Biol 112 Tamu Exam 3 Master copy
5.0(1)Studied by 3 people
Card Sorting
1/144
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:09 PM on 4/12/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
145 Terms
1
New cards
Chlorophytes, Charophytes & Plantae share
* multicellularity
* cell walls with cellulose
* chloroplasts with the same pigments (chlorophyll. a & b)
* storage molecule is starch
* cell walls with cellulose
* chloroplasts with the same pigments (chlorophyll. a & b)
* storage molecule is starch
2
New cards
Charophytes share with Planta
* similar flagellated sperm (liverworts)
* cellulose synthesis proteins (rings)
* cytokinesis process (cell plate formation)
* Sporopollen
* cellulose synthesis proteins (rings)
* cytokinesis process (cell plate formation)
* Sporopollen
3
New cards
Sporopollen
polymer that protects:
– zygotes = charophytes
– spores = seedless plants
–pollen grains = seed plants
– zygotes = charophytes
– spores = seedless plants
–pollen grains = seed plants
4
New cards
Green algae Growth
Pros:
* more resources; less competition
* \[CO2 \] higher, light intensity higher
Cons:
* Desiccation
* divided resources (air vs. land)
* no “support” in air
* more resources; less competition
* \[CO2 \] higher, light intensity higher
Cons:
* Desiccation
* divided resources (air vs. land)
* no “support” in air
5
New cards
Derived characteristics of Plants
1. Alternation of Generations
2. Walled haploid spores
3. Multicellular gametangia
4. Sporophyte embryos grow protected within female gametophyte
5. Apical Meristems
6. Waxy cuticle
7. Secondary compounds
8. Mycorrhizae
6
New cards
Alternation of Generations in Plants
multicells undergo meiosis → produces more unique spores
where charophytes meiosis → only 4 offspring
where charophytes meiosis → only 4 offspring
7
New cards
Walled Haploid spores
Spores protected but sporopollenin
8
New cards
Multicellular gametangia (What are they and what they contain?)
Sperm protected by Antheridium (Ant will get rid of em)
Eggs protected by Arch**eg(g)**onium (Also where fertilization happens)
Make haploid cells
Eggs protected by Arch**eg(g)**onium (Also where fertilization happens)
Make haploid cells
9
New cards
Sporophyte embryos grow protected within female gametophyte
Embryos are fed and protected by the Archeggonium
10
New cards
Apical Meristems
A bunch of cells always dividing at the “apex” or tips of plants
Roots and shoots grow
Roots and shoots grow
11
New cards
Waxy cuticle
Helps stop the loss of water as gas
Exchange of gases controlled by stomata
Exchange of gases controlled by stomata
12
New cards
Secondary compounds
chemicals hinder competitors, herbivores, & parasites
13
New cards
Mycorrhizae
Fungi helps absorb water and minerals
Around before actual roots
Around before actual roots
14
New cards
Diversification of Plants
1. Bryophytes (Nonvascular Plants)
2. Seedless Vascular Plants
3. Gymnosperms
4. Angiosperms
15
New cards
Bryophytes (Nonvascular Plants)
1. (Phylum) Hepatophyta- Liverworts
2. Bryophyta-Mosses
3. Anthocerophyta- Hornworts
\
16
New cards
Hepatophyta
\- Liverworts
17
New cards
Bryophyta
\-Mosses
18
New cards
Anthocerophyta
\-Hornworts
19
New cards
Bryophytes Characteristics
1. Haploid gametophyte = dominant form
2. Eggs & Flagellated sperm
3. No Vascular Tissue (uses diffusion)
4. Rhizoids used for attachment
5. Sporangium makes many haploid spores
20
New cards
“Moss Life cycle”
Peristome→ spores→ Protonema →
either male or female **gametophyte (**gametophore**) →**
**Antheridium sperm carried by water → Archegonium→**
Fertilization→ Sporangium (seta)→ peristome
either male or female **gametophyte (**gametophore**) →**
**Antheridium sperm carried by water → Archegonium→**
Fertilization→ Sporangium (seta)→ peristome
21
New cards
Bryophytes Ecological Importance
Pioneer species in poor soils
Primary producers in high/cold regions
Primary producers in high/cold regions
22
New cards
Seedless Vascular Plants
Lycophyta(Relict group): Lycophytes
Monilophyta: Monilophytes
Monilophyta: Monilophytes
23
New cards
Lycophytes
– club & spike moss
24
New cards
Monilophytes
–Whisk ferns (Psilotum)
–Horsetails (Equisetum)
–Ferns (large megaphylls, sori underside,
–Horsetails (Equisetum)
