Halogenation & Halohydrin Formation
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
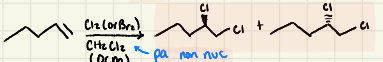
Halogenation of alkenes using Xs:
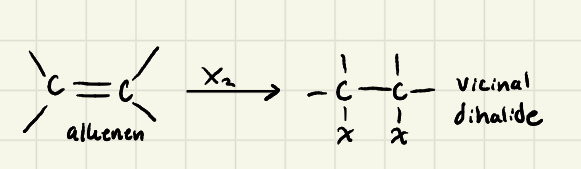
Halogenation Mechanism
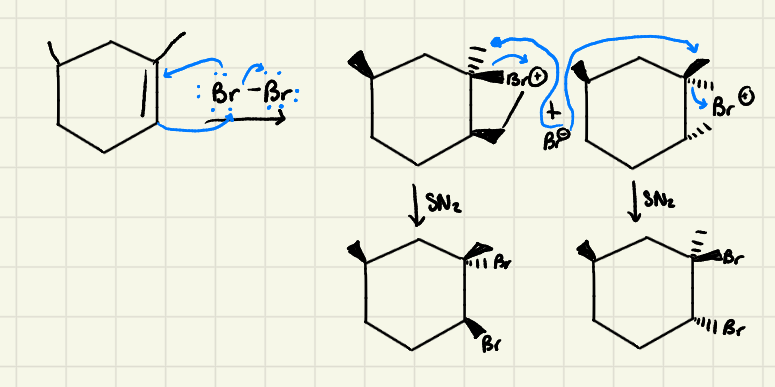
Halogenation: Because the nucleophilic attack of Br^- goes via an ______ (________) the product of the addition reaction is ______
SN2 (backattack) → antiaddition
Halogenation: The reaction is ______! Different starting steroisomers (E or Z) led to different products:
Stereospecific
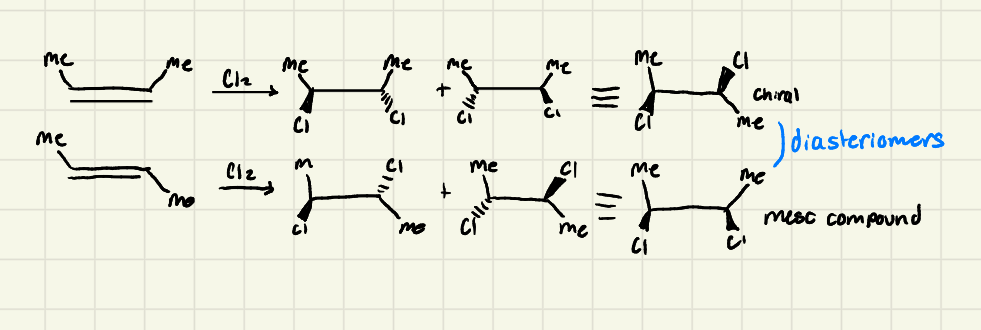
Halogenation: The more _______ X and ________ the alkene the alkene, the faster the halogenation
electronegative → substituted
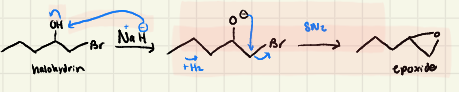
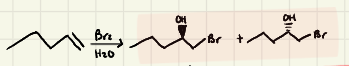
Halohydrin Formation:
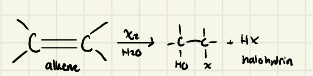
Halohydrin Mechanism:
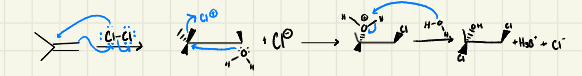
Halohydrin: The nucleophilic attack of H2O happens on the __________ carbon of the halonium ion
-It is an _______ of OH & X
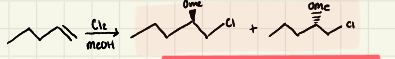
-_________ can also be used as nucleophiles instead of H2O, to form _______
-most substituted
-Anti-addition
-Alcohols → ethers

Epoxide formation