Ch. 56 Placenta
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
The decidua __ is the decidual reaction that occurs between blastocyst and myometrium.
basalis
The decidua __ is the reaction occurring over the blastocyst closest to the endometrial cavity.
capsularis
The decidua __ is the reaction in all areas except for beneath and above the implantation.
vera (parietalis)
The __ __ forms fetal part of placenta and contains villi
chorion frondosum
The __ __ is the nonvillious part of chorionic around gestational sac.
chorion laeve
The chorionic plate is the __ surface of the placenta; the basal plate is the __ surface of the placenta.
fetal; maternal
By 9 weeks, the yolk sac will diminish to less than __mm in diameter.
5
What is the condition where implantation occurs within the lower uterine segment?
placenta previa
When do the amnion and chorion fuse?
16 weeks gestation
What are the functional endocrine units of the placenta?
chorionic villi
What structure does Wharton’s jelly surround?
umbilical cord
Normal placenta rarely exceeds __cm in thickness.
4
What are placental lakes?
Areas of placental sonolucencies that are often a normal finding; will typically show slow, swirling flow; blood flow will typically not be detected with color Doppler
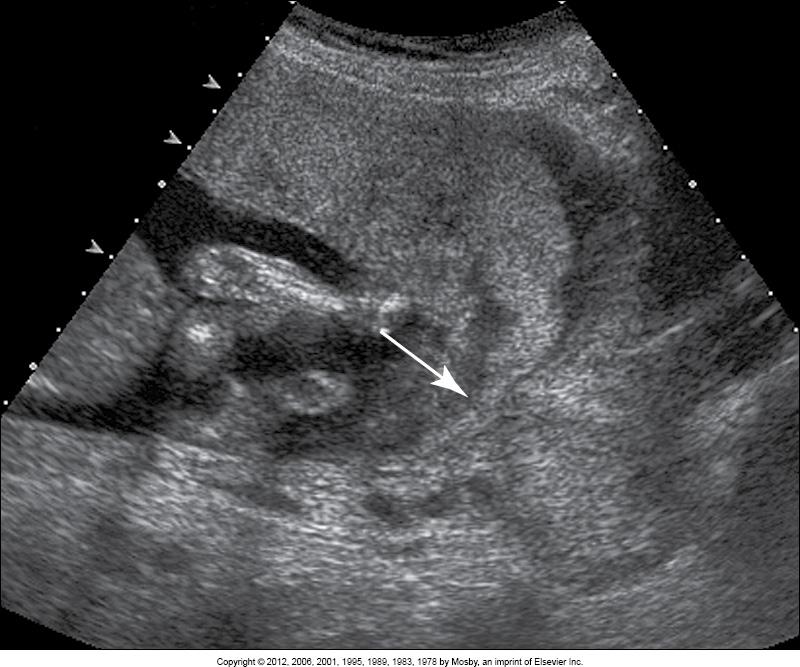
transabdominal image of __
placenta previa
what does this image show?
battledore placenta
What does this image show?
velamentous cord
What does this image show?
marginal abruption
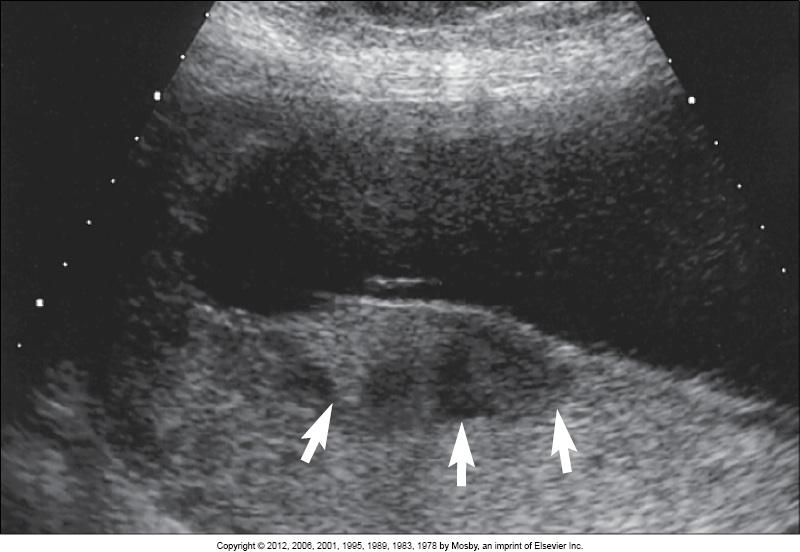
what does this image show?
