Genome Variation
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
How big is the human genome?
The human genome has roughly 3 billion bases and about 2000 genes. Only ≈1.5% codes for proteins, known as the exome. The rest include non-coding DNA, regulatory regions, and repetitive elements
Are we all genetically identical?
No, while around 99.7% of DNA is the same between any 2 people, around 9 million bars differ and these differences are called variants or polymorphisms. Some differences are harmless while others can cause disease eg point mutation in sickle cell anaemia
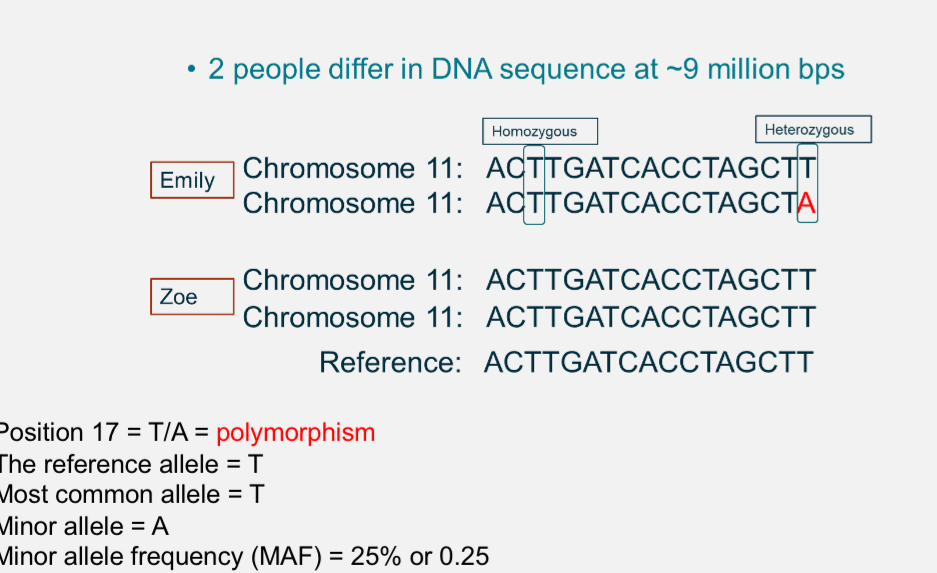
What is polymorphism?
Any point in the genome where DNA sequence varies between individuals.
Eg at position 17, some people have T and others have A
Reference allele: T
Minor allele: A
Minor allele frequency(MAF)= % of chromosomes with A(≈15%)
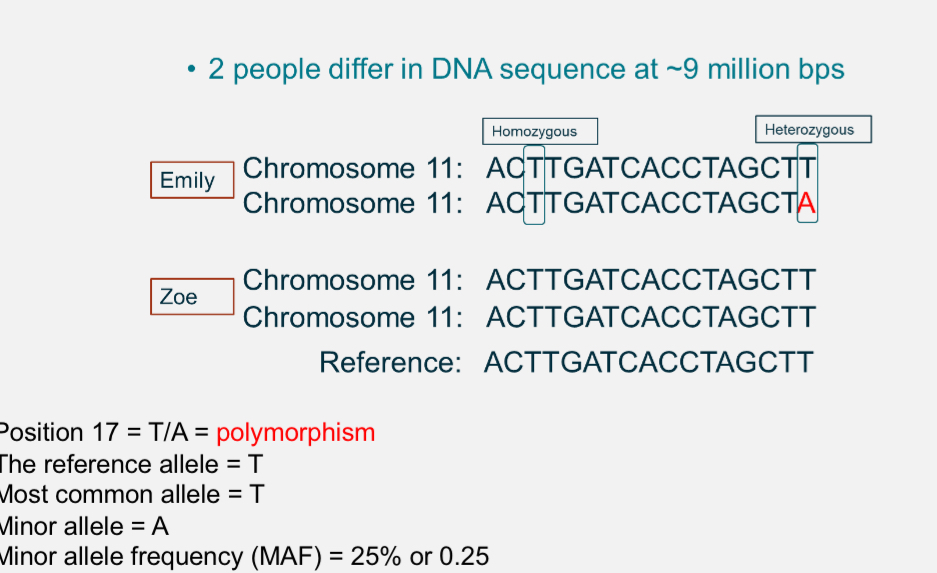
What is a Single Nucleotide Variant (SNV) / Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP)?
