BIOL 310 - Ch 19 Lecture Notes
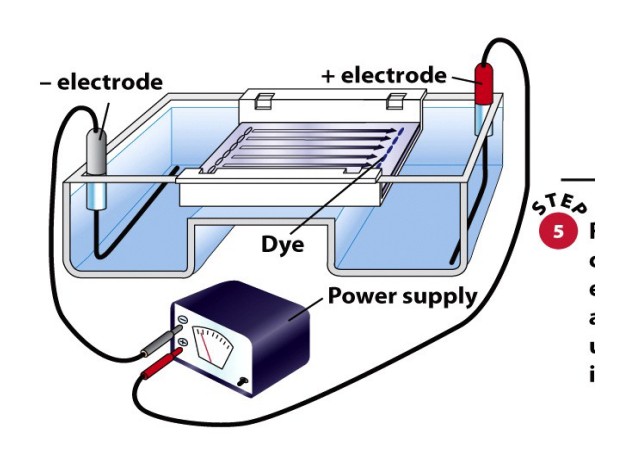
electrophoresis
separates macromolecules based on charge and size
DNA is negatively charged and will migrate towards the positive side of the well
large molecules migrate slowly, slow molecules migrate fast
standard / ladder is used to identify the sizes of the unknown samples
uses apparatus, agarose gel, buffer, electricity and stain
basic apparatus for DNA
restriction enzymes
endonucleases — cut DNA at very specific sites
type II: palindromic sequences e.g. GAATTC & CTTAAG
cohesive or blunt
evolved to protect bacteria from foreign DNA
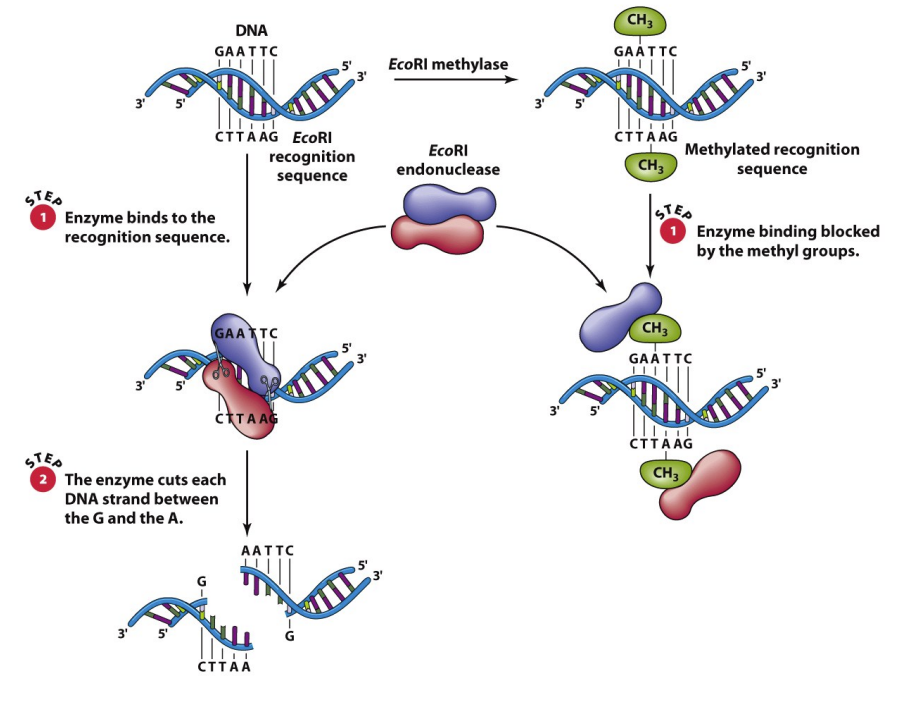
EcoRI has recognition site & the EcoRI methylase
restriction enzyme uses
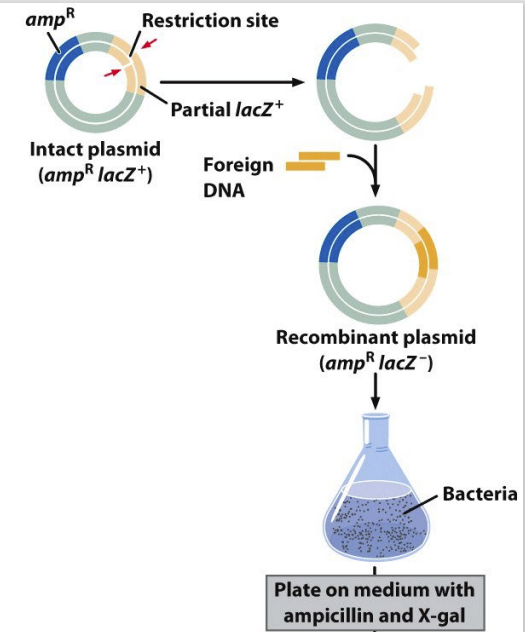
gene cloning — the isolation and amplification of a given gene in a non-host organism
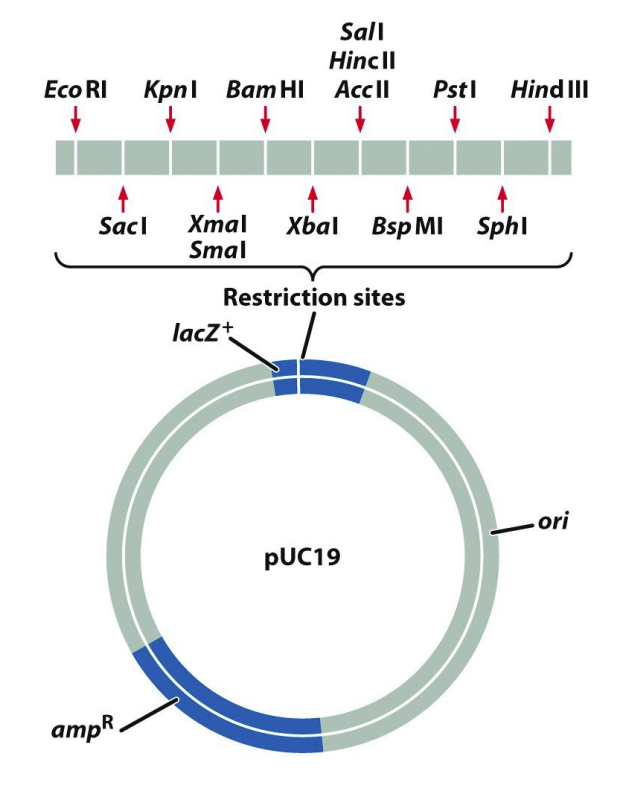
usually in a plasmid
small circular DNA
referred to as a vector — vector has a selector marker (if the cloning was successful or not); multiple unique RE sites
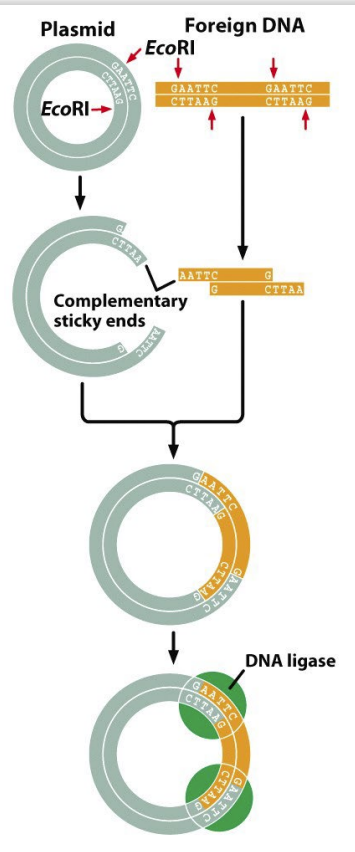
cloning process
necessary components: source DNA, acceptor plasmid, bacterial host, and restriction enzymes
