Lecture 11 - Renal II: Glomerular Filtration Rate and the Plasma Clearance
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Which substances are almost completely reabsorbed by the kidneys?
Water
Sodium
Glucose
Which substance is 50% reabsorbed and 50% excreted by the kidneys?
urea
___L of fluid is filtered daily while only __L is excreted in the urine
180L
1.5L
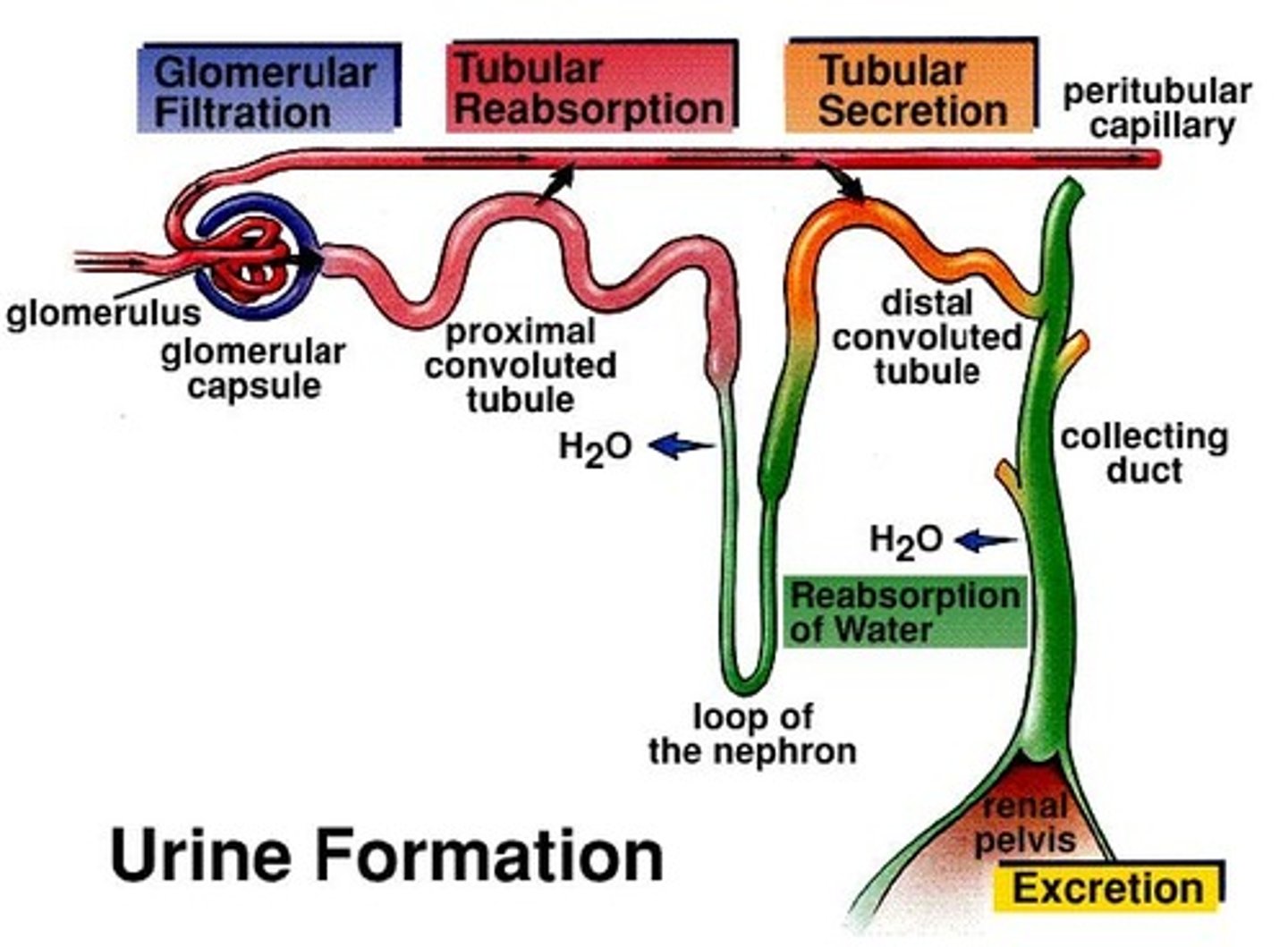
glomerular filtration
