AP Psychology - Biological Bases of Behavior, The Brain (Unit 1)
1/157
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
158 Terms
Evolutionary Perspective
The study of how psychological and behavioral traits have evolved to enhance survival and reproductive success.
Natural Selection
Where organisms survive in an environment that better suits their traits
Evolutionary Advantage
Individuals with better social intelligence has advantages in forming alliances, gaining social status, etc
Nature (natural)
Biological and genetic factors that influence an individual’s psychological development, traits, and behaviors.
Nurture (non natural)
Environmental influences and experiences that shape an individual’s psychological development and behaviors.
Twin Studies
Similarities, differences, and the influence of genetics and environment on traits and behaviors between identical and fraternal twins.
Adoption Studies
Similarities between adopted children and their bio and adoptive families.
Family Studies
Similarities and differences among family members to understand interplay of genetics and environment in how it shapes traits and behaviors within a family.
Heredity
Transmission of genetic info from biological parents to offspring
Genetic Predisposition
Inherited likelihood of developing specific trats or conditions due to genetic factors.
Which one of these is not an example of Genetic Predisposition
Birthmarks
Eugenics
A belief in improving genetic quality of the human population by selective breeding
Cerebral Cortex
Outer layer of the brain- responsible for higher level cognitive functions (the big boss)
How many lobes are there?
4
Frontal Lobes
Higher-level cognitive functions - decision making, problem-solving, planning, personality expression.
Prefrontal Cortex
Planning, decision making, self-control.
Motor Cortex
Controlling voluntary movements of the body (walking, talking, grabbing objects)
Parietal Lobes
At the top of the brain- Processing sensory information from the body (touch, temp, spatial awareness)
Somatosensory Cortex
Processing sensations from the skin, muscles, and joints.
Occipital Lobes
Your eyes in the back of your head, processes visual info.
Temporal Lobes
Sides of the brain- Processes auditory info, language comprehension and memory formation.
Corpus Callosum (CC)
Connects the left and right hemispheres of the brain and regulates communication.
Brainstem
Regulates basic life-sustaining functions (breathing, heart rate, sleep-wake cycle)
Medulla
(In the brainstem) Heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure
Reticular Activating System (RAS)
Arousal, attention, consciousness
Cerebellum
coordinates movement, balance, posture.
Limbic System
Brain structures involved in emotions, memory, and motivation.
Reward Center
Processes pleasurable experiences and reinforces behaviors associated with them.
Thalamus
Processes and relays sensory information (all senses but smell)
Hypothalamus
Regulates bodily functions like hunger, thirst, body temp. Helps maintain homeostasis in the body.
Pituitary Gland
Regulates hormonal activity and secretion throughout the body
Hippocampus
Forms and keeps new memories. (Camping the memories)
Amygdala
Processes emotions, particularly fear and aggression. (Flight-or-fight)
What are the 2 types of Nervous systems?
Peripheral and Central nervous system
What does the Central Nervous System do? (CNS)
Command center of the body, processes info, coordinates responses. (CEO)
What does the Peripheral Nervous System do? (PNS)
A communication network that transmits information from the body to the central nervous system. (a bunch of interns for the ceo)
Autonomic Nervous System
Regulates bodily functions without conscious control.
What are the two branches of the autonomic Nervous System?
Parasympathetic (decreases heart rate) and Sympathetic (increases heart rate).
Somatic Nervous System
Branch of peripheral nervous system that controls voluntary movements.
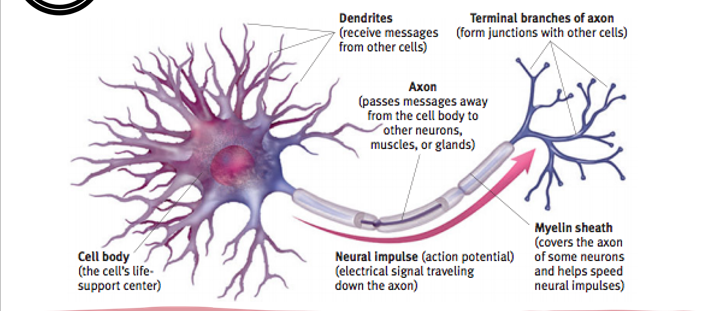
Neurons
A cell that transmits electrical and chemical signals throughout the body
Glidal Cells
the “support cells.” Provides structural support to neurons
Moter Neurons
Initiates and controls voluntary and involuntary movements. (sends signals from central nervous system to muscles, glands, and organs)
Sensory Neurons
Transmits sensory info from sensory receptors (skin, muscles, organs) to the central nervous system
Interneurons
Relays signals between sensory and motor neurons.
