Pharmacology week 1 and 2
1/210
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Pharmacology vocabulary flashcards for nursing students.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
211 Terms
The study of medications or drugs
Pharmacology
Movement of a drug through the body
pharmacokinetics
What acronym can be used to describe pharmacokinetics?
ADME
What is pharmacodynamics?
What drugs do to the body
Chemical Name
The name of a drug based on its chemical structure.
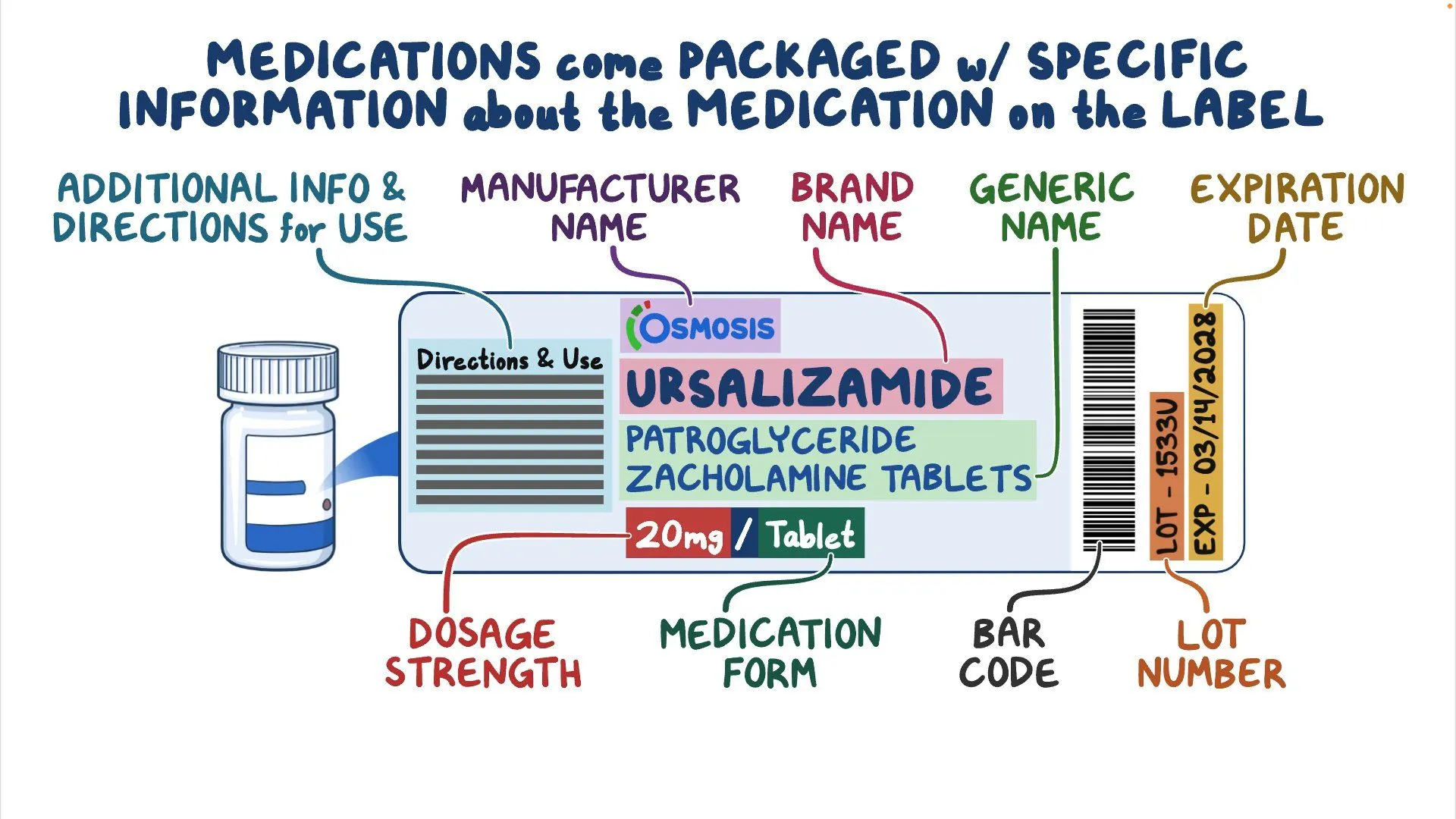
Generic Name
universal drug name
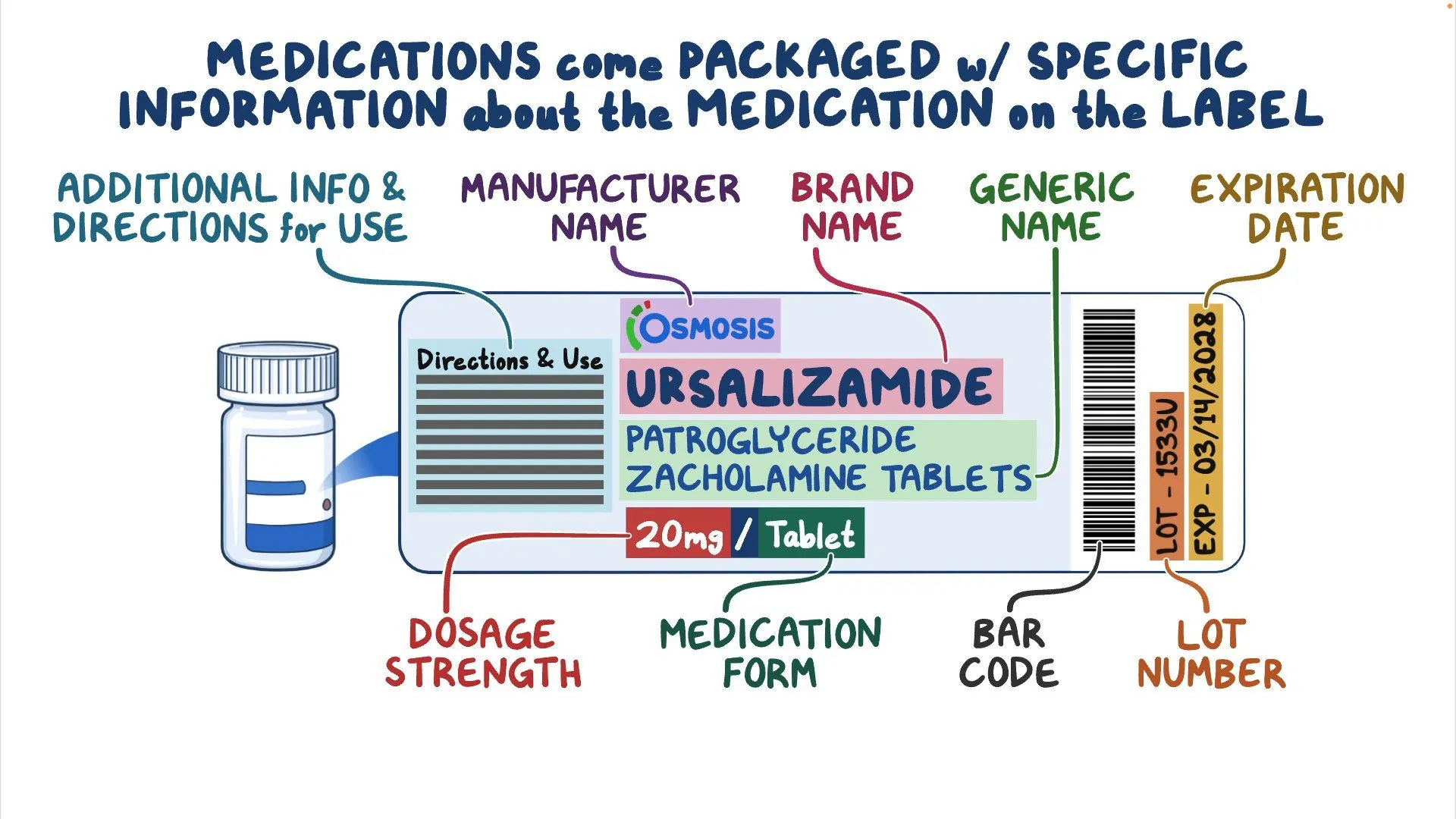
Trade (Brand) Name
Brand name… so many
Describe traits of the perfect drug
Effectiveness, safety, and selectivity
Effectiveness
Does the drug do what it says it will do
Safety
Drug causes no harmful effects
Selectivity
Drug only does what we needed to do and nothing else
What is the most important trait in an ideal drug?
