Intro to Microbes and Infectious Diseases; Bacterial Things
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
Microbe
something that requires a microscope to be seen
can’t see with the naked eye
EX: Influenza virus (Flu), Bacteria
Classes of Microbes
Eukaryotes (protists, Fungi)
Bacteria
Archaea
Virus (not alive, needs a host cell compared to the others)
Prion
collection of misfolded protein
considered as a class of microbe kind of
Microbes in Human Lives: Positive Effects
gut health
builds immune system
Fermentation
Vaccines/Medication
Microbes in Human Lives: Negative Effects
certain ones make you sick
Food spoilage
Roles of Microbial Organisms
Health
infectious disease/but also protection, digestion; food spoilage/but also food protection
Roles of Microbial Organisms
Biotechnology (Bioengineering)
production of drugs, hormones, etc
Roles of Microbial Organisms
Bioremediation
detoxification
Roles of Microbial Organisms
Environment
energy capture (photosynthesis)
geochemical cycling (EX: Nitrogen fixation)
Roles of Microbes in Biosphere
bacteria that lives on plants/photosynthesis)
can find microbes in ecosystem (inside and out of animals/plants etc…)
microorganisms play an essential role in cycling of nutrients (nitrogen fixation, bacteria in soil helps nitrogen cycle through)
Microbes in Human Evolution
fossil evidence of prokaryotic cells existing over 3 billion years ago
Endosymbiosis - early prokaryotes contributed directly to the evolution of eukaryotes
Symbiotic prokaryotic cells are the original source of chloroplasts and mitochondria (they have DNA & double membranes)
Microbes are extremely diverse in habitat, form, and function
Types of Symbiotic Relationships
Mutualism
both species benefit
Type of Symbiotic Relationship
Parasitism
one species benefits and the other is harmed
Type of Symbiotic Relationship
Commensalism
one species benefits, the other is not harmed (neutral)
History of Infectious Disease
Florence Nightingale - founder of modern nursing, found significance of infection using a quantitative approach (EX: Mortality due to infection)
helped lead to epidemiology (the study of disease in populations)
historical observations indicated that disease can be transmitted from person to person
microbes relationship to disease wasn’t established until the mid-1800s
“Germ” Theory
Koch establishes Bacillus anthracis (bacteria) as the cause of anthrax
Anthrax - disease found in livestock which can be transmitted to humans