intervillous thrombosis
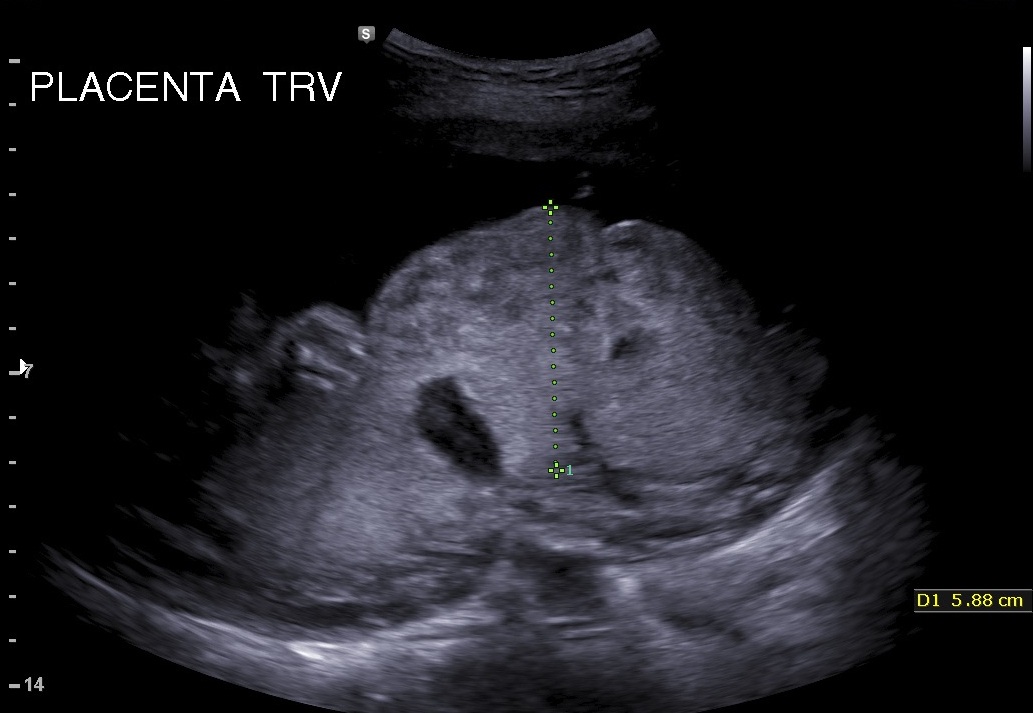
What does this image show?
enlarged placenta
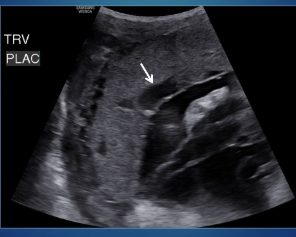
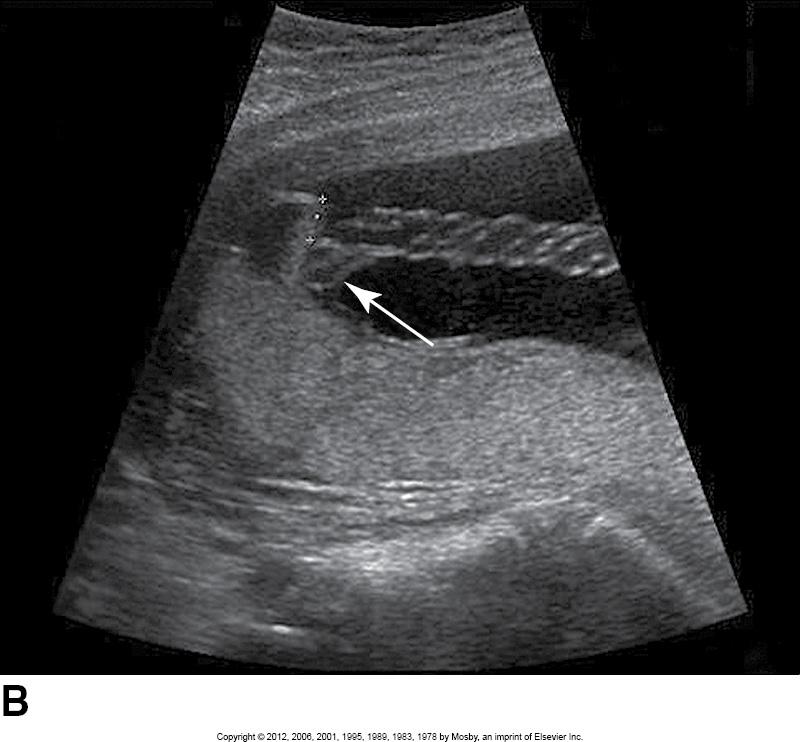
what is the arrow pointing to?