A change in a single base.
• Very common: 1 every 300 bases in the genome.
• Each person has ~3–5 million SNVs.
• Usually harmless, but some can alter protein function or gene regulation.
Origin: mistakes in DNA replication, often corrected by DNA mismatch repair.
Mutation vs. Polymorphism?
Polymorphism: MAF >1% in a population.
• Rare polymorphism: 1–5%
• Common polymorphism: >5
• Mutation: MAF <1% (rare, often recent or harmful)
👉 All variants begin as mutations. Evolutionary forces decide if they spread or remain rare.
What evolutionary forces affect variant frequency?
Mutation – creates new alleles.
2. Gene flow – migration introduces variants into new populations.
3. Genetic drift – random changes in allele frequency (especially in small populations).
4. Selection – alleles increase or decrease depending on whether they are beneficial (positive selection) or harmful (negative selection).
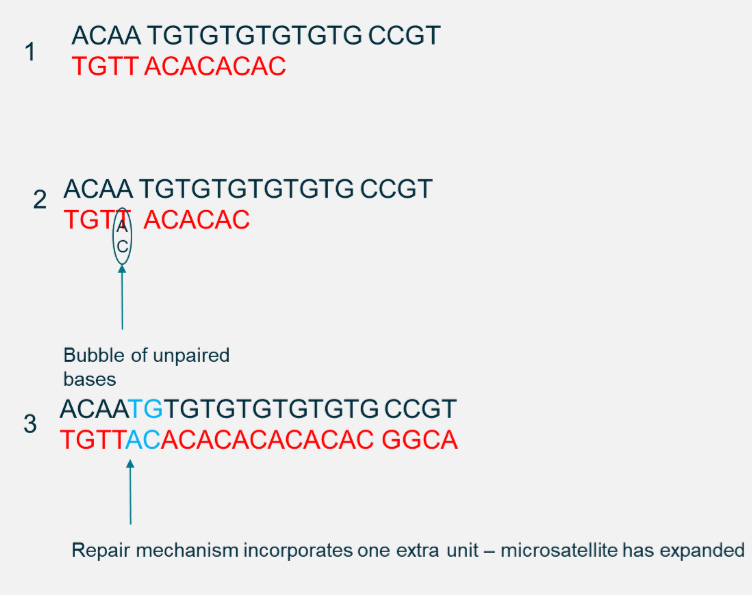
What are microsatellites and how do they arise?
Short tandem repeats (e.g., CA repeats).
Caused by DNA polymerase slippage during replication.
Found across genome (in genes and non-coding regions).
Can change protein length if inside a coding sequence (e.g., Huntington’s disease = CAG repeat expansion).
Multiallelic: multiple repeat numbers possible at a locus.
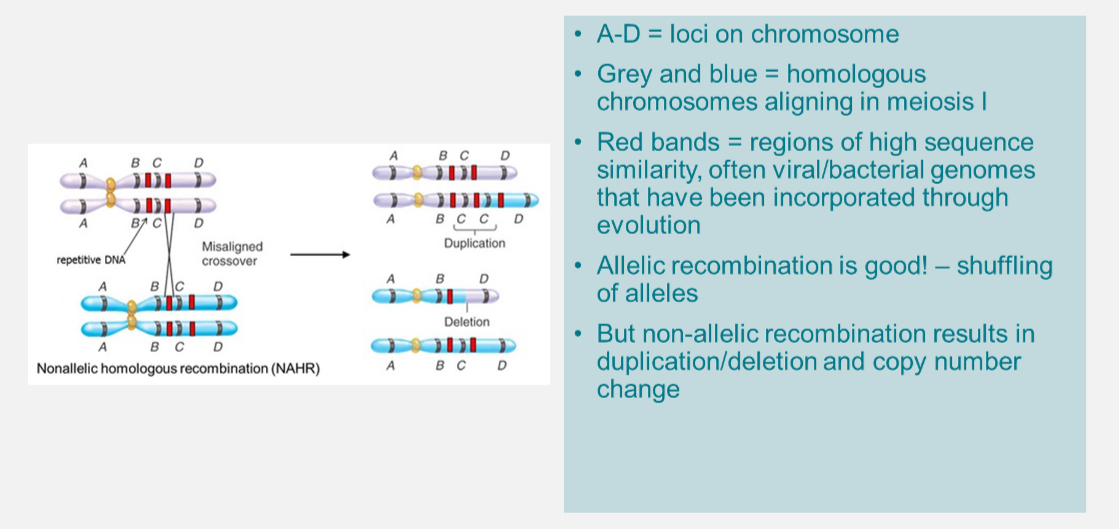
What is Copy Number Variation (CNV)?
