APES chapter 4 (heat and water)
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Where is heat the most concentrated?
around the equator
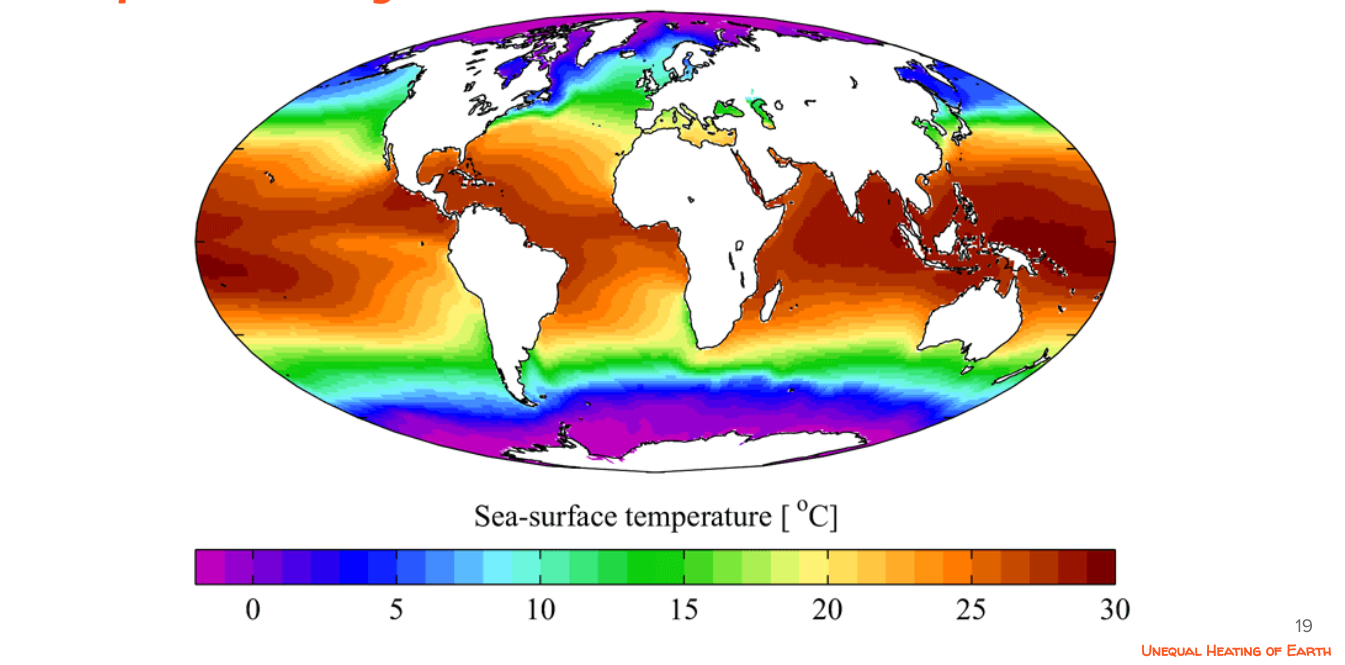
What are the 3 main causes of unequal warming of the earth?
1) Angle
2) Surface Area
3) Albedo
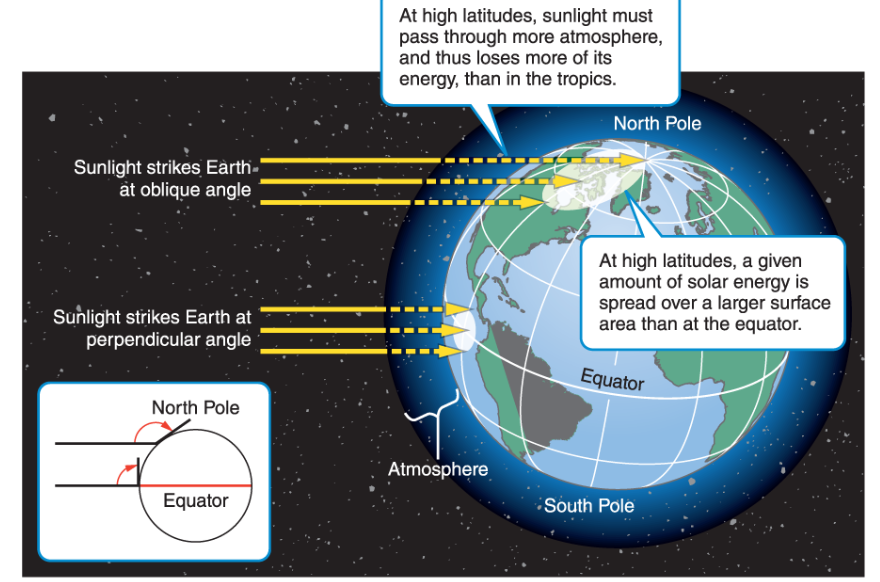
How does the angle impact the heating of the earth?
The angle causes heat to directly hits the equator constantly
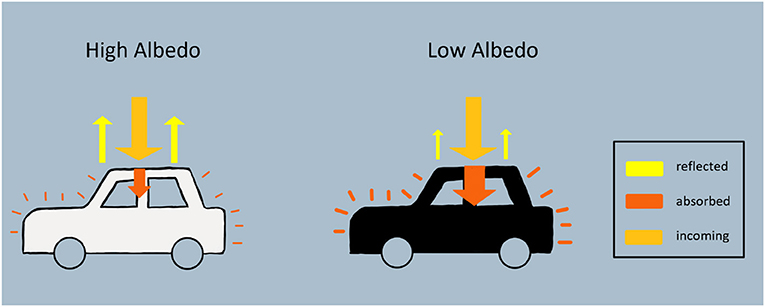
What is albedo?
the fraction of light a surface reflects (reflectivity)
what is the tilt of the earth (in degrees)?
23.5 degrees
What is saturation point?
the air cools and its saturation drops, water vapor condenses into liquid water that forms from clouds. The saturation point is basically how much water clouds can hold, causing rain.

Clouds are made of __________
liquid water droplets
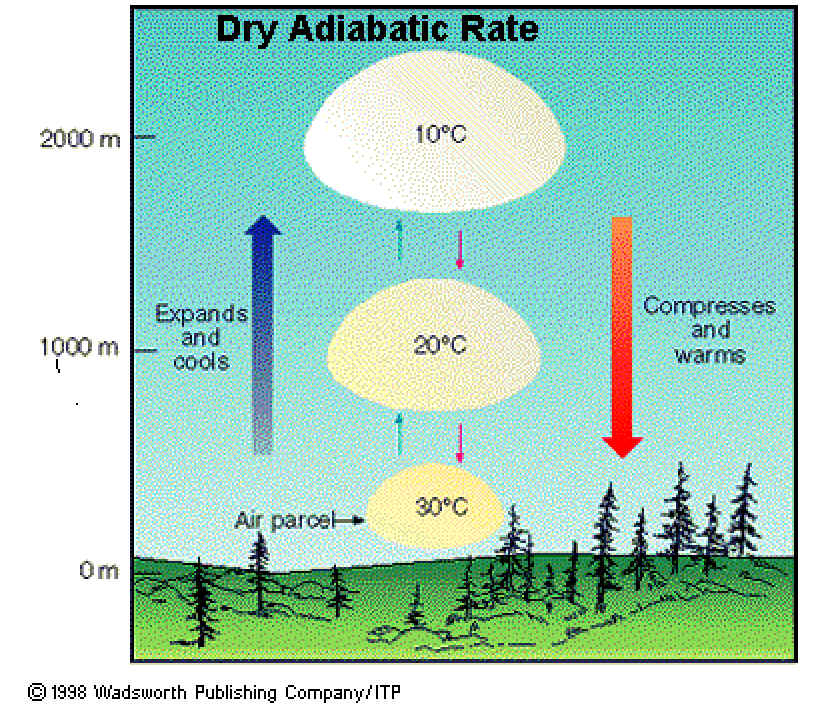
Adiabatic cooling
pressure decreases which results in a decrease in temperature
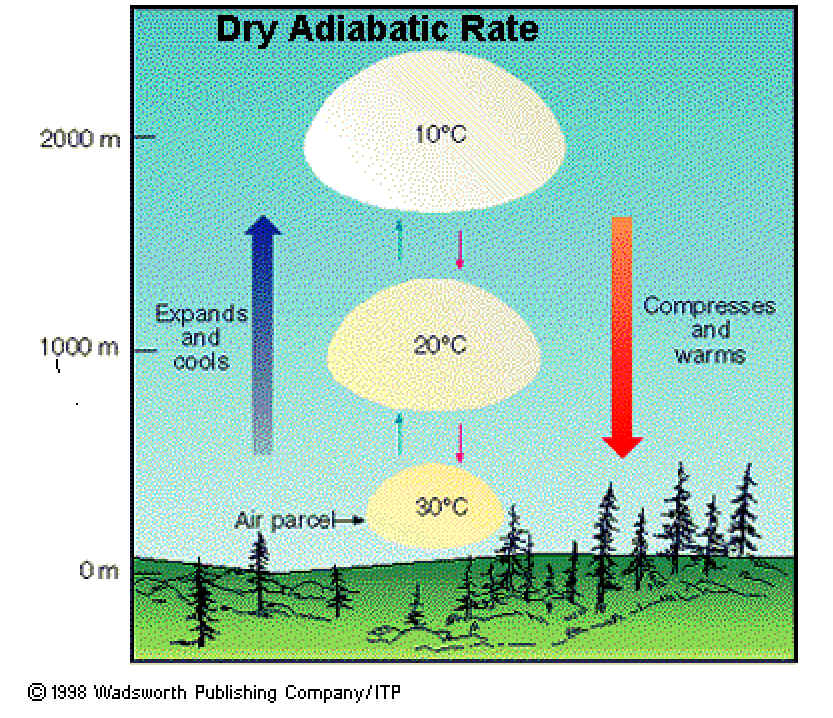
Adiabatic heating
pressure increases which results in higher temperature
Is warm air more or less dense than cooler air?
