Unit 2: Cell Structure and Function
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Cells, All Cells, Living Organisms
____: a groups of organelles and molecules working together to preform a specific task and help the organism maintain homeostasis
___ ____: are bound by a plasma membrane, contain cytosol, contain chromosomes, contain ribosomes.
______ ________: are all composed of at least one cell.
nucleus, membrane
Prokaryotes
Bacteria and Archaea
Single-celled only
No ______
No ________-bound organelles
Smaller and simpler cells
Oldest cells
celled, Evolved
Eukaryotes
Plants, animals, fungi, protists
Can be single-______ and multicellular
Have a nucleus
Have membrane-bound organelles
Larger and more complex cells
________ from prokaryotic cells
Both, Some, Both
Shared Characteristics of Eu and Pro Cells
____ Have: genetic material (DNA/RNA), cell membrane, ribosomes, cytosol.
____ Have: cell walls, flagella
____ Use: cellular respiration to make ATP energy.
Plants, Animals
Unique Cell Components
______: Chloroplasts, central vacuole, cell wall, plasmodesmata.
______: Lysosomes, centrosomes, flagella.
homeostasis, Shape, Shape, greater, demand, decreases
Cell Size: cells have to be big enough to fit all the DNA and organelles but also small enough to efficiently exchange nutrients, oxygen and waste with the extracellular environment to maintain __________.
Formula: SA/V Ratio = Surface Area of Cell ____/ Volume of Cell ____
High SA/V Ratio: optimizes exchange of materials at the plasma membrane. Nutrients and waste are exchanged efficiently, high rate of heat exchange, and reactions have a _______ impact.
Low SA/V Ratio: cellular _______ for resources increases, rate of heat exchange decreases.
Eukaryotic Cells: compartmentalization of organelles __________ reaction interference and increases reaction efficiency.
types, energy, stack
Cell Shape/ Function: the shape and the amount and _____ of organelles its has determines the function of the cell.
Sperm Cells: have long flagella and many mitochondria because they need ______ to swim toward the egg.
Plant Cells: have a cell wall and are square so they can _____ and give the plant structure.
not
Non-membrane Bound Organelles: organelles that do ___ have their own membrane inside the cell.
Examples: ribosomes, cell membrane, cell wall, cytoplasm.
different, big
Membrane-bound Organelles: organelles that have their own membrane inside the cell.
Examples: nucleus, vacuole, mitochondria, chloroplast, Golgi apparatus, smooth and rough ER.
Specialization: these types of organelles allow for different conditions which allow for different areas to preform _________ jobs and concentrate enzymes and substrate in the same physical area.
Folded Organelle Membranes: exist to increase surface area for reactions/enzymes without making the organelle too ___.
mutual, double, bacterial, fission, circular, ribosomes
Endosymbiotic Theory: eukaryotic cells evolved after ancestral prokaryotes ingested mitochondrion and chloroplast-like proto-prokaryotes and formed a close _____ relationship with them.
Chloroplast and Mitochondrial Evidence
Membranes: some organelles, including chloroplasts and mitochondria, have _______ membranes.
Antibiotics: susceptible to antibiotics, indicating possible ________ origin.
Division: reproduction occurs via ______-like process.
DNA: has own DNA which is naked and ________.
Ribosomes: identical prokaryotic __________.
(End of Notes 2.1)
bilayer
Cell Membrane: phospholipid ______ that surrounds the entire cell. Regulates what comes in and out of the cell and protects the cell interior.
structure, barrier
Cell Wall: rigid structure made of complex carbohydrates found in plants, fungi and bacteria. Provides ________ to cells, as well as acting as a "Permeability ______ for some substances, to the internal environment."
protein, ribosomal, messenger, synthesize, not, secreted
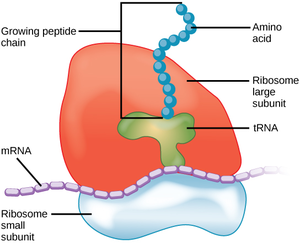
Ribosomes: found in all living organisms, they are made in the nucleus and are composed of ______ and _________ RNA, ribosomes read __________ RNA to _________ proteins, con be found attached to Rough ER of free-floating in the cytoplasm.
Free Ribosomes: suspended in cytosol, produces proteins that function in the Cytosol like enzymes. These ribosomes do ___ exit membrane.
Attached Ribosomes: bound to the rough ER or nuclear envelope, proteins produced by these ribosomes can be ________ from the cell or to the plasma membrane via transport vesicles.
nucleus, water
Cytoplasm: includes everything inside the cell membrane but outside the ________. Specifically, the cytosol, organelles, and the cytoskeleton.
Cytosol: liquid made of water, salt and other dissolved nutrients In the cell, helps both pro and eukaryotic cells maintain cell shape, site of many metabolic chemical reactions because it is _____-based.
animal, transported
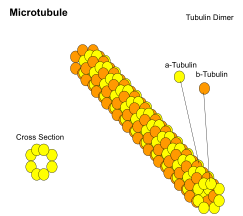
Cytoskeleton: helps maintain the shape of _______ cells, parts of the cytoskeleton helps vesicles get _________ around the cell. It is made of actin, microtubules, actin filaments.
