HTHSCI 3BB3 Final Exam Review
1/751
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
752 Terms
Why do we need to consume food?
1. Energy
2. Important nutrients that we can't make ourselves
Humans went from hunter-gatherers to:
establishing permanent settlements with reliable food supplies from domesticated crops and animals
What stimulates dopamine in the reward centre of our brain and provides positive feedback?
sugar
Chronic disease: a problem of nutrition?
- link to cardiovascular disease,
- alzeimher's --> cancer --> diabetes, heart cancer all related to nutrition
Countries with low-incidence of heart disease often followed which kind of diet?
mediterranean
What does the nutritional health look like in Canada?
- 1 in 3 kids, 2 in 3 adults overweight
- 1 in 5 adults have chronic diseases
- 1 in 3 people eat enough veggies
- 1 in 6 eat whole grains
- 1/3 eat plant based legumes, nuts, and seeds
What are Canadians eating?
- processed foods containing high saturated fats, sodium, and sugar
What are the top 3 leading causes of death in the Canada?
cancer, heart disease, stroke
Unit for energy
measured in Kilocalorie, Kcal or Calorie
One calorie (1/1000 of a Calorie) is:
the amount of heat it takes to raise one g of water one degree Celsius
One calorie is equal to _________ joules
4.18
One Kcal is typically enough energy to take _____ steps
~25 steps
T OR F: calorie / Calorie (kcal) is NOT interchangeable like it is in the public
true
Kcalories/Gram: carbs
4
Kcalories/Gram: lipids
9
Kcalories/Gram: protein
4
Kcalories/Gram: alcohol
7
How many calories would you expect to be produced a food that contains 20g of carbohydrates, 10g of lipids, and 4g of protein?
186 Kcal
Macronutrients:
Fats/Lipids, Carbohydrates and Proteins
and energy-producing macronutrients
T or F: Water is a macronutrient that doesn't produce energy
TRUE
Vitamins and Minerals are termed micronutrients (micro = small) because
we need a small amount of them
Micronutrients
- important for cellular function
- minerals
- vitamins
essential micronutrients:
we cannot make them and must get them from our diet, or
non-essential micronutrients:
we can make them, but they are also available in our diet.
A recent paper reported that hospitalizations in Ontario that were attributed to alcohol rose:
~240% in women aged 25-29
*In 2014, alcohol was attributed to $11.1 billion in healthcare costs
What is Health At Every Size® (HAES®)?
supports people in adopting health habits for the sake of health and well-being (rather than weight control).
Genetics versus Lifestyle:
- Physical activity or diet can equalize an individual's inherent risk to obesity and heart disease
- both have an impact
What is the scientific method?
observation, hypothesis, experiment, theory
PICO(T)
Population
Intervention
Comparison
Outcome
Time
What to look for in a well-designed experiment:
- Would this population provide information
to answer the question?
- Are the population demographic representative?
- Is the population large enough to draw a conclusion?
Interventional Studies:
- intervention is used in an experimental group as compared to a control (placebo) group to determine cause or effect
- RCTs
Observational Studies:
- Researchers carefully and systematically observe and record behavior without interfering with behavior.
- Correlations can be observed, although cause and effect cannot be determined
- Cohort studies and Case- control studies
Retrospective studies:
where you know the outcome but are looking back to find a possible cause
Prospective studies
are where you don't know the outcome yet and are looking forward to see the outcomes
Inverse Association
negative correlation
Direct Association
positive correlation
CRAAP
C - currency
R - relevance
A - authority
A - accuracy
P - purpose
When shopping for natural health products, look for:
- Look for a Natural Product Number (NPN)
*Claims are based on evidence, but usually relate to nutritional deficiency, not when consumed in excess of recommended dietary intakes
What should you look for when researching for nutrition?
Registered Dietitians (RDs), academics with nutrition degrees and MDs only if they have nutrition education
What to consider when writing a food guide?
