Histology of Blood Vessels and Lymphatics
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
LO: 1. Define the general three-tunic structure of blood vessels. 2. Describe the modifications of the three tunics that occur in arterioles, muscular arteries, elastic arteries, veins, and venules. 3. Describe the structural and functional features of continuous, fenestrated, and sinusoidal capillaries. 4. Discuss the structure and function of the lymphatic system.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Some blood plasma cannot make it back from the tissues into the capillaries and venous system, so _____________ carry away that fluid and return it to the bloodstream
Some blood plasma cannot make it back from the tissues into the capillaries and venous system, so lymphatic vessels carry away that fluid and return it to the bloodstream
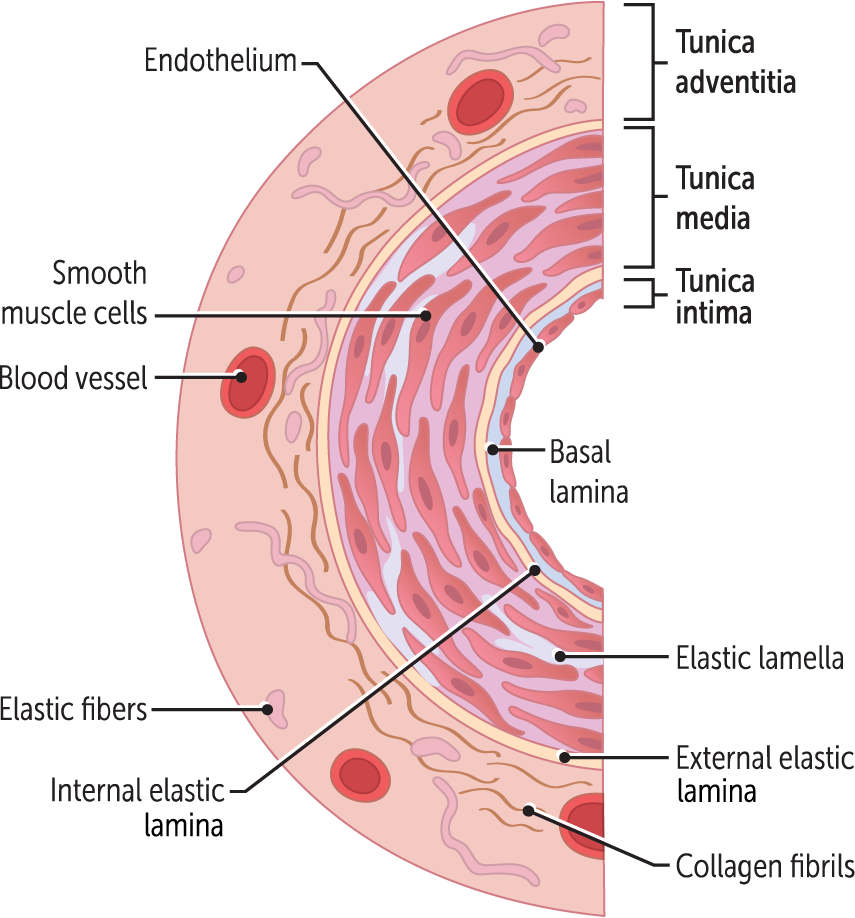
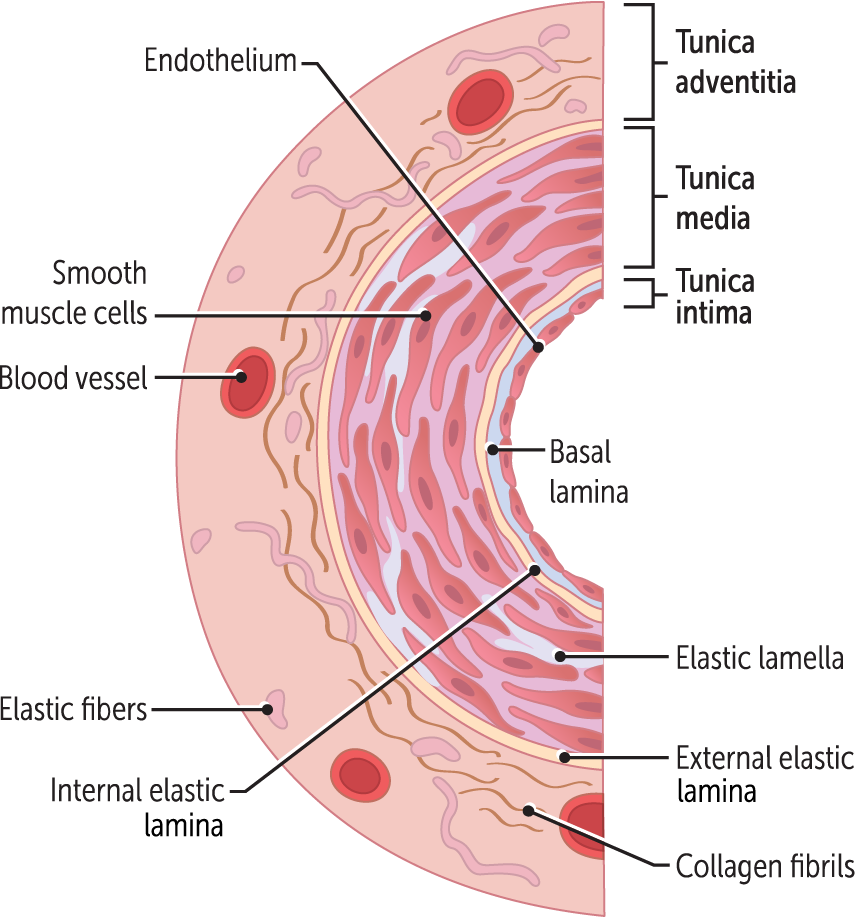
What are the three main layers of blood vessels?
