Lab Quiz 1 Study Flashcards
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
101 Terms
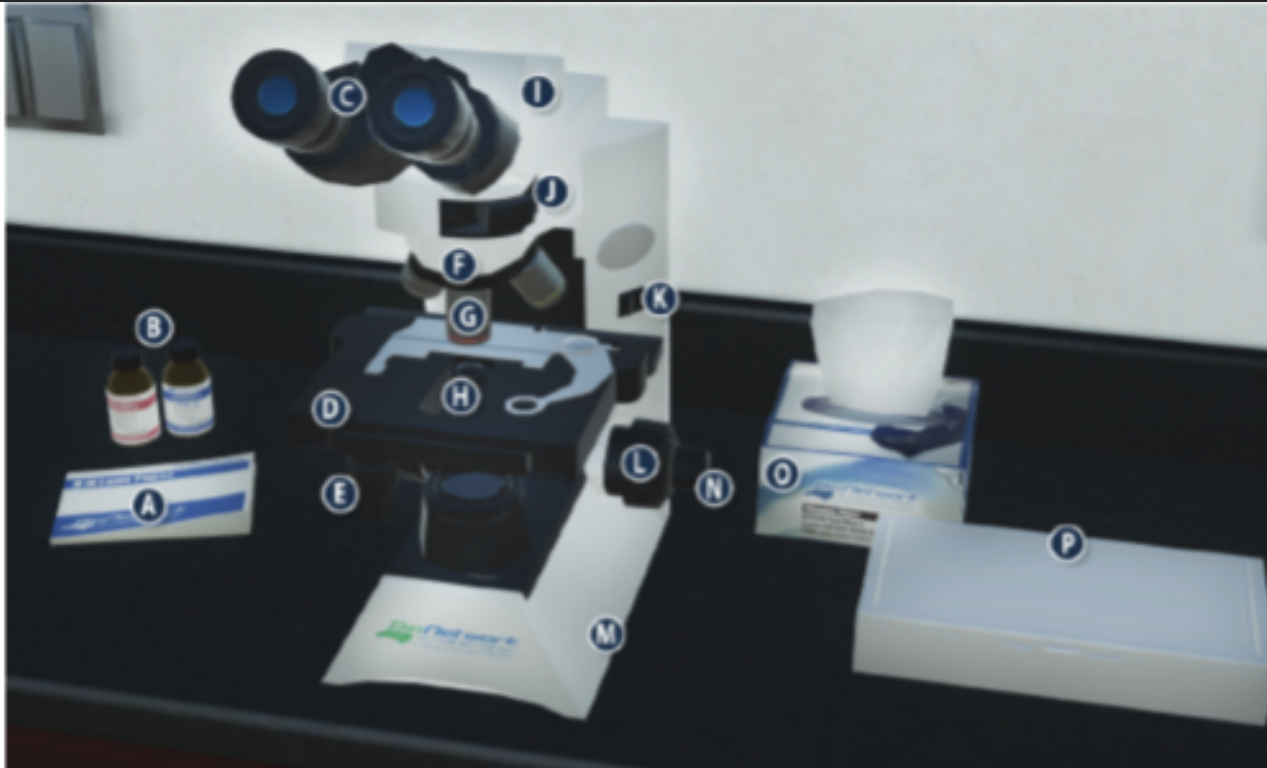
On/Off switch on a microscope (K)
Controls power
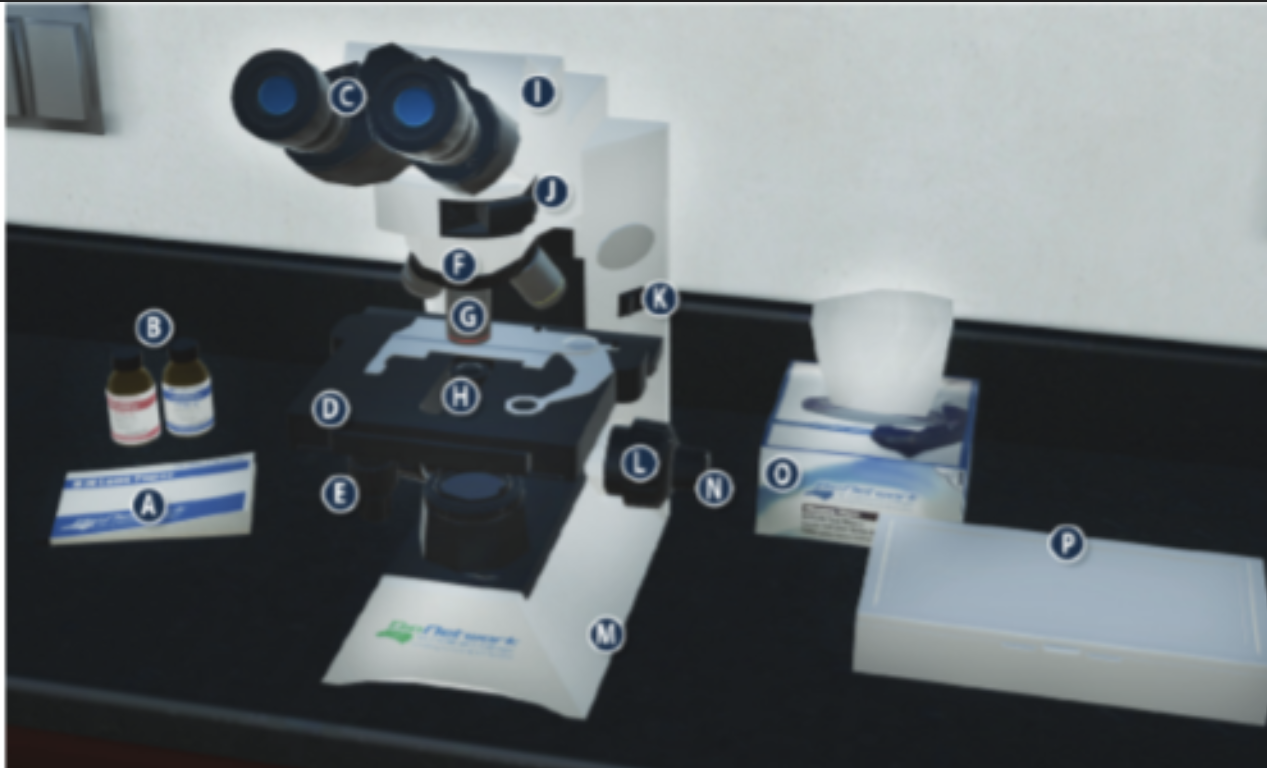
Eyepiece/ Ocular lens (C)
Comes in 10x, 5x, 15x, and 20x
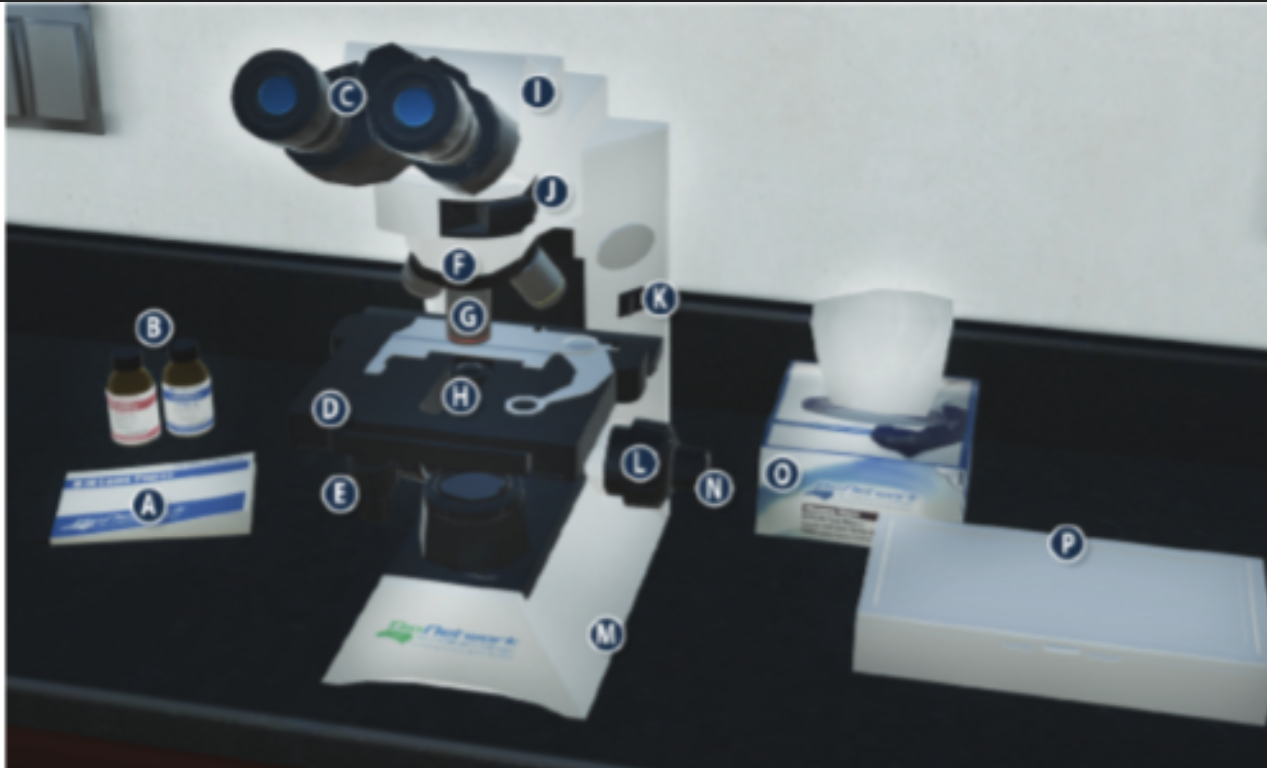
Arm (I)
area between tube and base to carry microscope.
