Grade 9 Chemistry
1/169
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
170 Terms
Physical property
A characteristic that can be observed or measured without changing the identity of the substance
Chemical property
A property that involves the ability of a substance to react with other material to form a new substance
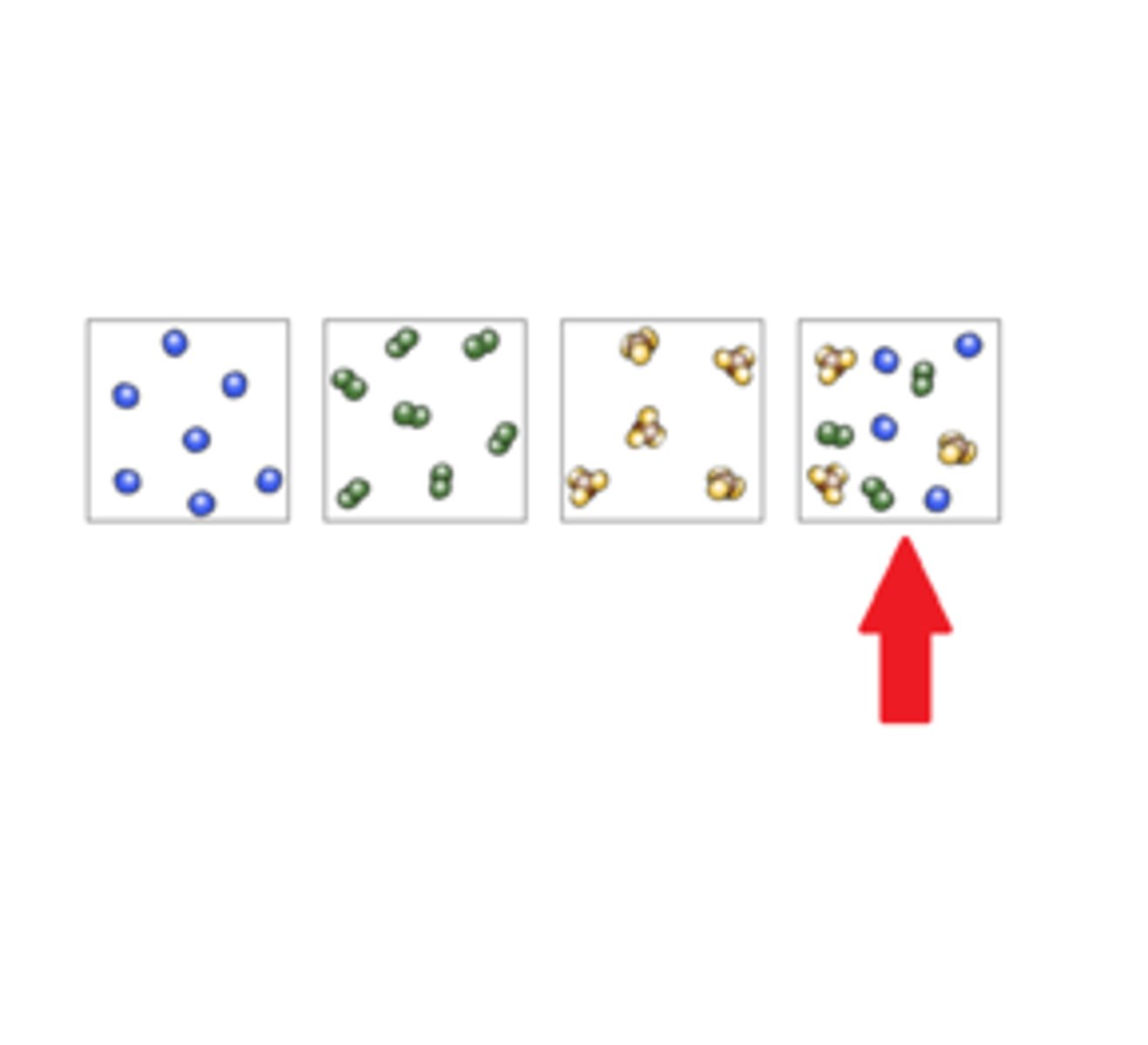
mixture
A combination of 2 or more substances that are not chemically combined.
mechanical mixture
a substances made of more than one kind of particle in which the particles are not uniformly scattered and are visible (you can see more than one substance); it is heterogeneous
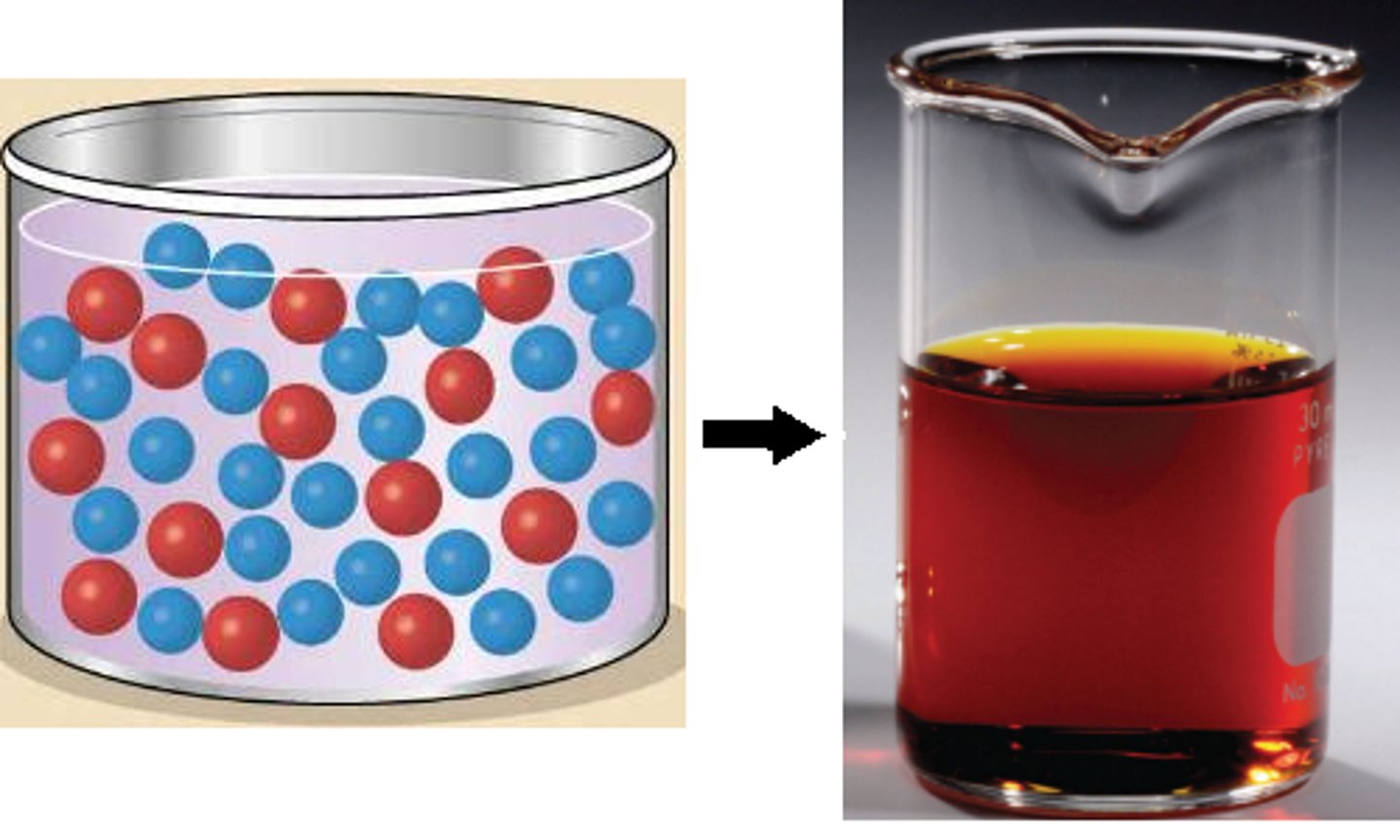
solution
A mixture that forms when one or more substances dissolve in another; it is homogeneous
pure substance
substance made of one type of particle
element
A pure substance made of only one kind of atom
compound
A pure substance made of two or more elements chemically combined
colloid
A heterogeneous mixture whose particles are in suspension and never settle down
suspension
A heterogeneous mixture that separates into layers over time
atom
Basic unit of matter.
Nucleus
the centre of the atom; it contains neutrons and protons
Proton
A subatomic particle that has a positive charge and that is found in the nucleus of an atom
Electron
A subatomic particle that has a negative charge... almost no mass, orbits nucleus
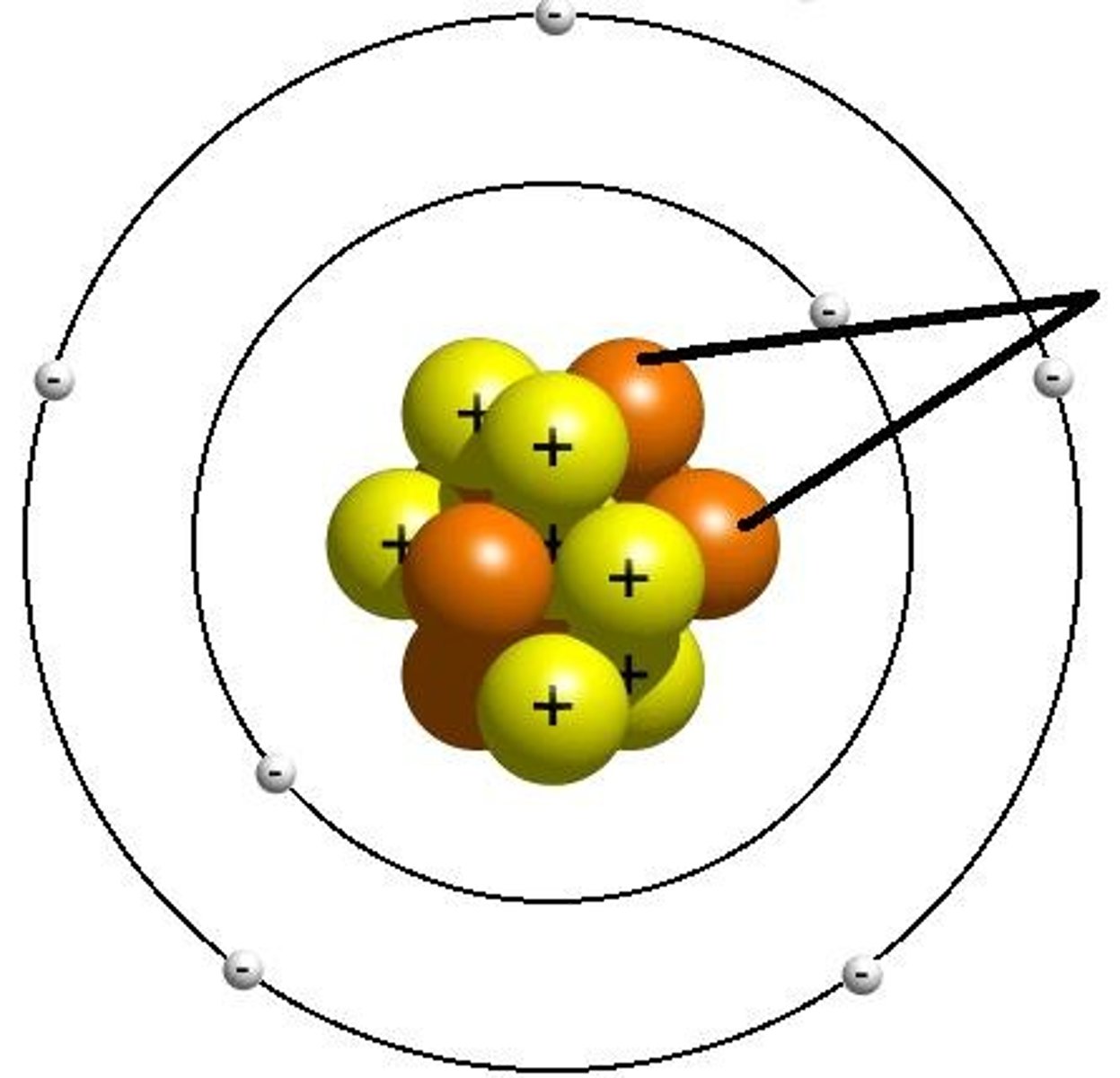
Neutron
A subatomic particle that has no charge and that is found in the nucleus of an atom
Dalton's Atomic Theory
1) elements are composed of atoms. 2) atoms of same element are identical, but differ from other elements. 3) elements can mix together 4) atoms only change when mixed with other elementsterm-95
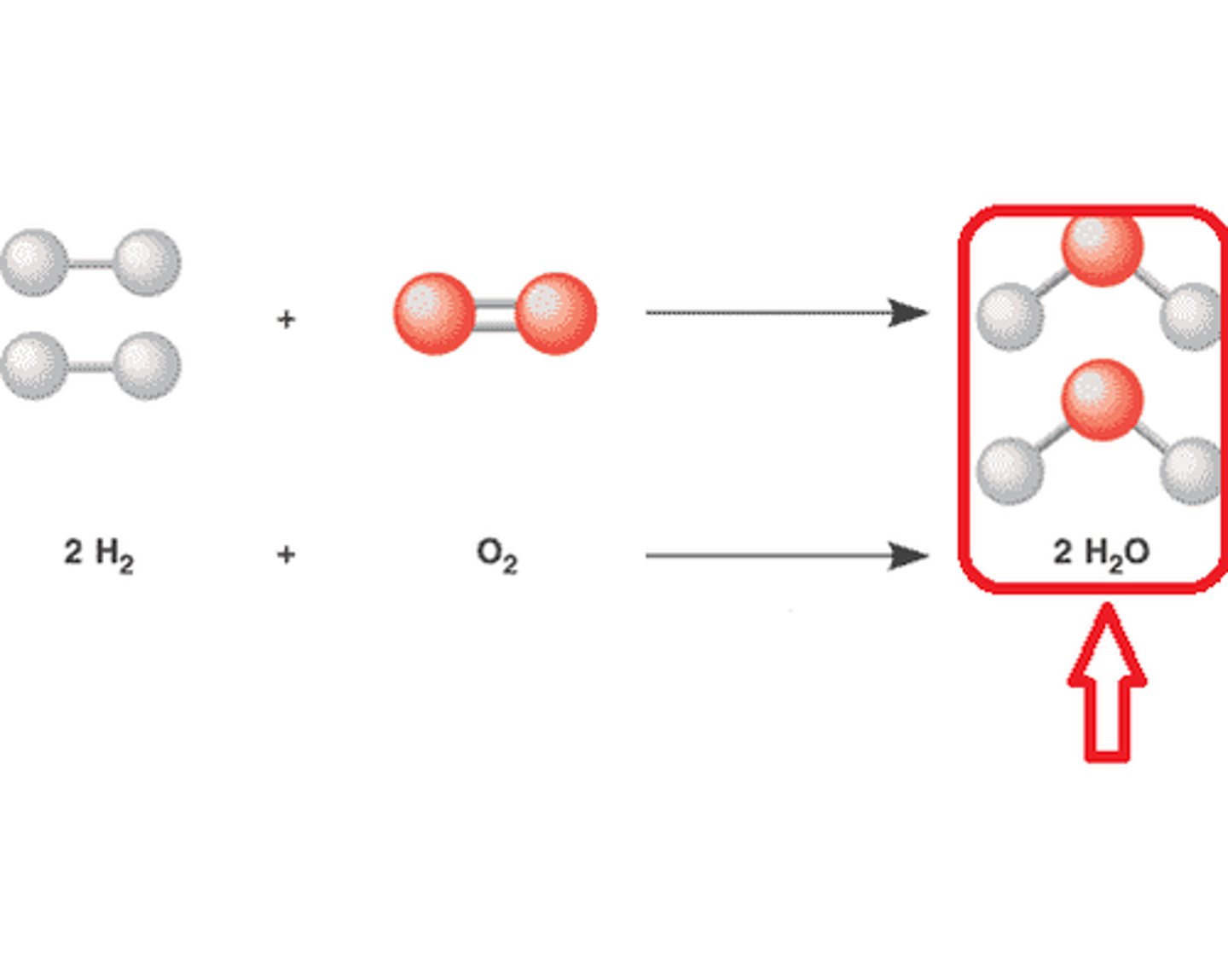
Law of conservation of mass
In a chemical reaction, the mass of the reactants are always equal to the mass of the products. Matter is not created nor destroyed in any chemical or physical change.
Law of Definite Composition
Chemical compounds are composed of a fixed ratio of elements as determined by mass.
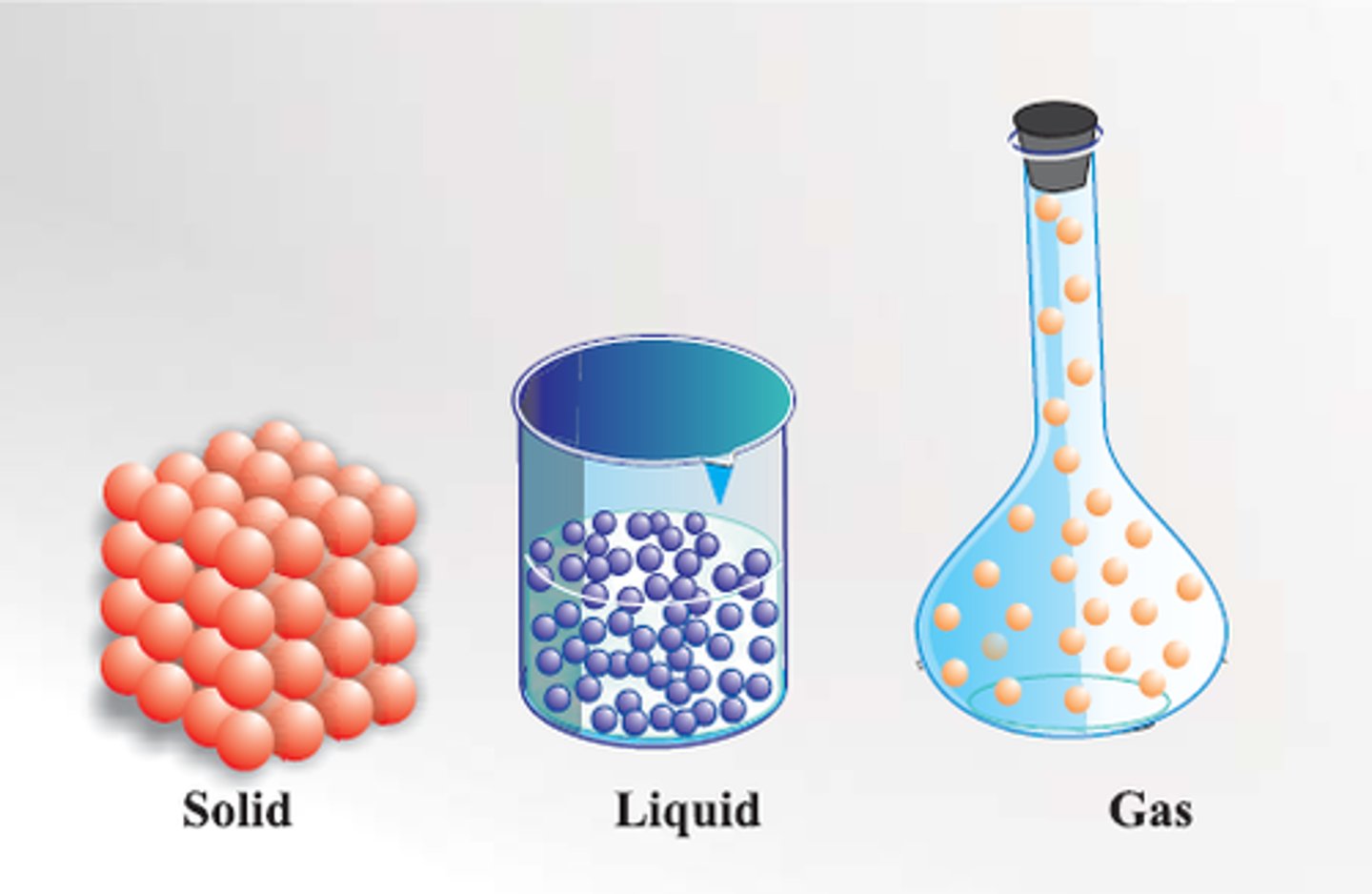
Particle Model of Matter
model that explains the behaviour of solids, liquids, and gases; it states that all matter is made up of tiny moving particles that attract each other and have spaces between them
John Dalton
English chemist and physicist who formulated atomic theory and the law of partial pressures
JJ Thomson
used the cathode ray tube to discover electrons and plum pudding model of atom
Ernest Rutherford
solar system model of the atom, gold foil experiment- fired negative ions at thin sheet of gold foil, discovered the atomic nucleus and proposed a nuclear model of the atom .
Niels Bohr
discovered that electrons move around the nucleus in orbits called electron shells.
qualitative property
a property of a substance that is not measured and does not have a numerical value, such as colour, odour, and texture
quantitative property
a property of a substance that is measured and has a numerical value, such as temperature, height, and mass
Physical change
A change that affects the appearance but not the chemical makeup of a substance.
Chemical change
A change in matter that produces one or more new substances
matter
Anything that has mass and takes up space
Molecule
A group of atoms bonded together
solubility
the ability of one substance to dissolve in another at a given temperature and pressure; expressed in terms of the maximum amount of solute that will dissolve in a given amount of solvent
lustre
shininess or dullness
malleability
Capable of being shaped without being damaged
ductility
Ability to be stretched or pulled into a wire without breaking
heterogeneous
not uniform throughout
homogeneous
Describes something that has uniform structure
Physical property

