Chapter 1 - Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Notes
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Anatomy
The study of the form of the human body.
Physiology
The study of the functions of the human body.
Cell
The basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms.
Metabolism
The sum of all chemical processes that occur within the body.
Reproduction
The biological process by which new individual organisms are produced.
Organ Systems
Groups of organs that work together to perform complex functions for the body.
Gross Anatomy
The study of body structures that can be observed with the naked eye.
Microscopic Anatomy
The study of structures that are too small to be seen without magnification.
Cytology
The study of individual cells.
Histology
The study of tissues.
Anatomical Position
The standard position of the body used as a reference in anatomy.
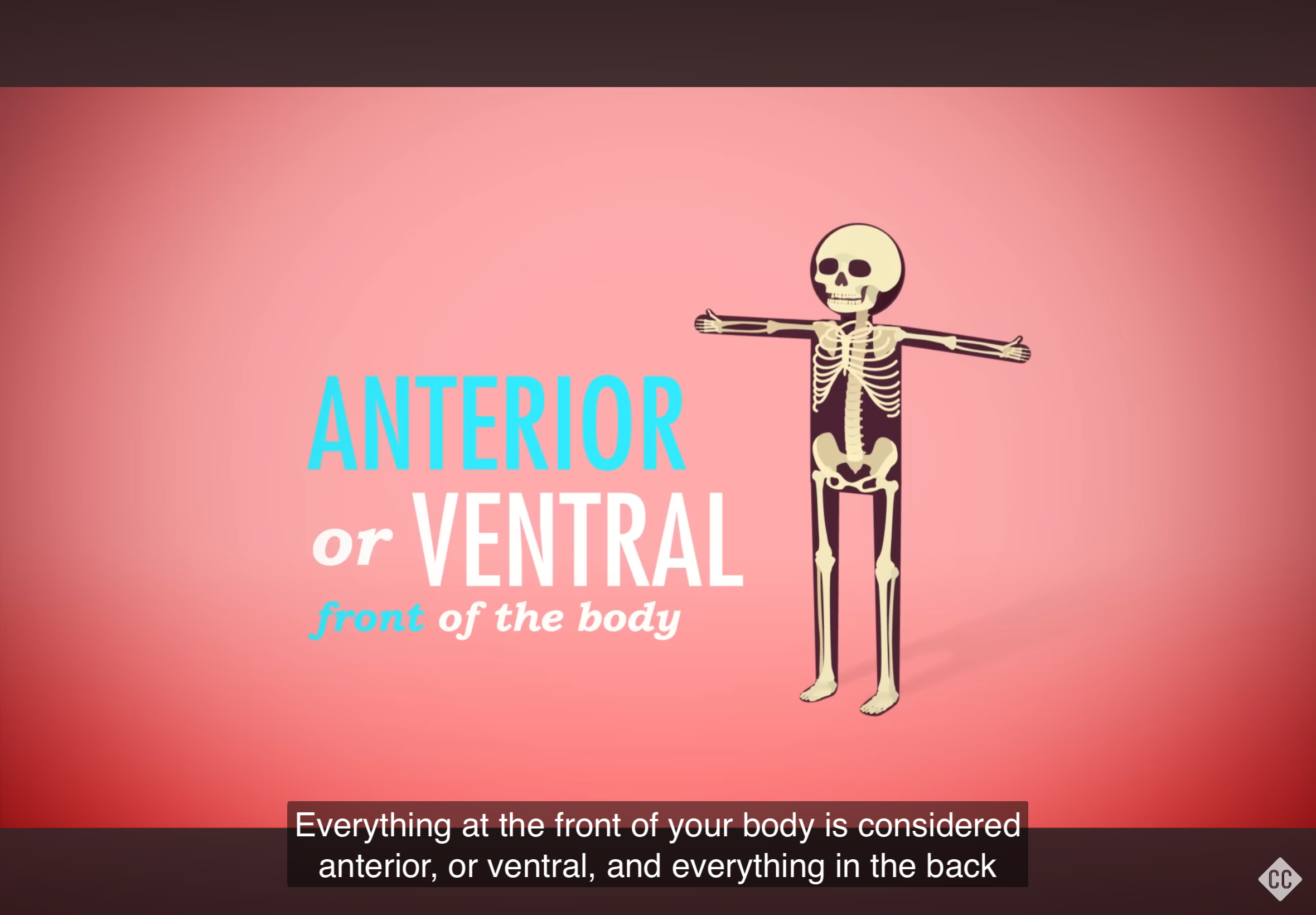
Anterior
Refers to the front of the body.
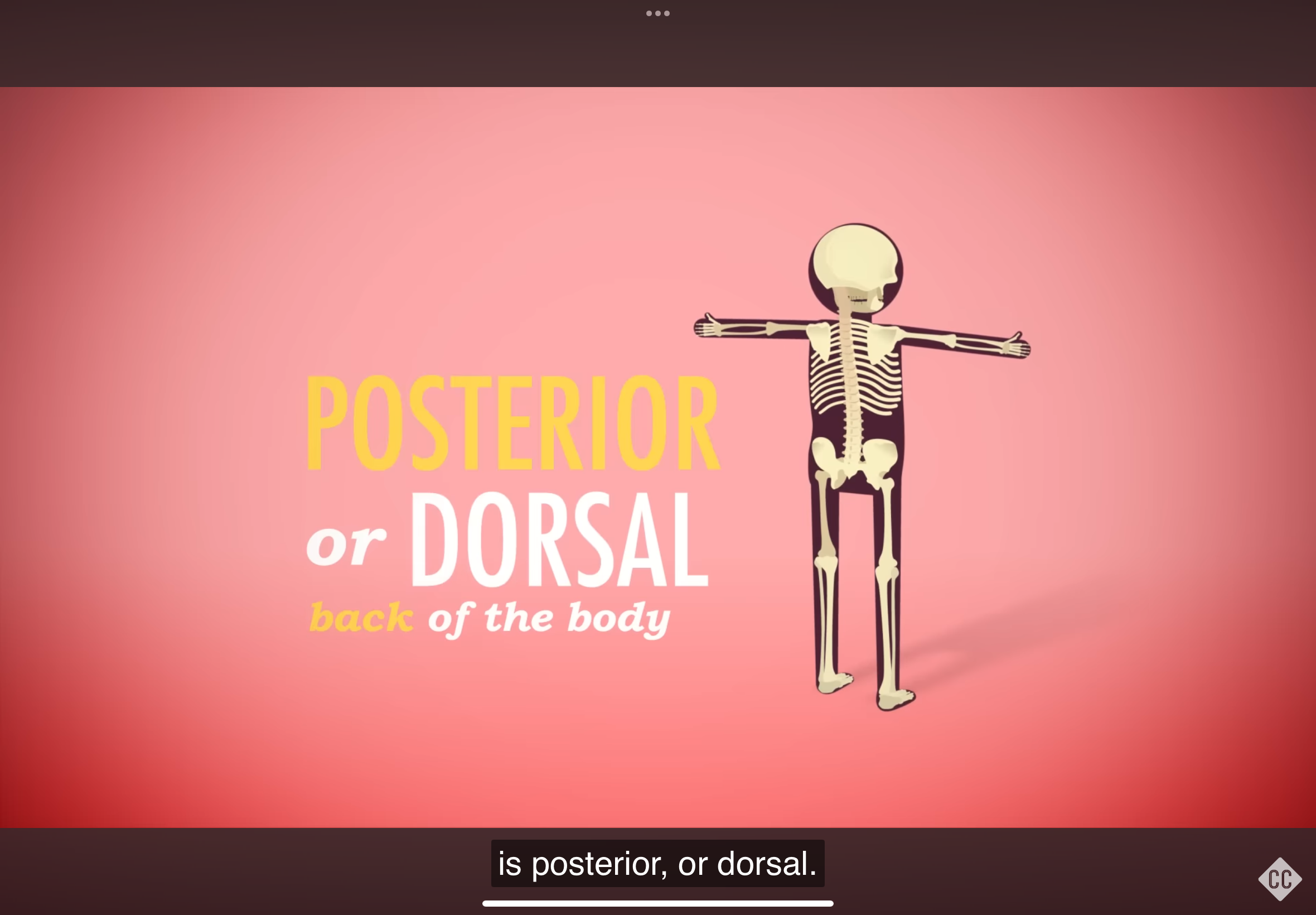
Posterior
Refers to the back of the body.
