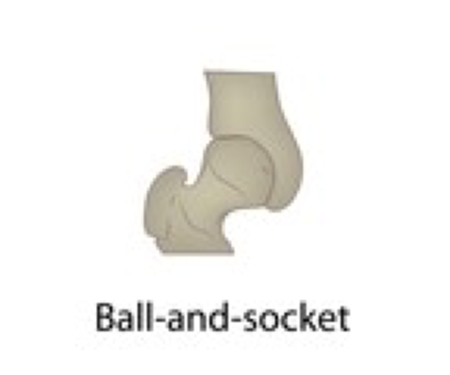
spherical head of a bone fits into a cup-like depression of anotherbone, allows for a very large range of motion
examples of ball and socket joint
shoulder and hip joint
hinge joint
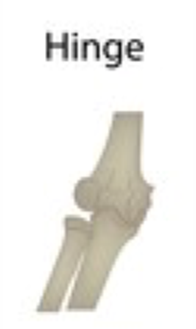
convex surface of one bone fits into concave of another, allows movement on a plane back and forth/flexion and extension
EXAMPLES OF HINGE JOINT
elbow and knee joint
pivot joint

poiinted end of a bone articulates with a ring of bone/ligament, allows for rotation
examples of a pivot joint
first and second, vertebrae (head rotation, radius and ulna
gliding joint
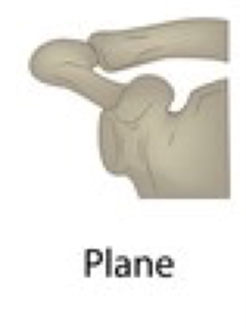