less dense
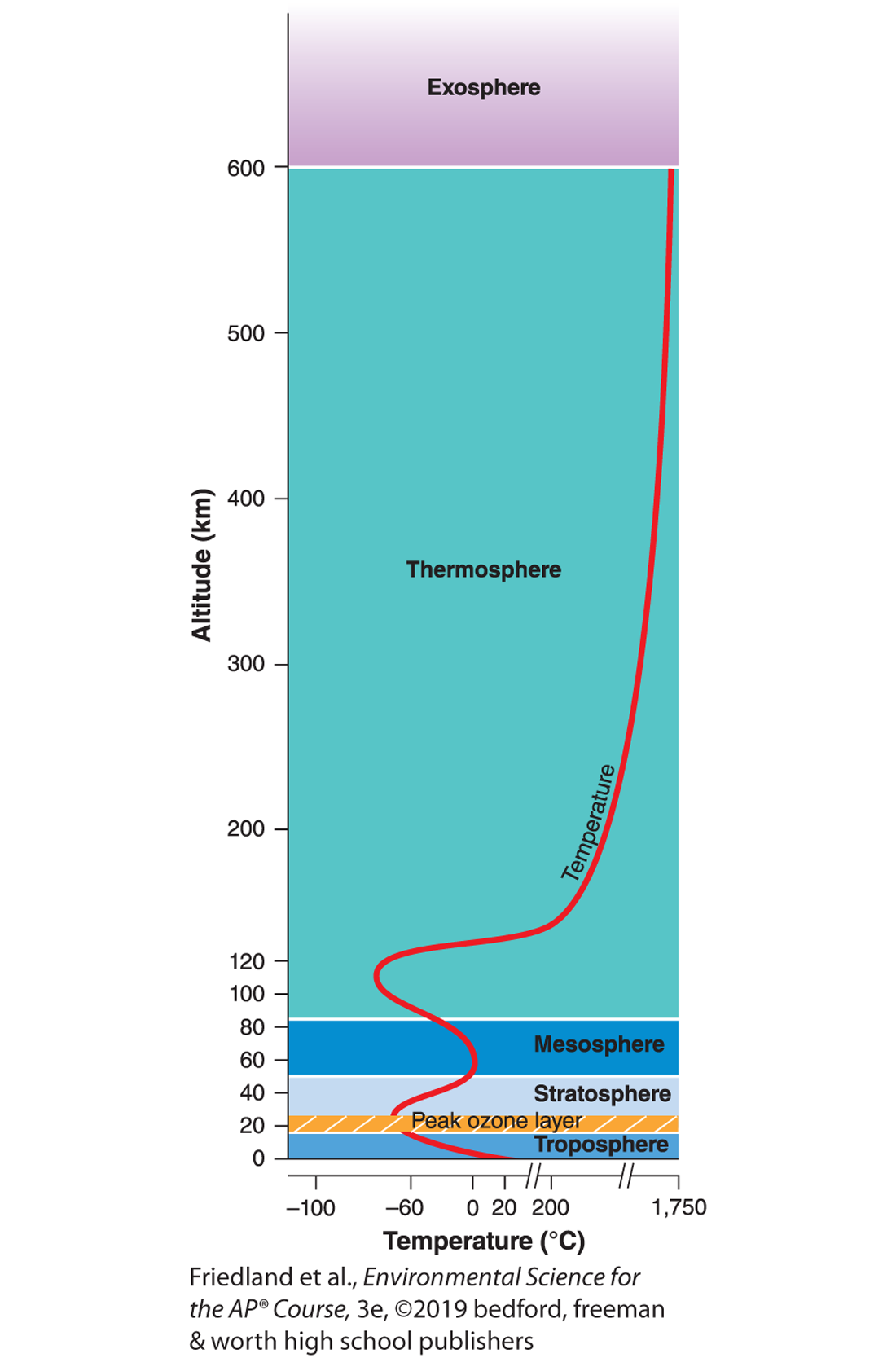
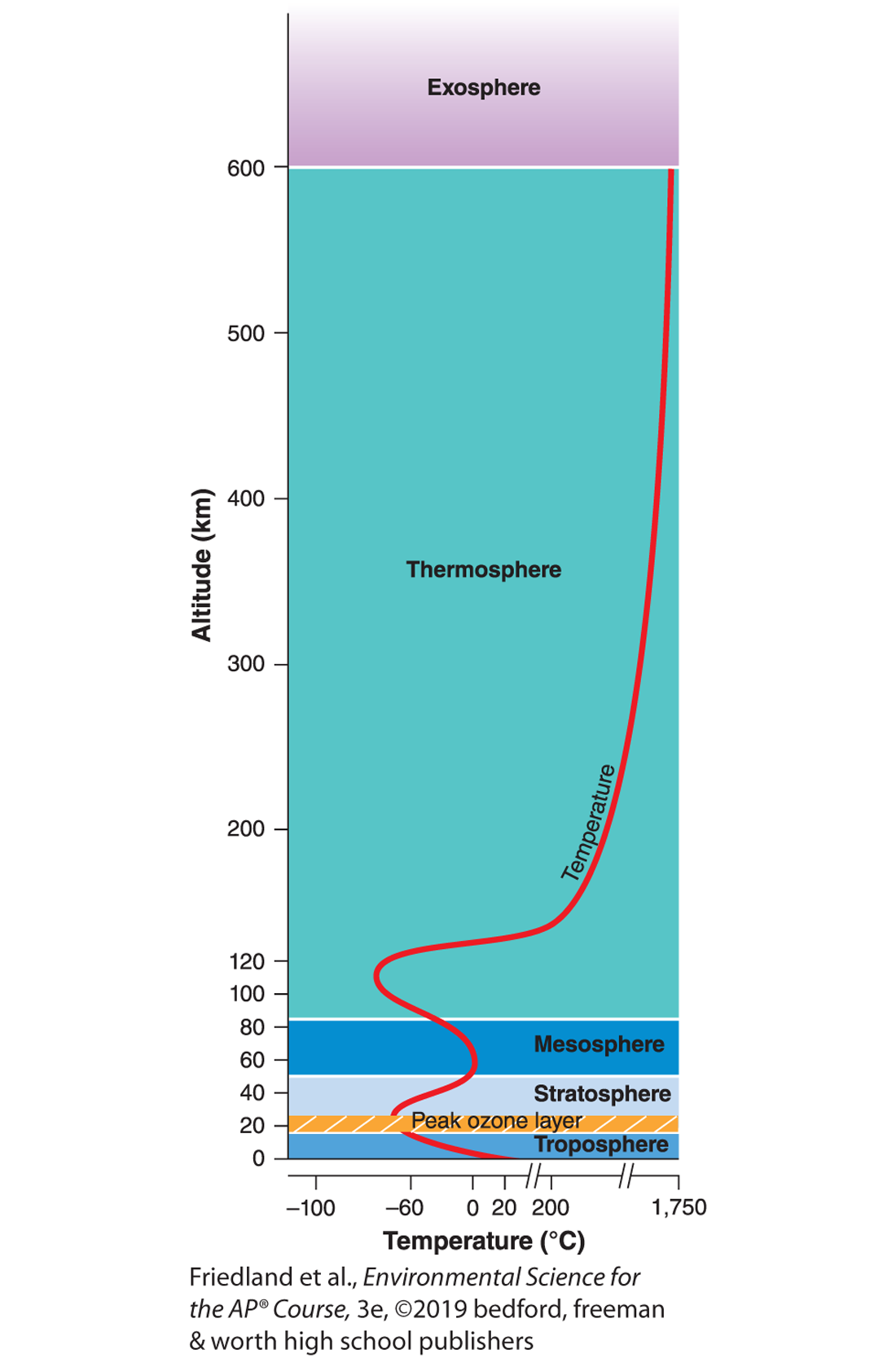
troposphere
closest to the Earth’s surface
the densest layer of the atmosphere
the layer where earths weather occurs
most of the atmosphere nitrogen, oxygen, and water vapor occur
atmospheric pressure is highest here
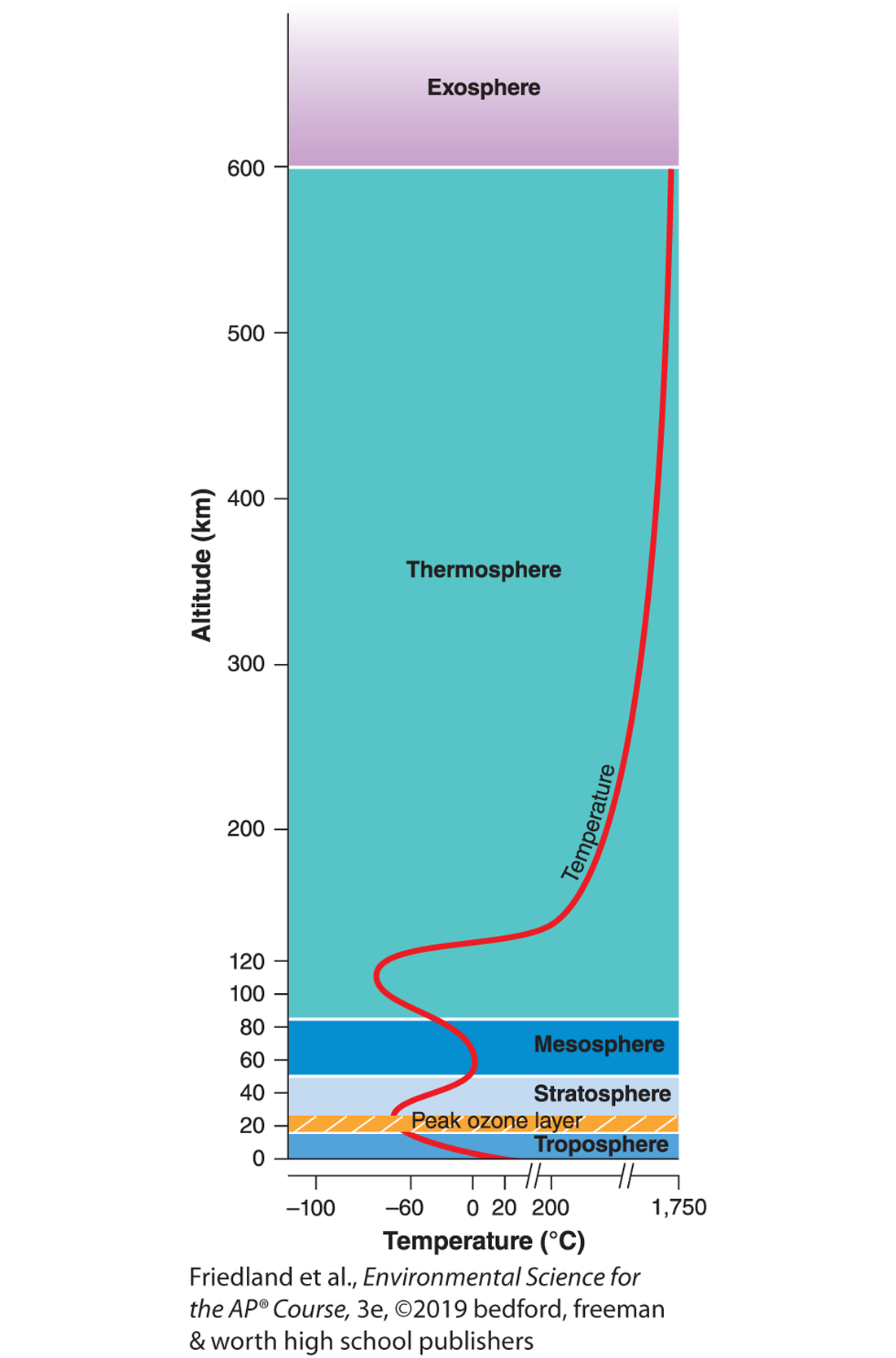
stratosphere
contains the ozone layer
absorbs most UV radiation
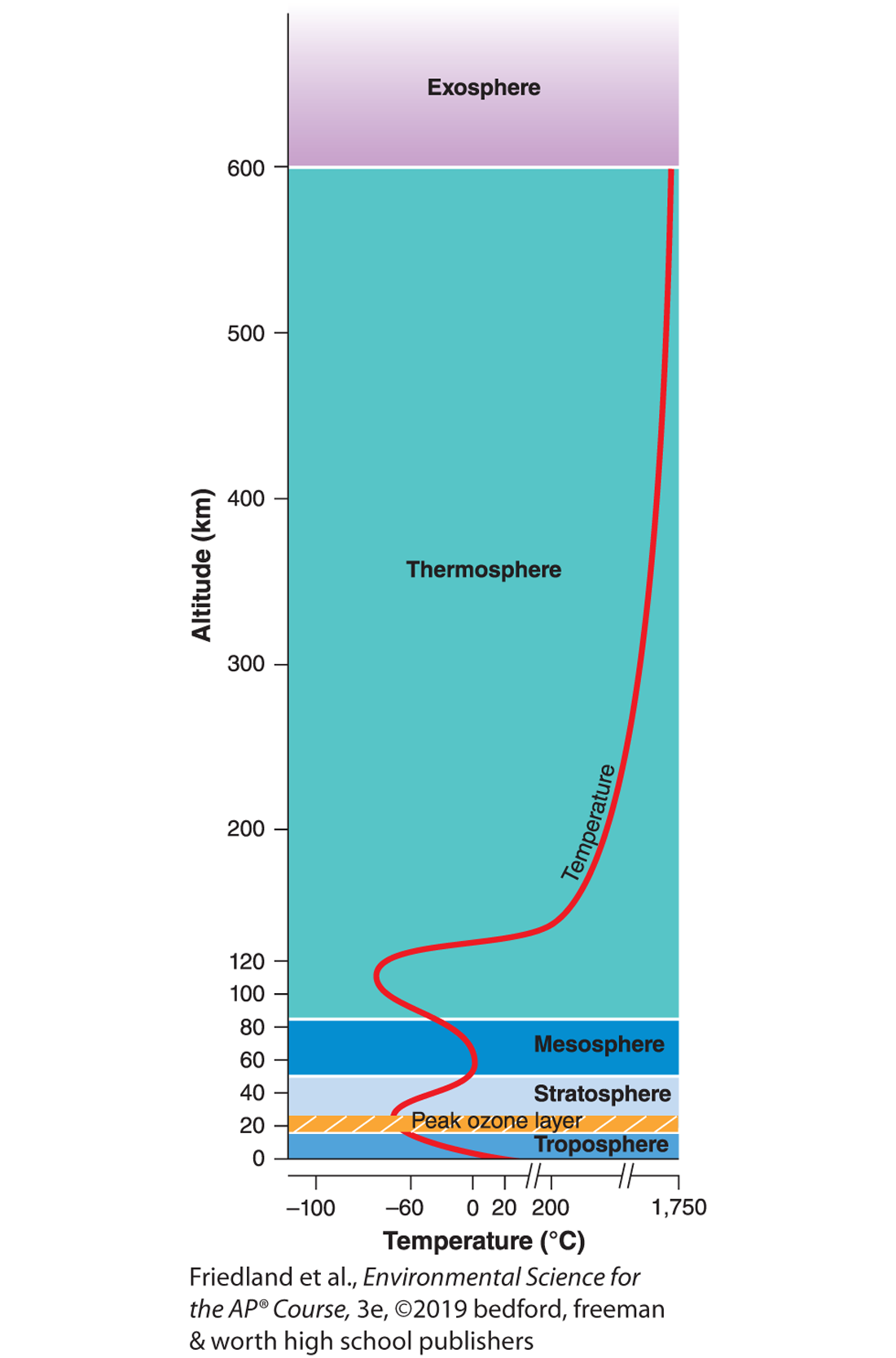
mesosphere
most meteors burn here before they can hit the earth
that’s it…. this layer is boring
what is the molecular formula for ozone
O3
thermosphere
aurora borealis (northern lights) occurs here
