electricity
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
what are conductors
materials that allow the flow of electrical charge
What must happen to circuits to make them complete
all switches must be closed for the circuit to work
if there is higher resistance what does this mean for energy
more energy is transferred
how to make a lamp dimmer
add resistor
what happens as electrical energy is transferred ( charge flows)
electrons will move through conductor and collide with atoms in metal
causes heating in wires so electrical energy will be transferred to thermal
examples of a conductor of electricity
metal
what are insulators
materials that don’t allow the flow of electrical charge
examples of insulator
plastic
resistance
how easy or difficult it is for electricity to flow / a measure how a component opposes the flow of electric charge
what does it mean if something has high resistance
hard for electricity to flow and has a low current
What is ohms law
Resistance = volts divide current
what does it mean if something has low resistance
easy for electricity to flow and has high current
current
the flow of electrons around a circuit
potential difference
a push around a circuit / the energy transfered or work done per unit of charge between two points in a circuit
when do resistors get hot
when current flows through them
what is heating effect caused by
collisions between moving charges and stationary atoms in wires
what does heating effect do
makes filament lamp hot enough to glow
why are metals good conductors
lots of free electrons to move
why are insulators bad conductors
don’t have free electrons to move
current equation
charge divide by time
time equation
charge divide by current
charge equation
current x time
what is potential difference
different in energy per unit of charge between 2 circuits
what happens in series circuit if u remove one component
current stops working so circuit stops
what happens to potential difference in series circuit
it is shared so total PD is all volts added together
In a series circuit describe relationship between resistance, pd,current
Current: same everywhere
Potential difference: shared between components so add voltage together
Resistance: add together
In a parallel circuit describe relationship between resistance, pd,current
Current: added together
Pd: same everywhere
Resistance: less then resistance of smallest resistor
How to connect ammeter in a circuit to measure current
Connect them in series with the component they are measuring current through
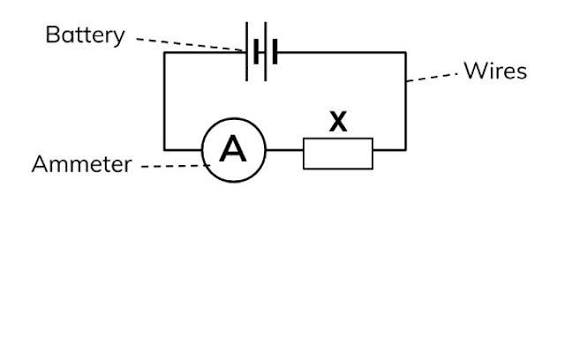
How to connect voltmeter in a circuit to measure potential difference
Voltmeter should be connected parallel to component they are measuring pd of
what is size of current determined by in series circuit
the total potential difference and resistance flowing
How to get total current in series circuit
It is the same everywhere
how to get total resistance in a series circuit
add all resistors together
when is current reduced
when resistor is added
what happens when u remove component in parallel circuit
circuit isn’t affected
what is potential difference like in a parallel circuit
it is the SAME everywhere
what happens to current in parallel
it is shared between components so add all together
what happens when u add resistor to parallel circuit
it reduces total resistance
how to get total resistance in a parallel circuit
total resistance is less than the resistor of smallest resistor
what is PD measured in
what is current measured in
what is resistance measured in
volts (V)
Amps (A)
Ohms (horse shoe)
equation linking pd, charge and energy transfer
pd= energy transferred divide by charge
what is charge measured in
Colombs (Q)
what is current
the flow of electric charge
what does greater charge mean in terms of current
greater current
when does charge flow
when there is potential difference
what does greater resistance of a component mean
smaller current for potential difference across a component
what is charge
the amount of charge flowing past a point in a circuit
what is resistance do to charge
slows charge flow down
what are components where current changes as resistance does
filament lamp
diode
what component does resistance not change as current changes
ohmic conductors / resistors
what is rule about resistance in ohmic conductors
resistance doesn’t change as current changes because at certain temperatures current is directly proportional to the potential difference across it
What is an ohmic conductor
a resistor
A conductor where current and potential difference are directly proportional
At constant temperatures resistance mains constant as current changes
List four components for which resistance is not constant as current changes
FILAMENT LAMP
LDR
THERMISTOR
DIODE
What happens to resistance if filament lamp as temperature increases and why
resistance increases
As at high temps Ions in wirel have more energy so more frequency of collisions with electrons and ions in current as flow through metal
Causing greater resistance to current flow as need more energy for current to flow
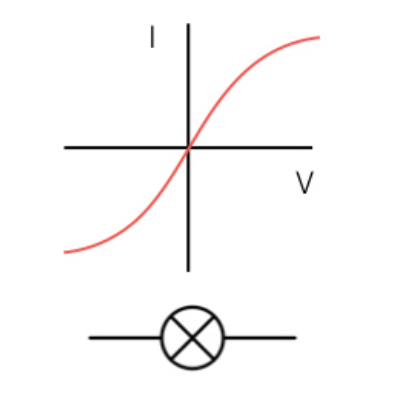
What does the filament lamp graph tell us
current and potential difference is not directly proportional - so resistance changes s current changes as
Current will increase, increases temp of filament lamp which causes resistance to increase as lamp gets hotter (end of graph)