Superior
Refers to a position above or higher than another part of the body.

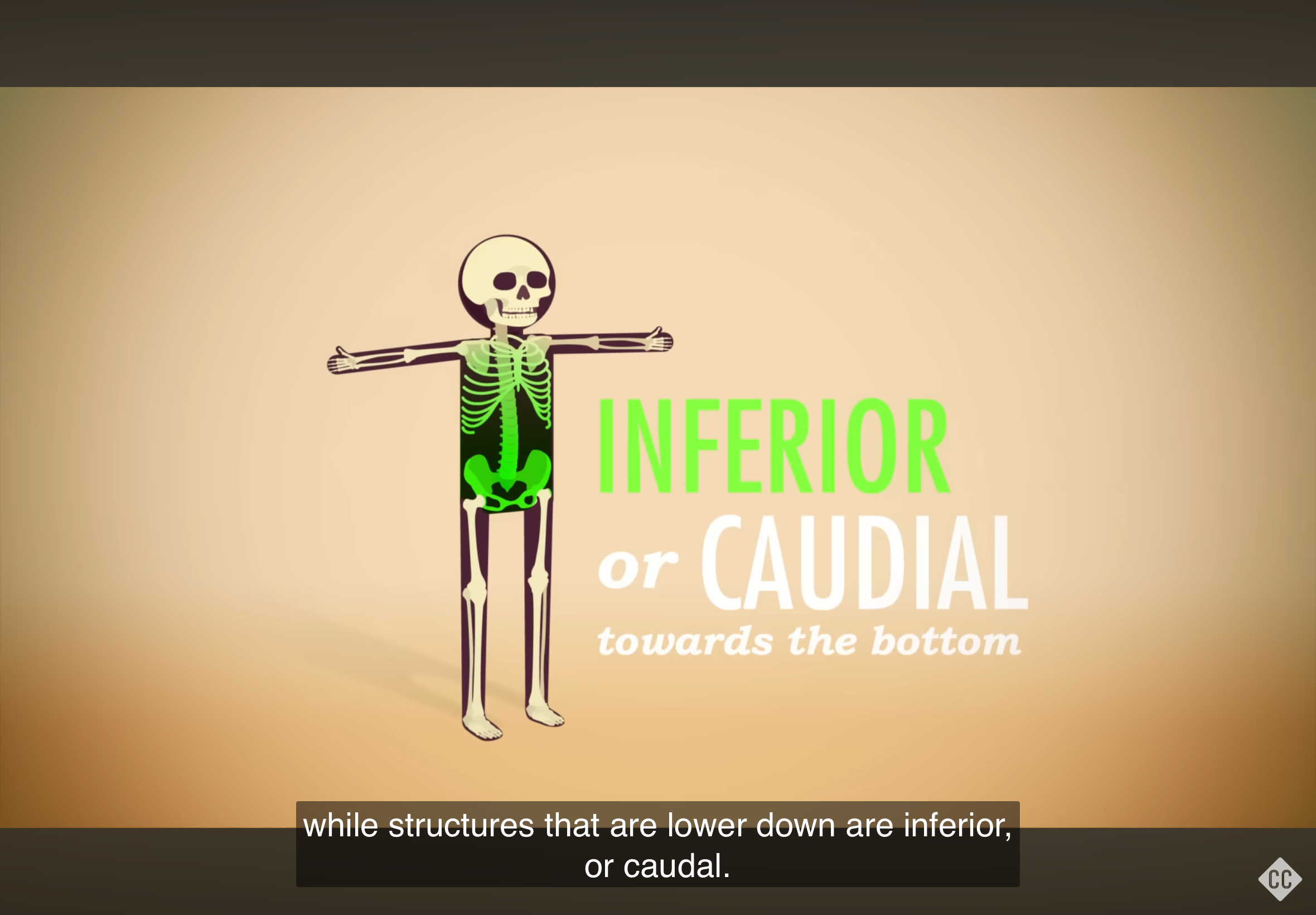
Inferior
Refers to a position below or lower than another part of the body.