placental lake
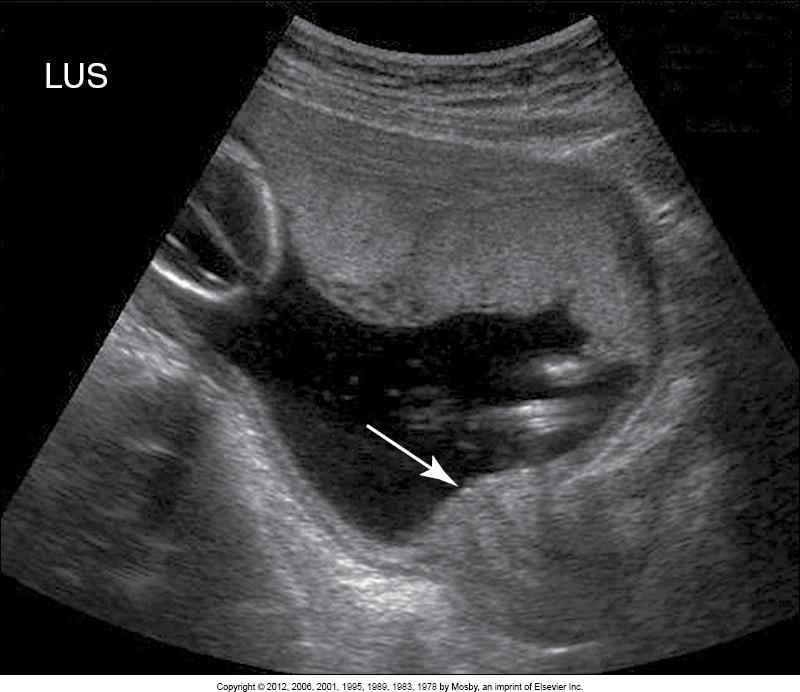
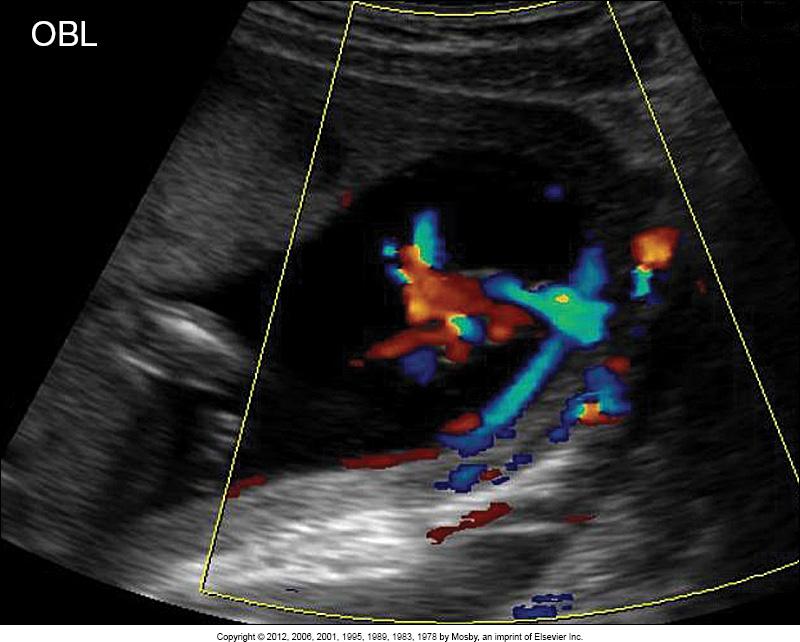
What does this image show?