Dietary Needs
Population Health & Wellness
Food Accessibility + Supply Chain
What is a Dietary Reference Intakes (DRIs)?
Acceptable range of quantities of vitamins and minerals for each gender and age group
If we measure the nutrition need of a specific nutrient for a healthy individual and plot it on a graph, we will get:
A single point
If we keep testing individuals in a population, we will get:
a spread of data...
Estimated average requirement or EAR, estimates:
amount of a nutrient to meet needs of 50% of the population
Recommended Dietary Allowance or RDA:
- The average daily intake of a nutrient that meets the requirements of nearly all (97% to 98%) healthy people of a given age and gender
- based on EAR, but higher to encompass needs of 97% of the population
What is the risk in setting the recommended daily intake at the estimated average requirement (EAR)?
The recommendation will NOT MEET the needs of 50% of the population
Tolerable upper intake level or UL:
amount below which there is little chance of adverse health effect
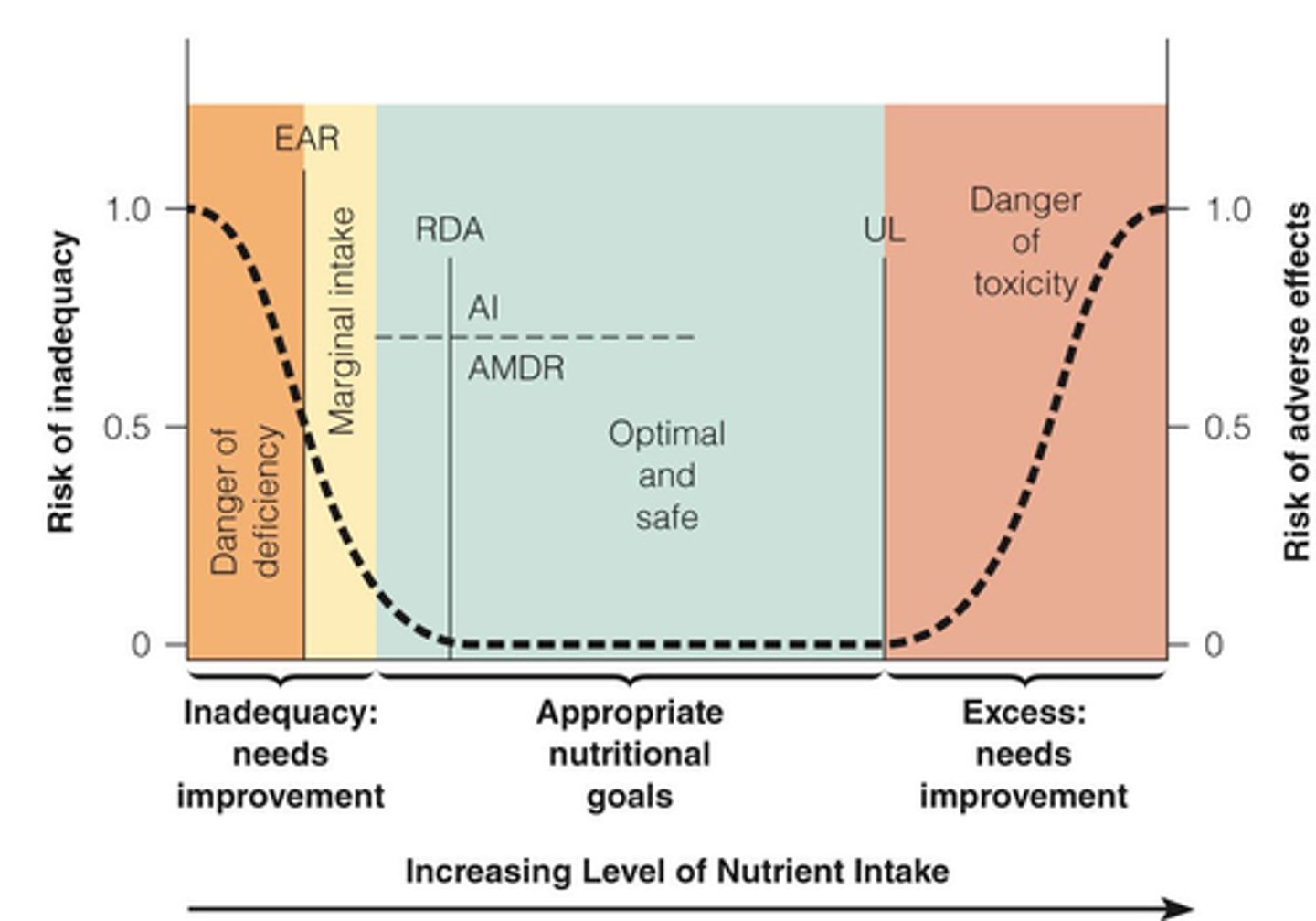
Adequate intake or AI
value used if there is insufficient data to calculate RDA
Estimated Energy Requirements:
Energy Consumed - Energy Used = 0 (Energy Balance)
What does it mean when a person is in a negative energy balance?
