03.2E BIO, C1 Eukaryotic Cell Structures (PART E)
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
What are the advantages of organelles? Why compartments?
Organelles form separate compartments or "rooms" within the cell:
1. making it easier to transport materials
2. providing separate places for different reactions to occur
3. Increasing the efficiency of chemical reactions (localize reactants and necessary enzymes)
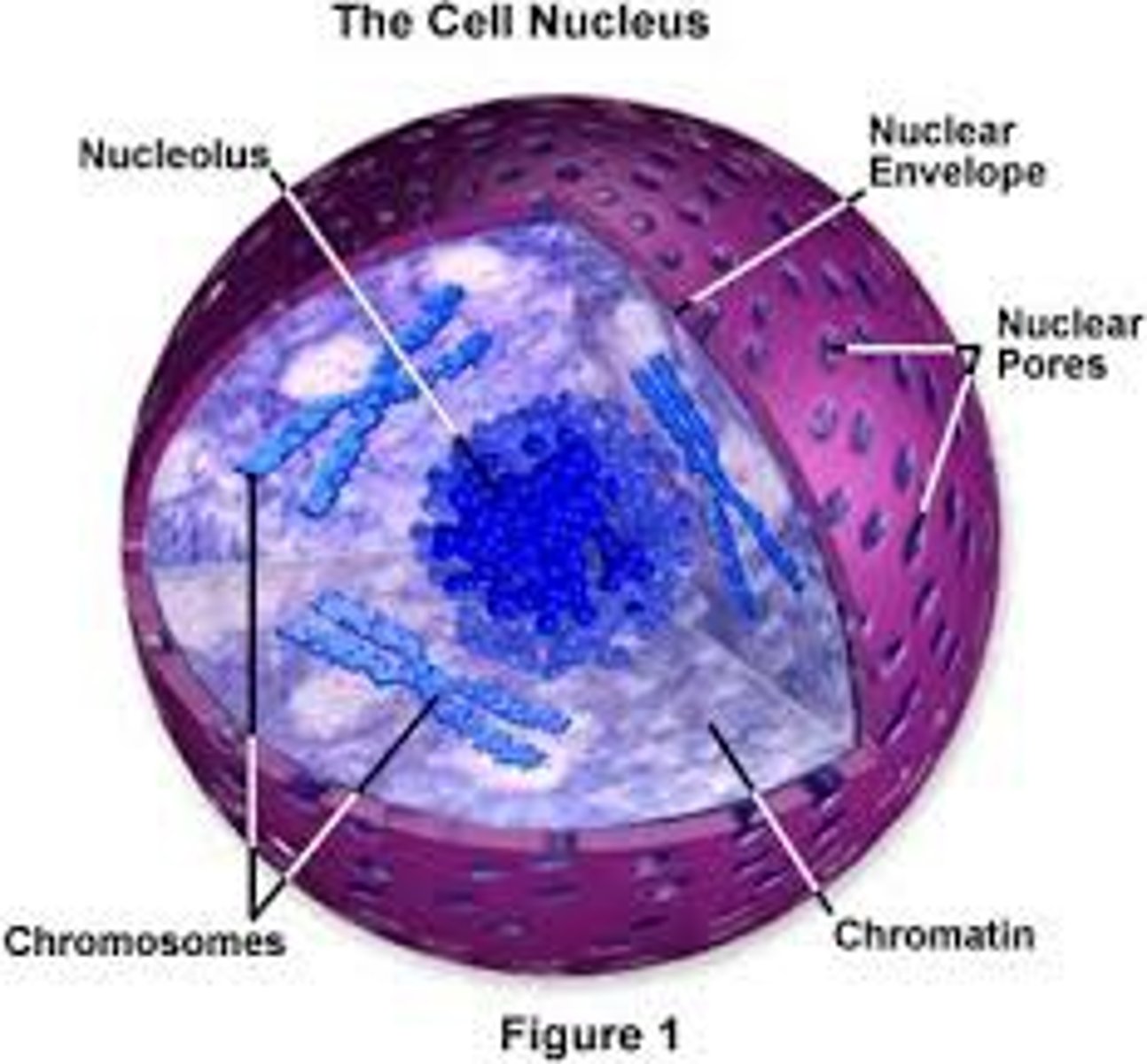
Nucleus
Complex of DNA and protein that controls cellular activity
Nucleoplasm
Gel-like cytoplasm found in the nucleus
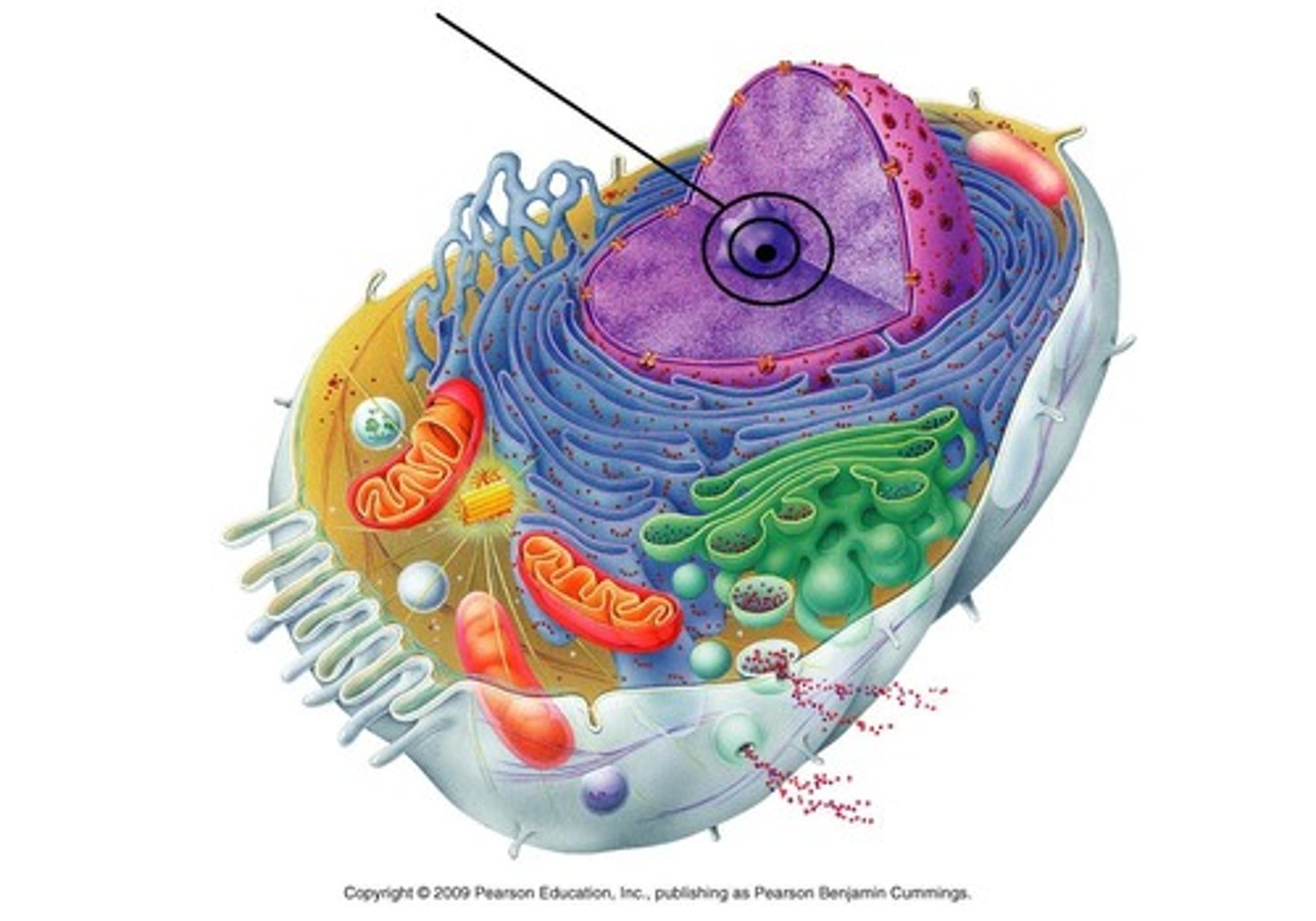
Nucleolus