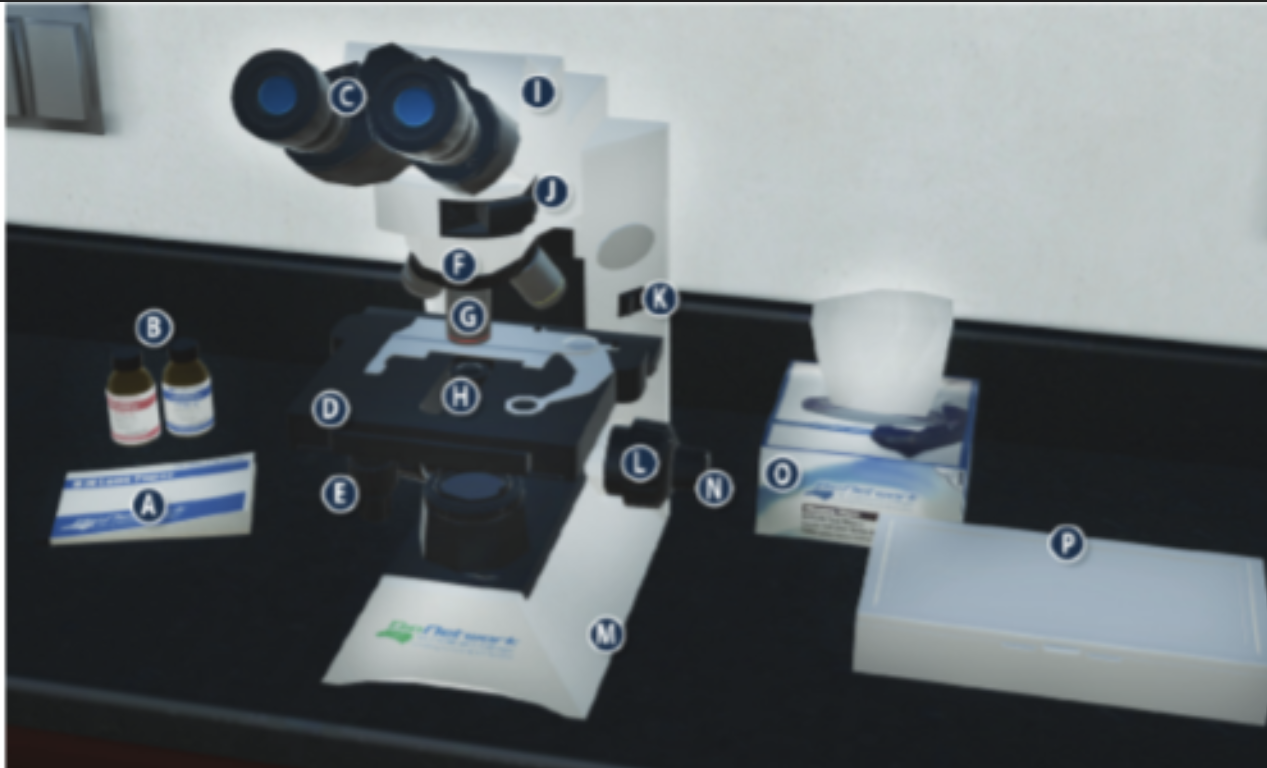
Nosepiece (F)
also called revolving nose piece. Holds the objective lens. Rotating this piece all objective lens to be switched.
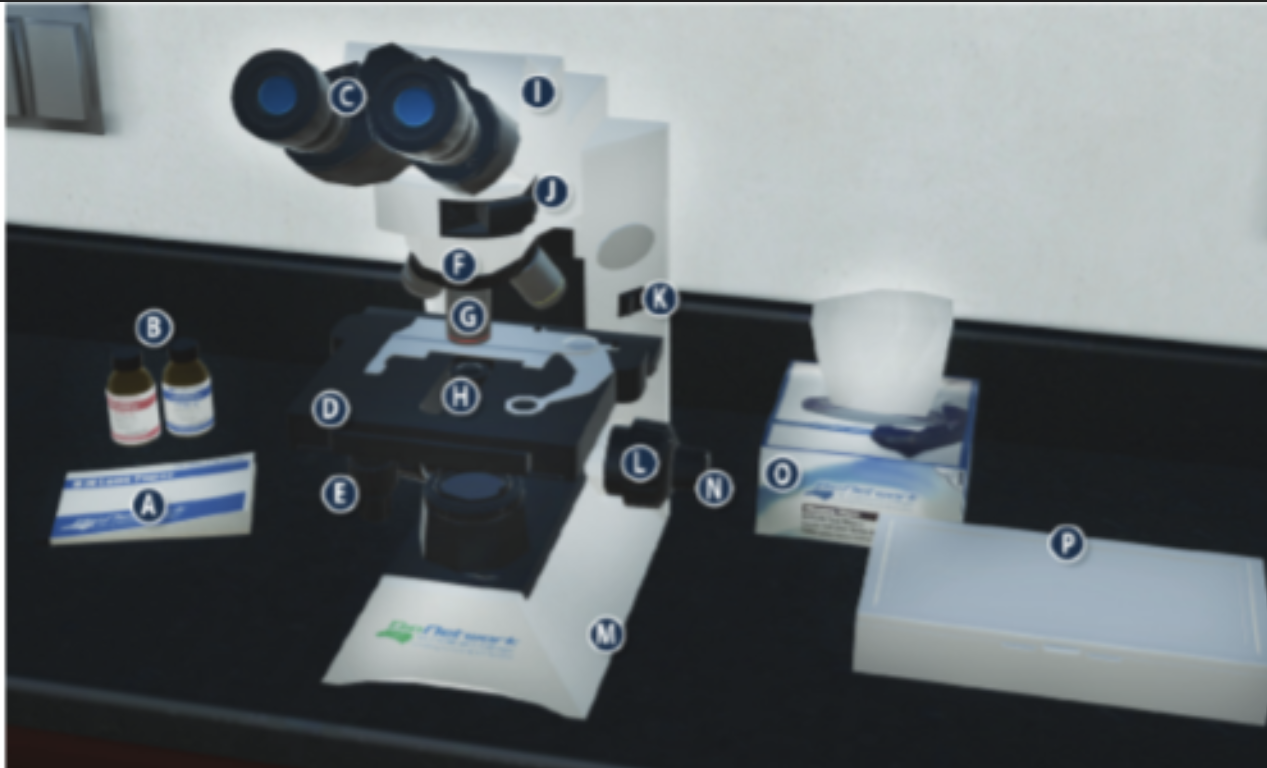
Objective lenses (G)
There are 4. each has different magnifications. 4x (scanning lens) 10x (Low power lens) 40x (high power lens) 100x (Immersion lens)
