Week 7 Pelvis, Gluteal Region, and Hip
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
boundaries of gluteal region
iliac crest, intergluteal cleft, gluteal fold
bony pelvis
consists of sacrum, coxa, coccyx
Coxa
consists of the ilium, ishium, and pubis
not fully fused until 20-25 yo
ilium
largest part, forms superior acetabulum
medial portions thick for weight bearing, thin ala for muscle attachment
iliac crest for muscle attachment and protection
anterior, posterior and inferior gluteal lines
auricular surface (medial, below PSIS)
ischium
forms postero-inferior border of acetabulum
ischiopubic ramus defines boundary of obturator foramen
ischial spine on posterior between greater and less sciatic notch
ischial tuberosity on posterior surface underneath spine, provides WB support when sitting
pubis
forms anteromedial border of acetabulum
attachment site for medial thigh muscles
comprised of body and superior/inferior rami; articulates at pubic symphysis
forms pubic crest for abdominal muscle attachment
sacrum
formed by 5 fused sacral vertebrae
sacral canal which houses cauda equina and 4 pairs of sacral foramina for spinal nerve exit
base formed by S1, surrounded by sacral promontory
articulates with L5 vertebra at lumbosacral angle (130-160 degrees)
sacral cornua: bump on either side of sacral hiatus (bottom opening)
lateral surface with auricular shape for articulation with ilium at sacroiliac joint, covered with hyaline cartilage
coccyx
composed of 4 fused coccygeal vertebrae
rep remnants of embryonic tail
first vertebra may remain separate with cornua that articulates with sacral cornua
can fuse further with age, results in beak like shape
posterior sacro-iliac ligament
spans from the posterior surface of the sacrum to the sacrotuberous ligament
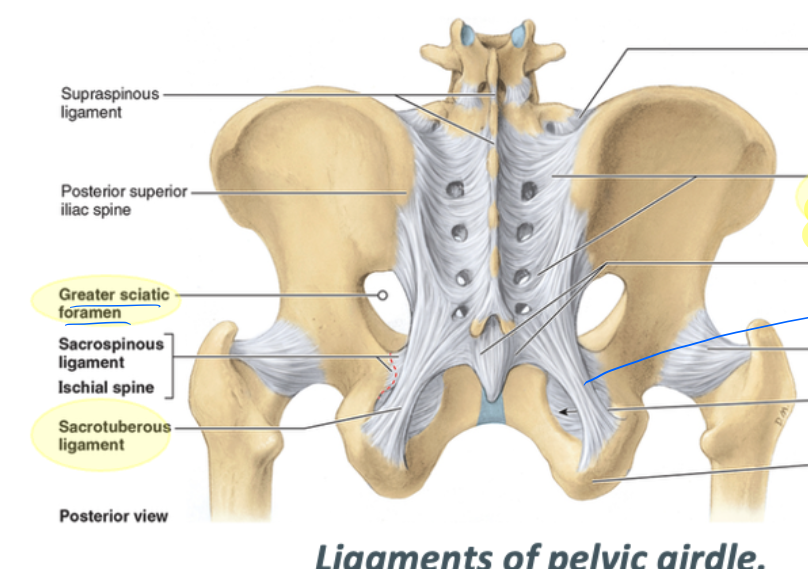
sacrotuberous ligament
spans from the posterior sacroiliac ligament to the ischial tuberosity
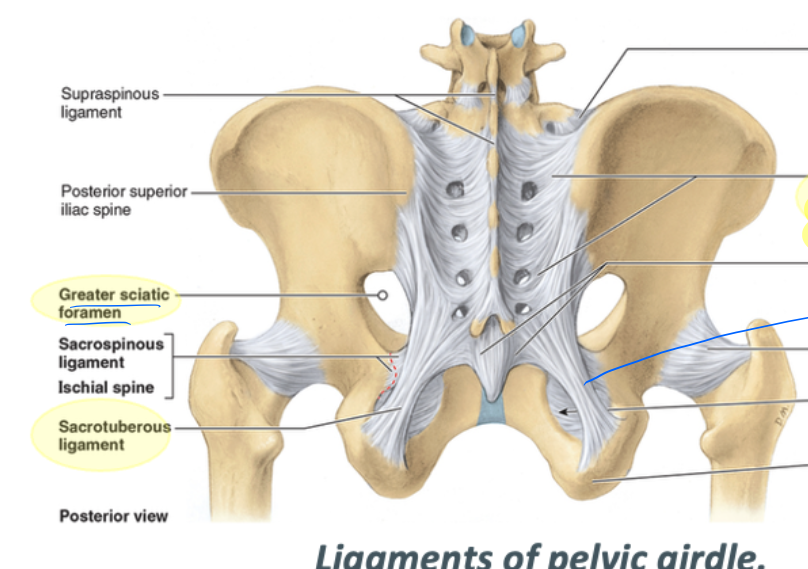
greater sciatic foramen borders
supero-inferior: greater sciatic notch
medial: sacrum
inferior: sacrospinous ligament