Koch’s Postulates definition
are used to determine if a particular microbe is the causative agent of disease
Koch’s Postulates: 1
the microbe is found in all cases of the disease but is absent from healthy individuals
Koch’s Postulates: 2
microbe is isolated from diseased host and grown in culture
Koch’s Postulates: 3
when the microbe is introduced into a healthy, susceptible host; the same disease occurs
Koch’s Postulates: 4
the same strain of microbe is obtained from the newly diseased host
Pathogen
can survive in or out of a cell
2 classes of pathogens
Primary Pathogen
cause of disease in an otherwise healthy host (EX: Influenza (flu))
Opportunistic Pathogen
not typically associated with disease
ability to cause disease depends on host resistance (typically immune function)
Virulence
severity of disease associated with infection by pathogen
LD50
the amount of pathogen required to cause death of half the animals
Types of Growth of Pathogens
Invasion
growth inside of host cells
Types of Growth of Pathogens
Invasiveness
ability to spread in tissue
Types of Growth of Pathogens
Host Range
the species that a particular pathogen can infect
General Mechanisms of Pathogenesis
Adherence
the ability of a pathogen to stick to a host
they must attach to their host, usually using specific receptors that determine the initial site of infection
General Mechanisms of Pathogenesis
Avoidance
avoid defenses or rapid immune responses will eliminate them before they can replicate
General Mechanisms of Pathogenesis
Growth
gain nutrients from host to grow
Disease Stages
Incubation
the subject gets exposed to the pathogen; microbe gets used to new surroundings within the host
Disease stages
Prodromal
start to see initial symptom; the person my feel a little sick or off
Disease Stages
illness
number of microbes is higher than immune response; peak sickness
Disease Stages
Decline
higher immune response against microbe; feeling a lot better
Disease Stages
Convalescent
still some microbial presence and can spread the illness but may be asymptomatic
Disease Stages
Long term
body has built immunity to microbe but can still track the microbe if it were to come back; it’ll be ready to “fight” it
Signs
are directly measurable or observable
Ex: Rash, Fever
Symptoms
are difficult to pinpoint in a sense of measuring
felt my the patient
Ex: Headache, muscle-pain, nausea
Descriptions of Infection
Focal
one spot; pinpoint location of infection
