12th grade Evolution & Classification
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
evolution
The gradual change in a species over time OR a population of organisms changing over time
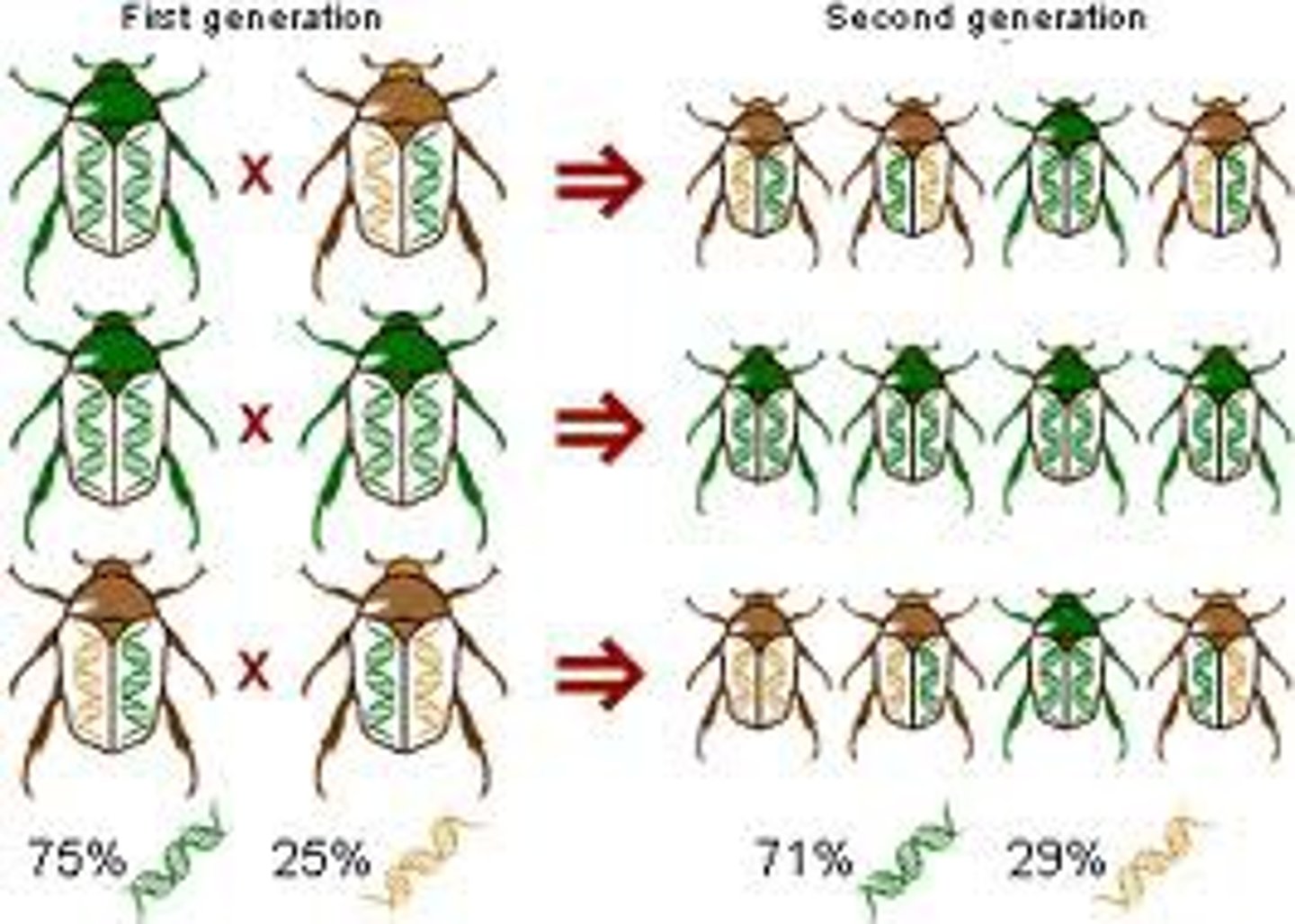
natural selection
mechanism by which individuals that have inherited beneficial adaptations survive and reproduce more on average than do other individuals. One mechanism by which populations change over time or evolve.
variation
the differences within a single species