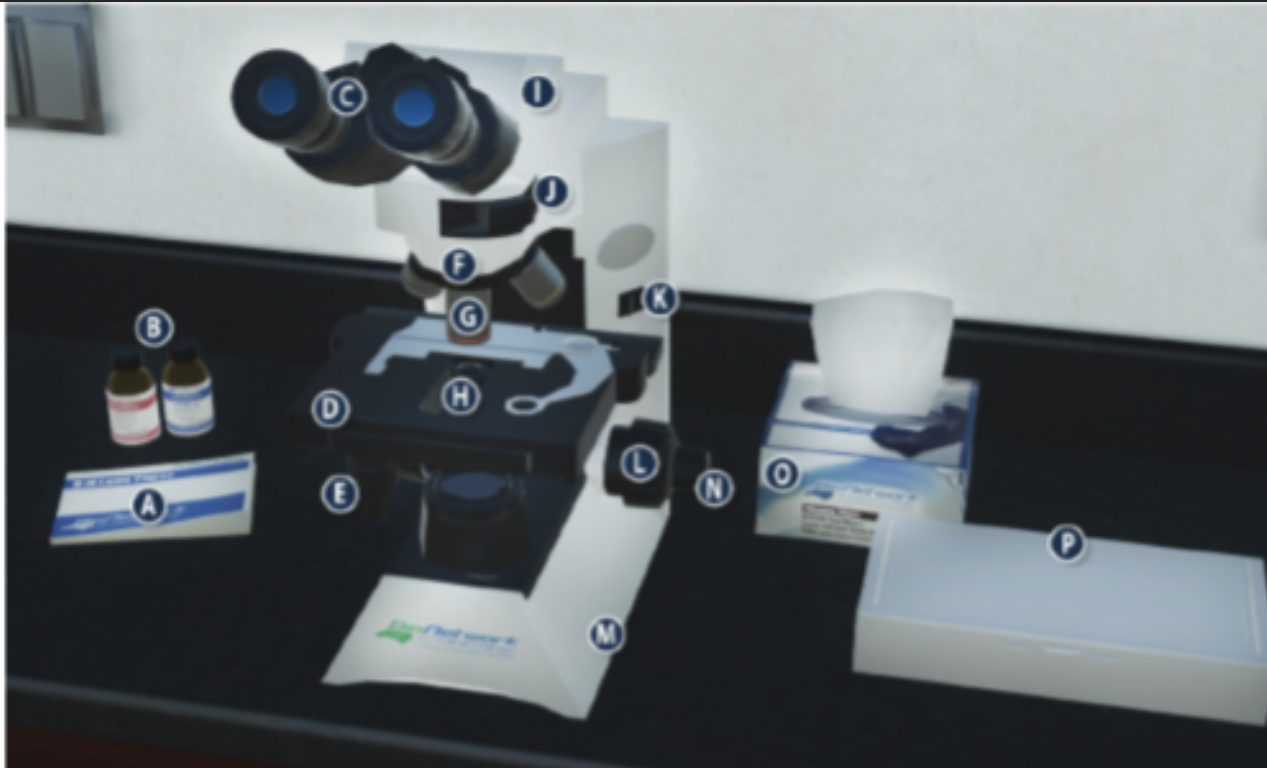
Stage (D)
Main flat space that holds the slide with the specemin
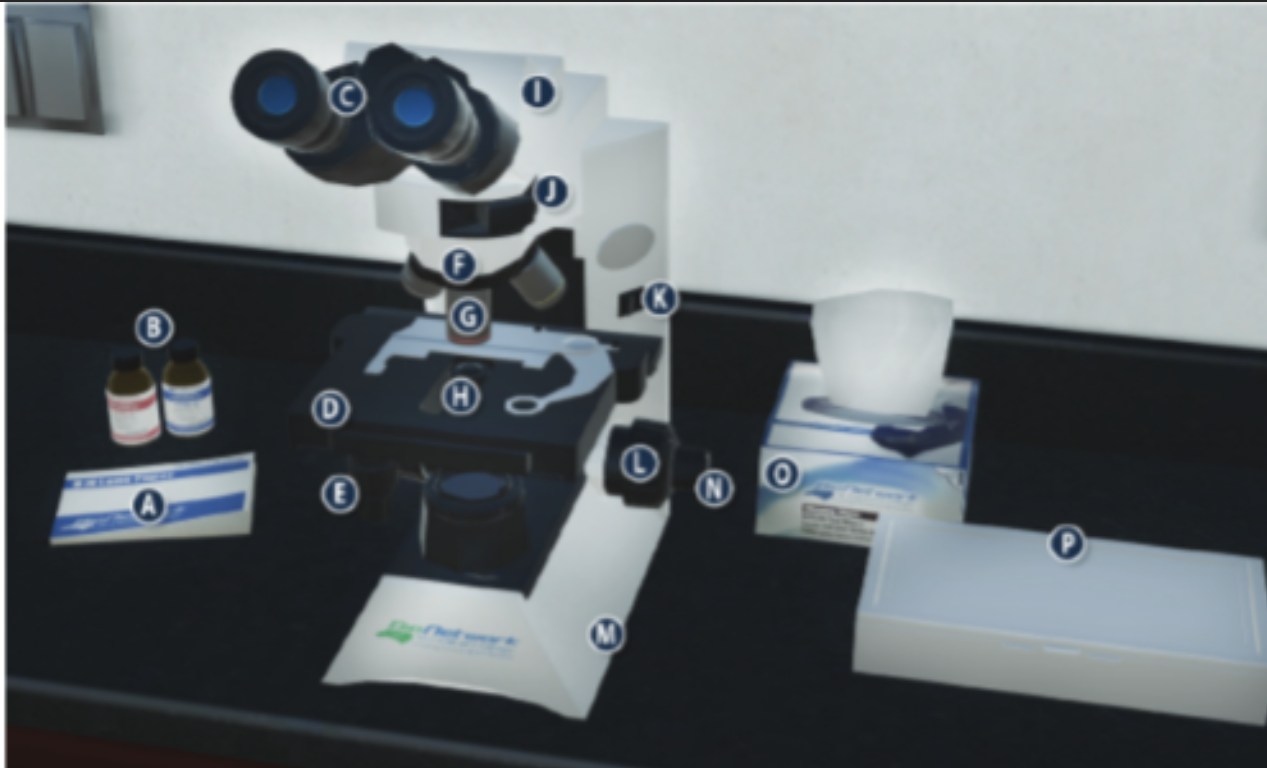
Diaphragm (H)
Most useful in high powers. is a five hole disk under the stage that works to adjust the amount of light passing through the stage. Each opening has a different diameter.