Ex: boil
Descriptions of Infection
Systemic
the infection is widespread throughout the body
Descriptions of Infection
Mixed Infection
various microbes involved or present
Descriptions of Infection
Primary/Secondary Infection
one infection comes first then a second infection is caused by the first one; different infections
Descriptions of Infection
Acute infection
very rapid onset of symptoms
Descriptions of Infection
Chronic Infection
symptoms develop slowly and resolve slowly as well
Descriptions of Infection
Nosocomial infection
infections acquired in a hospital
Descriptions of Infection
Iatrogenic infection
infections transmitted by a healthcare worker to a patient
Vector
a living organism that can transmit infectious pathogens between humans, animals, plants, etc…
Ex: a mosquito
Reservoir
organisms that harbor a pathogen and can be transmitted indirectly and directly through contact
Transmissions
Indirect
microbes can be transmitted indirectly by inanimate objects
by vehicle transmission
by insect vector
Transmission
Direct
microbes can be transmitted by direct contact or by aerosolization (sneeze, cough)(droplets)
Transmission
Vertical
transmission of infectious agent from parent to offspring
Transmission
Vehicle
microbes get transferred through fomites(inanimate objects) , food, water, or air
Zoonotic pathogens
can grow within animals, insects, and humans and they can act as reservoirs if the pathogen can grow
Yellow fever
caused by a virus (microbe)
Zika
caused by a bite from a mosquito (mostly)
acute, viral, systemic infection
Endemic disease
present at a relatively constant level
Epidemic disease
indicates a large increase above the baseline level in an area
Pandemic disease
a worldwide epidemic
Portals of Entry
the eye
oral (mouth)
Genital or Sexual transmission
respiratory
through skin (wounds)
Parenteral = pathogens injected into bloodstream by insect
Host Factors
Level of Immunocompetence = influenced by age, genetics, behaviors (alcohol consumption)
Exposure to pathogens = based on behaviors or occupations (healthcare, agricultural, recreation)
Microbial Structures of Biomacromolecules
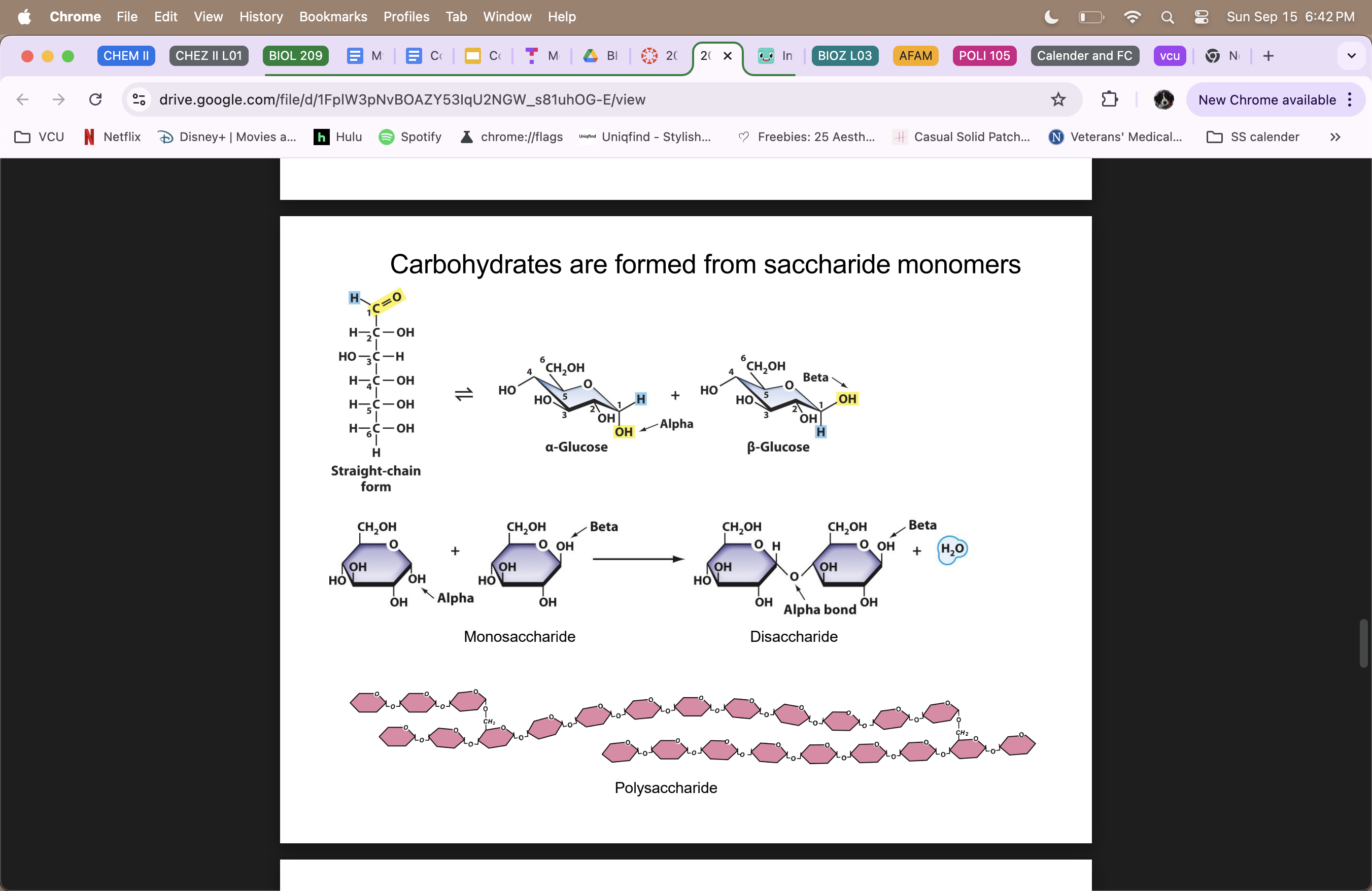
Carbohydrates
true polymer
formed from saccharide monomers
polysaccharides provide important structual and enegry storage molecules (cellulose = structural; starch = energy storage) and can also be attached to certain lipids and proteins
recognize hydroxyl groups (OH)
Microbial Structures of Biomacromolecules