Dense darker region found in the nucleus; site where ribosomes are made
Ribosomes
Made of ribosomal RNA and protein that are found on rough endoplasmic reticulum or free floating in the cytoplasm; site where protein synthesis occurs
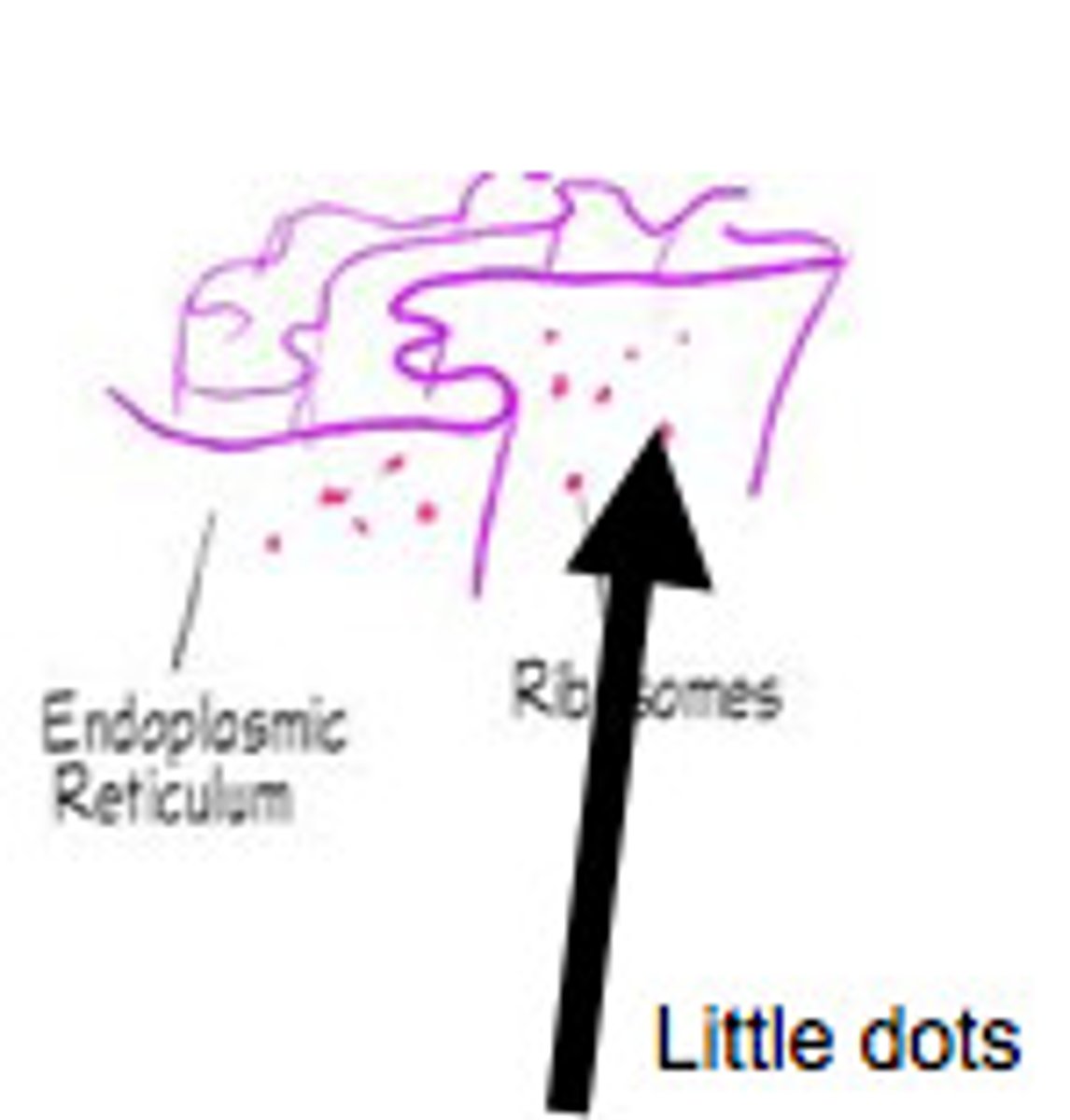
Ribosomes (Two Types)
Bound to ER
Free-floating in cytoplasm
Chromatin
Thread-like form of DNA present in the nucleus when the cell is NOT dividing
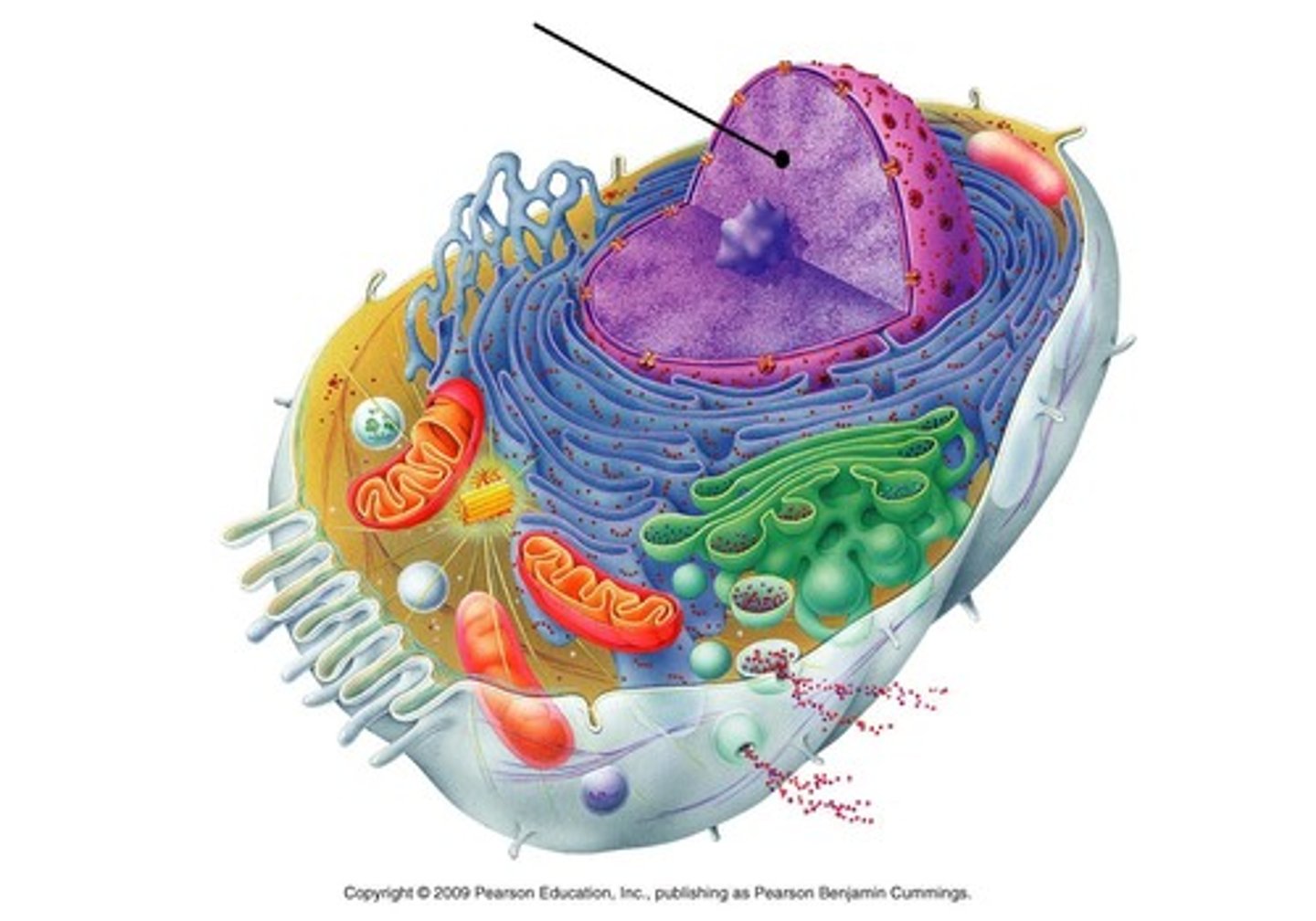
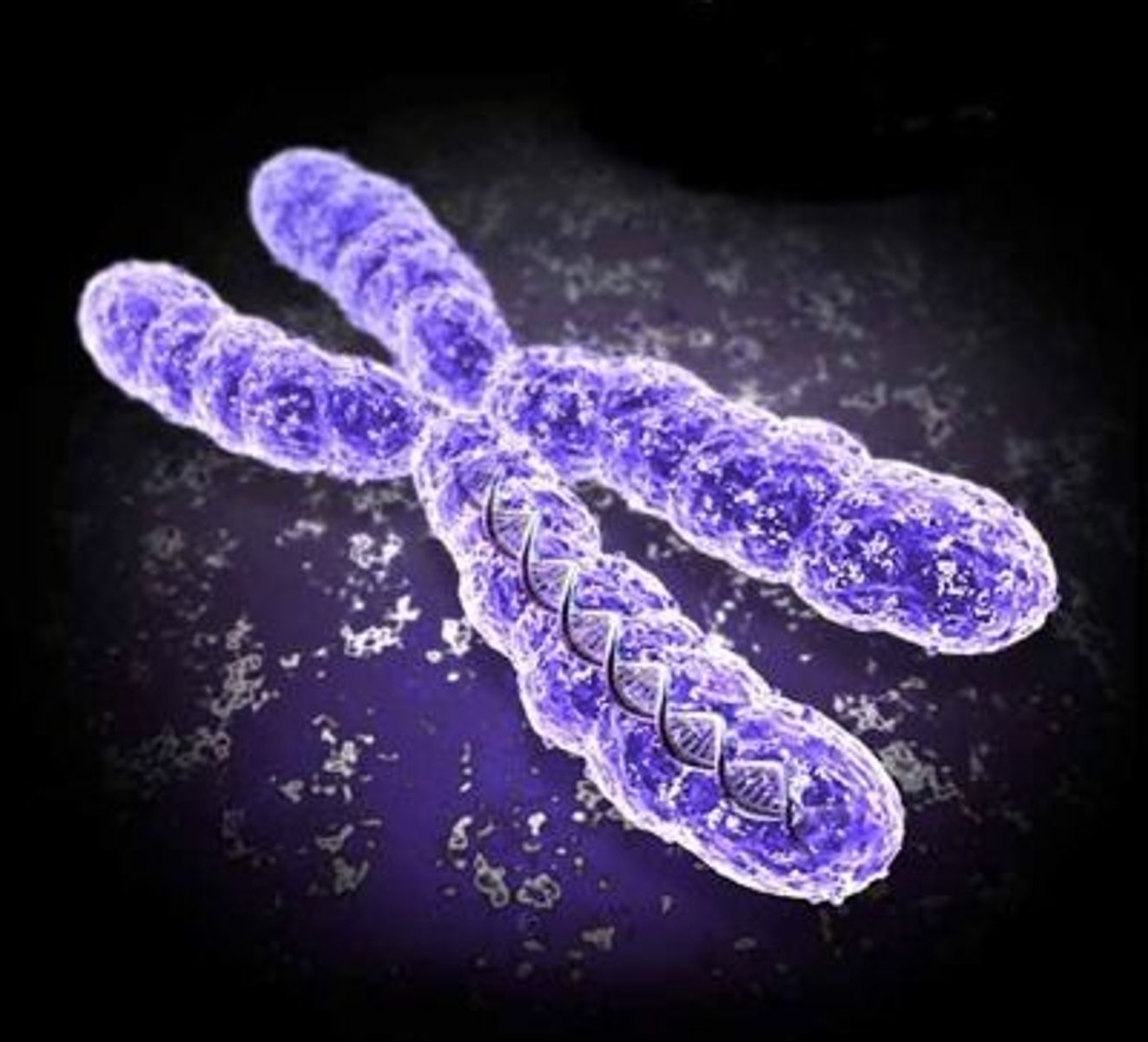
Chromosomes
Coiled form of DNA present when the cell is preparing to divide
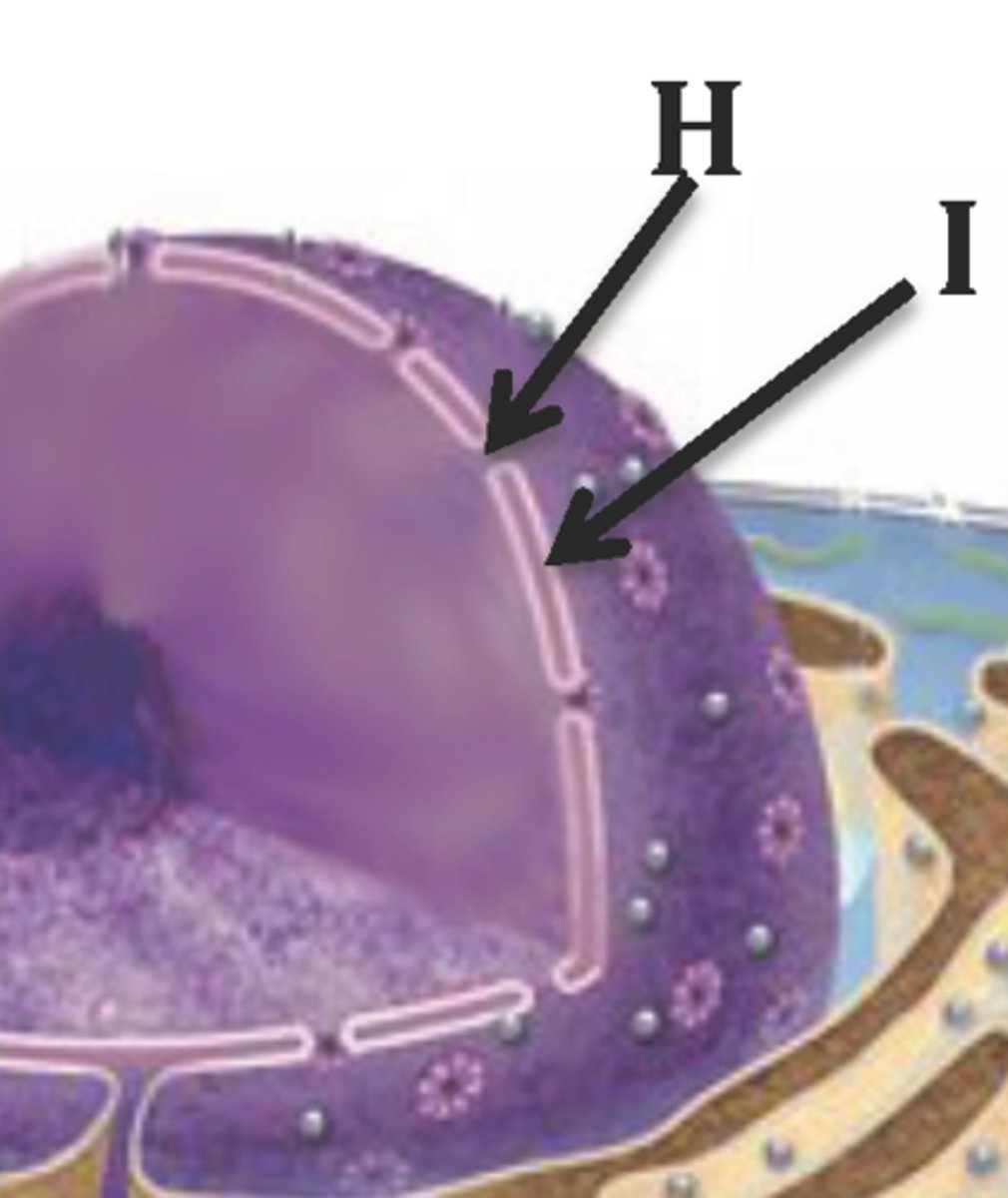
Nuclear pore
