AP Bio Organelles (study)
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
Nuclear Envelope
Double membrane enclosing the nucleus;perforated by pores;continuous with ER
Chromatin/ Chromosomes
Material consisting of DNA and proteins; visible in a dividing cell as individual condensed chromosomes
Nucleolus
Non Membranous structure involved in production of ribosomes; a nucleus has one or more nucleoli
Ribosomes
Make proteins
Smooth ER
ake lipids (fats, oils, waxes, cell membrane), & helps with cell detox
Rough ER
Vast membrane system extending from the nucleus; Proteins for export are made here and sent to the Golgi; has rough (ribosome-studded) regions
Golgi
Buffers proteins before shipping them to the membrane for export;organelle active in synthesis, modification, sorting, and secretion of cell product
Lysosomes
digestive organelle where macromolecules are hydrolyzed
Food Vacuoles
Formed by phagocytosis. Transports solutes (food).
Contractile Vacuole
Unicellular eukaryote. Pumps excess water out of cell, thereby maintaining a suitable concentration of ions and molecules inside the cell.
Central Vacuole
prominent organelle in older plant cells; functions include storage, breakdown of waste products, and hydrolysis of macromolecules; enlargement of the vacuole is a major mechanism of plant growth
Endomembrane System (overall)
Membrane lipids and proteins. Controls the cell’s compartmental organization.
Mitochondrion
organelle where cellular respiration occurs and most ATP is generated
Chloroplast
photosynthetic organelle; converts energy of sunlight to chemical energy stored in sugar molecules
Peroxisomes
organelle with various specialized metabolic functions; produces hydrogen peroxide as a by-product and then converts it to water
Microtubules, cytoskeleton
Hollow rods constructed from a globular protein (tubulin). Tracks where motor organelles can move
Microfilaments, cytoskeleton
Solid rods. Bear tension. Help cells and their mobility.
Intermediate filaments, cytoskeleton
Larger than microfilaments, but smaller than microtubules. Tension and provide permanent fixtures of cells.
Cell Wall
outer layer that maintains cell's shape and protects cell from mechanical damage; made of cellulose, other polysaccharides, and protein
Extracellular matrix
Cell “wall”. Glycoproteins and carbs = coordinate behavior of all cells of that tissue.
Plasmodesmata
cytoplasmic channels through cell walls that connect the cytoplasms of adjacent cells
Tight Junctions
Plasma membranes tight together. Prevents leaks from extracellular fluid across a layer of epithelial cells.
Desmosomes
Intermediate filaments made of sturdy keratin proteins anchor desmosomes in the cytoplasm.
Gap Junctions
Provide cytoplasmic channels from one cell to an adjacent cell. Membrane proteins that surround pore.
Prokaryotes
Single celled,No membrane bound organelles,Tiny cells,4 byo,Naked DNA (nucleoid)
Eukaryotes
Mostly multi-cellular,membrane bound organelles,Larger cells,2 byo,Chromatin (nucleus)
Prokaryotes & Eukaryotes both…
Membrane,Cytoplasm,DNA,Ribosomes
Golgi (#)
Single Membrane
ER (#)
Single Membrane
Vacuole (#)
Single Membrane
Lysosome (#)
Single Membrane
Peroxisomes (#)
Single Membrane
Flagella (#)
Single Membrane
Cilia (#)
Single Membrane
Nucleus (#)
Double Membrane
Mitochondria (#)
Double Membrane
Chloroplasts (#)
Double Membrane
DNA
codes for proteins
Parts of a Nucleus
Nuclear Envelope, Chromatin, Necleolus
Organelles in a Cytoplasm
Mitochondria, Chloroplasts
Endosymbiotic Theory
M & C were prokaryotic organisms that were swallowed by another larger prokaryote 3-4 byo via phagocytosis. Host cell failed to digest M & C and ultimately formed a: mutualistic symbiosis with their host.
Evidence for the Endosymbiotic Theory
M & C have independent DNA
M & C DNA is similar to prokaryotic DNA
M & C multiply independently from the rest of the cell
M & C have double membranes
Organelles in the Cytoplasm
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (rER), Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (sER), Golgi Apparatus,Lysosomes,Vacuoles,Vesicles
Cell structures NOT organelles
Ribosomes,Membranes,Cytoskeleton
Cell Membrane
Flexible barrier made up of a lipid bi-layer, Controls what enters and exits the cell
Cell Theory
All living things are made out of one or more cells
Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things
All cells come from other cells
Magnifying Power
how much a microscope can magnify an image
Resolving Power
the clarity of the image (focus)
Compound Light Microscope
Visible light is the radiation source
Glass lenses are used for magnification
Images are in color & potentially alive
Includes: two or more lenses plus a light source
Total magnification = lens 1 x lens 2
Maximum magnification = 400x
Electron Microscope
Electron beam is the radiation source
Lenses are electromagnets
Specimen is prepared (frozen/dead)
Images are enhanced by electronics and computers
Images are black and white
Electron Microscope (EM) maximum magnification = 50,000,000x
Transmission EM
Electron beam goes through thin slices of the specimen (2D)
Scanning EM
Electron beam scans over surfaces of the entire specimen (3D)
Cell Fractionation Process
Homogenize cells (blender)
Centrifugation the homogenate (spin at 10,000 rpm) at specific time intervals; Organelles will be in the pellet (bottom of tube); heaviest organelles first
Cell size
A larger Surface Area compared to the Volume helps smaller cells absorb/move materials a lot quicker.