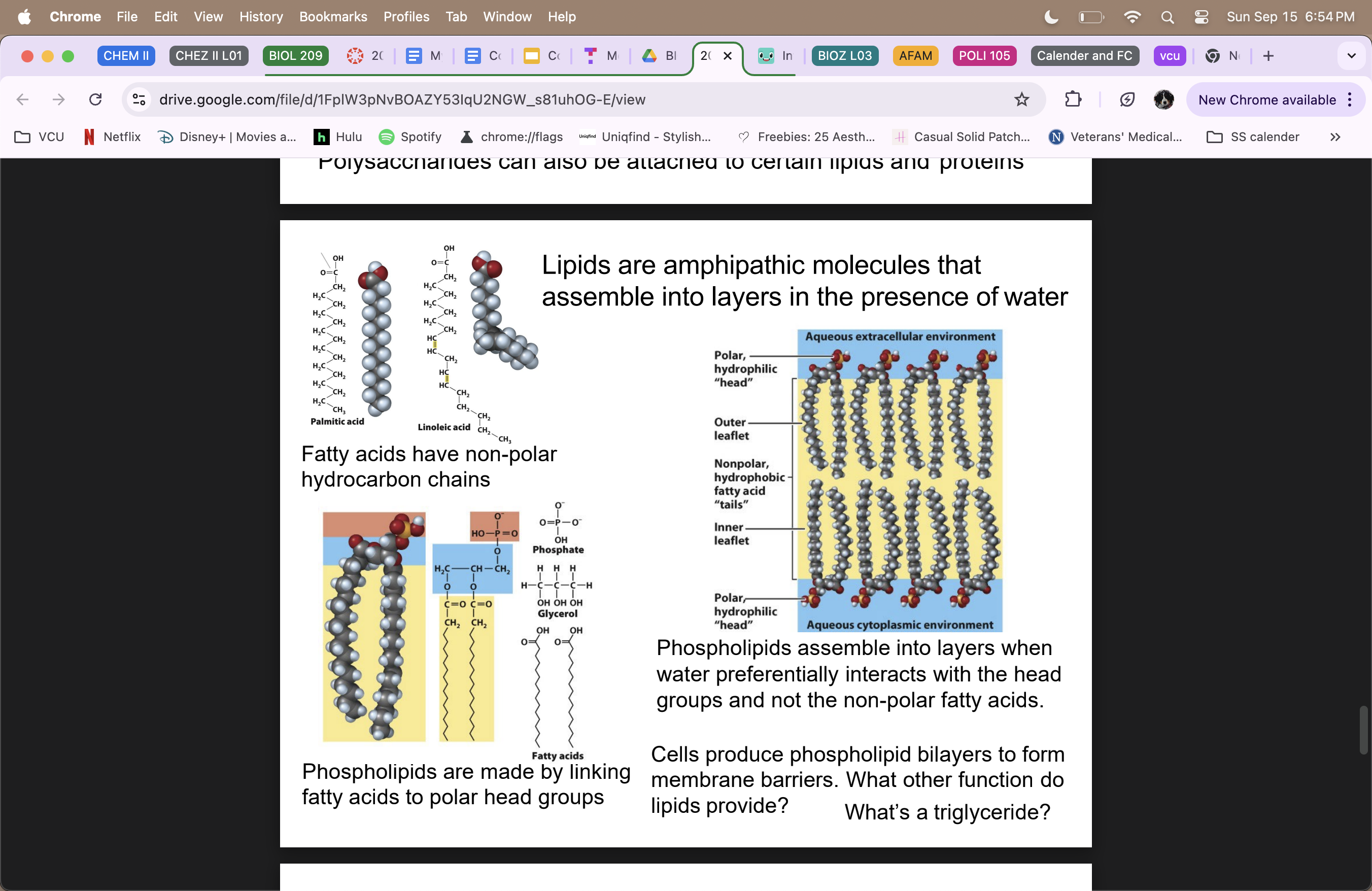
Lipids
are amphipathic (hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties) molecules that assemble into layers in the presence of water
not true polymers
fatty acids have non-polar hydrocarbon chains
phospholipids link fatty acids to polar head groups (phosphate head= hydrophilic; tails=hydrophobic)
Phospholipid bilayer (cells produce them to form membrane barriers)
triglyceride = 3 fatty acid chains connected to glycerol
Microbial Structures of Biomacromolecules
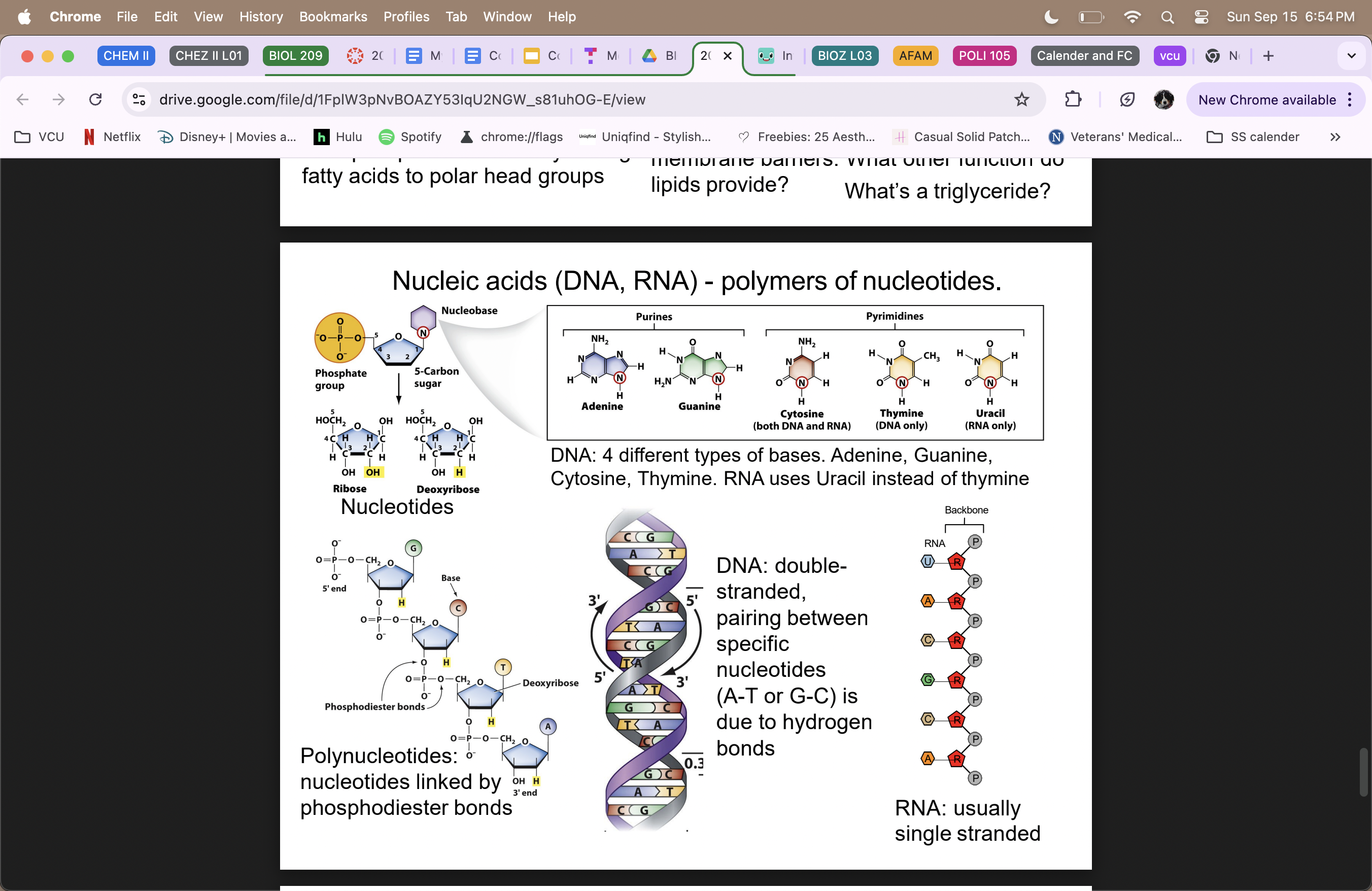
Nucleic Acids
DNA = double-stranded, information library (5’ end = phosphate group; 3’ end = hydroxyl group)
RNA = usually single stranded
true polymers
Adenine and Guanine (purines)
Cytosine, Thymine, uracil=used in RNA instead of T (pyrimidines)
phospate group, 5-carbon sugar, and Nucleobase (ATGC)
DNA to RNA (transcription)
RNA to proteins (translation)
Microbial Structures of Biomacromolecules
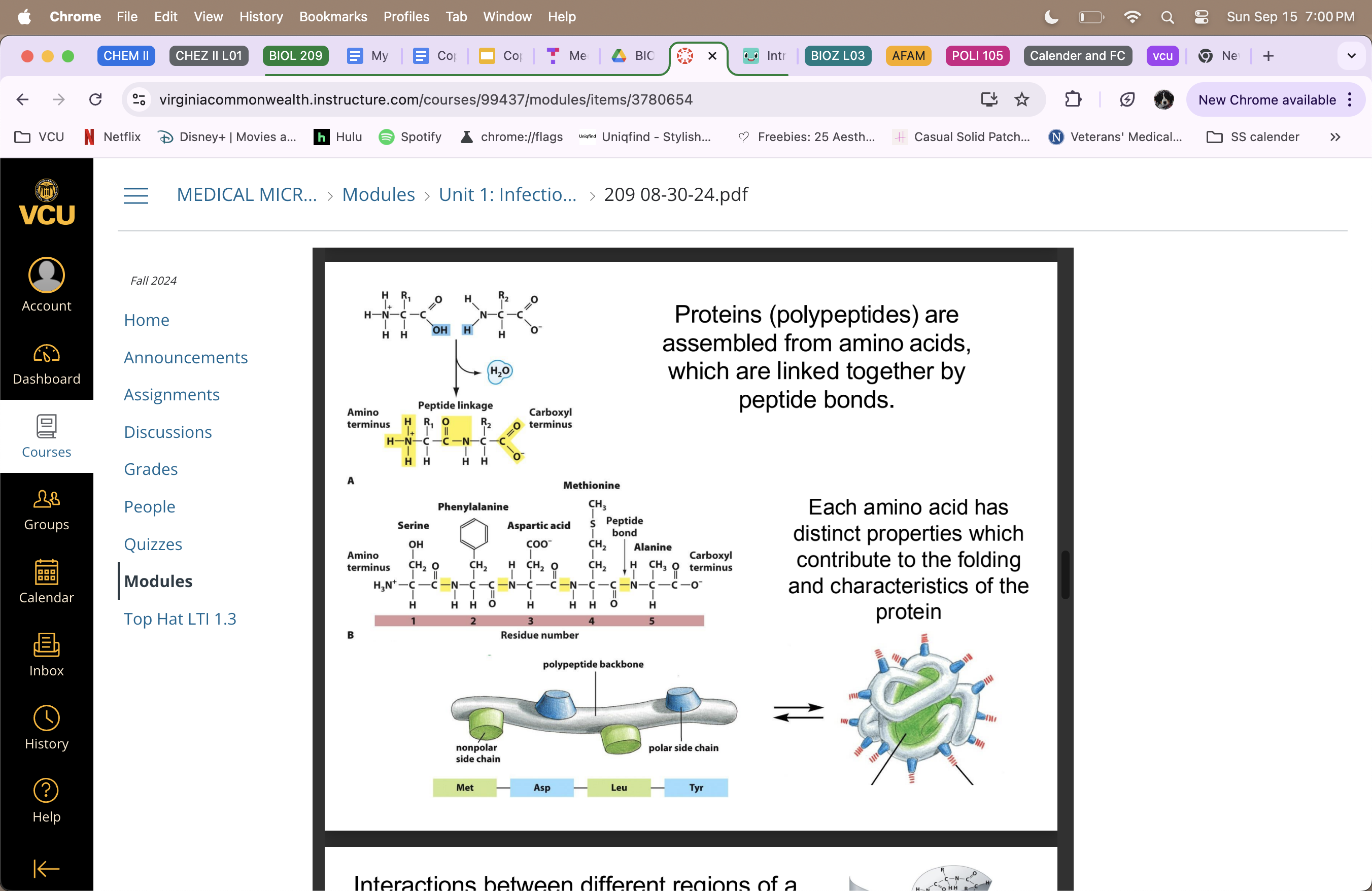
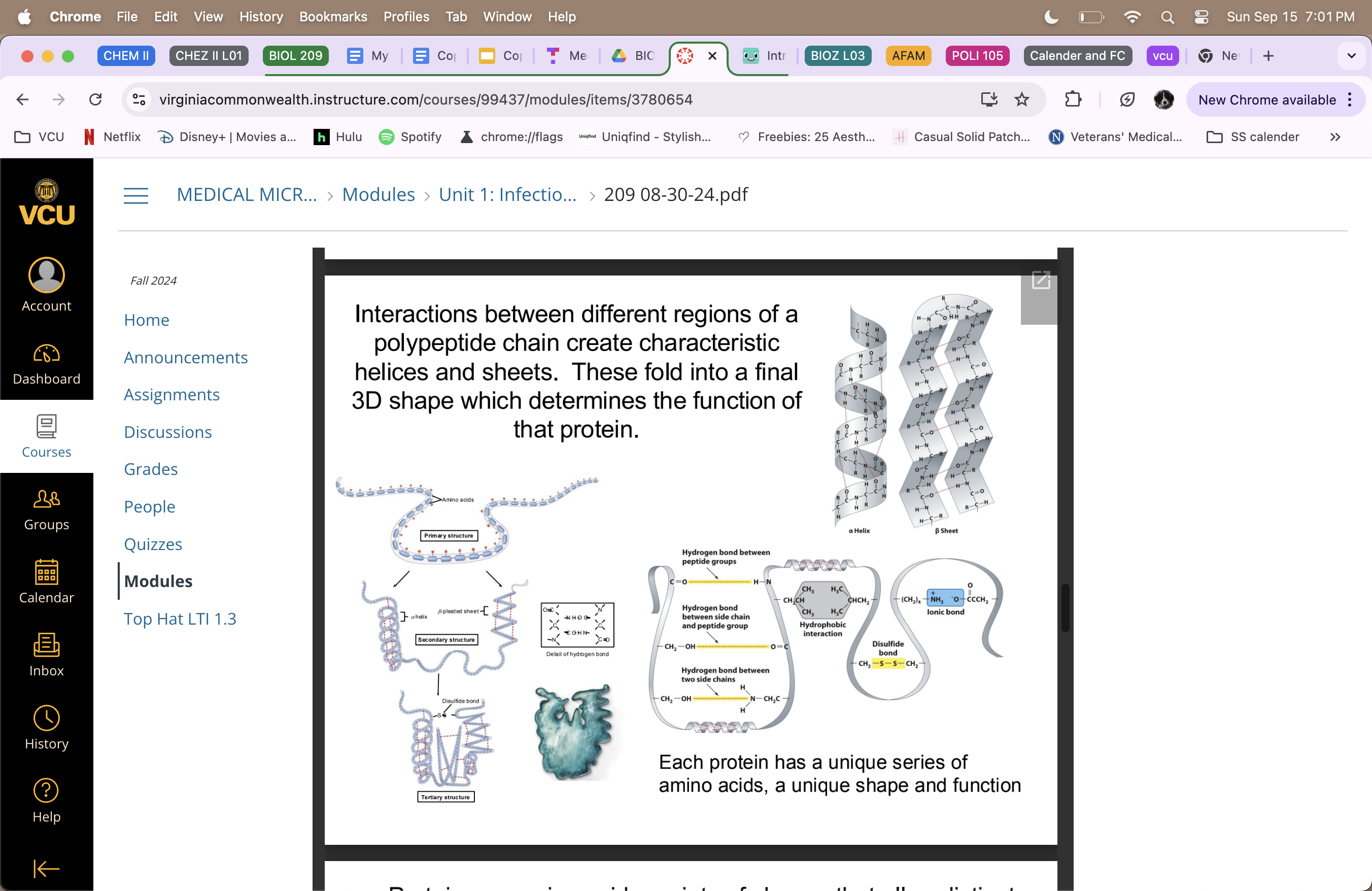
Proteins
(polypeptides) are assembled from amino acids, linked by peptide bonds
true polymers
enzymes
come in a variety of shapes that allow distinct functions