Small openings in the nuclear envelope that allows passage of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and messenger RNA (mRNA)
Cytoplasm
Gel-like substance that holds the contents of the cell
Cytosol
Watery portion of the cytoplasm
Cytoskeleton
Network of protein fibers that provides structural support; aides in cell movement and movement of vesicles within the cell
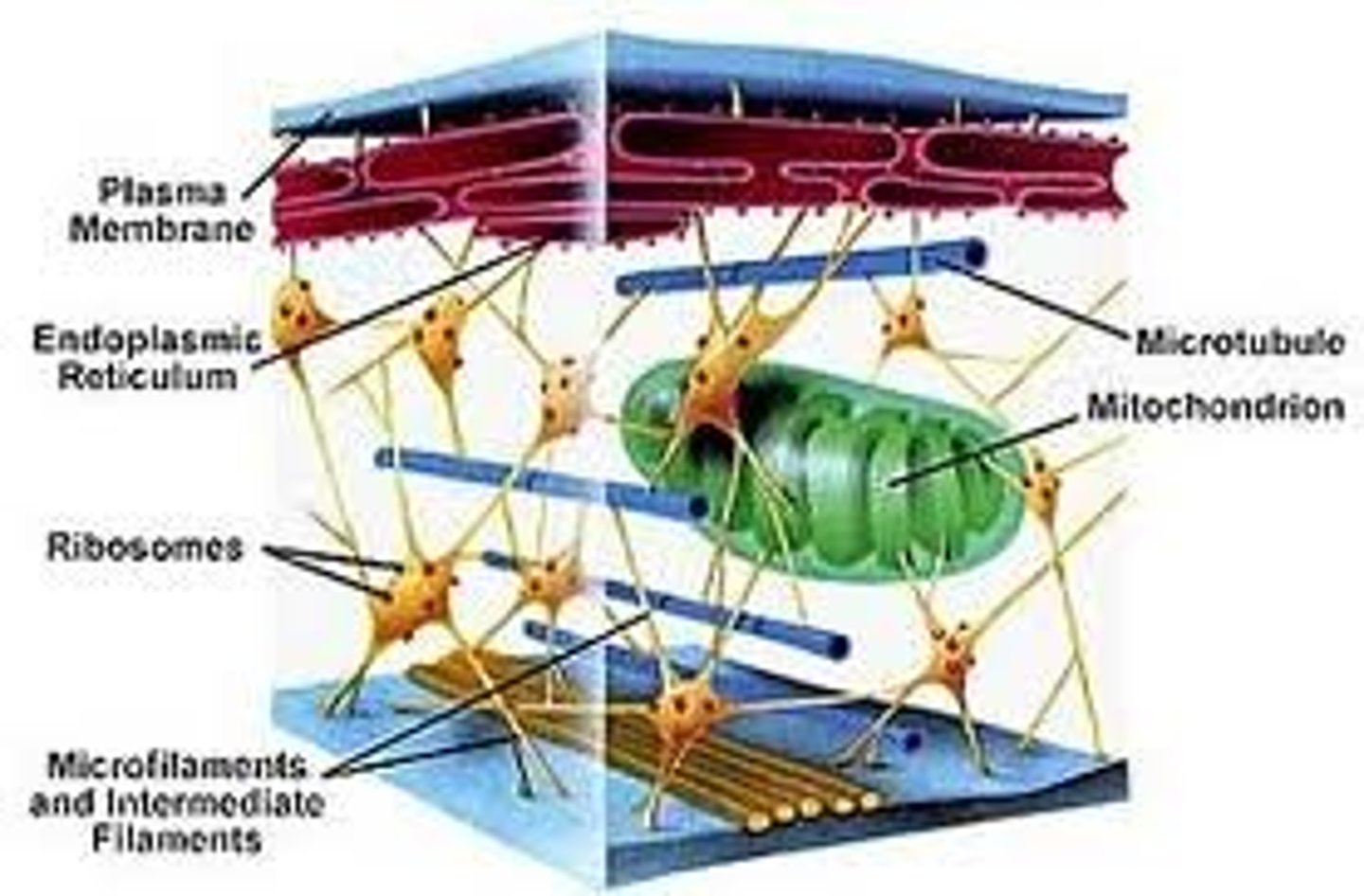
Endoplasmic reticulum
Extensive network of membrane-bound tubules and sacs that can be classified as rough or smooth; continuous with the nuclear envelope; provide compartments and surface area for reactions to occur