- Using more energy then is being consumed
- Consuming less energy then is being used
Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Ranges
Recommendations:
• Carbs 45-65%
• Fat 20-35%
• Protein 10-35%
What to consider when writing a food guide?
Evidence Review for Dietary Guideline
What are the Evidence Review for Dietary Guidelines?
- These guides review scientific evidence and the Canadian context with respect to chronic diseases of concern
• Cardiovascular disease,cancers,diabetes, osteoporosis were some of the areas of concerns
Association between foods and chronic diseases: convincing evidence
↑ Vegetables and fruit: ↓ CVD and ↓ Cancer
↑ Dietary fibre: ↓ CVD and ↓ Cancer
↑ glycemic index or load: ↑ Type 2 Diabetes
↑ Sugar sweetened beverages: ↑ Dental caries in children
What are the updates to the 2019 canada food guide?
• No more food groups
• No recommendation on serving sizes
- Advice on the importance of cooking, enjoying food and mindfulness
Being mindful of your eating habits means being aware of:
• how you eat
• why you eat
• what you eat
• when you eat
• where you eat
• how much you eat
Cooking and preparing food can support healthy eating habits. Cooking allows you to:
- learn new.skills
- rely less on highly processed foods
- control the amount of sauces and seasonings
- make foods that you and your family like and will eat
- save money by avoiding extra money spent on meals eaten out
- choose healthy ingredients
Enjoying your food includes:
- socializing at mealtime
- enjoying shopping for food
- preparing and cooking food
- growing or harvesting your own food
- getting to know the people that grow or produce your food
- involving others in meal planning, preparation and clean up
By eating with others you can:
- enjoy quality time together
- share food traditions across generations and cultures
- explore new healthy foods that you might not normally try
A portion:
the amount of food that you choose to eat for a meal or snack. It can be big or small, you decide.
A serving
a measured amount of food or drink, such as one slice of bread or one cup (eight ounces) of milk.
What is "portion distortion"?
The increase in portion sizes for typical restaurant and snack foods, observed over the last 40 years.
ABCDMV Principles of Diet Planning
Adequacy,
Balance,
Calorie control,
nutrient Density,
Moderation,
Variety
How can you assess nutritional health?
- Analysis of dietary intake
- Anthropometric measurements
- Medical history and physical exam
- Laboratory measurements
Laboratory measurements:
- Values of nutrients in blood
- Markers of disease
Analysis of dietary intake
- Food diaries or food intake records
- Food frequency questionnaire
- Diet history
Anthropometric measurements
- Heights, weight, BMI
- Waist circumference
- Weight change over time
CASE STUDY
23-year- old university student who came into the clinic reporting feeling tired and having difficulty concentrating in class. Has lost some weight and recently started a vegetarian diet.
What do you suspect may be the cause of Darra's symptoms?