Safety
What is it called when a patient has a lot of different medical conditions?
Co morbidities
Prescribed dose→ administered dose→ concentration at site =
Intensity of drug response
right patient, right medication, right dose, right route, and right time
golden rules
ADER (add ons)
Assessment, documentation, evaluation, refusal
What is it called when you are educating a patient based off of medications they are taking and effects that these medications may have?
Medication reconciliation
When does medication reconciliation occur?
At discharge or when they are leaving
Special populations
Pregnant, elderly and pediatrics
What is an anti-seizure med category that we cannot administer during pregnancy because they are a risk?
Teratogenic
2/3 of these types of patients take at least one medication that could be Used to treat nausea and vomiting, increased blood glucose, or blood pressure
Pregnant
65 and +
Elderly
What are some problems that the elderly population may Have causing them to be prescribed medications?
Decreasing organ functionality, Comorbidities, Polypharmacy and adherence
What list introduces a categorized criteria of inappropriate medication uses in older adults
Beers
What common medications should be avoided in older adults?
Anticholinergic cardiovascular, CNS endocrine and pain
16 and under
Peds
What list introduces a categorized criteria of inappropriate medication uses in pediatrics
KIDs list
Pediatric meds are used by what type of dosing?
Weight based
Side effects and toxicity
Adverse drug reactions
Mild and expected drug reactions can be called…
Side effects
An adverse drug reaction that has a negative physiological effect on the body.
Toxicity
This adverse reaction triggers a response from the sensitive immune system penicillin‘s common
Allergic
What is an adverse effect due to genetic predisposition like G6PD enzyme deficiency
Idiosyncratic effect
An adverse reaction that result in an opposite effect and expected like insomnia and restless from benzodiazepines
Paradoxical effect
An adverse reaction affect that is caused by the meds like the side effect of Parkinson’s from antipsychotic drugs
iatrogenic
An adverse reaction that results in an adaptation to drug exposure that abstinence will cause negative effects, most common with opioids
Physical dependence
An adverse reaction in the case where the med may cause cancer
Carcinogenic effect
In adverse reaction that result in a drug induced birth defect
Teratogenic effect
Hepatotoxic Drugs
Drugs that are toxic to the liver
Why are nephrotoxic drugs harmful to the body?
Inability to excrete drugs out of the body
In drug testing what population group does pre-clinical testing occur with?
Animals
drug clinical testing occurs with what population?
Humans
In 1906 the FDA was introduced. What did they work to enforce?
Drug labeling and purity
In 1938 the FDA worked to accomplish…
Safety testing
In 1970 the controlled substance act (CSA) was able to do what…
Create five categories with different schedules of potential for drug abuse
In drug legislation is schedule 1 drug has potential for what?
Abuse, no medical benefits
Drug legislation drug schedule two through five have what types of risk for abuse
Some medical benefit, declining risk for abuse
Site of administration→ blood
Absorption
Blood→ tissue cells
Distribution
Alteration of drug enzymes through the liver
Metabolism
Removal of drugs from body, most common through urine
Excretion
In what organ do most drugs get absorbed in?