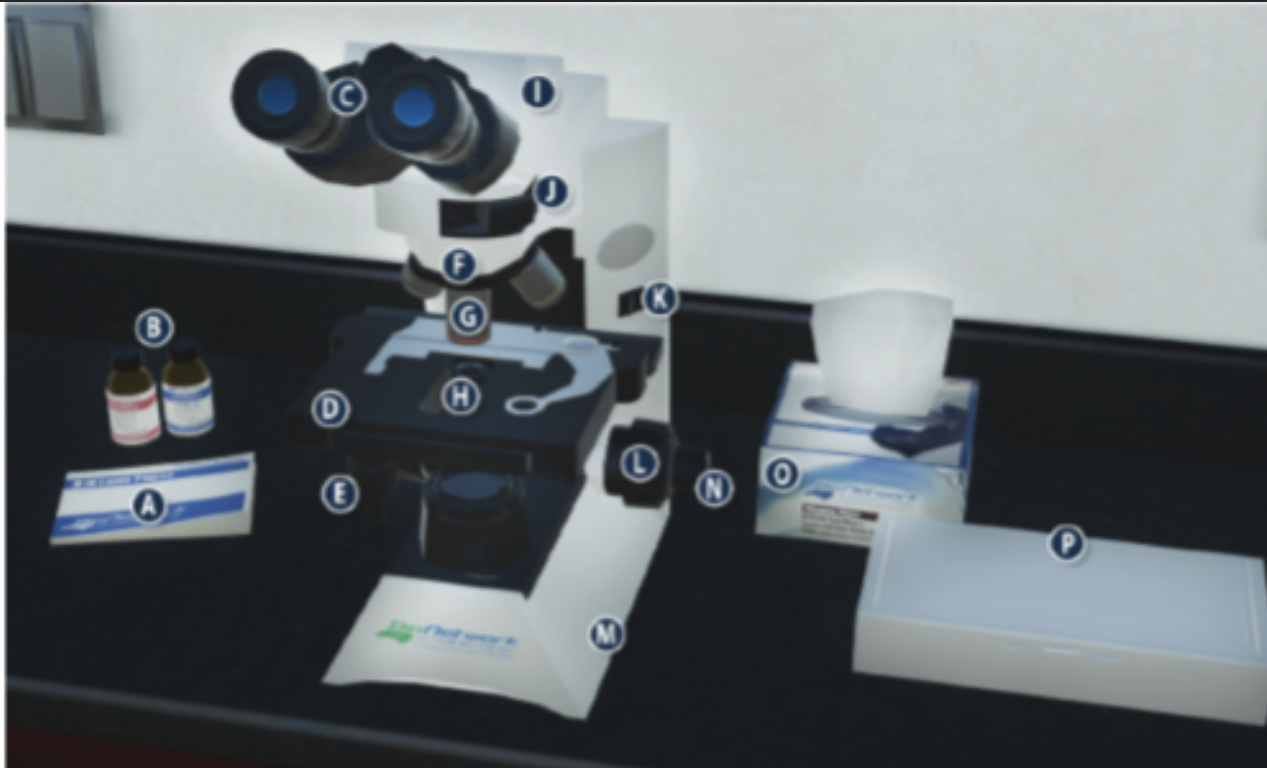
Stage adjustment knob (E)
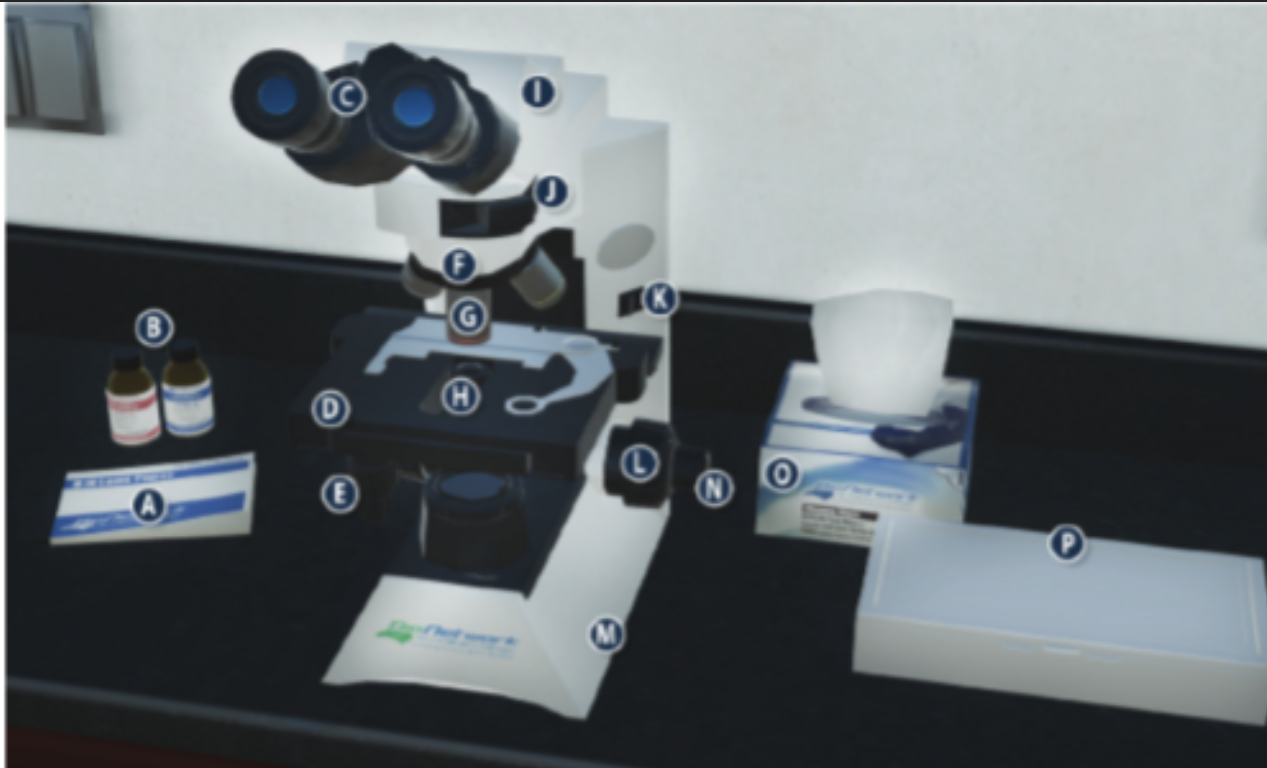
Base (m)
Bottom support
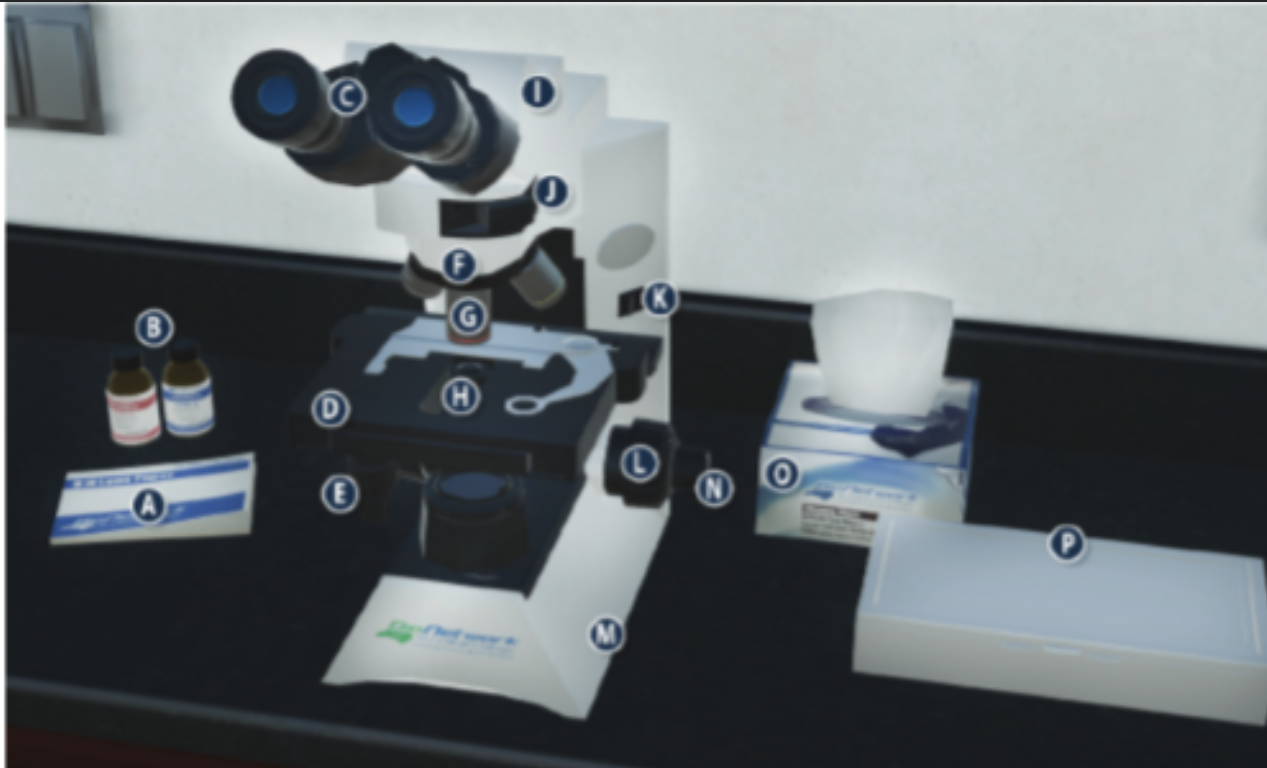
Coarse adjustment knob (L)
The larger of the two adjustment knobs. Moves the objective lens closer or farther from the specemin.