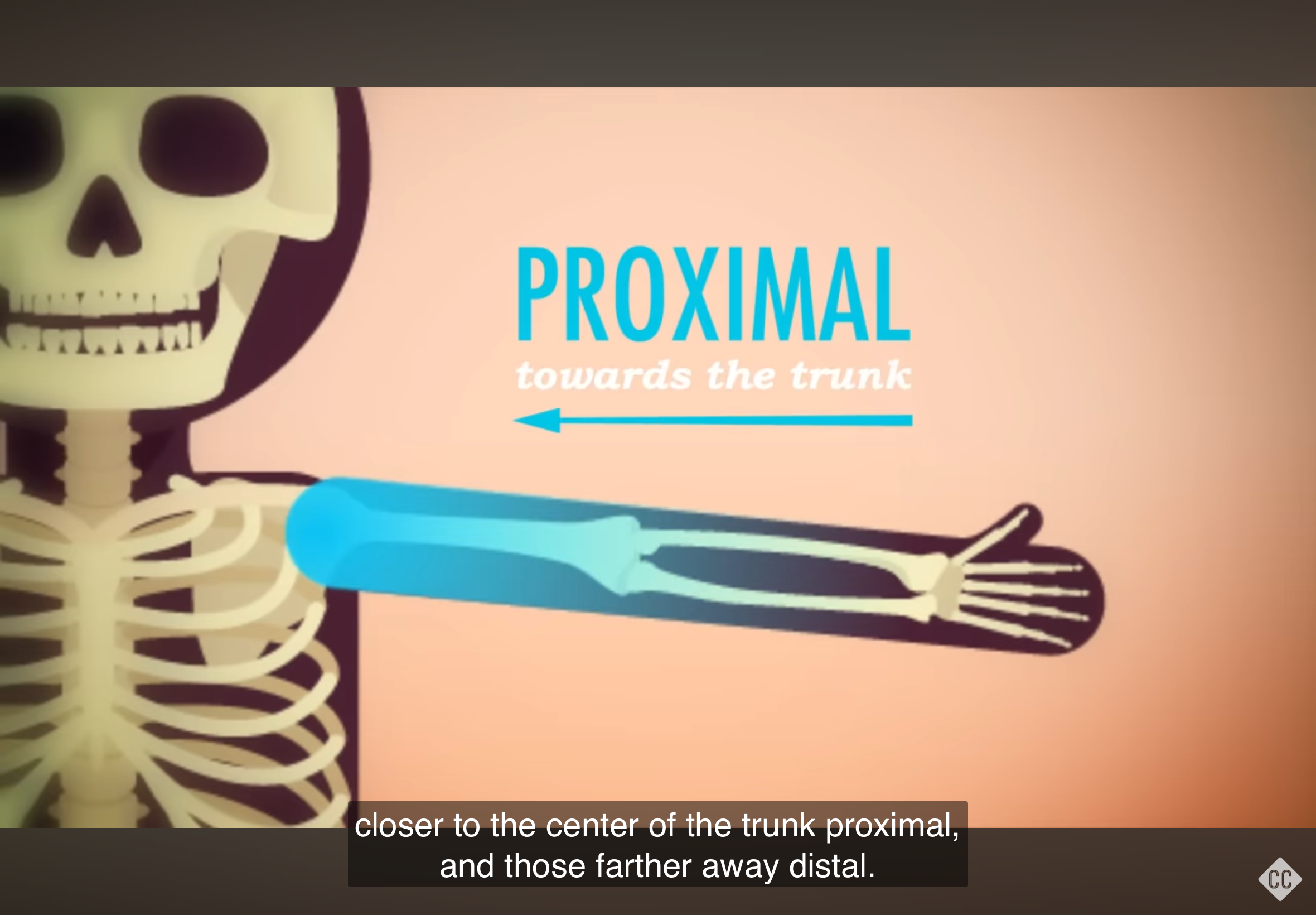
Proximal
Refers to a position closer to the trunk of the body.
Distal
Refers to a position farther from the trunk of the body.

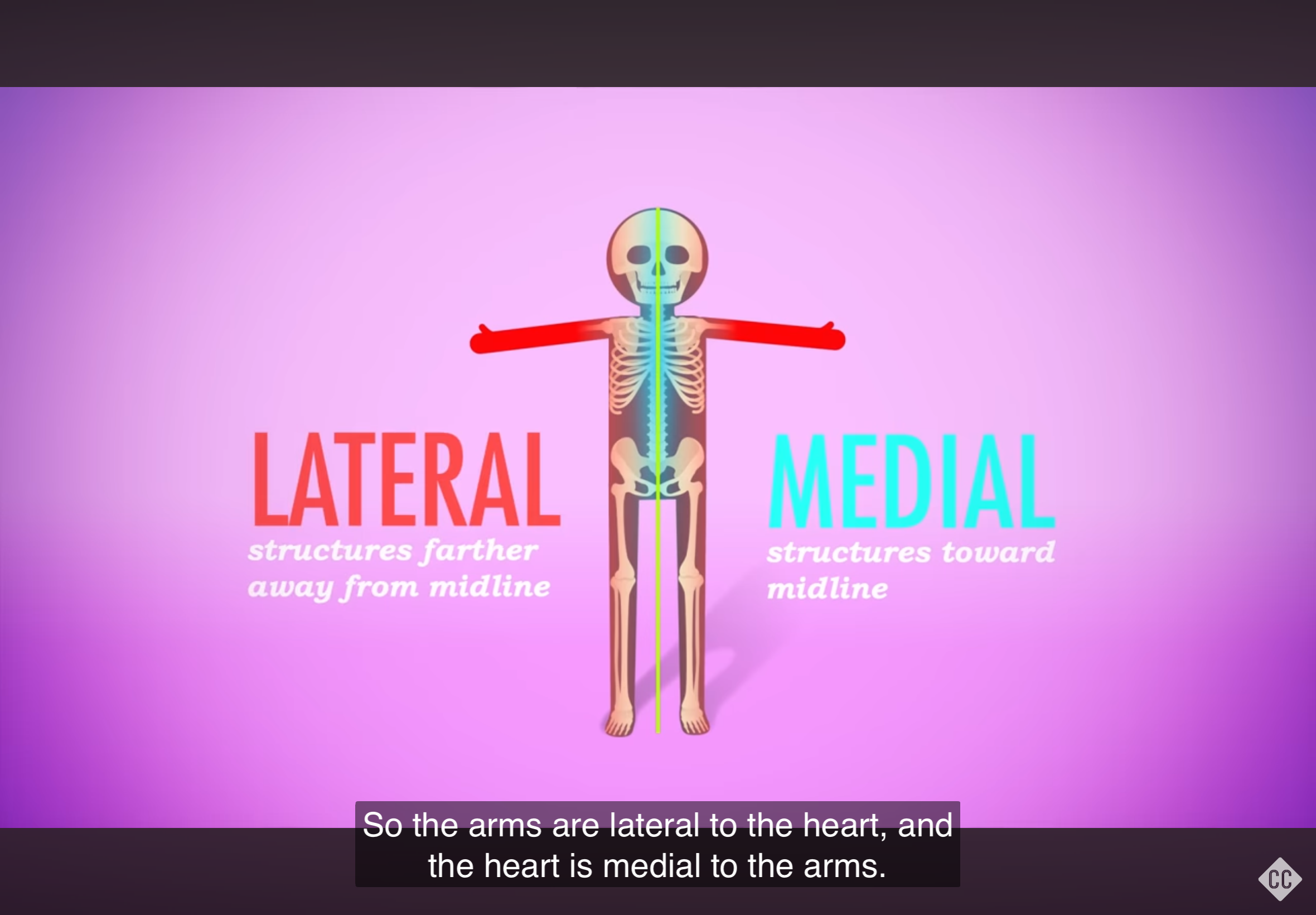
Medial
Refers to a position closer to the midline of the body.

Lateral
Refers to a position farther away from the midline of the body.
Superficial
Refers to a position closer to the surface of the body.
Deep
Refers to a position farther away from the surface of the body.
Axial Region
Includes the head, neck, and trunk of the body.