placenta is implanted away from the cervical os (arrow)
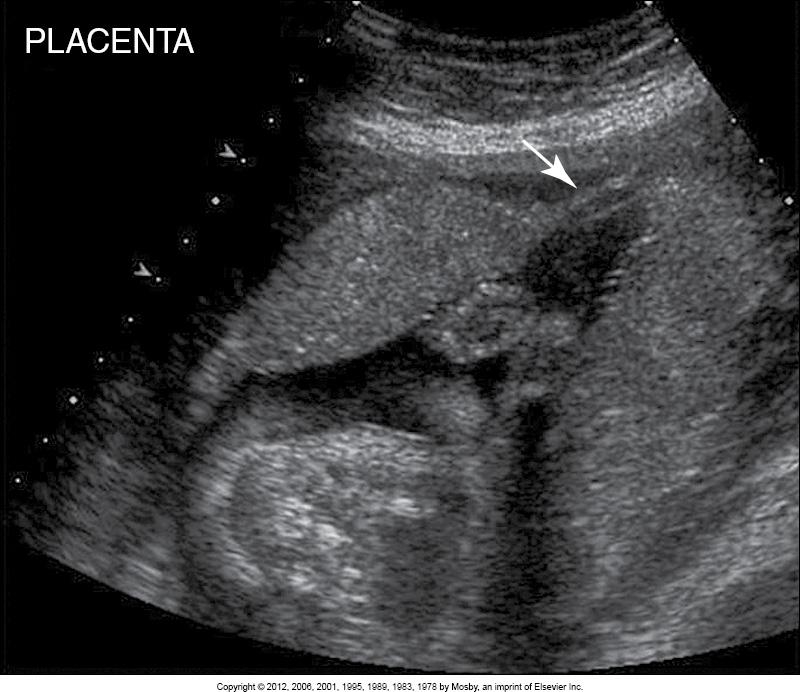
What does this image show?
succenturiate placenta
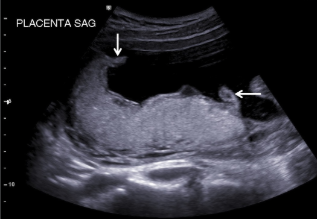
What does the arrow point to?
circumvallate/circummarginate placenta
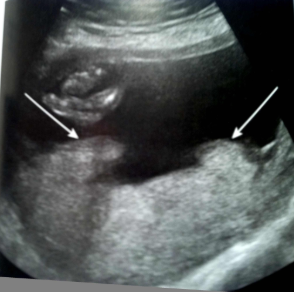
What are the arrows pointing to?
circumvallate/circummarginate placenta
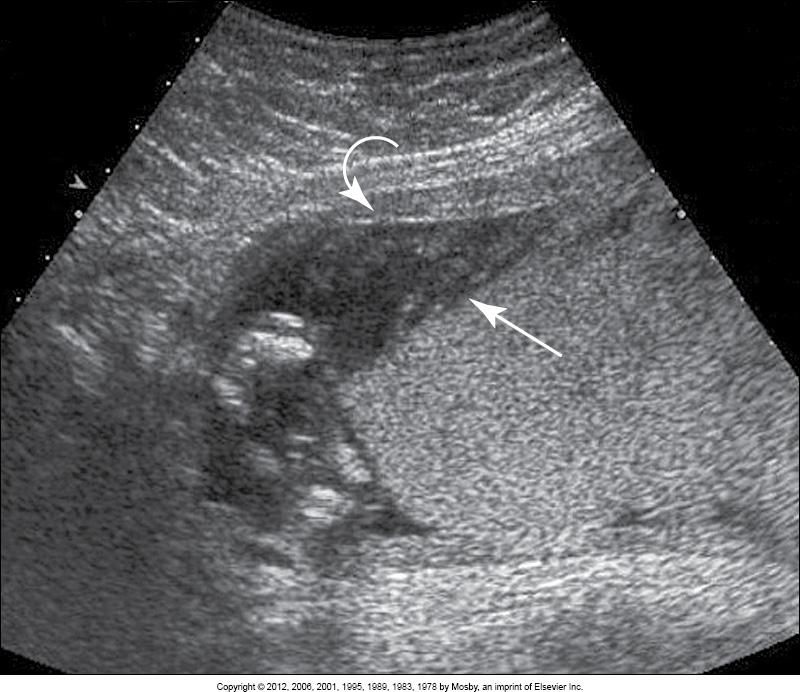
What is this image showing?
retroplacental abruption
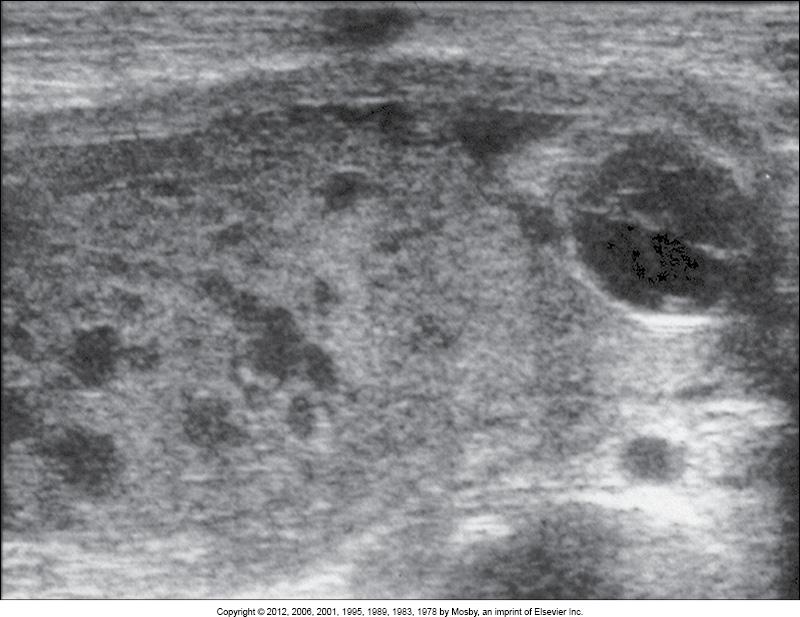
what is this image showing?