tunica intima
tunica media
tunica adventitia
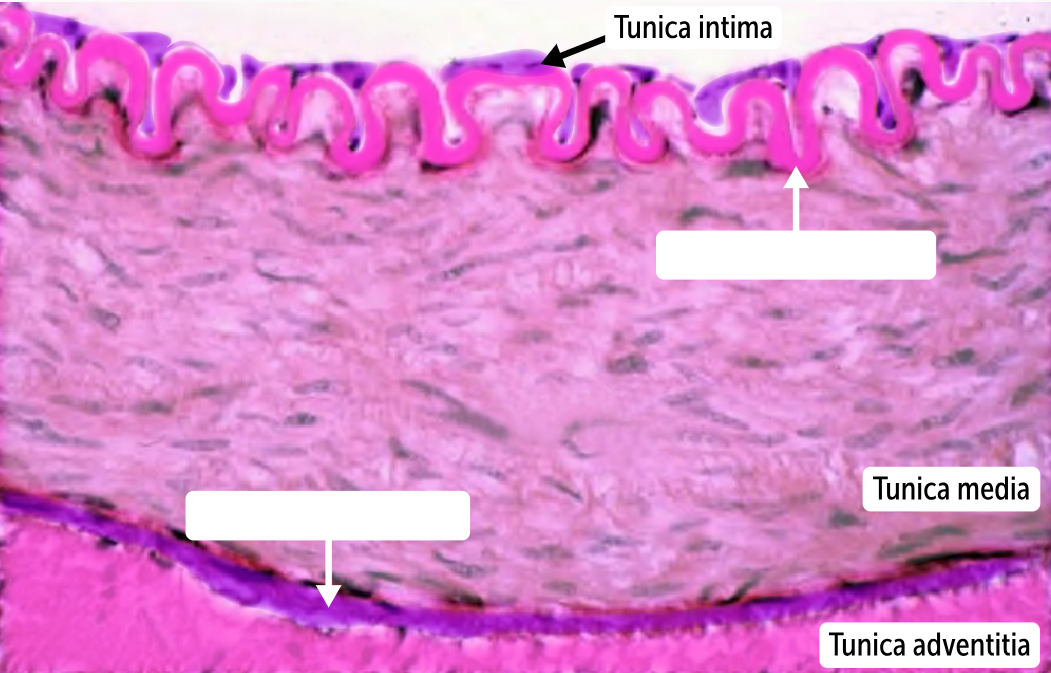
_______________
the innermost layer of the vessel
comprises endothelium, an underlying basement membrane, and a subendothelial layer (connective tissue).
The endothelial layer is simple squamous epithelium characterized by a smooth, nonadherent surface. The nonadherent surface allows red blood cells and platelets to pass by without sticking.
Tunica intima (aka, tunica interna)
the innermost layer of the vessel
comprises endothelium, an underlying basement membrane, and a subendothelial layer (connective tissue).
The endothelial layer is simple squamous epithelium characterized by a smooth, nonadherent surface. The nonadherent surface allows red blood cells and platelets to pass by without sticking.
The _________ is clinically important because it prevents clot formation. If it is disrupted, blood, specifically platelets, becomes exposed to thrombogenic factors, and clots begin to form.
The tunica intima is clinically important because it prevents clot formation. If it is disrupted, blood, specifically platelets, becomes exposed to thrombogenic factors, and clots begin to form.
Tunica media
the middle, muscular layer of the vessels.
formed by smooth muscle cells along with variable amounts of elastin (elastic fibers). These cells are ellipsoid in shape and lack striations.
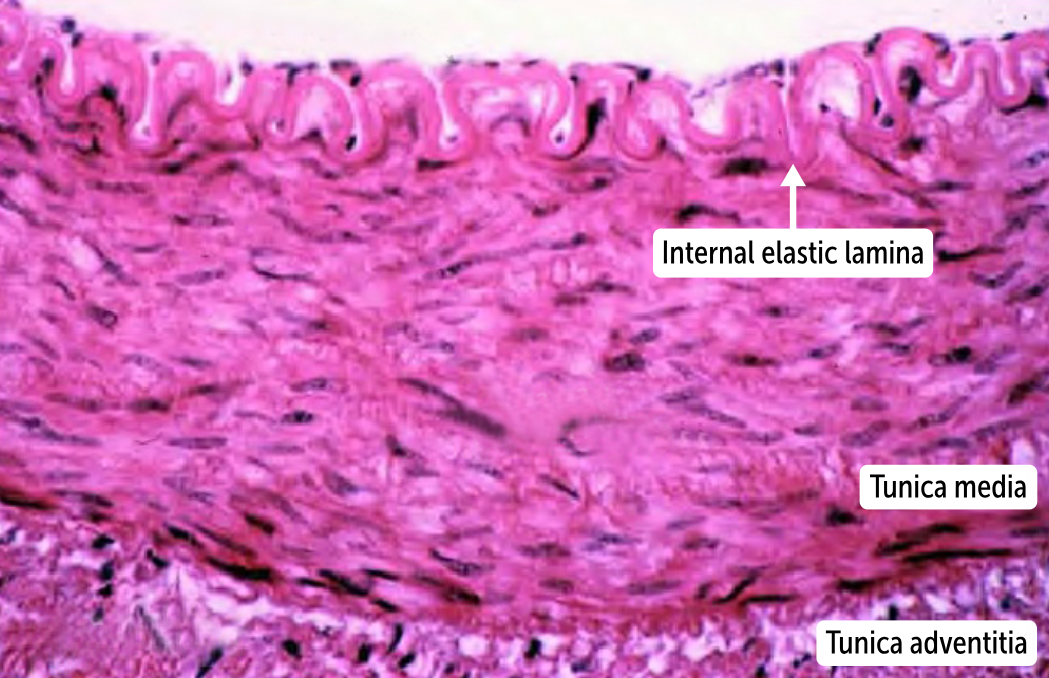
Between the tunica intima and tunica media in arteries and arterioles lies the internal _________ lamina. The external _________ lamina lies between the tunica media and tunica adventitia in larger, muscular arteries. These thin layers of ___________ tissue divide the three major layers of the blood vessels from one another
Between the tunica intima and tunica media in arteries and arterioles lies the internal elastic lamina. The external elastic lamina lies between the tunica media and tunica adventitia in larger, muscular arteries. These thin layers of elastic tissue divide the three major layers of the blood vessels from one another
Aortic dissection is a tear in the aorta that runs parallel to the vessel lumen. This tear has gone straight through the tunica intima and has developed a “false lumen” in the middle of the __________
Aortic dissection is a tear in the aorta that runs parallel to the vessel lumen. This tear has gone straight through the tunica intima and has developed a “false lumen” in the middle of the tunica media
__________________
the outermost layer of the blood vessels
is made up of loose connective tissue (collagen) covered externally by a layer of simple squamous epithelium.
In larger arteries such as the aorta, it is so far from the vessel lumen that it requires its own blood supply.
Tunica adventitia (aka, tunica externa)
the outermost layer of the blood vessels
is made up of loose connective tissue (collagen) covered externally by a layer of simple squamous epithelium.
In larger arteries such as the aorta, it is so far from the vessel lumen that it requires its own blood supply.
The vessels that supply the tunic adventitia and outer parts of the tunica media are called the ________
The vessels that supply the tunic adventitia and outer parts of the tunica media are called the vasa vasorum.