Chemical property

Physical change

Chemical change

matter
mixture

mechanical mixture
solution
pure substance
element
compound
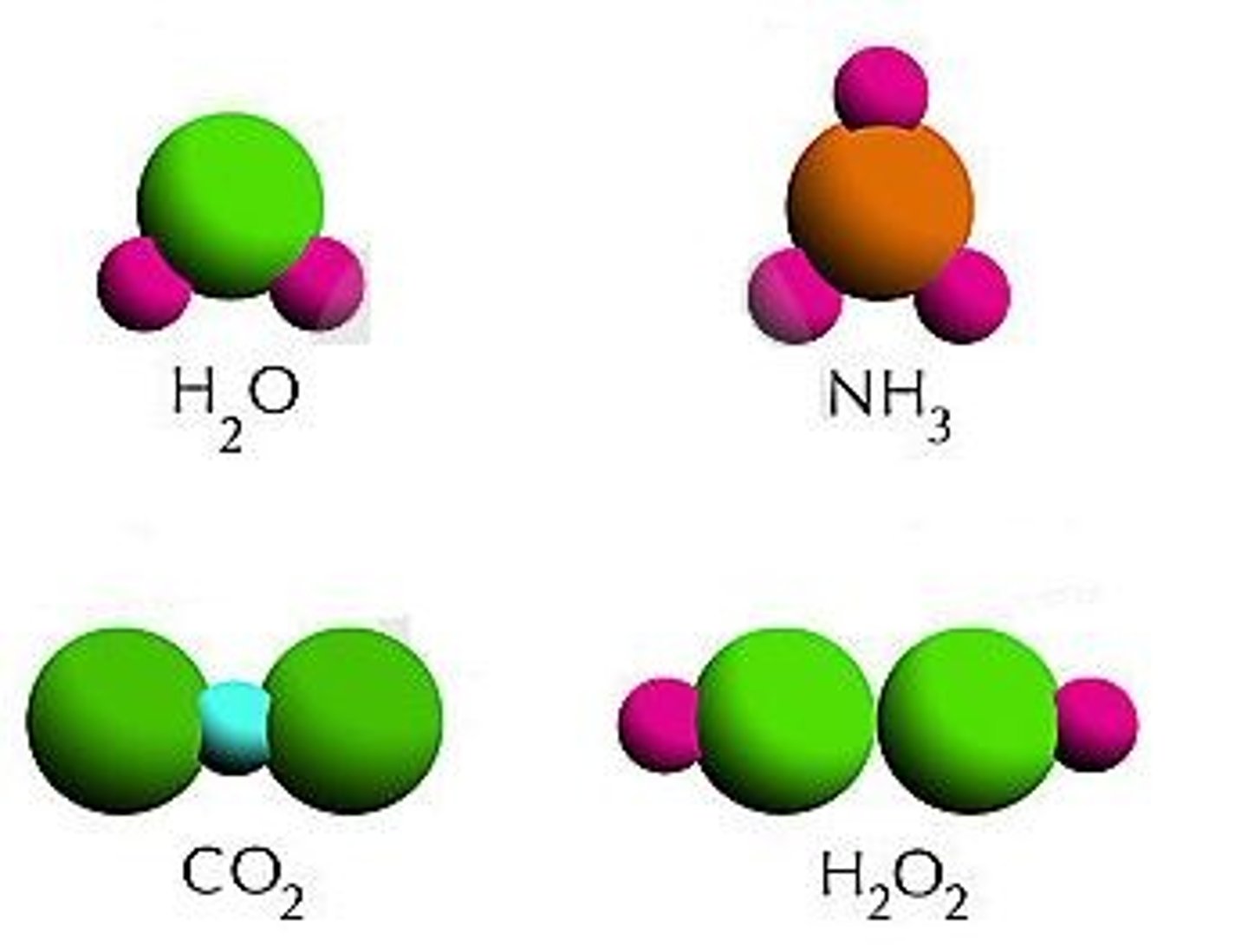
colloid