Vesicles
Small packages for transport
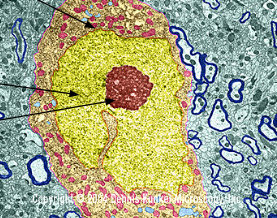
Red
Nucleolus
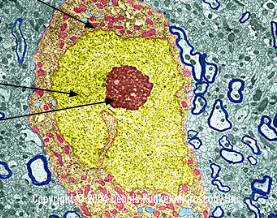
Orange
Nuclear Envelope
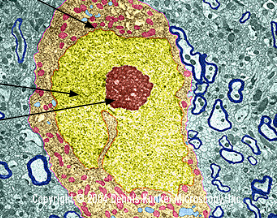
yellow
Chromatin
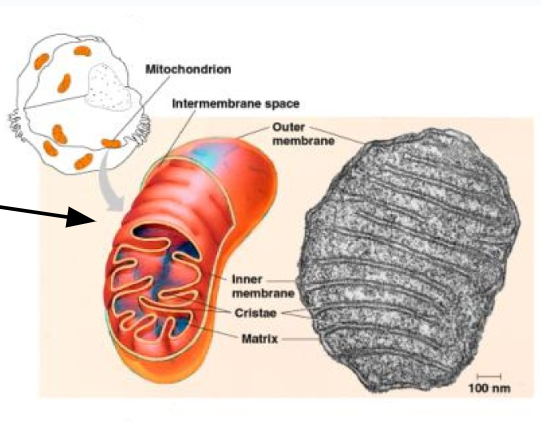
Mitochondria
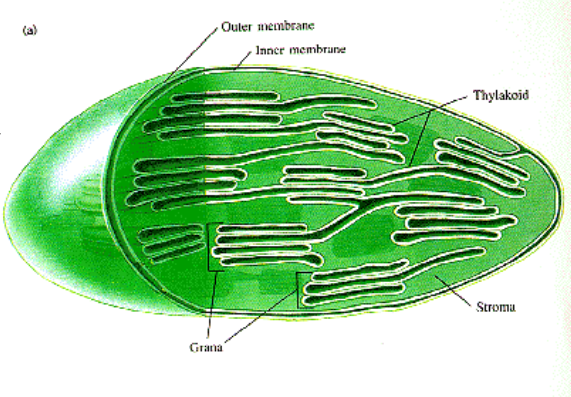
Chloroplast
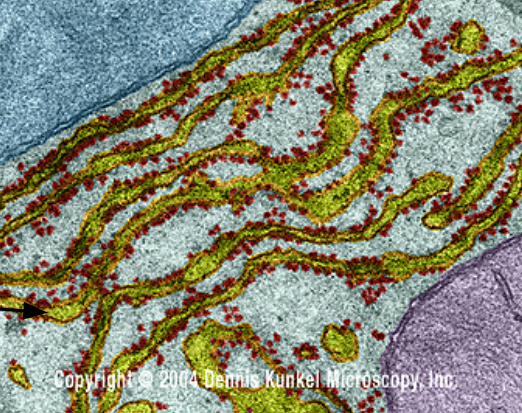
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (rER)
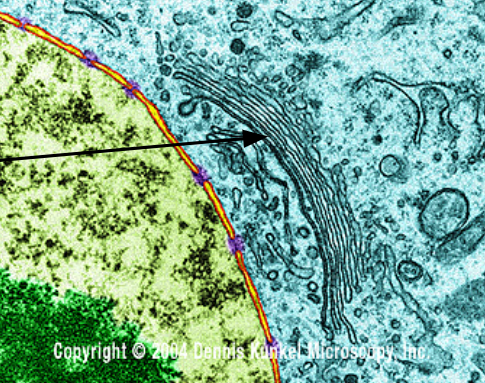
Golgi Apparatus

Scanning EM
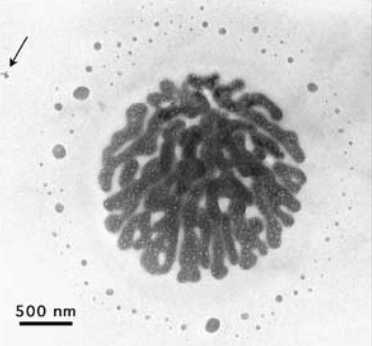
Transmission EM