biological species concept
group of similar organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring

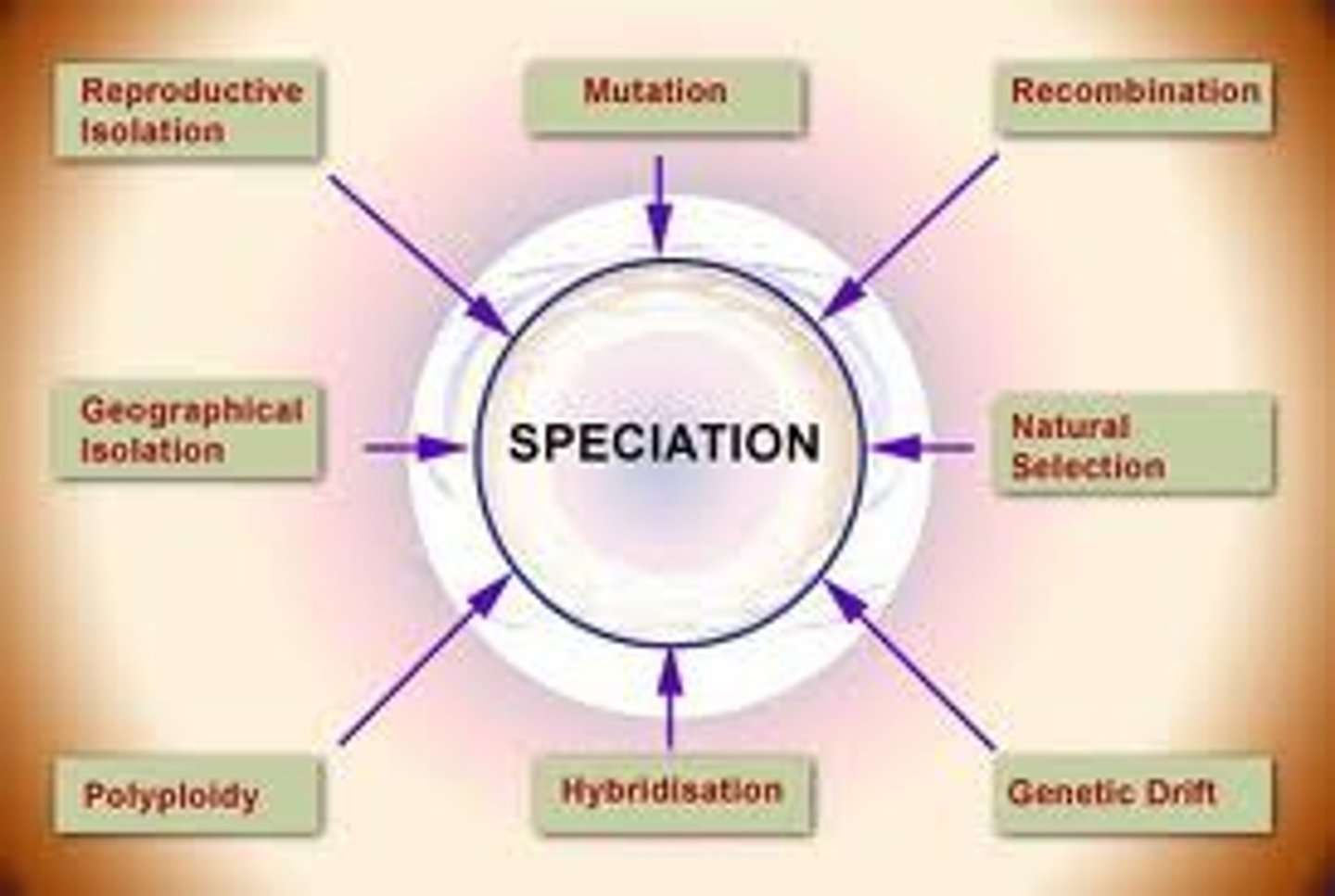
speciation
formation of new species
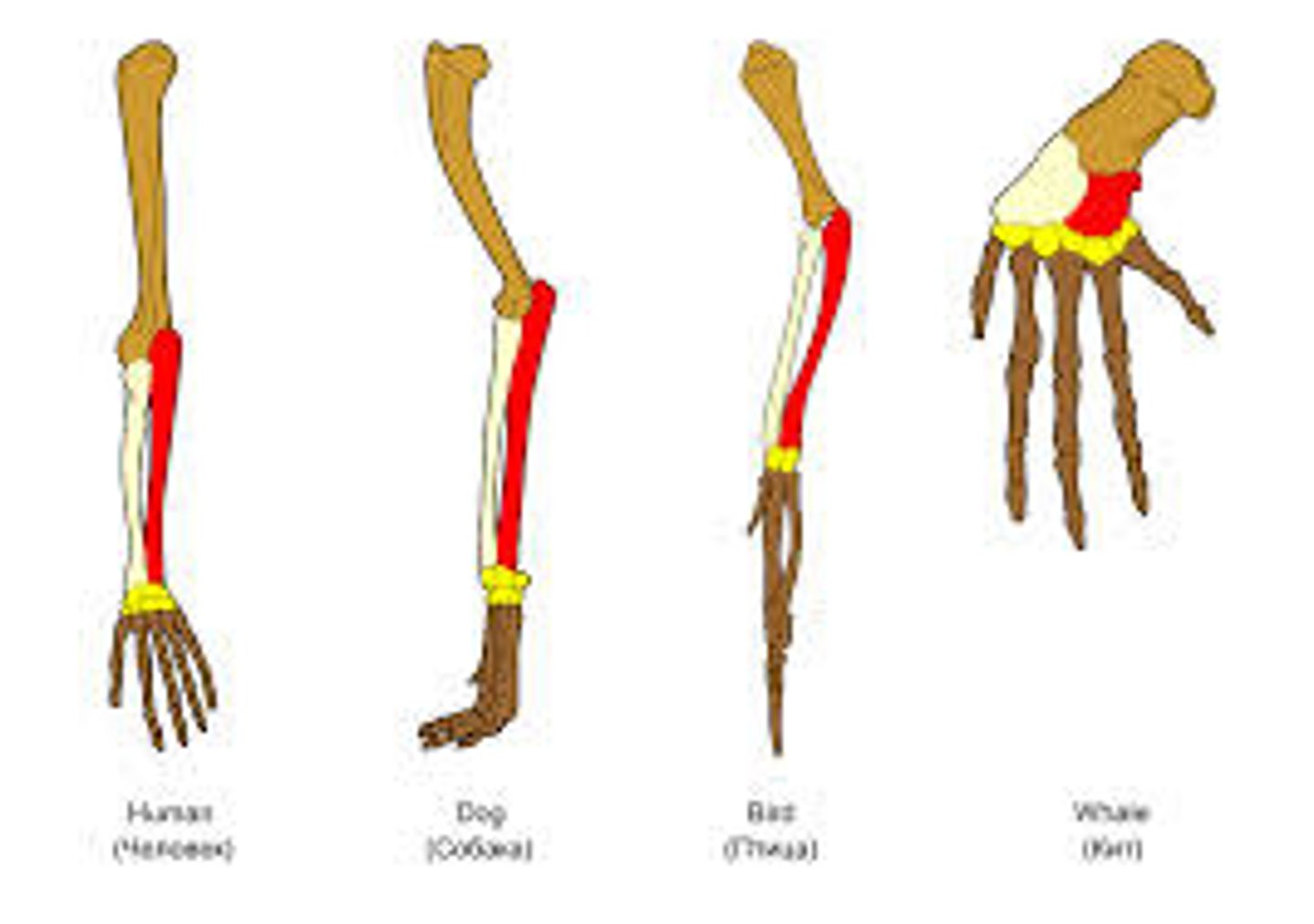
homologous structures
structures that have slightly different functionality forms in different organisms but have a lot of similarities in structure and development ; evidence of common ancestry
behavioral isolation