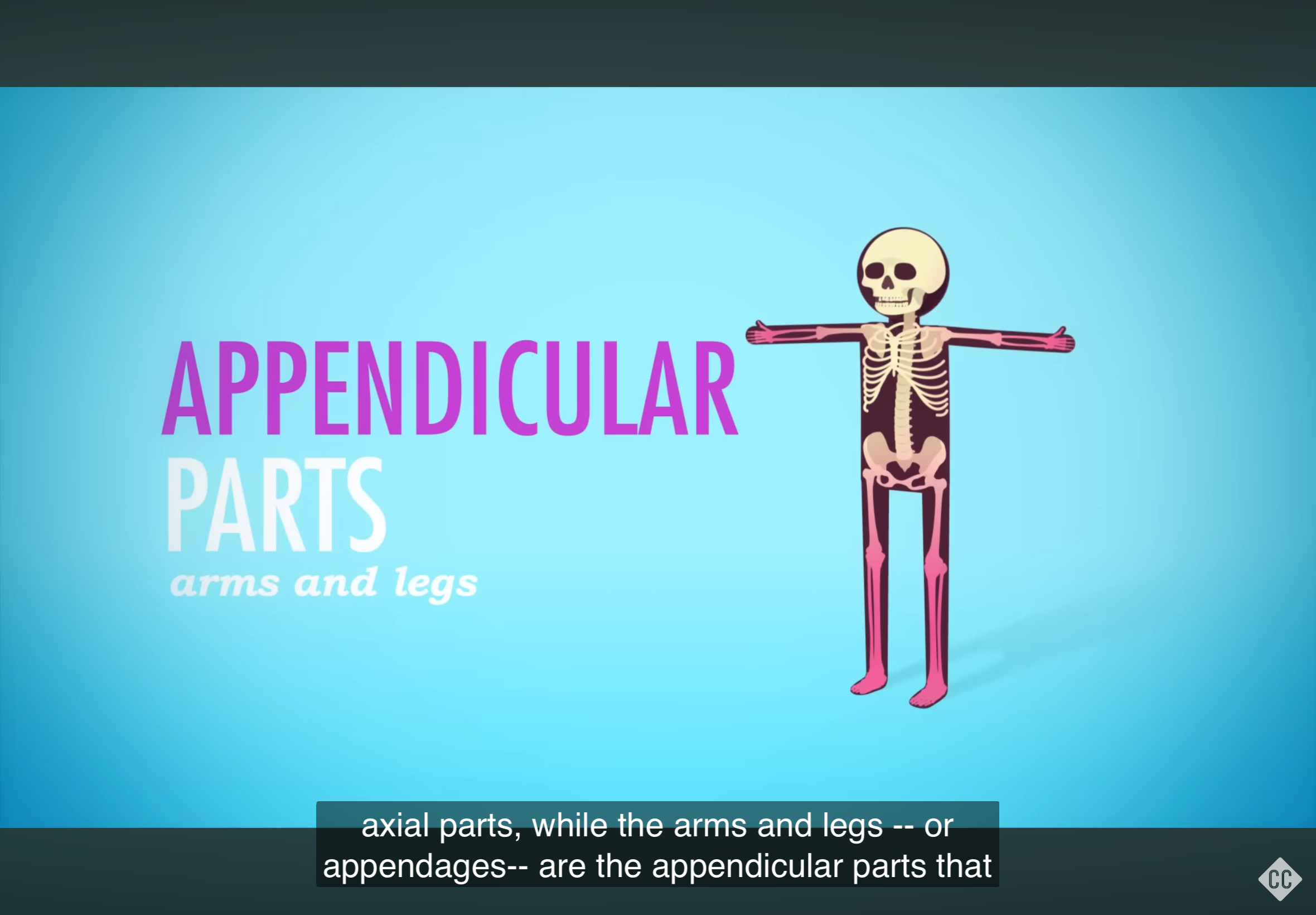
Appendicular Region
Includes the upper and lower limbs of the body.
Sagittal Plane
A vertical plane that divides the body into left and right parts.

Frontal Plane
A vertical plane that divides the body into anterior and posterior parts.