make, pull
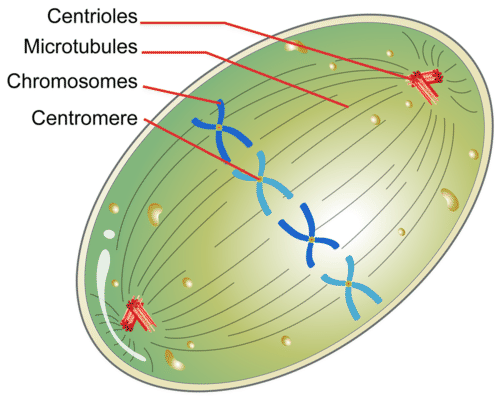
Centrioles/ Spindle Fibers: centrioles ____ spindle fibers during mitosis and meiosis, spindle fibers help ____ chromosomes apart during mitosis and meiosis.
shorter, beating
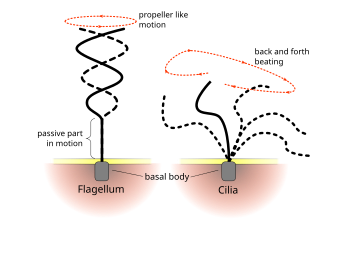
Flagella/ Cilia: help the cell move. Flagella are longer and more propellor-like. Cilia are much ______ and move in back-and-forth ______ motions.
vesicles, nuclear, rough, secretory
Endomembrane System: membranes that are related either through direct physical continuity or by the transfer of membrane segments as tiny ________ which are sacks made of membrane.
Protein Secretion: follows a specific path starting at the _______ envelope → _____ ER → _________ vesicle → Golgi apparatus→ secretory vesicle → membrane for release.
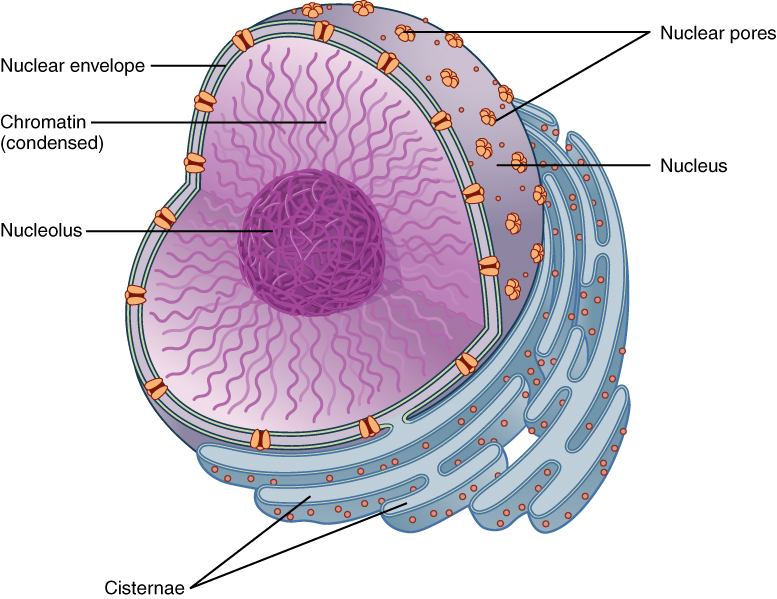
chromatin, envelope, pores, messenger, ribosomal
Nucleus: contains ________ (protein / DNA genetic information) enclosed by a nuclear _________ (double membrane containing pores). It's ______, regulate the exit and entry of materials.
Nucleoplasm: the substance within the nucleus that surrounds the chromosomes and nucleolus. Where DNA is transcribed into ________ RNA
Nucleolus: dense region of the nucleus where ________ RNA is synthesized. This type of RNA is combined with proteins to form large and small subunits of ribosomes, subunits exit via nuclear pores.