structures that pass through the greater sciatic foramen
sciatic nerve, pudendal nerve, nerve to quadratus femoris, nerve to obturator internus, posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh, superior and inferior gluteal nerves and arteries
lesser sciatic foramen borders
lateral: lesser sciatic notch
superior: sacrospinous ligament
inferiomedial: sacrotuberous ligament
structures that pass through the lesser sciatic foramen
pudendal nerve, obturator internus, nerve to obturator internus
sacrospinous ligament
spans from posterior sacrum to the ischial spine
pelvic girdle
formed by sacrum, left and right hip bones, connects to axial skeleton and supports abdomen, pelvis, perineum
functions in weight transmission by transmitting weight from vertebral column to the femurs via hip joints
hip region
over the greater trochanter and extends to the ASIS
Hip/Acetabulofemoral/Coxofemoral Joint
strong, multiaxial ball and socket
2nd most moveable joint
weight transmission
femoral head in acetabulum, most of head covered by articular cartilage except for small fovea that has a ligament that houses artery to supply blood to hip joint
acetabular labrum
deepens the acetabulum by 10%
transverse acetabular ligament
bridges the notch of the acetabular articular area
optimal congruence vs mobility
though optimal congruence of the hip is at 90 degrees flexion, 5 degrees abduction, and laterally rotated 10 degrees, and upright mobility sacrifices some stability, it is still highly stable bc of the deep socket, joint capsule, and muscular attachments
important features of the proximal femur
head, neck, greater trochanter, lesser trochanter, intertrochanteric line, intertrochanteric crest, gluteal tuberosity (posterior, below intertrochanteric crest)
hip joint capsule
comprised of an outer fibrous later and an inner synovial membrane, fibrous layer attaches to acetabulum and femoral neck at intertrochanteric line, contains spiraling fibers and orbicular zone around neck
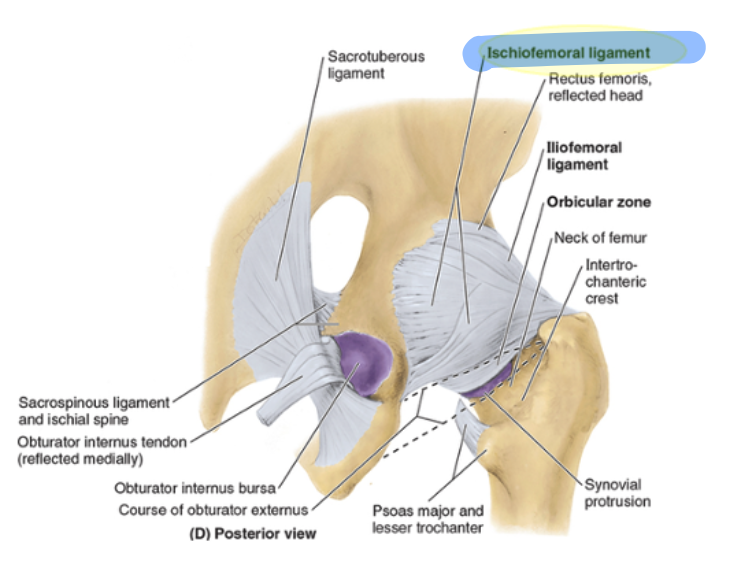
iliofemoral ligament
y shaped, prevents hyperextension, and anchors femoral head