suspension
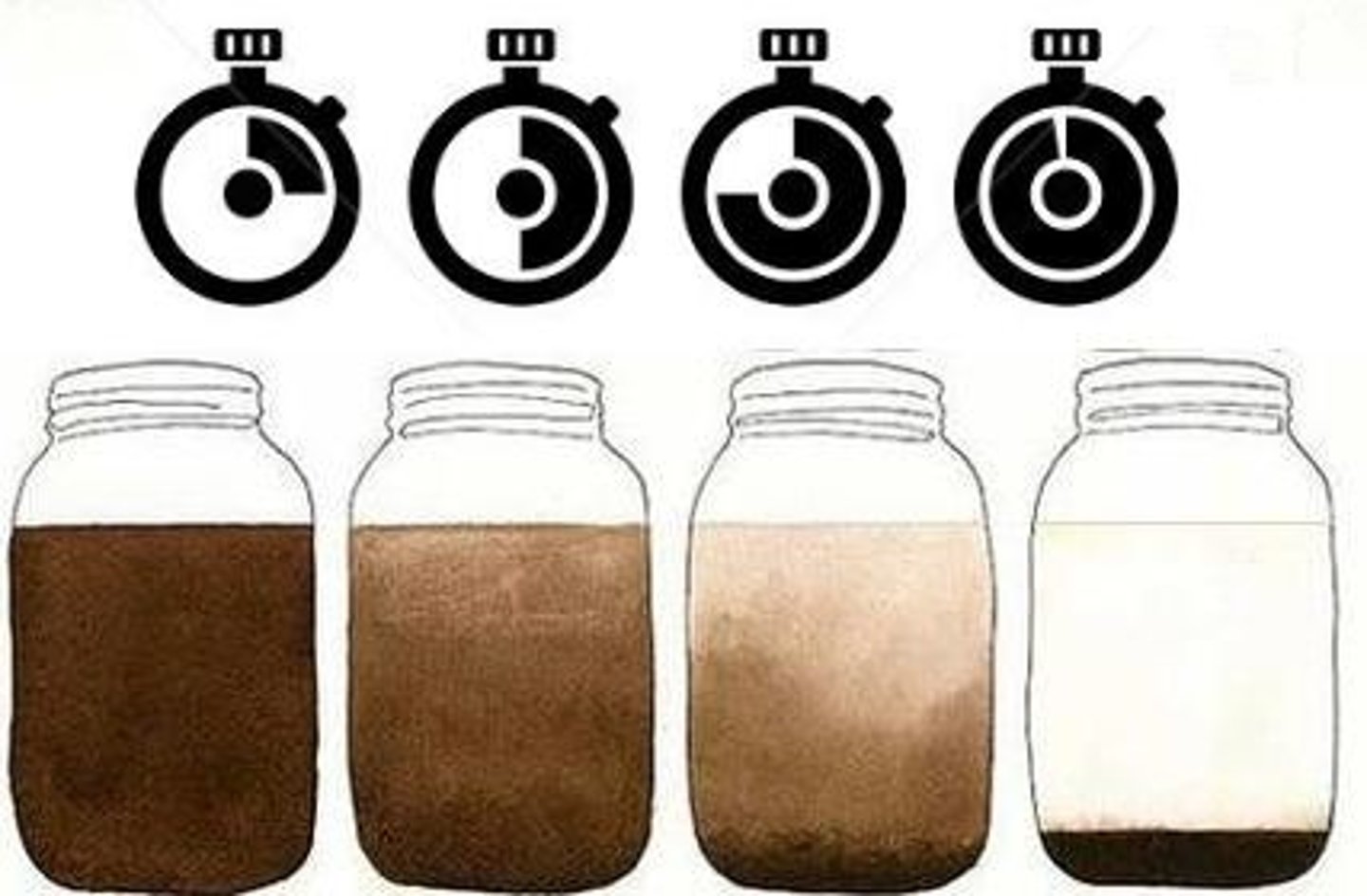

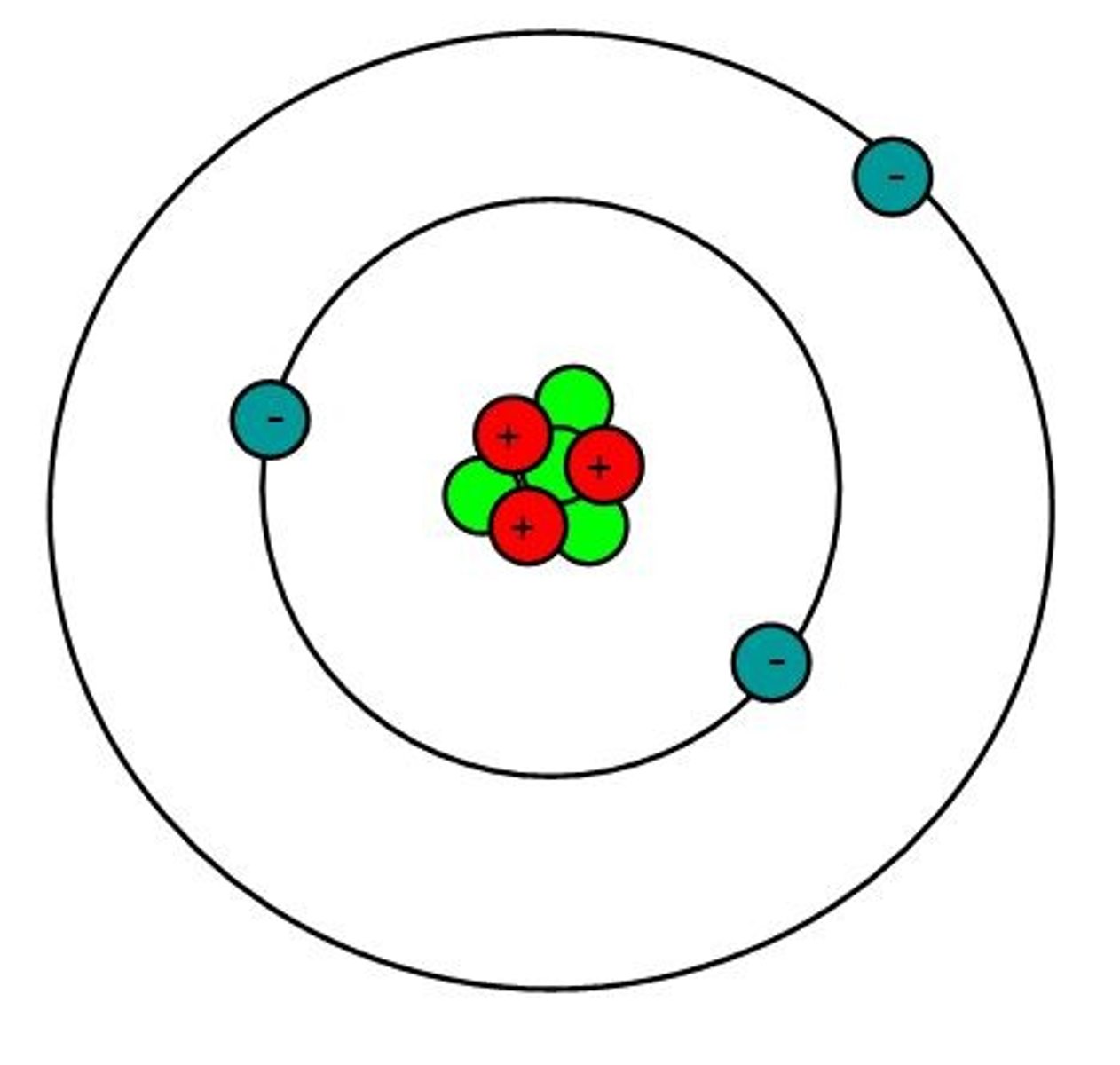
atom
solubility

lustre

malleability
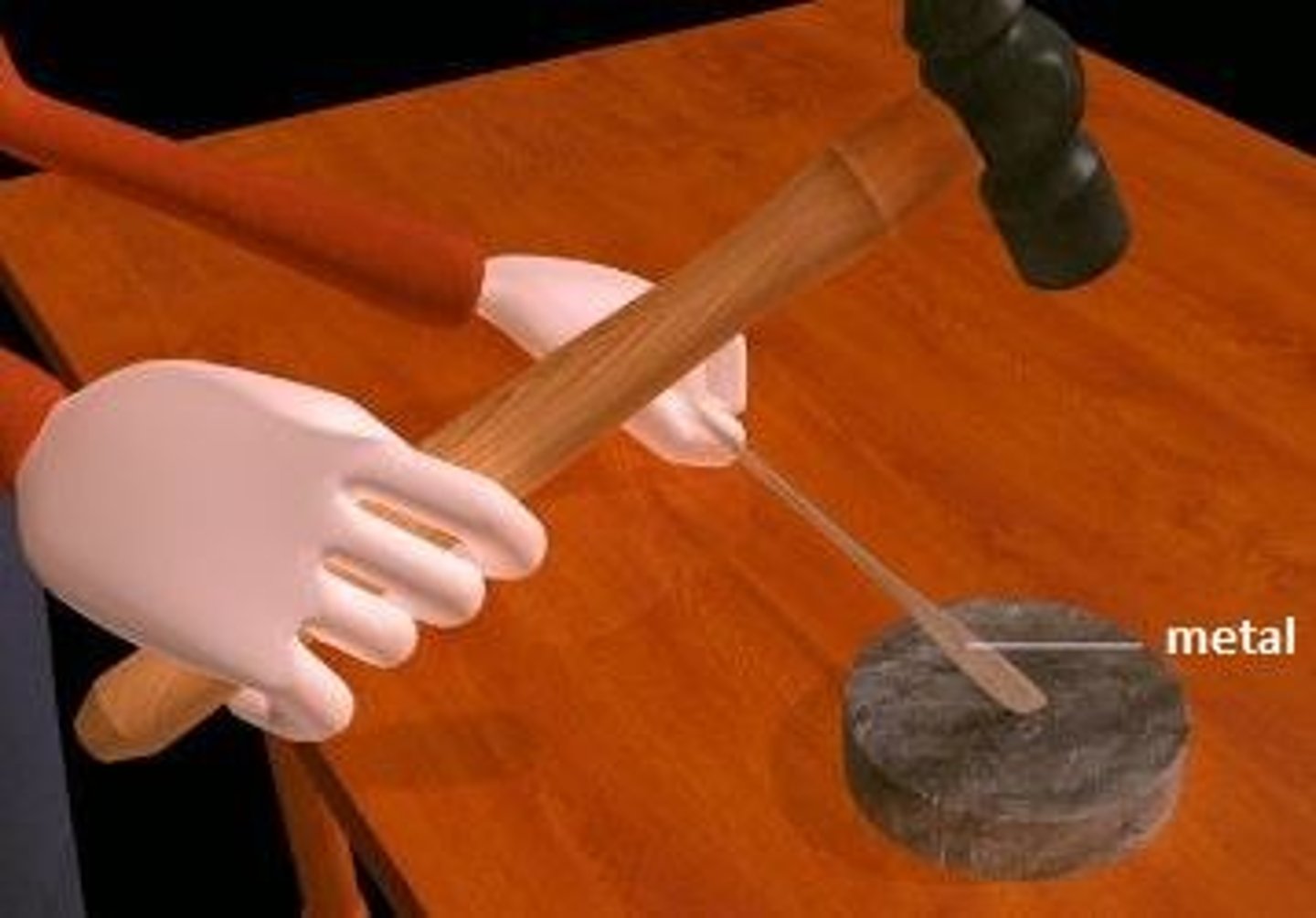

ductility
heterogeneous

homogeneous

WHMIS
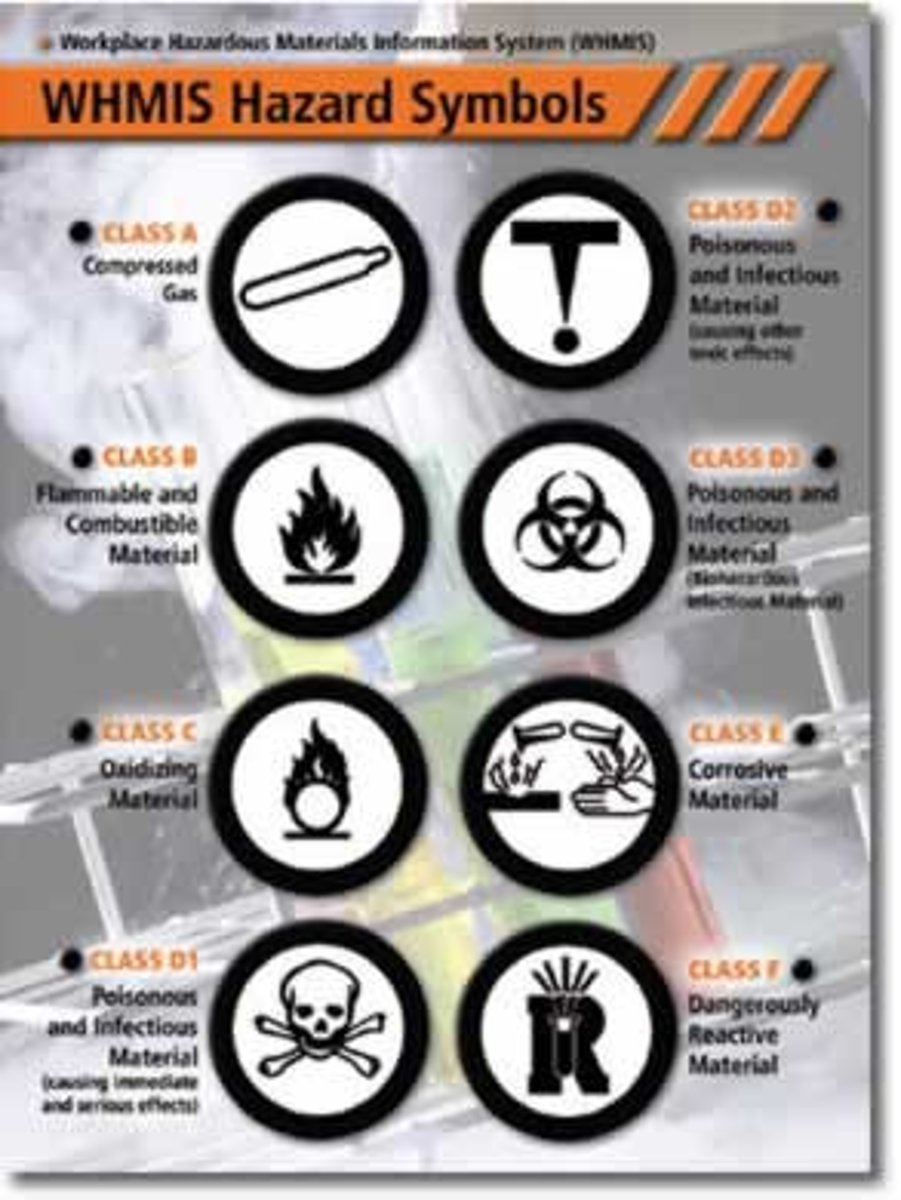
WHMIS
Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System
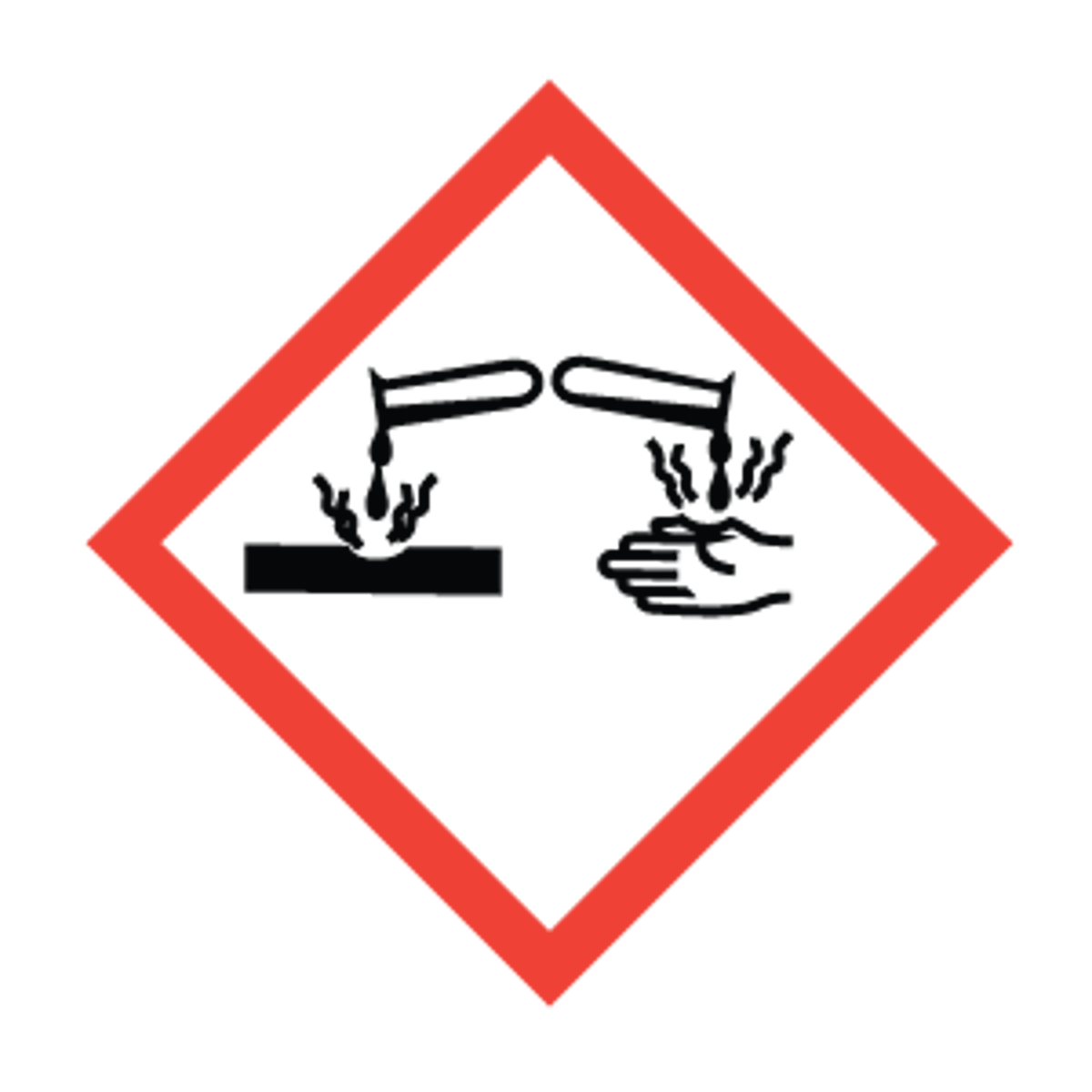
Corrosive
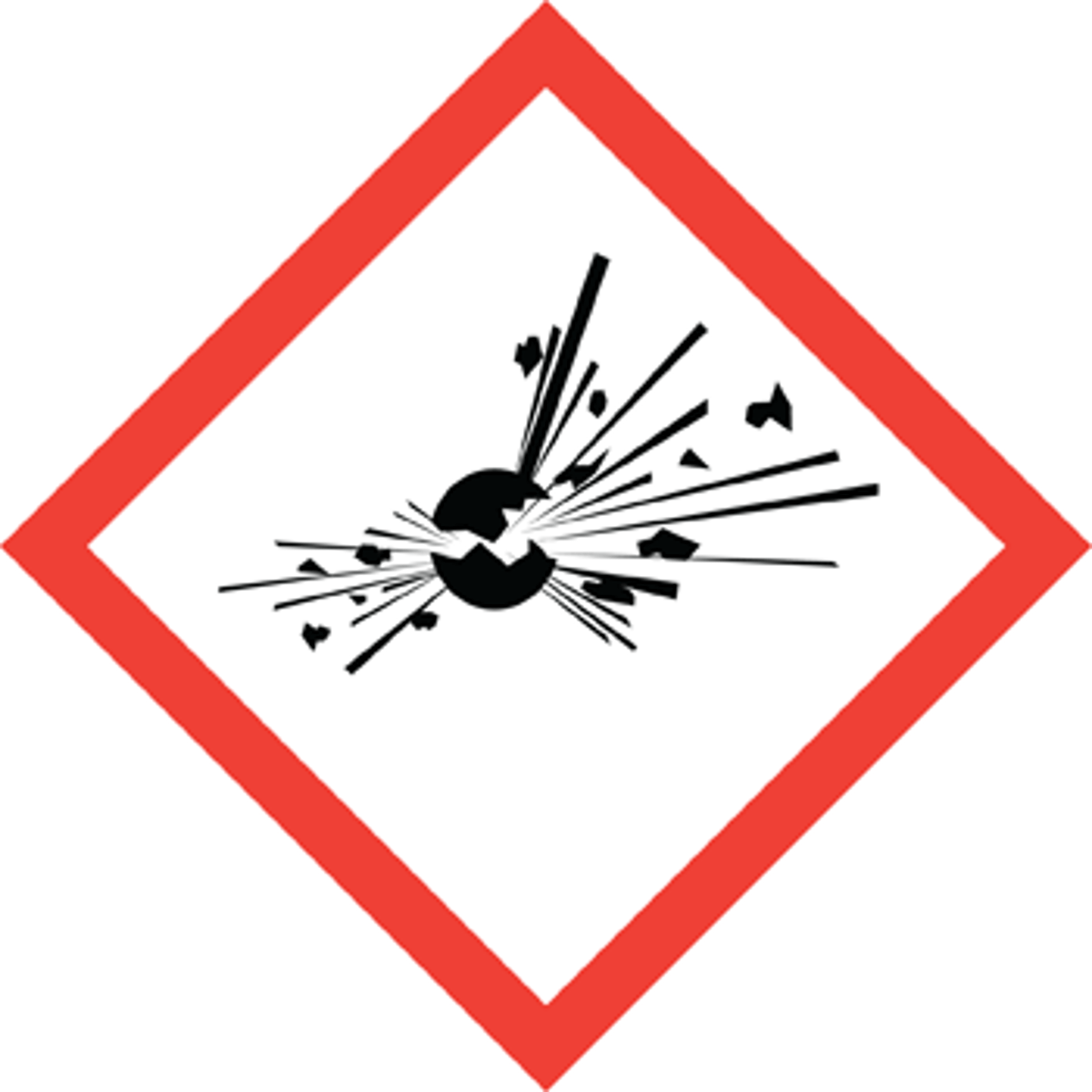
Explosive