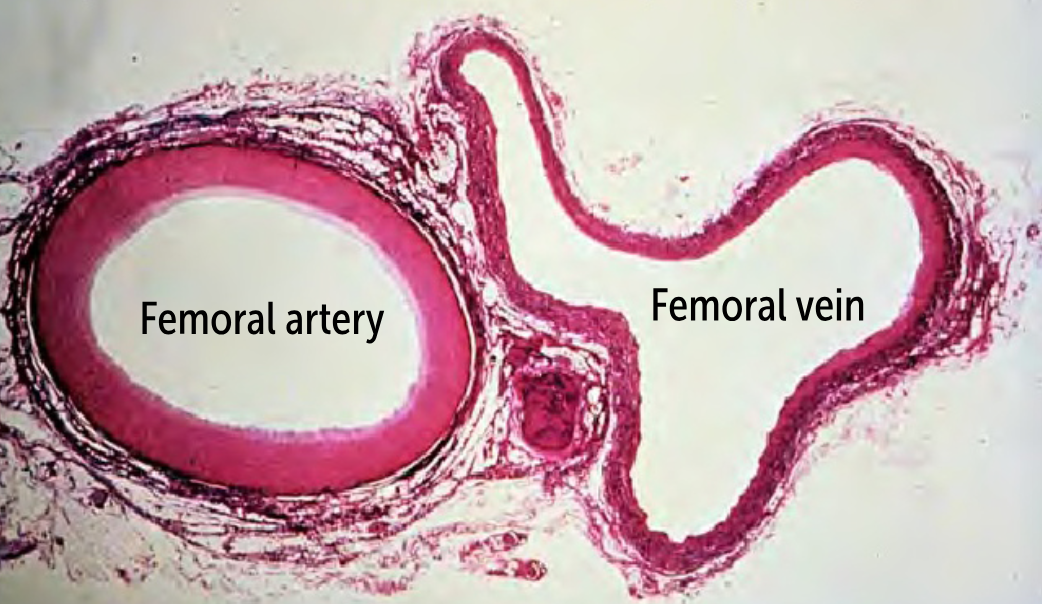
Because arteries must withstand _______ _______ than most veins, they have a very thick tunica media, so the arterial wall is much thicker than the venous wall.
Because arteries must withstand higher pressure than most veins, they have a very thick tunica media, so the arterial wall is much thicker than the venous wall.
_______________
the largest type of artery
has a high density of elastic fibers in the tunica media to be able to expand quickly during systole and contract during diastole.
Ex. aorta, larger branches of the aorta (ie, brachiocephalic, subclavian, carotid, iliac), and the pulmonary arteries
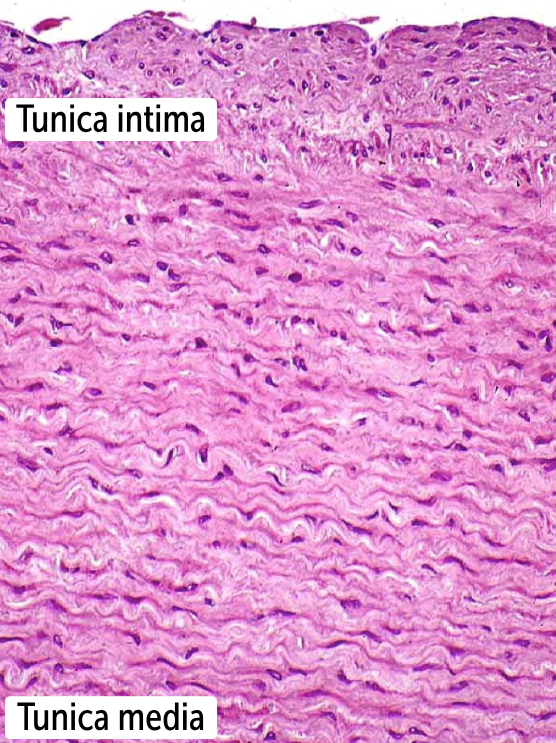
Elastic arteries
the largest type of artery
has a high density of elastic fibers in the tunica media to be able to expand quickly during systole and contract during diastole.
Ex. aorta, larger branches of the aorta (ie, brachiocephalic, subclavian, carotid, iliac), and the pulmonary arteries
______________
a step down a size from elastic arteries.
Ex. smaller branches off the aorta (ie, the coronary and renal arteries).
The defining feature is the relatively scant elastin in the tunica media
Thick walls to contain the high pressures but don’t require a lot of elastin because they don’t deal with large systolic-diastolic pressure differences (they are farther from the heart).
These arteries maintain perfusion to key organs like the heart and kidneys. In hypotensive states, they can contract quite a lot to do so.
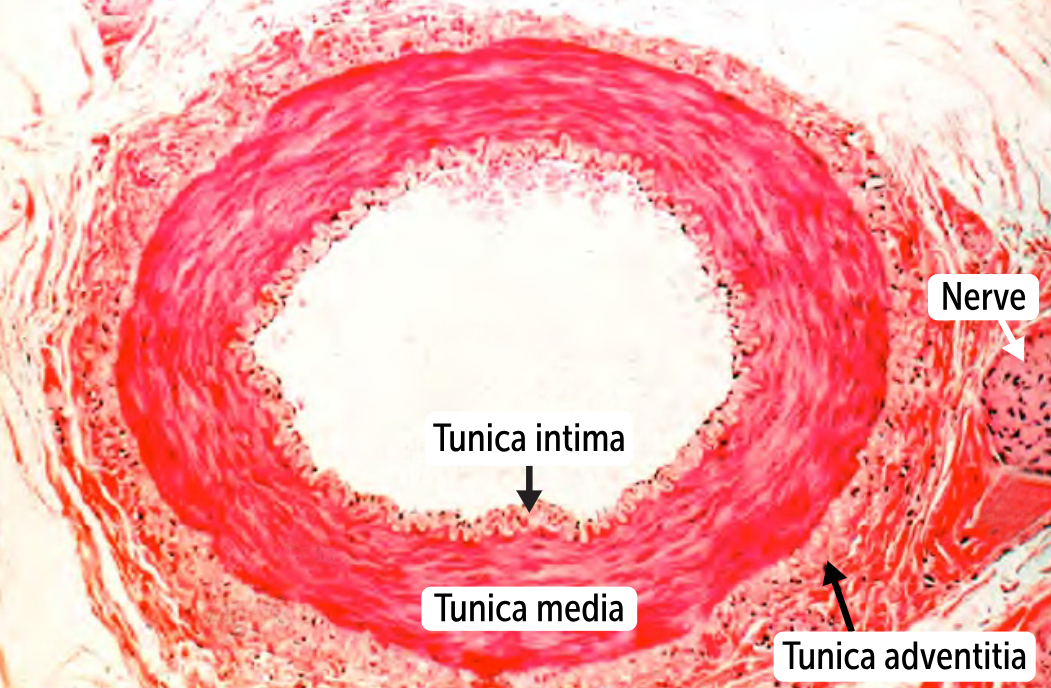
Muscular arteries
a step down a size from elastic arteries.
Ex. smaller branches off the aorta (ie, the coronary and renal arteries).
The defining feature is the relatively scant elastin in the tunica media
Thick walls to contain the high pressures but don’t require a lot of elastin because they don’t deal with large systolic-diastolic pressure differences (they are farther from the heart).
These arteries maintain perfusion to key organs like the heart and kidneys. In hypotensive states, they can contract quite a lot to do so.