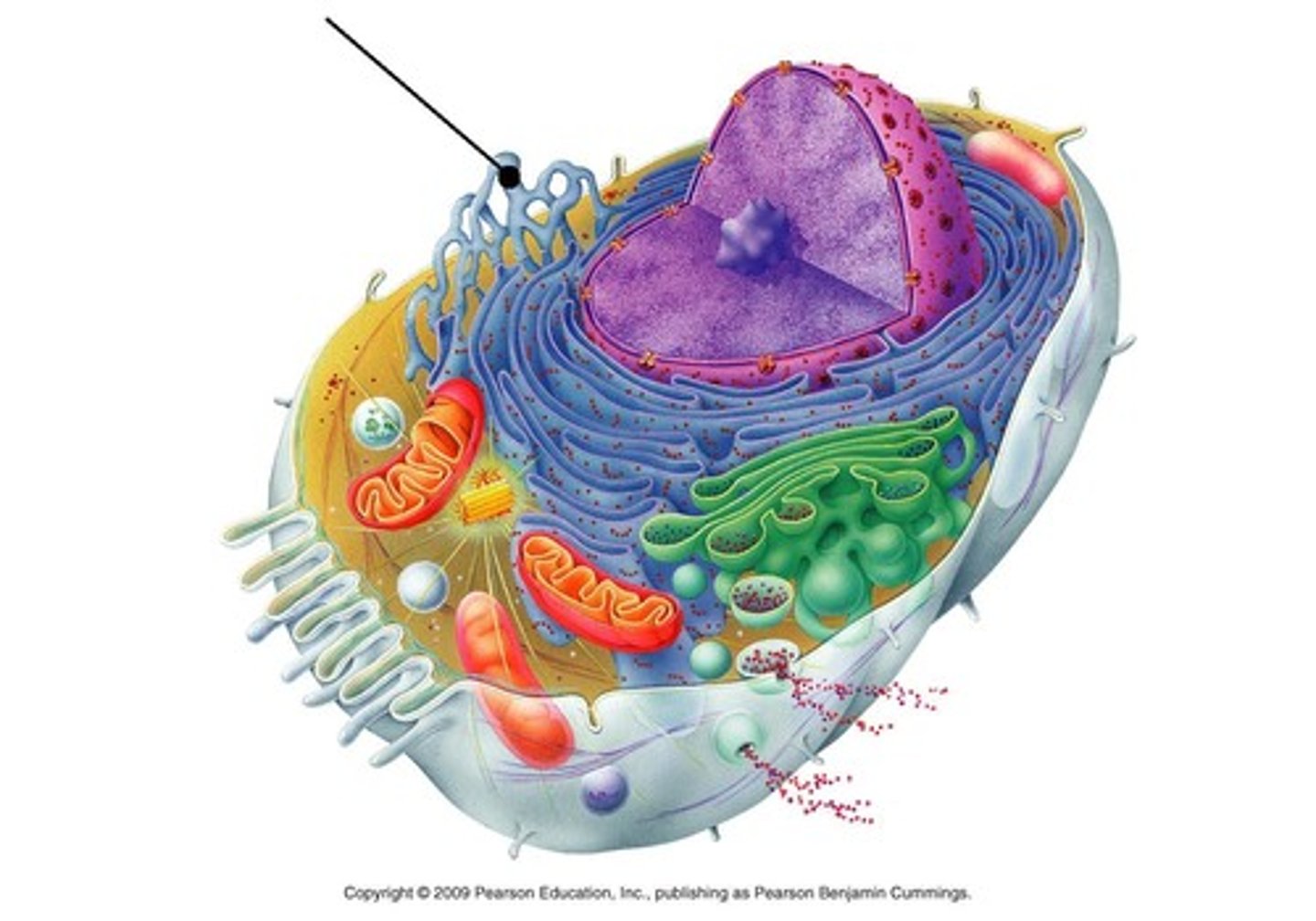
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER)
System of folded membranes that do NOT contain ribosomes; site of lipid synthesis: (Structure B)
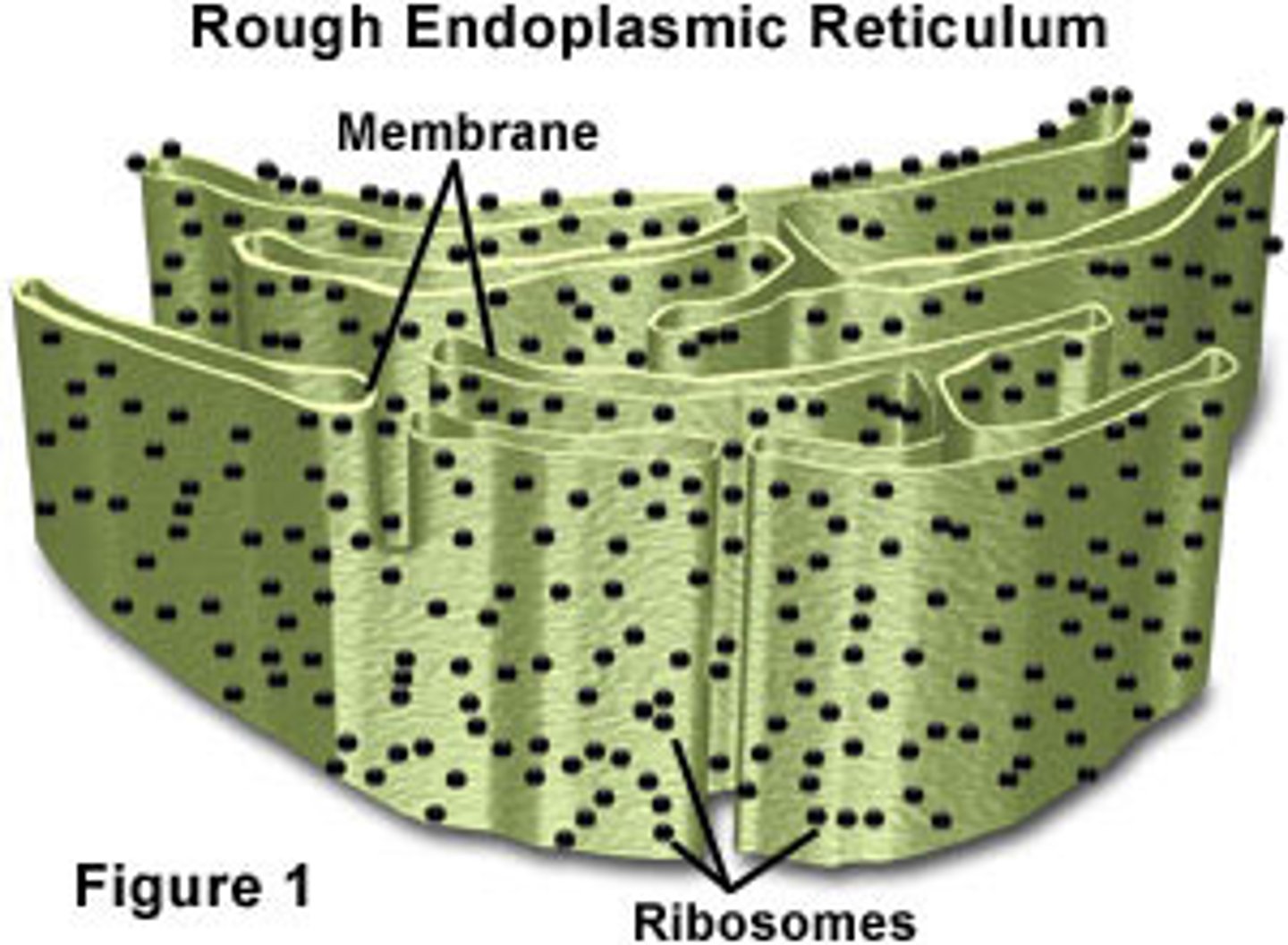
Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)
System of folded membranes that DO contain ribosomes that look like dots on the surface, site of protein synthesis; (Structure A)
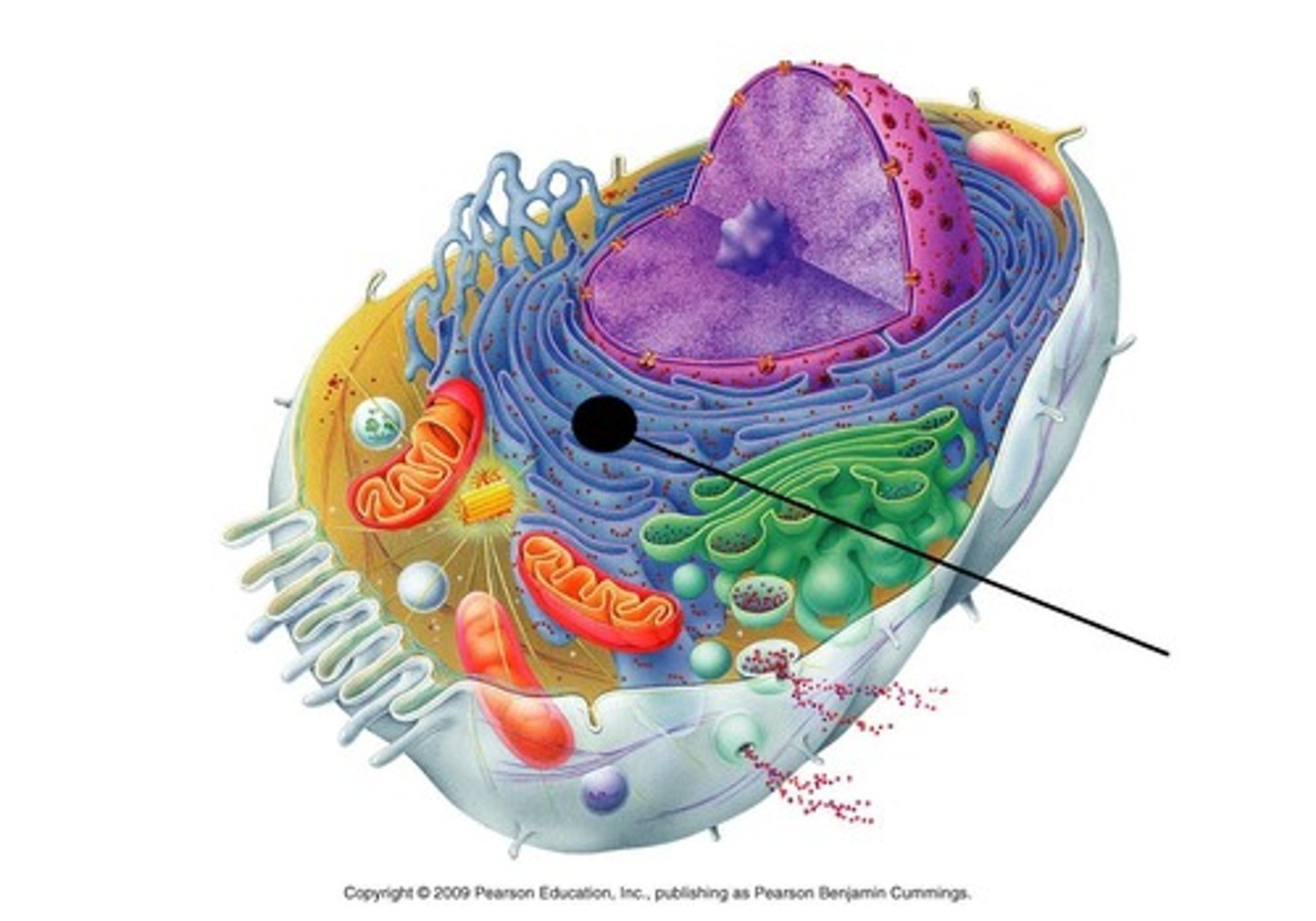
Golgi apparatus
Series of flattened membrane sacs that modifies, warehouses, sorts, and ships the proteins that are produced by the rough endoplasmic reticulum;