Form of reproductive isolation in which two populations have differences in courtship rituals or other types of behavior that prevent them from interbreeding

temporal isolation
form of reproductive isolation in which two or more species reproduces at different times
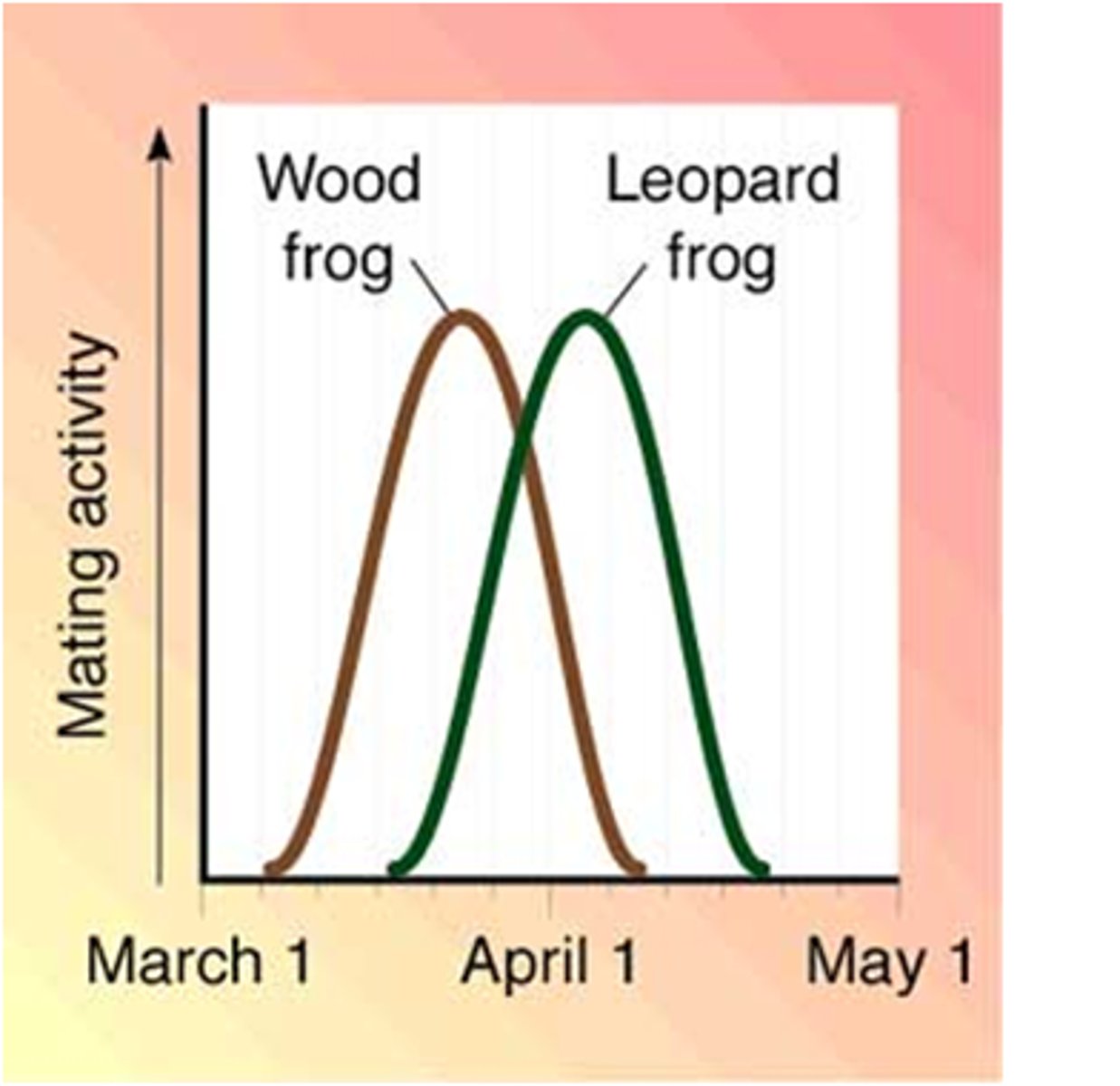
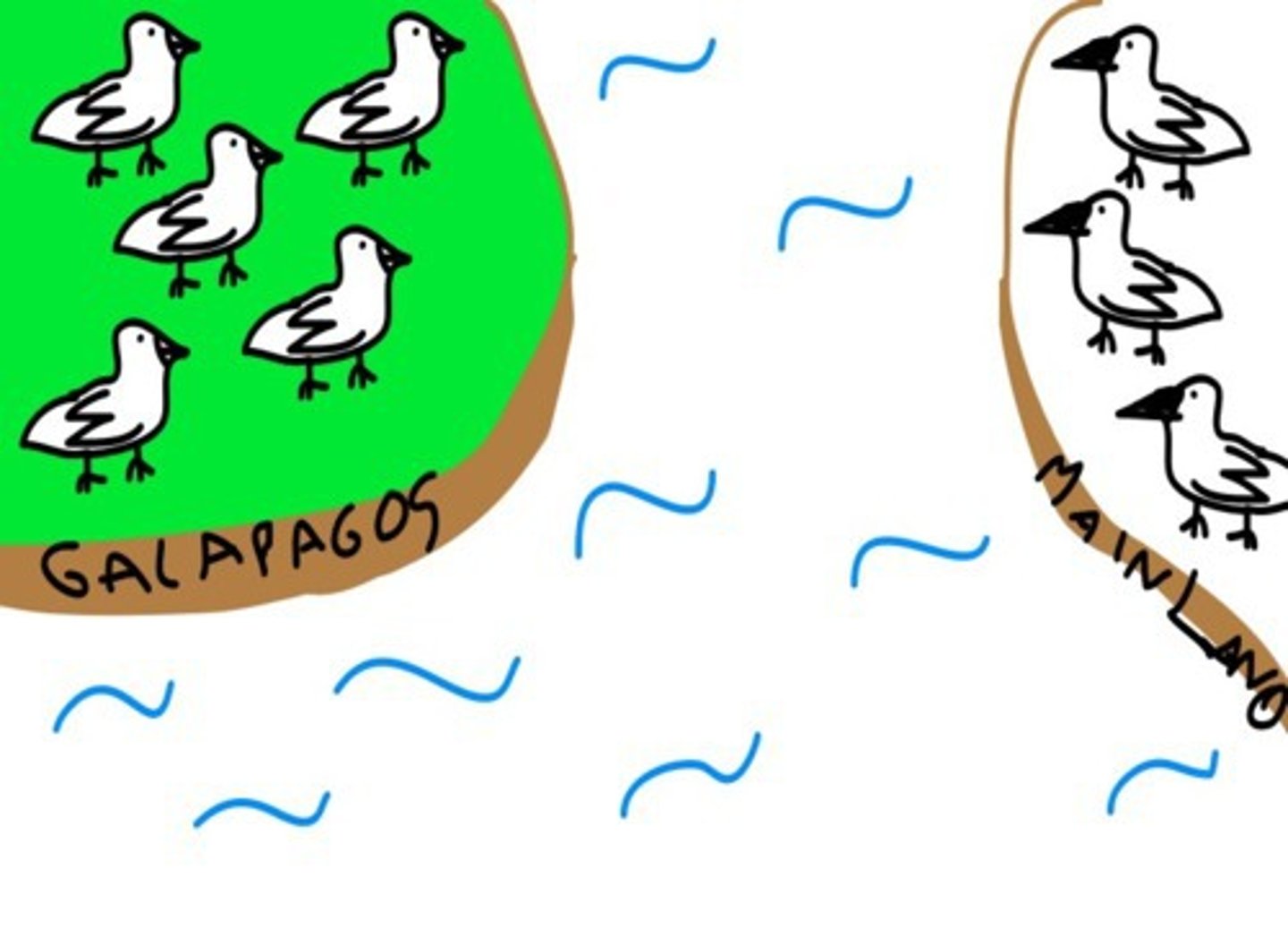
geographic isolation
form of reproductive isolation in which two populations are separated physically by geographic barriers such as rivers, mountains, or stretches of water
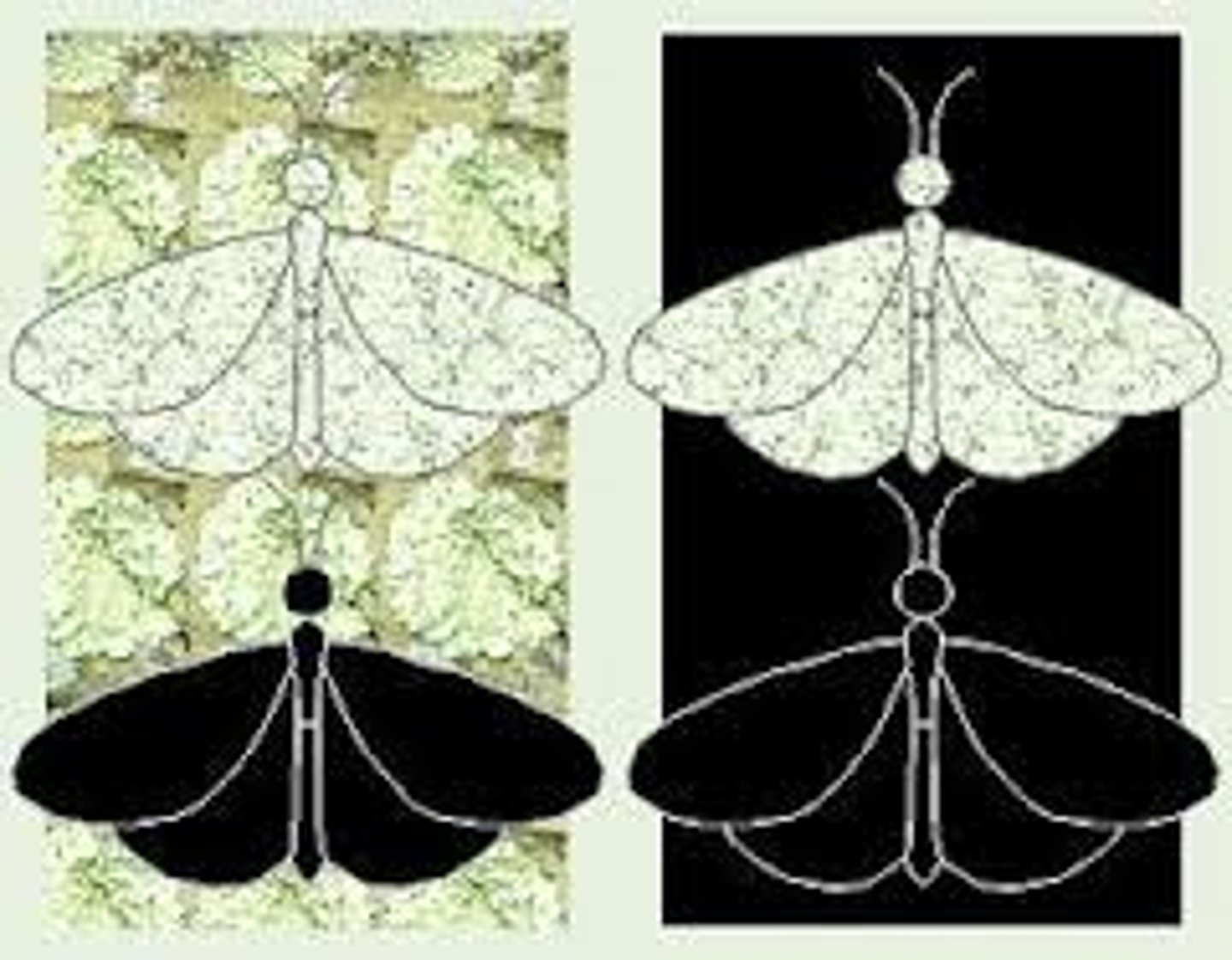