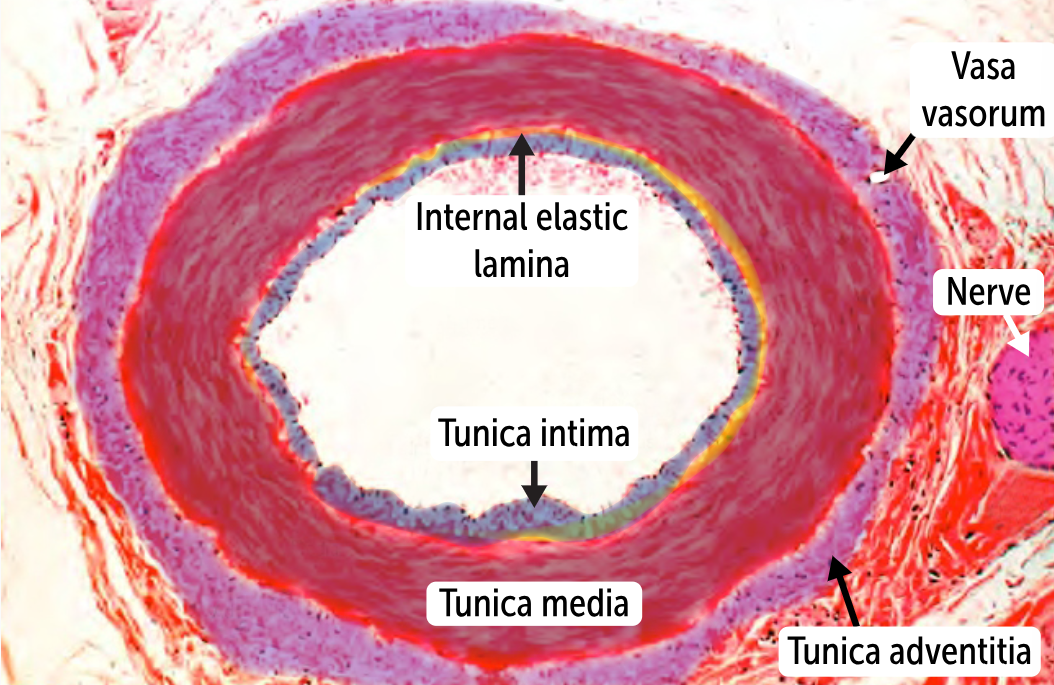
_______________
The smallest type of artery
lack an external elastic lamina,
the internal elastic lamina is often incomplete
don’t have to deal with systolic-diastolic pressure changes (the blood pressure is uniform by the time the blood gets to these small vessels), so they need the least amount of elastin.
Arterioles
The smallest type of artery
lack an external elastic lamina,
the internal elastic lamina is often incomplete
don’t have to deal with systolic-diastolic pressure changes (the blood pressure is uniform by the time the blood gets to these small vessels), so they need the least amount of elastin.
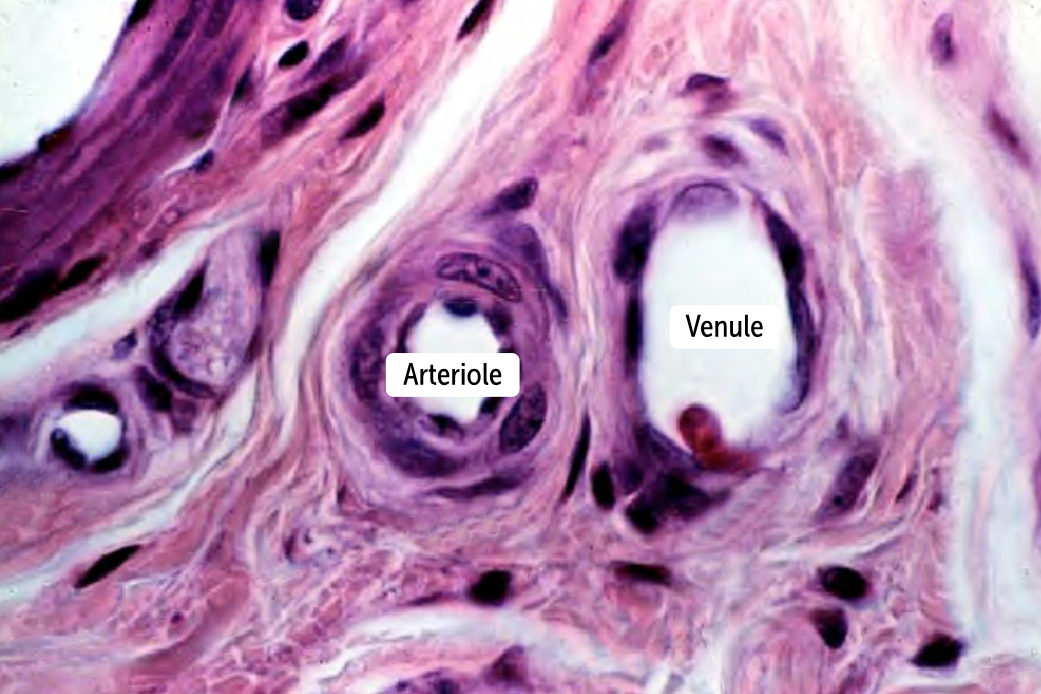
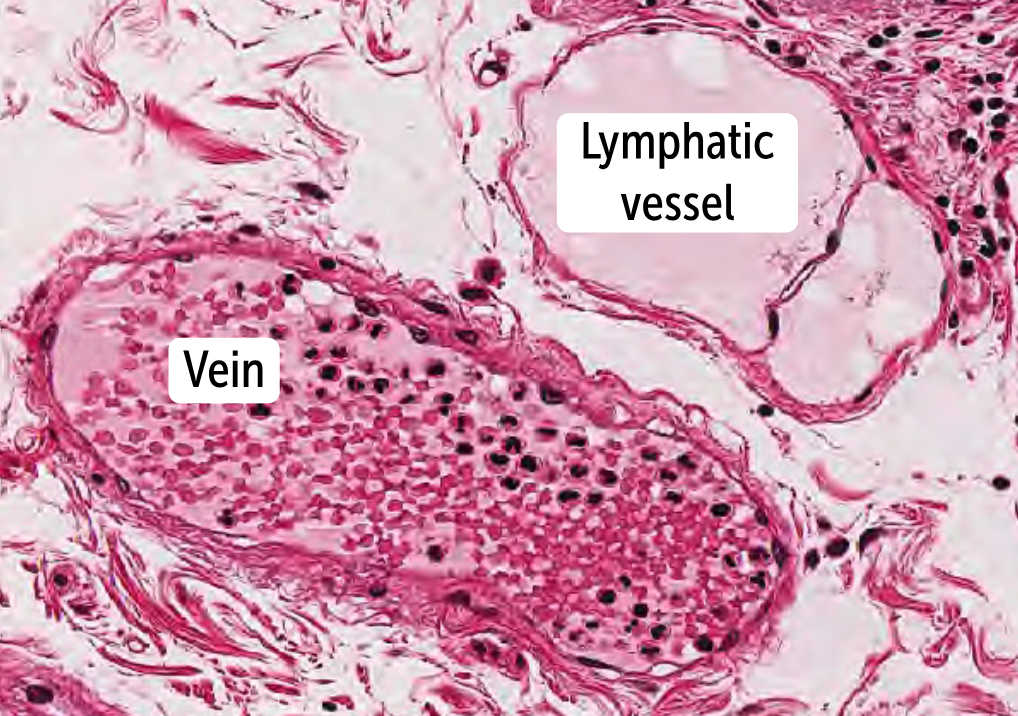
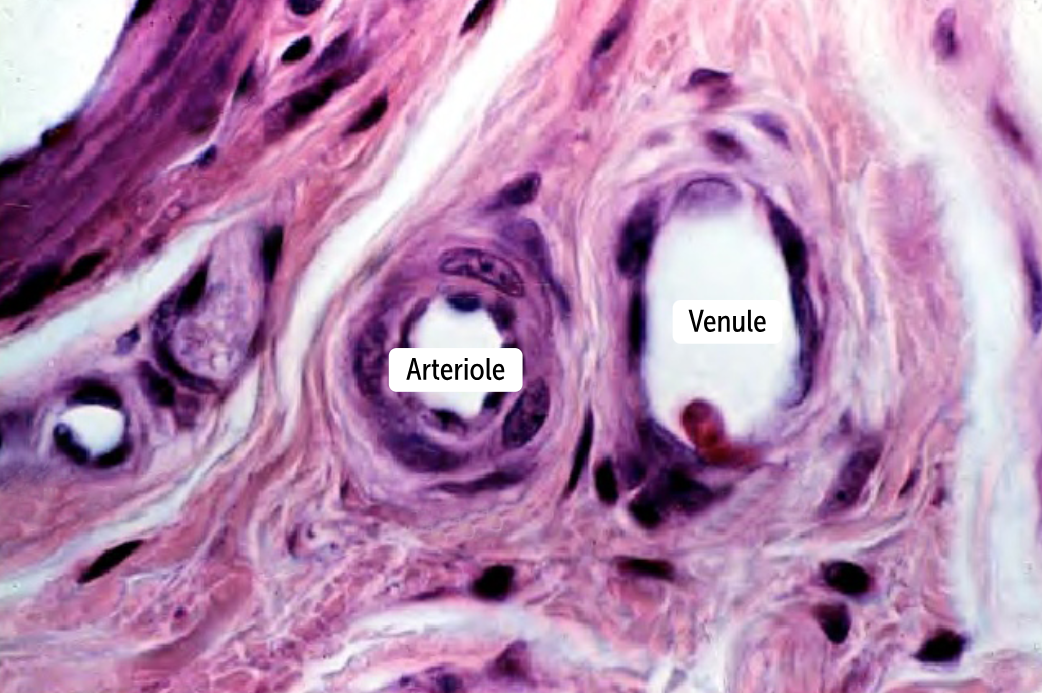
___________ are the smallest vessels and provide a connection between arteries and veins
Capillaries are the smallest vessels and provide a connection between arteries and veins
How do arteries and veins differ histologically?
The main histological difference between these vessels is that arteries have thick tunic media that veins lack
____________
the smallest of the veins
They have a tunica intima like that of arteries but a thin tunicae media and adventitia.
Postcapillary ________ lack the smooth muscle cells and elastic fibers that characterize the tunica media, so postcapillary venules have much less capacity to stretch (because of a lack of elastic) and vasoconstrict (because of an insufficient number of smooth muscle cells).
Postcapillary ________ drain into muscular venules before draining into veins.