has two sides; Cis side (enter) and trans side (exit);
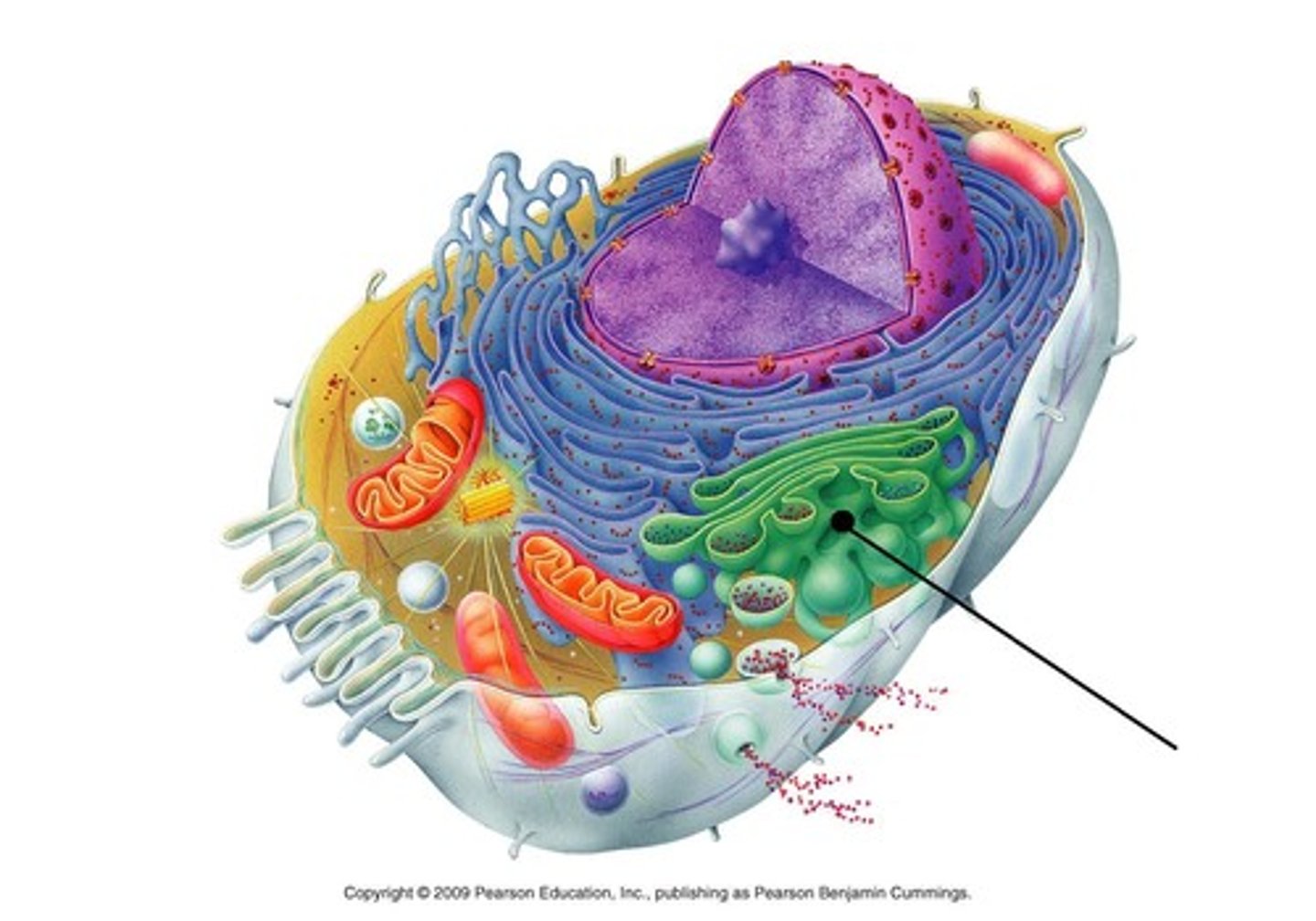
Vesicle/vacuole
Membrane covered sac that can store water, food, enzymes, etc. and transport material from one part of the cell to another
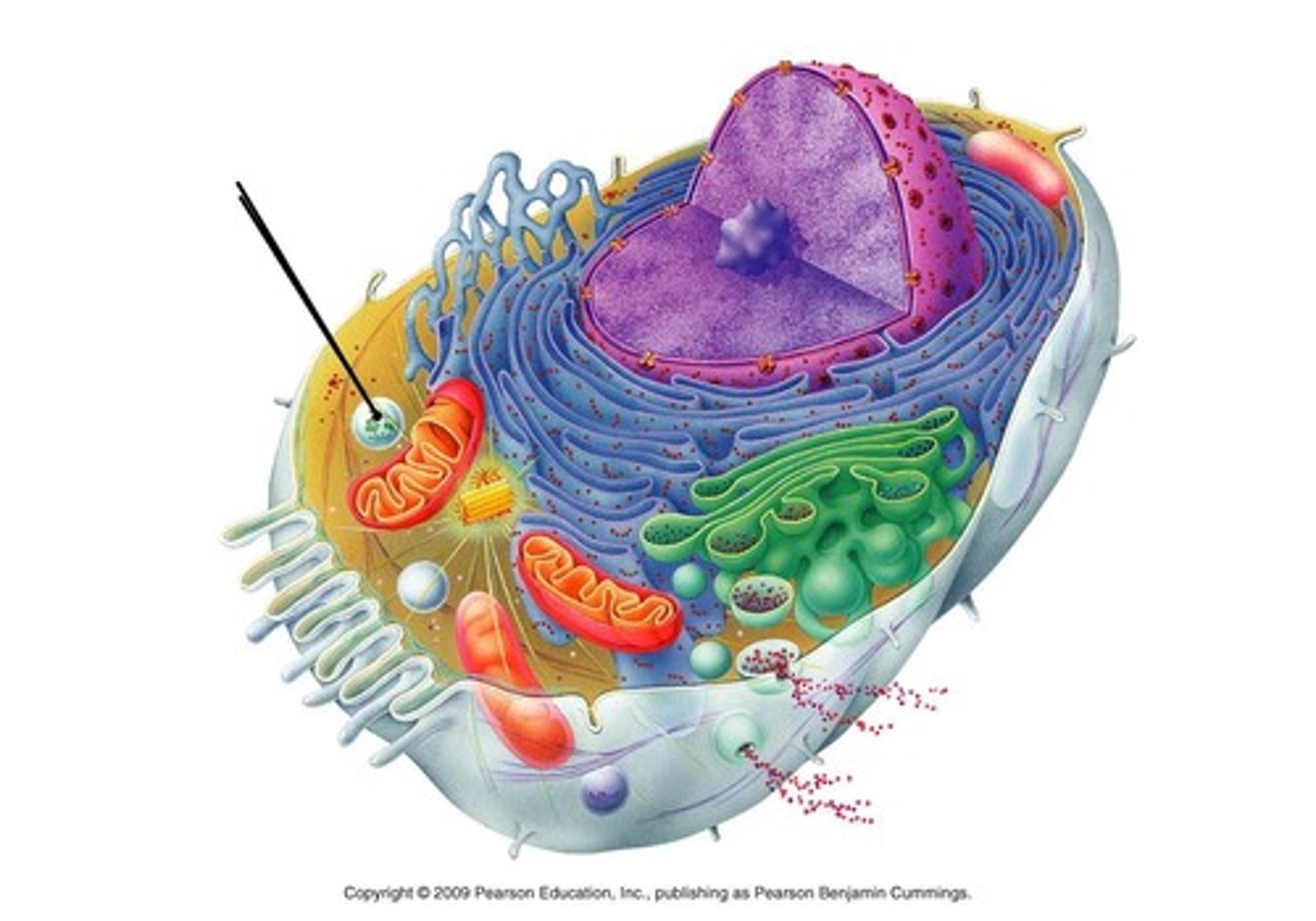
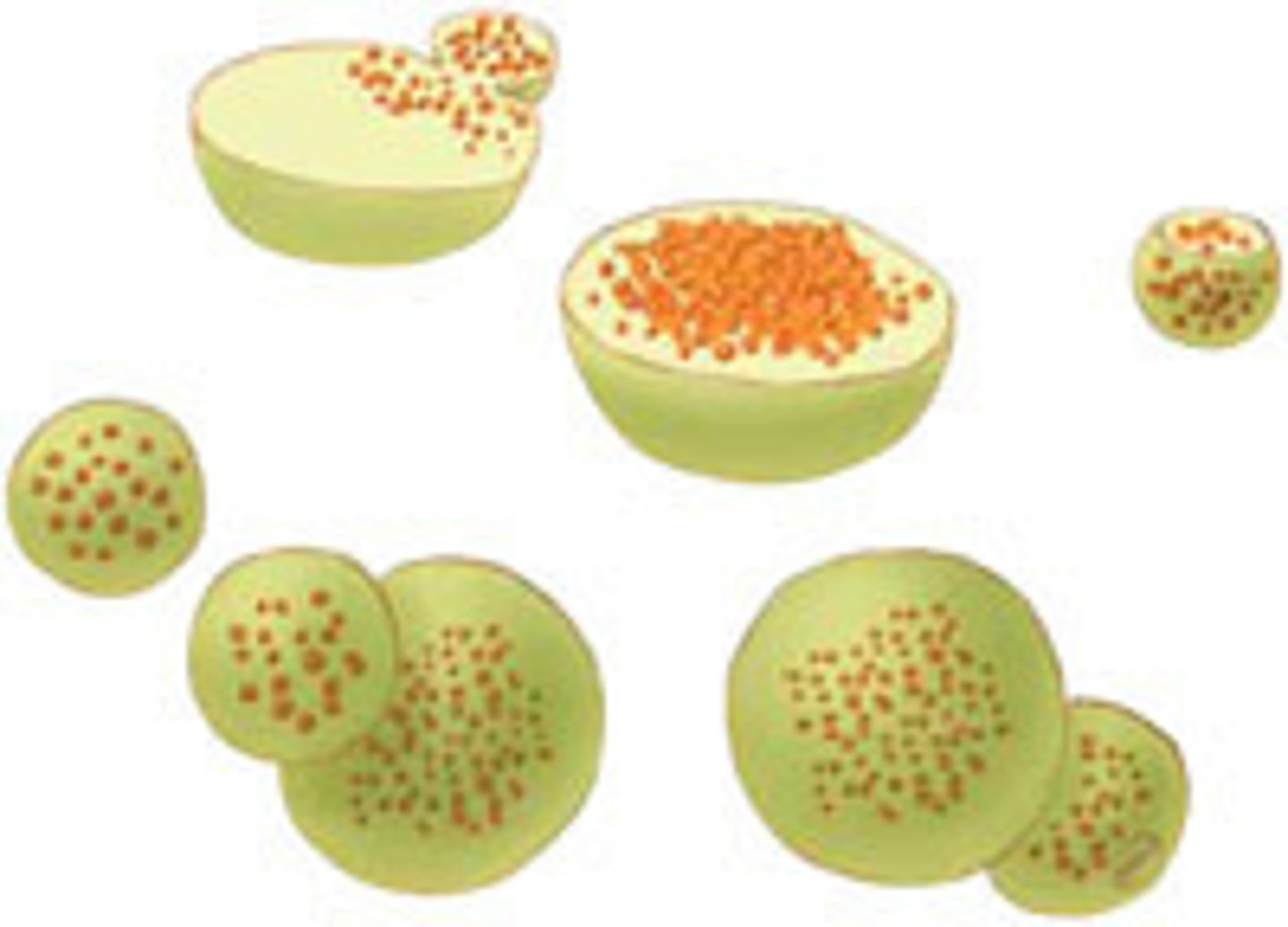
Lysosomes
Membrane bound sacs derived from the Golgi that contain digestive enzymes that break down food, dispose of worn out organelles or destroy bacteria and viruses
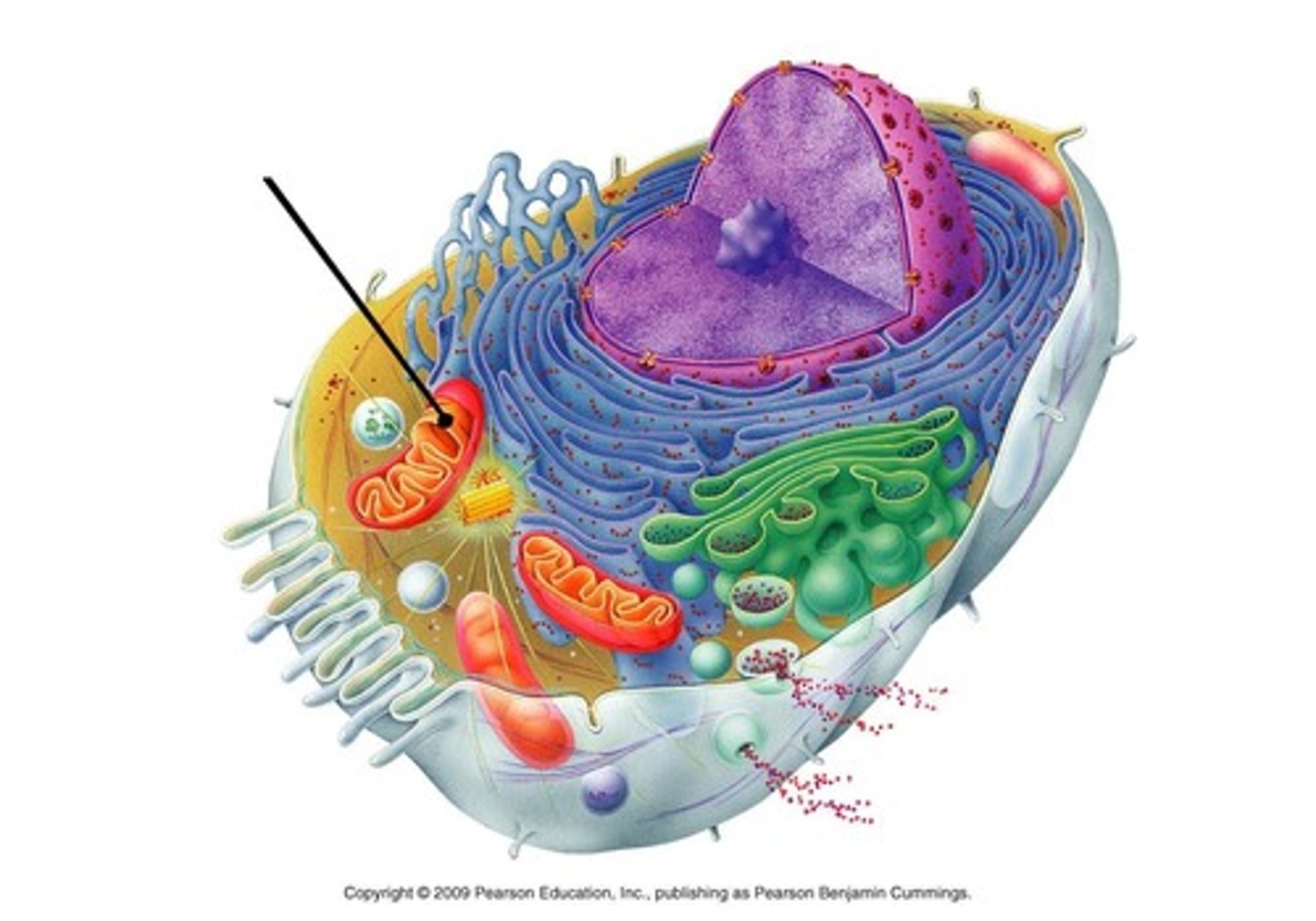
Mitochondria
Kidney bean shaped double-membrane bound organelle that converts energy from food into ATP; often