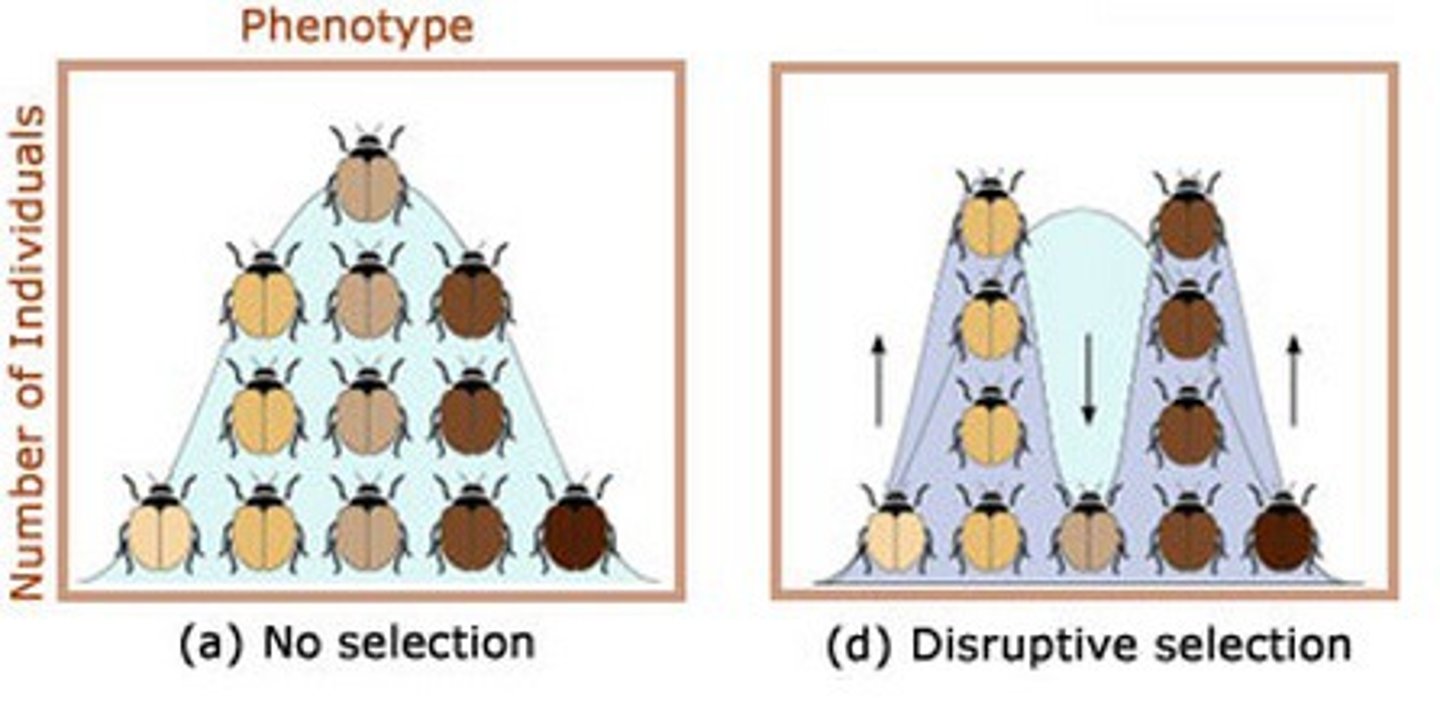
disruptive selection
form of natural selection in which a single curve splits into two; occurs when individuals at the upper and lower ends of a distribution curve have higher fitness than individuals near the middle
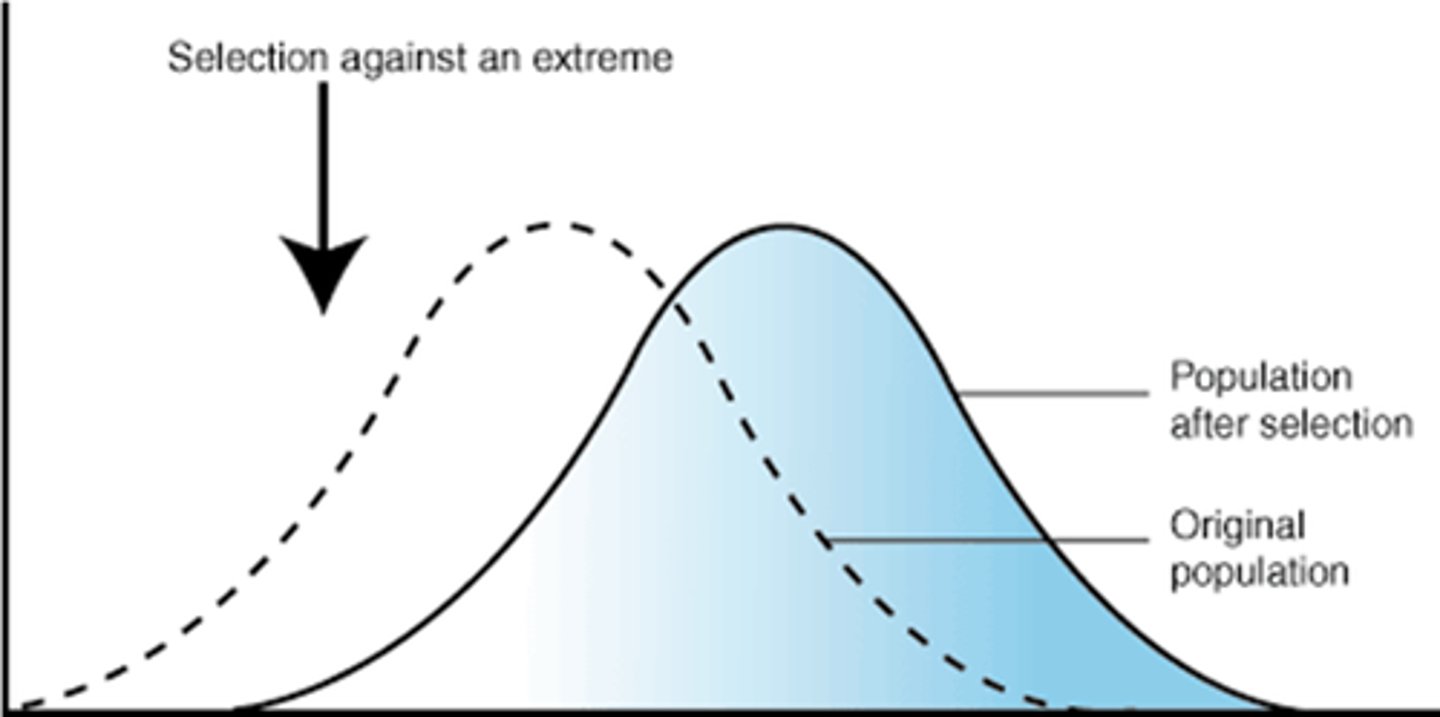
directional selection
Form of natural selection in which the entire curve moves; occurs when individuals at one end of a distribution curve have higher fitness than individuals in the middle or at the other end of the curve
