healthcare unit 1
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Anatomy
The study of the structure of the body and its parts.
Gross Anatomy
Anatomy visible without aid.
Microscopic Anatomy
Anatomical details you can see with magnification.
Level of Organization
Atoms, molecules, cells tissues, organs, organ systems, organisms.
Homeostasis
Maintaining a constant level or “steady state” despite changes in the environment.
Anatomical Position
Standing, face forward, palms out.
Dorsal Cavity
Cranial (contains brain), and spinal (vertebral, spinal cord).
Cranial Cavity
Cavity that includes the brain.
Spinal Cavity
Cavity that includes the spine and vertebral.
Thoracic Cavity
Cavity that includes the heart, lungs, and esophagus.
Abdominal Cavity
Cavity that includes the stomach, intestine, spleen, liver, etc.
Pelvic Cavity
Cavity that includes the bladder and reproductive organs.
Diaphragm
Separates the dorsal and ventral cavities.
Ventral Cavity
Thoracic (chest, lungs, heart, esophagus) and abdominopelvic (abdominal: stomach, liver, spleen. pelvic: bladder, rectum, reproductive organs.)
Oral/Digestive Cavities
Mouth, contains teeth and tongue.
Nasal Cavity
Within and posterior to the nose.
Orbital Cavities
Eye sockets.
Middle Ear Cavities
Medial to the ear drum, contains bones for hearing.
Synovial Cavities
Joint cavities, contains fibrous capsule.
Upper left abdominal region
Right hypochondriac
Mid left abdominal region
Right lumbar
Lower left abdominal region
Right iliac
Upper mid abdominal region
Epigastric
Center abdominal region
Umbilical
Top right abdominal region
Left hypochondriac
Mid right abdominal region
Left lumbar
Bottom right abdominal region
Left iliac
Integumentary System
Forms external body covering. Includes skin, hair, nails.
Skeletal System
Protects and supports body organs, provides framework.
Muscular System
Locomotion of body and movement within body (skeletal, cardiac, and smooth)
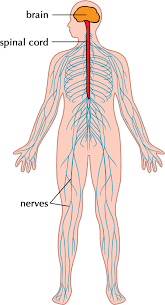
Nervous System
Responds to internal and external changes. Includes brain and nerves.
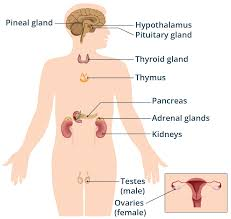
Endocrine System
Hormones that regulate processes.
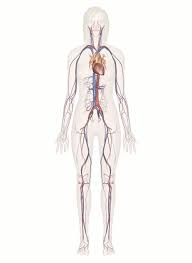
Circulatory System
Heart, blood, blood vessels, provide nutrients/wastes.
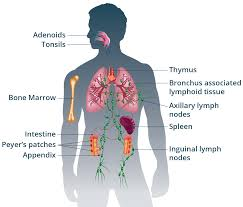
Lymphatic System
Picks up fluid leaked from blood vessels. Includes lymph nodes.
Respiratory System
Supplies oxygen and removes carbon dioxide. Includes trachea, lungs, nose, esophagus.
Urinary System
Eliminates nitrogenous wastes
Digestive System
Breaks down food into units to enter blood
Immune System
Protects body from diseases/illnesses. Thymus, bone marrow, lymph nodes
Epithelial Tissue
Found throughout the body and covers all body surfaces inside and out. Functions: protection, secretion, absorption, excretion, sensory perception
Simple Squamos
Found in air sacs of lungs, walls of capillaries. Function: diffusion and filtration.
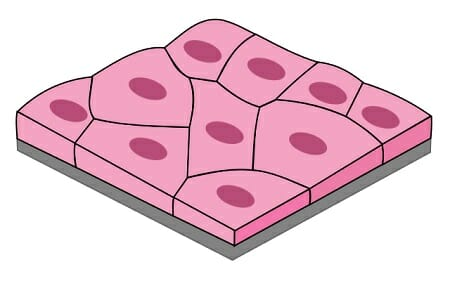
Simple Cubodal
Lining of kidney tubules, ducts of glands, covering surface of ovaries. Function: secretion and absorption.
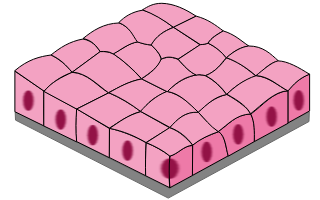
Simple Columnar
Lining of digestive tract and uterus. Function: protection, absorption, secretion.
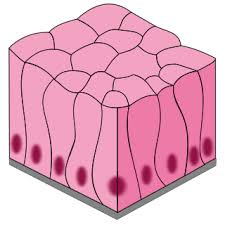
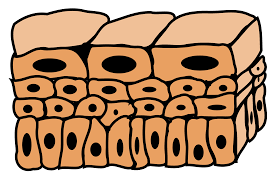
Stratified Squamos
Lining body cavities like the mouth and outer layer of skin. Function: protection.
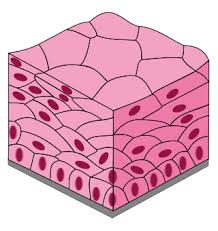
Psuedostratified Columnar
Lining air passages like the trachea and tubes of the reproductive system. Function: secretion and cilia-aided movement.
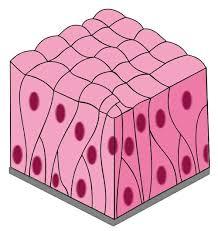
Transitional Epithelium
Lining of the urinary bladder. Function: stretchable.
Loose CT
Binds skin to underlying organs and organs to organs, space between muscles, throughout body.
Adipose Tissue
Protective cushion, insulation to preserve body heat, stores energy. aka fat.
Fibrous CT
Dense tissue, closely packed, thick collagenous fibers and fine network of elastic fibers. Tendons and ligaments.
Hyaline Cartilage
Most common cartilage. Covers ends of bones and joints, noise, and respiratory passages.
Elastic Cartilage
More flexible cartilage, external ear and larynx.
Fibrocartilage
Very tough cartilage, large numerous collagenous fibers, menisci.
Bone Tissue
Osseous tissue. Rigid due to mineral salts. Lamellae, haversian canals, osteocytes.
Blood Tissue
Tissue that circulates throughout body.
Smooth Muscles
Muscle in hollow organs like the stomach.
Cardiac Muscles
The muscles that make up the walls of the heart.
Neurons
Tissue that transmit signals.
Neuroglia
Nerve tissue that offers protection and support.
Prophase
During which the chromosomes become visible as paired chromatids and the nuclear envelope disappears.
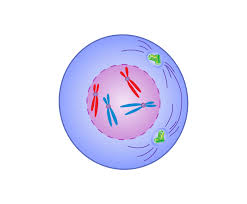
Metaphase
During which the chromosomes become attached to the spindle fibers.
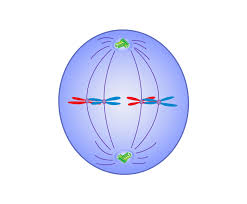
Anaphase
The stage in which the chromosomes move away from one another to opposite poles of the spindle.
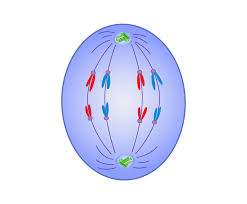
Telophase
The final phase in which the chromatids or chromosomes move to opposite ends of the cell and two nuclei are formed.