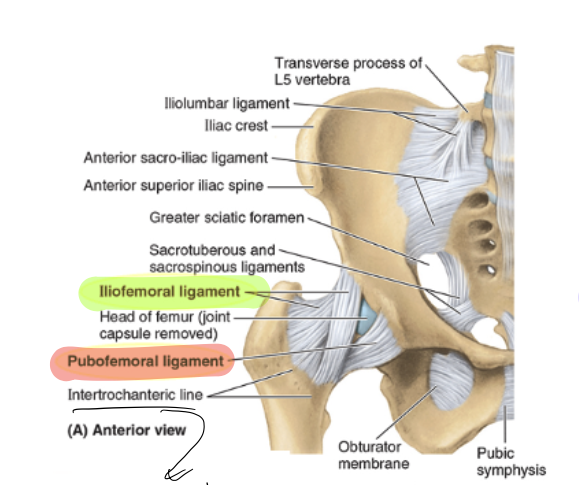
pubofemoral ligament
arises from the pubic bone, prevents over-abduction, tightens during extension/abduction
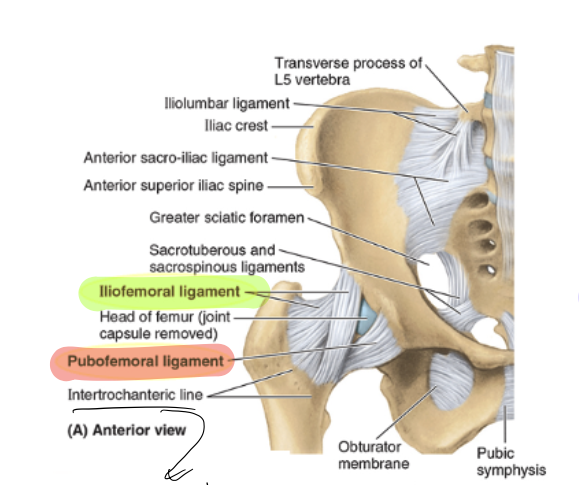
ishiofemoral ligament
weakest, spirals from ischium to femoral neck, tightens during flexion, internal rotation (adduction probably?)
stabilizing forces on the hip joint
ligaments and medial rotators
synovial membrane of hip joint
lines inner surfaces, contains retinacula with blood vessels
ligament of the head of the femur
conducts a small artery, minor role in joint strength
fat pad
located in acetabular fossa, accommodates joint movement, cushions
abduction vs adduction
abduction more extensive, with approx 60 degrees possible
superficial layer of gluteal region
gluteus maximus, medius, minimis, tensor fascia latae
attachment of superficial gluteal muscles
external surface of ilium
deep layer of gluteal region
piriformis, obturator internus, superior gemelus, inferior gemelus, quadratus femors
action and attachment of deep layer
lateral rotation of thigh and stabilization of hip, near the intertrochanteric crest of the femur
gluteus maximus
O: ilium posterior to posterior gluteal line; dorsal surface of sacrum and coccyx, sacrotuberous ligament
I: iliotibial tract, which inserts into lateral condyle of tibia, some fibers on gluteal tuberosity
Inn: inferior gluteal n (L5, S1, S2)
A: extends hip joint, and assists in lateral rotation, fixes hip and assists in rising from sitting position
gluteus medius
O: external surface of ilium between anterior and posterior gluteal lines
I: lateral surface of greater trochanteric line
Inn: superior gluteal. n (L5, S1)
A: abducts and medially rotate hip; keep pelvis level when ipsilateral limb is WB and advance opposite side during its swing phase
gluteus minimus
O: external surface of ilium between anterior and inferior gluteal lines
I: anterior surface of greater trochanter of femur
Inn: superior gluteal n (L5, S1)
A: abduct and medially rotate hip, keep pelvis level when ipsilateral limb is WB and advance opposite side during its swing phase