Dendrites
receives messages from other cells
Cell Body
cells life support center
Axon
Passes messages from cell body to other neurons
myelin sheath
covers the axon to speed up neural impulses
Terminal Branches of Axon
forms junctions with other cells
Reflex Arc
Controls reflex actions
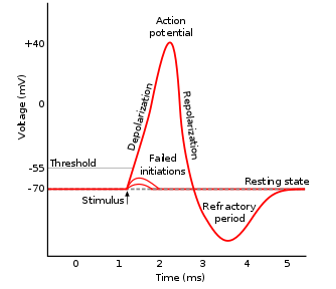
Neural Transmission
The process which neurons communicate with each other through electrical and chemical signals
Threshold
level of stimulation required to trigger an action potential in a neuron
All-or-Nothing Principle
Once a neuron reaches its threshold of excitation, it will fire an action potential at full strength
Depolarization
A floodgate suddenly opens and allows a rush of positive ions to flow into the cell
Refractory Period
Brief period where after an action potential a neuron is unable to generate another action potential
Resting Potential
stable, negative electrical charge that exists across the cell membrane of a neuron when its not transmitting signals
Reuptake
Neurotransmitters have been released into the synapse are reabsorbed from where they were originally released
Neurotransmitters
transmit signals between neurons, allowing communication
Excitatory Neurotransmitters
increases the likelihood of an action potential to occur
Glutamate
Involved with learning, memory, and neural plasticity
Inhibitory Neurotransmitters
the likelihood of an action potential to occur int he postsynaptic neuron
GABA
Promotes relaxation and reduces anxiety
Dopamine
Regulates mood, reward, motivation, and movement (ex: entertainment from phone)
Serotonin
regulates mood, sleep, appetite, and stress (happiness)
Endorphins
natural pain relievers and mood enhancers (released when stressed, in pain, or during an intense physical activity)
Substance P
transmits pain signals in the nervous system
Acetylcholine
involved in muscle contraction, memory, and learning
Hormones
chemical messenger that travels through the bloodstream to target cells or organs, where then regulate various processes and behaviors.
Ghrelin (growling)
Stimulates appetite and promotes hunger (hunger hormone)
Leptin
regulates energy balance and appetite (tells you that you are full)
Melatonin
regulates the sleep-wake cycle, ensures restful sleep
Oxytocin
key role in social bonding (the love hormone)
Adrenaline
A key role in the body’s stress response, referred to as fight or flight response
Norepinephrine
Neurotransmitter that responds to stress levels and enhances your cognitive functions to focus. (ex: last minute studying)
Plasticity
The brains ability to reorganize and adapt throughout life in response to experiences, learning, and environmental changes.
Split Brain Research
studies individuals who have gotten their two hemispheres disconnected
Contralateral Hemispheric Organization
Each hemisphere of the brain controls the opposite side of the body.
Hemispheric Specialization
Concept where each hemisphere of the brain has specialized functions and abilities.
Linguistic Processing
Understanding and producing language.
Broca’s Area
responsible for speech production and language processing
Broca’s Aphasia
Language disorder where there’s difficulty to produce fluent speech and grammatically correct sentences.
Wernicke’s Area
Helps interpret the meaning of words and sentences
Wernicke’s Aphasia
Can speak fluent but has difficulty understanding spoken and written language
Electroencephalogram “EEG”
neuroimaging technique used to record the electrical activity of the brain
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging “fMRI”
technique used to measure brain activity by detecting changes in blood flow and oxygen levels
Lesioning
Research on brain function by intentionally damaging or destroying specific areas of the brain on experimental animals.
Vision is also known as… and what does it do?
Sight- Perception of light and color
Hearing is also known as…. and what does it do?
Audition- Perception of sound waves
Smell is also known as… and what does it do?
Olfaction- Perception of odors
Taste is also known as… and what does it do?
Gustation- Perception of flavors
Touch is also known as… and what does it do?
Tactile- perception of pressure, temp, and texture
Transduction
Conversion of sensory stimuli into neural impulses
Where does sight take place? (think specific!)
Retina (specifically in rods and cones)
Where does audition take place? (think specific!)
Cochlea (hair cells in the Organ of Corti)
Where does olfaction take place? (think specific!)
Olfactory epithelium (in the nasal cavity)
Where does gustation take place? (think specific!)
Taste buds (on the tongue, roof of mouth, throat)
Where does tactile take place?
Receptor cells in the skin.
Absolute Threshold
Point at which a stimulus becomes noticeable to an individual
Just-Noticeable Difference (JND)
Smallest change in a stimulus that can be detected by an individual