amino terminus and carboxyl terminus
primary structure = amino acids
secondary structure = alpha helices and beta-pleated sheets linked together by hydrogen bonds on there perspective sides
tertiary structure = helices and sheets come together and are bound by disulfide bonds
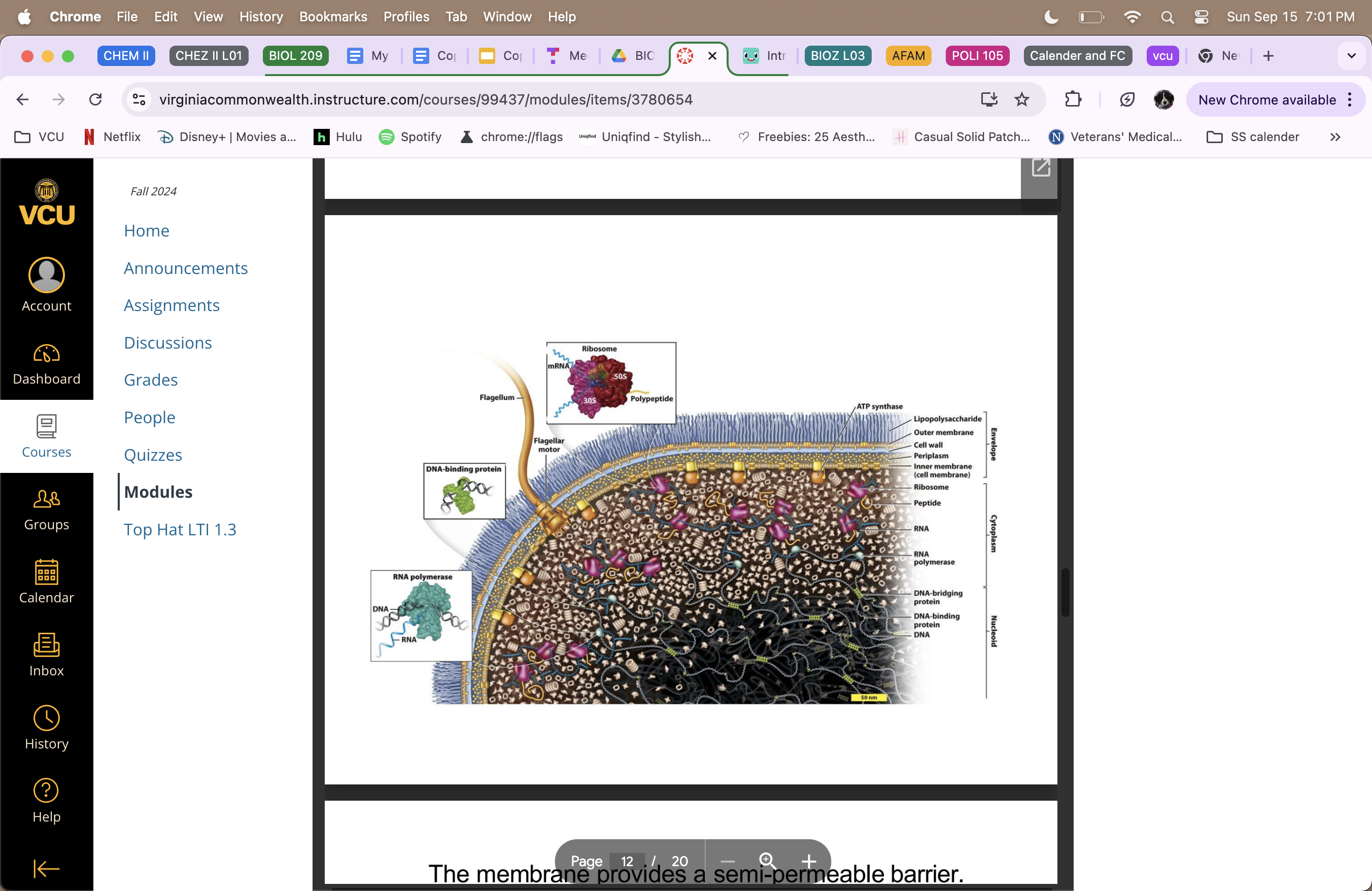
Bacteria Cell
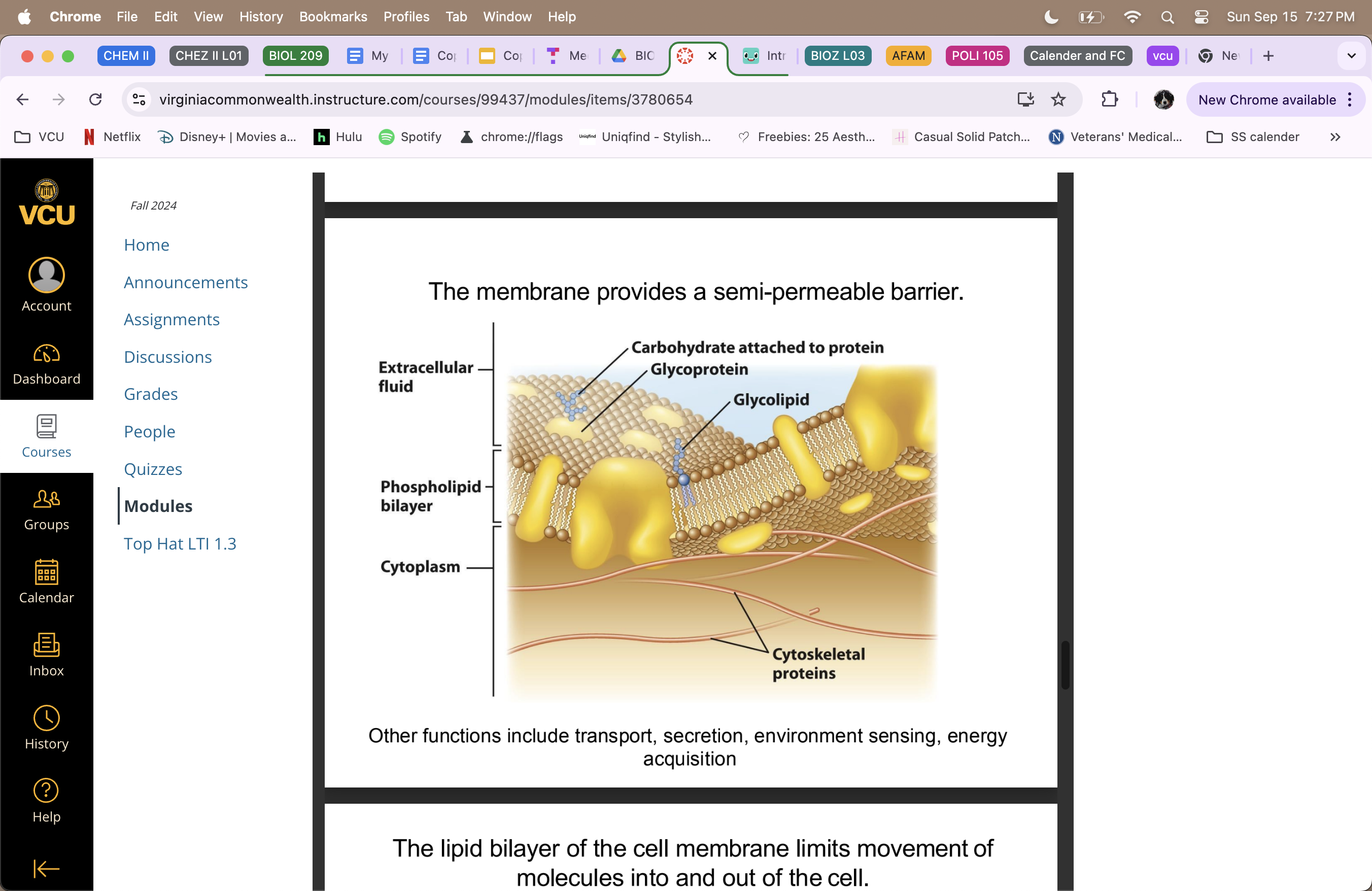
The membrane
provides a semi-permeable barrier
fluid structure
transport, secretion, environment sensing, energy acquisition
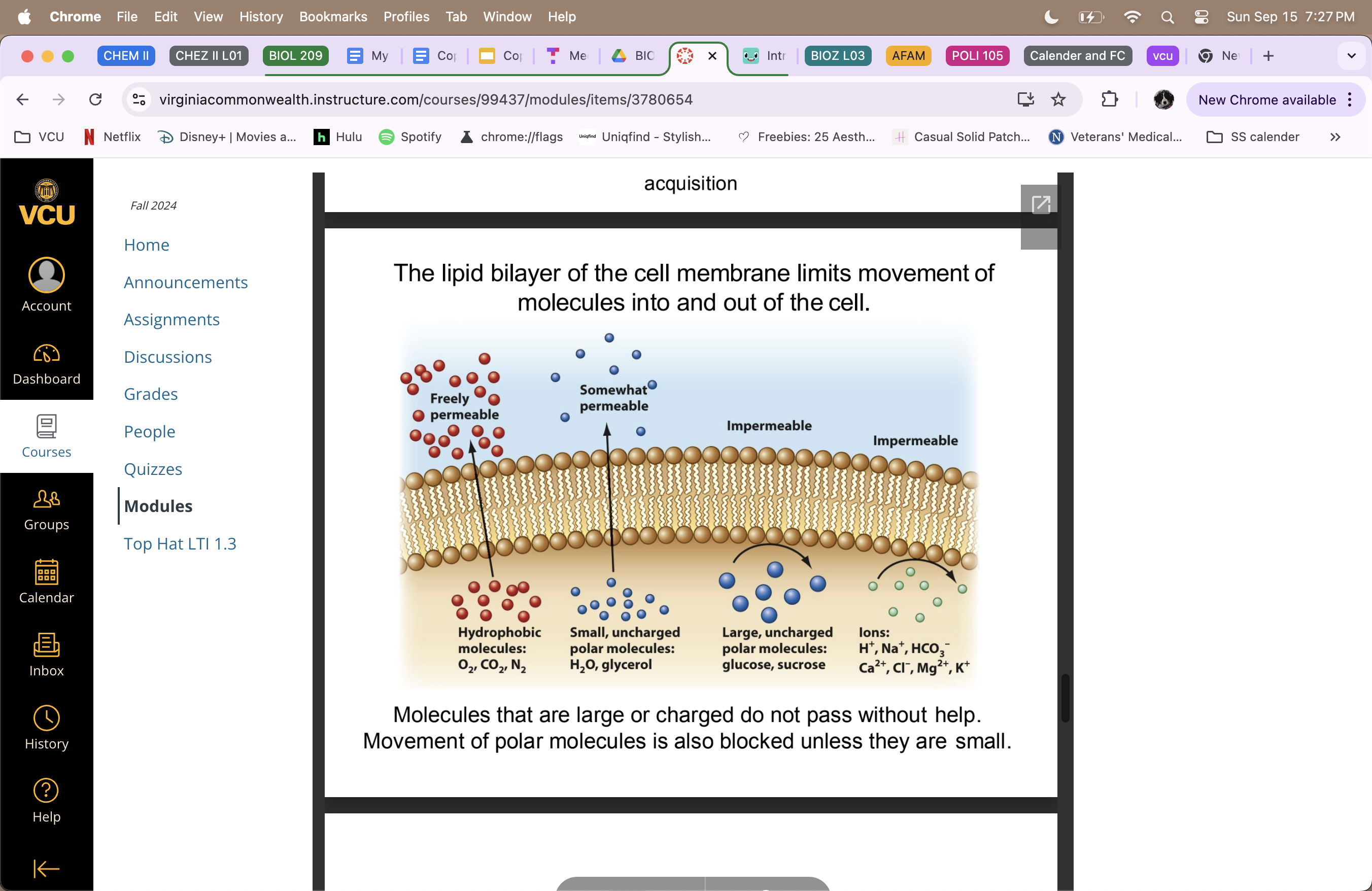
Lipid Bilayer
limits movement of molecules into and out of cell (part of the cell membrane)
Freely permeable = hydrophobic molecules (O2, CO2, N2)
Somewhat permeable = small uncharged polar molecules (H2O, glycerol)
Impermeable = large uncharged polar molecules (glucose and sucrose)
Impermeable = Ions (H+, Na+, HCO3-, Ca2+ , Cl-, Mg2+, K+)
Osmosis
special type of diffusion that deals with the movement of water (high to low concentration)
Isotonic
inside and outside of cell is equal (salt content)
no change to cell size
Hypertonic
more salt on the outside of cell
water moves out of cell; which decreases its size
Hypotonic
more salt in the cell
so water comes into the cell which increases the cell size