CH15: AMINES
1/130
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
131 Terms
ammonia structure
NH3
ammonium ion structure
NH4+
in ammonia, N atom as ___ v e-
5
in ammonia, ___ e- from N and ___ e- from ___ H atoms form ___ polar covalent bonds
3 (all spots)
ammonia is a ___ molecule
polar
in ammonia the remaining 2 e- (lone pair of nonbonding e-) can serve as ___ or ___.
H+ acceptor
e- donor
ammonia is a ___.
base
ammonium ion (cation) form a ___ w/ 4th H+ b/c H+ has ___ to form a bond.
coordinate bond
no e-
amine group is a functional group ___ from ammonia (NH3), in which 1 or more H atoms are replaced by ___.
derived
R-groups (alkyl or aryl)
amines can be classified as ___, ___, or ___, according to how many ___.
primary, secondary, tertiary
R-groups are individually bound directly to the N atom
primary amine definition
N atom is attached to only 1 R-group and 2 Hs
can be located on the end or attached to an internal C of a chain
primary amine general formula
R—NH2
secondary amine definition
N atom is attached to 2 R-groups and 1 H
secondary amine general formula
R2—NH
tertiary amine definition
N atom is attached to 3 R-groups and 0 Hs
tertiary amine general formula
R3—N
quaternary amine definition
N atom is attached to 4 R-groups and a (+) charge
quaternary amine general formula
R4—N+
amines are ___ b/c the N atom has a lone pair of e-, and this lone pair can accept a H+, leading to the formation of ___.
bases
an ammonium ion
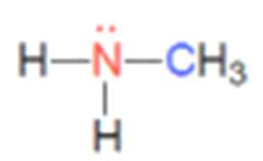
what class of amine is this
primary amine
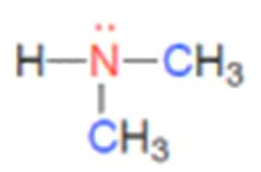
what class of amine is this
secondary amine
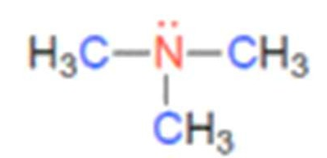
what class of amine is this
tertiary amine
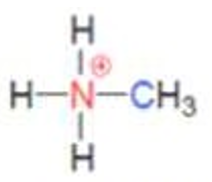
what class of ammonium ion is this
primary ammonium ion
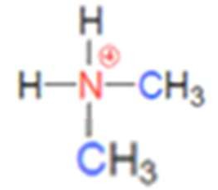
what class of ammonium ion is this
secondary ammonium ion
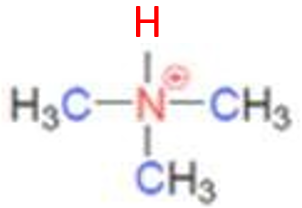
what class of ammonium ion is this
tertiary ammonium ion
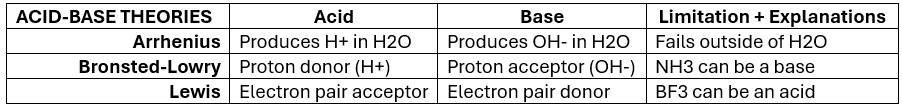
Acid-Base Theories — Summary Chart (KNOW)
nonpolar covalent bond’s electronegativity difference between atoms
0 — 0.4
polar covalent bond’s electronegativity difference between atoms
0.5 — 1.9
ionic bond’s electronegativity difference between atoms
2.0 and above
conjugate acid-base pairs definition
occur within acid-base equilibrium rxns
an acid and its conjugate base, as well as its base and conjugate acid, differ only by 1 proton.
HA + B ←→ A- + HB+
[acid + base ←→ conjugate base + conjugate acid]
amine + acid —> ___ + base
ammonium ion
3 major types of amines depends upon ___.