Structural variant where a region of DNA is duplicated or deleted.
Usually >1 kb in size.
Caused by non-allelic homologous recombination during meiosis.
~12% of the genome is affected by CNVs.
Each person carries ~100 CNVs.
Can delete or duplicate genes → sometimes pathogenic.
What are the main types of common genetic variation?
SNPs – ~17 million known; ~3 million per genome.
2. Microsatellites – ~3% of genome.
3. CNVs – >2000 identified; ~100 per genome.
How do common variants relate to disease?
Most common variants are neutral, not causing single-gene (Mendelian) disorders.
They often influence complex traits like height, memory, diabetes risk, and even behaviours.
Used in research to find disease-causing genes via linkage studies and GWAS (Genome-Wide Association Studies).
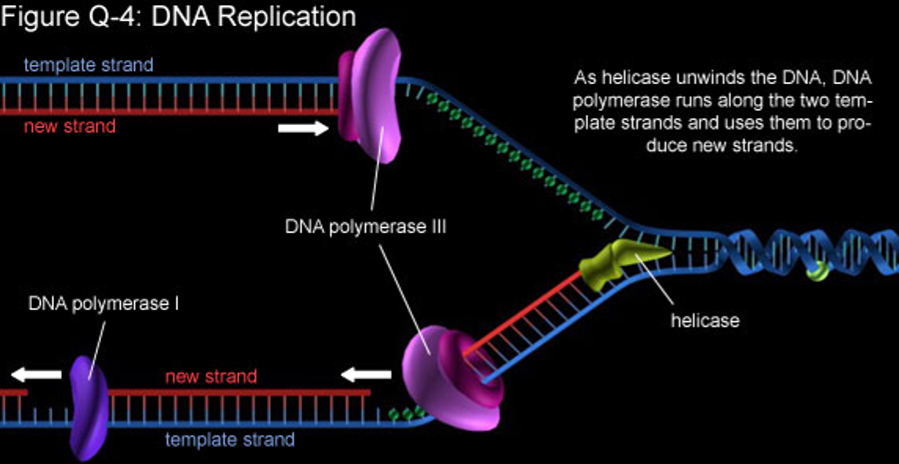
How do SNVs arise through DNA mismatch repair?
During DNA replication, DNA polymerase can insert the wrong base. Normally, the mismatch repair system detects and fixes these errors:
• Recognition: proteins detect mismatched bases (e.g., A–G instead of A–T).
• Excision: enzymes cut out the incorrect base.
• Repair: DNA polymerase fills in the correct nucleotide, and ligase seals the strand
If this system fails, the wrong base remains → SNV (single nucleotide variant). Over generations, these become SNPs if frequent in populations.
How are microsatellites inherited?
Microsatellites = repeated short DNA sequences (e.g., CA repeats).
• Each person inherits one microsatellite allele from each parent.
• Alleles differ by number of repeats, making them multiallelic (many possible versions in a population).
• They follow Mendelian inheritance (dominant/recessive patterns depending on location in coding or non-coding regions)
Example: Huntington’s disease → expansion of CAG repeats in the HTT gene, where severity and onset depend on repeat number.
Book analogy for genome variation
Genome = entire book.
Chromosome = chapter. (Deleting/duplicating a chapter = CNV, large effect).
CNV = deleting/duplicating a paragraph.
Microsatellite = repeating words in a sentence (annoying but not fatal).
SNP = typo in a letter (often little effect).
Key glossary terms
Locus: unique position in genome (can be 1 base or large region).
Allele: a version of a sequence at a locus.
Genotype: the two alleles an individual carries at a locus (homozygous/heterozygous).
Biallelic = 2 alleles exist. Triallelic = 3. Multiallelic = >3.
Allele frequency = proportion of chromosomes in a population with that allele.