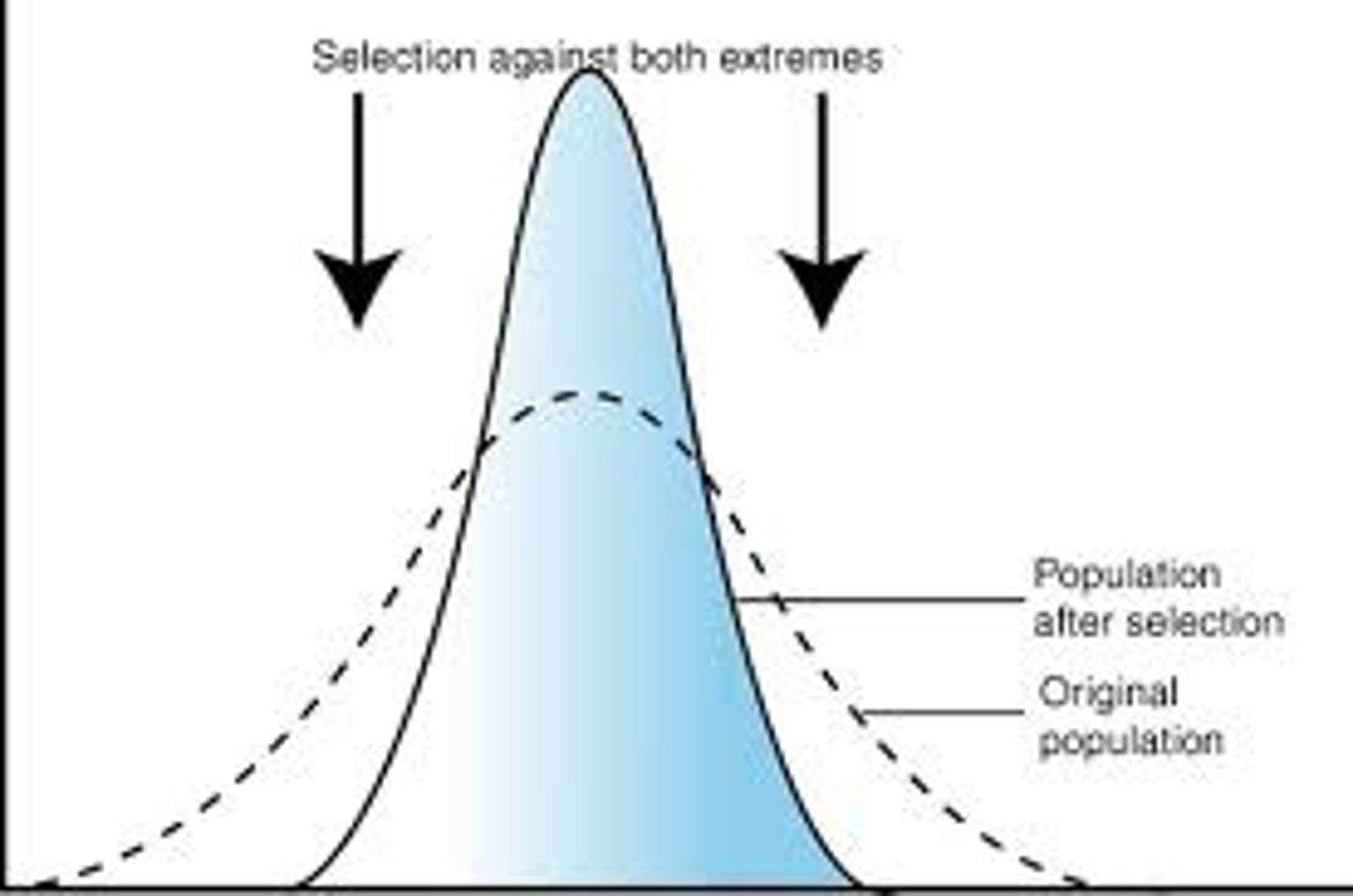
stabilizing selection
Natural selection that favors intermediate or "average" variants by acting against extreme phenotypes
Domain Eukarya
Domain of all organisms whose cells have nuclei, including protists, plants, fungi, and animals
Domain Archaea
One of the three domains of life; contains prokaryotic cells that often live in extreme habitats. Are surprisingly similar to eukaryotic cells because they have introns and their DNA wrapped around histone proteins