the structure of the backbone
3 major types of amines are
aliphatic
heterocyclic - saturated and unsaturated
aromatic
aliphatic amine definition
N atom bonds only to alkyl or alkyl-like group(s)
NO aromatic rings bind directly to the N atom
heterocyclic saturated amine definition
N is part of a ring structure; categorized as either secondary or tertiary amine
heterocyclic unsaturated amine definition
N is part of a ring structure; categorized as either secondary or tertiary amine - BUT THE RING IS UNSATURATED (CONTAINS DOUBLE BONDS)
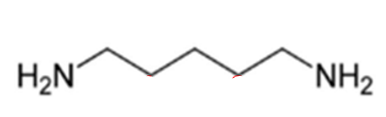
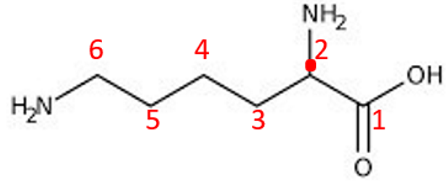
ID this structure
cadaverine - derived from Lysine
ID this structure
lysine - amino acid
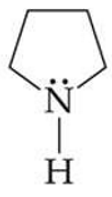
ID this structure
pyrrolidine
what is pyrrolidine in?
nicotine and other alkaloids
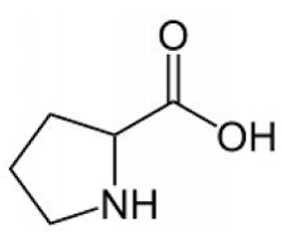
ID this structure
proline - amino acid
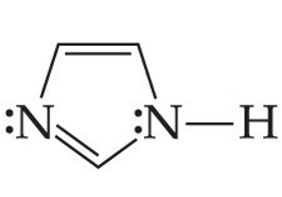
ID this structure
Imidazole
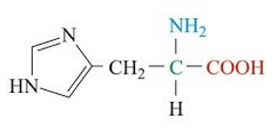
ID this structure
Histidine - amino acid
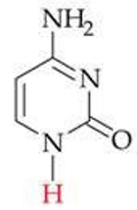
ID this structure
cytosine (C) - DNA, RNA
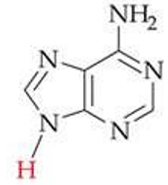
ID this structure
adenine (A) - DNA, RNA
aromatic amine definition
aromatic ring directly attached to an amine functional group
___ is the simplest amine and is used as the root name of its derivatives
aniline
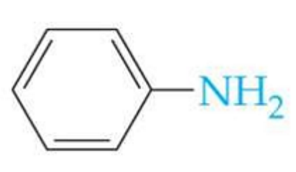
ID this structure
aniline
the ranking of functional groups holds significance in nomenclature since the higher-priority group represents the ____, determining the compound's organic family. Additionally, it is usually numbered to obtain the _____.
primary functional group
lowest possible location number
rank the functional groups from highest priority to lowest priority
Carboxylic Acid
Ester
Amide
Aldehyde
Ketone
Alcohol
Thiol
Amine
Ether
Alkene = Alkyne
Alkyl = Halide
naming primary amines: ID the Alkyl group that bonds to the NH2 group. Name as ____.
"alkylamine"
naming primary amines: If amine group is bound to a cycloalkane, name as ____.
"cycloalkylamine"
naming Secondary & Tertiary Amines w/ Identical Alkyl Groups: Name the identical alkyl groups bonded to the N atom. For secondary, use ___ before the alkyl group name and then add the suffix ___. For tertiary, use the ____ before the alkyl group name.
"di-"
"-amine"
"tri-"
naming Secondary & Tertiary Amines w/ Different Alkyl Groups: ID and name the alkyl groups attached to the N atom. The ____, gets the root name.
longest alkyl group w/ N
naming Secondary & Tertiary Amines w/ Different Alkyl Groups: The shorter alkyl group(s), add the prefix ___ to each and put them in ____.
"N-"
alphabetical order
naming Secondary & Tertiary Amines w/ Different Alkyl Groups: If any 2 substituent alkyl groups are identical (w/in tertiary), name as ____.
"N,N-" (NO numbers)
naming ammonium ions: same rules the others, but after naming the alkyl group, follow it with ____.
“ammonium ion”
naming primary aromatic amines: Aryl amines are named using ____as the parent, w/ the C attached to the amine group as ____. Substituents are then numbered based upon ____.
"aniline"
"1"
their position
Simplest aromatic amine consists of a phenyl group attached to an amine group and is commonly called ____, which can accept a H+ to form ____.
aniline
anilinium ion
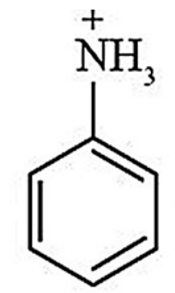
ID this structure
anilinium ion
naming Secondary & Tertiary Amines Derived from Aniline: ID the parent compound and use ____ as the root name.
aniline
naming Secondary & Tertiary Amines Derived from Aniline: Name the substituent(s), add the prefix ____ to each and place in ____.