atmospheric temperatures are highest and lowest here
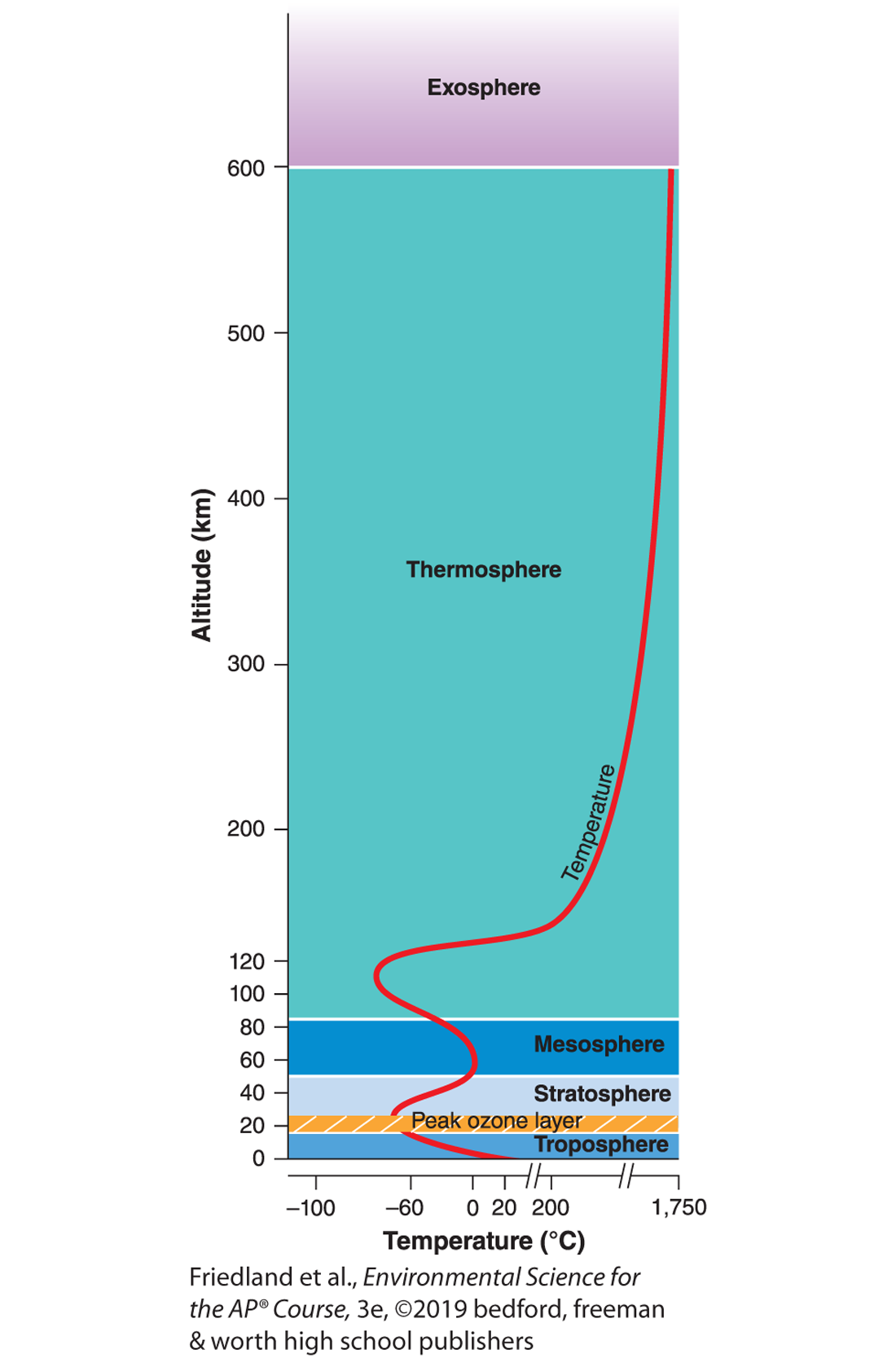
exosphere
atmospheric pressure is lowest here
the outermost layer of the atmosphere
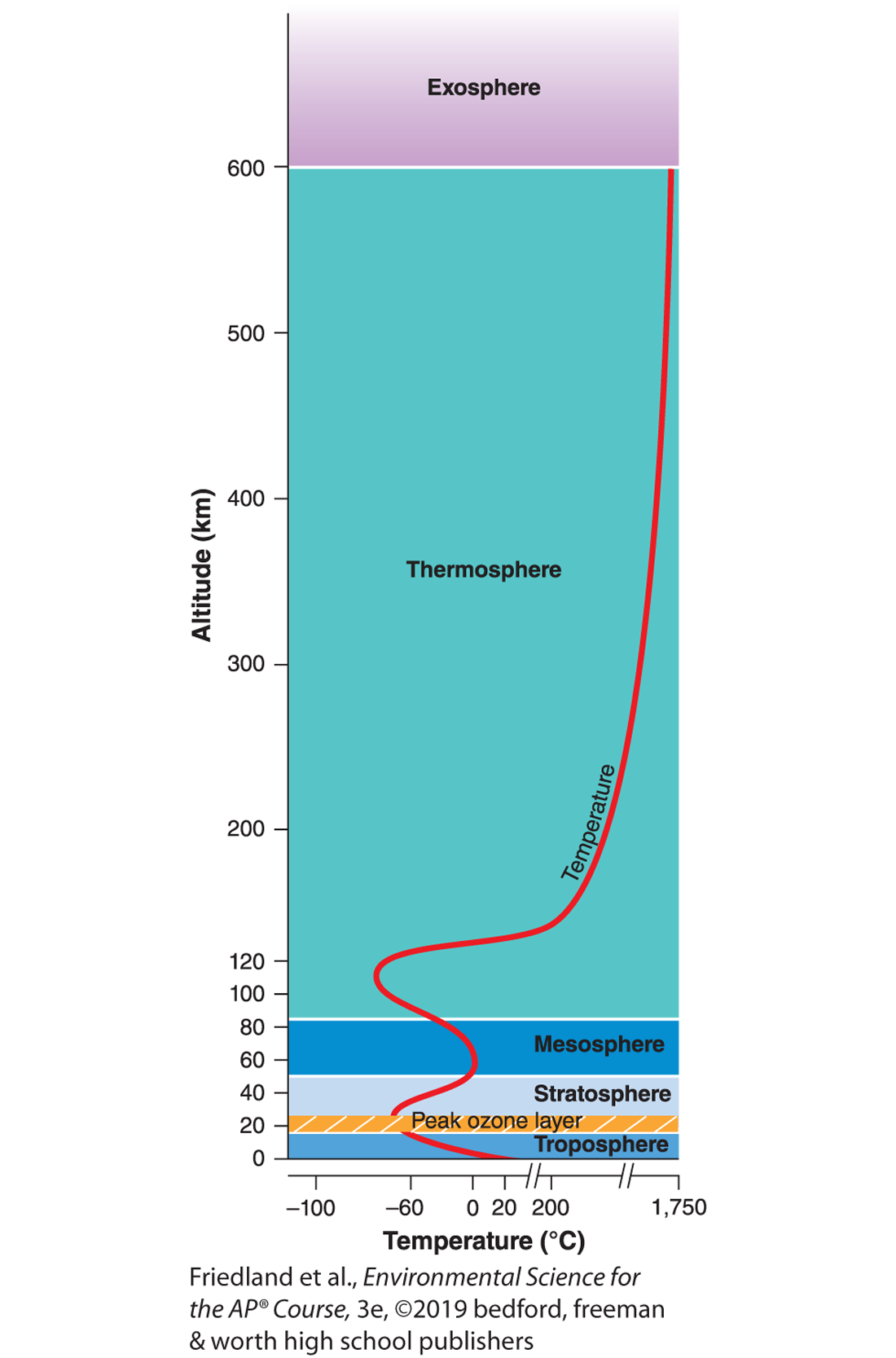
why is ozone important
it stops harmful UV rays from reaching earth
what holds the layers of the earth together and how does mass and density play a part in the layers order?
gravity holds everything together and the layers closer to the earth have greater mass and vice versa
what are the 4 properties of air that determine how it circulates the atmosphere?
1) density
2) adiabatic heating and cooling
