Required Practical: Investigating Insulation
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
what is the aim of the experiment?
The aim is to investigate the effectiveness of different materials as thermal insulators and the factors that may affect the thermal insulation properties of a material
what is the independent variable?
Type of material
what is the dependent variable?
Temperature, T (°C)
what are the 3 control variables?
Volume of water
The temperature of the water at the start of the experiment
The thickness of each material
how many pieces of equipment are needed?
8
list all the pieces of equipment needed
small beaker
large beaker
kettle
water
thermometer
piece of card with hold for thermometer
at least 3 other different materials with a hole for the thermometer
stopwatch
purpose of the small beaker
to hold the water and thermometer
purpose of the large beaker
to hold the small beaker inside and the materials placed on top
purpose of the kettle
to boil water
purpose of the water
substance to measure the temperature of
purpose of the thermometer
to measure the temperature of the thermometer
purpose of the card with the hole in it
to determine how good of an insulator it is
purpose of the other materials with a thermometer hole
to determine how good of an insulator they are
purpose of the stopwatch
to record how long it takes for the water to cool
what is the resolution of each piece of measuring equipment?
Thermometer = 1 °C
Stopwatch = 0.01 s
how many steps are there to the method?
6
step 1:
Set up the apparatus by placing a small beaker inside the larger beaker
step 2:
Fill the small beaker with boiling water from a kettle
step 3:
Place a piece of cardboard over the beakers as a lid. It should have a hole suitable for a thermometer and place the thermometer through this hole and into the water in the small beaker
step 4:
Record the temperature of the water in the small beaker and start the stopwatch
step 5:
Record the temperature of the water every 2 minutes for 20 minutes, or until the water reaches room temperature
step 6:
Repeat the experiment, each time changing the cardboard for another insulating material (in any order) and also without any insulation at all
what is the method of the experiment?
Set up the apparatus by placing a small beaker inside the larger beaker
Fill the small beaker with boiling water from a kettle
Place a piece of cardboard over the beakers as a lid. It should have a hole suitable for a thermometer and place the thermometer through this hole and into the water in the small beaker
Record the temperature of the water in the small beaker and start the stopwatch
Record the temperature of the water every 2 minutes for 20 minutes, or until the water reaches room temperature
Repeat the experiment, each time changing the cardboard for another insulating material (in any order) and also without any insulation at all
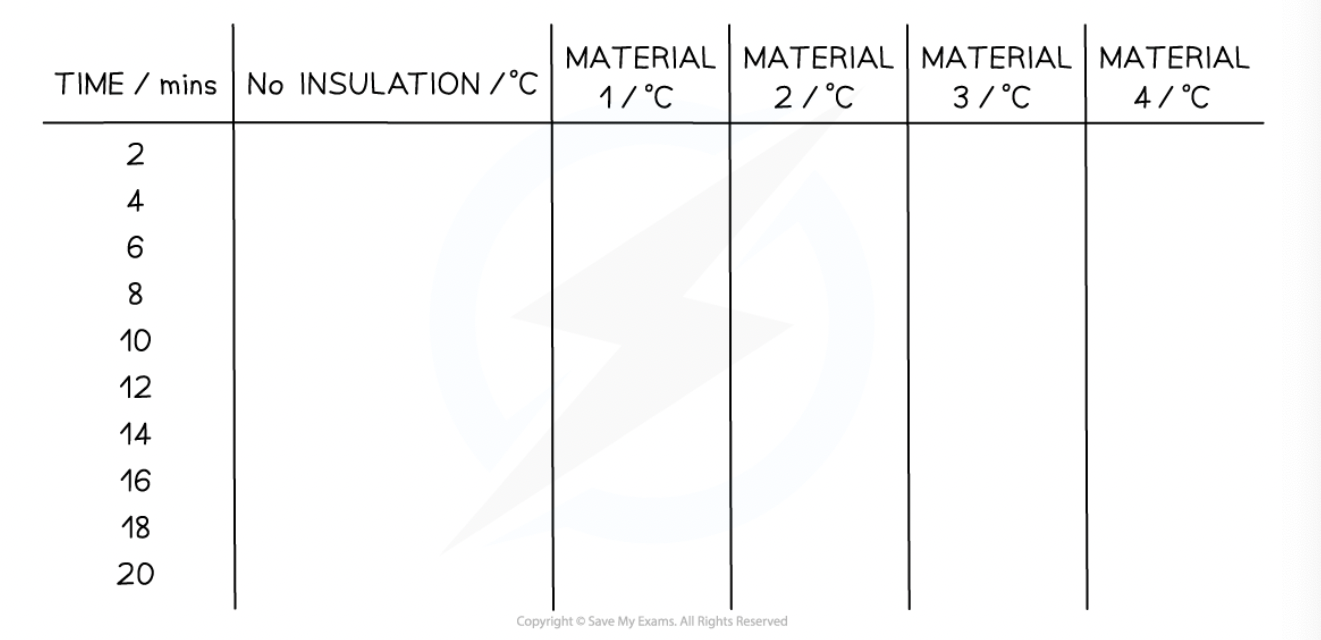
list the variables in a results table
time /mins → no. insulation → material 1 (temp) → material 2 (temp) → material 3 (temp) → material 4 (temp)
how would you analyse the results
Plot a graph of temperature against time and draw a curve of best fit
Plot all the curves for each material on the same axis
what should the graphs show?