tensor fascia latae
O: anterior superior iliac spine, anterior part of iliac crest
I: iliotibial tract, which attaches to lateral condyle of tibia
Inn: superior gluteal n (L5, S1)
A: abducts and medially rotates hip joint, keeps pelvis level when ispilateral limb is WB and advance opposite side during swing phase
piriformis
O: anterior surface of sacrum, sacrotuberous ligmment
I: superior border of greater trochanter of femur
Inn: branches to anterior rami of S1 and S2 (nerve to piriformis)
A: laterally rotates the extended hip and abduct hip when flexed, stabilize hip joint
obturator internus
O: pelvic surface of obturator membrane and surrounding bones
I: medial surface of greater trochanter of femur
Inn: nerve to obturator internus (L5, S1)
A: laterally rotate the extended hip and abduct hip joint when flexed, stabilize hip joint
superior and inferior gemeli
O: superior: ischial spine, inferior: ischial tuberosity
I: trochanteric fossa
Inn: superior: nerve to obturator internus, inferior: nerve to quadratus femoris
A: laterally rotate the extended hip and abduct the flexed hip, stabilize hip joint
quadratus femoris
O: lateral border of ischial tuberosity
I: quadrate tubercle of intertrochanteric crest of femur and area inferior to it
Inn: nerve to quadratus femoris (L5, S1)
A: lateral rotation of extended hip, abduction of flexed hip, stabilization of joint
trochanteric bursa
largest bursa, located between the greater trochanter and gluteus maximus, present at birth
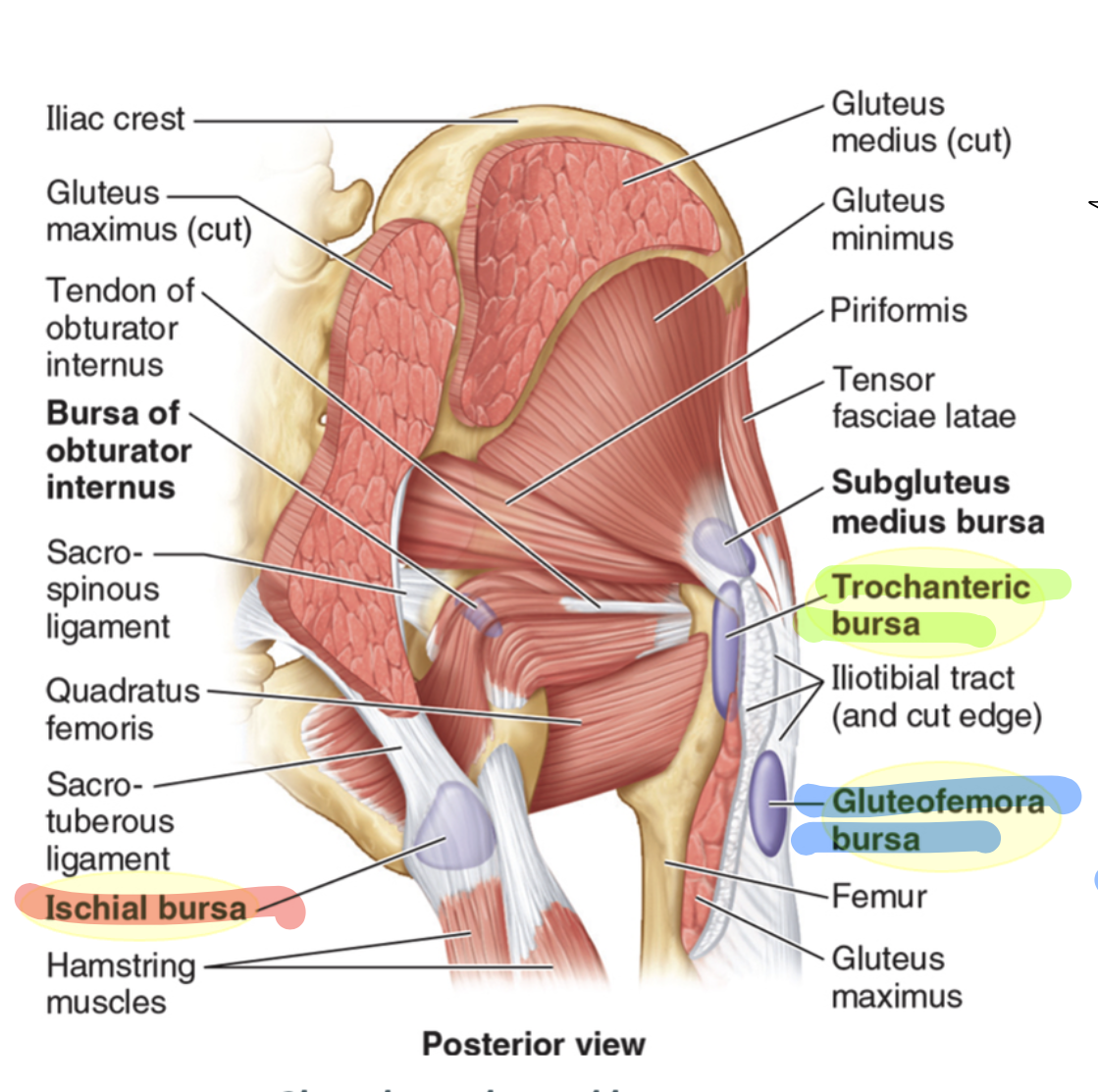
ischial bursa
separates the inferior gluteus maximus and ischial tuberosity, often absent
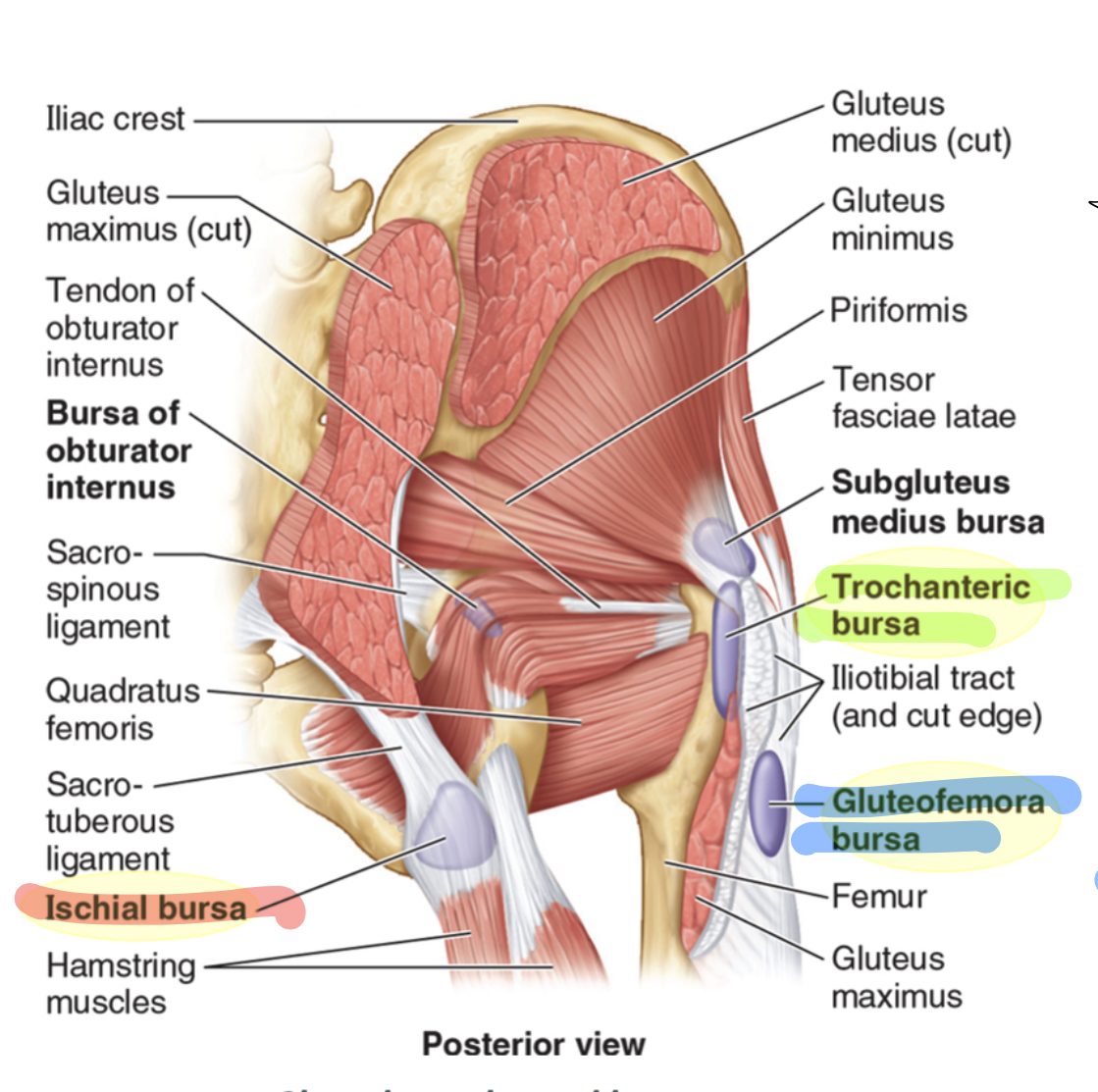
gluteofemoral bursa
located between IT tract and vastus lateralis attachment, helps facilitate movement
arterial supply of the gluteal region
abdominal aorta branches into the R and L common iliac arteries, which branches at the the start of gluteal supply to the R and L internal iliac artery and external iliac arteries. The internal iliac branches into the superior and inferior gluteal arteries, and lower the pudendal artery, the external iliac continues as the femoral artery