called the "powerhouse of the cell"; site of cellular respiration; largest of organelles; inner folded membrane called cristae increases surface area; number vary based upon cell type and energy requirements
Chloroplast
Double-membrane bound organelle found in plants where photosynthesis occurs
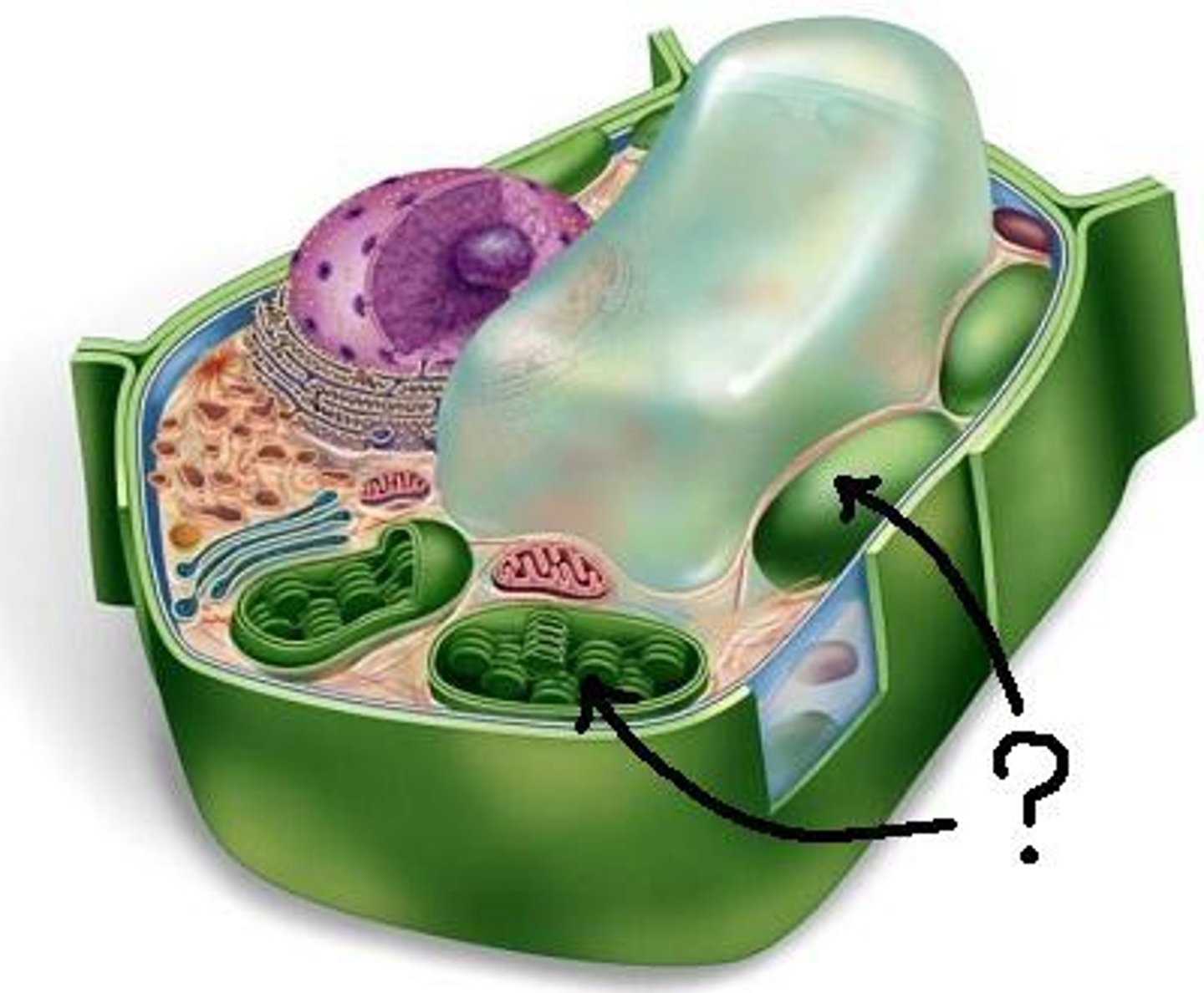
Centrioles
Found only in animal cells; serve as an organizing center for microtubules called spindle fibers that are involved in cell division
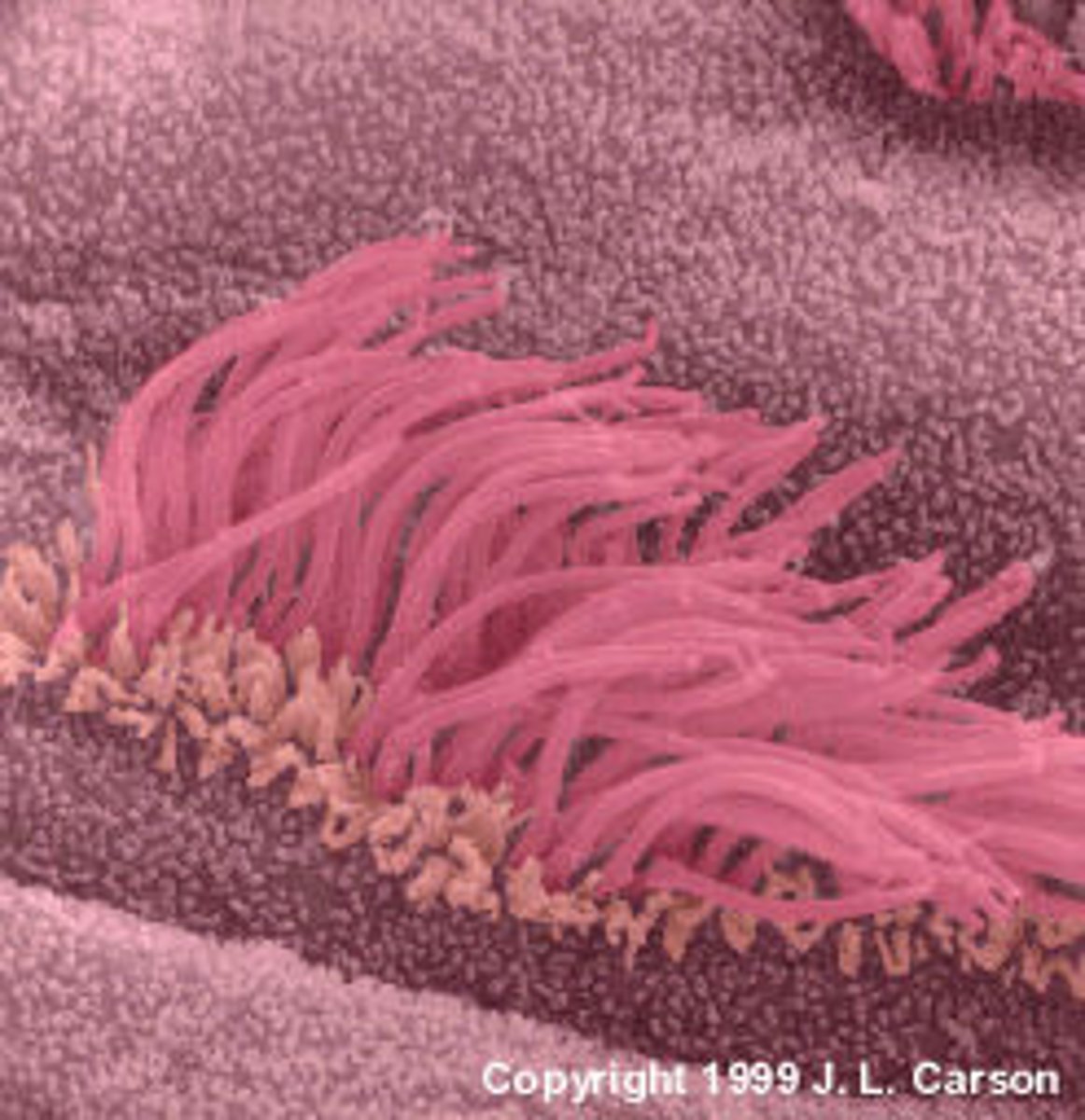
Cilia
Numerous, short cellular hair-like extensions that move in a wave-like motion; aides in movement of organism or fluids over the surface