–Ferns (large megaphylls, sori underside,
25
New cards
Seedless Vascular Plants Characteristics
1. More sporangium then Bryophytes
2. Vascular tissue = Taller sporophytes
3. Sporophyte becomes a dominant part (Doesn’t rely on Gametophyte for food)
4. Roots evolved from misgrown stems?
5. **Microphylls**: single vein Leaves evolve from branched stems
1. **Megaphylls**: branched veins
6. Sporangia → Leaves = Sporophylls
1. sori = clusters of sporangia on sporophylls (Think Balls)
2. strobilus = cone-like group of sporophylls (Think Corn)
26
New cards
Success of Seedless Vascular Plants led to
Increased O2 levels, more food for herbivories, helped land animals
27
New cards
Phloem
moves sugars & organic products
28
New cards
Xylem
carries water & minerals
29
New cards
Seed Plants
Gymnosperms
Angiosperms
Angiosperms
30
New cards
Seed Plants Characteristics
* Reduced & Retained Gametophytes
* Ovules
* Pollen
* Seed
* Ovules
* Pollen
* Seed
31
New cards
Reduced & Retained Gametophytes
Heterosporous(in Seed plants)
Heterosporous(in Seed plants)
“produces both types of spores”
Megaspores →Female Gametophyte
Microspores → Male Gametophyte
(mature in the sporangia)
Megaspores →Female Gametophyte
Microspores → Male Gametophyte
(mature in the sporangia)
32
New cards
Ovule in Seed plants
the megasporangium with retained megaspore
33
New cards
Pollen
* microspores retained; mature into pollen grains while within microsporangium
* pollen grains = mature male gametophytes (2-3 cells) in sporopollenin
* pollen grains = mature male gametophytes (2-3 cells) in sporopollenin
34
New cards
Pollination
Pollen travels, lands on megasporangium(2n) and asks megaspore(n) for permission to enter
Pollen tube is formed towards megaspore
\
\
Pollen tube is formed towards megaspore
\
\
35
New cards
Seed (2n)
Fertilized ovule(pollination has occurred) = Seed
Has all the food and water protection to further spread the organism
Can grow underground with nutrients and/or wait to good conditions to grow
Has all the food and water protection to further spread the organism
Can grow underground with nutrients and/or wait to good conditions to grow
36
New cards
Sporangium
A space where asexual spores are formed
37
New cards
Gymnosperms
Ginkgophyta
Cycadophyta
Gnetophyta
Coniferophyta
Cycadophyta
Gnetophyta
Coniferophyta
38
New cards
Phylum Ginkgophyta
Ginkgos
Fleshy seeds
flagellated sperm
Fleshy seeds
flagellated sperm
39
New cards
Phylum Cycadophyta
cycads
fern-like fronds radiate from a central stem
flagellated sperm
fern-like fronds radiate from a central stem
flagellated sperm
40
New cards
Phylum Gnetophyta
Gnetophytes
Fe/Male Strobili, sperm can’t move
Fe/Male Strobili, sperm can’t move
41
New cards
Phylum Coniferophyta
Conifers
Most diverse gymnosperm
–male pollen cone, Sperm can’t move, Female Ovulate cone
Evergreen, High places
Most diverse gymnosperm
–male pollen cone, Sperm can’t move, Female Ovulate cone
Evergreen, High places
42
New cards
Angiosperms (Phylum Anthophyta)
Monocots
Eudicots
Magnoliids
Basal Angiosperms: Amborella • Water Lilies • Star anise & relatives
Eudicots
Magnoliids
Basal Angiosperms: Amborella • Water Lilies • Star anise & relatives
43
New cards
Monocots
Mature seed has alot of endosperm leftover
only 1 cotyledon (seed leaf)
Parallel veins
Scattered Vascular Tissue
Fibrous root system (no main root)
Flowers in multiples of 3
Ex: Corn, wheat, rice, Coconut, Onion
only 1 cotyledon (seed leaf)
Parallel veins
Scattered Vascular Tissue
Fibrous root system (no main root)
Flowers in multiples of 3
Ex: Corn, wheat, rice, Coconut, Onion
44
New cards
Eudicots
Endosperm usually absorbed completely