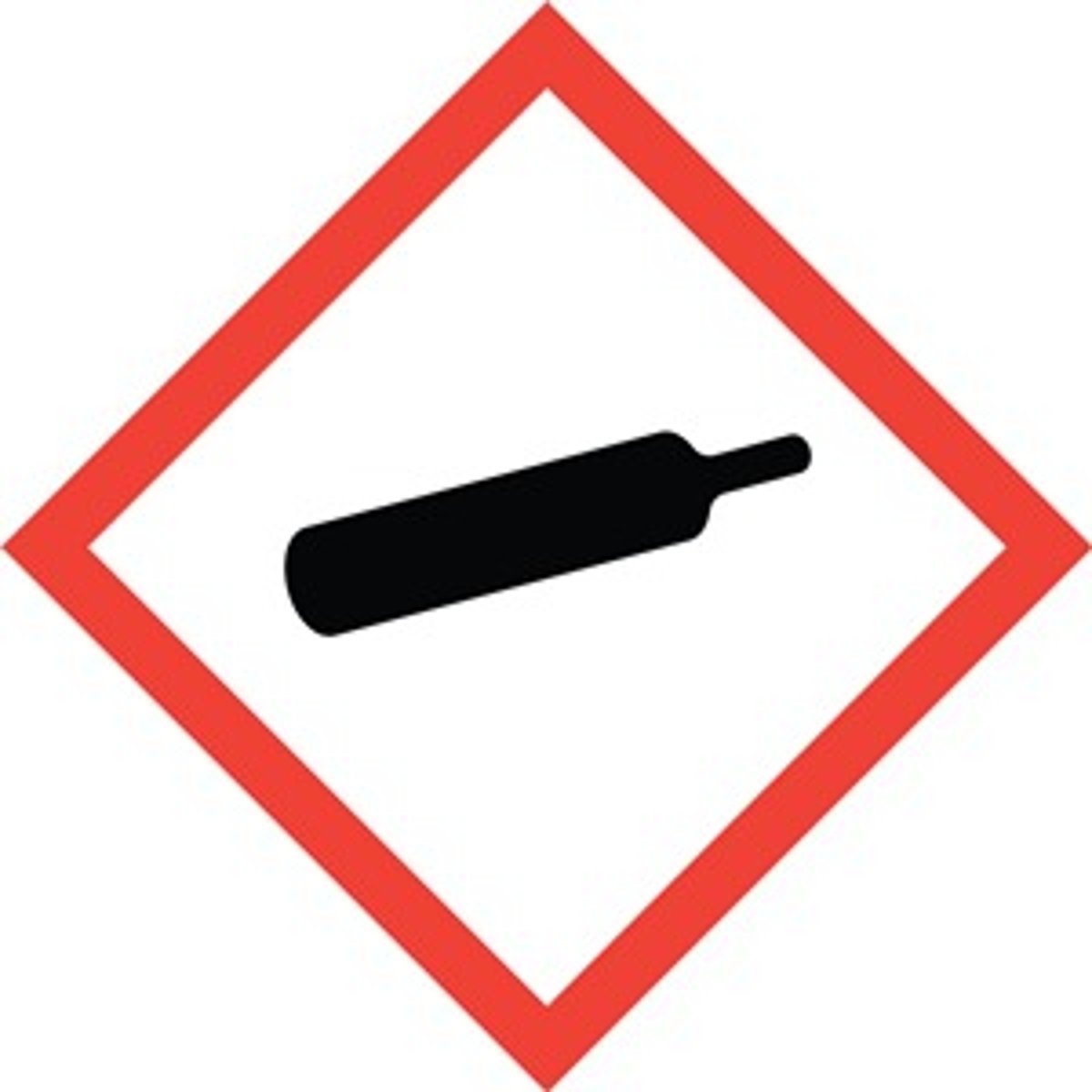
Compressed gas

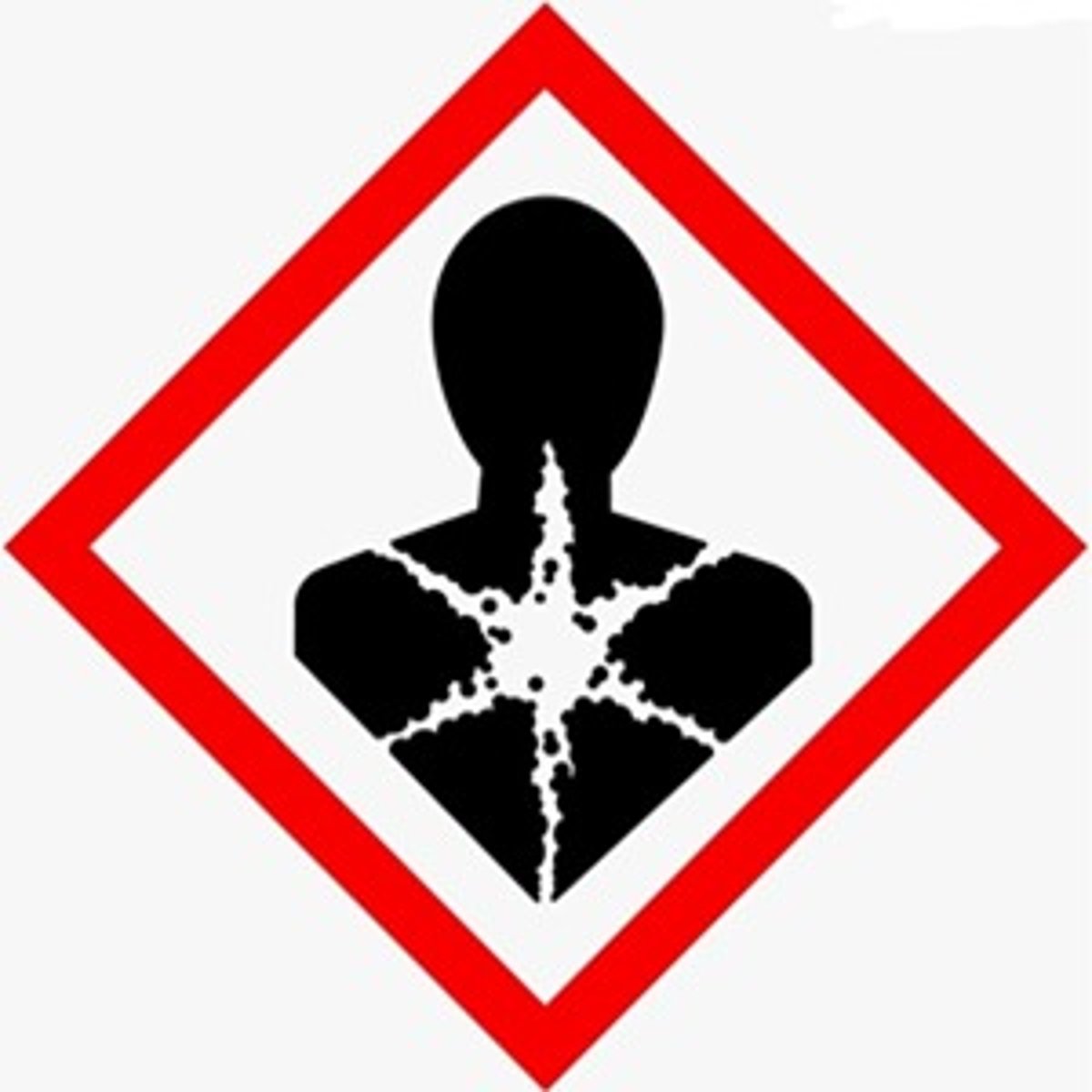
Health hazard

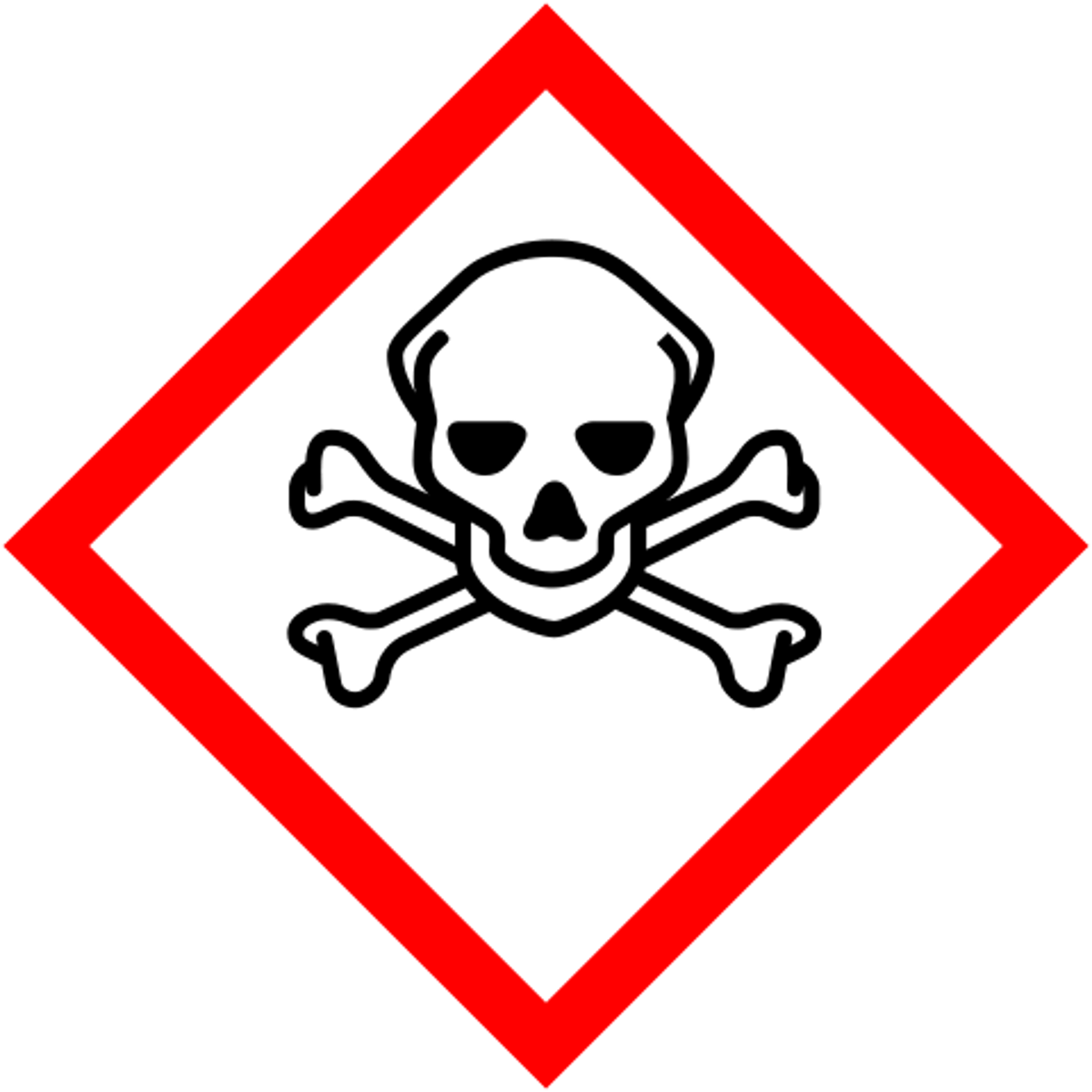
Harmful or Fatal

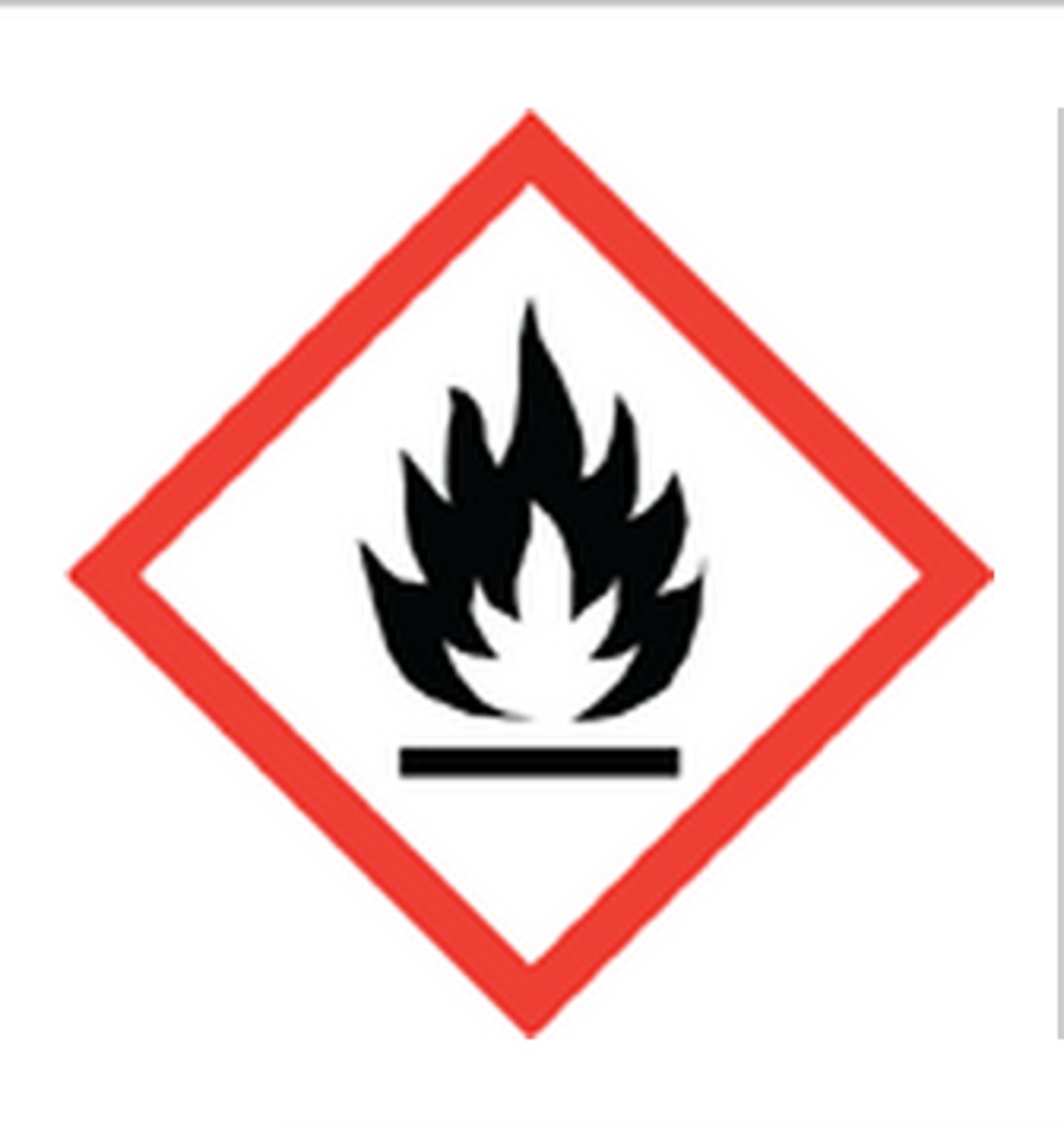
Flammable

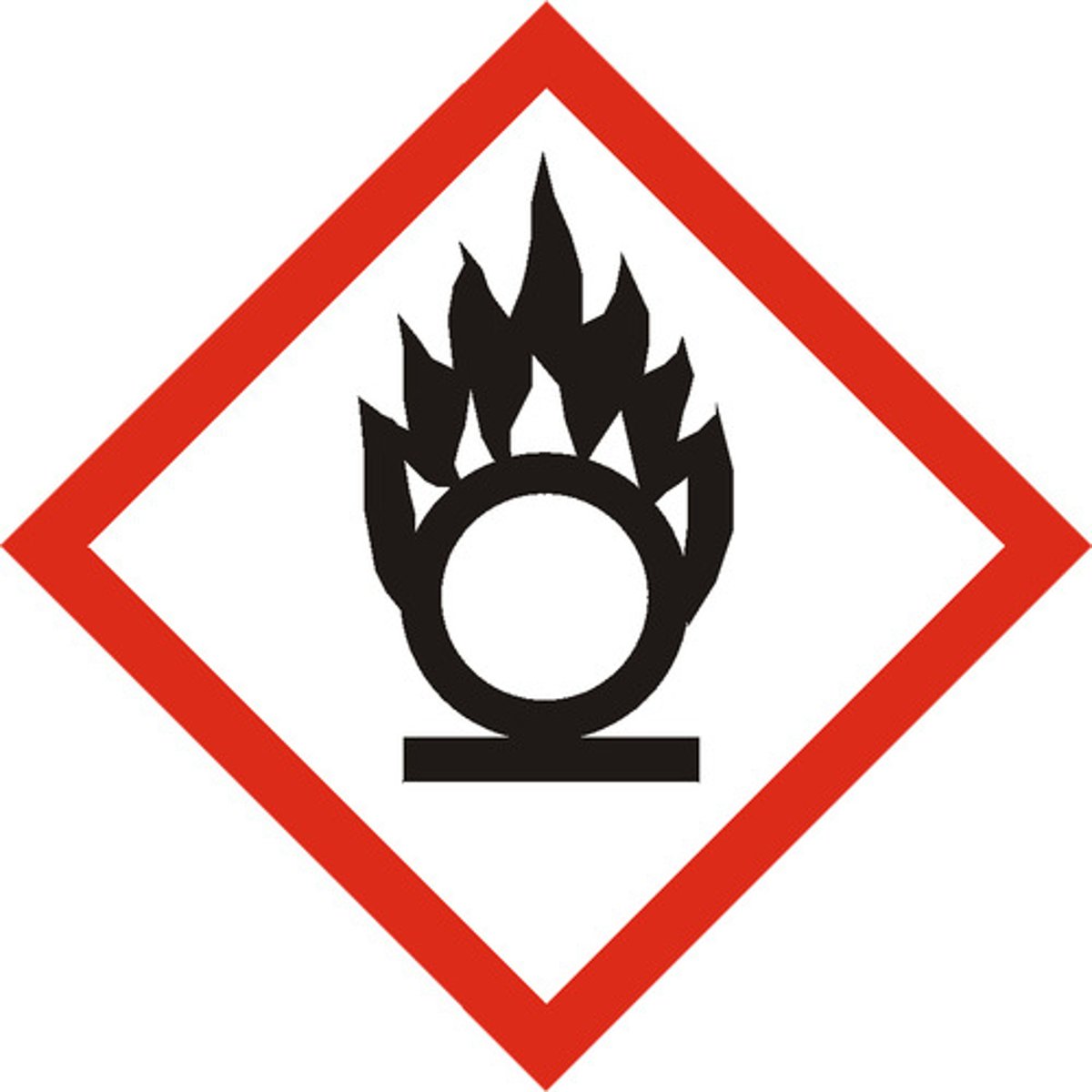
Oxydizing

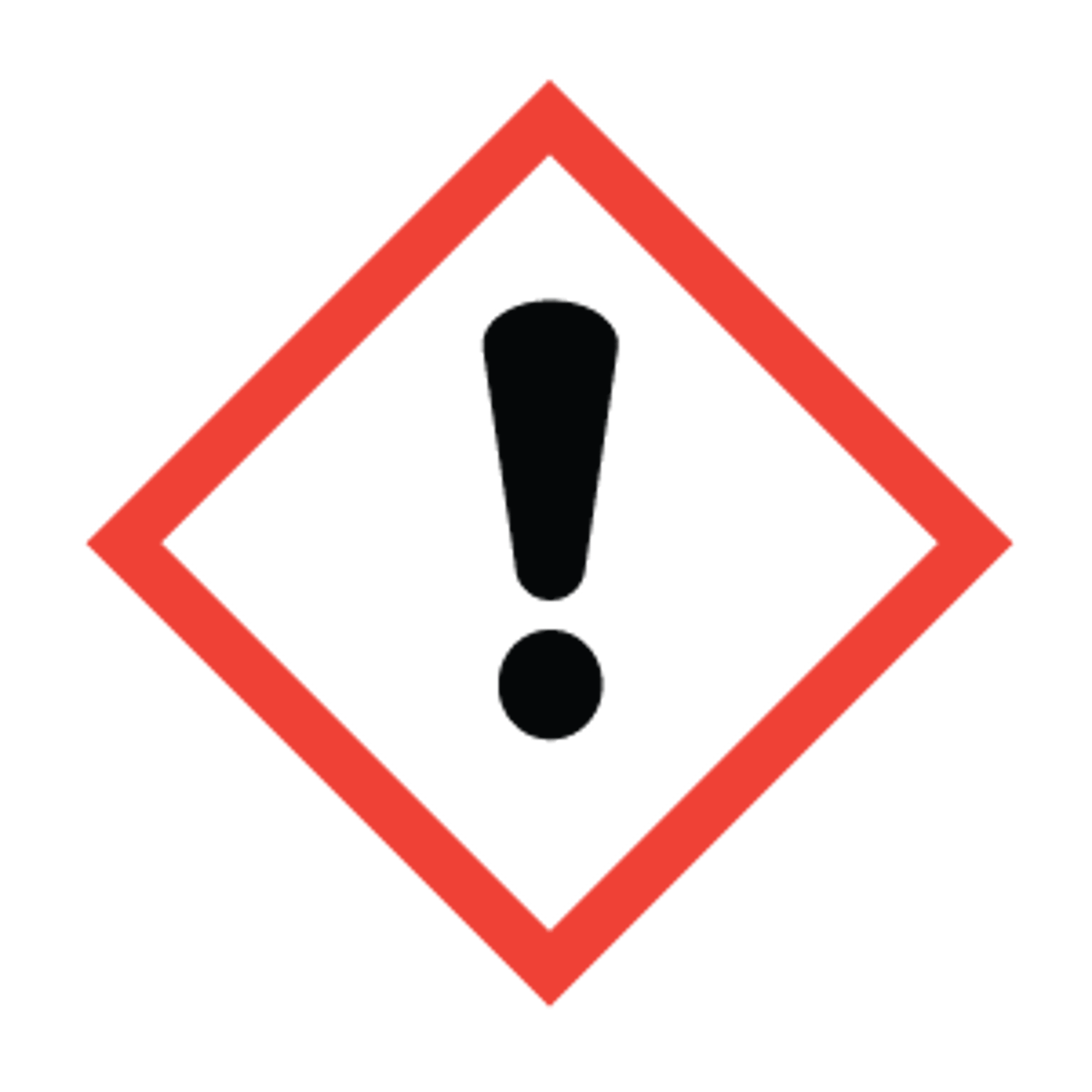
Harmful

Harmful to the Environment

Biohazardous infectious material

Combustion