steps:
1) restrict gene of interest
2) restrict vector
3) mix vector & gene & ligase
4) introduce recombinant (plasmid DNA & source DNA present) molecule into host
5) grow host
6) determine success
cloning uses
research
recombinant DNA molecule
in vitro gene expression
expression vector is used: putting a gene into a plasmid under promoter and operator system so the bacteria will make that gene (@15:00)
cloning vectors
plasmids: accept 0.1 to 5kb of DNA insert
cosmids: accept 30-40 kb DNA insert
BACs: accept 150-300 kb DNA
YACs: accept 300-500 kb DNA
genomic library (x3 of genes stored to ensure all the DNA is present - some redundancy)
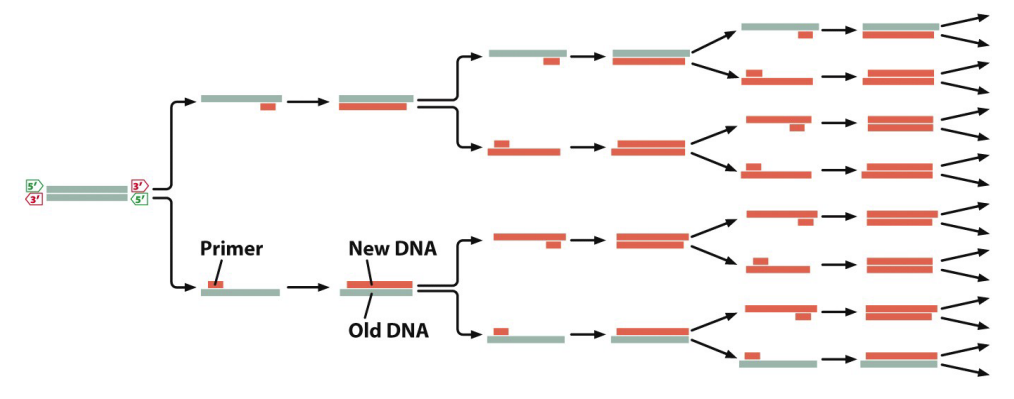
polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
DNA replication in vitro
billions of copies from single template
necessary components: template, primers (3’-OH), Taq DNA polymerase (thermophile), free dNTPs, buffer, magnesium, thermal cycler
two finite strands (before 25:00)
PCR process
initial denaturation (94o C for 2 minutes)
30 cycles
denaturation (94o C for 30 seconds)
primer annealing (50-60o for 30-60 seconds)