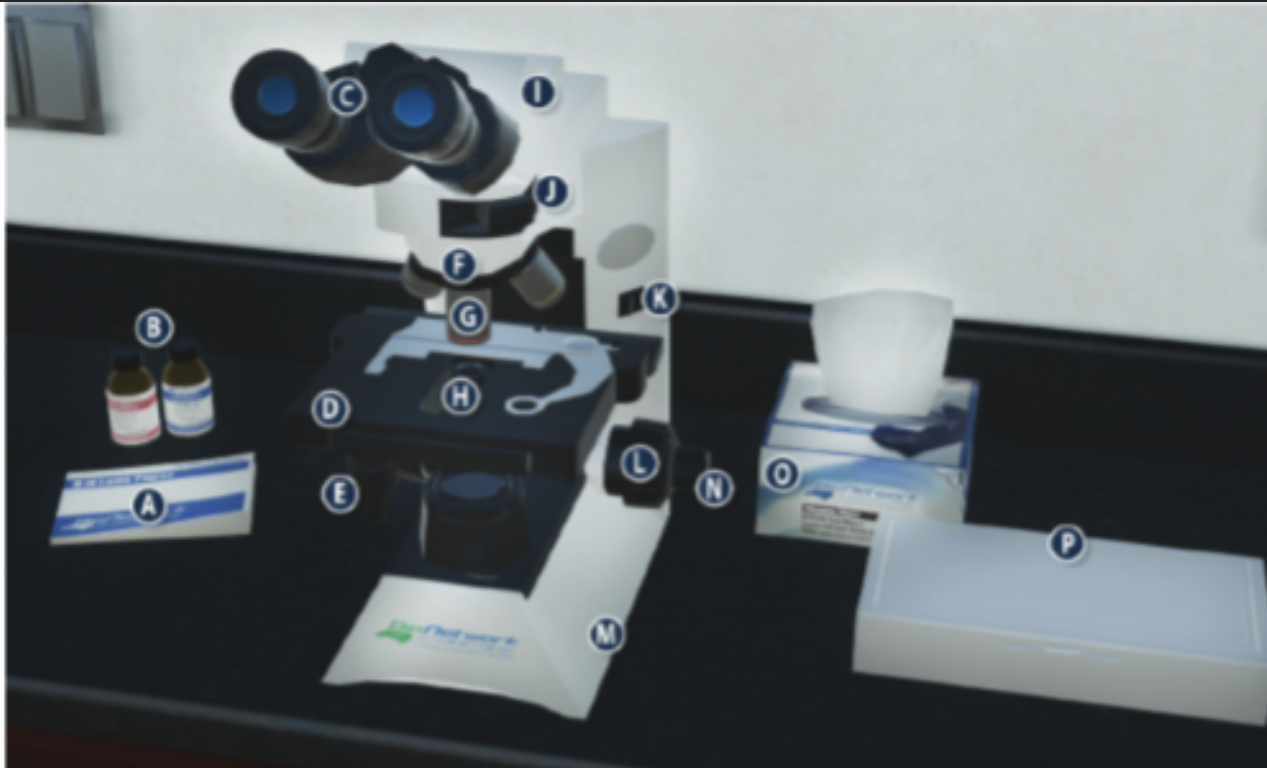
Lens paper (A)
Special paper for cleaning lenses and other glass materials
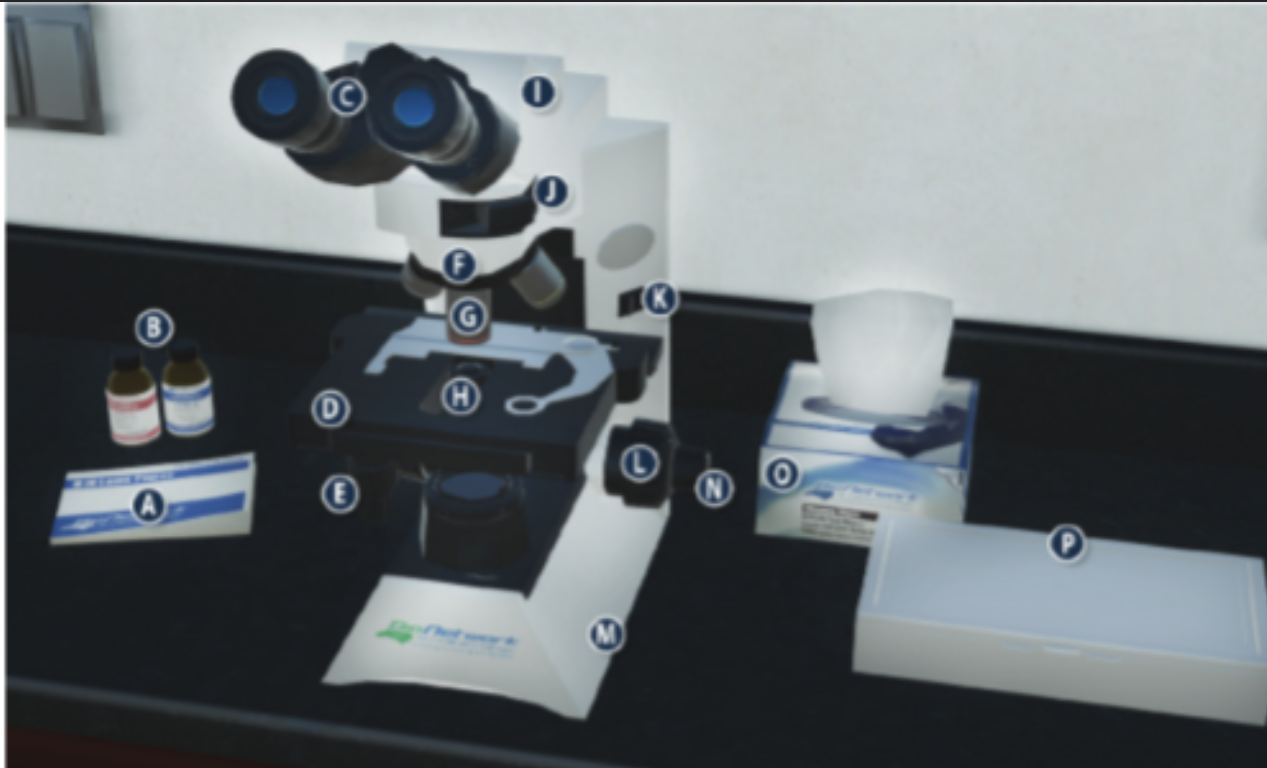
Fine adjustment knob (N)
The smaller of two adgustment knobs. uses very small steps to get objective lens closer or farther from specemen
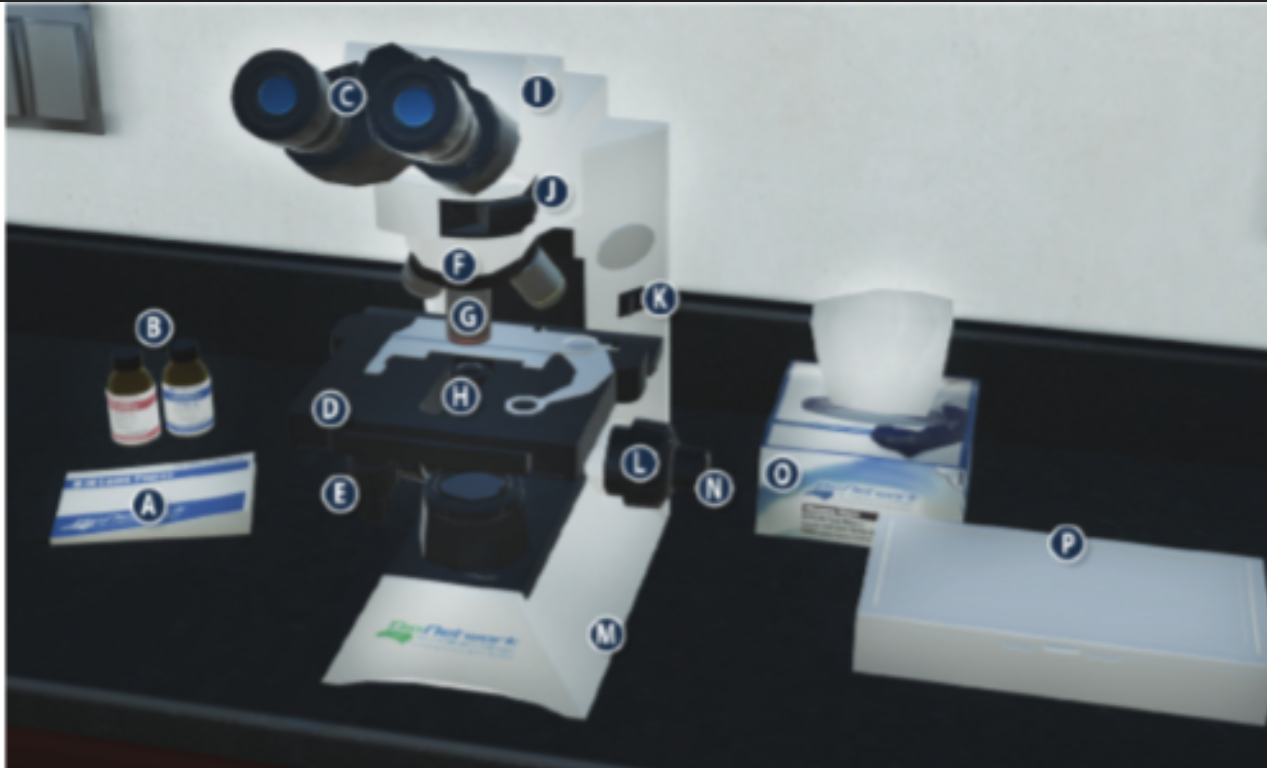
Immersion oil (B)
OIl is added to lens of high power (100x). INcreases resolution. Helps to focus light.