"N-"
alphabetical order
amine functional group is ___.
polar
Electronegativity refers to an atom's ____.
capability to draw e- towards itself in a covalent bond
Both the C-N and N-H bonds exhibit polarity due to ____.
N's electronegativity
In the case of N on primary amines, it bonds w/ 2 Hs, showcasing its ability _____.
to participate in H-bonding
Amines are the only ___ functional group.
BASIC
In primary amines, the N atom has a lone pair of e- that can act as a ____, while the 2 Hs bound to N can act as ____.
H-bond acceptor
H-bond donors
primary amines can form a total of 3 H bonds w/ ___.
other amine molecules as well as w/ H2O molecules, enhancing their intermolecular interactions and H2O solubility.
Primary, secondary, and tertiary amines all exhibit ____! And only primary and secondary amines exhibit ____.
LDFs and Dipole-Dipole forces
H-bonding capabilities w/ each other, but tertiary amines cannot due to the absence of an H atom bound to N.
Primary amine has 2 N-H bonds + 1 lone pair e-, which means it can ____.
H-bond w/ itself & H2O
Secondary amine has 1 N-H bond + 1 lone pair e-, which means it can ___.
H-bond w/ itself & H2O
Tertiary amine has 0 N-H bonds + 1 lone pair e-, which means it can ____.
H-bond acceptor w/ H2O, only
Primary and Secondary amines, but not Tertiary amines, ____.
can form intermolecular H-bonds
Primary amines can form ____ than Secondary Amines.
1 more H-bond
boiling point variations in amines is all due to ____.
H-bonding ability
highest to lowest BPs in amongst amines
primary
secondary
tertiary
O is more ___ than N. —OHs have stronger ___ than amines.
electronegative
dipole-dipole force and H-bonding
increased EN = increased ___
polarity
highest to lowest BPs amongst alkanes, amines, and alcohols
alcohols
amines
alkanes (of similar Molecular Weight)
differences in molecular weight could be 1 but have a large impact on ___.
BP differences
All classes of amines can form ____.
1 or more H-bonds w/ H2O
Small amines w/ 1-5 Cs are ___ in H2O.
SOLUBLE
As H-C hydrophobic parts increase in size, larger amines have _____.
less H2O solubility
Larger amines w/ 6 or more Cs are ____ in H2O — relates to molecules and their ____.
INSOLUBLE
non-polar vs. polar parts
Ammonia is a base b/c _____, resulting in the formation of an _____.
its lone pair of e- can form a covalent bond w/ H+ from H2O or acids
ammonium cation (NH4+)
generally, ionic compounds are more _____ than neutral non-ionic compounds.
H2O soluble
Like ammonia, aliphatic amines act as bases b/c _____.
the lone pair on the N can accept a H+ to form ammonium salt (also called amine salt)
Factors Affecting Basicity: e- donating groups (alkyl groups push e- density towards N) _____.
increase basicity (more negative)
Factors Affecting Basicity: e- withdrawing groups (benzene rings) _____.
decrease basicity (more positive)
lower pKb =
stronger base
higher pKb =
weaker base
Alkyl amines are _____ than ammonia
more basic
The alkyl groups donates more e- than H to N. Hence, the e- density on the alkyl amine's N is ____ than the N of ammonia — making the lone pair on alkyl amines a stronger ____ and stronger ___.
greater
H+ acceptor
base
Aniline is a much ____ than Ammonia
Weaker Base
Aromatic amines are ____ than ammonia.
weaker base
In aniline, the lone pair of e- on N are drawn towards _____. Hence, the lone pair in aniline is ____. As a result, aniline is a ____ than ammonia.
the resonance e- in the benzene ring
no longer fully available to combine w/ H ions as in ammonia
weaker H+ acceptor and a weaker base
most to least basic ranked b/t ammonia, aniline, and alkyl amine
alkyl amine
ammonia
aniline
Amine salt is formed when ____ reacts w/ an acid.
amine base
characteristics of amine salts
generally odorless (compared to amines general bad smell)
ionic compound