Small intestine
What route of drug administration is an inhaler a transdermal patch an intramuscular injection or a subcutaneous injection?
Parenteral
Which method of drug administration skips the absorption step?
IV
This route of drug administration is most convenient and economical also most safe.
PO
What route of drug administration is by PO or PR?
Enteral
What route of drug administration shows a disadvantage that requires patient compliance and bio availability can be erotic and incomplete?
PO
What route of drug administration is valuable for emergency use and permits titration
IV, IVP
What route of drug administration has the disadvantage of increased risk of adverse side effects?
IV, IVP
What drug absorption, bypasses absorption, and potential immediate effects is suitable for large volumes and irritating substances?
IV, IVP
What route of drug administration can be prompt or slow when drug absorption is occurring and can be affected by changes in blood flow to the tissue?
Subaru
What route of drug administration has the advantage of being suitable for self administration?
Subcutaneous
What route of drug administration has the disadvantage of not being suitable for large volumes and possible pain or necrosis at the site?
SUBQ
Which route of drug administration has the disadvantage of being contradicted with anticoagulant?
Intramuscular
Within distribution, what does bio availability mean?
How much of the drug reaches the bloodstream
What is the initial passing of meds being broken down by the liver called?
First pass effect
When medication is stored in the fat and bone due to excessive adipose tissue, it is later distributed into the body when the drug levels are low. What is this called?