3) water vapor capacity
4) latent heat release
less dense air….
rises
more dense air….
sinks
cold air is _____ dense than warm air
more
warm air is _______ dense than cool air
less
hot air ______ and cold air _____
hot air RISES and cold air SINKS
warm air has a ________ capacity to hold water vapor
higher
when temperature rises, its saturation point….
increases
How are clouds formed?
When the air temperature falls, its saturation point decreases leading to condensation, cloud formation, and precipitation.

when air pressure increases the temperature….
increases
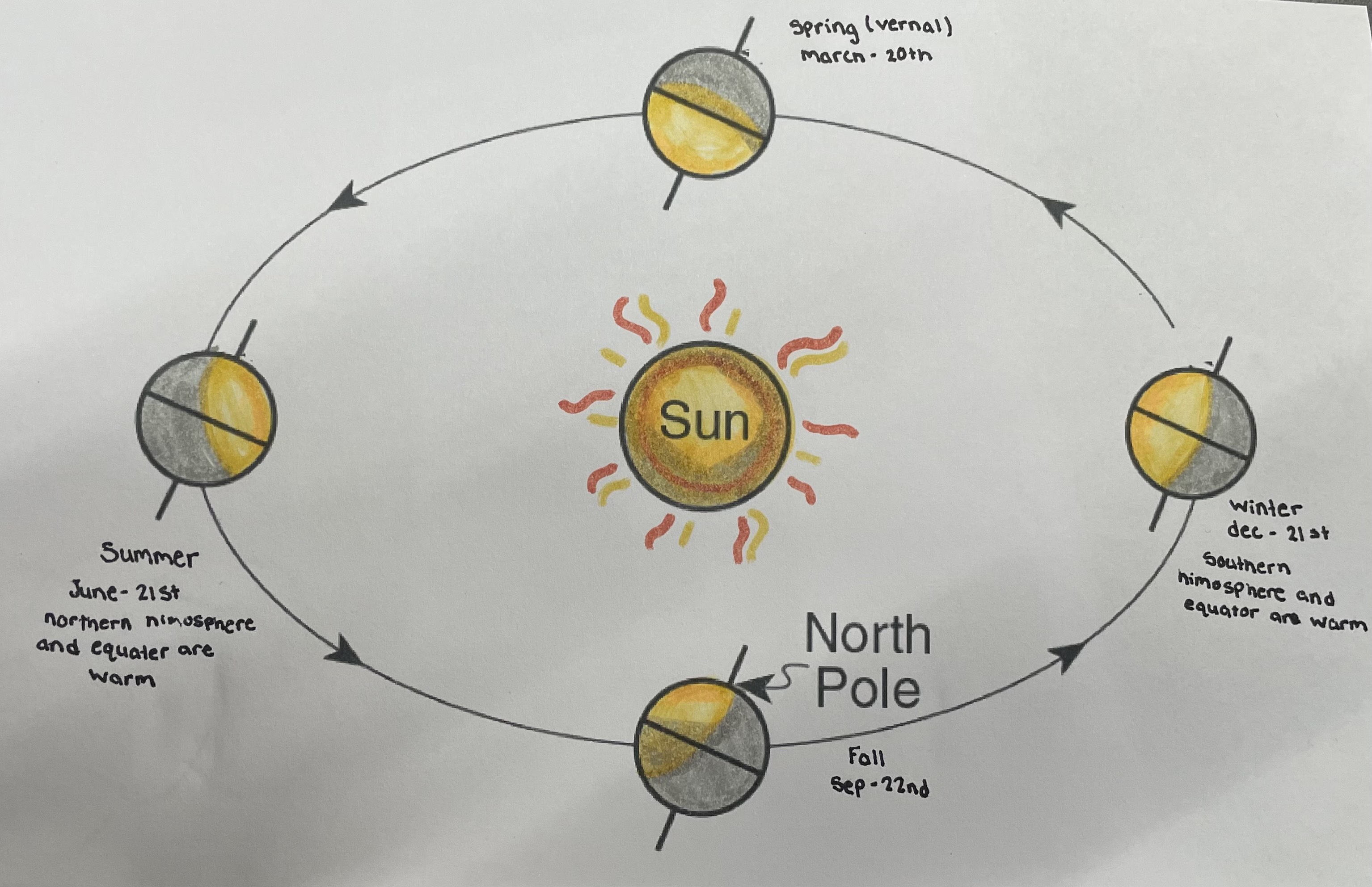
what causes the seasons?