nucleus, proteins, hormone
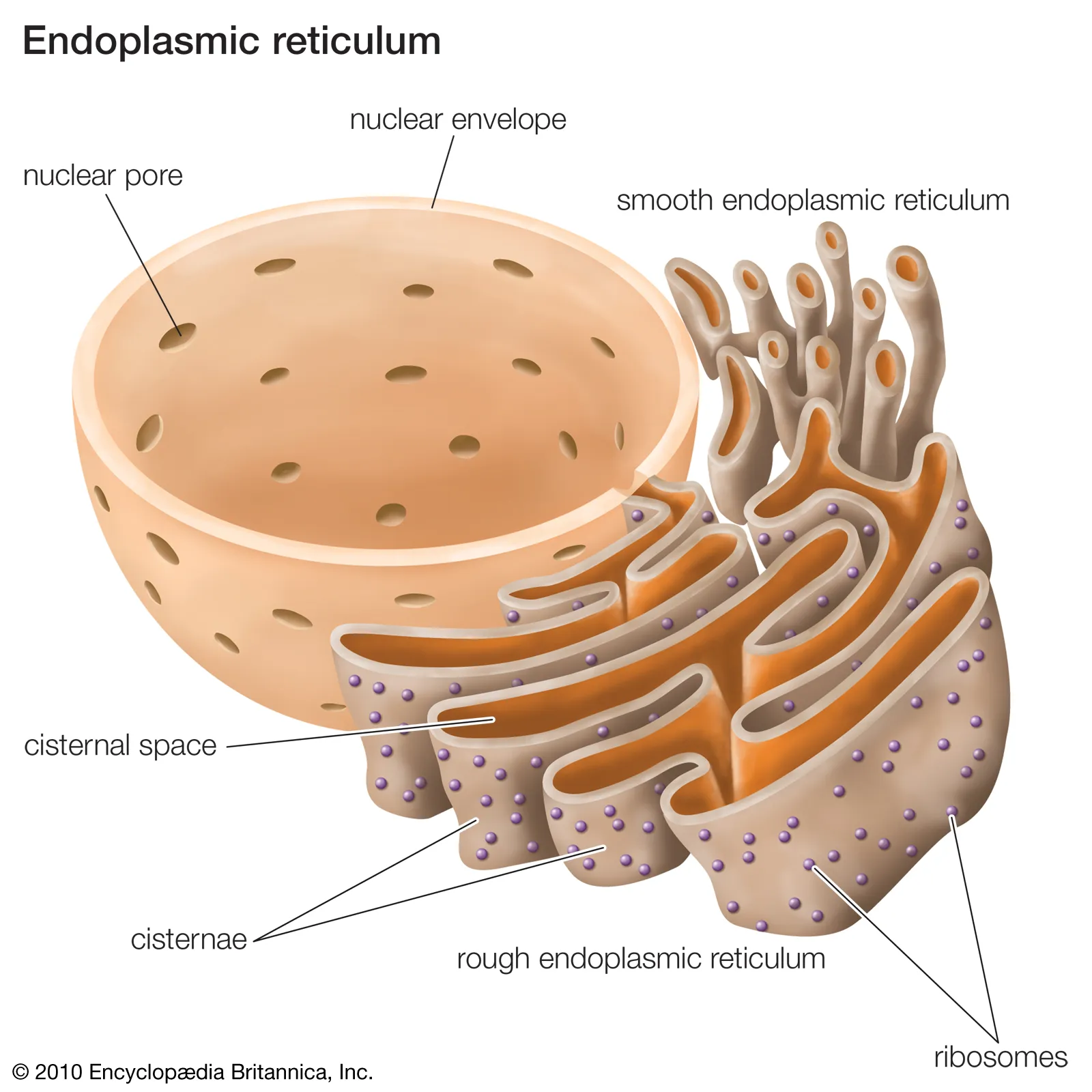
Endoplasmic Reticulum: a network of membranous tubes, synthesizes membranes, compartmentalizes the cell by keeping proteins formed in the rough ER separate from those formed by the free ribosomes.
Rough ER: contains ribosomes on its surface, highly folded organelle that is joined with the _______, it’s responsible for packaging _______ and sending them to the Golgi apparatus.
Smooth ER: lacks ribosomes on its surface, responsible for lipid/______ synthesis and detoxification of cell wastes. Synthesized lipid polymers and hormones get sent to the Golgi apparatus.
fold, vesicles, secretion
Golgi Apparatus: the "post office" of the cell, helping ____ and modify proteins, packaging proteins/ lipids into ________, sending these vesicles to their intended intra or extracellular destination.
Cisternae: flattened membranous sacs, each Cisternae is not connected.
Directionality: allows for smooth transfer between ER and other locations.
Cis Face: receives vesicles from the ER.
Trans Face: sends vesicles back out into cytosol to other locations or to the plasma membrane for ________.
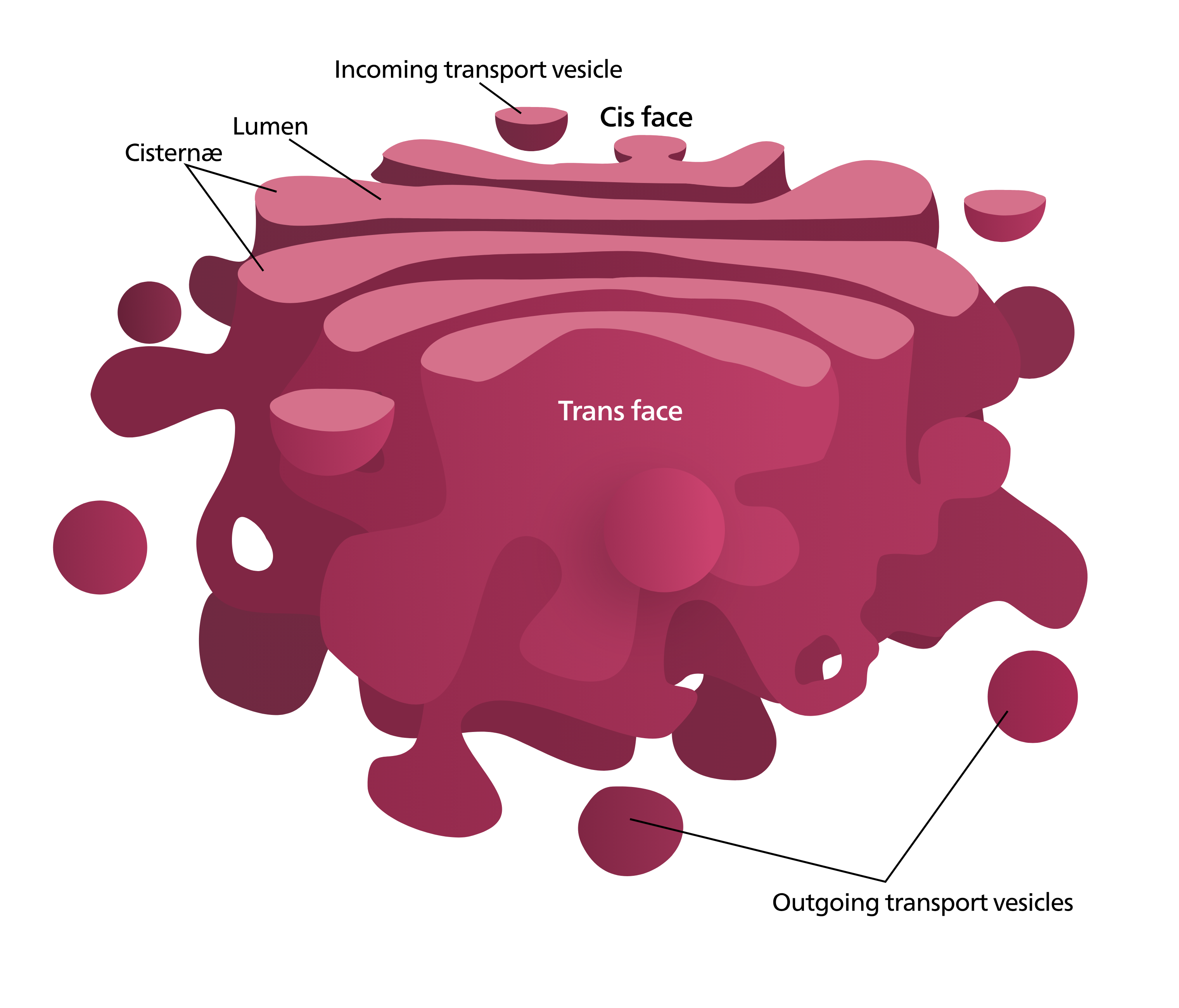

enzymes, proteins, death
Lysosome: lipid bubble full of hydrolytic ________ that break down cell waste and denatured _______ into their monomers.
