3.4.1 mass transport in animals (not complete)
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Describe the role of red blood cells and haemoglobin in oxygen transport
red blood cells contain lots of haemoglobin
HB associated with/ binds/ loads oxygen at gas exchange surfaces (lungs) where partial pressure of oxygen is high
This forms oxyhaemoglobin which transports oxygen
HB dissociates from/ unloads oxygen near cells/ tissues where partial pressure of oxygen is low
Describe the structure of haemoglobin
protein with a quaternary structure
Made of 4 polypeptide chains
Each chain contains a haem group containing an iron ion
What are some structural advantages of the red blood cells
no nucleus and biconcave so…
more space for haemoglobin
High SA:V
Short diffusion distance
What are haemoglobins
A group of chemically similar molecules found in many different organisms
Describe the transport of oxygen in respiring tissues
areas with low partial pressure of oxygen
So HB has low affinity for oxygen
So oxygen readily unloads/ dissociates with HB
So % saturation is low
Describe the transport of oxygen in gas exchange surfaces
areas with high partial pressure of oxygen
HB has a high affinity for oxygen
So oxygen readily loads/ associated with HB
So % saturation is high
Explain how the co-operative nature of oxygen binding results in a sigmoid (s-shaped) dissociation curve
binding of first oxygen changes tertiary/ quaternary structure of haemoglobin
This uncovers haem group binding sites, making further bindings of oxygen easier
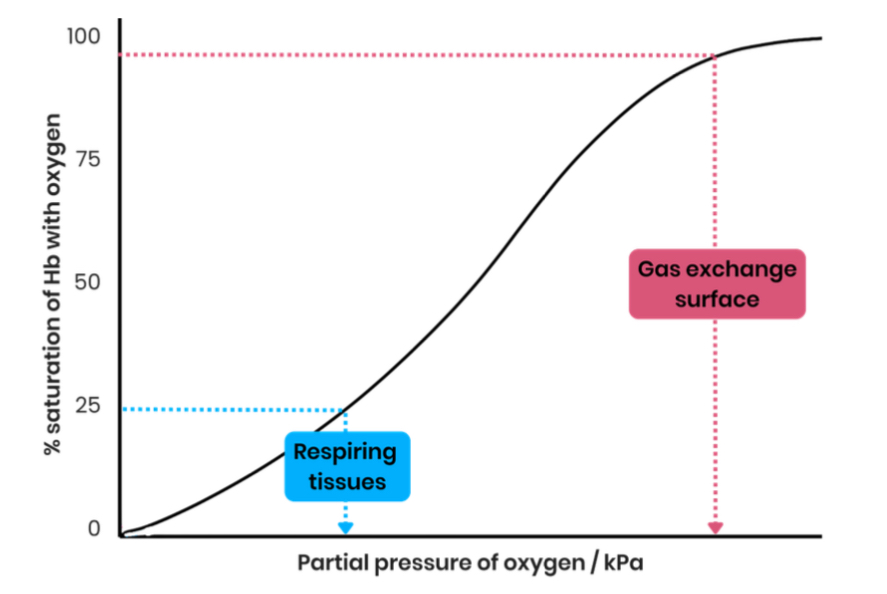
Describe evidence for the cooperative nature of oxygen binding
at low partial pressure of oxygen, as oxygen increases there is little/ slow increase in % saturation of HB with oxygen
This is when the first oxygen is binding
At a higher partial pressure of oxygen, as oxygen increases there is a rapid increase in % saturation of HB with oxygen
Showing it has got easier for oxygens to bind
What is the Bohr effect
the effect of CO2 concentration on dissociation of oxyhaemoglobin
Curve shifts to the right
Explain the effect of CO2 concentration on the dissociation of oxyhaemoglobin
increases blood CO2 (due to increased respiration)
Lowers blood pH (more acidic)
Reducing Hb’s affinity for oxygen as shape/ tertiary/ quaternary structure changes slightly
So more/ faster unloading of oxygen to respiring cells at a given partial pressure of oxygen
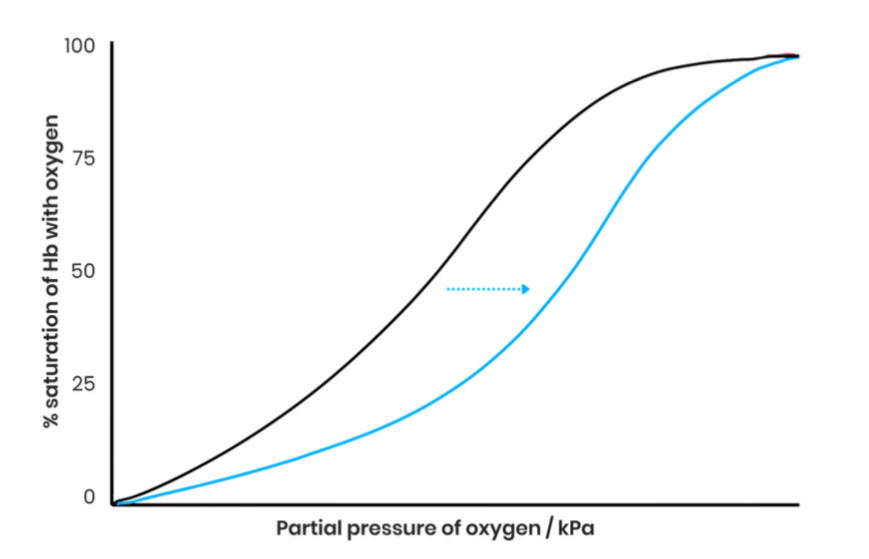
Describe evidence for the Bohr effect
At a given partial pressure of oxygen, the saturation of haemoglobin with oxygen is lower
Explain an advantage of the Bohr effect (e.g during exercise)
more dissociation of oxygen
So faster aerobic respiration/ less anaerobic respiration
So more ATP produced