Corrosion

Exothermic

Endothermic
Reactants
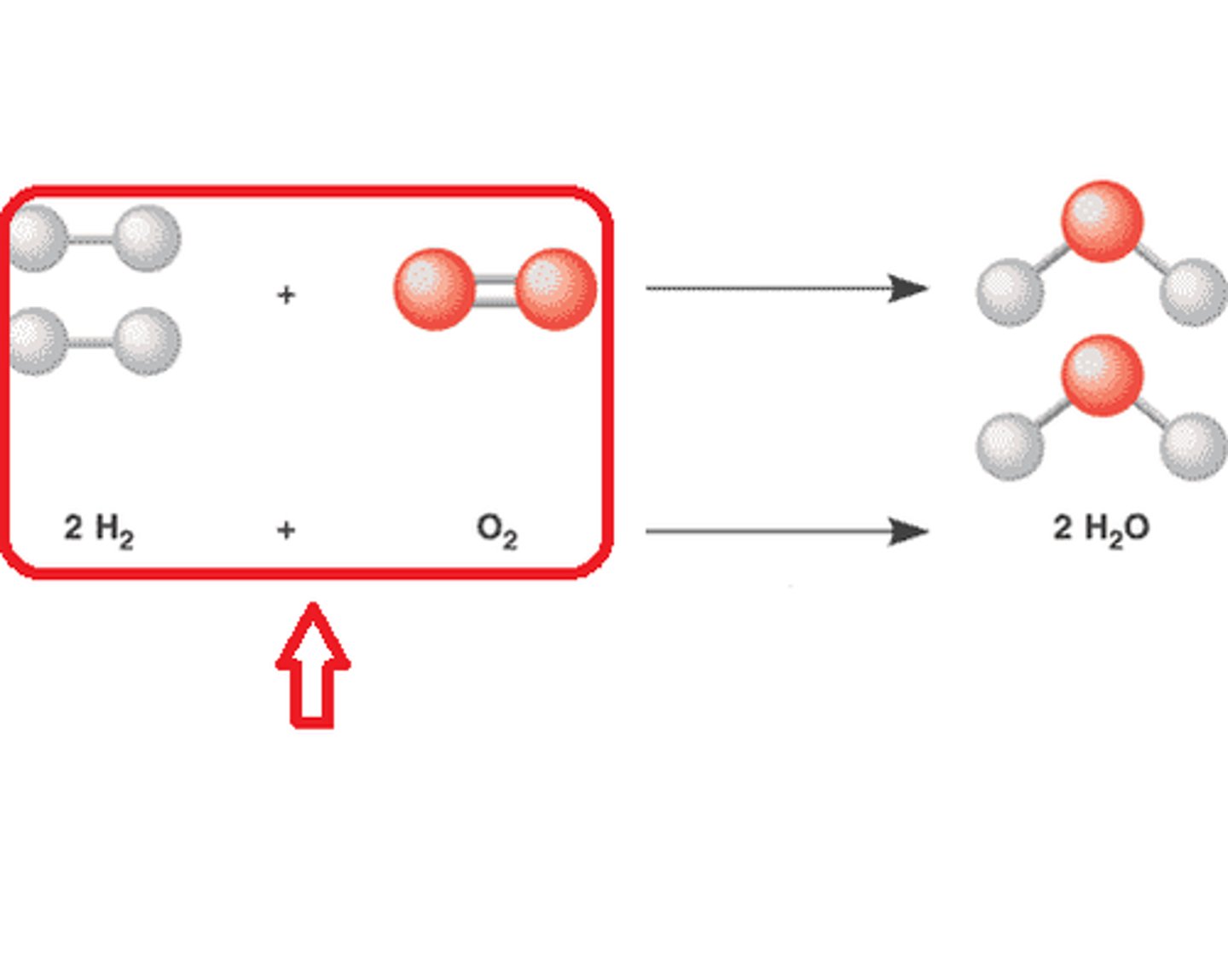
Products
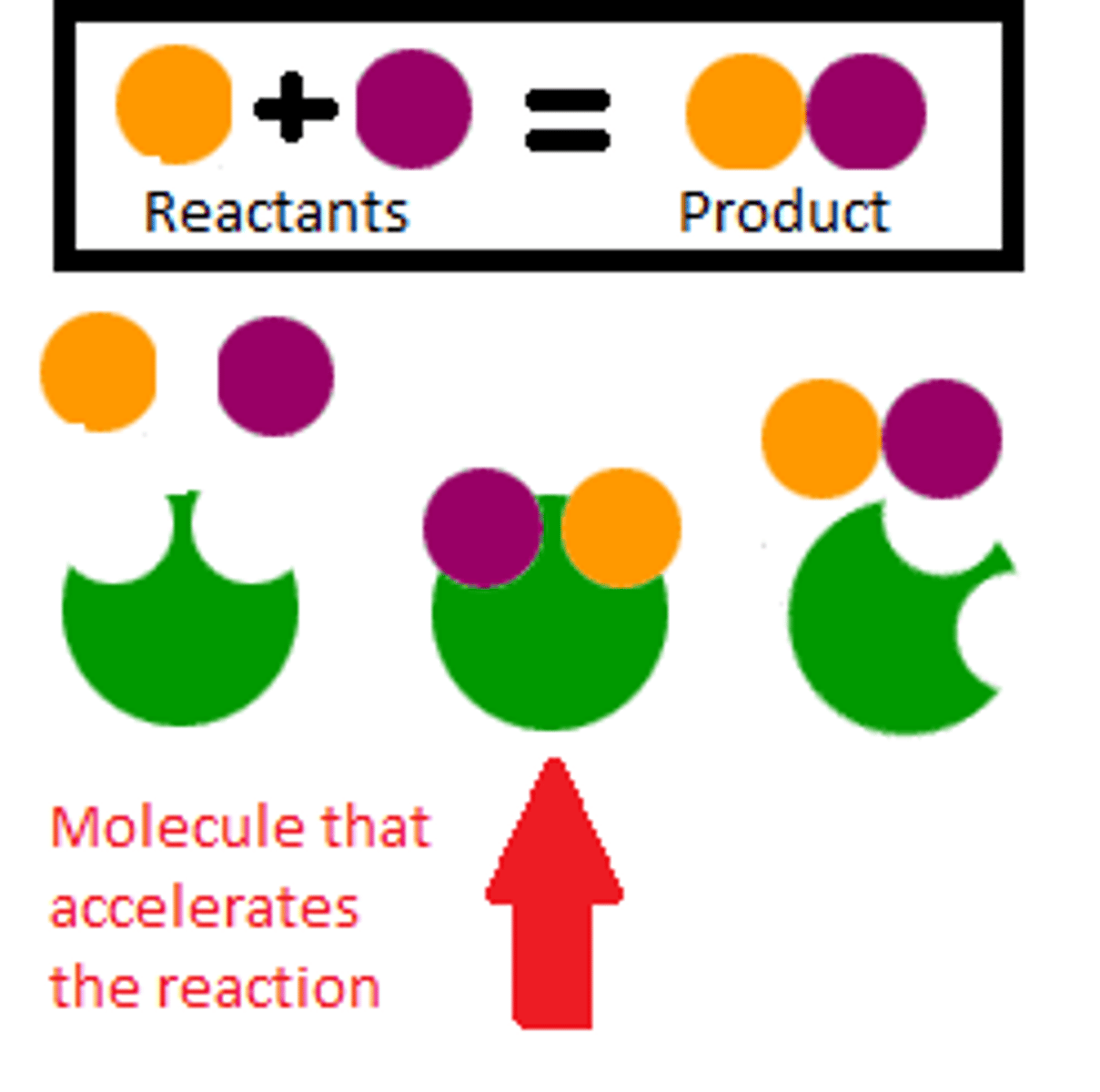
Catalyst
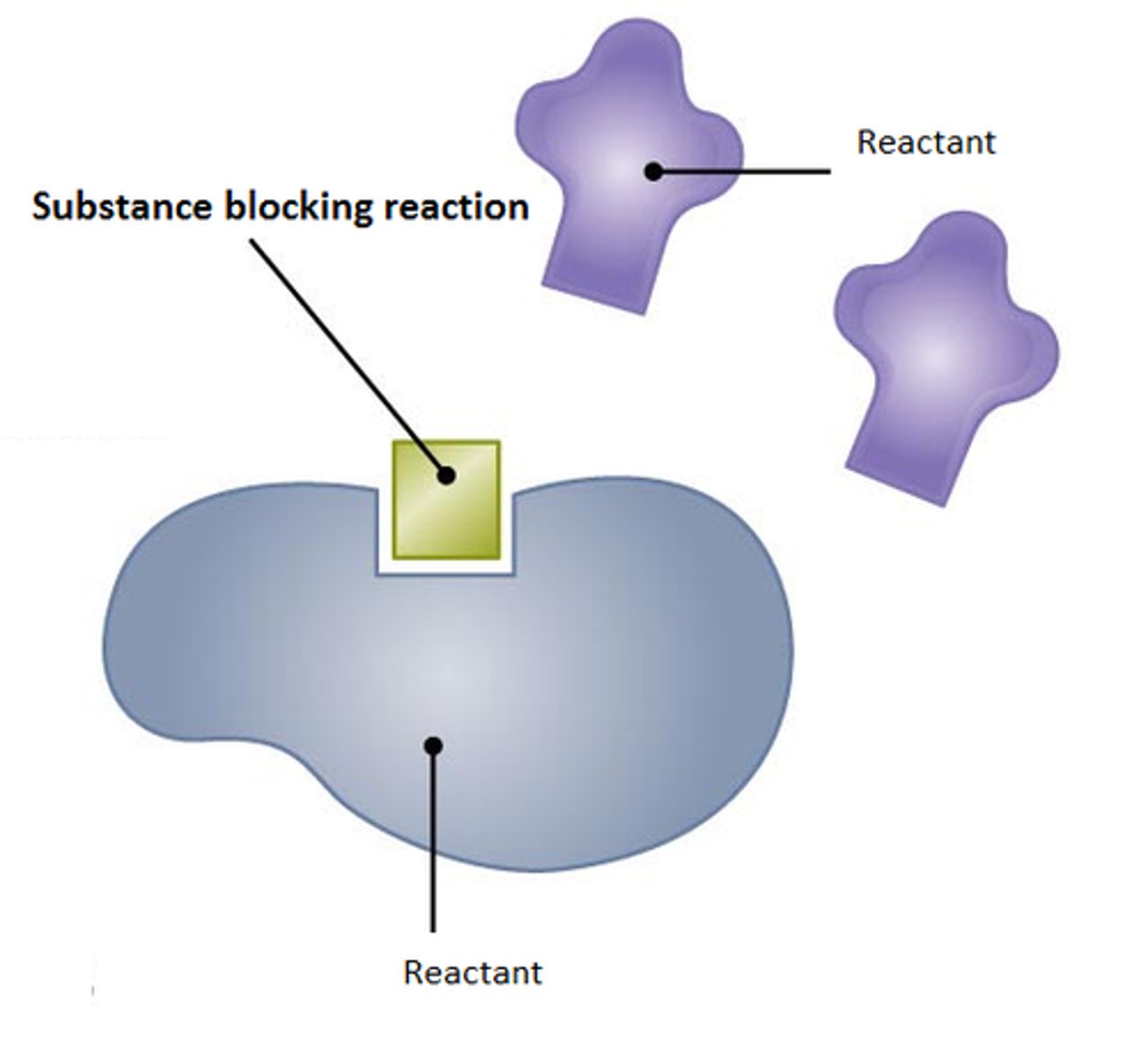
Inhibitor
Nucleus
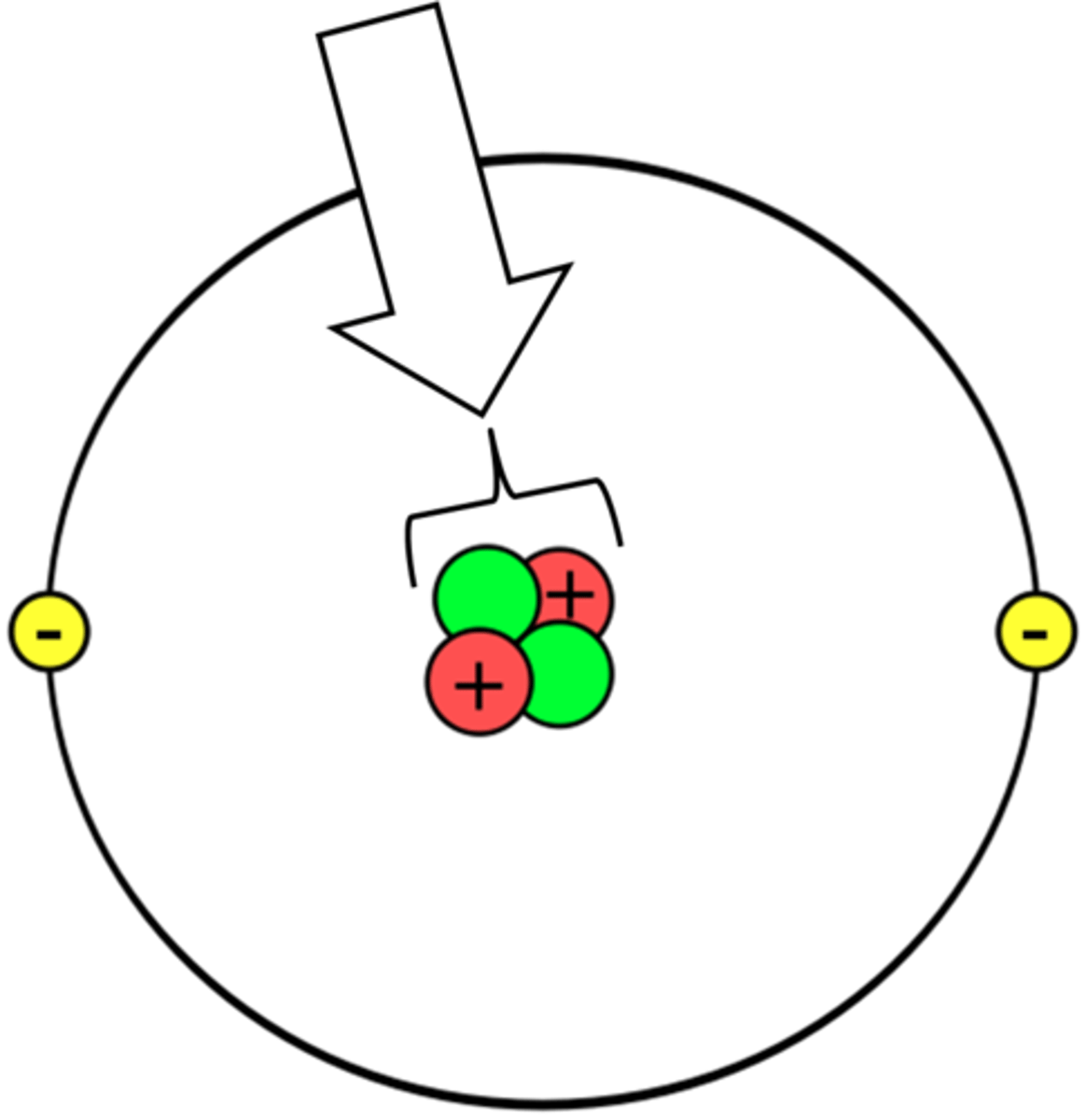
Proton
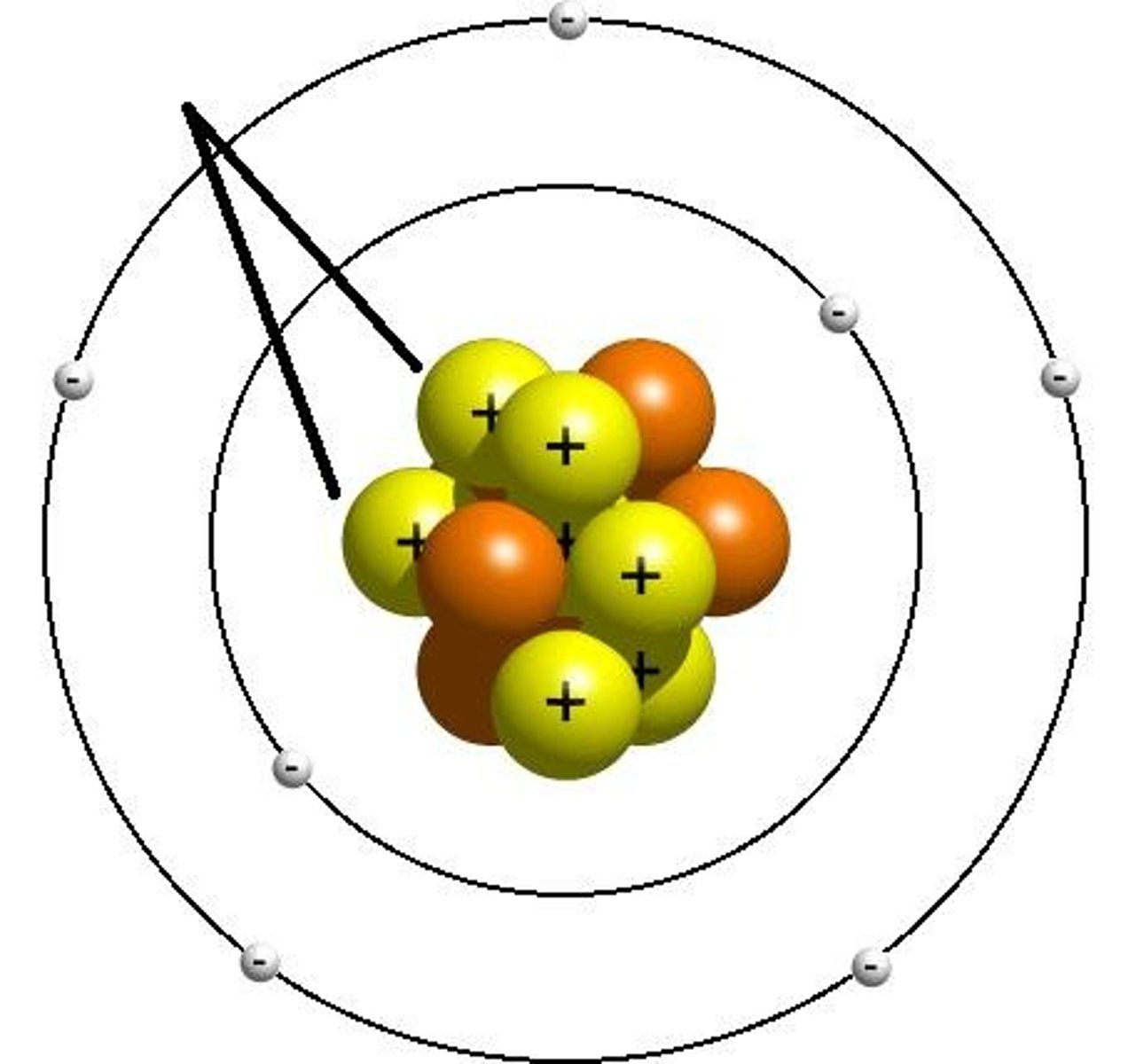
Electron
Neutron
Ion
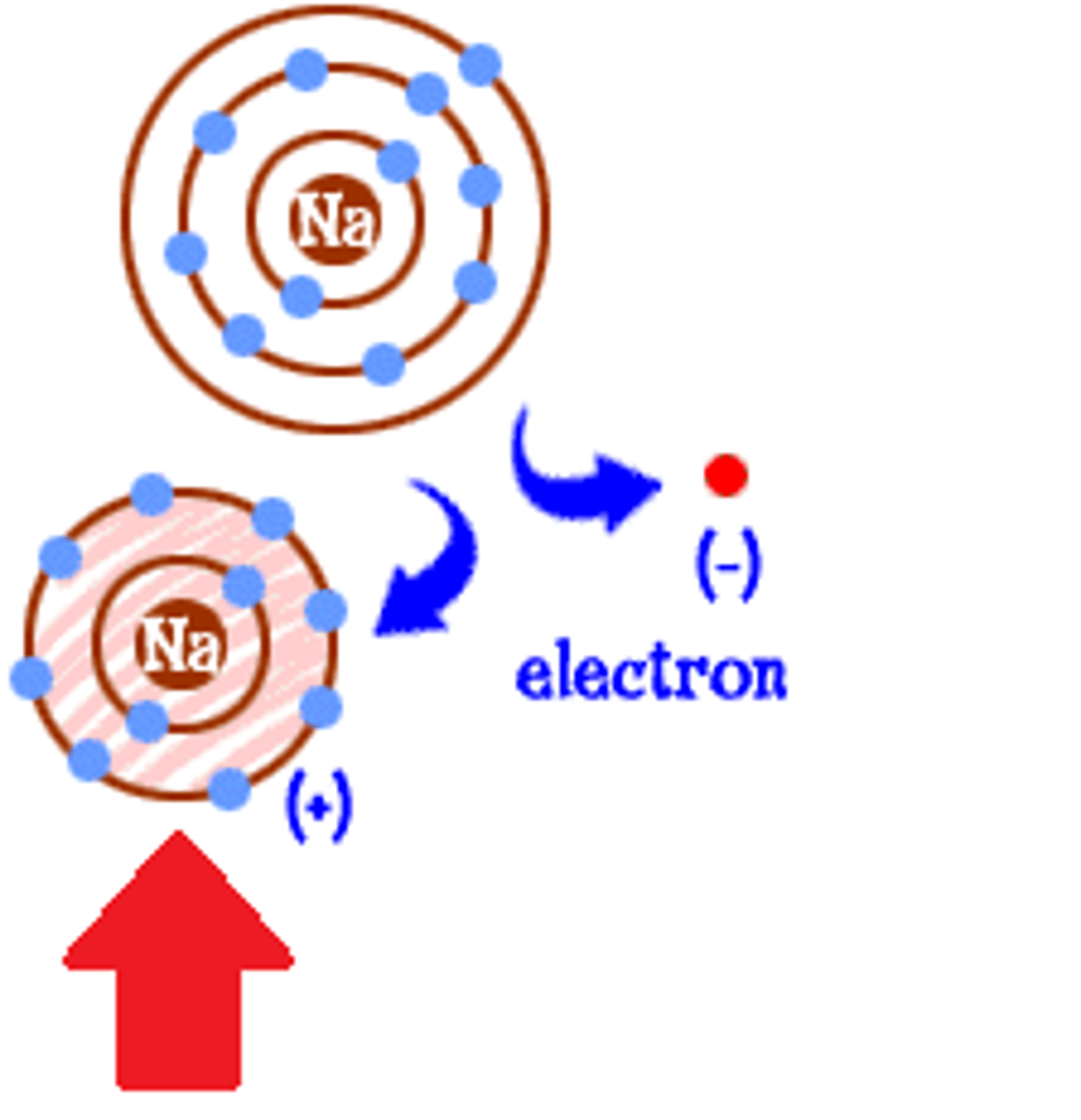
Ionic charge
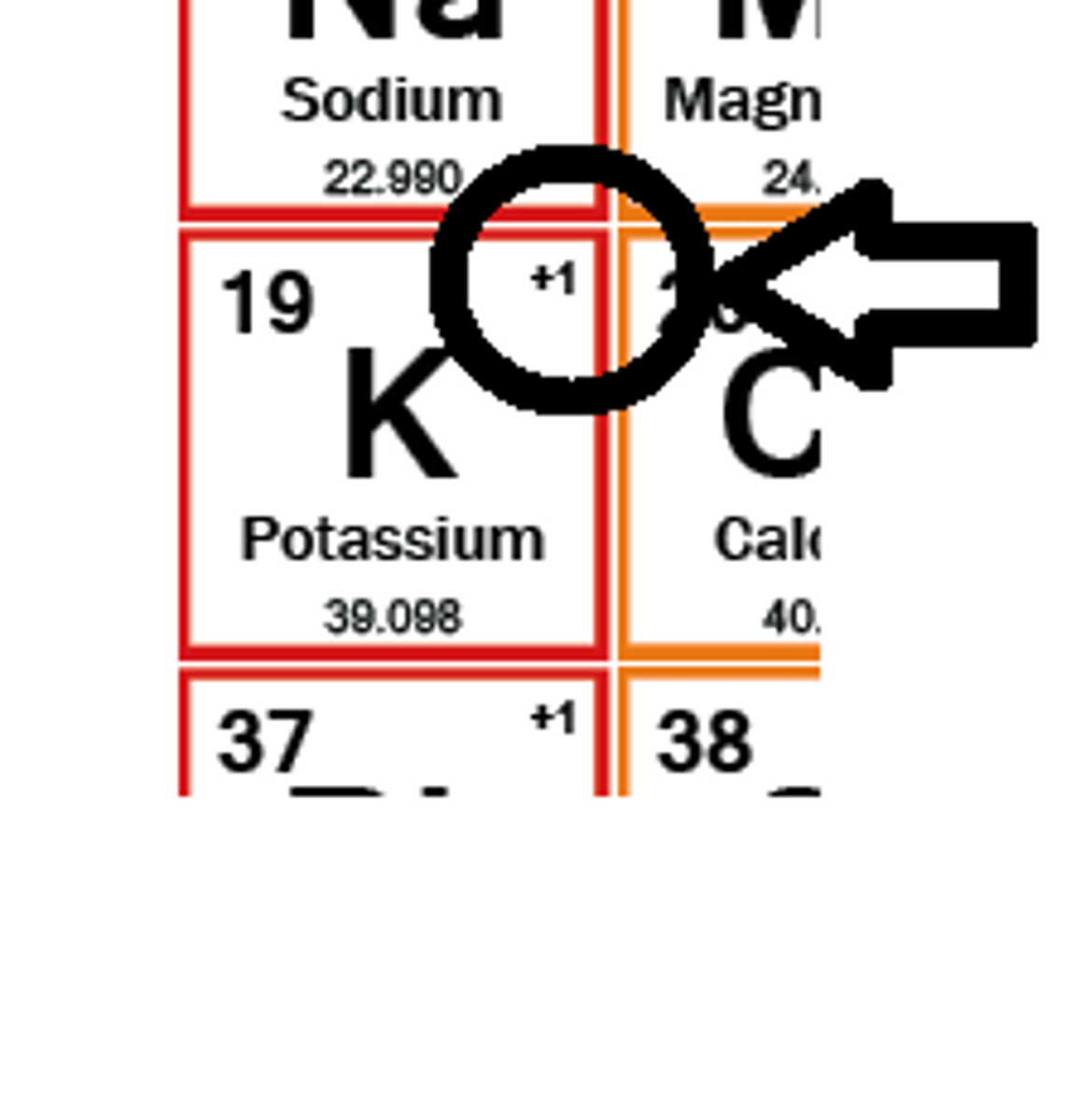