Slide/ slide box (P)
made of either plastic or glass. Is usd to hold the specemin
Kimwipes (O)
special paper/wipes for cleaning labratory equipment but not lens!
What is the proper way to carry a microscope?
With one hand hold the arm on the microscope and place the other and beneath the base on the microscope.
What is the typical magnification of an ocular lens? What other magnifications are possible?
The typical magnification of the ocular lens is 10x but can also be 5x, 15x or 20x
What are the magnification abilities of each of the objective lenses? What is the total magnification with each objective?
a) Scanning ( small lens ), red ring = Magnification ability: 4x
b) Low-power ( medium lens ), yellow ring = Magnification ability: 10x
c) High-power ( large lens ), blue ring =Magnification ability: 40x
d) Oil immersion ( largest lens ), white ring = Magnification ability: 100x
Why do you use immersion oil with 100X objective lens?
Immersion oil is used on high power lens to provided higher resolution and contrast to the specimen being viewed. This is because the immersion oil helps to refocus that light that is otherwise refracted without the oil.
Total magnification
Ocular lens x objective lens
What is a diaphragm? What does it do?
The diaphragm is a 5-hole disk under stage that can be moved to adjust the amount of light passing through the stage. It is able to do so because each “hole” has a different diameter
Describe the difference between the coarse focus and the fine focus
The coarse focus works for large and primary adjustments to the microscopes view. The fine focus allows for more precise and crisp focus of the specimen.
Explain how immersion oil helps when viewing a specimen on the slide using the 100X objective.
Immersion oil helps when viewing a specimen on the slide 100x because it helps to focus that light better to provide better resolution.
What is the relationship between field of view (FOV) of a microscope and total magnification of a lens. As total magnification increases, field of view of a microscope
Decreases
what serves to capture and focus light from the lamp below onto the slide mounted on the stage.
Condenser lenses
Why is it often advisable to use the coarse adjustment knob with the low power objective?
It is advisable because the coarse adjustment knob allows large adjustments that allow for specimen to be in focus faster. This also prevents the risk of the specimen getting too close and damaging the lens.
Describe what to do if more light is needed to view the specimen.
To adjust the light the diaphragm can be rotated to provide more light to directly hit the specimen.
What is magnification?
the degree to which something is or can be magnified
What is parfocal?
the ability of a microscope to stay relatively in focus as the user switches among the objectives
What is resolution power
In microscopy, resolution power (or resolving power) refers to the ability of a microscope to distinguish between two closely spaced objects as separate entities
What is the purpose of aseptic technique? When do we use it in this laboratory?
aseptic technique is used to transfer bacteria cultures to a fresh medium without any other contaminating microbes. This technique is used to ensure that microorganisms are not spread and are handled properly to obtain better results when examining bacteria cultures.
What is the function of flaming the mouths of tubes prior to and following inoculation.
Flaming the mouth is another measure to ensure that no contamination of unwanted microbes occurs. Flaming sterilizes the environment as the collection of bacteria occurs.
What is the objective of streaking microbial cultures over a broad agar surface
The purpose is to isolate individual colonies of bacteria from mixed colonies for examination.
Why are Petri plates normally incubated bottom-side up after streak isolation?
Petri dishes are incubated bottom side up showing agar side because as petri dishes are incubating, condensation forms. Having the petri dish bottom up prevents the condensation from getting on and contaminating the bacteria colony being examined.
Describe the procedures that are part of aseptic technique
The procedures that are part of aseptic technique vary on the type of transfer but most include some similar steps. Sterilizing the inoculating loop or needle using Bunsen burner. Sterilizing any tubes with liquid or bacteria culture before and after inoculation by flaming the mouth of the tube. Lastly after collecting bacteria and placing into desired tube, liquid or agar plate, sterilize inoculation loop or needle by burning it.
is it true that You will add a new loopful of bacteria when streaking each area or quadrant.
False
In streak isolation technique, quadrant 1 shows heavy confluent growth. Quadrant 4 shows discrete colonies. What happened with the numbers of bacteria between the two quadrants?
The numbers of bacteria between the two quadrants decreased. This is due to the fact that after each quadrant the inoculation loop gets sterilized and only one swipe of the zig-zag on the quadrant will cross the quadrant before. This thus makes the first quadrant the most dense and the rest start to decrease from there.
What are the gram stain procedures?
1) Primary stain is added (usually Crysal violet or another dye). This will initially die everything one color (in this case purple)
2) Mordant is added next. In this lab the mordant was grams iodine. This substance will fix the dye to the cell wall and make it permeant.
3) Decolorizer is added. In this experiment the decolorizer was alcohol. This will wash off any access dye and gram negative cells are decolorized.
4) Counterstain is the last addition. This is a reagent like safranin that will stain gram negative bacteria pink
What is the basis for identifying gram postitive and gram negative bacteria?
Gram positive: Stains purple because it has a think peptidoglycan layer that binds to the violet stain.
Gram negative: Stains pink because it has a very thin peptidoglycan layer that does not securly bind to the purple stain.
What is the base for gram stain (related to the structure of cell wall of bacteria)
The Gram stain is based on the chemical and physical properties of bacterial cell walls, specifically the differences in their peptidoglycan and lipopolysaccharide content
What would happened to a cell if you unintentionally grabbed the wrong bottle of reagent and decolorize your cells with water rather than the acetone/alcohol solution?
If you decolorize your cell with water instead of alcohol it will cause the osmotic gradient to change. The outcome is a hypotonic solution. Here the water will enter the cell causing it to swell and eventually burst.
Give explanation as to why gram stain works best on bacterial cells that are young or less than 24 hours old.
Younger cells are better because older cells tend to have more damage. There is a risk that the older cells may have a damaged cell wall and thus leading to false and inaccurate information.
Explain why old cultures of gram-positive cells can stain pink rather than purple.
older cells may have degraded cell walls. In gram positive bacteria it can cause them to have characteristics of gram negative bacteria. In this case having. Thin layer of peptidoglycan.
When you do gram stain on human cells, what do the results look like? Think about the different steps in the staining procedure and what they are staining.
The gram stain technique is not used on human cells because they lack the peptidoglycan cell wall that helps differentiate bacterial cells. The dyes that are used in gram stain only react to the peptidoglycan cell wall therefore no staining would be evident if the gram stain technique was used on human cells
Is it true that In Gram positive cells when the peptidoglycan is dehydrated by the decolorize the peptidoglycan ‘shrinks’ and condenses into a thick layer trapping the primary stain and mordant
True
Is it true that If safranin is not applied at the end of a gram stain, all the gram-negative cells will look colorless
True
What is McConkey Agar used for?
MacConkey agar is a differential medium used to identify bacteria based on their ability to ferment lactose
How do lactose fermenting bacteria look on McConkey Agar?
When lactose-fermenting bacteria (like E. coli and Klebsiella spp) is present it causes the neutral red indicator to turn pink or red
How do non-lactose fermenting bacteria look on McConkey Agar?
Conversely, bacteria that cannot ferment lactose, such as Salmonella, Shigella, Proteus, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, colonies will remain colorless or appear as a pale pink
What type of media is MacConkey agar?