2 cotyledons
Net-like veins
Ring-like Vascular Tissue
Tap root (Main root) present
Flowers in multiples of 4 or 5
Ex: Most veggies/fruits and trees/eudicots
2 cotyledons
Net-like veins
Ring-like Vascular Tissue
Tap root (Main root) present
Flowers in multiples of 4 or 5
Ex: Most veggies/fruits and trees/eudicots
45
New cards
Angiosperms Characteristics
Flower
Fruit
Fruit
46
New cards
Flower
protects ovules within ovary
promotes efficient pollen transfer, especially by animal pollinators
promotes efficient pollen transfer, especially by animal pollinators
47
New cards
Fruit
enhances seed dispersal
protects dormant seed
protects dormant seed
48
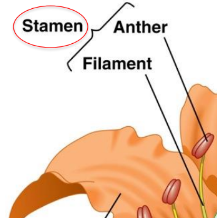
New cards
Stamen
Anther (tip)
Filament (string on the flowers)
Filament (string on the flowers)
49
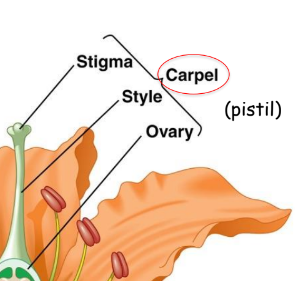
New cards
Carpel
Stigma (place to accept pollen)
Style (The length of the pollen-accepting tube)
Ovary (The place with the egg)
Style (The length of the pollen-accepting tube)
Ovary (The place with the egg)
50
New cards
Wind-Pollinated
no petals are necessary
51
New cards
Infloroscence
A bunch of grouped flowers that spread at the tip of the plant rather than ending
52
New cards
Pollinator Loyalty
Plants shifted from giving pollen (expensive) as reward to giving nectar (cheap but effective)
53
New cards
Dry fruits
Fruits that don’t have a fleshy outer layer (pericarp)
Spread by wind, air, animals, “throwing themselves”
Protect dormant seeds
Spread by wind, air, animals, “throwing themselves”
Protect dormant seeds
54
New cards
Double Fertilization
2 sperm cells enter → One fuses with egg forming 2n zygote (think normal fertilization)
Other sperm (n) fuses with the 2 central nuclei(2n) which makes endosperm (3n) which is food supply for seed
(Think as this one sperm taking one for the team and getting the ugly friend in order to support his buddy)
Other sperm (n) fuses with the 2 central nuclei(2n) which makes endosperm (3n) which is food supply for seed
(Think as this one sperm taking one for the team and getting the ugly friend in order to support his buddy)
55
New cards
Multicellular Eukaryotes have
Differentiated cells, tissues, organs, organ systems
56
New cards
Features of Animal Kingdom
No cell walls
Collagen in protein-rich ECM (Extracellular Membrane) binds cells together
* Nerve system/ response
* Sensory neuron → interneuron → motor neuron →muscle
* Integrated organ systems
* Ingestive heterotrophs (gotta eat)
* Sexual Reproduction in most
* Diploid life except when egg and sperm
\
Collagen in protein-rich ECM (Extracellular Membrane) binds cells together
* Nerve system/ response
* Sensory neuron → interneuron → motor neuron →muscle
* Integrated organ systems
* Ingestive heterotrophs (gotta eat)
* Sexual Reproduction in most
* Diploid life except when egg and sperm
\
57
New cards
Hermaphroditic
Both Male and Female gametes present
58
New cards
Parthenogenesis
Virgin females produce eggs that develop into offspring (Asexual but no sperm fertilizes so DNA is similar to mother)
59
New cards
“Hox” genes
Genes that control the growth and development of an embryo
60
New cards
Embryonic Development
Zygote(2 cells together)→ Cleavage( 8 cells)→ Blastula (a full formed ball of cells)→ Gastrulation → Gastrula
61
New cards
Gastrulation
The process when the Blastula invaginates into itself
62
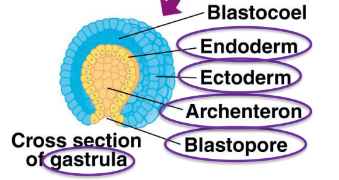
New cards
Archenteron
The most center space in the center of the embryonic layers
63
New cards
Blastopore
The opening formed from the ball of cell caving in on itself
64
New cards
Which group is closest protist group to animals?