produces cell-and protein-free filtrate
tubular reabsorption
Selectively returns 99% of substances from filtrate return to the blood in the different renal tubules and collecting ducts
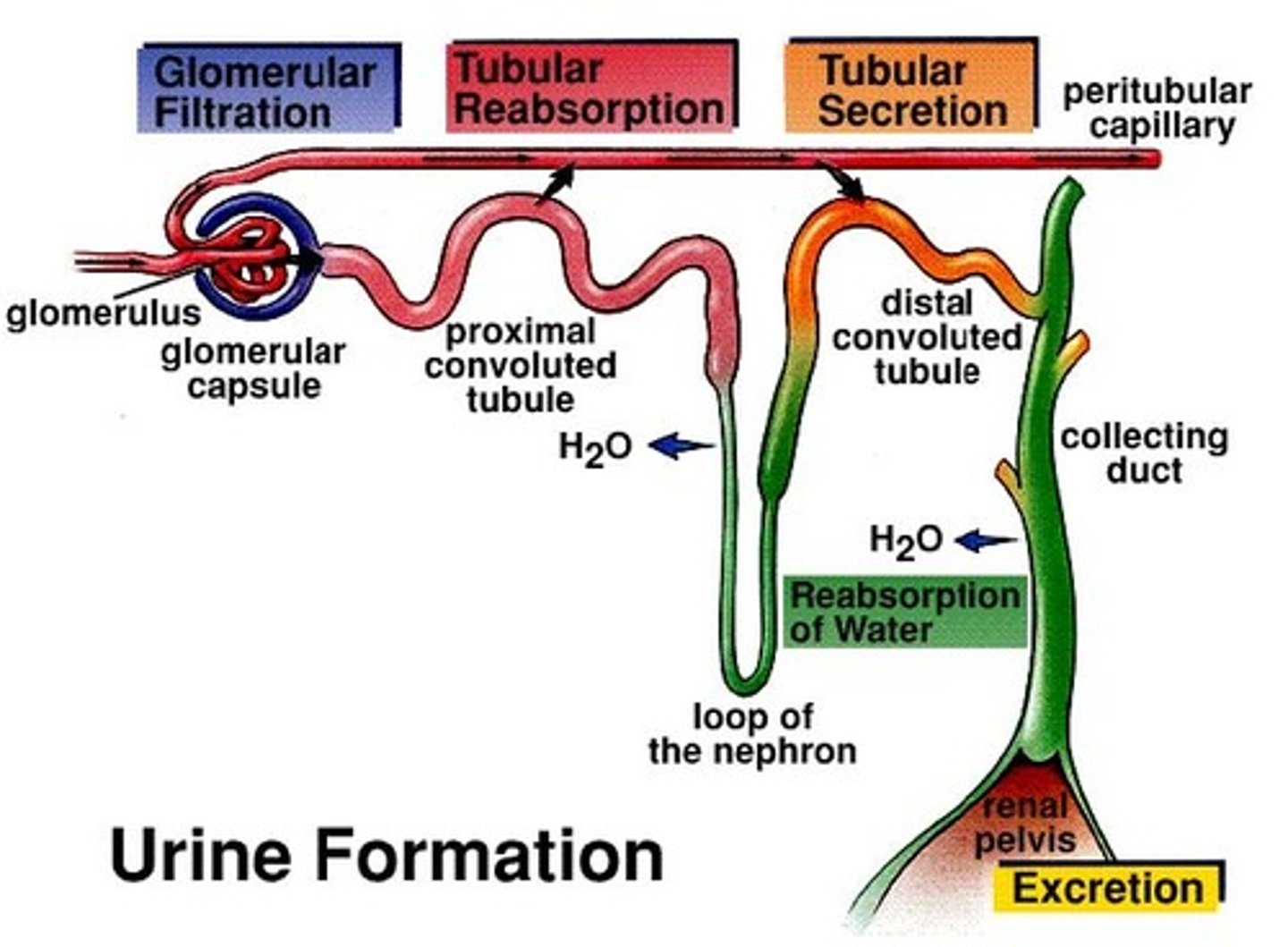
Tubular secretion
Selectively moves substances from blood to filtrate in renal tubules and collecting ducts
How is creatinine in the blood made?
From muscle breakdown
What amount of creatinine filtered by the kidneys is reabsorbed?