Venules
the smallest of the veins
They have a tunica intima like that of arteries but a thin tunicae media and adventitia.
Postcapillary venules lack the smooth muscle cells and elastic fibers that characterize the tunica media, so postcapillary venules have much less capacity to stretch (because of a lack of elastic) and vasoconstrict (because of an insufficient number of smooth muscle cells).
Postcapillary venules drain into muscular venules before draining into veins.
Venous valves prevent blood pooling in the lower extremities; when they break down, venous pooling worsens, causing _____(1)_____ and _____(2)_____
Venous valves prevent blood pooling in the lower extremities; when they break down, venous pooling worsens, causing deep vein thromboses and venous stasis dermatitis.
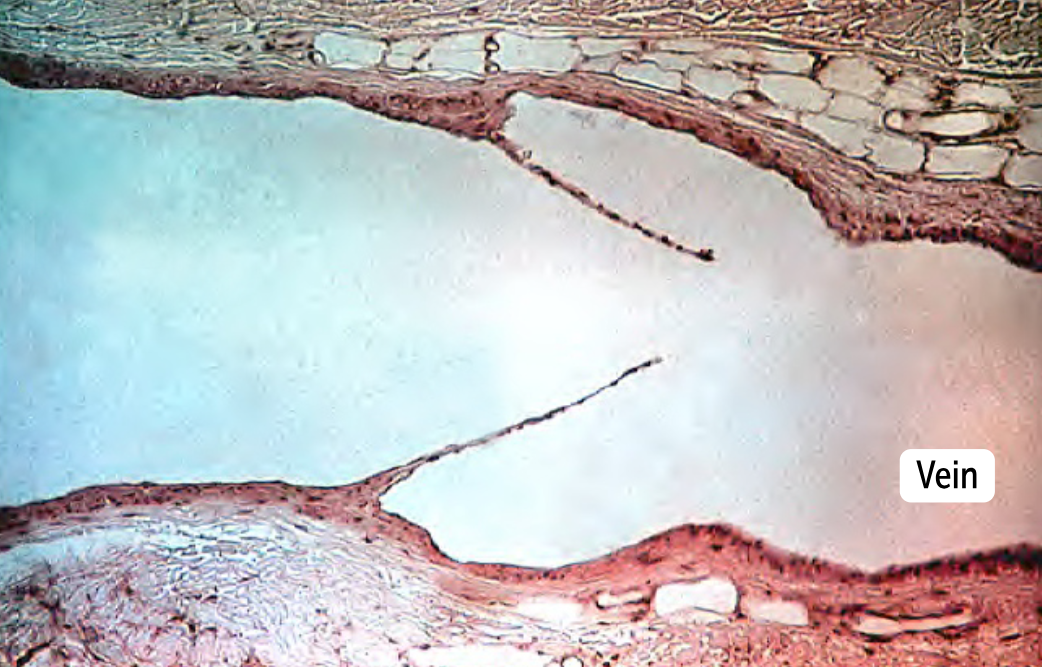
________
Histologically very similar to venules
Have one-way valves that maintain unidirectional flow. These valves are formed by outpouchings of the tunica intima into the venous lumen
Veins
Histologically very similar to venules
Have one-way valves that maintain unidirectional flow. These valves are formed by outpouchings of the tunica intima into the venous lumen
Forward flow in the venous system is largely created by the _____________________, which helps pump blood back to the heart, especially from the legs, pumping against gravity.
Forward flow in the venous system is largely created by the contractile action of the surrounding muscles, which helps pump blood back to the heart, especially from the legs, pumping against gravity.