Fat and bone sequestration
Bio transformation results in the enzymatic alteration of a drug structured. What stage in the drug movement process is this?
Metabolism
Lipophilic drugs are more difficult to eliminate from the body so metabolized to become more polar…
Lipophobic
A drug That is metabolized to turn on the liver is called
Prodrug
A super family of enzymes used to metabolize things in the body
CYP 450
How many members are in the CYP 450 family
12
How many members in the CYP family and which members in the CYP family are used to metabolize drugs
CYP1, CYP2, and CYP3
The other nine members in the CYP family are used for What type of metabolism breakdown?
endogenous
Drugs that are looking to bind to the enzymes are considered what
Substrates
As a drug is bonded to the enzyme, it’s looking for what process to happen
Looking to get metabolized and then excreted
Steady state occurs after around how many half lives
3 to 5
The therapeutic Level is reached and provides what benefits
Max effectiveness of the drug
Time required for the amount of a drug in the body to decrease by 50%
Half life
A larger first dose than the smaller dose so that we could get to the therapeutic range faster is called…
Loading dose
When a loading dose is administered via IV what is that called?
Bolus
How do you calculate the therapeutic index?
LD/ED
The Highest point of the curve measuring the effects of a drug is called what
Maximum efficacy
A medication that requires a lower dose that has the same effects compared to a drug with a higher dose has a higher…
Potency
The ability to activate a receptor upon binding
Intrinsic activity
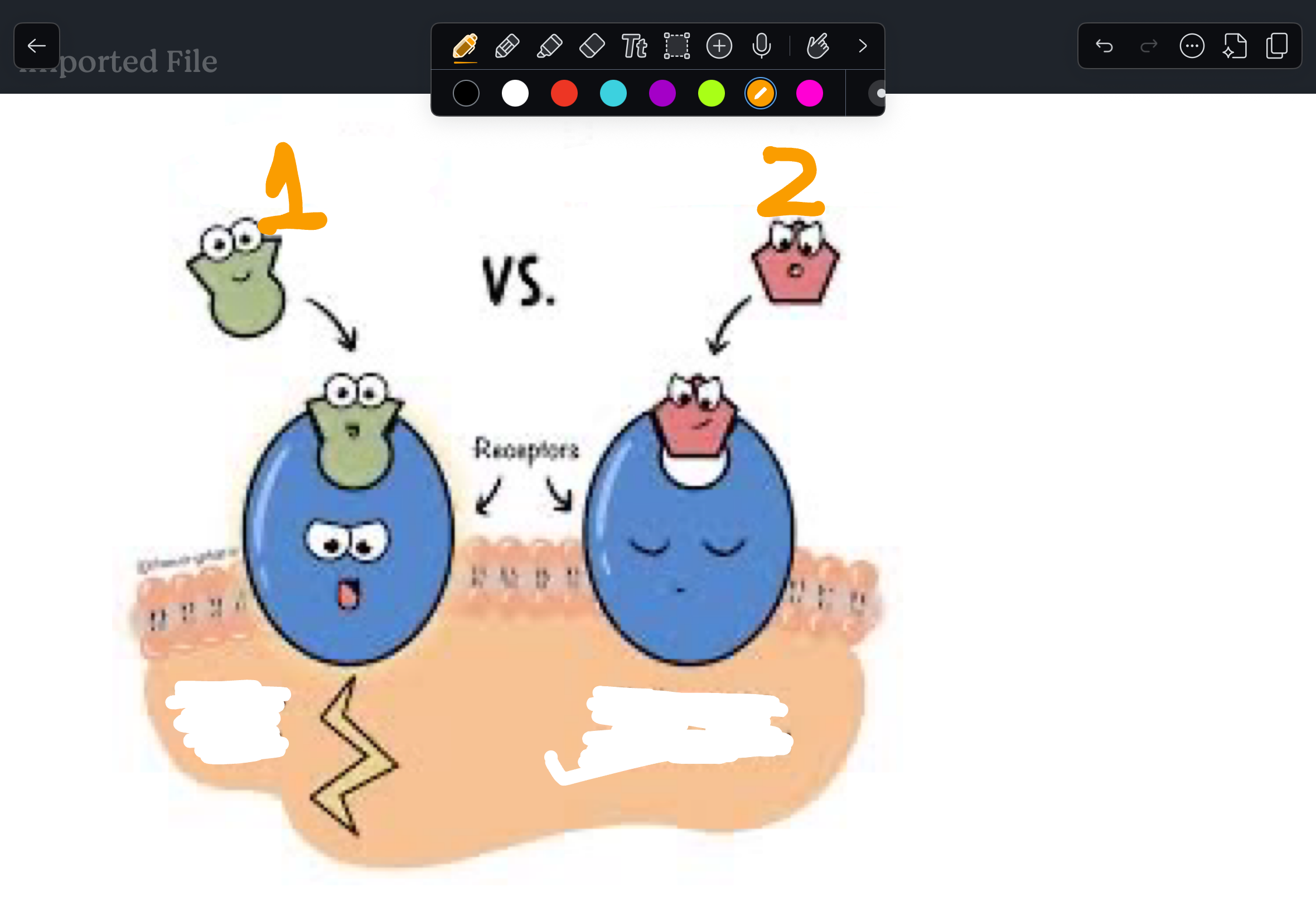
1.