two bones that move alongside one another, allows for limited movement in either side-to-side or back-and-forth
examples of gliding joint
between carpal bones, sternum and clavicle
saddle joint
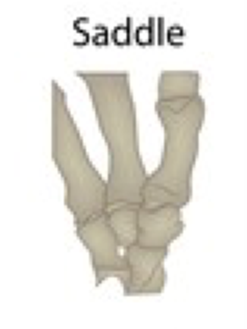
concave and convex bones fit together like a saddle
examples of a saddle joint
thumb joining to hand, metacarpal to carpal
condyloid joint
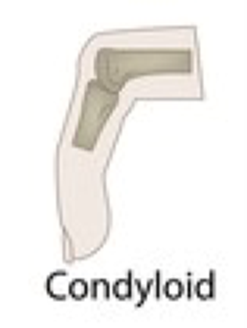
slightly convex bone fits into slightly concave bone, allows for limited range of motion both side to side and back and forth
examples of a condyloid joint
between phalanges and metacarpals, radius and carpals
keeping joints together, factors that keep the articular surfaces of synovial joints together
the fit of the articulating bones, the strength of joint ligaments, the tension provided by the muscles around the joint
the fit of articulating bones example
the way the head of the humerus fits into the socket of the scapula to form the shoulder joint
the strength of the joint ligaments holding the bones together example
hip joint
the tension provided by the muscles around the joint example
in the knee joint, the fibrous capsule is formed principally from tendons attached to the muscles acting on the joint
movement at joints
flexion and extension, abduction and adduction, rotation
flexion