earth spins on its axis and it tilts, this tilt causes the sun to hit certain himospheres which causes seasons
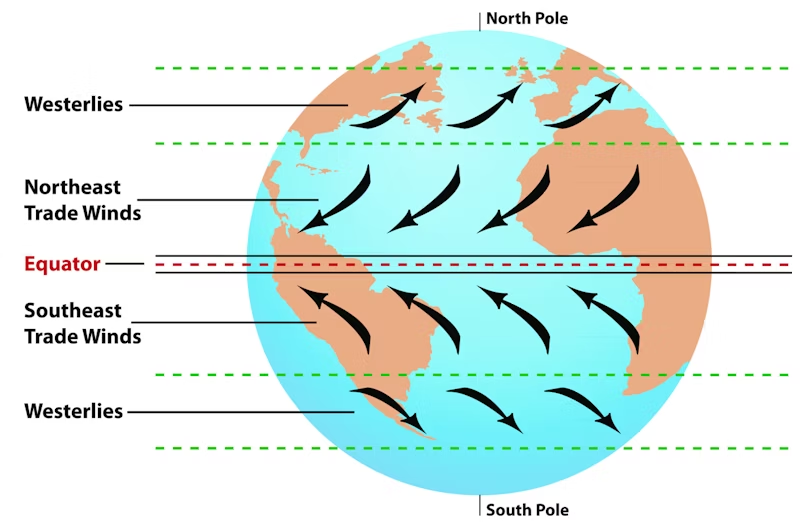
prevailing winds
winds that blow consistently in a given direction over a particular region on Earth ex) most weather blows west
water changing from liquid to gas is called ___________ and ________ heat energy
water changing from liquid to gas is called evaporation and requires heat energy
water changing from gas to liquid is called ___________ and ________ heat energy
water changing from gas to liquid is called condensation and releases heat energy

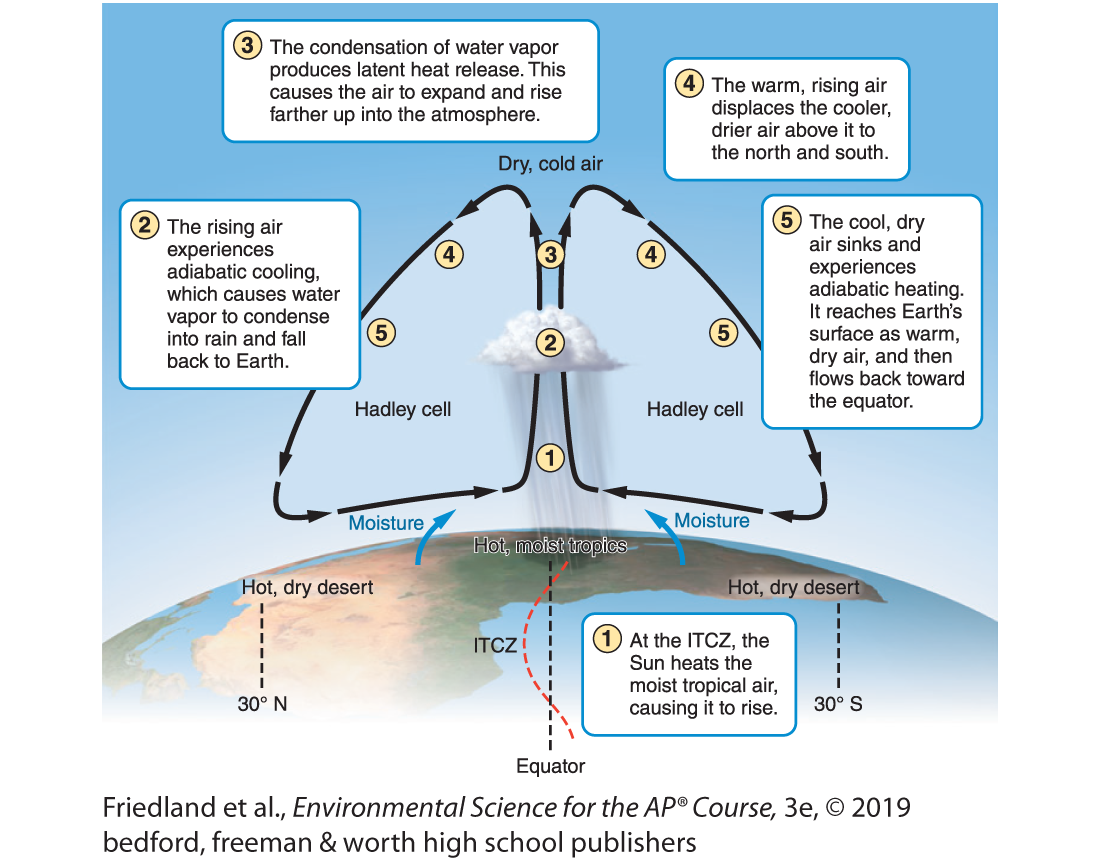
inter-tropical conversion zone (ITCZ)
sun heats the moist tropical air causing it to rise
Coriolis effect
why the weather patterns spin
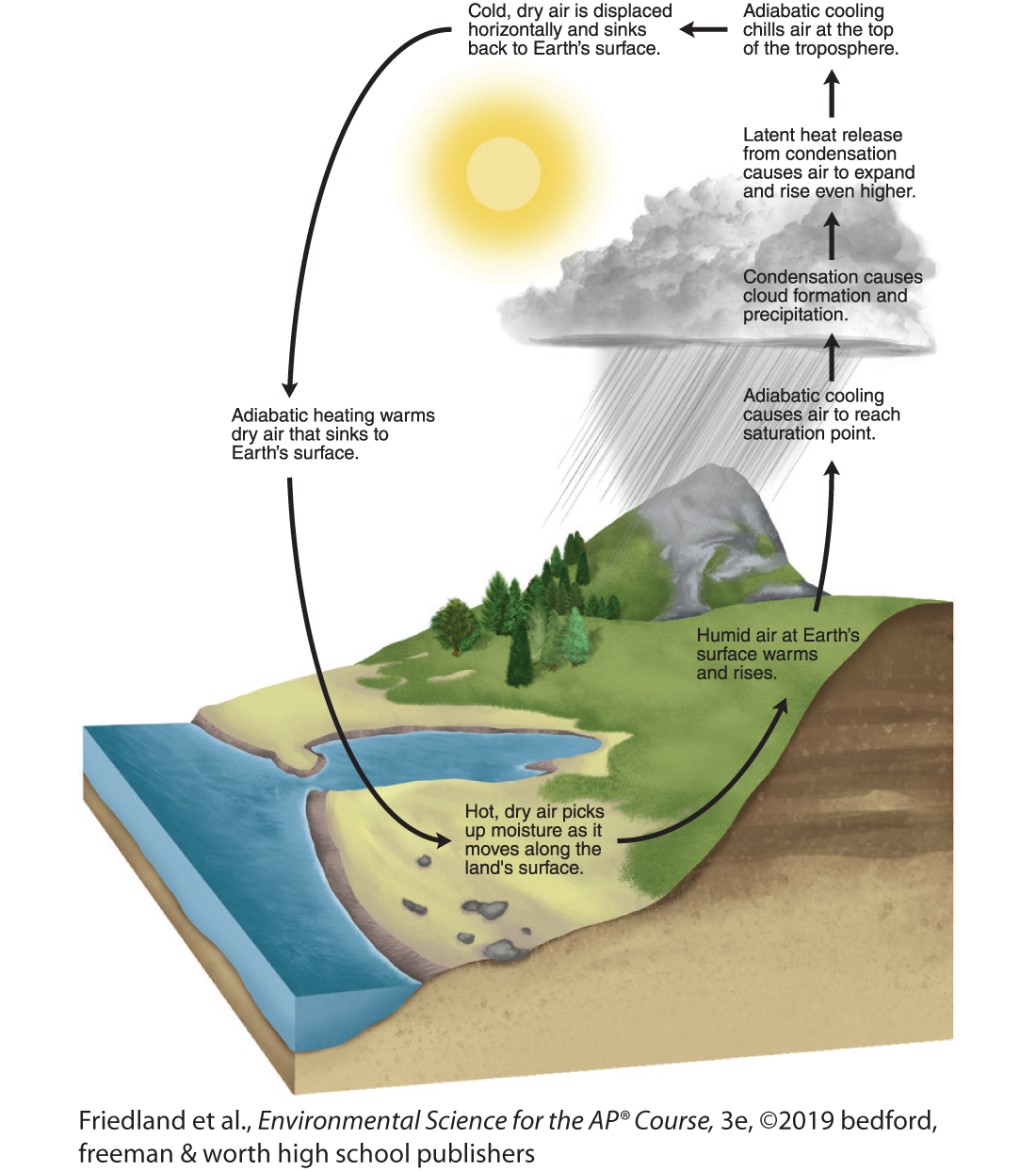
What is latent heat release?
the release of energy when water vapor in the atmosphere condenses into liquid water
what is an atmospheric convection current?
Global patterns of air movement that are caused by the unequal heating of the earth
what causes the Coriolis effect?
the earth’s rotation on its axis
What is the Hadley Cell?