Domain Eubacteria
unicellular, prokaryotic, suited to pretty much any environment on this planet except for the most extreme ones. Also is killed by antibiotics, lacks introns & histones for DNA to wrap around
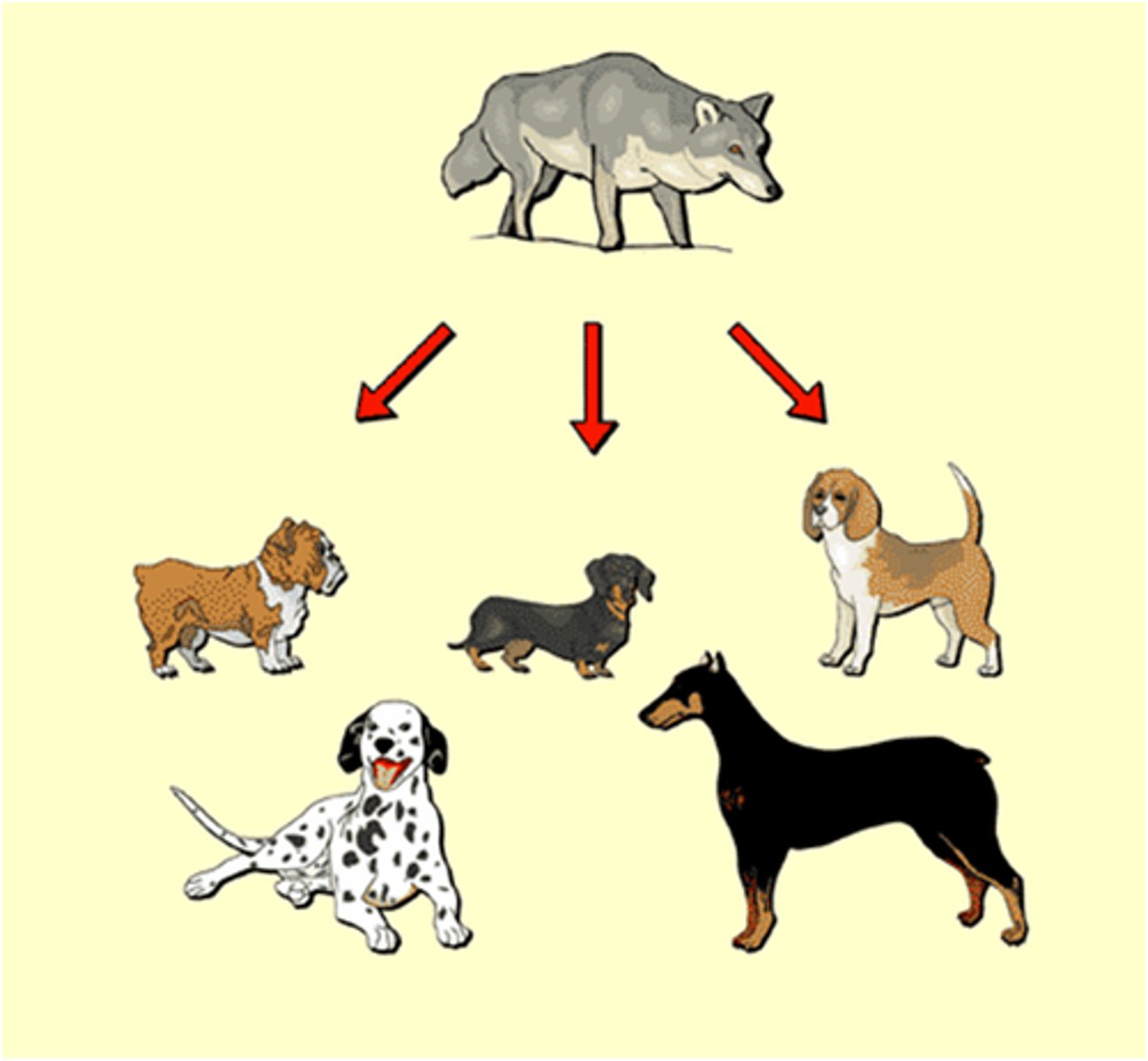
selective breeding
the human practice of breeding animals or plants that have certain desired traits- serves as evidence the CHANGE over time (Evolution) is possible
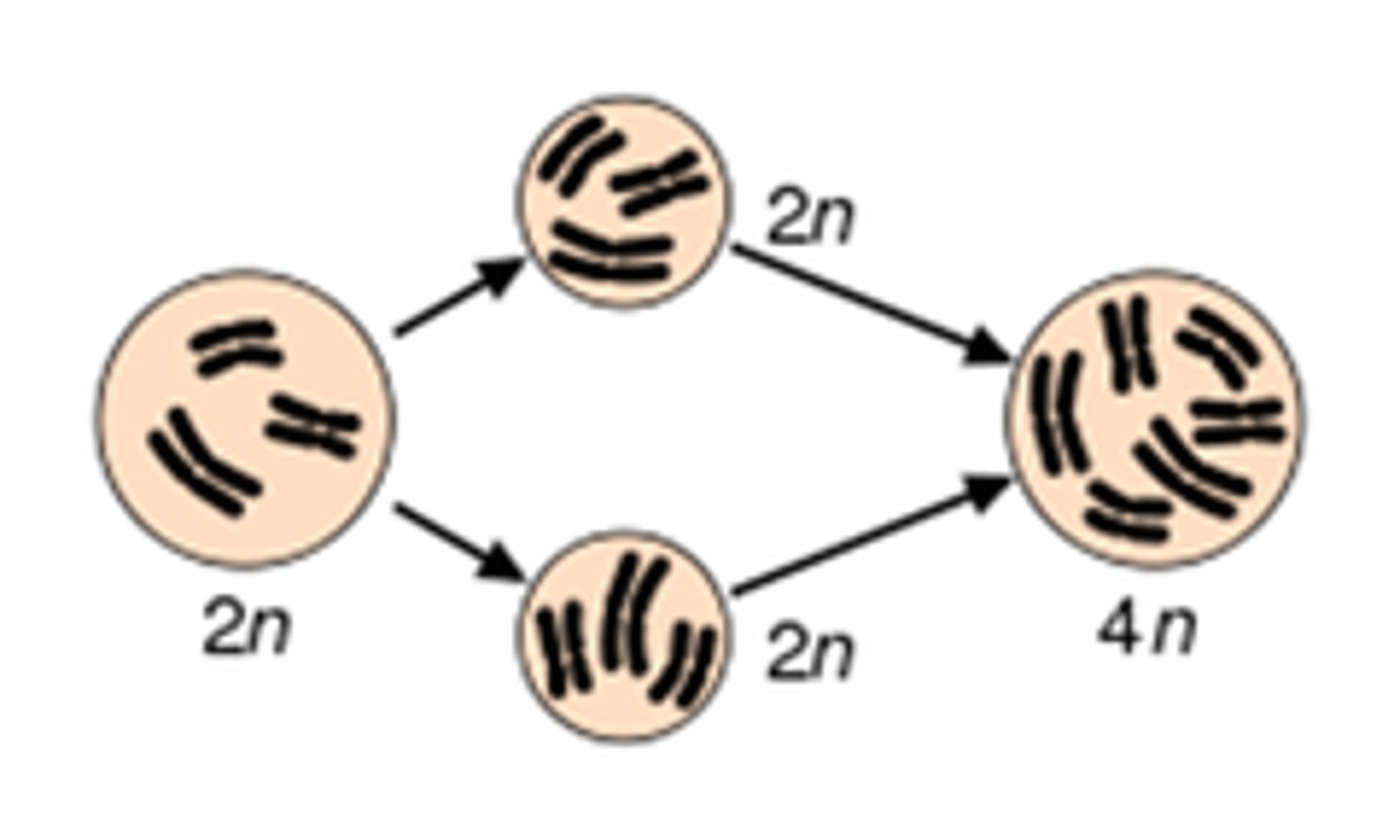
Polyploidy