superior gluteal artery
branch from the internal iliac artery, enters through the greater sciatic foramen, superficial branch passes onto deep surface of gluteus maximus, deep branch travels between medius and minimus
inferior gluteal artery
branches from internal iliac artery, enters through greater sciatic foramen, supplies (inferior) gluteus maximus, piriformis, and quadratus femoris, anastomoses with SGA
medial and lateral circumflex femoral arteries
supply the hip joint, as branches of the profunda femoris or the femoral artery itself
artery to the head of the femur
variable sized branch from the obturator artery, supplies the head of the femur (aka acetabular branch)
retinacular arteries
along with the circumflex femoral arteries are the primary blood supply of the hip joint, though medial CFA provides more blood and these are fewer and smaller and penetrate the iliofemoral ligament
superior and inferior gluteal veins
accompany the corresponding SGA and IGA, connect with femoral vein for alternative blood return routes from the lower limb
internal pudendal vein
drain blood from external genitalia, forms a single vein that enters internal iliac vein
perforating veins
drain blood from posterior thigh into profunda femoris vein, communicate with popliteal vein and inferior gluteal vein
deep buttock lymph
follows vessels to superior/inferior gluteal lymph nodes , then to iliac and lateral lumbar nodes
superficial lymph
from gluteal region/thigh enters superifical inguinal lymph nodes, sending efferent vessels to external iliac nodes
anteriomedial aspect of lower limb
most arterial blood and venous drainange occurs on this aspect because well protected (flexor muscles are more protected)
sacral plexus
general innervation of the gluteal region, gives rise to key nerves in the region: superior and inferior gluteal nerves, pudendal nerve, sciatic nerve
only superfical nerve from the sacral plexus
pudendal nerve
superior gluteal nerve