A convection current in the atmosphere that cycles between the equator and 30 ∘ N and 30 ∘ S
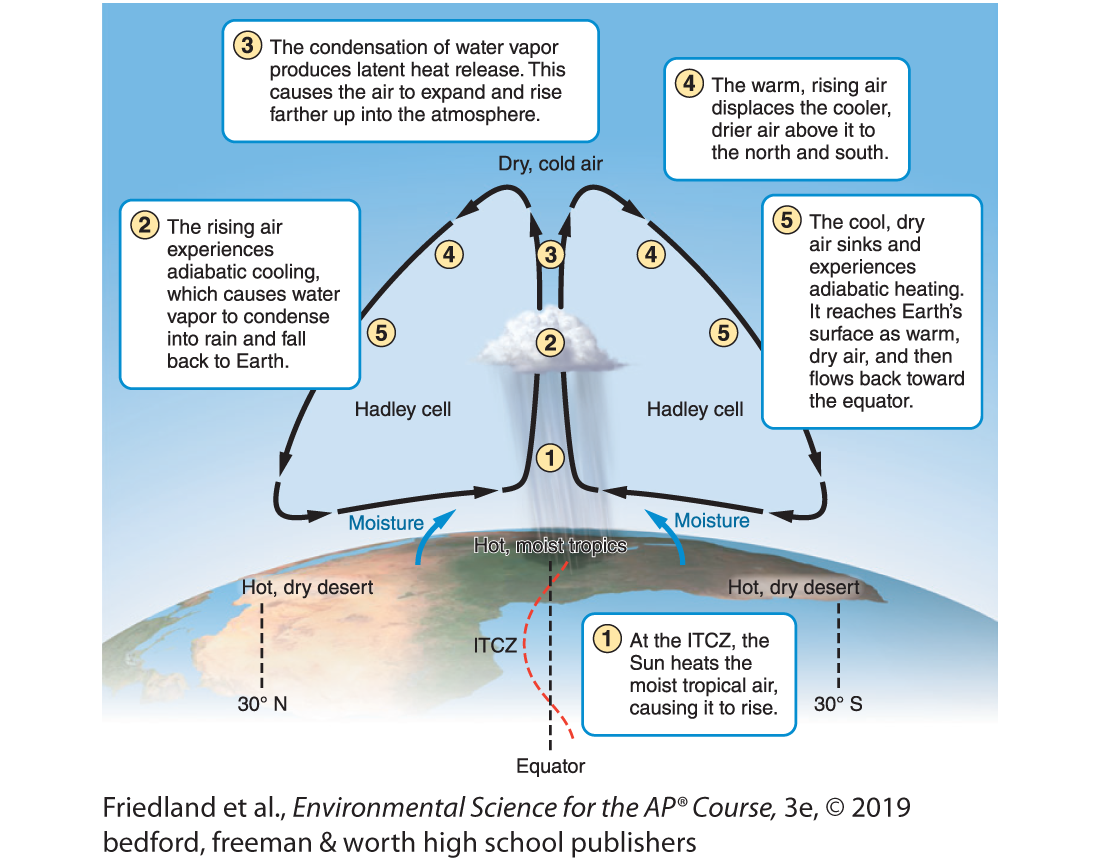
Why does earth move faster at is equator?
The earth is wider at the equator than at the poles
what 6 things drive ocean currents?
Temperature
Gravity
Prevailing winds
The Coriolis effect
Salinity
Location of continents

Gyres
Moves warm water up and cold water down, the circulation of water
(Clockwise N. Hemisphere / Counterclockwise S. Hemisphere)
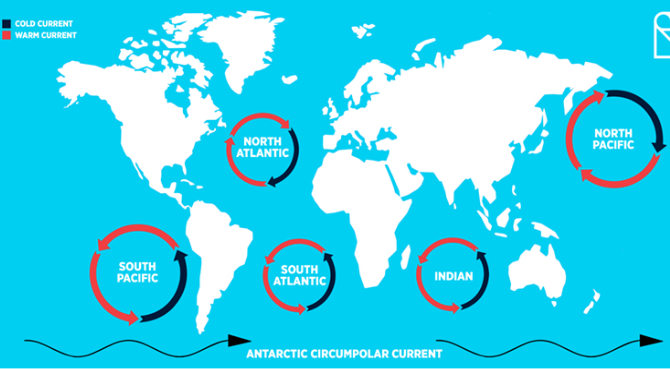
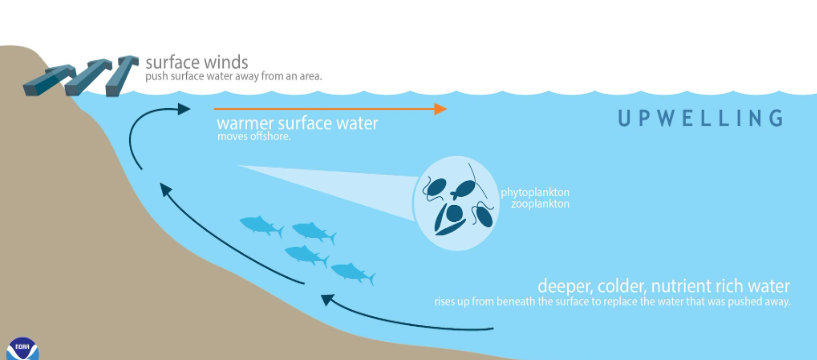
Upwelling
where currents separate deep waters rise up towards the surface- leads to high primary productivity
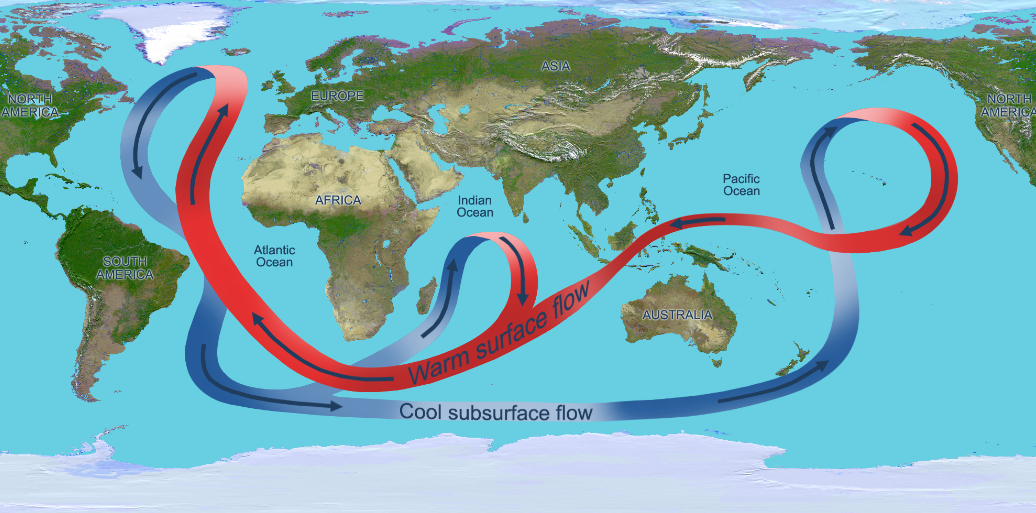
Thermohaline Circulation
warmer and cooler waters pulling each other around, it is important because it supplies heat to polar regions - it takes hundreds to happen
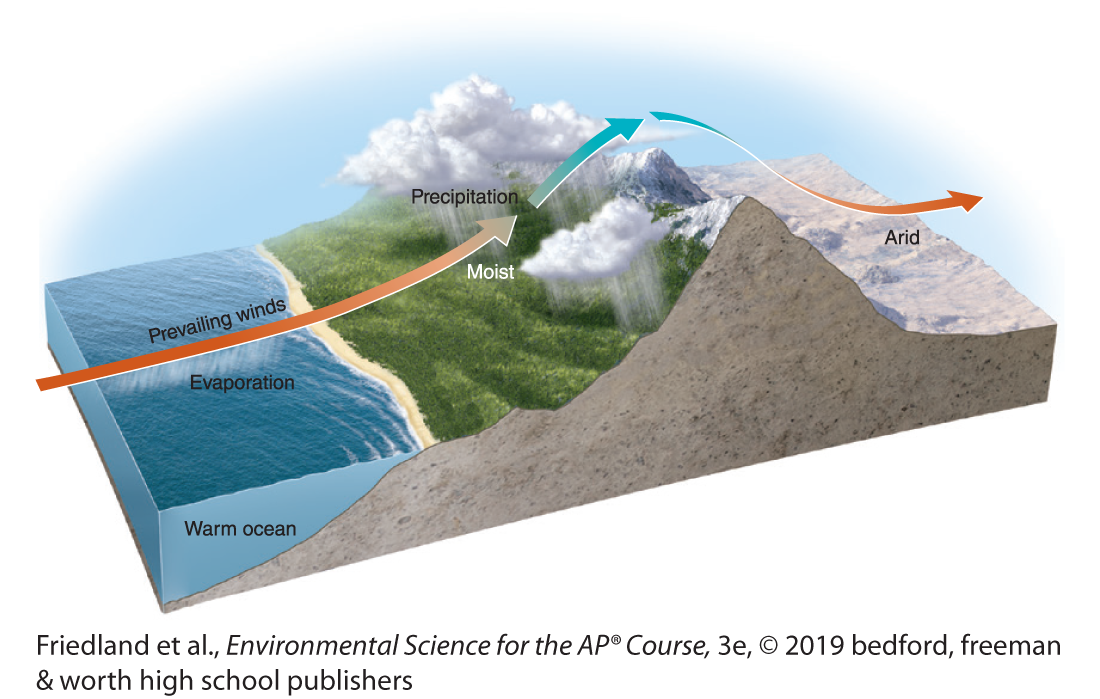
what is a rain shadow?
causes mountains to be dry on one side ex) the Sierra Nevada mountains
How is climate different from weather?
Climate is the average of weather, weather is short term atmospheric conditions
what are the 5 conditions associated with weather?
temperature, humidity, clouds, precipitation, and wind speed.
What 3 factors affect how climate differences arise around the world?