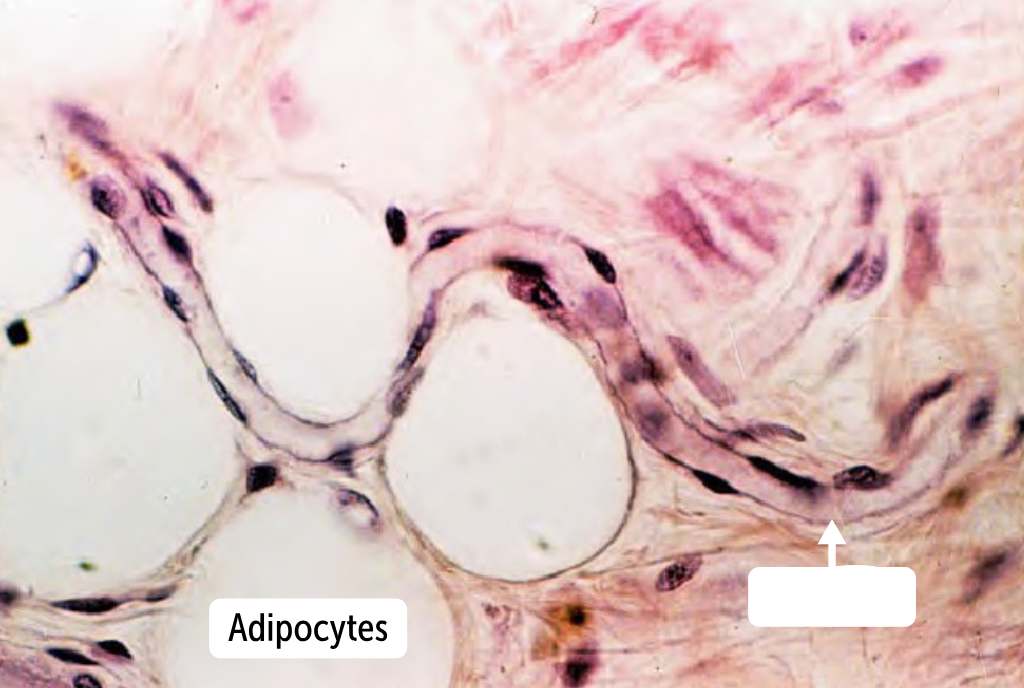
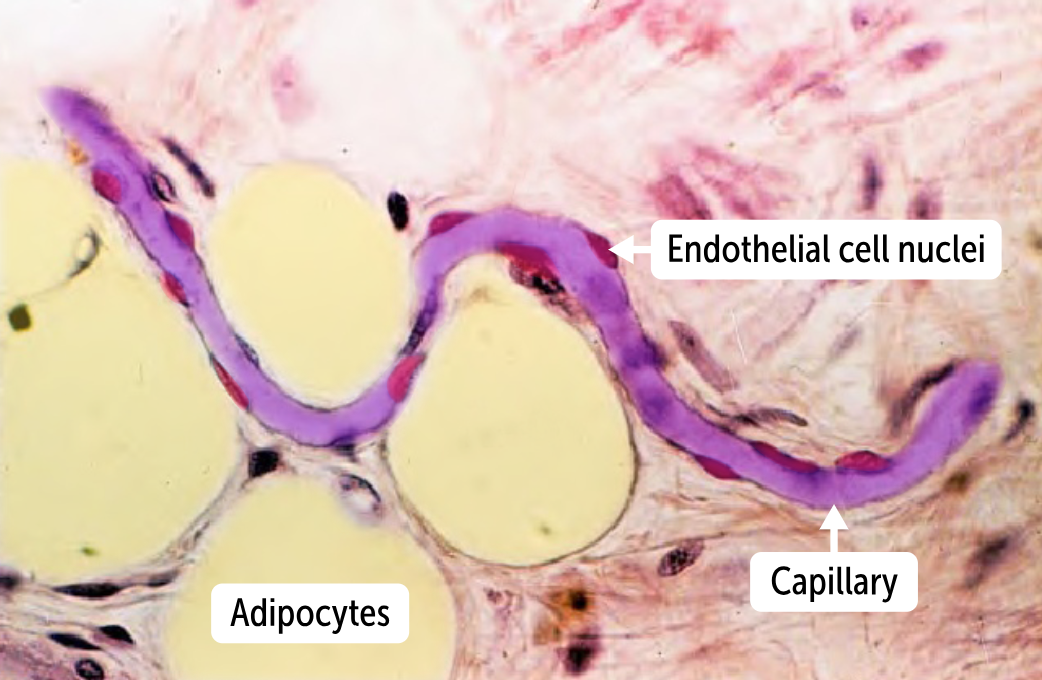
__________ are only one cell layer thick (to increase diffusion capacity. They have only a tunica intima, histologically, they show only an endothelium and the associated basement membrane.
Capillaries are only one cell layer thick (to increase diffusion capacity. They have only a tunica intima, histologically, they show only an endothelium and the associated basement membrane.
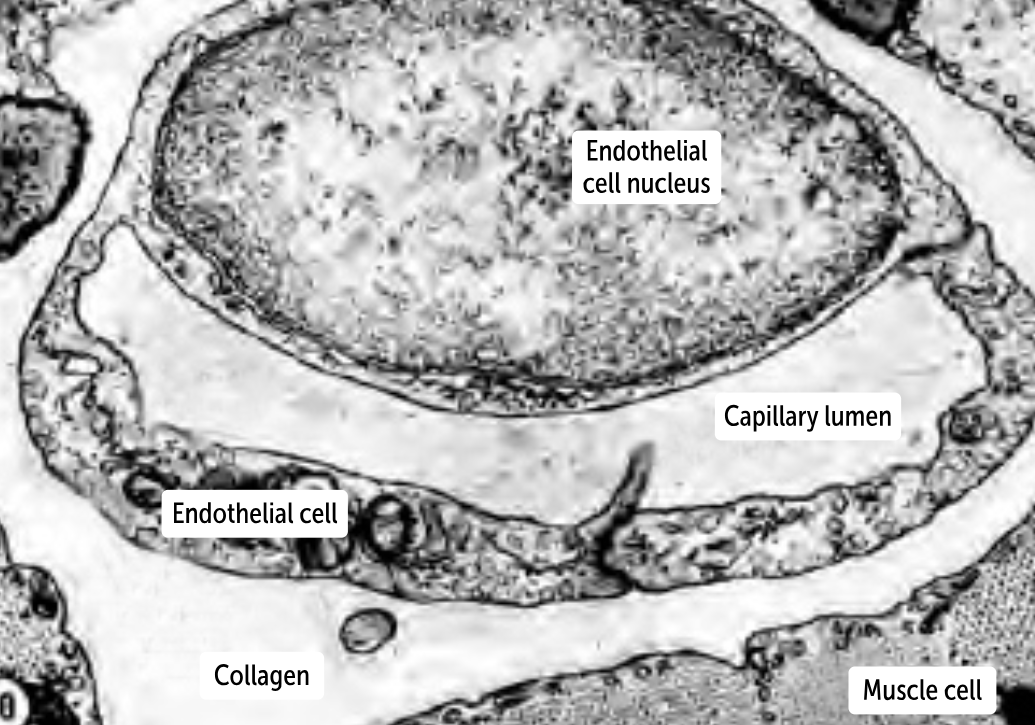
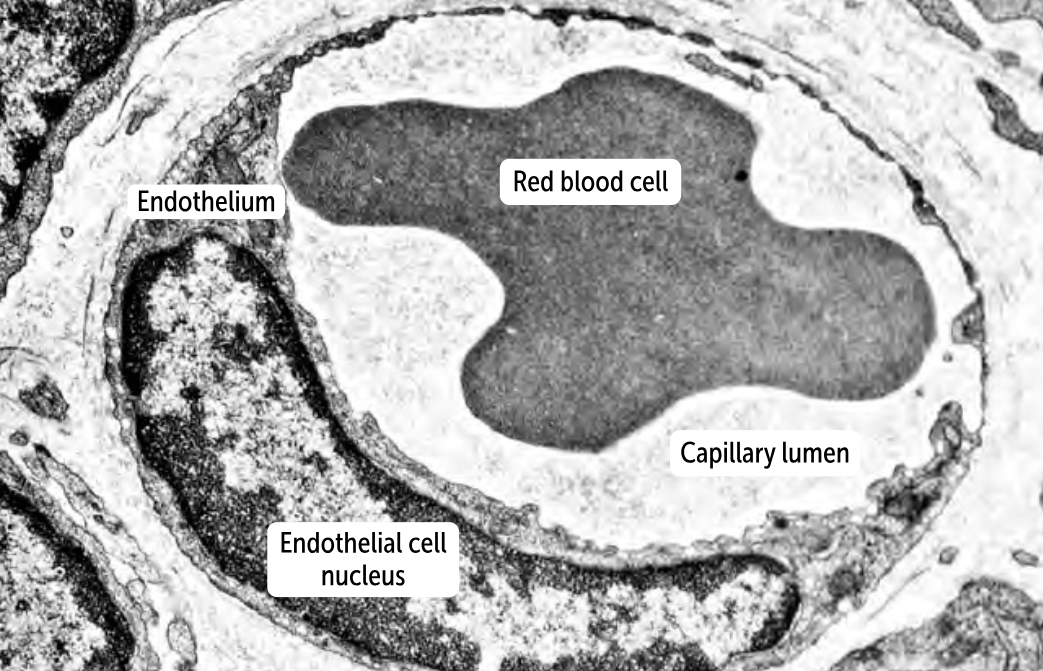
______________
they have a continuous layer of endothelium and a continuous basement membrane. Therefore, no gaps occur between the endothelial cells or within the basement membrane
the least permeable of the capillaries
can be found in muscles, connective tissue, the lungs, and the skin.
Continuous capillaries
they have a continuous layer of endothelium and a continuous basement membrane. Therefore, no gaps occur between the endothelial cells or within the basement membrane
the least permeable of the capillaries