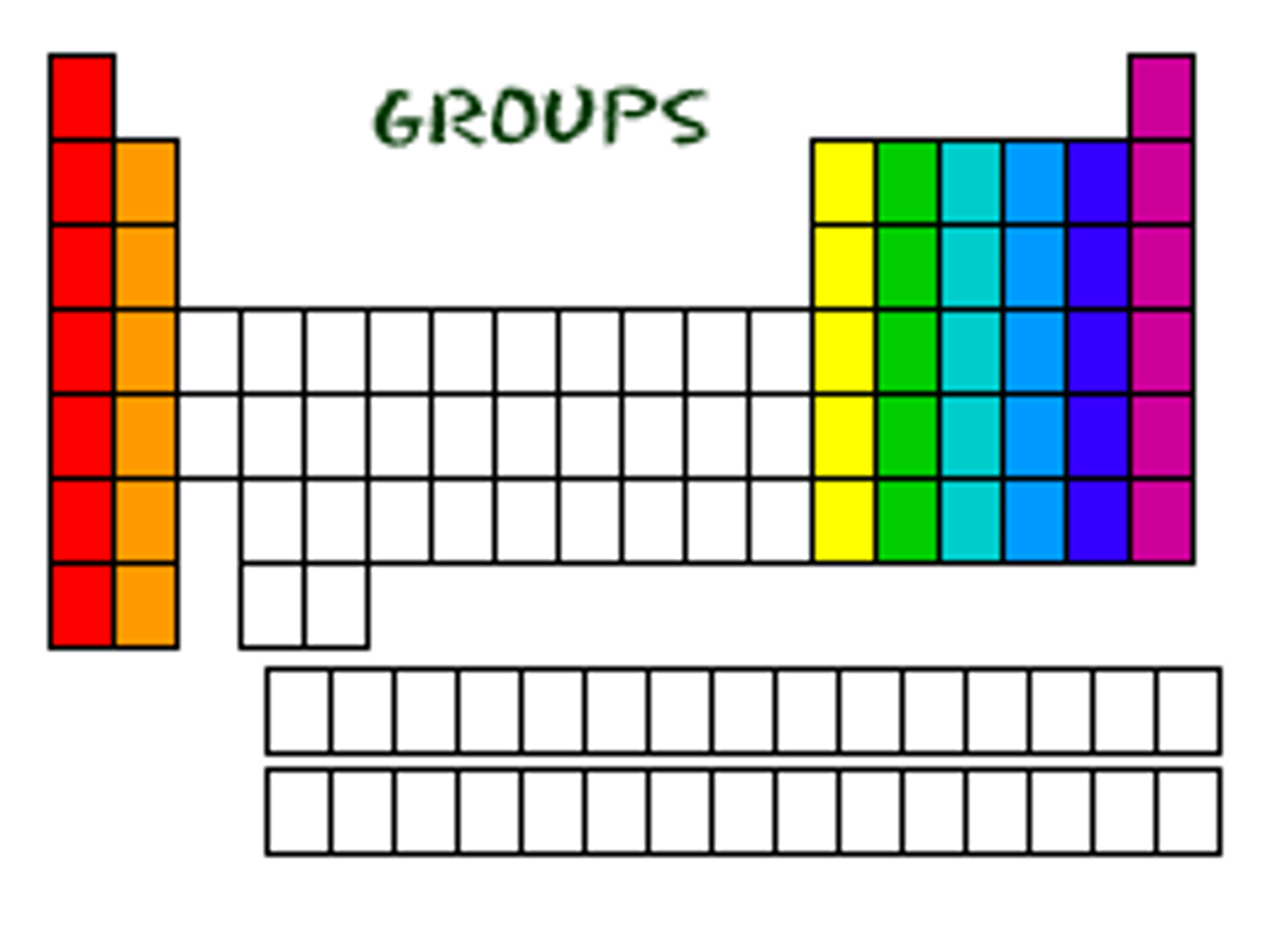
Group
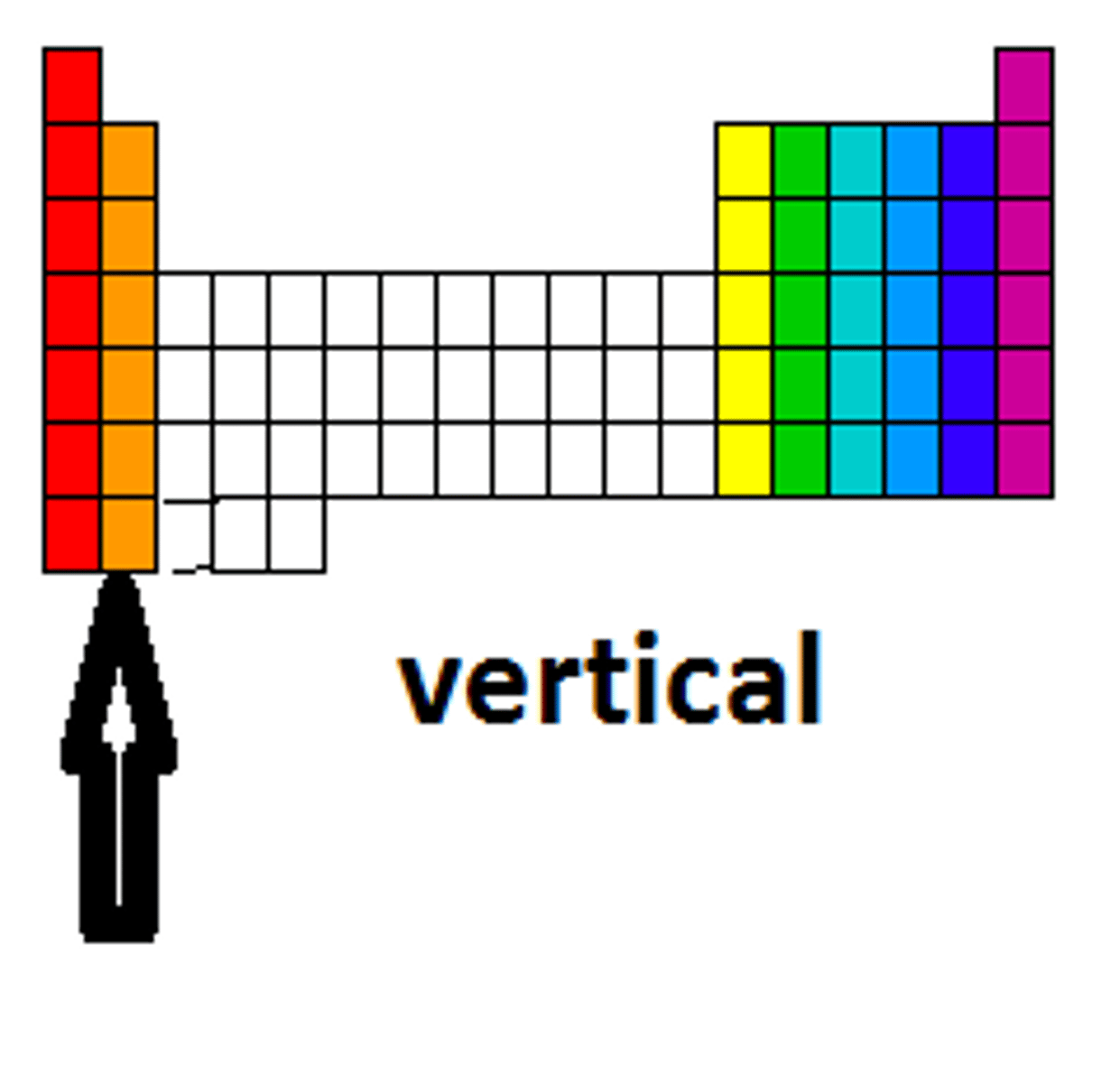
Family
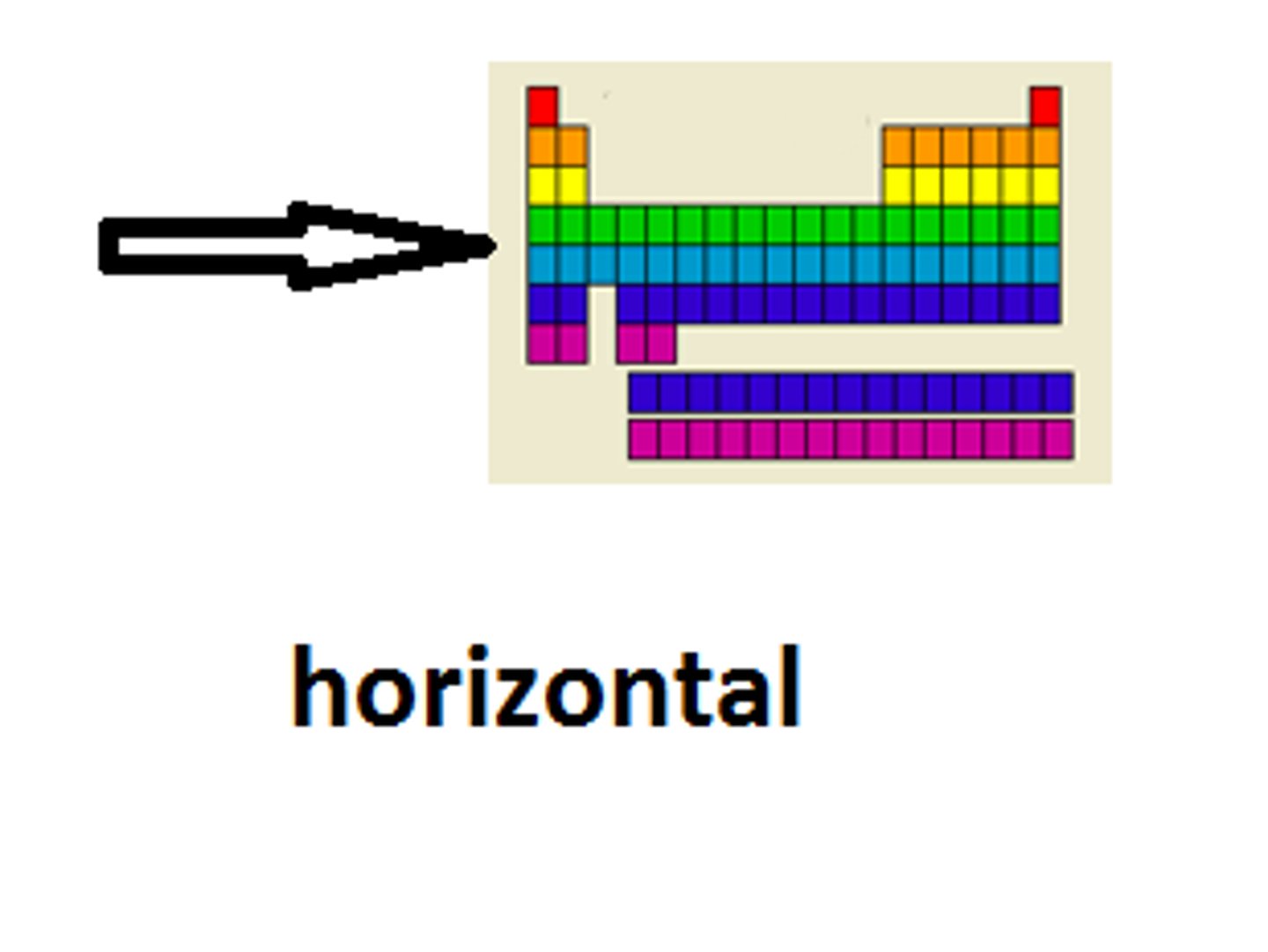
Periods
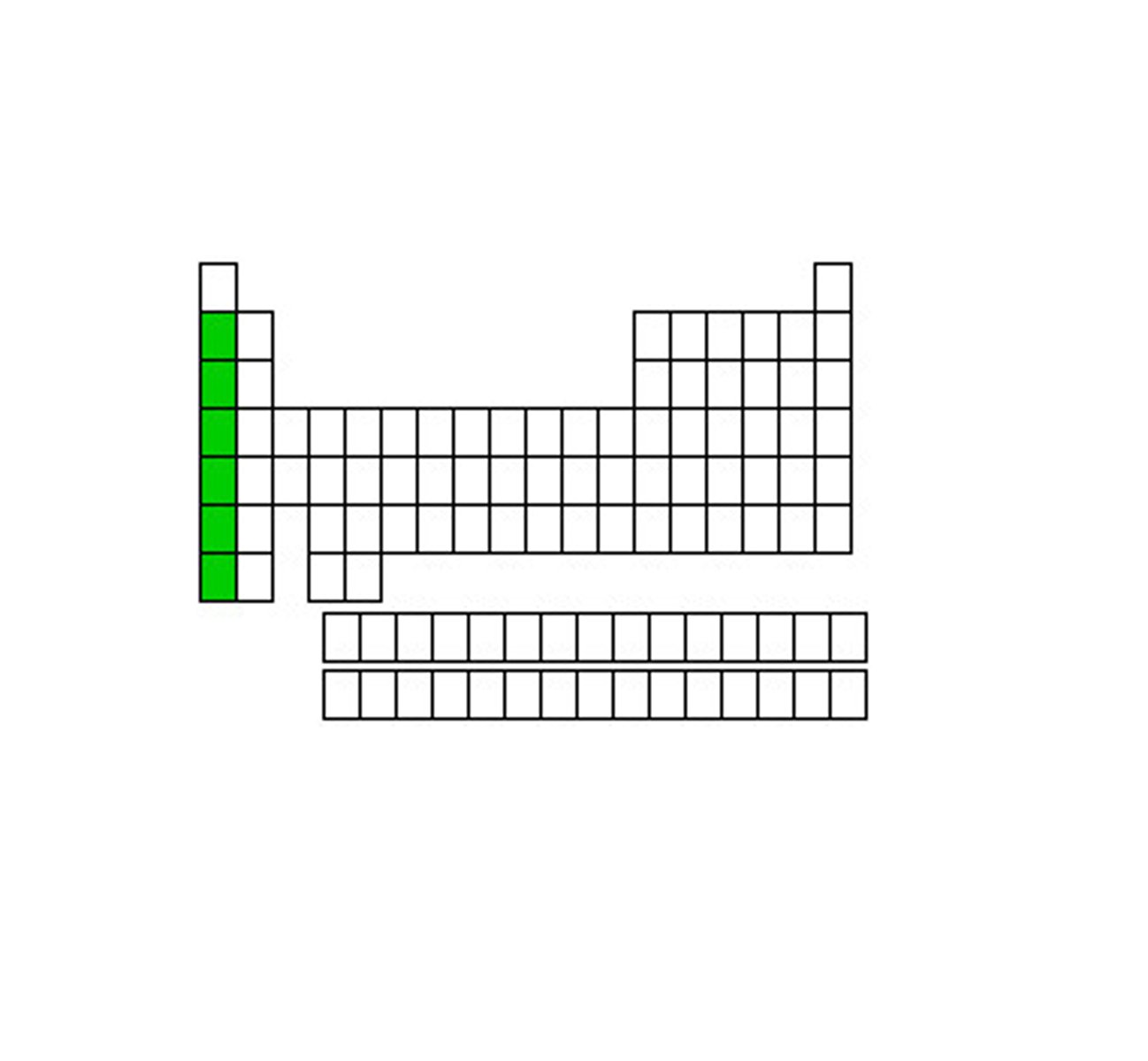
Alkaline earth metals
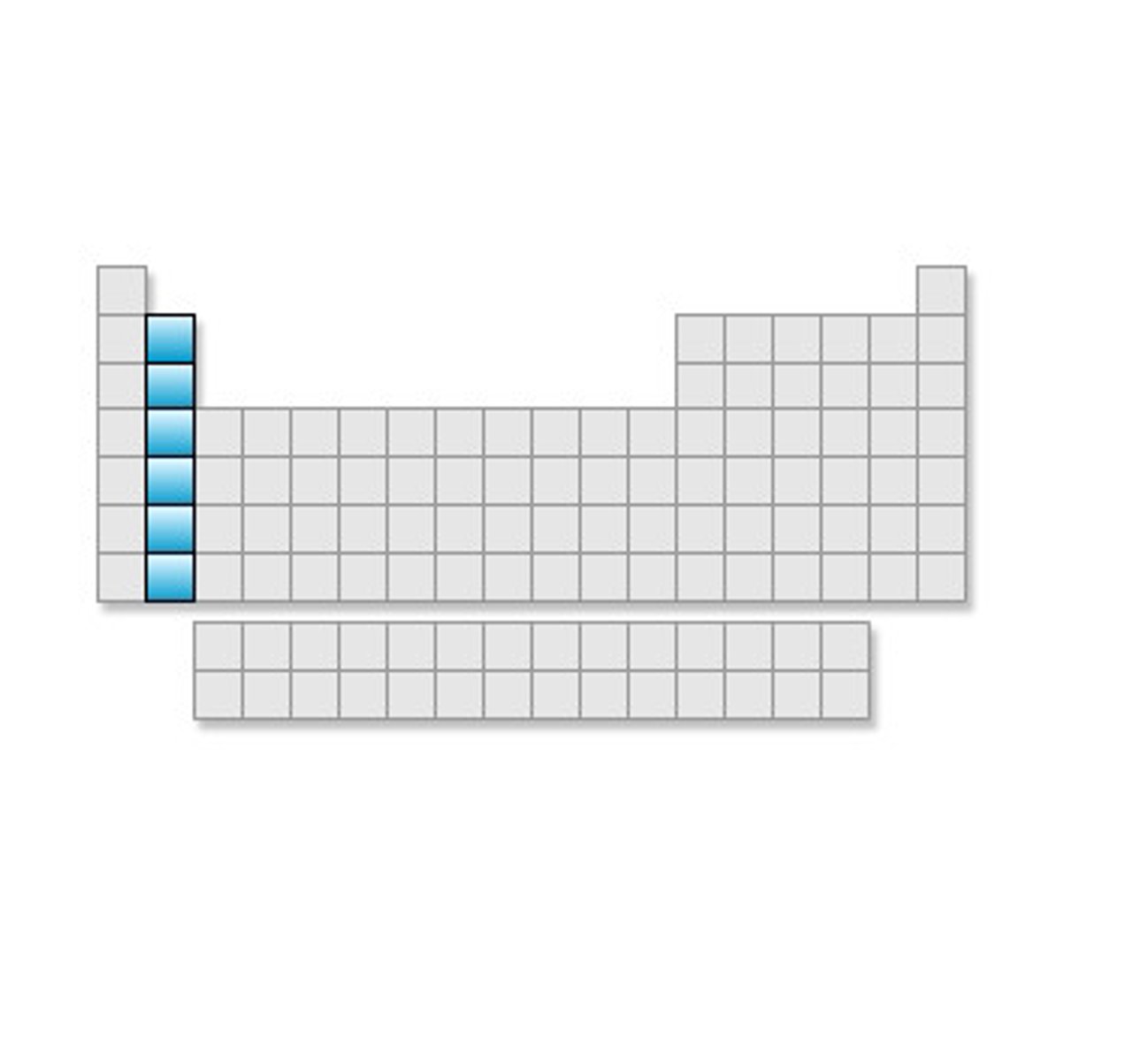
Alkali metals
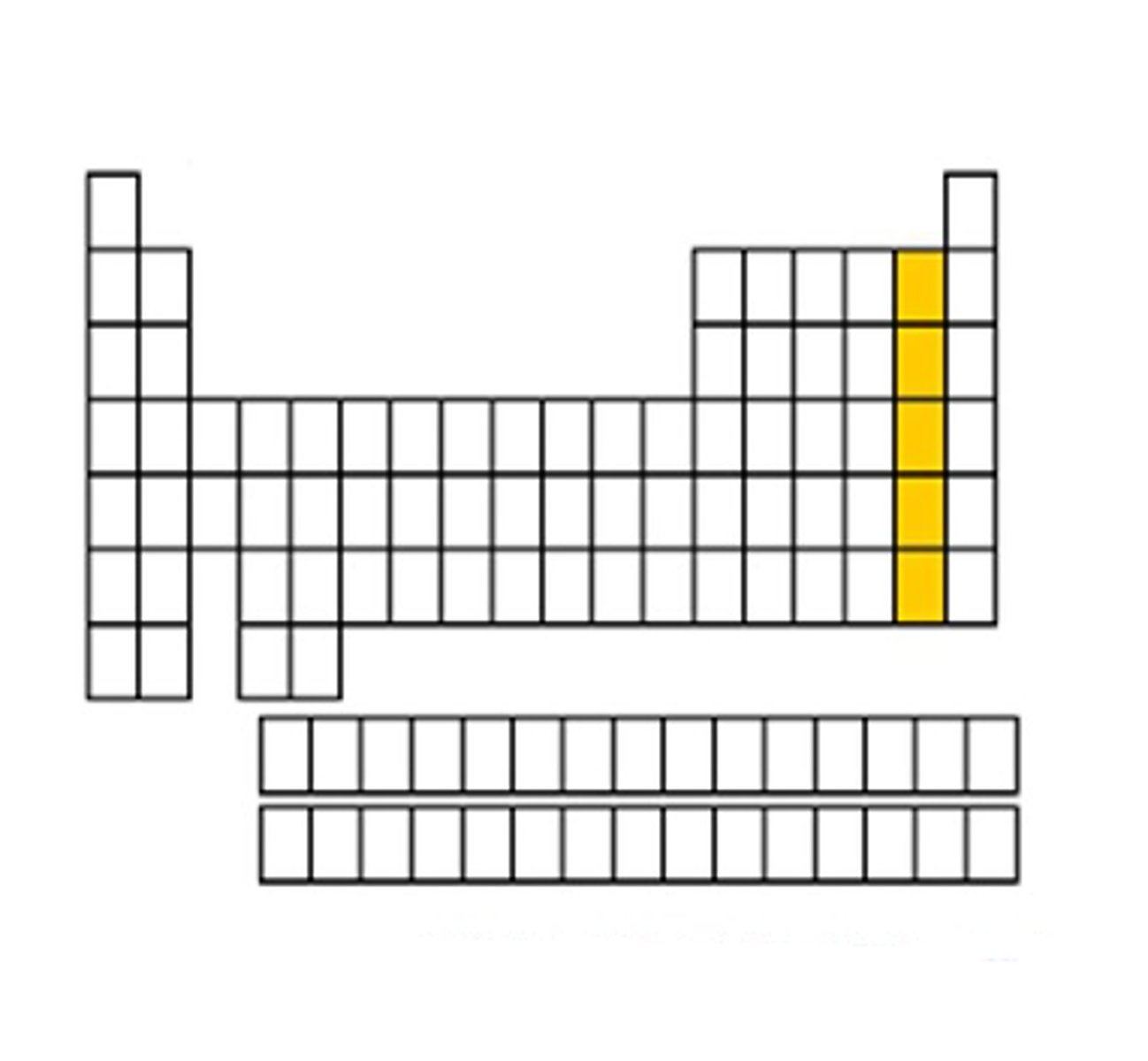
Halogens
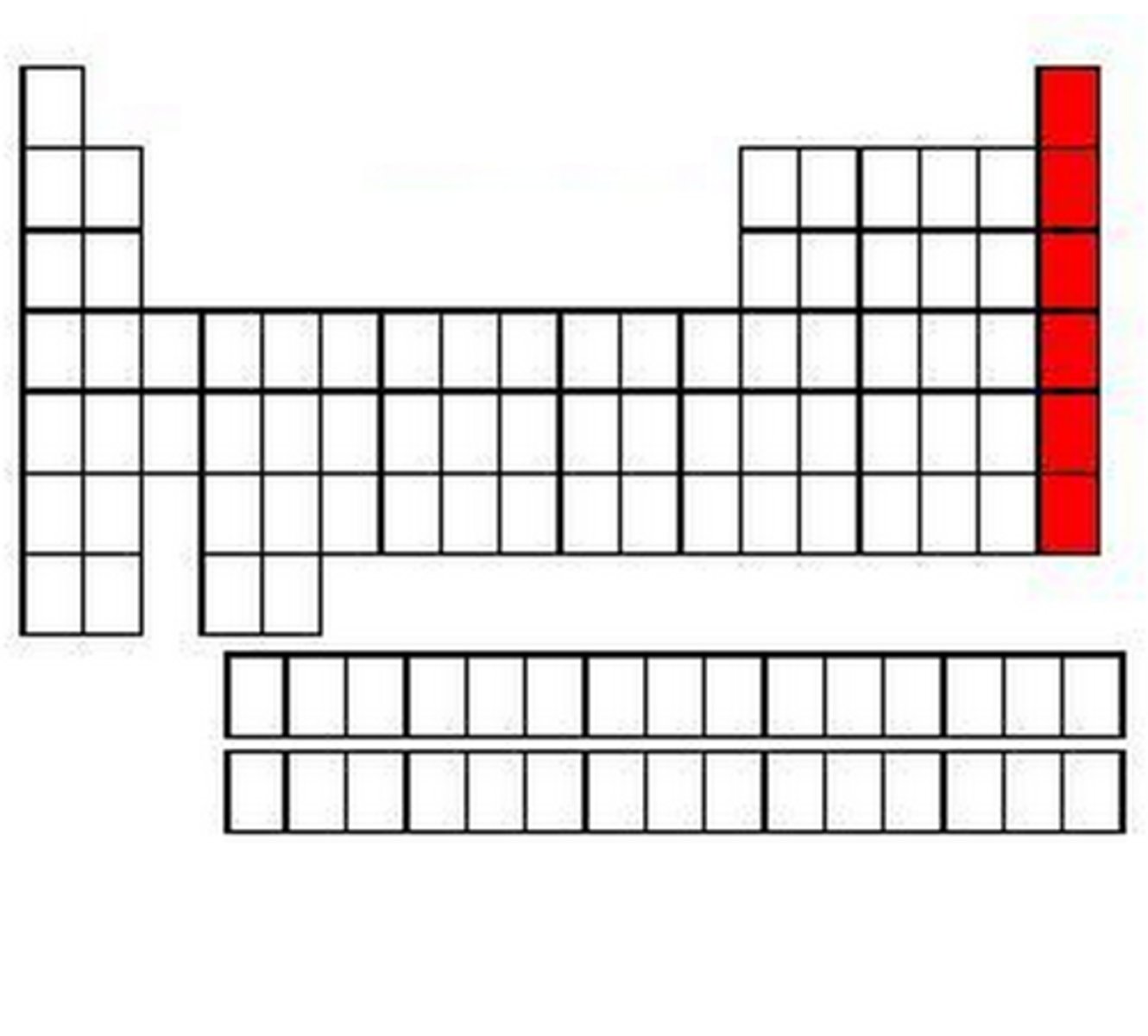
Noble gas/Inert gas
Alloy