Explain why different types of haemoglobin can have different oxygen transport properties
different types are made of polypeptide chains with slightly different amino acid sequences
Resulting in different tertiary/ quaternary structure/ shape
So they have different affinities for oxygen
How are organisms adapted to their environment by having different types of haemoglobin: HB has higher affinity for oxygen (curve shift left)
more oxygen associated with HB more readily
At gas exchange surfaces where the partial pressure of oxygen is lower
E.g Organisms in low oxygen environments (high altitudes, underground, foetuses)
How are organisms adapted to their environment by having different types of haemoglobin: HB has lower affinity for oxygen
more oxygen dissociated from HB more readily
At respiring tissues where oxygen is needed
E.g organisms with high rates of respiration/ metabolic rate (may be small or active)
Describe the general pattern of blood circulation in a mammal
closed double circulatory system - blood passes through heart twice for every circuit around body
Deoxygenated blood in the right side of the heart is pumped to the lungs, oxygenated blood returns to the left side
Oxygenated blood in the left side of the heart to the rest of the body, deoxygenated blood returns to the right
Suggest the importance of a double circulatory system
prevents mixing of oxygenated/ deoxygenated blood
So blood pumped to body is fully saturated with oxygen for aerobic respiration
Blood can be pumped to body at a higher pressure (after being lower from lungs)
Substances taken to/ removed from body cells quicker/ more efficiently
Draw a diagram to show the general pattern of blood circulation in a mammal
.

Name the blood vessels that carry deoxygenated blood
vena cava transports deoxygenated blood from respiring blood tissues to the heart
Pulmonary artery transports deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs
Name the blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood
pulmonary vein transports oxygenated blood blood from lungs to the heart
Aorta transports oxygenated blood from heart to respiring body tissues
Name the blood vessels entering and leaving the kidneys
renal arteries - oxygenated blood to the kidneys
Renal veins - deoxygenated blood to vena cava from kidneys
Name the blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood to the heart muscle
coronary arteries - located on surface of the heart, branching from aorta
Label a diagram to show the gross structure of the human heart (inside)
.
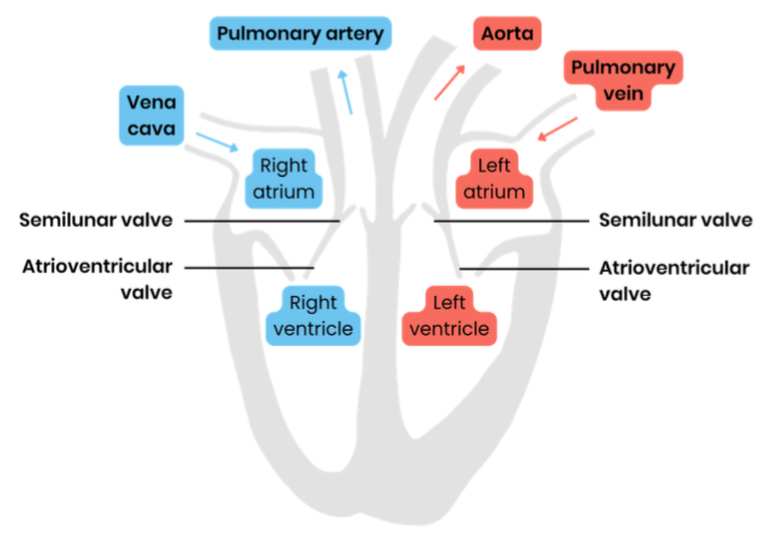
Suggest why the wall of the left ventricle is thicker than that of the right
thicker muscles to contract with greater force
To generate higher pressure to pump blood around the entire body