can be found in muscles, connective tissue, the lungs, and the skin.
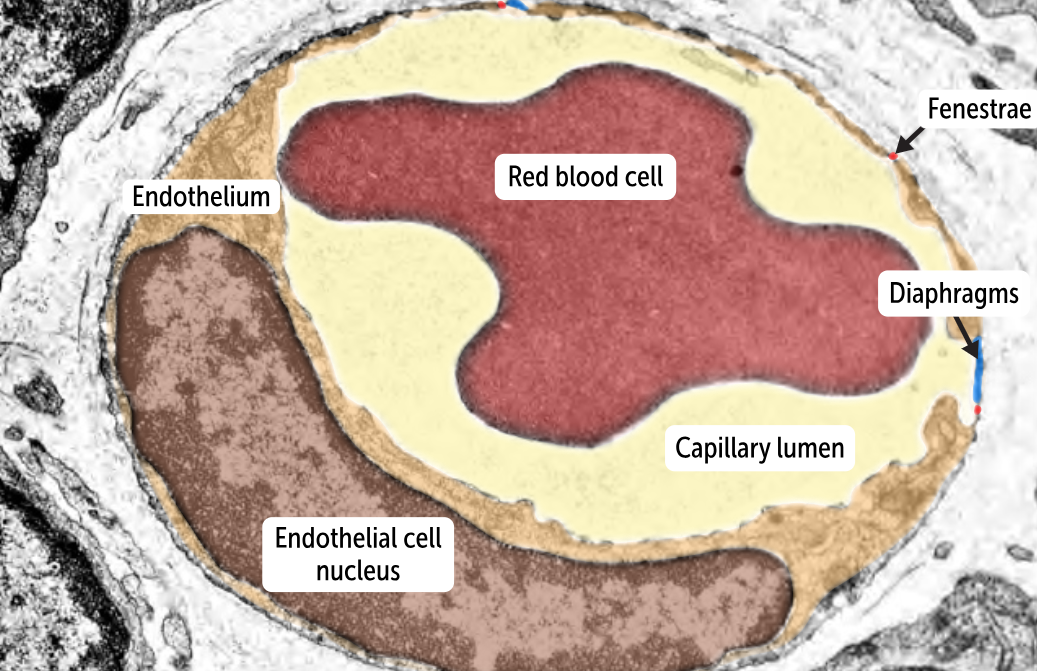
__________________
more permeable than continuous capillaries
has tiny holes or pores (fenestrae) in the endothelial cells that allow the passage of substances across the capillary wall
Sometimes, the fenestrae are covered with thin membranes (or diaphragms) that allow greater control over which substances are allowed to pass through the capillary wall.
has an intact basement membrane.
found in the glomeruli of the kidney but also appear in the intestines, endocrine glands, and the pancreas. (These are tissues with more extensive transit of fluid and molecules between capillary and tissues)
Fenestrated capillaries
more permeable than continuous capillaries
has tiny holes or pores (fenestrae) in the endothelial cells that allow the passage of substances across the capillary wall
Sometimes, the fenestrae are covered with thin membranes (or diaphragms) that allow greater control over which substances are allowed to pass through the capillary wall.
has an intact basement membrane.