Transverse Plane
A horizontal plane that divides the body into superior and inferior parts.

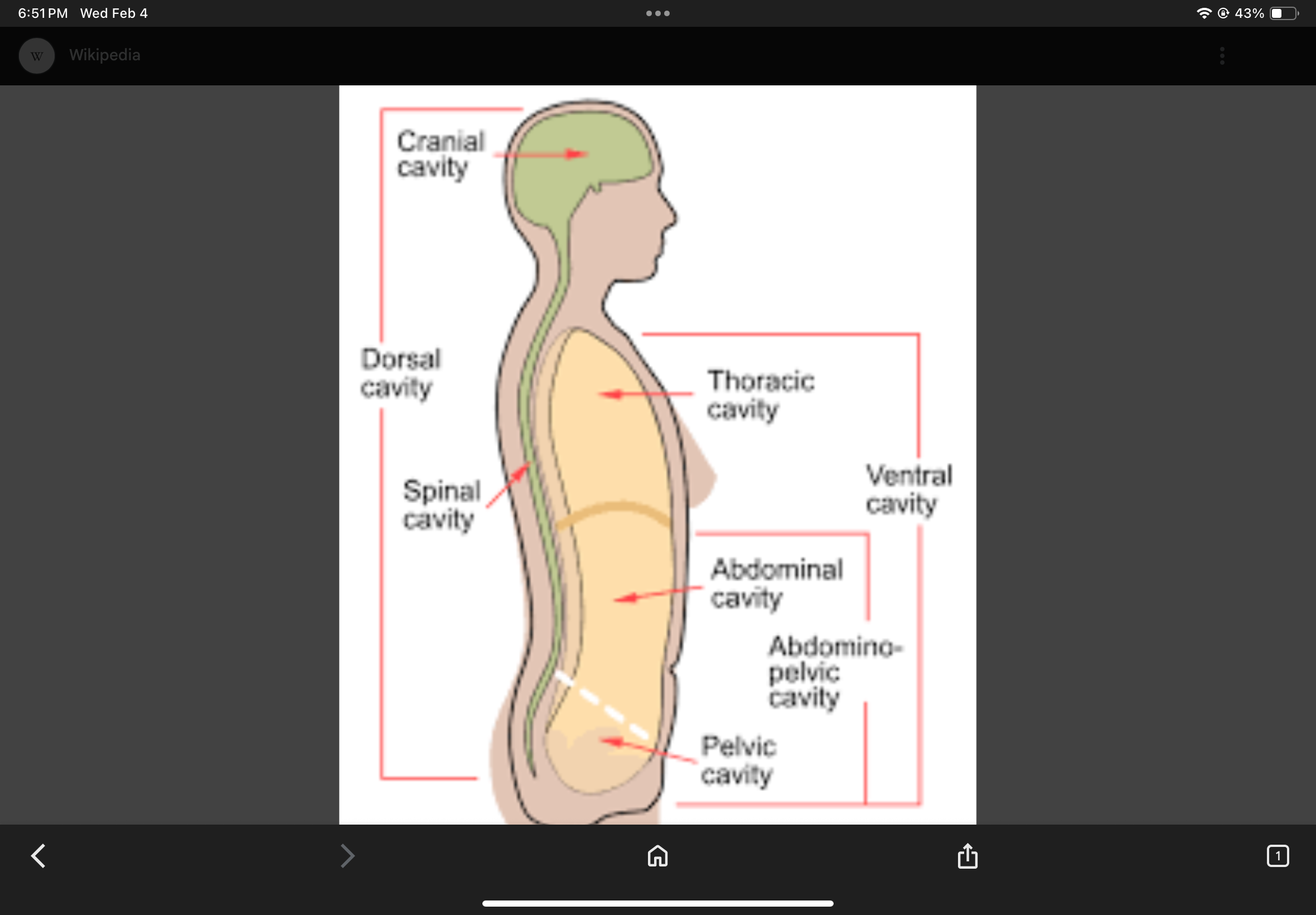
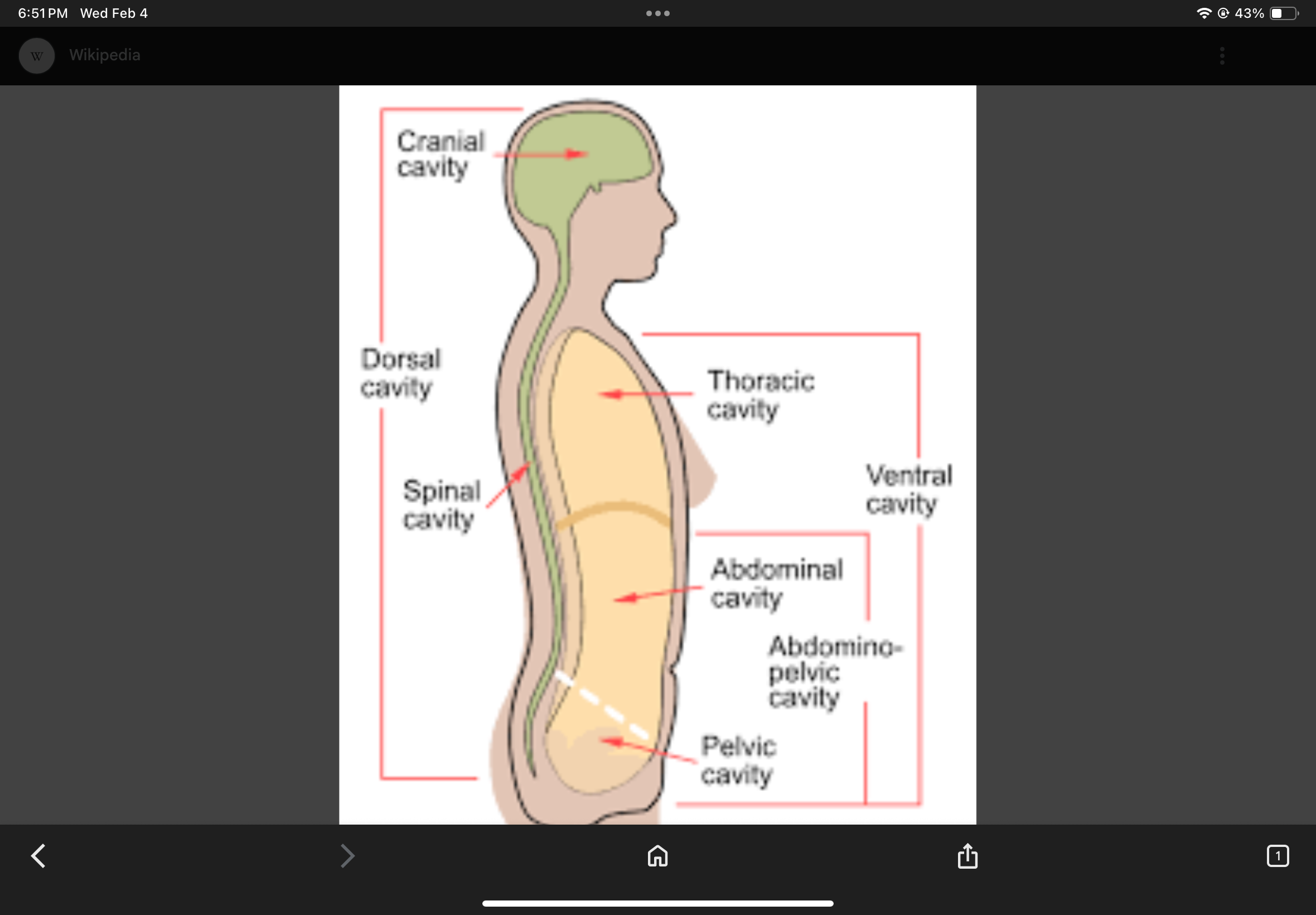
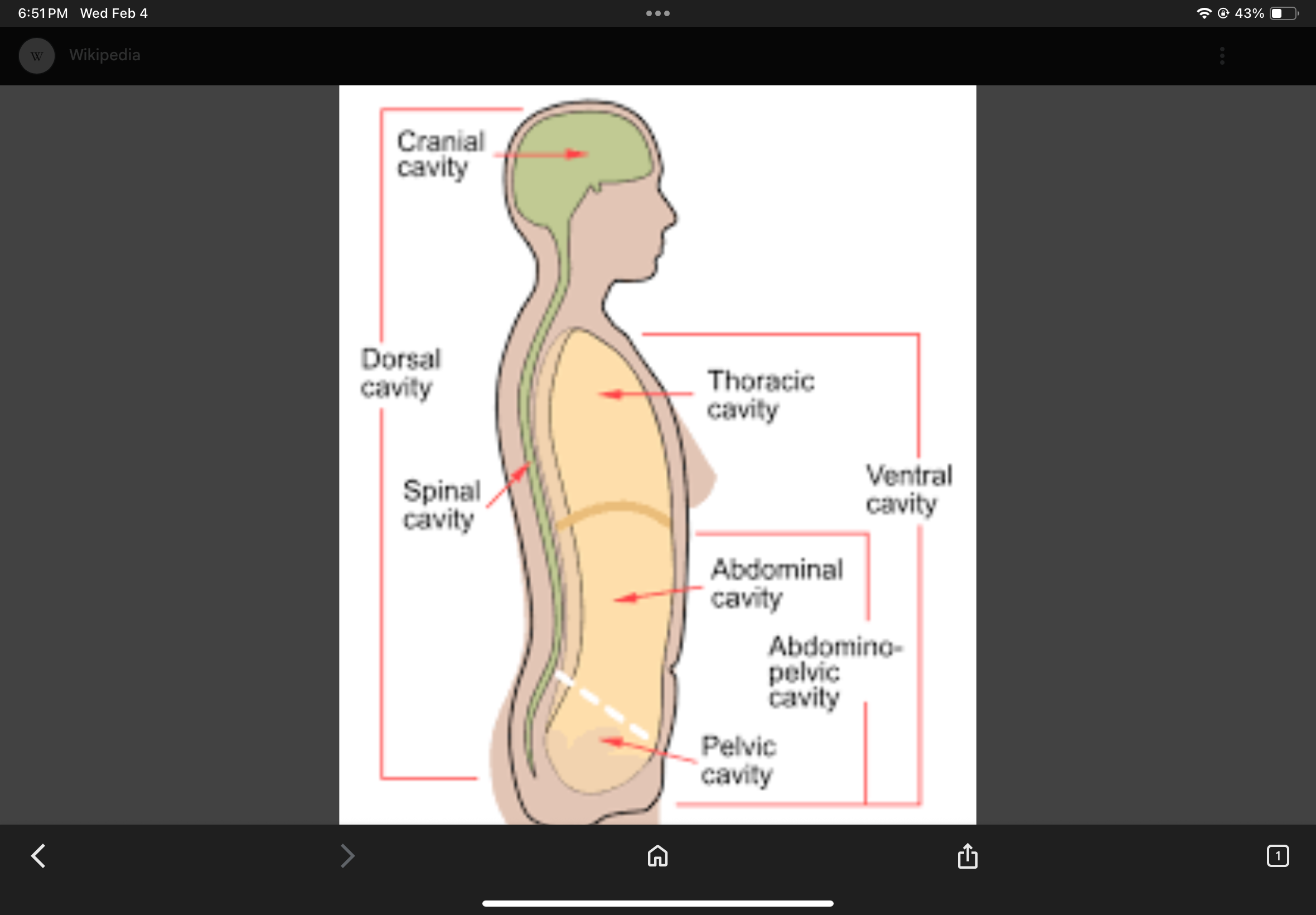
Posterior Body Cavity
Contains the cranial and vertebral cavities.