Agonist
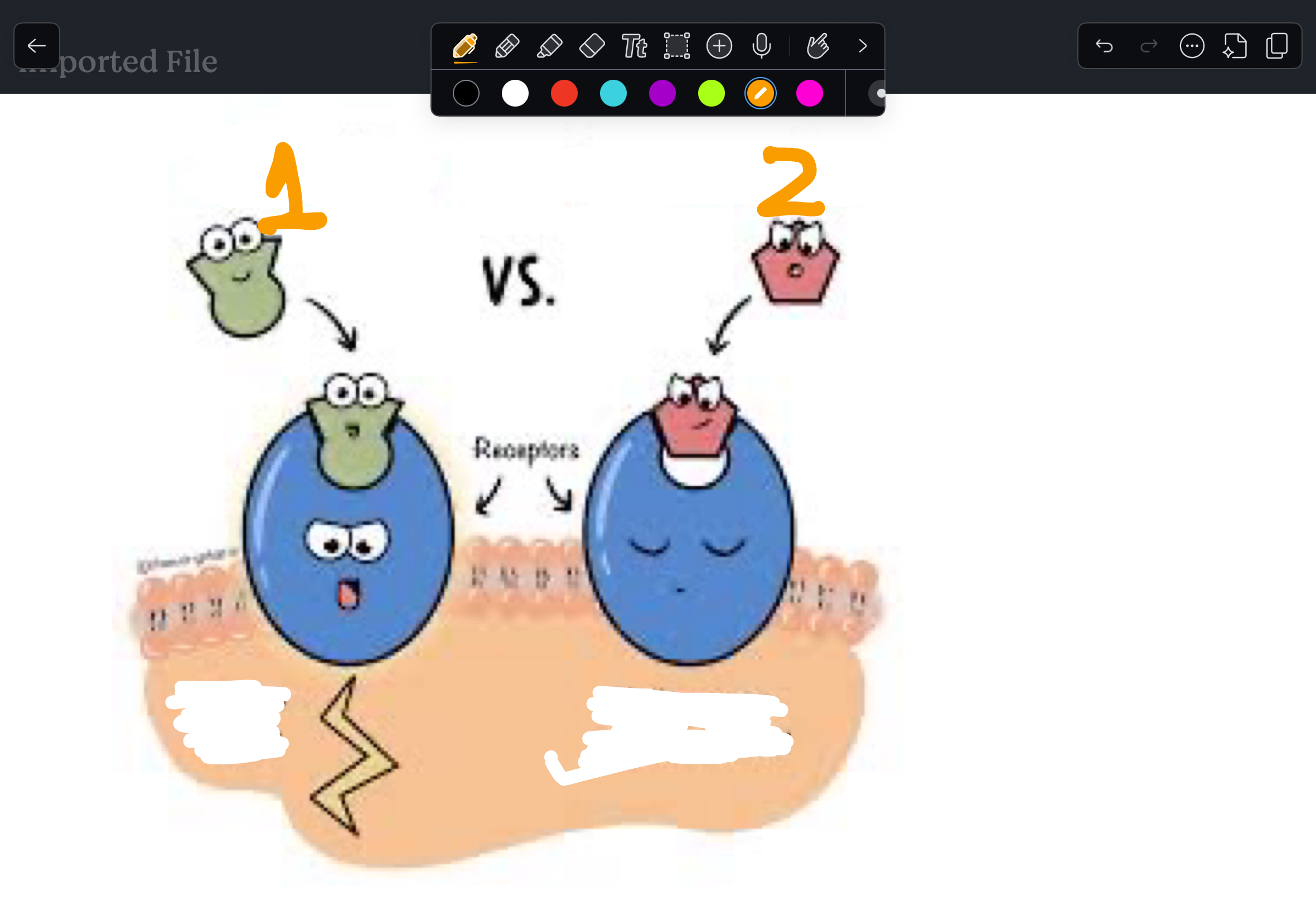
2.
Antagonist
An antagonist that cannot be reversed
Non-competitive antagonist
An antagonist that can be reversed
Competitive antagonist
Continues exposure to an agonist results in what type of regulation
Down regulation
Continuous exposure to an antagonist results in what type of regulation
Up regulation
What changes the pH of stomach contents
Antacids
What drug type acts without binding to a receptor
Antacids
What are some diverse example examples of suppression or excitation of neural activity that plays into Neuro pharmacology?
Depression, epilepsy, hypertension, and asthma
Central nervous system And…
Peripheral nervous system
What are the two sub categories for the Peripheral nervous system?
Somatic and autonomic
Which sub category of the peripheral nervous system is responsible for skeletal muscles
Somatic
What sub category of the peripheral nervous system is responsible for internal organs
Autonomic
The autonomic nervous system breaks into two sub categories. What are those sub categories?
Parasympathetic and sympathetic
Fight or flight represents what sub category of the autonomic nervous system
Sympathetic