located between the gluteal medius and gluteus minimus, travels alongside the deep branch of the superior gluteal artery, divides into two branches: superior branch to gluteus medius, inferior to gluteus medius, minimus, and tensor fascia latae
inferior gluteal nerve
innervates gluteus maximus, exits the pelvis underneath piriformis
sciatic nerve
largest nerve in the body, supplies posterior thigh, leg, and foot muscles, branching into tibial and common fibular nerves
nerve to quadratus femoris
exits the pelvis in front of the sciatic nerve and obturator internus
passes over the posterior surface of the hip joint
provides an articular branch to the hip joint
innervates the inferior gemellus muscles and quadratus femoris
posterior cutaneous nerve of the thigh
supplies sensation to the perineum, inferior buttocks, posterior thigh, and proximal leg, lies deep to fascia lata
pudendal nerve
exits the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen
enters the perineum via the lesser sciatic foramen
supplies perineal structres
does not supply gluteal region or posterior thigh
nerve to obturator internus
arises from L5- S2, innervates superior gemellus and obterator internus, enters perineum
clunial nerves
superior, middle, and inferior clunial nerves innervate the gluteal skin
femoral nerve
hip flexors innervation
nerve to obturator internus, nerve to quadratus femoris, nerve to piriformis, IGN
hip lateral rotators innervation, IGN just to gluteus maximus
superior gluteal nerve
hip abductors innervation
iliac tubercle
can be palpated 5-6 cm posterior to ASIS, marks the widest point of the crest at the L5 vertebral level
surface anatomy of pubic bones and symphysis
located one hand’s width below the umbilicus, pubic tubercle is 2 cm from the symphysis
femoral head surface anatomy
a thumb’s breadth below the midpoint of the inguinal ligament
greater trochanter surface anatomy
palpable 10 cm below the iliac crest on the lateral thigh, indicates pelvis width
highest points of iliac crest
L4-L5
PSIS surface anatomy
located at posterior ends of iliac crest, about 3.75 cm from midline, indicated by skin dimples