Apoptosis: programmed cell ____ caused by lysosomes.
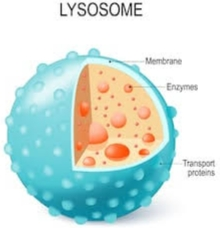
hydrolysis, peroxide, mitochondria
Peroxisomes: responsible for lipid ________ and also using catalase (an enzyme) to break down hydrogen _________ (toxic to the cell). Lipids are broken down into fatty acid monomers, which are sent to ___________ to help generate ATP.
shape, turgor
Vacuole: responsible for storing and releasing fluids/ biomolecules, store cellular waste products until they can be broken down.
Plant Vacuole: very large and help maintain plant cell ____ and _____ pressure, also storage of water.
Animal Vacuole: usually very small.
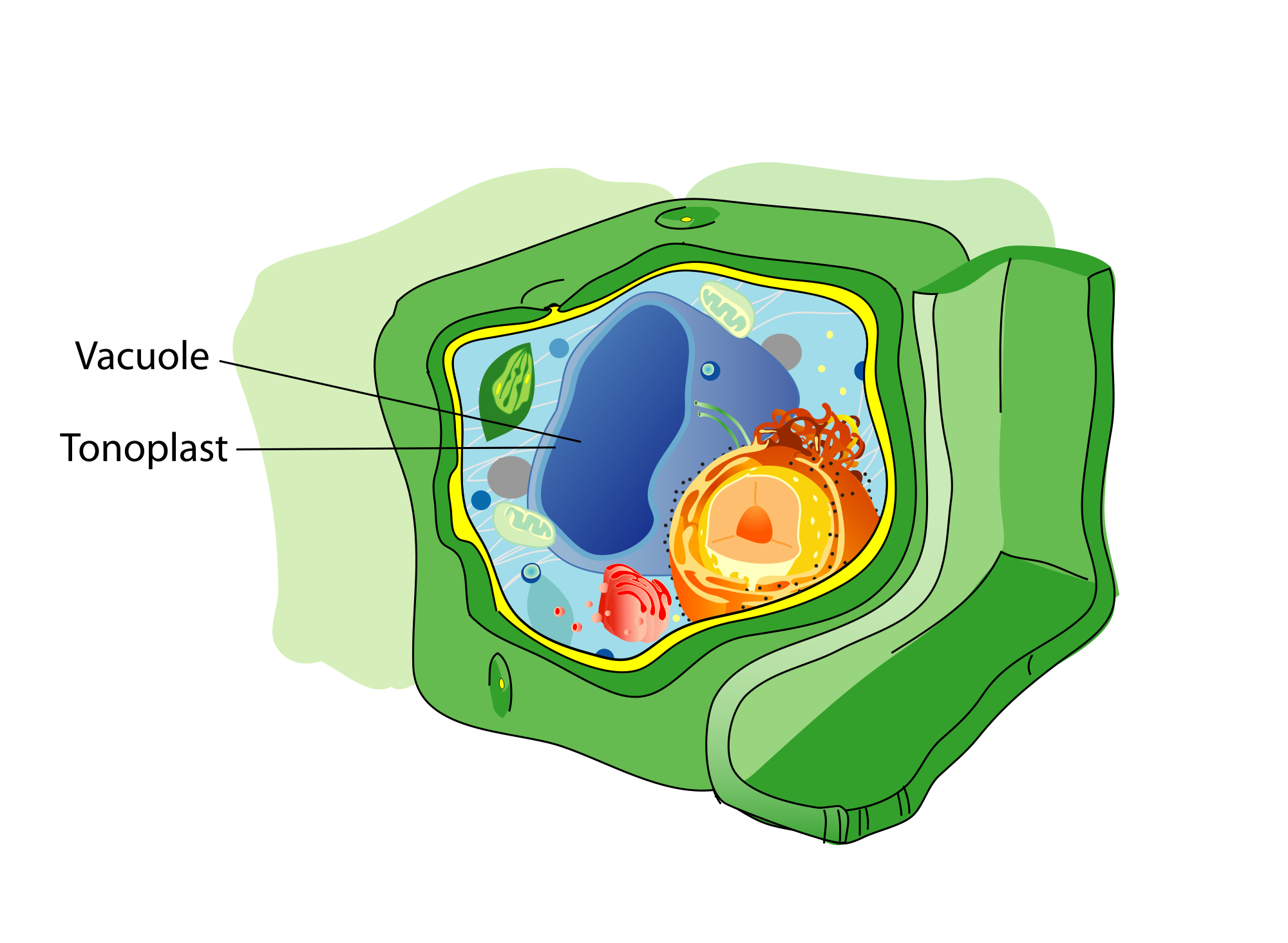

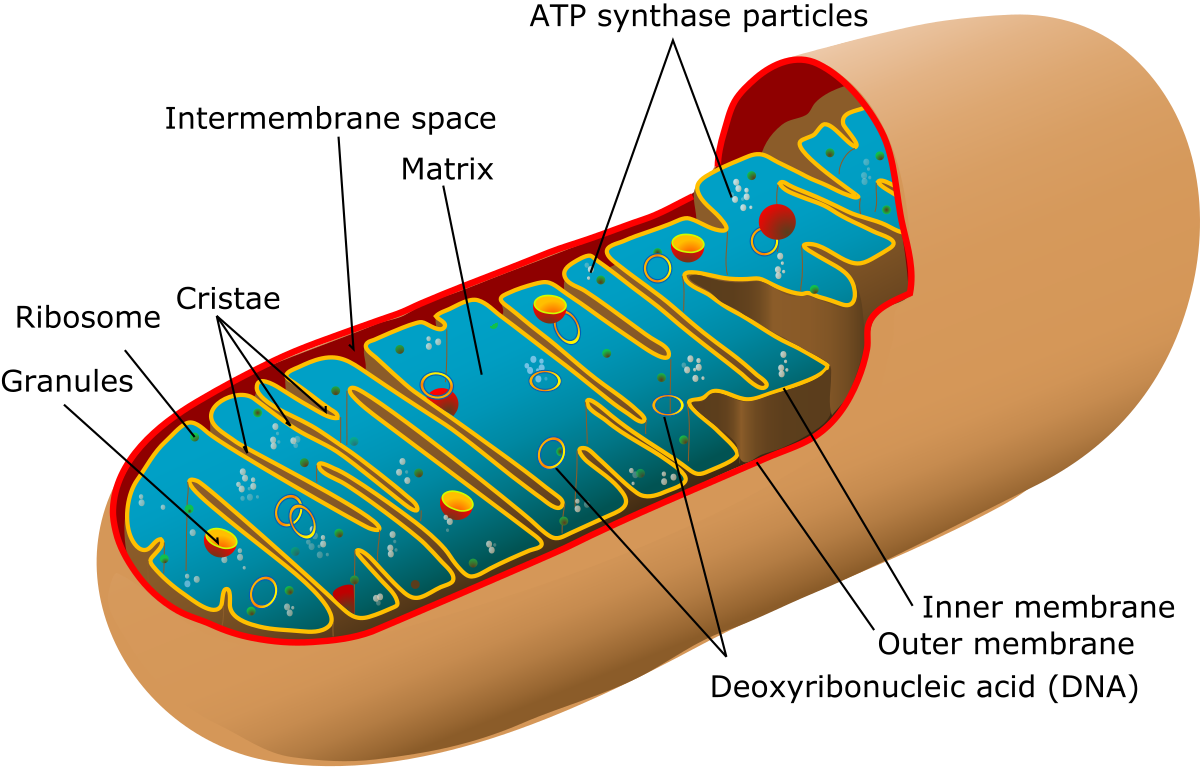
two, replicate, ATP, glucose, oxygen
Mitochondria: responsible for some of the processes that synthesize ATP. Has ___ membranes, which allows for compartmentalization of different chemical reactions. Has its own free-floating circular DNA which allows it to _______.