Choanoflagellates are closest protist group to animals
65
New cards
Timeline of animals
Proterozoic→ Paleozoic Era→ Later Paleozoic Era→ Mesozoic Era→ Cenozoic Era
66
New cards
Proterozoic Era
Oldest known animals,
all soft-bodied
all soft-bodied
67
New cards
Paleozoic Era
“Cambrian Explosion”
Dramatic diversification of animals
1st shells
Dramatic diversification of animals
1st shells
68
New cards
Later Paleozoic Era
Vertebrate Fishes dominate the oceans but begin to move onto land
Arthopods dominate lands
Arthopods dominate lands
69
New cards
Mesozoic Era
Dinosaurs
When birds/mammals become more present
When birds/mammals become more present
70
New cards
Cenozoic Era
Modern day animals
71
New cards
Radial Symmetry
The same all the way around: 360 degrees
Usually doesn’t move or free-floating
Usually doesn’t move or free-floating
72
New cards
Bilateral Symmetry
Usually has a head (Cephalization)
Divides in 2 easily
Divides in 2 easily
73
New cards
Dorsal
on top of the organism
74
New cards
Ventral
Below the organism
75
New cards
Anterior
“At the head” (Anthony has a big ass head)
76
New cards
Posterior
“Back of the Butt”
77
New cards
Diploblastic
Having two germ layers
(Endo and ectoderm)
(Endo and ectoderm)
78
New cards
Triploblastic
Having 3 germ layers
(endo, meso and ectoderm)
(endo, meso and ectoderm)
79
New cards
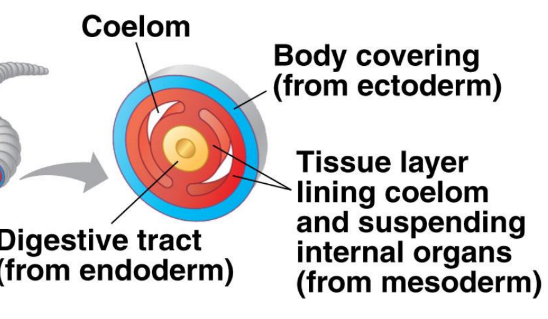
True Coelomates
Coelom (body cavity) is filled around by the mesoderm
80
New cards
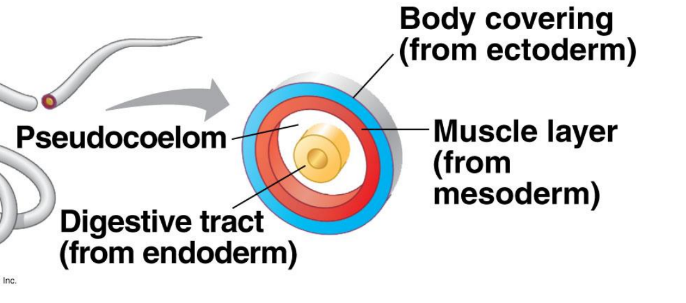
Pseudocoelomates
Mesoderm and endoderm don’t touch (There is a gap between the two
81
New cards
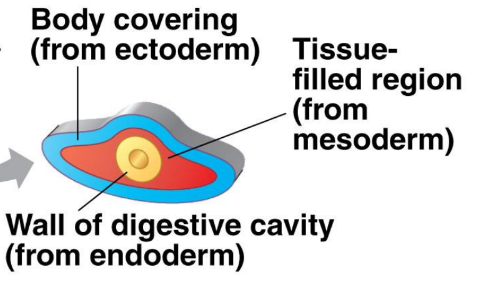
Acoelomates
No coelom (body cavity/gaps) between the mesoderm and endoderm
\
\
82
New cards
Protostomes Development
Blastopore (opening in the gastrula) becomes the mouth first
cleavage is spiral (Expands in a circle) & determinate (Each cell’s fate is predetermined)
cleavage is spiral (Expands in a circle) & determinate (Each cell’s fate is predetermined)
83
New cards
Deuterostome development
blastopore of gastrula becomes adult anus first (2nd hole is mouth)
cleavage is radial (expands upwards) & indeterminate (any early cell can be it’s own organism)
cleavage is radial (expands upwards) & indeterminate (any early cell can be it’s own organism)
84
New cards
Torpor
Low activity and metabolism drastically decreases
85
New cards
Hibernation
“long-term torpor”
86
New cards
Summer Torpor
“Estivation”
87
New cards
Regulator
Uses it’s own body to change when temperature changes (Ex: Humans)
88
New cards
Conformer
Allows it’s body temperature to change with the weather
89
New cards
Homeostasis
Usually maintained by a negative feedback which gets it back to a set point
90
New cards
Acclimatization
The homeostasis of an organism can adjust to different enviroments
91
New cards
Proferia
Sponges
92
New cards
Phylum Proferia
Aquatic Intracellular Lack true tissue Hermaphrodritic Lack Symmetry Flagellated Larvae Totipotent( cells can take any function) Sessile Adults
93
New cards
Where are gametes formed in Proferia?
Mesohyl
94
New cards
Choanocytes function in Proferia
Create currents to capture tiny bits of food(phagocytosis)
95
New cards
Ameobozans function in Proferia
Distribute food
96
New cards
Eumetazoans : Cnidaria
Sessile Polyps or Free swimming Medusa(Some cycle between both forms) Radial symmetry Sit and wait carnivores Sexual and/or Budding Diploblastic w/ gel in between tissue
97
New cards
Eumetozoans: Ctenophora
Radial Symmetry Diploblastic Transparent Medusa body 8 comb like plates fused Marine carnivores “Comb Jellies” Sticky thread to capture prey
98
New cards
Lophoarochozaons: Platyhelminthes
Flatworms Flat Triploblastic No body cavity(acoelomate) Bilateral Symmetry Simple nervous system Proteonephidria “kidneys”
99
New cards
Name the parts of the simple nervous system of Platyhelmithes
Gangila (simple brain) Ventral nerve cords Eyespots
100
New cards
What is the role of protonephridra
Act as a kidney in that they contain flame bulbs that remove excess water and waste