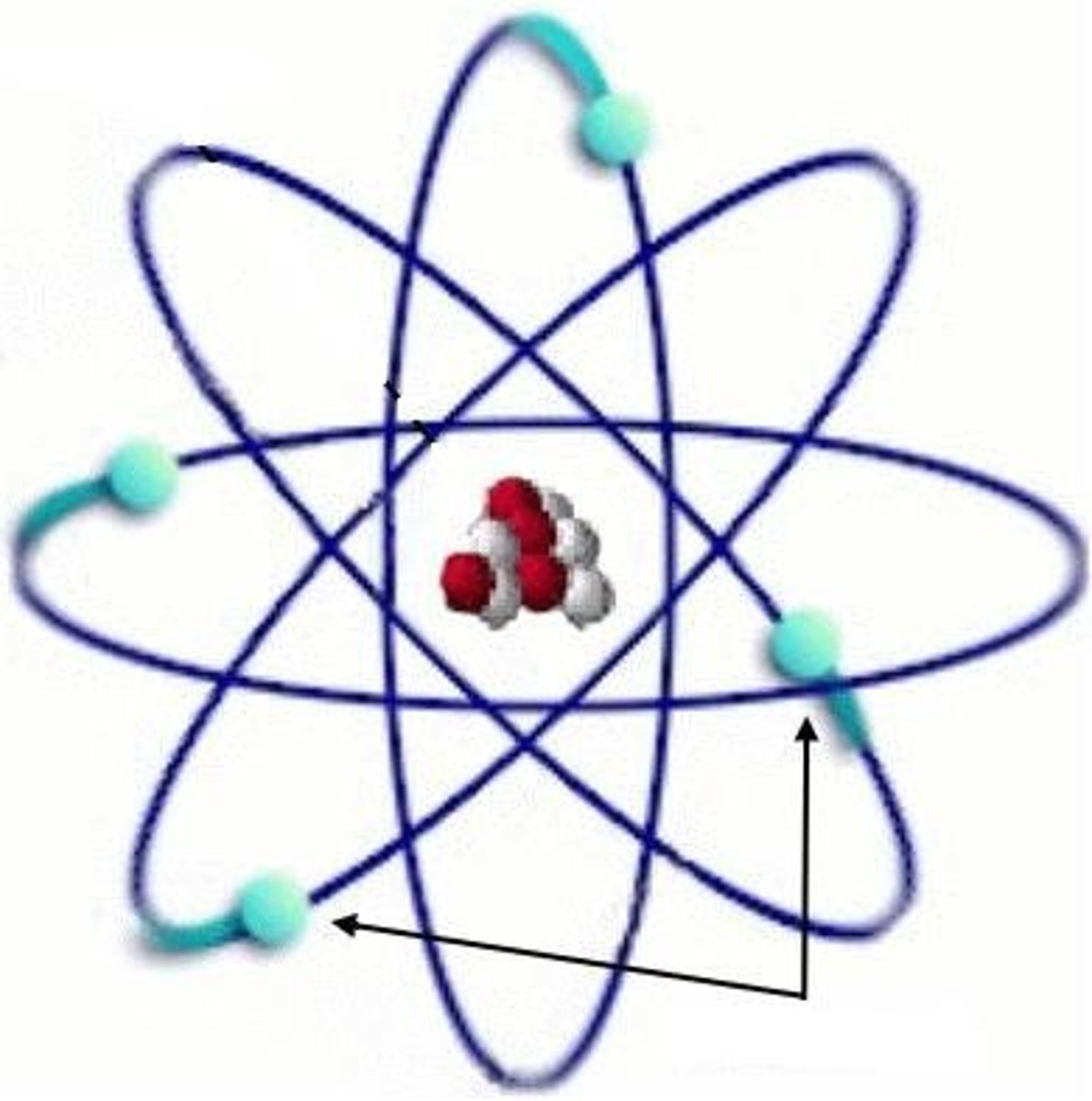
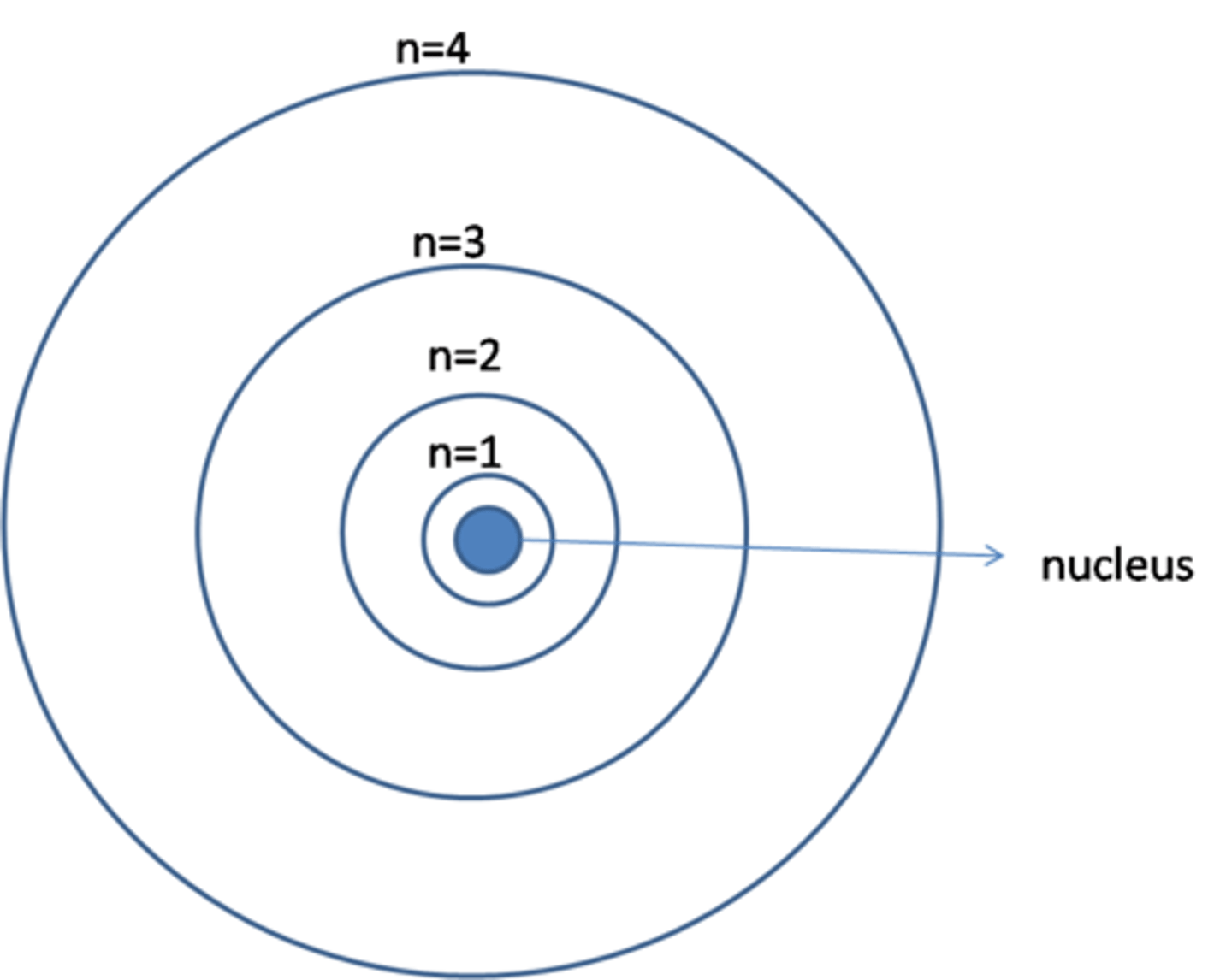
Energy levels
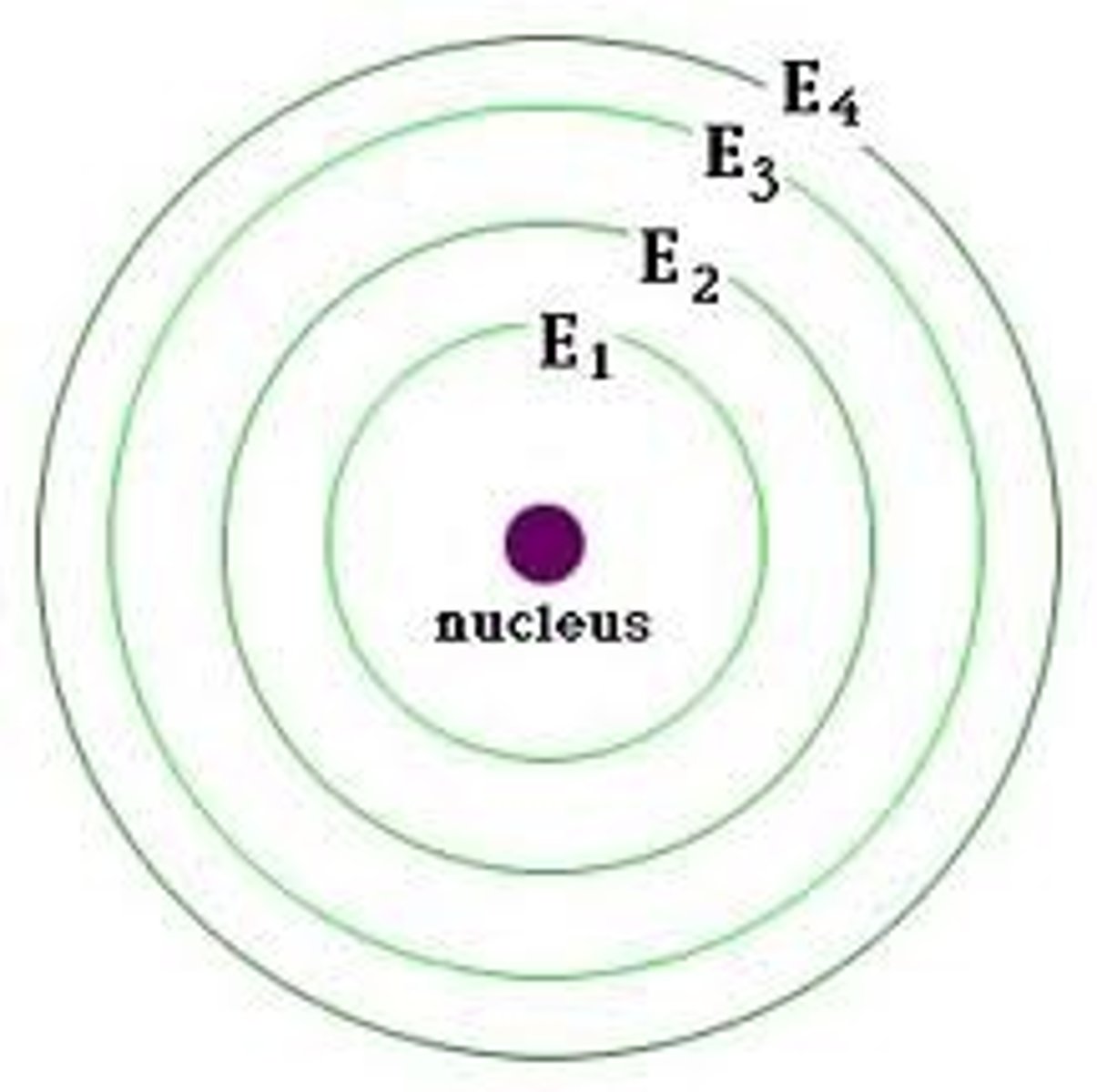
electron orbits
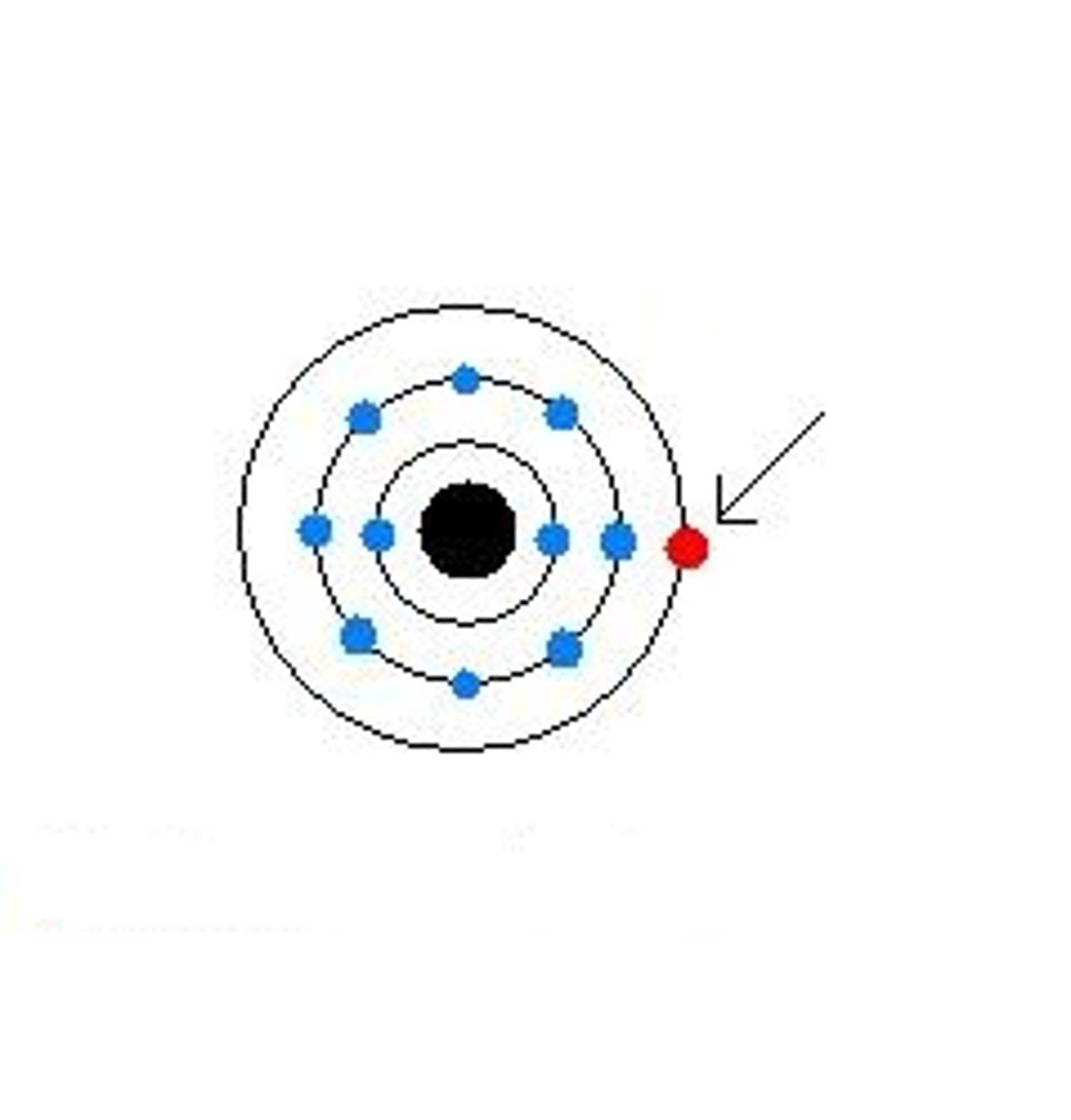
Valence electrons
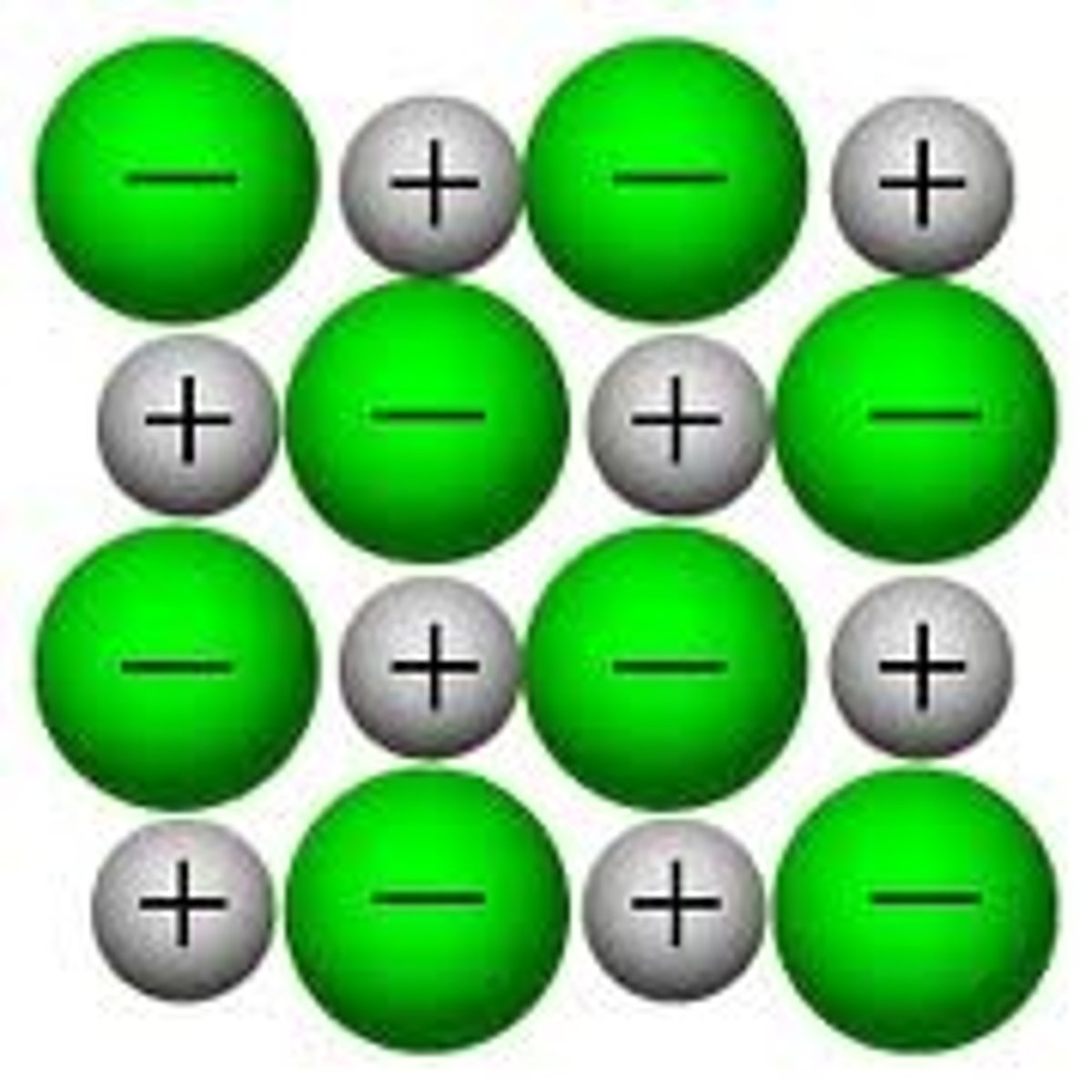
Ionic compound
Molecular compound