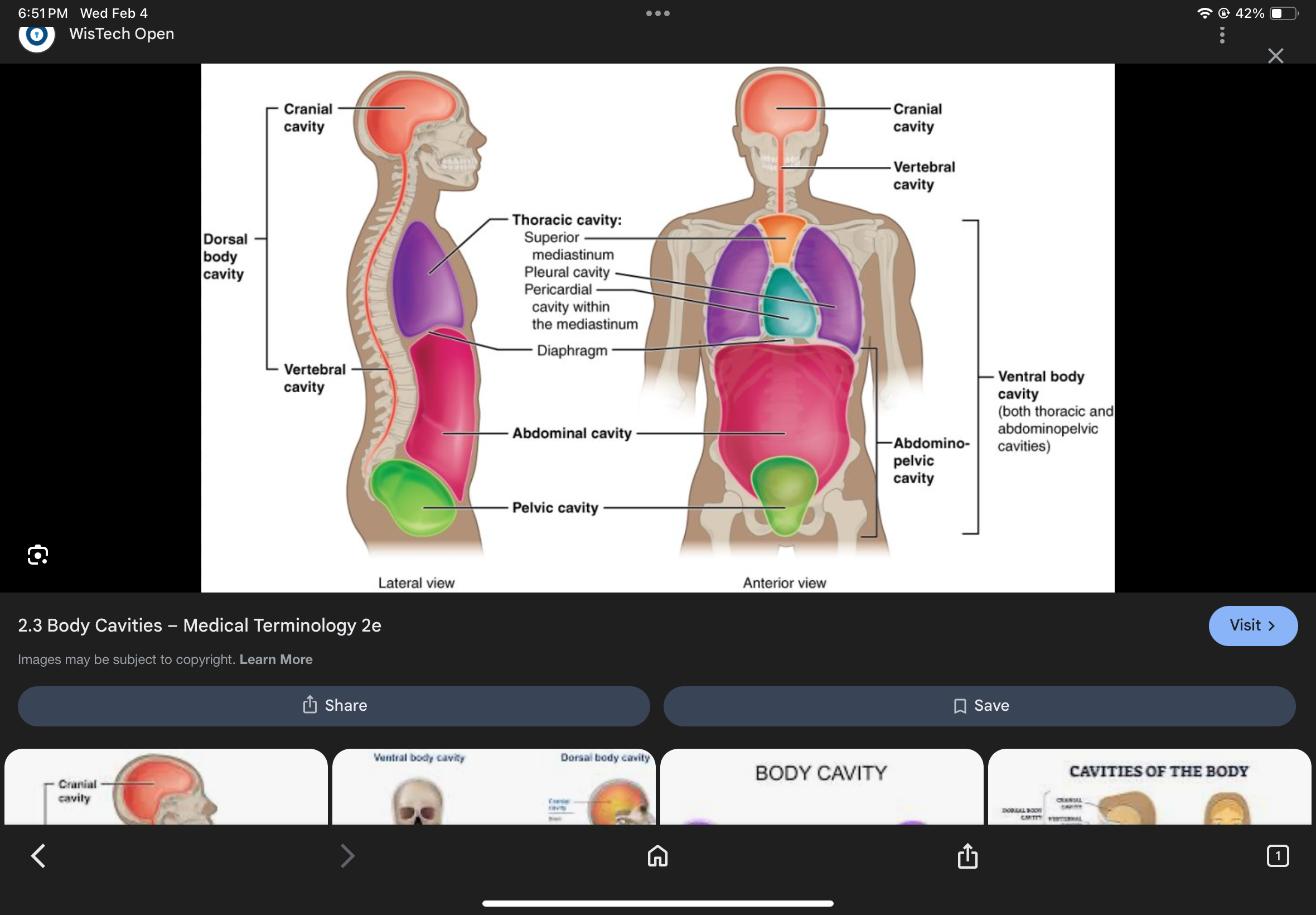
Cranial Cavity
The cavity that houses the brain.

Vertebral Cavity
The cavity that houses the spinal cord.
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
The fluid found in the posterior body cavity that protects and cushions the brain and spinal cord.

Anterior Body Cavity
Contains the thoracic cavity and abdominopelvic cavity.