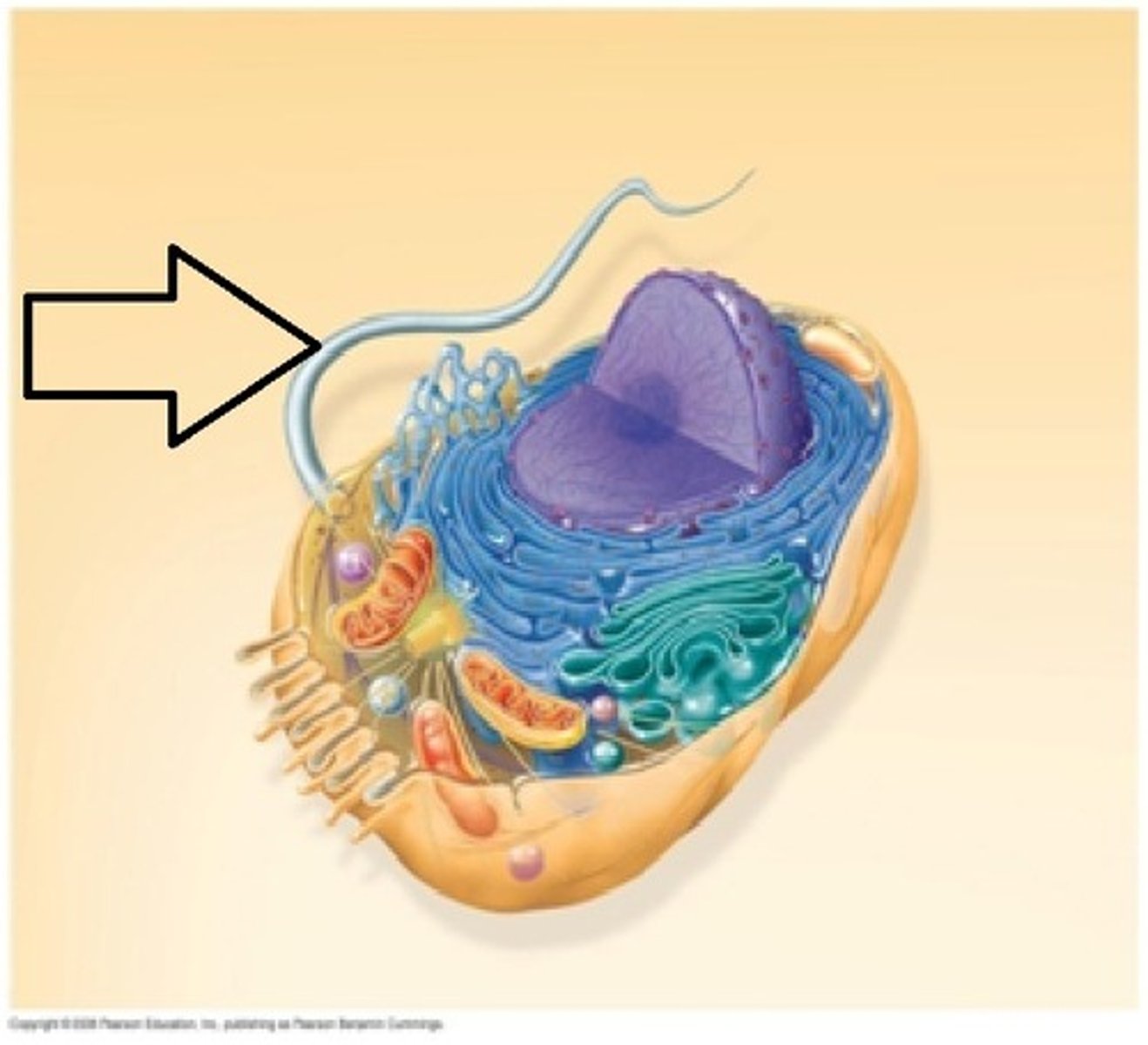
Flagella
Long cellular extensions that move in a whip-like motion; aides in movement of cell or organism; typically only a few are present
Plasma membrane
Selectively permeable phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins that surrounds the cell and regulates what enters and leaves the cell; also called the cell membrane
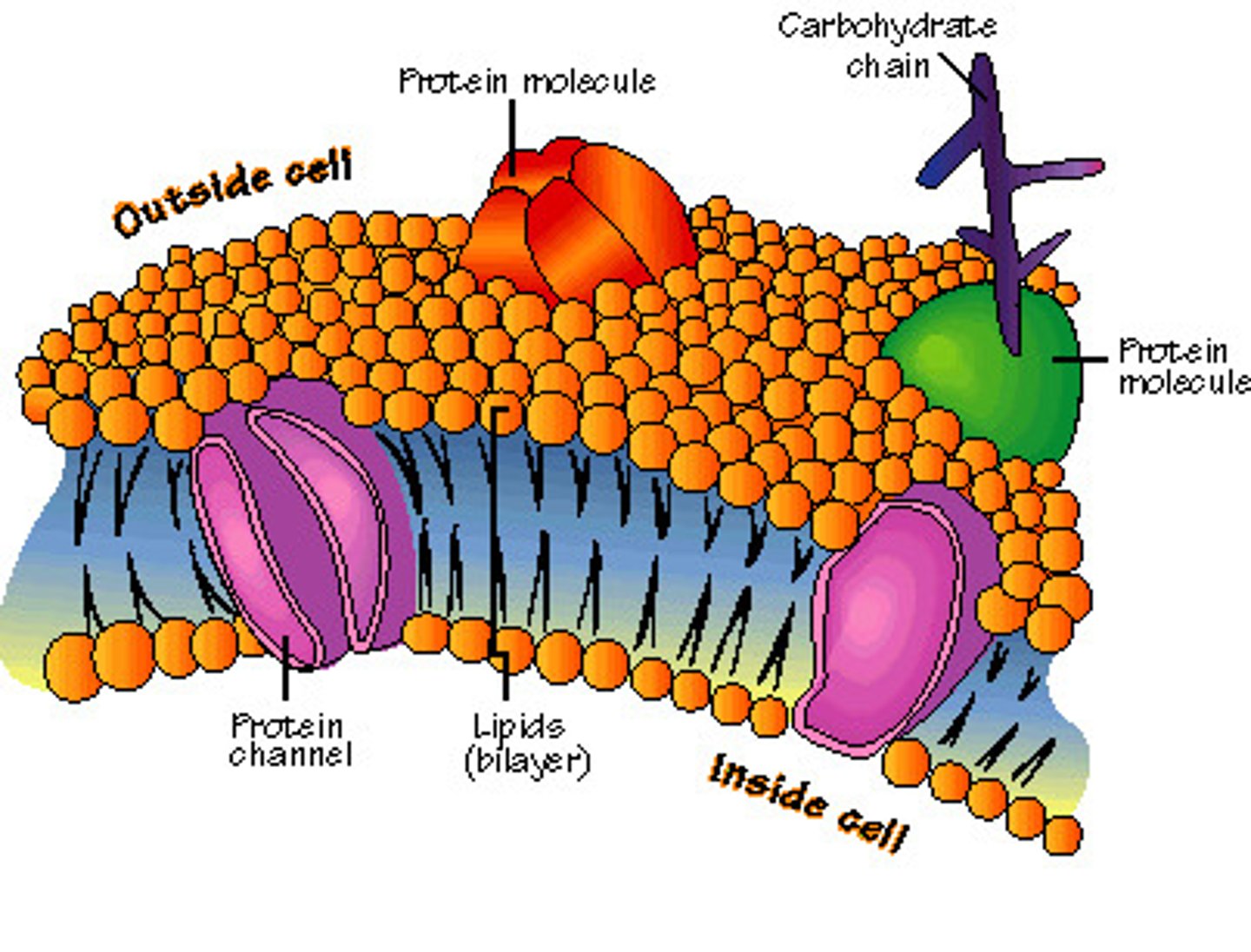
Membrane proteins
Proteins embedded in the plasma membrane that can aide in transport, serve as enzymes or marker proteins; can aide in cell-to-cell communication or provide structural support