0% - none of the creatinine is reabsorbed
Clearance
volume of plasma from which all the substance has been completely removed and excreted into the urine
GFR
glomerular filtration rate
GFR equation
(UxV)/P
- U = urine creatinine conc (mg/ml)
- V = urine flow rate (ml/min)
- P = plasma creatinine conc (mg/ml)
Why is creatinine concentration used to measure GFR?
creatinine is freely (all) filtered
Rearranged GFR equation
(GFR)(P) = (V)(U)
Why creatinine concentration higher in the urine?
A lot of it is filtered and therefore will go to the urine
eGFR
estimated glomerular filtration rate defined by the modification of diet in renal disease (MDRD)
Cockcroft and Gault equation
Ccr = ((140-age) x kg) / (72 x SCr)) (x0.85 for women)
- Ccr = creatinine clearance (ml/min)
- Scr = serum creatinine (mg/dL)
MDRD GFR
unit: ml/min per 1.73m2
GFR according to Cockcroft and Gault equation
GFR = ((140-age) x kg x 1.2 (x0.85 for women))/ Pcr
Can the clearance of urea be used to calculate GFR?
No, 50% is reabsorbed
If plasma clearance of a certain substance is less than GFR what can be assumed?
the substance was reabsorbed
If plasma clearance of a certain substance is more than GFR what can be assumed?
the substance was secreted
Why is it that the lower the GFR, the higher the plasma creatinine?
The lower the GFR, the less effectively the kidneys can filter creatinine from the blood. As a result, creatinine levels in the plasma increase.
PAH
para-aminohippuric acid
PAH excretion
PAH is filtered by the glomerulus and secreted by the proximal tubular cell
Input of PAH
renal artery (Ppah x RPF)
RPF
renal plasma flow
RBF
renal blood flow
Output of PAH
Renal vein + ureter (Upah x V)
What is the average clearance of PAH?
585ml/min (much higher than GFR)
Why is the clearance of PAH so high?
it is also secreted
When PAH is infused at low doses...?
90% of the PAH in the arterial blood is removed in a single circulation circuit
RPF equation
(Upah x V)/(Ppah x Epah)
Epah
Extraction ratio for PAH
What is the maximum secretion rate of PAH?
80mg/min
juxtaglomerular apparatus
Specialized cells (JG and macula densa) next to the glomerulus that help to regulate
- systemic blood pressure
- filtrate formation
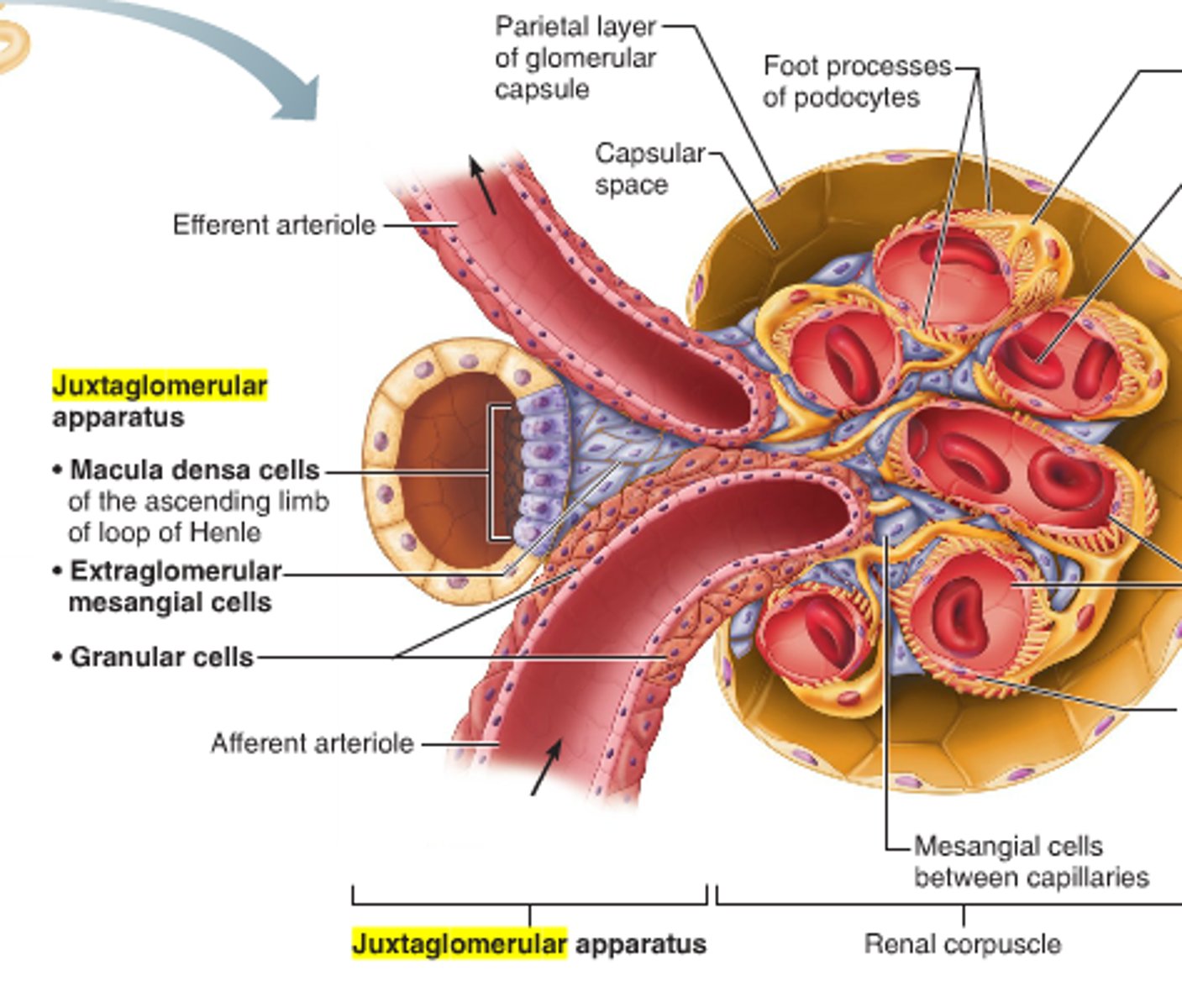
Arteriole walls are made of what?
JG cells (granular cells)
JG (granular) cells
enlarged smooth muscle cells - mechanoreceptors; secrete renin
Tubule walls are made of what?
macula densa cells
Macula densa cells
chemoreceptors or osmoreceptors - monitor filtrate & adjust GFR accordingly
Intrinsic mechanisms