condition in which an organism has extra sets of chromosomes. These organisms with extra CANNOT reproduce with their diploid relatives and are therefore brand new species (just after 1 generation)
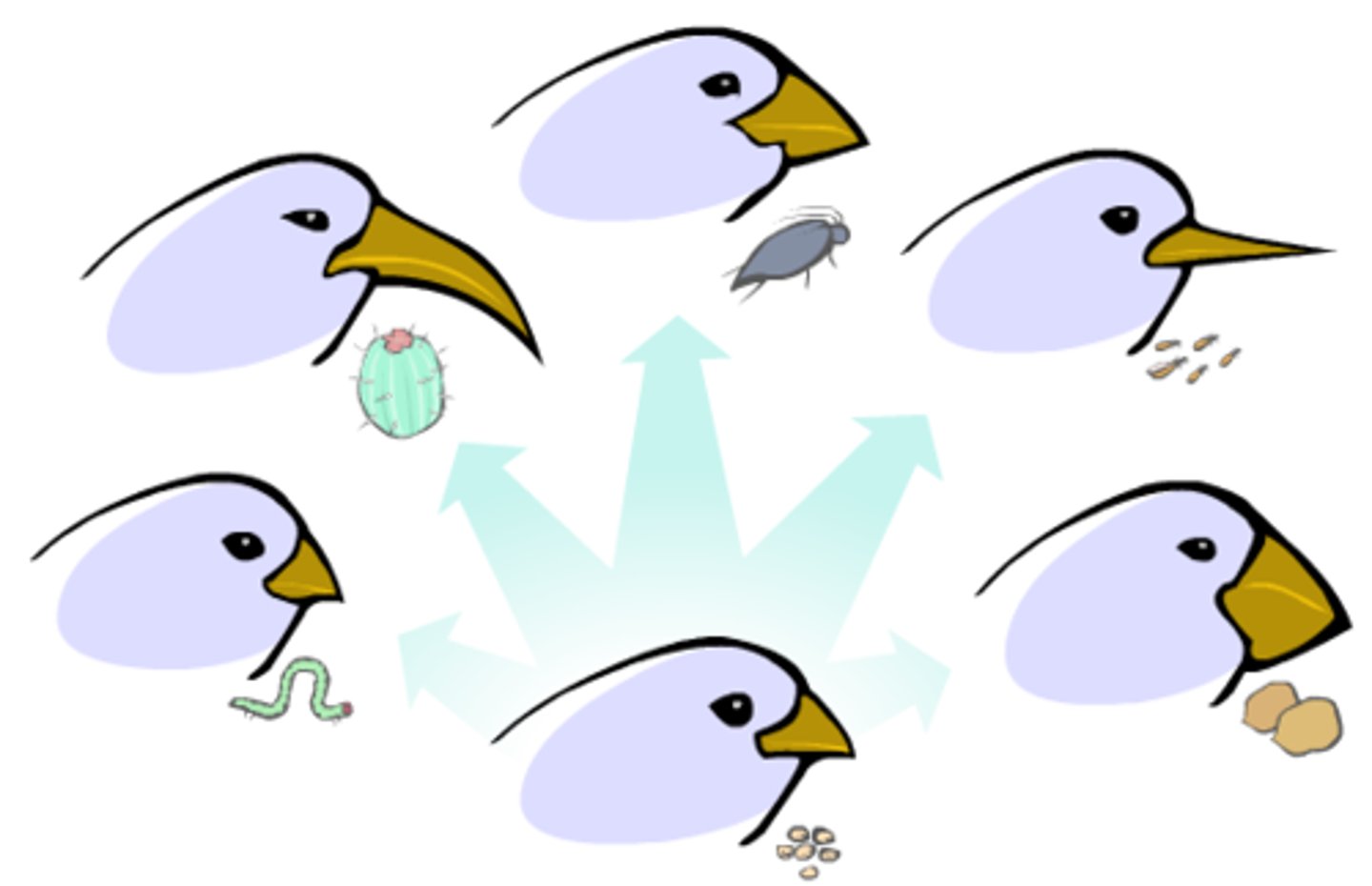
adaptive radiation
An evolutionary pattern in which many species evolve from a single ancestral species. (As seen in Galapagos finches)
Node on a cladogram
On a cladogram, shows the point at which 2 or more species share a common ancestor. The point from which they split into different species through speciation.
outgroup
in a cladogram, the species that is LEAST related to the others shown
clade
evolutionary branch of a cladogram that includes a single ancestor and all its descendants
primitive characteristic
the characteristic found in all members of the cladogram
derived characteristic
Characteristic that appears in recent parts of a lineage, but not in its older members
alelle frequency
The measure of the relative frequency of an allele at a genetic locus in a population; expressed as a proportion or percentage.