ATP Synthesis: two processes that create ATP are the Citric Acid Cycle which occurs in the matrix and Oxidative Phosphorylation that occurs on the inner membrane.
Outer Membrane: Smooth and not folded.
Inner Membrane: folding of inner membrane increases surface area to allow for more/ faster ___ production.
Cellular Respiration: mitochondria break down _______ in the presence of _______ to produce ATP, which stores chemical energy. The process also produces carbon dioxide and water as waste products.
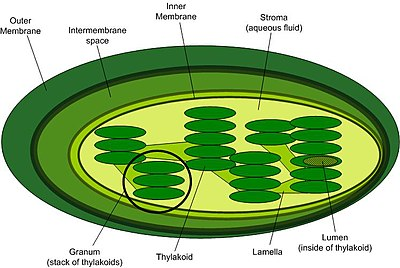
grana, increase
Chloroplast: has two membranes, which allows for compartmentalization of different chemical reactions. Internal anatomy is arranged in stacks of thylakoid membranes called ____. Multiple thylakoids ________ surface area so more reactions can occur. Has its own free-floating circular DNA which plays a role in photosynthesis.
(End of Notes 2.2)
bilayer
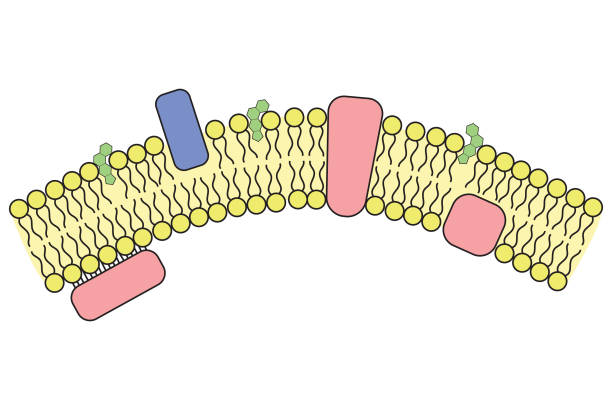
Cell/Plasma Membrane: also known as the phospholipid _______, is a lipid membrane that surrounds the cells of all living organisms. Responsible for what enters and exits the cell.