what happens in a filament lamp when it gets hot
causes resistance to increase which decrease current and causes lamp to glow
describe the trend in the filament lamp
as the bulb gets hot the resistance increases which decreases current
as potential difference increases, current begins to slowly no longer increase as more collisions in wire which causes wires to heat up increasing resistance
iwhat does resitance depend on diode
direction of current
which way does current flow diode and why
one direction because the diode has a high resistance in reverse direction so if it flows in direction of resistance it wom’t allow current to flow as high resistance
how are diodes useful
they can control the flow of current in circuit because in the forward direction the current will increase as potential difference increased
when does diode have high resistance
in reverse direction of current flowing
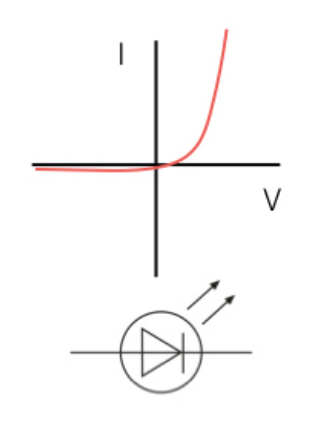
what does LDR depend on
light intensity
factors affecting LDR resistance and its use
increased light intensity = resistance decreases
decreased light intensity = resistance increases
USE: automatic night light
Give an LDR use and why is it used for this
Use: automatic night lights (street lamps
As when light levels become too low res they light gains current to turn light on as temp increases which causes light to turn on
And resistance will increase due to decreased light
factors affecting thermistor resistance and use
temperature increase = decreased resistance
2 temperature decrease = resistance increase
USE: electronic thermostats
give two examples when a thermistor may be used
In thermostats - as temperature becomes too low resistance will increase causing a change in potential difference which circuit will detect causing heating to turn on. (Opposite if temp becomes to high)
In a freezer, when temp becomes too high resistance decreases along with potential difference (energy) in which the circuit detects , it then turns compressor on to cool the freezer down which will cause resistance to increase along with potential difference again.
earth wire
green and yellow
stops appliances coming live
only carries current if fault
live wire
brown
provides alternating potential difference which is 230v
neutral wire
blue
completes circuit
current flows through it
0v
what is alternating current
what is direct current
current that constantly changes direction
current always flowing in same direction
Uk mains supply voltage
230v
frequency AC mains supply
50h*2
why is live wire dangerous
if touch it a large potential difference is produced across wire which will produce a high amount of current flowing through you which can lead to electric shock
why is connection between live and earth wire dangerous
it creates low resistance path so current increases which transfers high heat energy which can result in a fire
what does national grid do
transfers electrical power from power stations all over grid in britain to where needed like homes
when is demand high for electricity
when it’s dark
when it’s cold
when tv events are on
when people are coming home from school or work
how do power stations cope with high demand
they often run below maximum power output so there is spare capacity to cope with higher demand
what does national grid have in terms of pd and current
low current, high potential difference
why does national al grid use low current and high pd
because high current requires a lot of energy and wires will heat up from high current making it transfer to thermal store which is wasted (inefficient)
why is national grid efficient
it uses high potential difference so there is a low current
lower current means so less energy is wasted as heat
why does national grid use high pd
cheaper to boost than current and keeps low current
what does step up transformer do
potential difference increased as more turns in secondary coil than primary coil
what does step down transformer do
decreases potential difference as more turns on primary coil than secondary
Why do potentioal difference need to be decreased between transmission lines before passed into homes
Lower potentials are safer for deomestic use and reduce likelihood of electrocution
Appliances deigned for 230v
do appliances transfer all energy usefully and why
no as bigger current means more energy transfer to thermal store
what do electrical appliances do
transfer energy in circuit when current flows
what does total energy transferred in electrical appliances depend on
how long appliance has been on for and it’s power
what does it mean if an electrical appliance transfer transfers more energy in given time
it has a higher power
what happens if two insulators are rubber
electrons transfer from one insulator to the other and form positive on one and negatively charged ions on the other
what happens when conductors are rubbed
positive static charge on an object that loses electrons and negative static charge on an object that gains electrons
Describe energy transfers in a battery powered motor
battery transfers chemical energy to electrical energy
Motor converts electrical energy into kinetic energy aswell as waste energy to thermal store due to friction
Describe energy transfer in a battery powered torch
battery converts chemical energy into electrical energy
Bulb converts electrical energy into light aswell as waste energy in form of heating