1)unequal heating of Earth
2)air currents
3)ocean currents.
what are trade winds?
winds that blow towards the equator
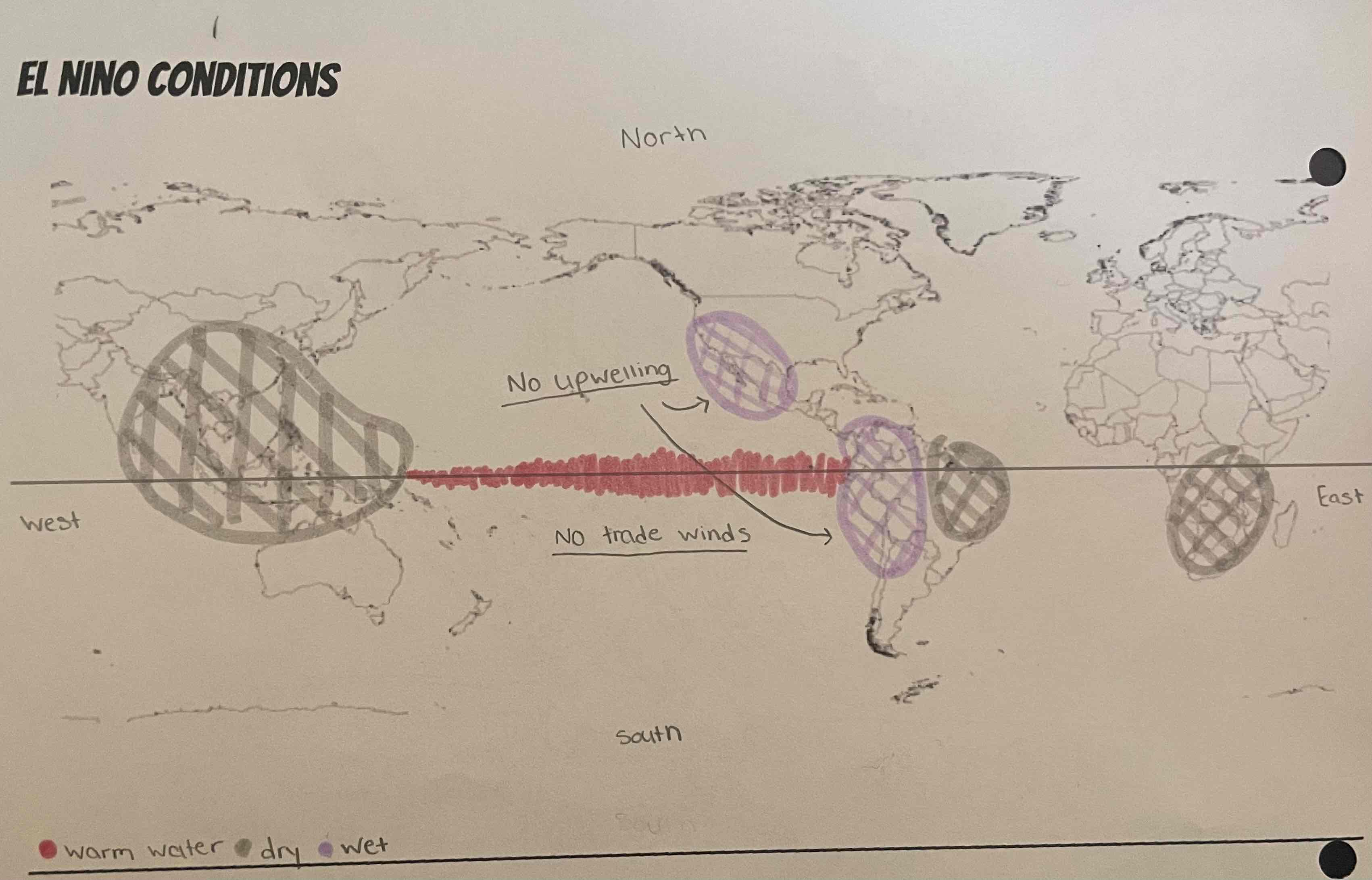
What is El Nino?
happens every 3/7 years
trade winds reverse/ stop
normal conditions essentially reversed
No Upwelling
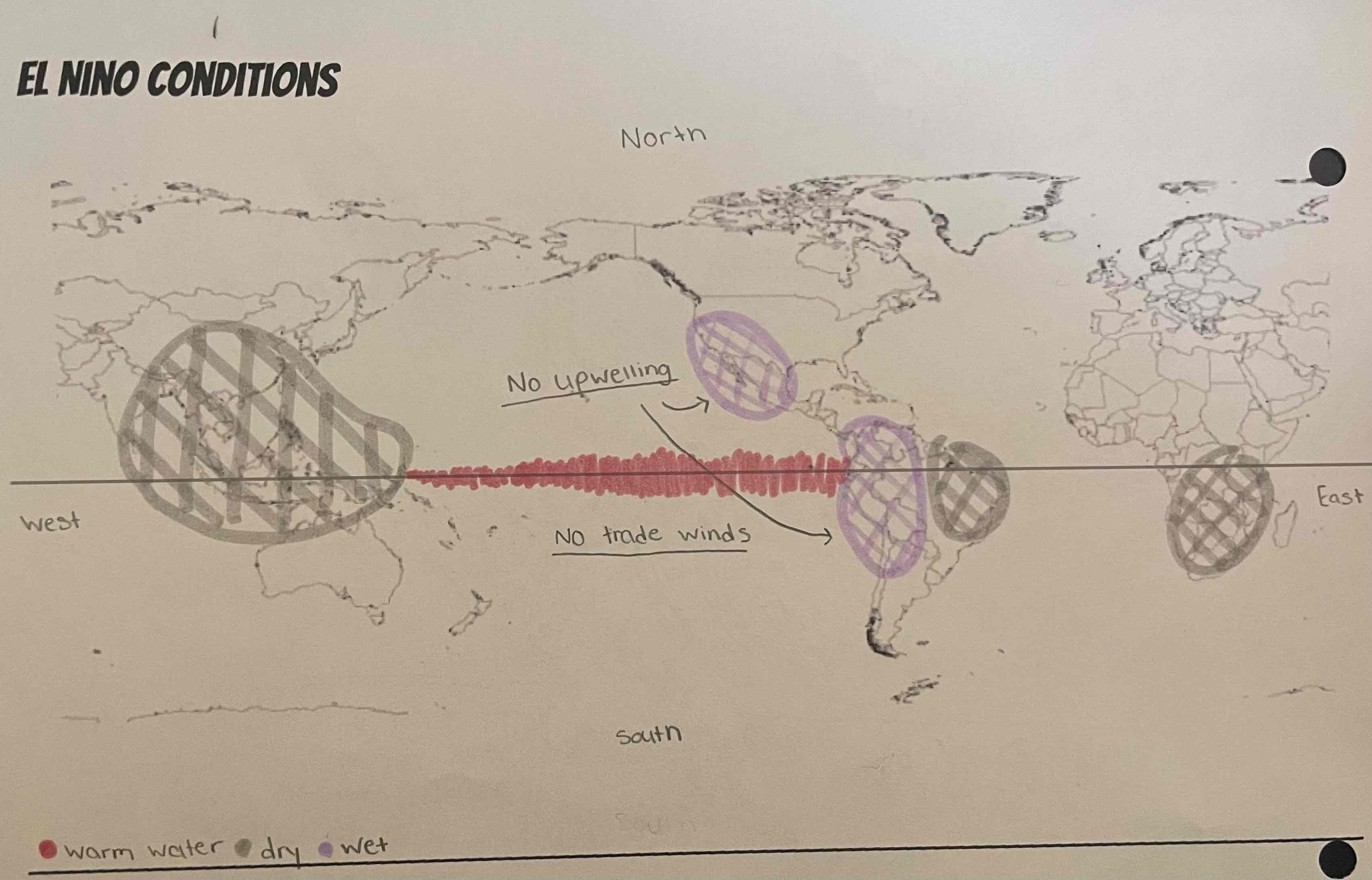
What is the issue with El Nino?
bad fishing conditions
Hurricane damage in areas that are not used to wet conditions
drought conditions affects crops
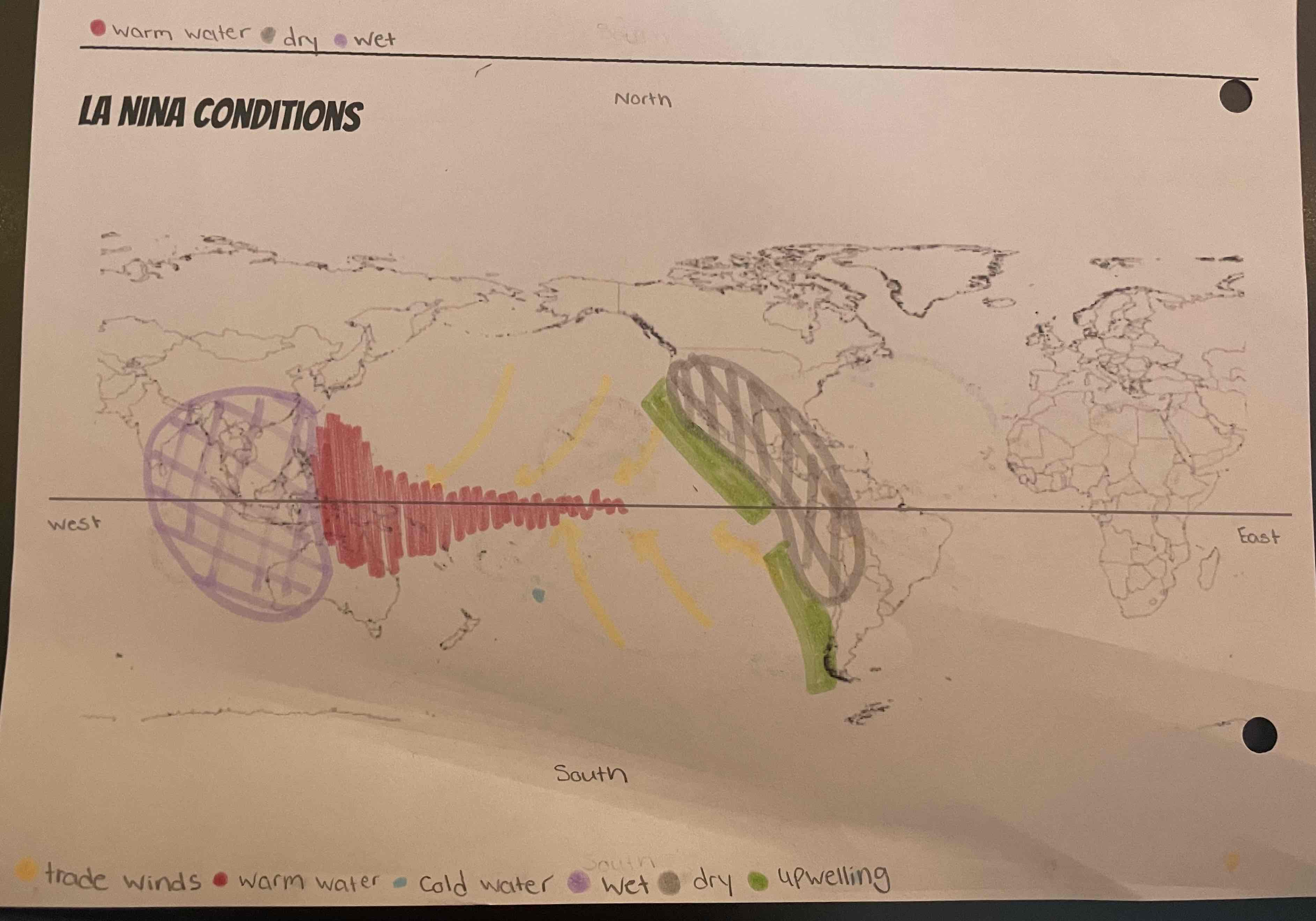
What is La Nina?