found in the glomeruli of the kidney but also appear in the intestines, endocrine glands, and the pancreas. (These are tissues with more extensive transit of fluid and molecules between capillary and tissues)
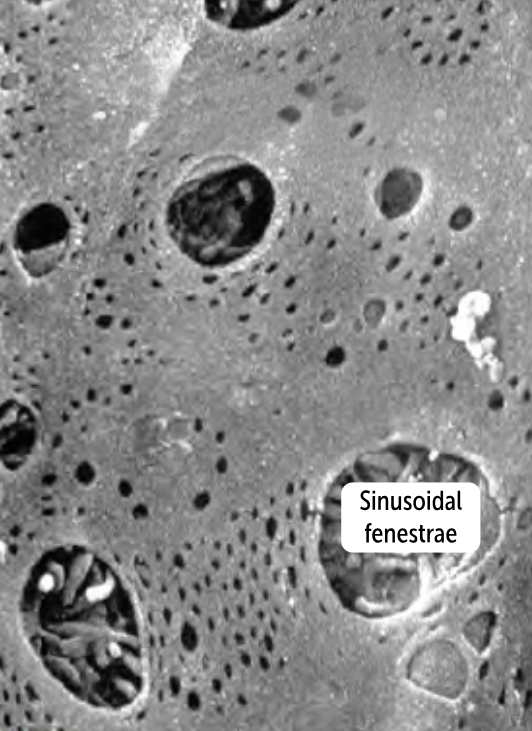
________________
the most permeable capillaries
has big gaps between the endothelial cells and within the basement membrane, called clefts
found in the liver and spleen, organs whose primary roles are filtering out larger molecules
Sinusoidal (Discontinuous) Capillaries
the most permeable capillaries
has big gaps between the endothelial cells and within the basement membrane, called clefts
found in the liver and spleen, organs whose primary roles are filtering out larger molecules
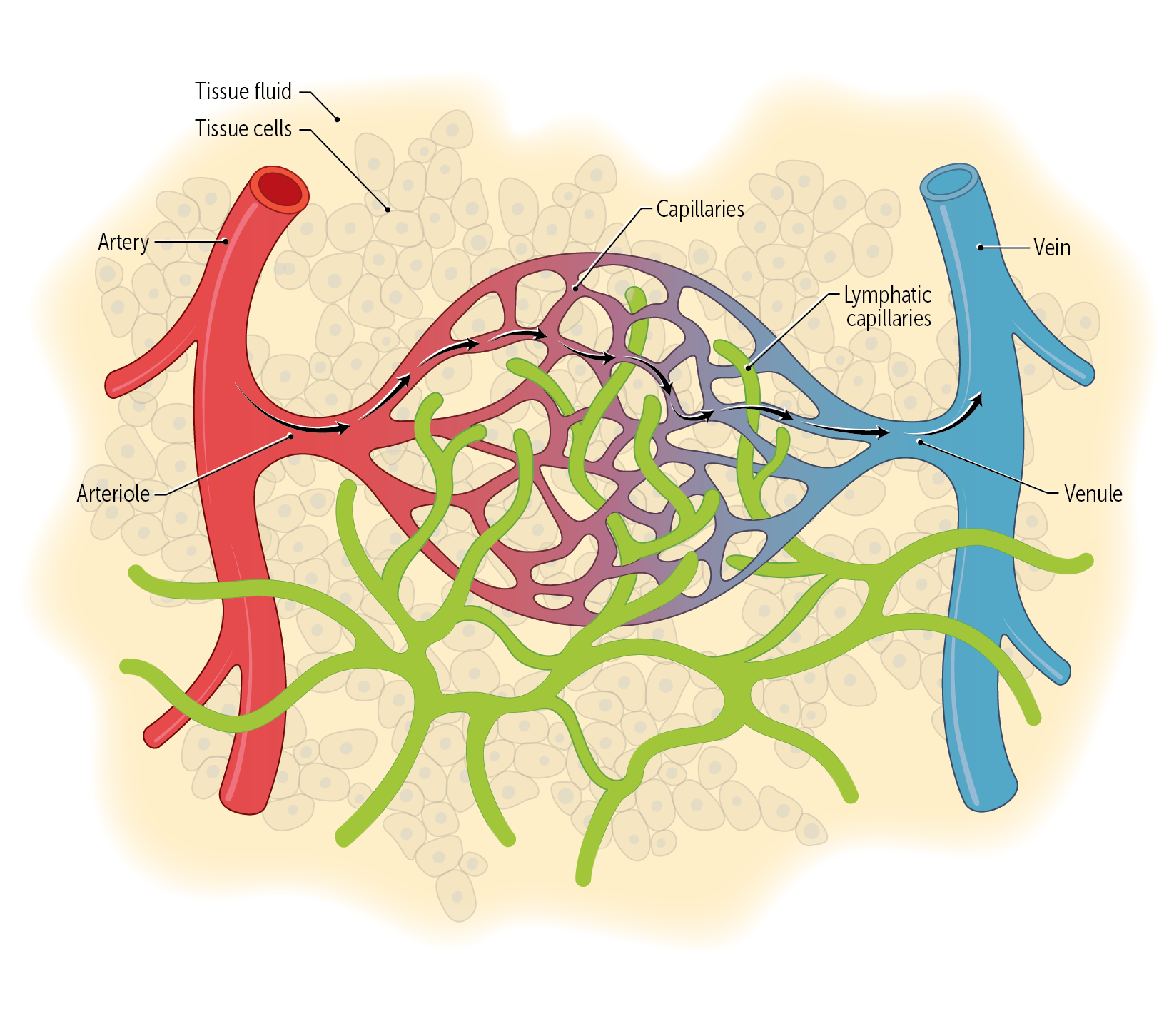
The lymphatic system has two main functions: to remove excess fluid from interstitial tissues and to conduct _________ from the periphery to lymph nodes for immune sampling.
The lymphatic system has two main functions: to remove excess fluid from interstitial tissues and to conduct antigens from the periphery to lymph nodes for immune sampling.
The vascular system empties into the lymphatic system at the level of the ________________. Fluid diffuses out of the _______________into the interstitium and from there enters the lymphatic capillaries
The vascular system empties into the lymphatic system at the level of the capillaries. Fluid diffuses out of the capillaries into the interstitium and from there enters the lymphatic capillaries
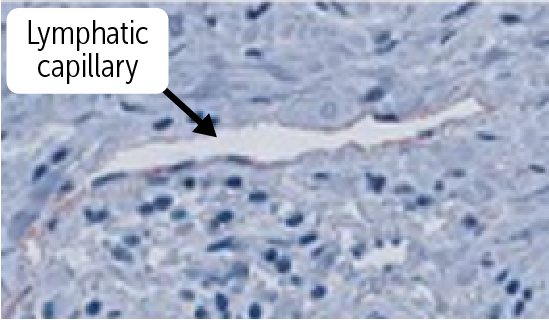
_________________
has a thin, simple squamous endothelium overlying a discontinuous basement membrane, do not contain a muscular layer, and have a poorly defined adventitia.
The wall is only one cell layer thick, much like the vascular capillaries
Lymphatic capillaries
has a thin, simple squamous endothelium overlying a discontinuous basement membrane, do not contain a muscular layer, and have a poorly defined adventitia.
The wall is only one cell layer thick, much like the vascular capillaries
____________________
contain a layer of smooth muscle (akin to the tunica media) that helps propel lymph back to the heart.
can be distinguished from veins by a thinner wall and smaller lumen
has one-way valves to maintain unidirectional lymphatic flow toward the heart.
They join as they rise through the body, forming lymphatic ducts, such as the right lymphatic duct and the thoracic duct.
Lymphatic collecting vessels
contain a layer of smooth muscle (akin to the tunica media) that helps propel lymph back to the heart.
can be distinguished from veins by a thinner wall and smaller lumen
has one-way valves to maintain unidirectional lymphatic flow toward the heart.
They join as they rise through the body, forming lymphatic ducts, such as the right lymphatic duct and the thoracic duct.