Saponification Reaction: Making Soap
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
What is saponification?
It is the hydrolysis of natural fatty acid esters (fats) under alkaline conditions to produce glycerol and soap (salts of fatty acids).
What is the general reaction for saponification?
Fat (ester) + Strong base (NaOH or KOH) → Glycerol + Soap (fatty acid salts)
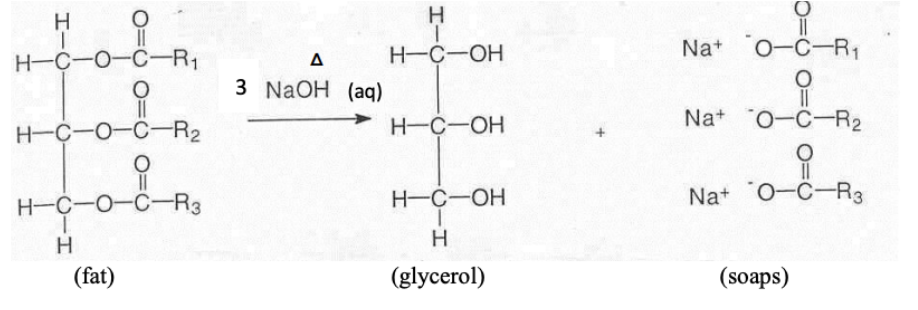
What is soap?
Soap is a mixture of salts of fatty acids, made up of:
Cation: Na⁺ or K⁺
Anion: RCOO⁻ (fatty acid anion)
How does soap clean?
Soap molecules have a hydrophobic (nonpolar) tail and a hydrophilic (polar) head.
The tail traps grease and oils; the head interacts with water.
This forms micelles that lift dirt and grease away when rinsed.
What are saturated fats? What soap does it make?
No carbon-carbon double bonds (only single bonds).
Result in harder, less soluble soaps.
What are unsaturated fats? What kind of soap does it make?
Contain one or more carbon-carbon double bonds.
Lead to softer, more soluble soaps.
How does the "make-up" of fats and oils affect soap properties?
Fats with more saturated fatty acids → harder, less soluble soap.
Fats with more unsaturated fatty acids → softer, more soluble soap.
How does the alkali (NaOH vs. KOH) affect soap's physical properties?
NaOH makes hard bar soap (solid at room temperature).
KOH makes liquid soap (softer and more soluble).
Why is ethanol used in the saponification reaction?
Helps mix nonpolar fat with polar NaOH solution by acting as a co-solvent.
Creates a more uniform reaction mixture.
Why is the reaction mixture refluxed during soap-making?
Maintains a constant temperature.
Prevents loss of ethanol and reactants.
Ensures full completion of the saponification reaction.
Why is saturated sodium chloride (NaCl) solution used after saponification?
"Salts out" the soap by decreasing its solubility.
Causes the soap to coagulate and separate from the aqueous phase.
What is "soap scum"?
An insoluble precipitate formed when soap reacts with calcium (Ca²⁺) or magnesium (Mg²⁺) ions from hard water.
What is the chemical reaction for soap scum formation?
2 RCOO⁻ (soap anion) + Ca²⁺ → (RCOO)₂Ca (soap scum, insoluble solid)
2 RCOO⁻ (soap anion) + Mg²⁺ → (RCOO)₂Mg (soap scum, insoluble solid)