Different Names: cell membrane, plasma membrane, phospholipid bilayer.
Composition: primarily phospholipids, also proteins, carbohydrates, and cholesterol.
allow, tightly, unfavorable, both
Phospholipid Structure
Head Group: contains phosphate, choline, and glycerol. Is polar and hydrophilic, meaning it interacts with water but does not _____ non-polar molecules like glucose to pass.
Fatty Acid Tails: contains a saturated and unsaturated fatty acid. Is non-polar and hydrophobic meaning it avoids water.
Unsaturated Fatty Acid: prevents phospholipids from packing too _______ together and allows for membrane fluidity because it has a kink caused by its double bond.
Formation: In a water based solution it is energetically __________ for the hydrophobic tails to be exposed to water, this drives the formation of the phospholipid bilayer.
Hydrophilic Head Groups: face the aqueous cell interior and exterior
Hydrophobic Tails: form the dense hydrophobic core of the membrane.
Amphipathic: refers to the quality of having ____ hydrophobic and hydrophilic areas.
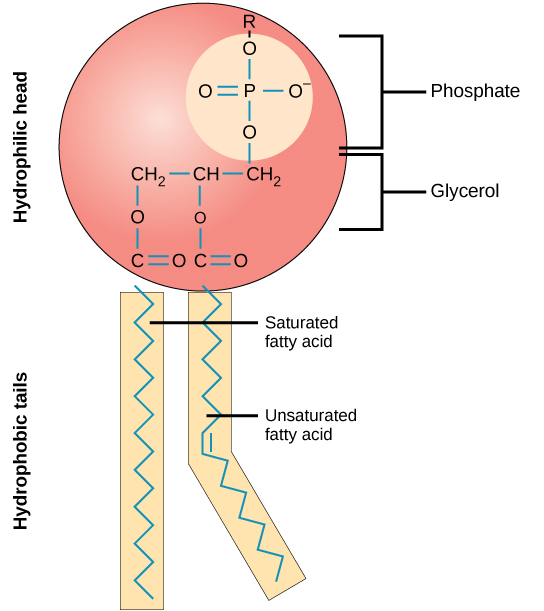
fluidity, carbohydrate, tissues
Membrane Components
Cholesterol: the cell membrane is rigid and may break in the cold and too fluid and won't hold shape in the heat, cholesterol regulates membrane _______ in response to temperature charges.
Glycolipids: a ___________ attached to a phospholipid. Facilitates cell-to-cell adhesion and recognition.
Glycoproteins: a carbohydrate attached to a protein. Allows cross-linking of cells, which gives the ________ strength.
attached, embedded, all
Membrane Proteins
Peripheral Proteins: found ________ to the inside or outside surface of the cell membrane, typically used for cell signaling.
Integral Proteins: fully or partially _________ in the membrane, usually used for cell signaling.
Transmembrane Proteins: a special type of integral protein, they go ___ the way through the membrane. Usually found as channel proteins that move polar/large molecules in and out of the cell.
channel, transport, full, not, bind
Channel Proteins VS. Receptor Proteins
Channel Proteins
Presence of Channel: a transmembrane protein with a _______ through the middle.
Purpose: Used for _________ of large, polar, or charged molecules across the membrane.
Polarity vs. Charge: polar molecules (e.g. water) have partial charges (due to uneven electron sharing), while charged molecules (e.g. positive Na) have ___ positive or negative charges.
Receptor Proteins
Presence of Channel: transmembrane or peripheral proteins that do ___ have a channel.
Purpose: Used for cell signaling. Ligands ____ to the receptor and cause the cell to respond accordingly.
parts, move, weak, low, reducing, packing, many
Fluid Mosaic Model: the cell membrane is referred to as a fluid mosaic because it is made of many _____ that can _____ laterally in the membrane.
‘Fluid’: membrane is held together by ____ hydrophobic interactions and can therefore move and shift.
Temperature: affects fluidity.
Unsaturated Hydrocarbon Tails: help maintain fluidity at ___ temps by preventing the tight packing of phospholipids.
Cholesterol: helps maintain fluidity by _________ movement at high temps and reducing tight ________ of phospholipids at low temps.
‘Mosaic’: comprised of _____ macromolecules.
diffuse, majority, unfavorable, core
Selective Permeability: the cell membrane only lets small, non-polar molecules ______ freely through spaces between the phospholipids.
Examples: oxygen, carbon dioxide, and water.*
Water: will diffuse in small quantities, but the _______ will use aquaporins since they are more quick and efficient.
Not Permitted: large, charged, polar molecules. Because it is energetically _______ for them to interact with the hydrophobic fatty acid tails at the ____ of the membrane.
(End of Notes 2.3)
Importance of Cell Transport
Waste: is transported out of the cell, which maintains pH and salt balance.
Signal Proteins: are transported outside the cell, which helps them communicate.
Proteins: are absorbed into the cell
Respiration: oxygen is let in the cell and carbon dioxide leaves the cell.
Apoptosis: con assist in programmed cell death in infected cells.
Etc.
same, efficiency
Cell Transport Efficiency: the rate of diffusion of a substance is the _____ regardless of the cell size but a higher SA:V ratio is preferred. Having projections, like vili, on a cell will increase the SA:V ratio, increasing cell _________.
difference, concentration, high, low
Concentration Gradient: the _________ in concentration of molecules across a space.