Mechanisms built into the kidney to regulate renal blood pressure
- myogenic
- tubuloglomerular feedback
Myogenic mechanism
Smooth muscle cells in afferent arterioles 'react' to increased/decreased blood pressure
Myogenic mechanism in response to increased blood pressure
causes muscle stretch, constriction of afferent arterioles which restricts blood flow into glomerulus
renal autoregulation can maintain constant glomerular filtration rate within __ to __ mm Hg systemic blood pressure.
80 to 180 mmHg
In relation to renal autoregulation what happens during hypovolemic shock? (<70mmHg systemic bp)
renal autoregulation and filtrate formation shuts down
What is smooth muscle's response to being stretched?
it contracts
Myogenic mechanism in response to decreased blood pressure
afferent arterioles dilate which increases renal blood flow
Tubuloglomerular feedback mechanism
flow-dependent mechanism directed by macula densa cells
Tubuloglomerular feedback: slow filtration/low osmolarity
vasodilation of afferent arteriole
Tubuloglomerular feedback: fast filtration/high osmolarity
vasoconstriction of afferent arteriole
Adenosine comes from?
the break down of ATP
Adenosine effect on afferent arteriole
constricts the afferent arteriole
Extrinsic mechanisms
mechanisms external to the kidney that regulate renal blood pressure
- Sympathetic NS
- Renin-angiotensin mechanism
Neural control of renal blood pressure
sympathetic ns, during times of extreme stress, overrides renal autoregulation & shunts blood to heart, brain, skeletal muscles at expense of kidneys
Sympathetic nervous system effect on renal blood pressure
If blood pressure is low, NE and E are released causes systemic vasoconstriction and constriction of afferent arterioles which decreases GFR to restore blood pressure
renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
There are three pathways for renin release by granular cells.
Renin triggers a cascade of events that increases systemic blood pressure.
Sympathetic NS pathway for renin release by granular cells
1. direct stimulation of granular cells by sympathetic NS to release renin
Aldosterone effect
Retains Na which causes water reabsorption to increase blood volume
Macula densa pathway for renin release by granular cells
Stimulation by activated macula densa cells when filtrate NaCl concentration is low activate the granular cells to release renin
stretch pathway for renin release by granular cells
Reduced stretch of granular cells. These cells act as mechanoreceptors. Decrease blood pressure reduces the tension in the granular cells and stimulates the release of renin.