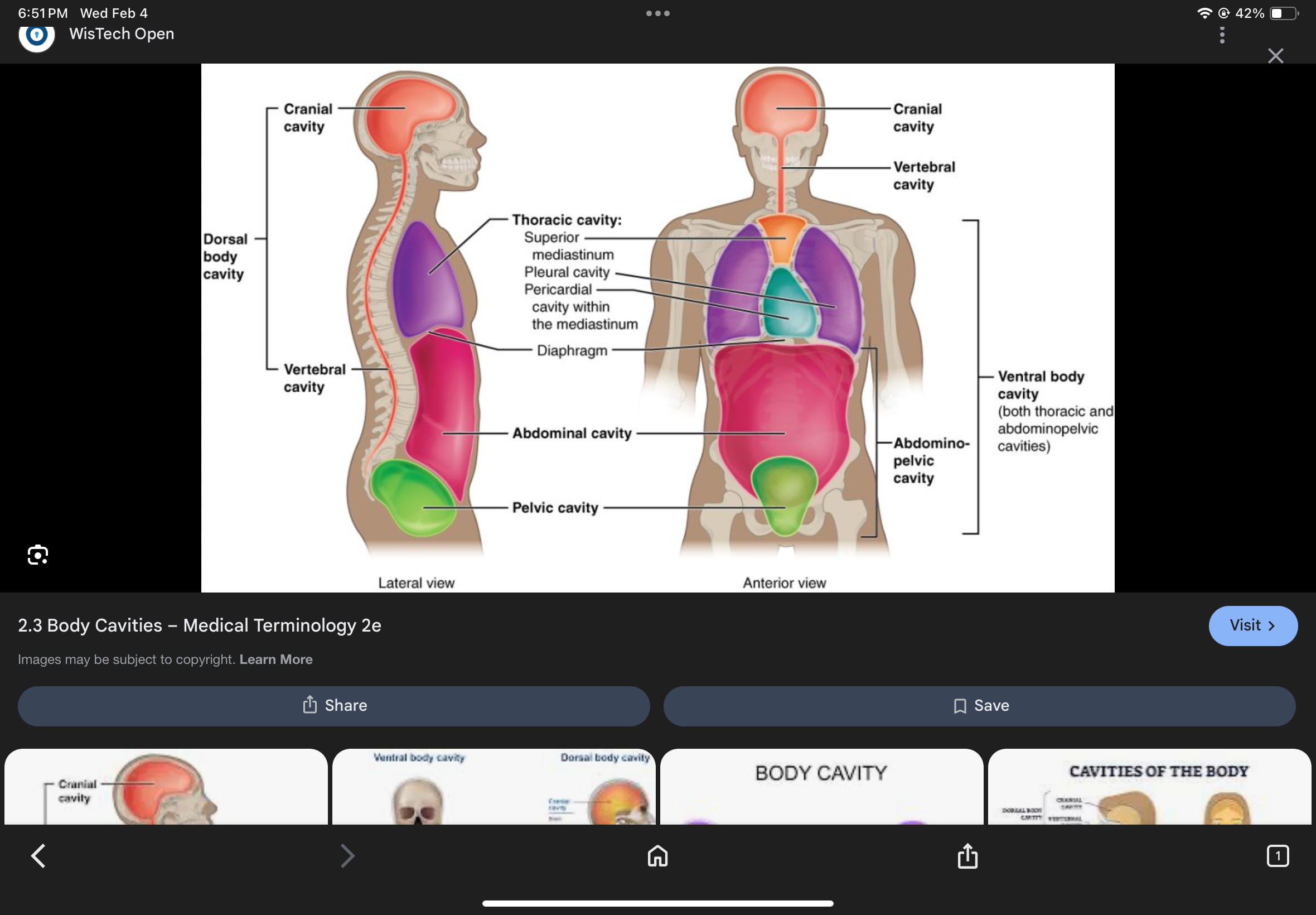
Thoracic Cavity
The cavity superior to the diaphragm containing pleural and pericardial cavities.
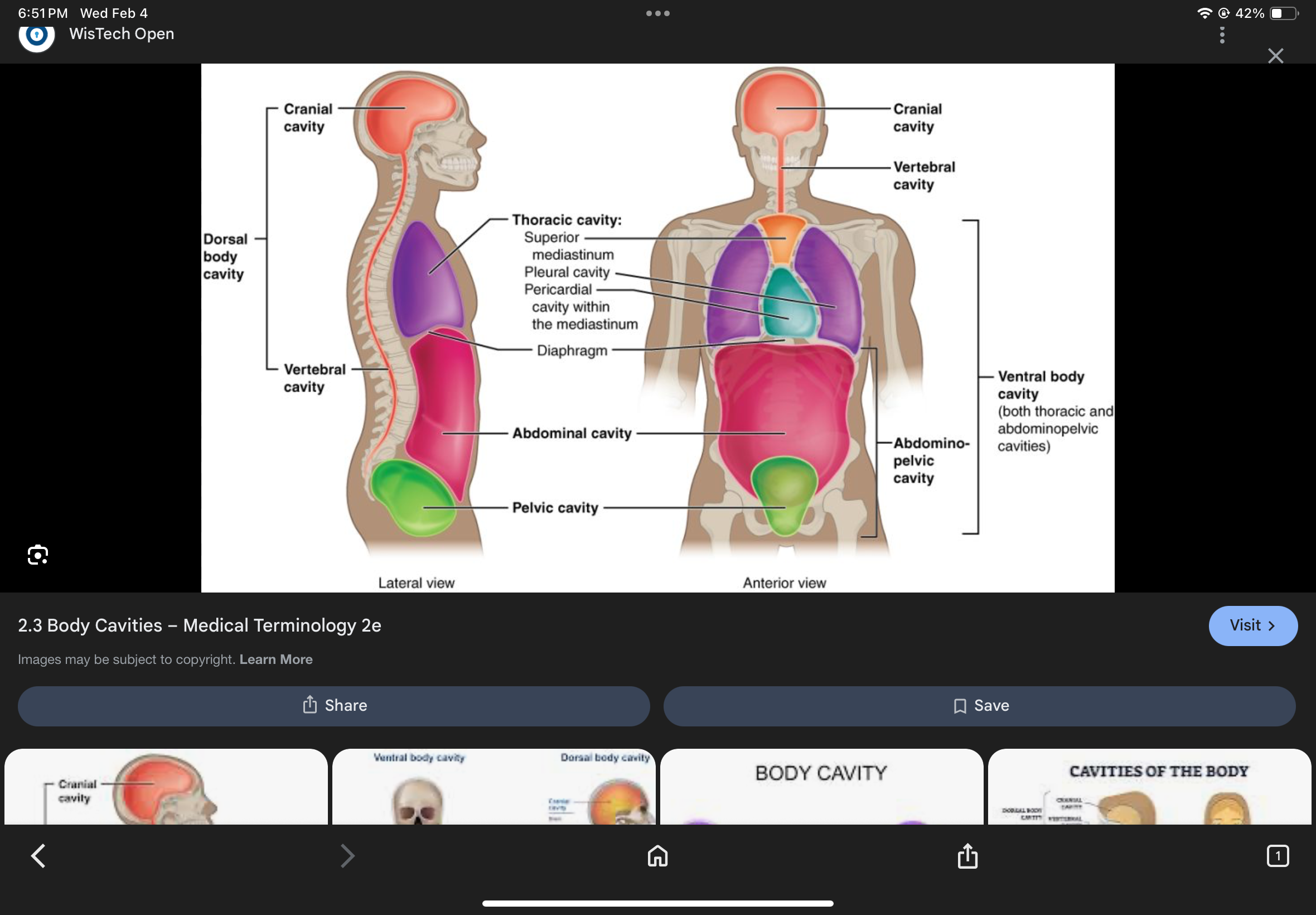
Abdominopelvic Cavity
The cavity inferior to the diaphragm containing abdominal and pelvic cavities.