Low iron in her diet
What are the stages of deficiency?
1. Inadequate intake
2. decreased stores and tissue levels
3. altered biochemical and physiological functions
4. physical signs and symptoms of deficiency
What do atoms form?
atoms form molecules which make up the proteins and lipids that form cells and tissues and the glucose that is used for energy
What is the role of the digestive system?
it breaks food into compounds small enough to be absorbed into the body
What does the Gastrointestinal Tract consist of?
mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine and anus
T or F: Digestion, Absorption and Excretion take place within the GI tract
true!
Transit time
amount of time it takes food to pass the length of the GI tract
When does digestion begin?
as soon as food enters the mouth
Digestion in the mouth:
- Chewing mechanically breaks down food into smaller pieces
- Saliva lubricates food and contains the enzyme amylase which starts to break down starch (carbohydrates) in the mouth
Digestion in the stomach:
- HCl (acidifying the stomach)
- Pepsinogen, inactive form of the enzyme pepsin
- Once activated by HCl, pepsin begins breaking down proteins
- children, rennin is released which helps digest milk
- stomach muscles churn the contents, aiding in digestion
- Chyme leaves the stomach in about 2-6 hours and enters the small intestine
Digestion in the SI:
pancreas - Bicarbonate (neutralizes the
acidic chyme), enzymes
gall bladder - Emulsify lipids, separating them it into smaller fat droplets which are more soluble and accessible to enzymes
Most absorption occurs in the:
small intestine
Villi and microvilli (protrusions from the stomach lining):
increase the surface area of the small intestine
Single sugars, amino acids and short chain fatty acids enter the ....
portal vain and go the to liver
Long chain fatty acids enter the ...
lymphatic system and go directly to the blood stream
T or F:Chyme moves through the small intestine in 3-5 hours
TRUE
How long is the SI?
6 meters
Gut bacteria break down:
unabsorbed food and can produce beneficial compounds for the body
How long does biological material stay in the large intestine:
~24-36 hours before being excreted
The immune system is interconnected within the GI Tract to prevent....
pathogens from entering
Phagocytes such as _______________________ and _______________________ such as __________ and __________- are present below the mucosa
macrophages and lymphocytes ( B-cells and T-cells)
Food allergies occur when:
the immune system reacts to a protein in our food and triggers an immune response
What disease have been linked with the gut microbiome?
Obesity, cancer, inflammation, cardiovascular disease, liver disease have all been linked with gut microbiota
The gut microbiome:
synthesize small amounts of short chain fatty acids and some vitamins which can be used by cells of the large intestine
Where does the microbiome come from?
- newborn is inoculated with bacteria during birth
- born vaginally have an initial microbiome that resembles the mother's vaginal microbiome
- Infants born via a c-section have a microbiome that resembles the mother's skin microbiome
Those with lower bacterial numbers (and with higher BMI) harboured which species of bacteria?
more pro- inflammatory species
Bacteriatransplantedintogerm-freemice from either lean or obese twins conferred that:
phenotype and metabolic profile on the mice
Lactose intolerance
Lactase = enzyme in SI that can break down the sugar molecule lactose
- expressed highly during infancy, but typically decreases as a child transitions to solid foods
- if amount of lactase in the small intestine is insufficient to handle the lactose in the diet, some lactose will escape and enter the large intestine where bacteria will use it for energy
IBS
A bacterial protein has a similar sequence to the human insulin epitope that contributes to:
- T1D
- bacteria may trigger/modify/prime an immune response to insulin and T1D onset
Which hormone is released by the pancreas after a meal?
insulin
What happens when we eat?
- Glucose, fatty acids, and amino acids enter blood from the intestines
- liver = gets first access because of the portal vein
- Insulin released from pancreas from high blood-glucose levels, glucagon is decreased
Nutrients can either:
1. Broken down for energy - CATABOLISM
2. Used to make new molecules - ANABOLISM
3. Stored for use later