EXTREME normal
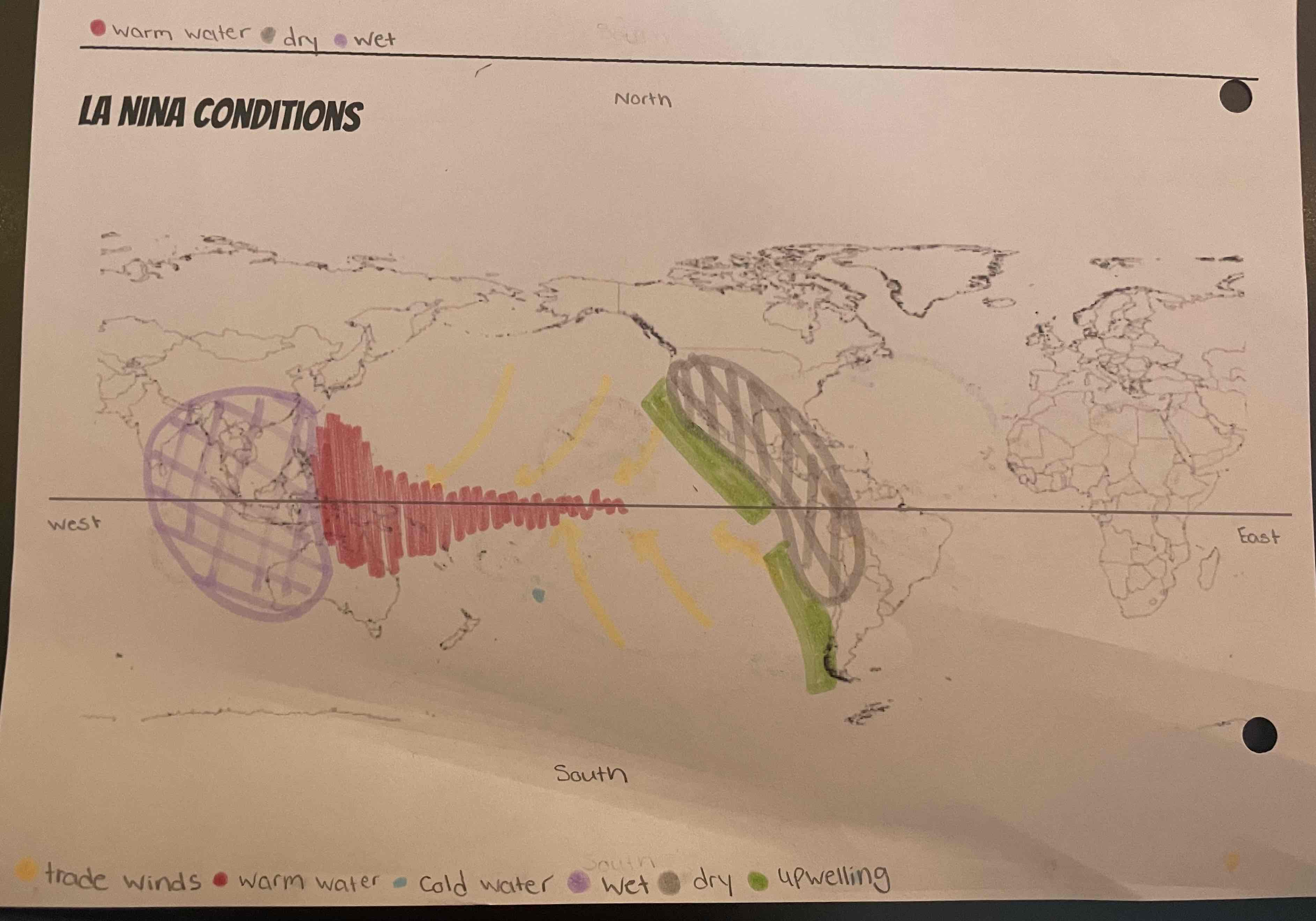
What are the consequences with La Nina?
flooding out west
crops struggle
The northeast is very dry
very good fishing conditions
we live in the….
troposphere!
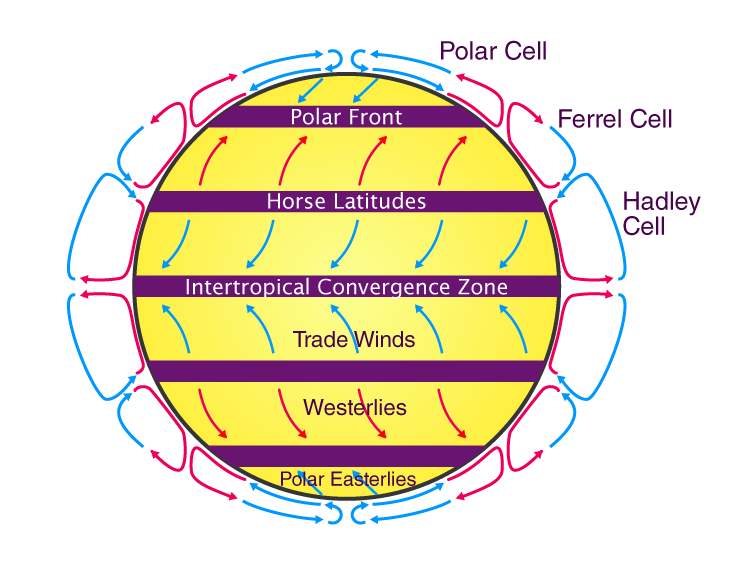
What is the order of the trade wind cells?
Polar cell
Ferrel cell
Hadley cell
Hadley cell
Ferrel cell
Polar cell
(PFHHFP)
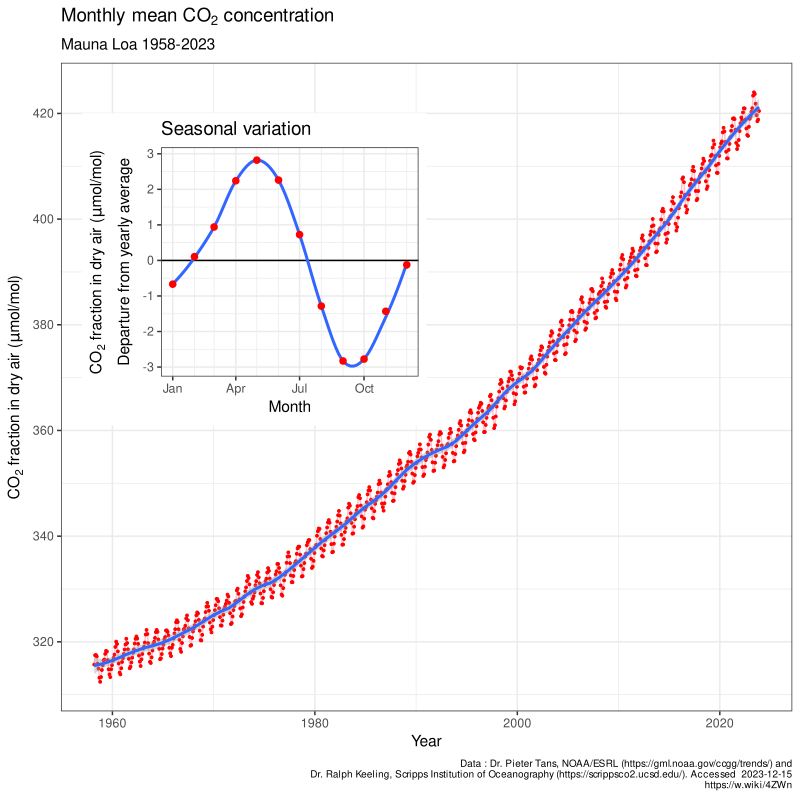
Why is there so much CO2 variability in seasons?
because plants grow and die with the seasons so the CO2 levels fluctuate with the plants
Which Biome is found at 30 degrees north and 30 decrease south?
Deserts