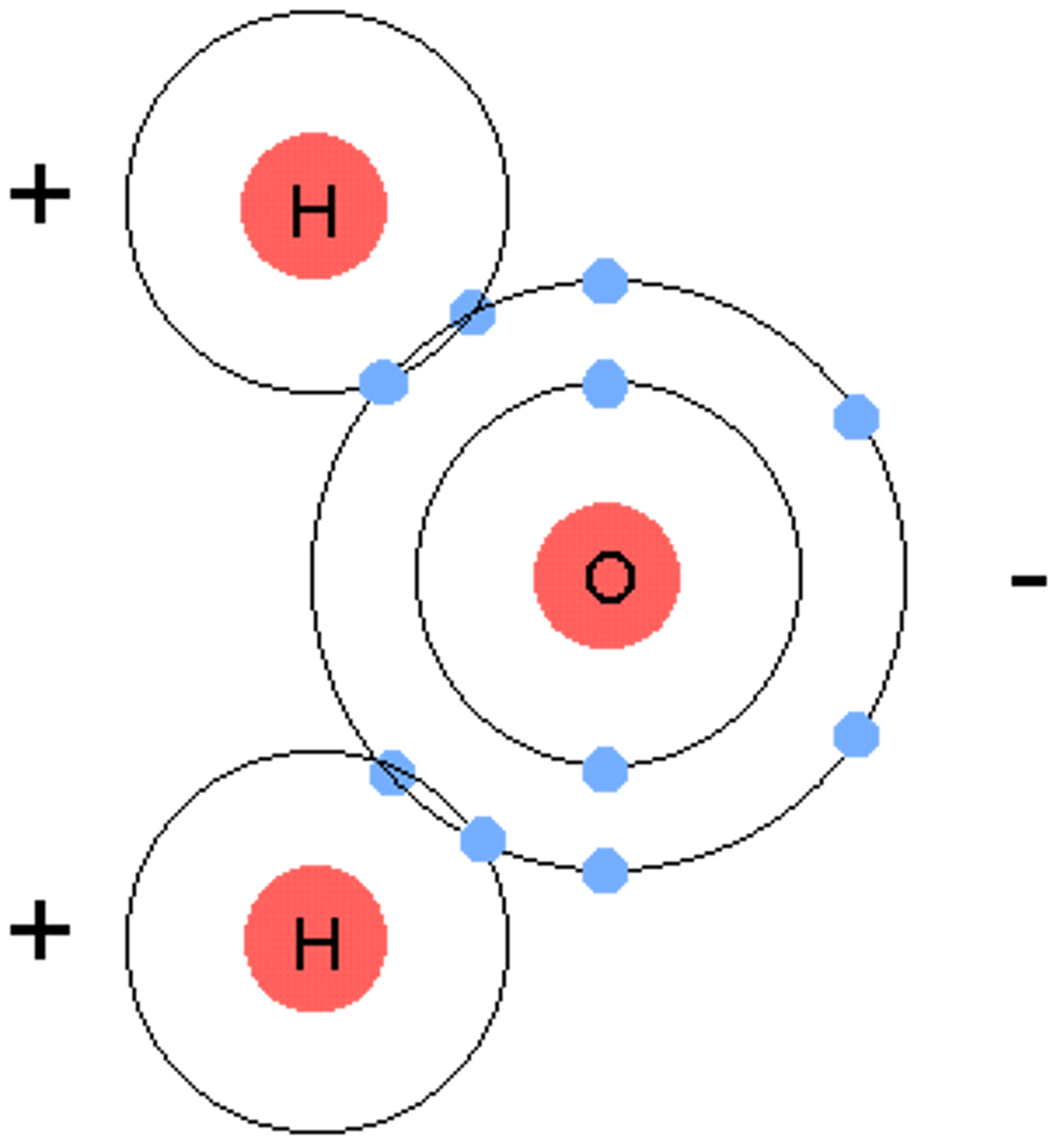
Chemical equation
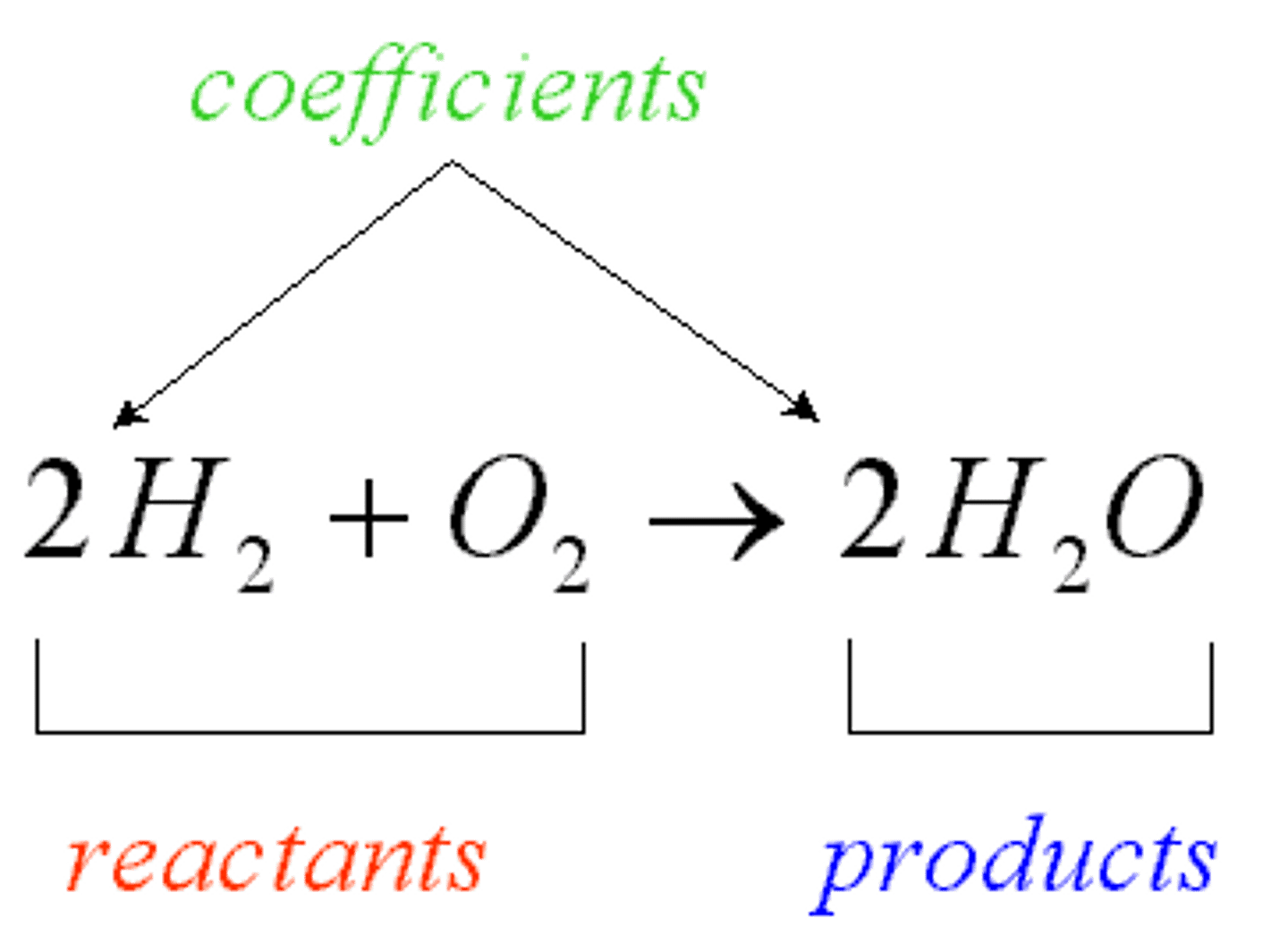
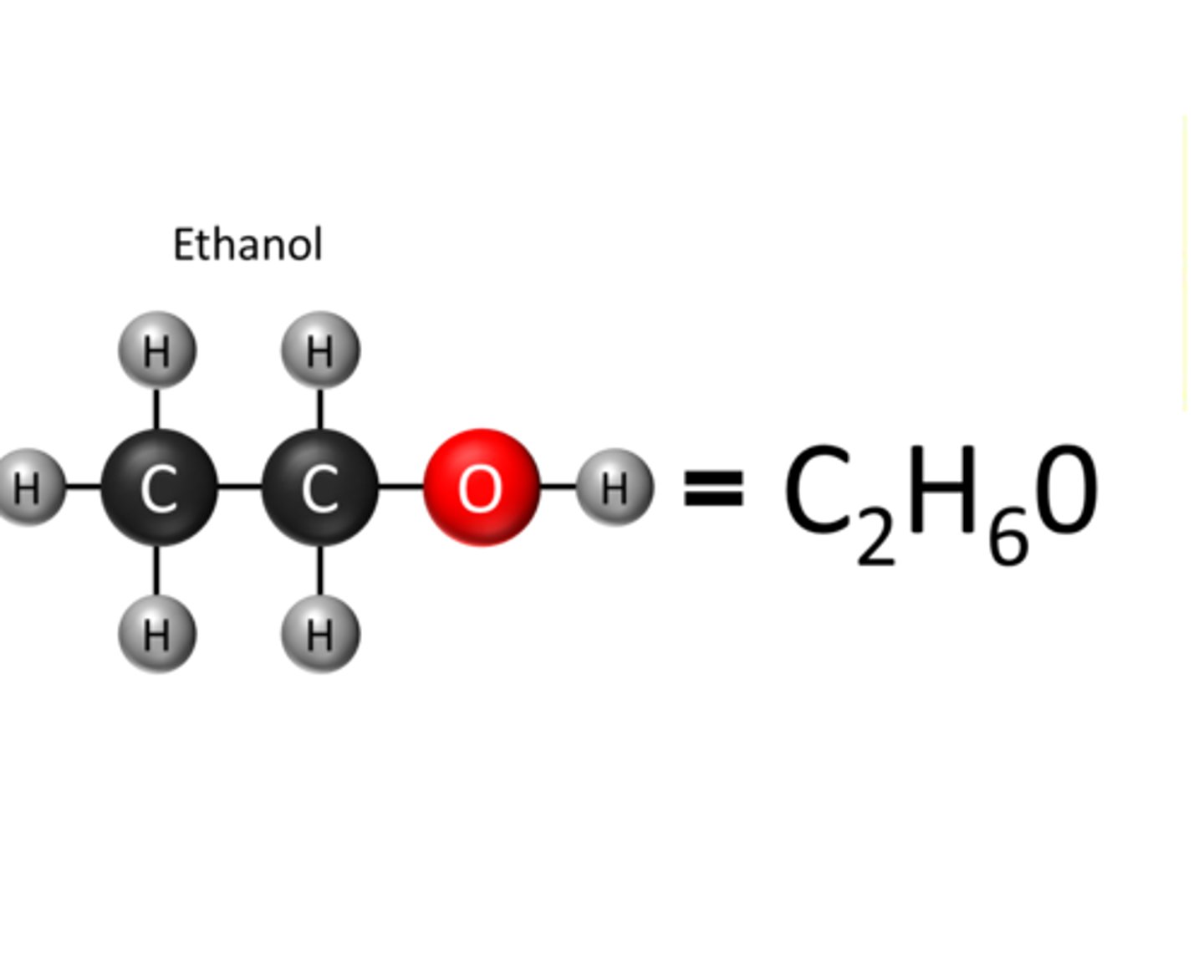
Chemical formula
Metal
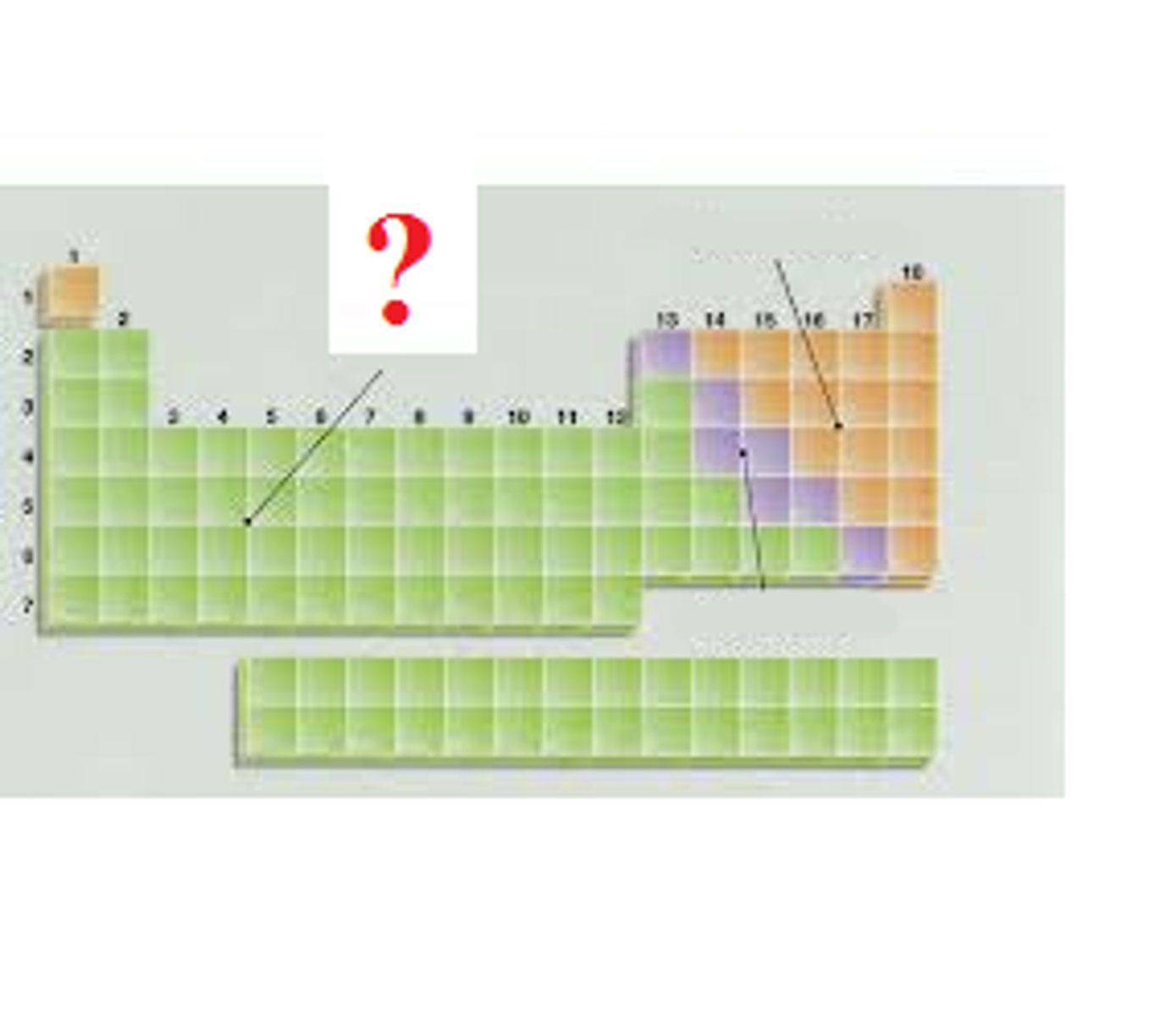
Metalloid
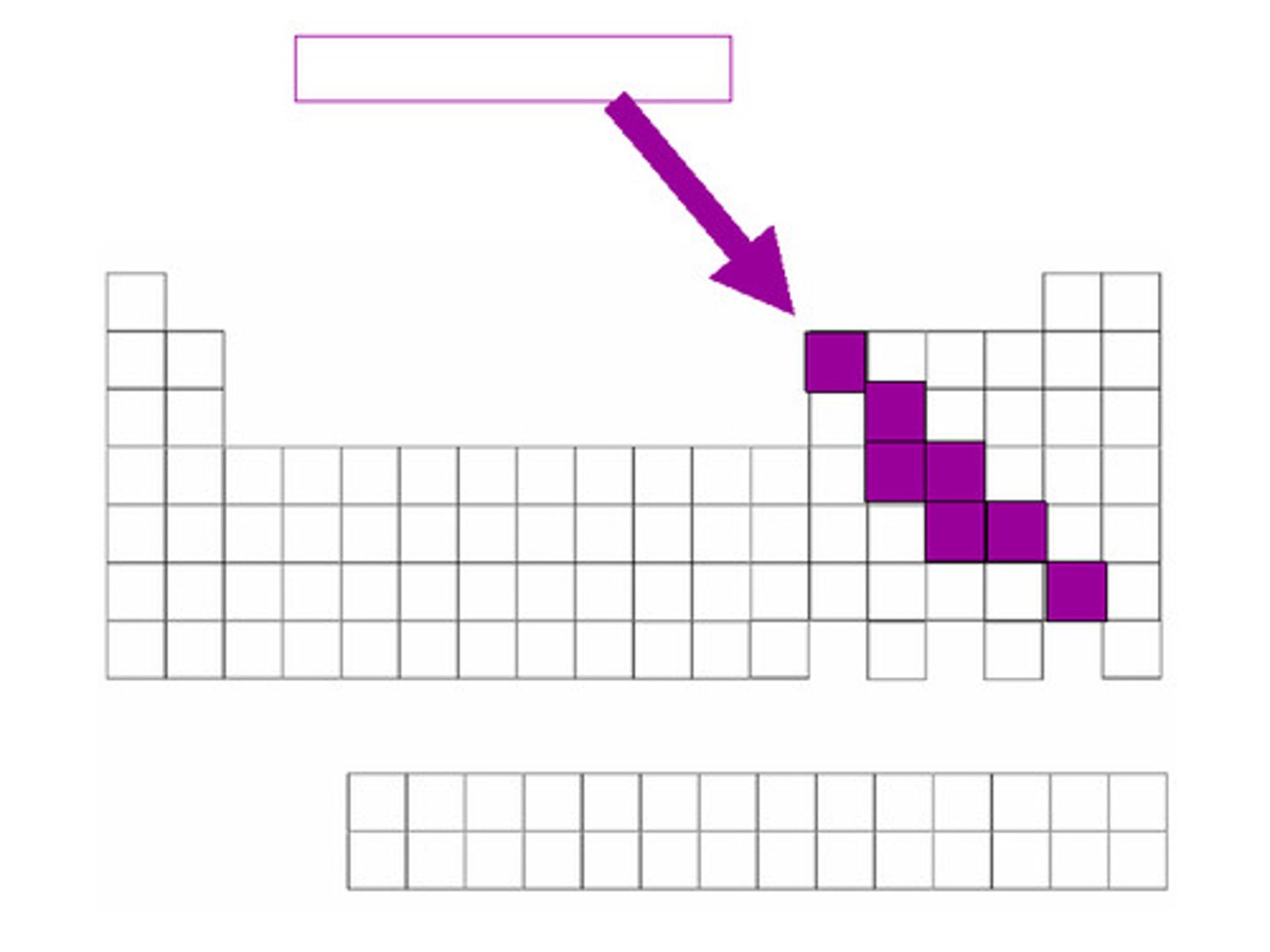
Non metal
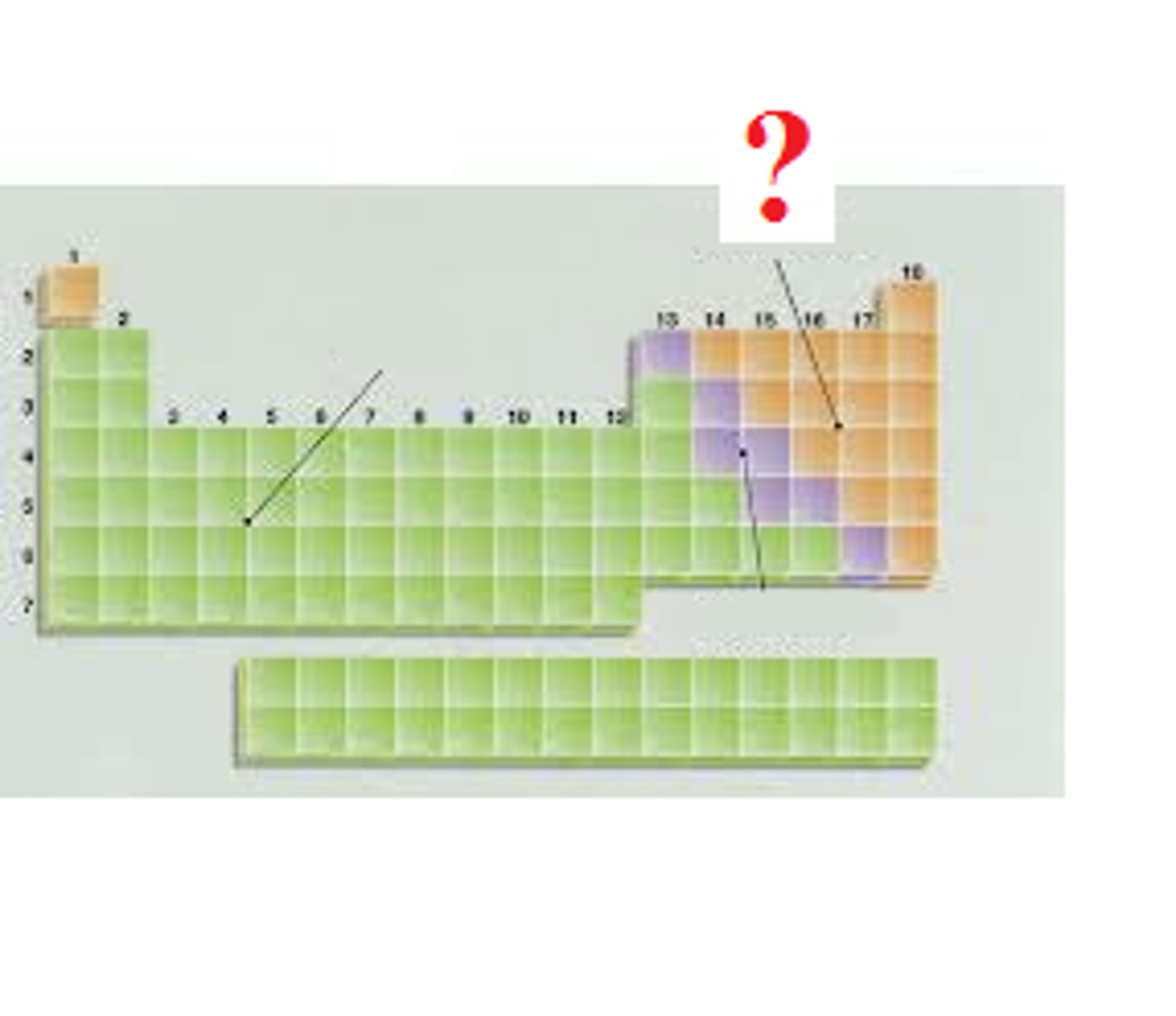
Ionic bond