MacConkey agar is a selective and differential culture medium. It's designed to selectively grow gram-negative bacteria and differentiate them based on their ability to ferment lactose
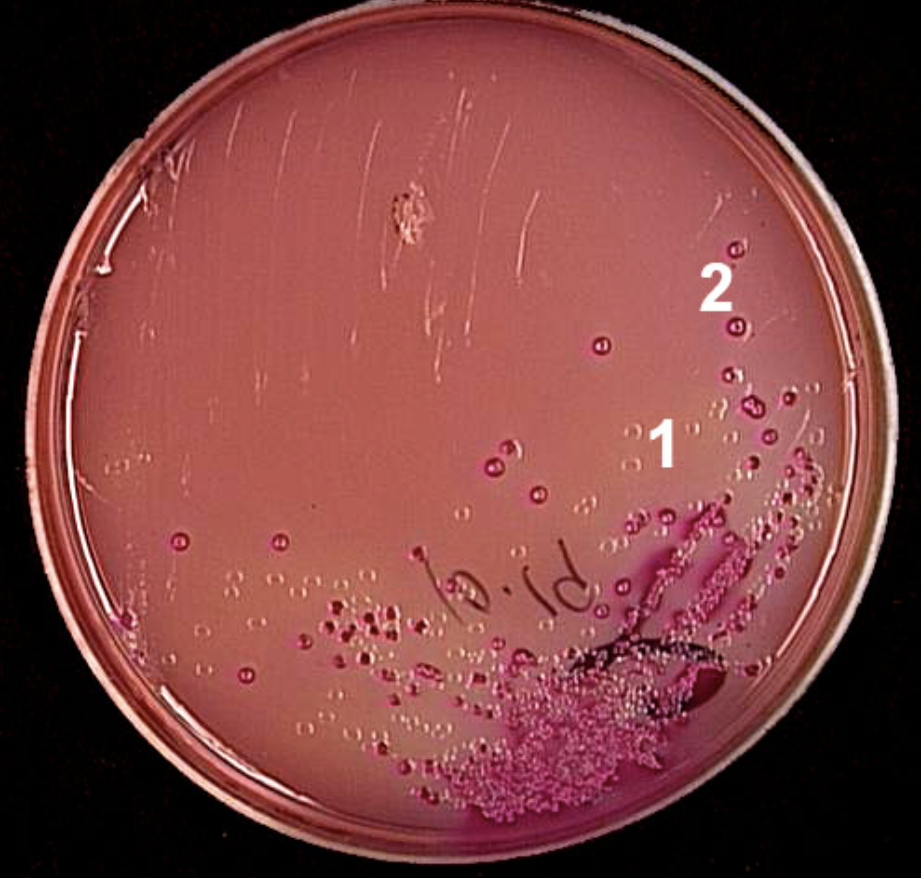
What are the colonies in section 2 showing?
Lactose fermentation
In the virtual lab (although not in real life), which bacterium utilizes citrate for growth?
Klebsiella pneumoniae
Which test is used to distinguish between staphylococci and streptococci?
Catalase
Why is the Catalase test used to differentiate staphylococci and streptococci?
Staphylococci are catalase-positive, meaning they produce the enzyme catalase, which breaks down hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen, producing bubbles.
Streptococci, on the other hand, are catalase-negative and do not produce these bubbles when exposed to hydrogen peroxide
What does a negative catalase test look like?
When hydrogen peroxide is added to bacteria on a clean slide, no bubbles appear.
Which procedure always followed performing a streak plate in this virtual lab?
Gram stain
According to the lab, which objective lens is used for examining the Gram stains of the bacteria?
100x, oil immersion
what is alpha hemolysis on blood agar?
is a type of incomplete lysis of red blood cells, resulting in a greenish or brownish discoloration of the agar surrounding the bacterial colony
what is gamma hemolysis
Gamma hemolysis is characterized by the absence of any change or lysis of red blood cells around the bacterial colony
What causes beta hemolysis in blood agar?
complete lysis of the red blood cells
Which normal skin inhabitant is gamma hemolytic on blood agar?
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Which of these pairs of tests is used to help identify Group A streptococci or Streptococcus pyogenes?
PYR and CAMP
What is the purpose of a PYR test?
The PYR test is a rapid colorimetric method used to identify Streptococcus pyogenes (group A).
What is the purpose of a CAMP test?
The CAMP test is primarily used to identify Streptococcus agalactiae (group B). It also helps differentiate it from other Streptococci.
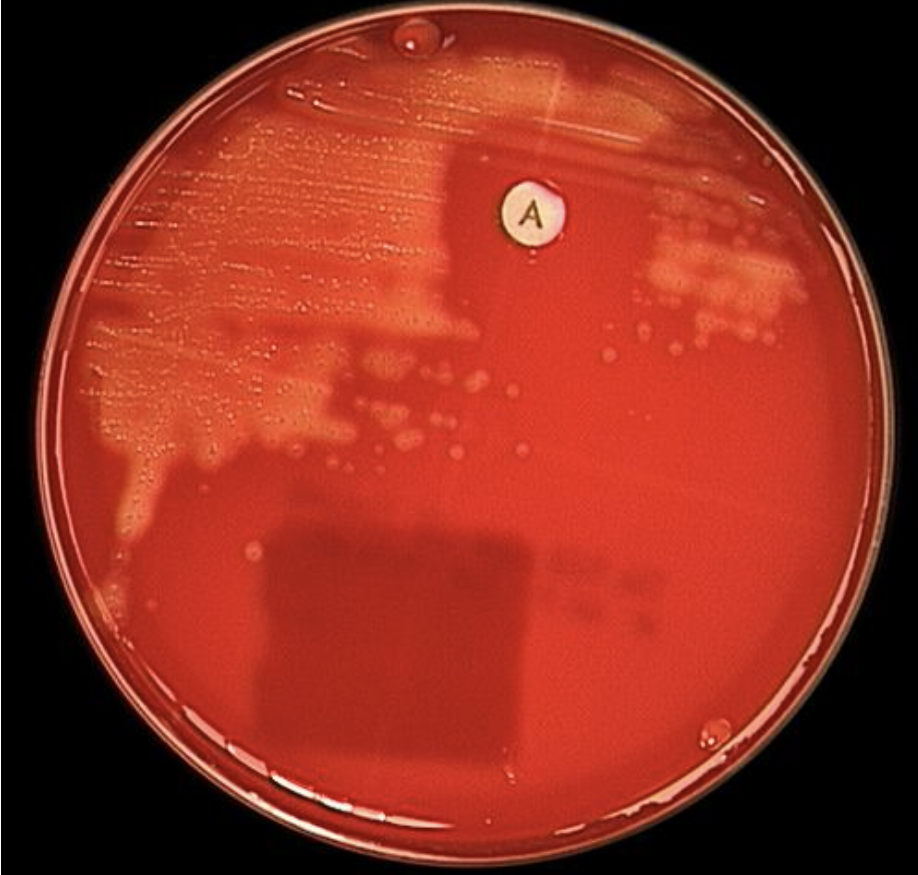
What does the photo show?
There is a zone of inhibition around a disk containing antibiotic, such as bacitracin.
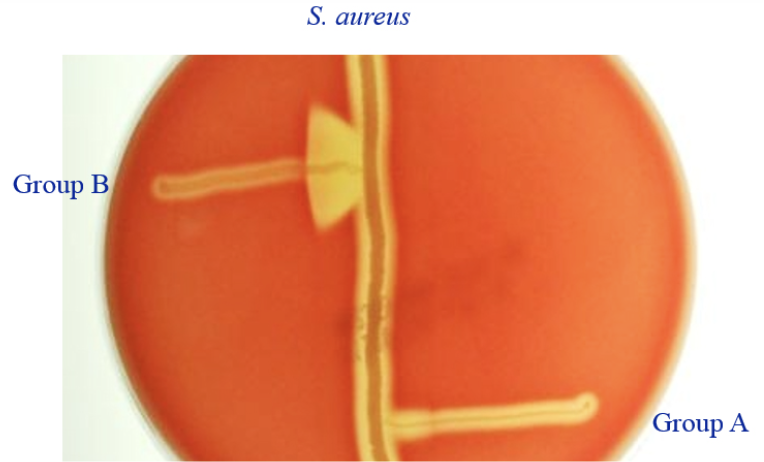
The photo shows an example of what kind of test?