Biological Concentration Gradient: occurs when there is a difference in the _____________ of biomolecules, water, or ions across the cell membrane.
Movement: molecules moving with the concentration gradient are moving from an area of ____ concentration to an area of ___ concentration of the molecule that is moving.
energy, random, overall
Molecular Energy: atoms and molecules have an inherent _____ that causes them to vibrate and move around. The direction in which the molecules move is ________.
Net Movement: the ______ direction that most molecules move, typically in the direction of the concentration gradient.
concentration, net, reset
Dynamic Equilibrium: occurs when molecules moving with the concentration gradient reach the same net ___________ on both sides of the membrane.
Movement: molecules are still moving, but ____ movement is zero.
Cells: will remain in dynamic equilibrium unless work, using ATP energy, is done to _____ the concentration gradient.
with, not, without, not, pass, stimulus, changes
Passive Transport: the net movement of molecules is ____ the concentration gradient until the system reaches dynamic equilibrium.
Energy Used: Relies on the inherent energy of the concentration gradient. Does ___ require the input metabolic energy ATP to occur.
Simple Diffusion: net movement of small, non-polar molecules with the concentration gradient ________ the aid of a channel protein.
Only With: O2, N2, CO2, and small amounts of water.
Selective Permeability: molecules diffuse directly across the membrane, molecule type varies with diffusion rate.
Facilitated Diffusion: net movement of molecules with the concentration gradient that require the use of channel proteins to occur but does ___ require energy to occur.
Occurs With: large, polar, charged molecules or some combination thereof.
Channel Proteins: provide a channel for molecules and ions to ____, channel is hydrophilic.
Gated Channels: only allows for passage when there is a _______.
Carrier Proteins: undergo conformational ______ for substances to pass.
Aquaporins: channel protein for water.
against, vesicle, Phagocytosis, Pinocytosis, charge, negative, ions, Electrochemical
Active Transport: the net movement of molecules is ______ the concentration gradient. The system will not reach dynamic equilibrium.
Energy Used: Requires a net input of metabolic energy (hydrolysis of ATP) to occur.
Endocytosis: process by which cells take in molecules into the intracellular space. Requires formation of a ______ for bulk import of substances.
__________: when a cell engulfs particles later to be digested by lysosomes. The process goes: packages particles into a food vacuole, food vacuole fuses with a lysosome to be digested.
___________: nonspecific uptake of extracellular fluid containing dissolved molecules. Cell takes in dissolved molecules in a protein coated vesicle, protein coat helps mediate the transport of molecules.
Membrane Potential: unequal concentration of ions across the membrane, resulting in an electrical _____ across the plasma membrane.
Cytoplasm: relatively _______ in comparison to extracellular fluid.
Battery-like: when ____ change concentrations on both sides of the membrane through transport, the membrane can become polarized and fire an electrical signal.
_____________ Gradient: ions move from high concentration to low concentration (chemical), and from areas of like charge to areas of opposite charge (electrical).
hydrogen, voltage, gradient, potential, out, in, negative
Active Transport Pumps
Proton Pump: pumps _________ ions (H+) out of the cell, used in cellular respiration and photosynthesis.
Used By: plants, fungi, and bacteria.
Electrogenic Pump: proteins that generate ______ across membranes, which can be used later as an energy source for cellular processes.
Sodium Potassium Pump: a membrane bound enzyme that actively transports Sodium (Na+) and Potassium (K+) ions across the cell membrane. Crucial for maintaining the proper electrochemical _______.
Purpose: to maintain a high concentration of sodium ions outside the cell and potassium ions inside the cell. Contributing to the resting membrane _______.
Process:
1.) Three sodium ions from the cytoplasm bind to the Na+/K+ pump protein. 2.) The pump is phosphorylated by ATP meaning ATP donates a phosphate group to the pump which changes the pump's conformation (shape), activating it.
3.) The conformational change releases the three sodium ions outside the cell, against their concentration gradient (higher concentration of Na+ outside).
4.) Two potassium ions from the extracellular fluid bind to the pump's newly exposes sites.
5.) The phosphate group is released from the pump, causing another conformational change that returns the pump to its original shape.
6.) Two potassium ions are released into the cytoplasm.
Outcome: For one cycle, one ATP molecule is used, 3 Na+ ions are pumped ___, 2 K+ ions are pumped __, a net _______ charge inside the cell is established.