The graphs should show that the temperature falls quickly at high temperatures, then more slowly (shown by the graph levelling out)
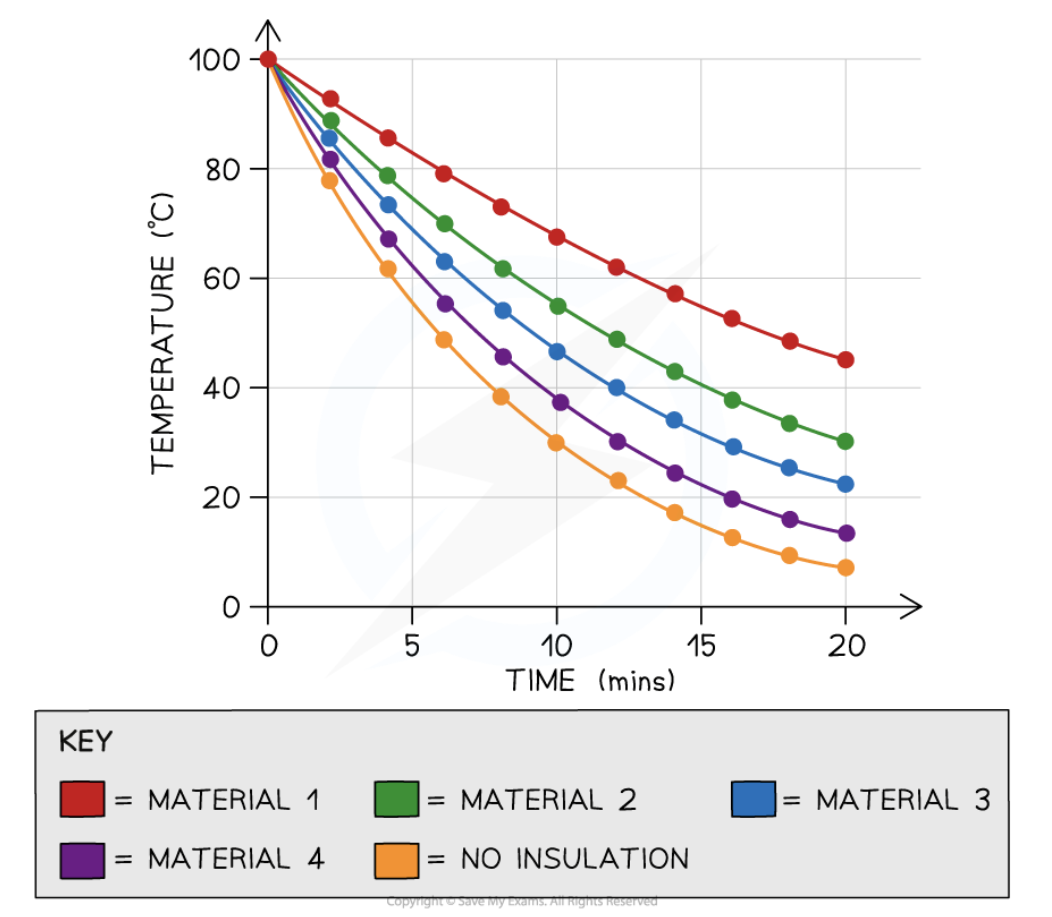
what conclusions should be drawn from the graph (3)
When the water is at a high temperature, there is a greater temperature difference between it and room temperature. Therefore there is a greater energy transfer by heating
When the water is at a low temperature, there is less temperature difference between it and room temperature. Therefore, there is a lesser energy transfer by heating
The curve which takes the longest time for the temperature to drop is the shallowest
This material is the best insulator
what are 3 ways to prevent systematic errors?
Make sure the starting temperature of the water is the same for each material since this will cool very quickly
It is best to do this experiment in pairs to coordinate starting the stopwatch and immersing the thermometer
Only the top of the beaker is covered, so that energy is transferred by conduction through the glass
Use a data logger connected to a digital thermometer to get more accurate readings
suggest an alternative to the experiment to prevent systematic errors
An alternative to this experiment could be:
Putting the insulating materials around the beaker as well as on top of it
Using one material with different thicknesses. This will show that the thicker the material, the better the insulation
what are three random errors for this experiment?
Make sure the hole for the thermometer isn't too big, otherwise, energy will be transferred through the hole
Take repeated readings for each insulator
Read the values on the thermometer at eye level, to avoid parallax error
what are 6 ways for safety considerations?
Keep water away from all electrical equipment
Make sure not to touch the hot water directly
Run any burns immediately under cold running water for at least 5 minutes
Do not overfill the kettle
Place the small beaker inside the large beaker first before pouring water in, since the small beaker will become very hot
Make sure all the equipment is in the middle of the desk, and not at the end to avoid knocking over the beakers
Carry out the experiment only whilst standing, in order to react quickly to any spills
Why and how must the temperature, thickness of material and water volume be controlled (3)
energy is transferred more quickly when the temperature difference between two substances is greater, so we have to control this by making sure that the initial temperature of the water is the same for each material we test.
the thickness of a material affects its conductivity, so we need to control this by making sure that the materials we use are the same thickness.
it takes longer for a larger volume of water to cool than for a smaller volume of water, so we need to control this by using the same volume of water for each material we test.
why do we have to control the factors that affect the dependent variable?
By controlling the factors that affect the dependent variable, we are making sure that the investigation is a fair test and that the results are valid.
If we fail to control these factors, then it would be impossible to tell if the results we get are because we changed the material or because of one of these other factors.