elongation (68-72o for 1 min/kbp)
exponential amplification of DNA
copy # = 2n where n = # of cycles
cycle vs copies
1= 21= 2
3= 23 = 8
DNA denatured, the primers will bind based on polarity for cycle 1; a strand of DNA is created of unknown size (29:00)
when amplifying one part of a strand, the next replication cycle already has the ____👎👎
applications of PCR
diagnosis of inherited human diseases
pathogen subtypes
identification of individuals in forensic cases
micro-satellites
coupled with sequencing
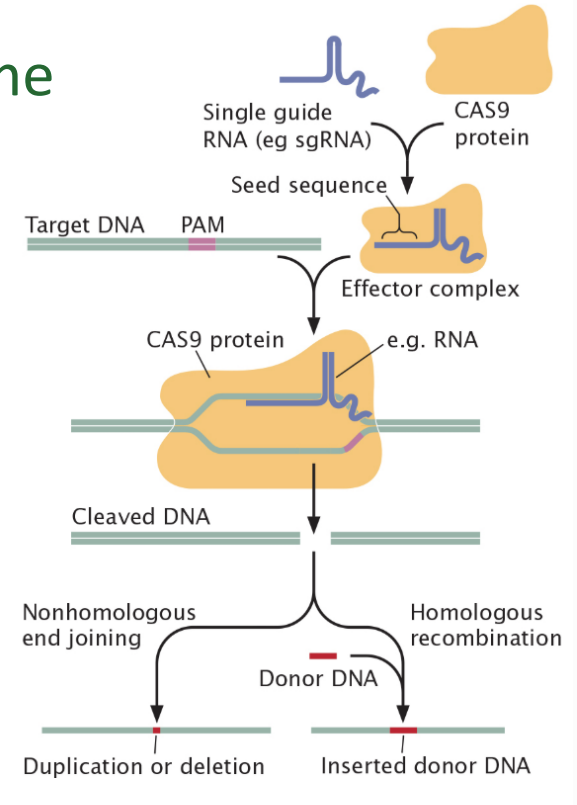
CRISPER - Cas genome editing
clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats
evolved as immunity in bacteria and archaea
cut foreign DNA
insert it into the host genome
memory built for next infection; better able to recognize the virus
cut and destroy foreign DNA
introduce Cas9 & guide RNA
effector complex binds target DNA
double stranded break
homologous recombination with donor DNA (repair)
non-homologous end joining (disrupt)
pros
long guide RNA provides specific targeting
used in intact cells
use alternate PAM sites (CAS from diff. species)
challenges
large protein
hard to place in living tissue