CAMP
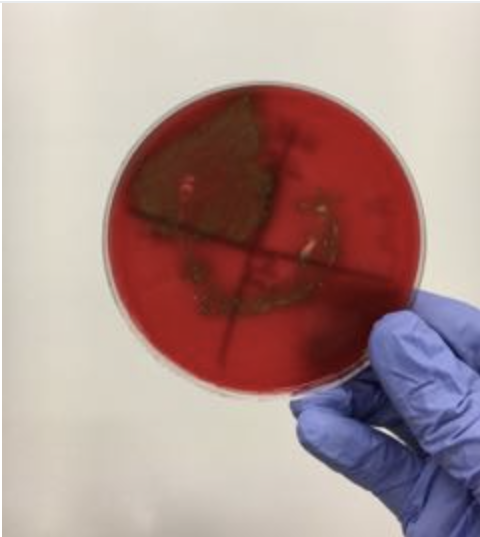
If you got this result on blood agar and a positive optichin test result, then according to the virtual lab you have identified the bacteria as
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Which two tests distinguish viridans strep from the other streptococci.
alpha hemolysis and a negative optichin test
what is an optichin test
The optochin test is a diagnostic method used in microbiology to differentiate between Streptococcus pneumoniae and other alpha-hemolytic streptococci
What does the Phadebact or coagglutination test detect?
The antibody reagent reacts with Group A antigens if they are present on the bacteria and causes them to clump.
Which one of these groups was not covered in this lab?
Gram-positive cocci
Which pair of Gram stain reagents form a complex that is not easily removed?
crystal violet and iodine
What is differential media?
Media containing indicators that cause bacteria to appear differently on culture media.
what bacteria can be eliminated as a possibility if a Gram stain shows purple cocci when viewed with immersion oil (1,000x magnification)?
Klebsiella pneumoniae
which bacteria usually show diplococci arrangement? (meaninnf dividing into one plane/ staight line)
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Which reagent is added after iodine in the Gram stain?
95% alcohol
Which one of the following tests yields a pink color as shown above when it is positive?
PYR
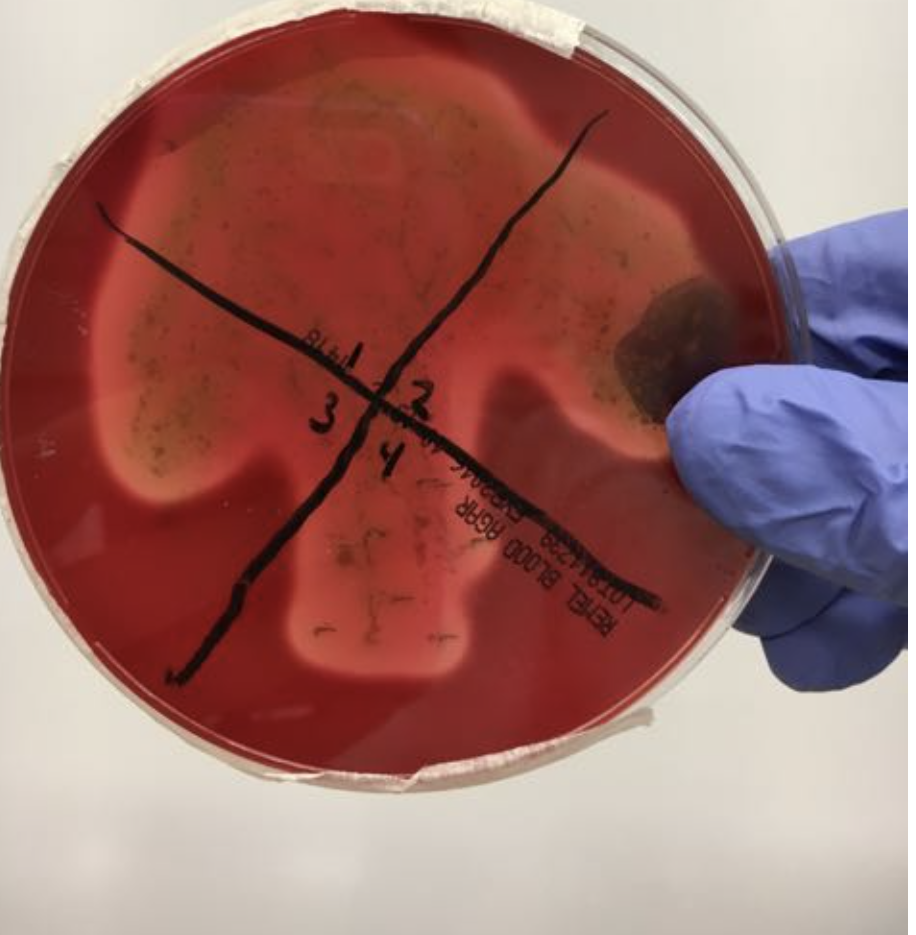
If you got these results in the blood agar test what do you do next?
PYR, Phadebact, and Bacitracin
If a streak plate of a patient's throat secretions on blood agar yielded colony growth, but the agar around the colonies remained red, which type of hemolysis resulted?
gamma (no hemolysis)
What is 16S rDNA?
The gene that codes for 16S rRNA, which is a component of bacterial ribosomes
is it true that All ribosomes (both eukaryotic and prokaryotic) are made of proteins and RNA.
True
what are some facts about identifying pathogens using traditional methods?
1) some pathogens grow only in liquid culture
2) closely related strains of pathogens are hard to differentiate
3) DNA techniques are used to distinguish different strains of a pathogen.
In PCR, Why do you put your sample into a water bath after digesting the cell wall?
This is done to denature and inactivate the enzymes that found in the current sample so that other enzymes can be introduced
you amplify or increase the amount of DNA using universal primers that bind to any bacterial 16SrRNA sequence – so why are you using 16srRNA to identify your organism?
This sequence is used because it is what contains the section of a bacteria that is able to be amplified by the PCR process. This amplification thus allows for the identification of the specific organism
After 30 cycles of PCR, how many copies of DNA are produced?
1 million copies are produced
The final collection tube after PCR will have what?
many pieces of 1,500 bp-long 16S rDNA, and with a very small amount of longer DNA strands
Outline the basic DNA extraction procedure
Collect cheek cells by swabbing
Burst the collected cells to release DNA
Separate the DNA from proteins and debris
Isolate the concentrated DNA
What is DNA extraction used for?
Can be used for a variety of tests including genetic testing, body identification and analyzing forensic evidence to solve crime scenes.
Which substance is used to break down the phospholipids from the cell membrane and nuclear membrane?
The first solution added, a lysis solution is what will breakdown phospholipids. It contains two components. For the destruction of phospholipids specifically the detergent portion does so by disrupting the cell membrane and thus releasing the cells DNA
What substance is used to separate the proteins from the DNA
After the lysis solution is added a salt solution is added to the sample of DNA that had been released. The lysis solution breaks apart the proteins that are intertwined in the DNA and the salt solution clumps up the broken apart proteins and debris together and separates them from the DNA
what is the The substance that is used to cause precipitation of DNA
The last step of the extraction is to isolate/precipitate DNA. This is done thanks to isopropyl alcohol that is added to the solution. Since DNA does not mix with the alcohol, it will clump up together and be visible.
what is the function of Agarose in gel electrophoresis?
This is the medium that provides the structure where DNA samples will be inserted and will also maneuver though this gel to be analyzed.
Wat is the function of Electrophoresis buffer (1XTAE)?
This is the component that allows electricity to flow through the Agarose gel and separate the DNA based on size.
What would happen if you added water instead of the 1X TAE buffer and ran the gel with the water?
If water is used instead of 1X TAE buffer in gel electrophoresis, the DNA samples will not migrate properly through the gel
The electrophoresis gel box generates an electrical field with positive and negative poles at the ends of the gel. Do DNA particles travel toward the positively or negatively charged electrodes? Explain why
It is important of understand that the backbone of DNA, phosphate, is negatively charged. Therefore, DNA will move to the positive pole because opposites attract.
What size fragments (large or small) would you expect to move through the agarose gel matrix most quickly? Explain why
DNA moves through the agarose gel in a snaking movement. Therefore, smaller fragments are expected to move faster because they have less trouble moving through the gel then larger fragments.
Why would different restriction enzymes generate different DNA fragments if they are all cutting the same DNA molecules?
Restriction enzymes cut DNA based on specific restriction sites on the DNA. Each restriction enzyme has different restriction sites therefore each one cuts at different sited of the same DNA.
What is a marker or ladder in gel electrophoresis?
a marker or ladder is a set of DNA fragments with known sizes used as a reference to determine the size of unknown DNA fragments in a sample
Why is a ladder or a marker considered a standard in this lab?
This is a standard practice because it allows researchers to accurately estimate the length of DNA fragments in their experimental samples by comparing them to the known sizes in the ladder
How can you tell that the restriction enzyme digestion has occurred in gel electrophoresis?
successful restriction enzyme digestion is indicated by the presence of multiple DNA fragments of distinct sizes, rather than a single band of the original undigested DNA