decreases angle between articulating bones, e.g when the elbow is flexed, the lower arm with raidus and ulna moves closer to the upper arm with the humerus
extension
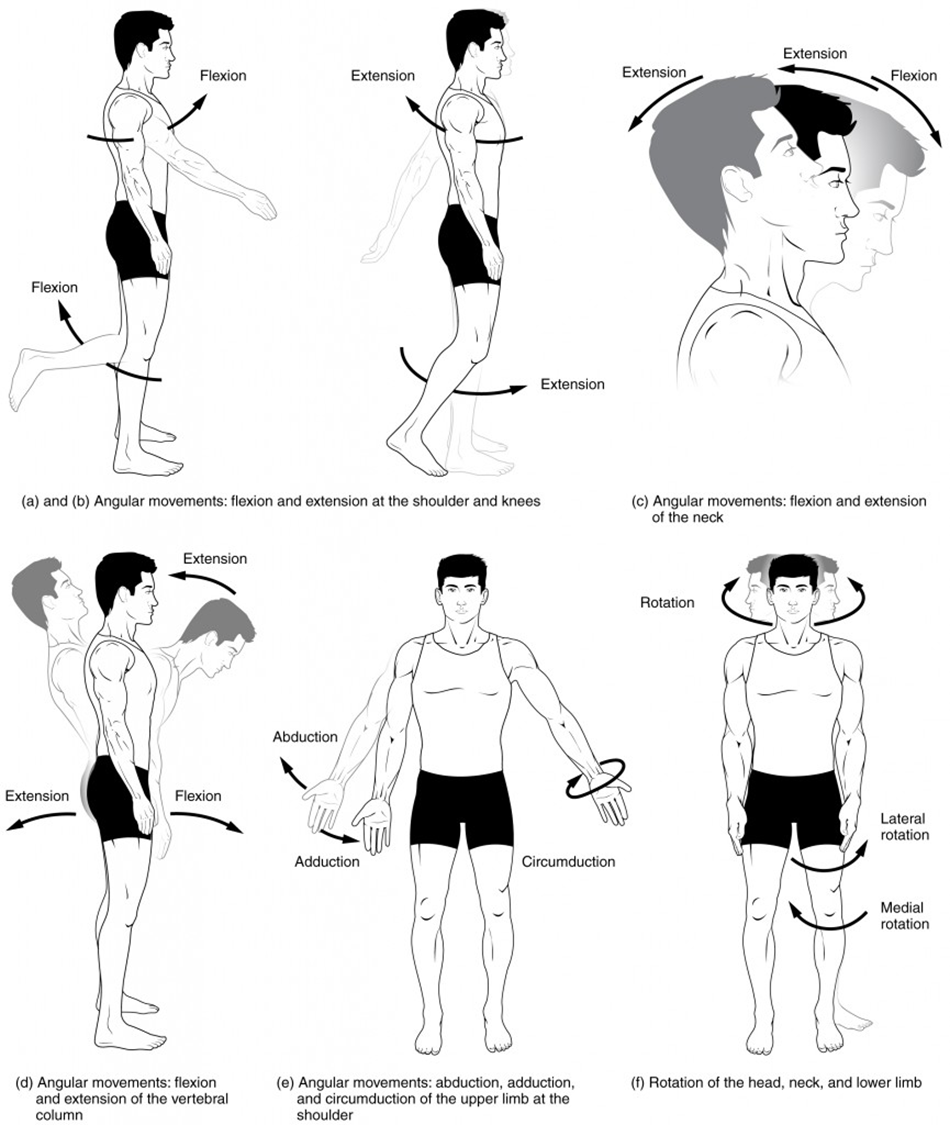
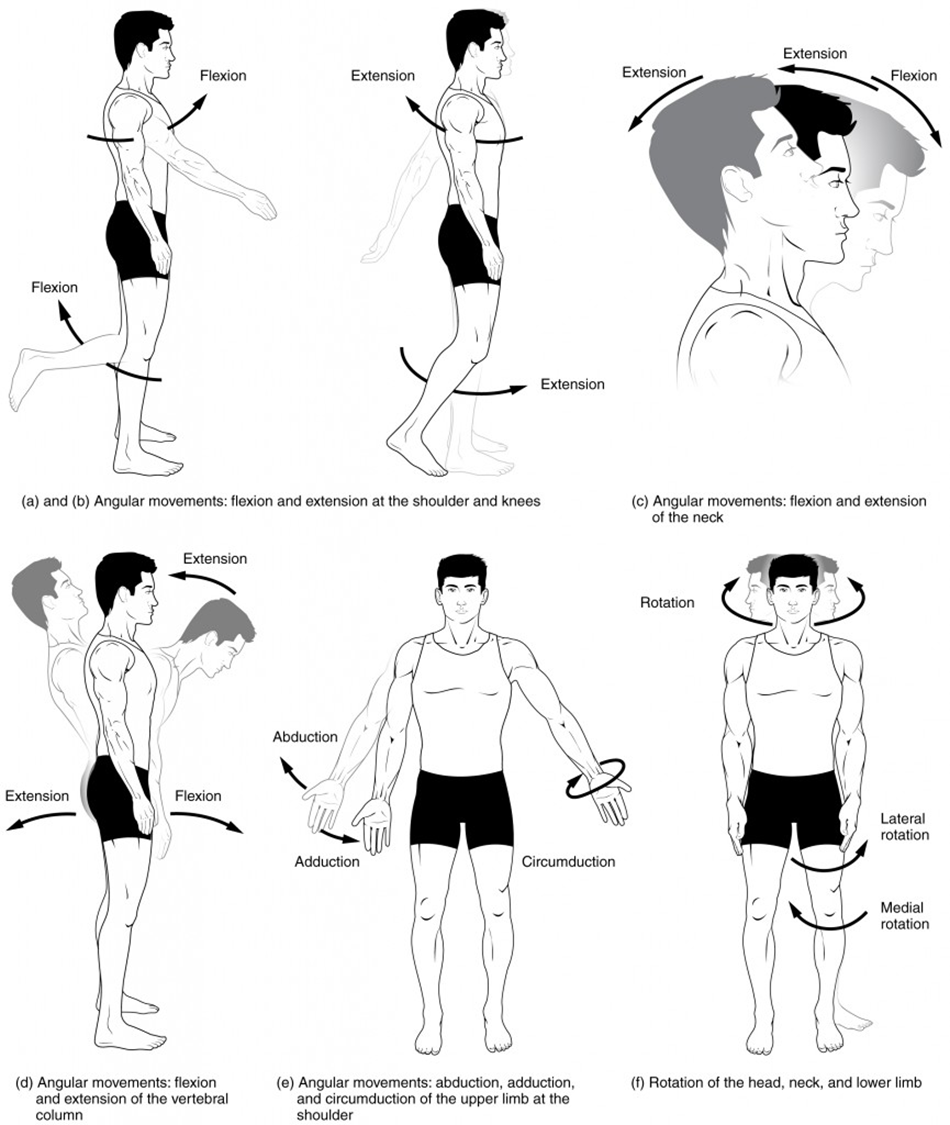
increases angle between articulating bones e.g when the knee is extended, the lower leg with tibia and fibula moves away further away from the upper leg with the fermur
abduction
movement away from midline of the body like lifting arms away from body
adduction
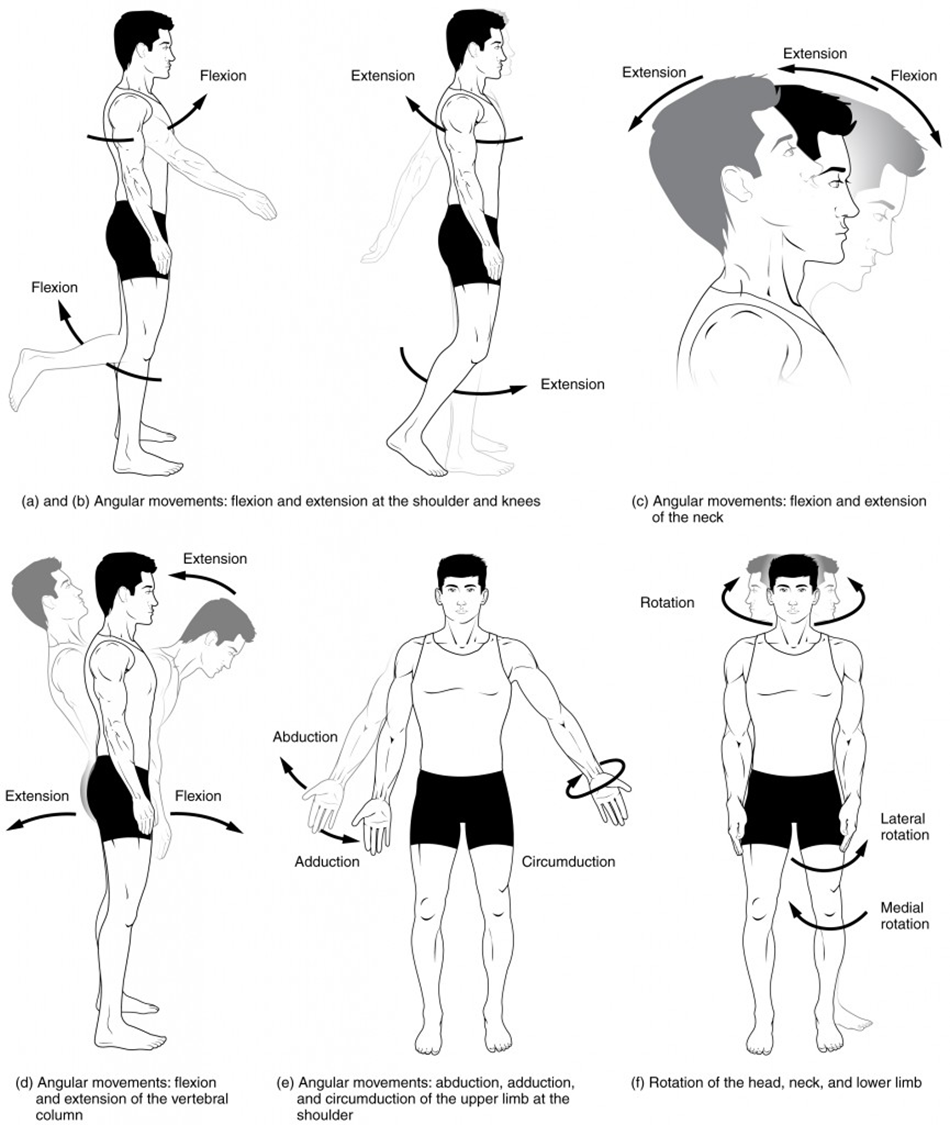
movement towards midline of the body like bringing arms inwards towards the body
rotation
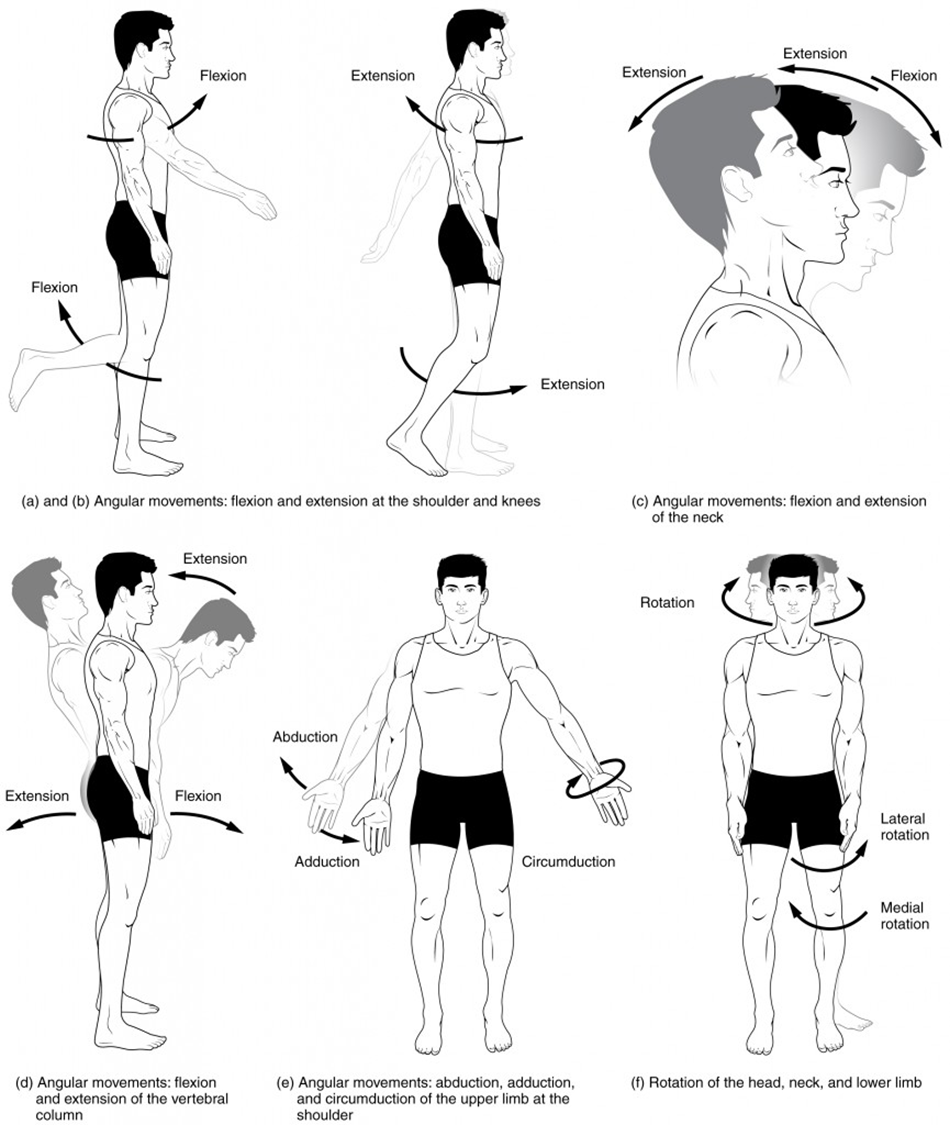
movement along the long axis of a bone, like moving head left to right