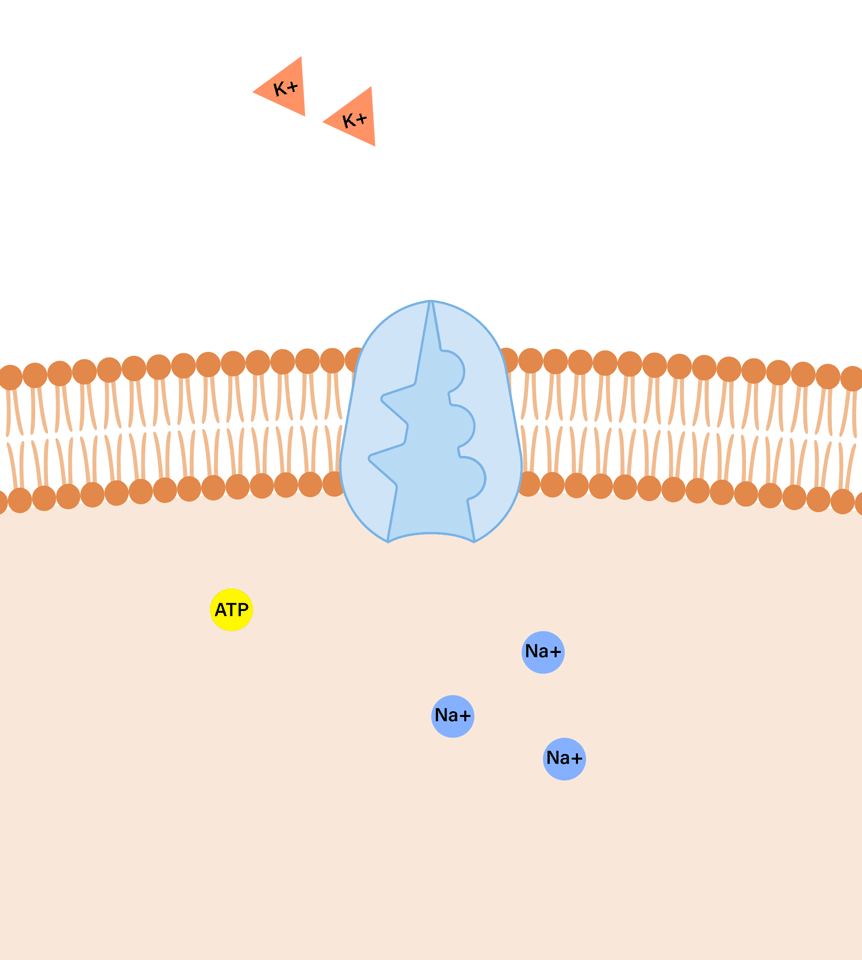
cross
Facilitated Transport: large, polar, and charged molecules require the facilitation of channel proteins to ____ the dense hydrophilic core of the membrane. This is true regardless of energy use by the channel proteins.
Example: facilitated diffusion, active transport.
(End of Notes 2.4)
control, die
Osmoregulation: maintaining water balance allows organisms to ______ their internal solute composition/water potential.
Cells: most maintain of osmoregulation or else they will ___.
high, cross
Osmosis: diffusion of water across a semi-permeable membrane from ____ water concentration to low water concentration.
Semi-permeable Membrane: solutes cannot ____ these types of membranes.
solute
Tonicity: how much _____ is dissolved in the solvent.
Solute: substance being dissolved.
Solvents: substance doing the dissolving.
solute, lower, equal, greater
Solution: a homogenous mixture of two or more substances where the ______ is evenly distributed within the solvent.
Tonicity: of the solution a cell is in can be determined by comparing the extracellular solute concentration to the intracellular solute concentration.
Hypotonic: a solution that has a ______ concentration of solute compared to another liquid, cells in this solution will absorb water.
Isotonic: a solution that has a solute concentration _____ to another liquid. If that other liquid is a cell’s cytosol, there will be no net movement of water and dynamic equilibrium.
Hypertonic: has a ______ solute concentration compared to another liquid. If that other liquid is a cell’s cytosol, water will move outside the cell.
shape, water
Osmosis in Plants: water has to move through the cell wall and cell membrane in plants. Water is stored in large vacuoles that exert turgor pressure on the cell wall, the cell wall exerts force back, maintaining the _____ of the cell. This determines how much ______ can get into the cell and also provides structure for plant cells.
low, high
How Water Moves
From high concentration of water to low concentration of water
From areas of high water potential to areas of low water potential.
From areas of low solute concentration to areas of high solute concentration
From areas of ____ or osmolarity to areas of ____ osmolarity.
move, solute, negative, decreases, not, breaks
Water Potential Equation: allows for quantification of water potential on both sides of the membrane, giving us a quantified way to determine where the water will _____.
Formula: ψ = ψp + ψs; measured in bars.
Water Potential (ψ): the water potential of pure, distilled water is always 0.
Pressure Potential (ψp): how much pressure is being exerted on the cell or solution.
Pressure Exerted: by the atmosphere for solutions in an open beaker, or by the cell wall/membrane, for solutions inside cells.
AP Bio Purposes: always set equal to zero unless told otherwise
Solute Potential (ψs): also known as osmotic potential, measures the amount of ______ dissolved in a solvent. Solute potential is given a _______ value because adding solute to a solution always _________ the overall water potential.
Formula: ψs = -iCRT; measured in bars.
“i”: the number of ions a solute breaks into when put in water.
"C": molar concentration of the solution.
"R": gas constant is equal to 0.0831.
"T": temperature in Kelvin (°C +273).
Covalently Bonded Molecules: like sugars, will have an "i" of 1 because they do ___ ionize in water.
Ionically Bonded Molecules: like salt (NaCl), will have an "i" equal to the number of ions the compound ______ into in water.
Example: NaCl has an “i” Value of 2 because it ionizes into two ions in water: Na+ and Cl-.
structure, full, equal, shrinks
Turgor Pressure: the pressure exerted by the water-filled central vacuole of a plant cell against the cell wall. It is a crucial force that helps maintain the rigidity and ________ of plant cells.
Turgid State: when a cell is placed in a hypotonic solution, its central vacuole becomes ___. This causes the cell to swell and its membrane to push against the cell wall.
Normal/Flaccid State: when a cell is placed in an isotonic solution, water moves in and out of the cell at ____ rates. The cell maintains a balanced state with no pressure exerted on the cell wall.
Plasmolysis: when a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution, the central vacuole ______ as water leaves the cell. The cell membrane pulls away from the cell wall.
(End of Notes 2.5)