gestational trophoblastic disease
What is the term for a placenta that implants near or over the internal os and occurs at increased risk when a patient has a history of a c-section?
placenta previa
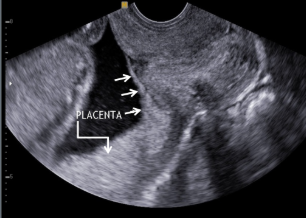
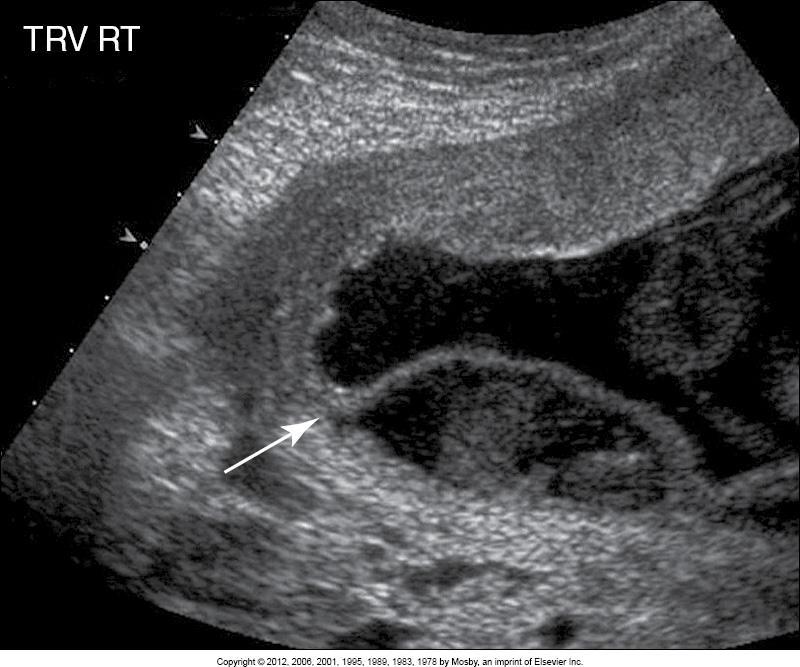
what is this image showing?
placenta previa
What are the most common causes of vasa previa?
Velamentous insertion of umbilical cord into placental membranes, which cross over the cervix
Succenturiate lobe present, which connects the vessels across the cervix
Type of placental invasion where the chorionic villi attach to myometrium without muscular invasion.
placenta accreta
Type of placental invasion where the chorionic villi into the myometrium.
placenta increta
Type of placental invasion where chorionic villi penetrate through the uterus.
placenta percreta
What is the term for attachment of placental membranes to fetal surface of placenta rather than to underlying villous placental margin?
circumvallate or circummarginate placenta
A patient is diagnosed with a folded placental margin that is thickened and elevated with underlying fibrin and hemorrhage. What is the condition associated with this?
circumvallate/circummarginate placenta
What is the most common type of abruption (and its aka)?
marginal abruption aka subchorionic bleed
What type of abruption presents as a “low-pressure'“ bleed and arises from the edge of the placenta?
marginal abruption
What is the result of intraplacental hemorrhage caused by breaks in the villous capillaries? Is this low or high risk to the fetus?
intervillous thrombosis - usually little risk to fetus
What are focal discrete lesions caused by ischemic necrosis? It is usually found in 25% of pregnancies with little to no clinical significance
placenta infarcts
Complete moles generally have a __ karyotype and no fetal tissue; partial/incomplete moles usually have a __ karyotype with fetal tissue often present.
diploid; triploid
What is the most common tumor of placenta? Is it benign or malignant?
chorioangioma - benign vascular tumor
What labs may be elevated with chorioangioma?
AFP in the AF or maternal serum
What are the risks involved with monochorionic pregnancy?
enlargement of umbilical cord