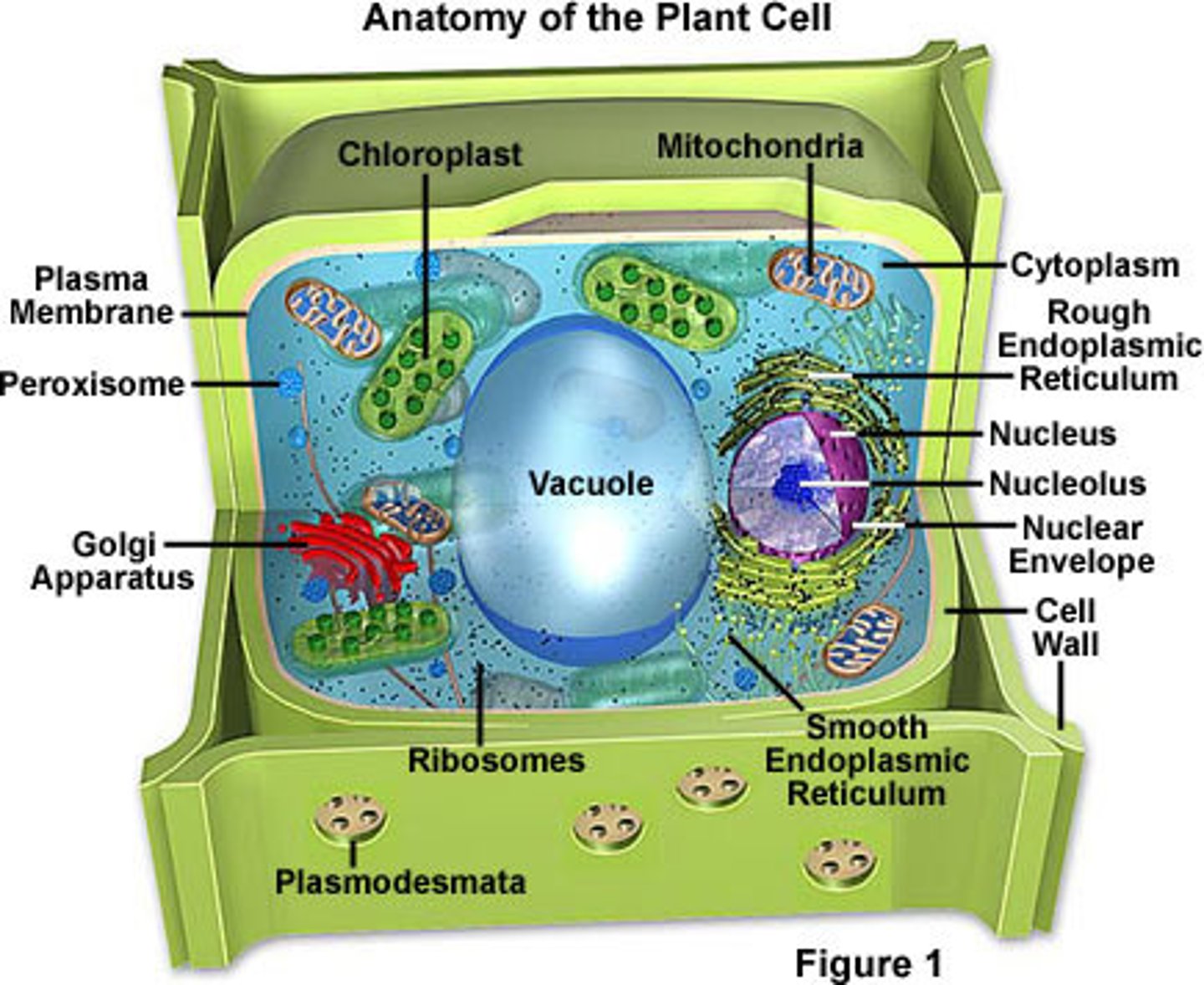
Plant Cell
Cells that unlike animal cells contain chloroplasts, a large central vacuole, and a cell wall
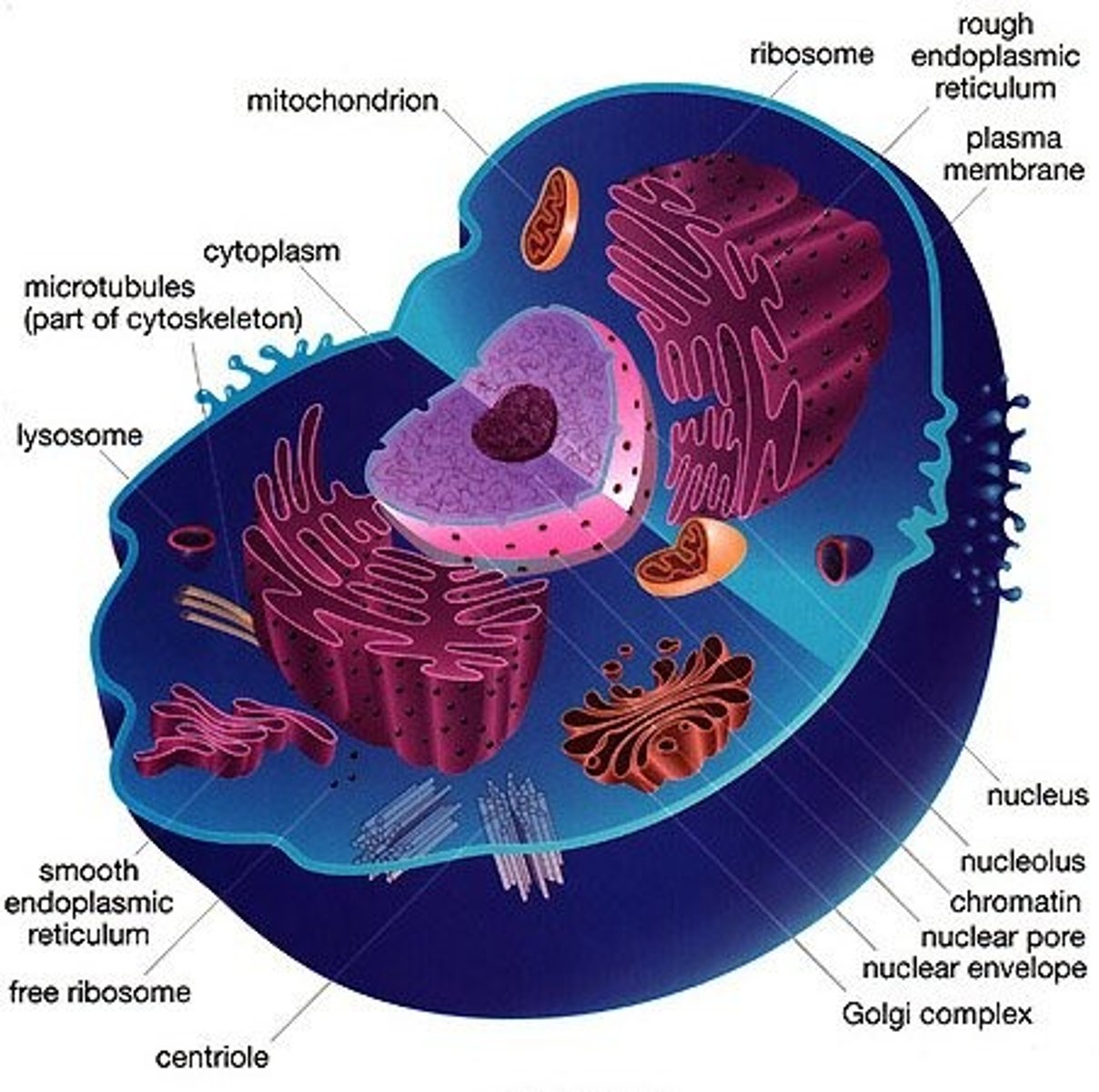
Animal Cell
Cells that unlike plant cells contain centrioles and lysosomes
Eukaryotic cells
Any organism whose cells contain a nucleus and other organelles enclosed within membranes, Can be unicellular or multicellular
Organelle
Any of the membrane-enclosed structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform specific structures. Examples include the nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, and mitochondria.