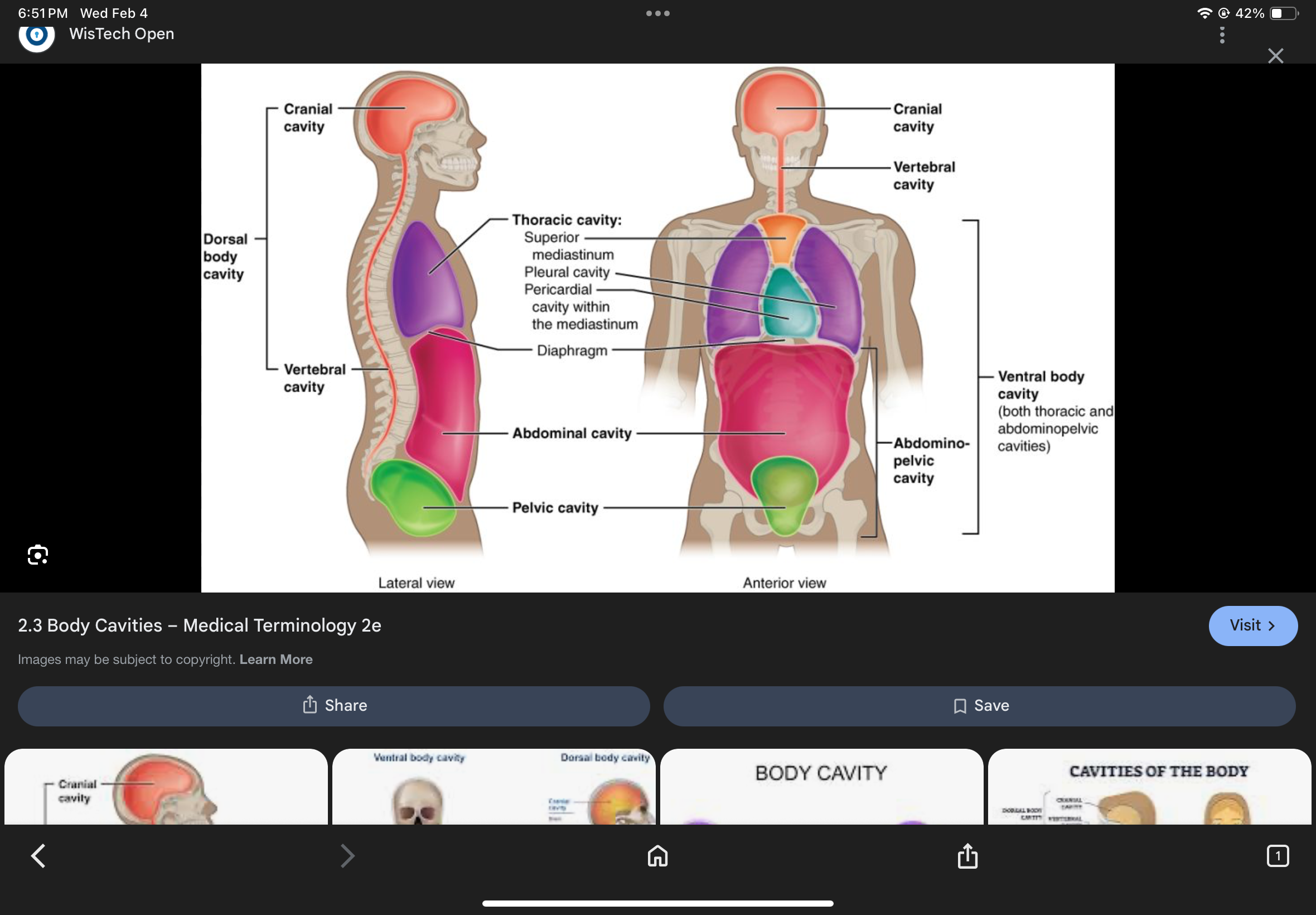
Pleural Cavities
The cavities that contain the lungs.
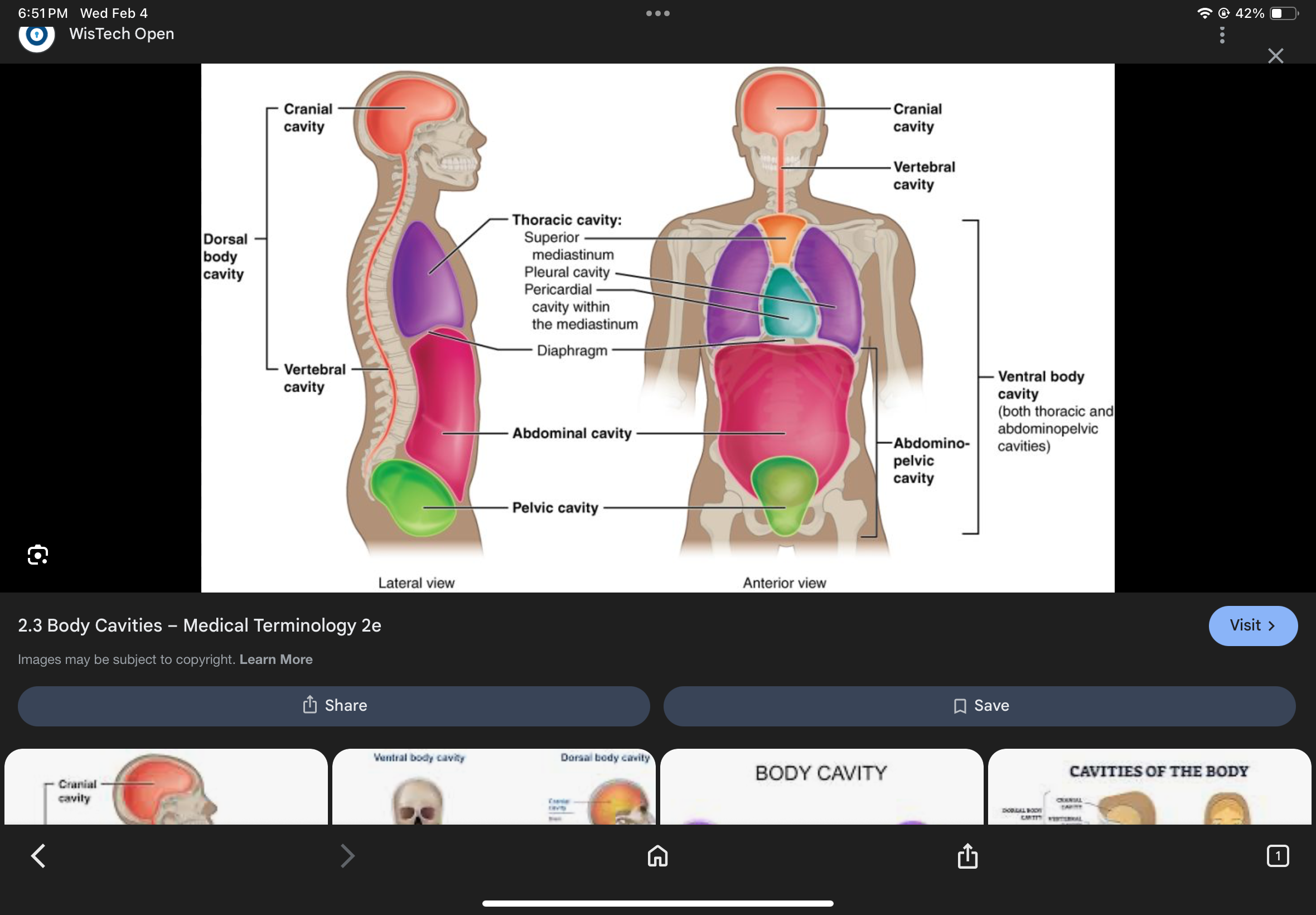
Pericardial Cavity
The cavity that contains the heart.
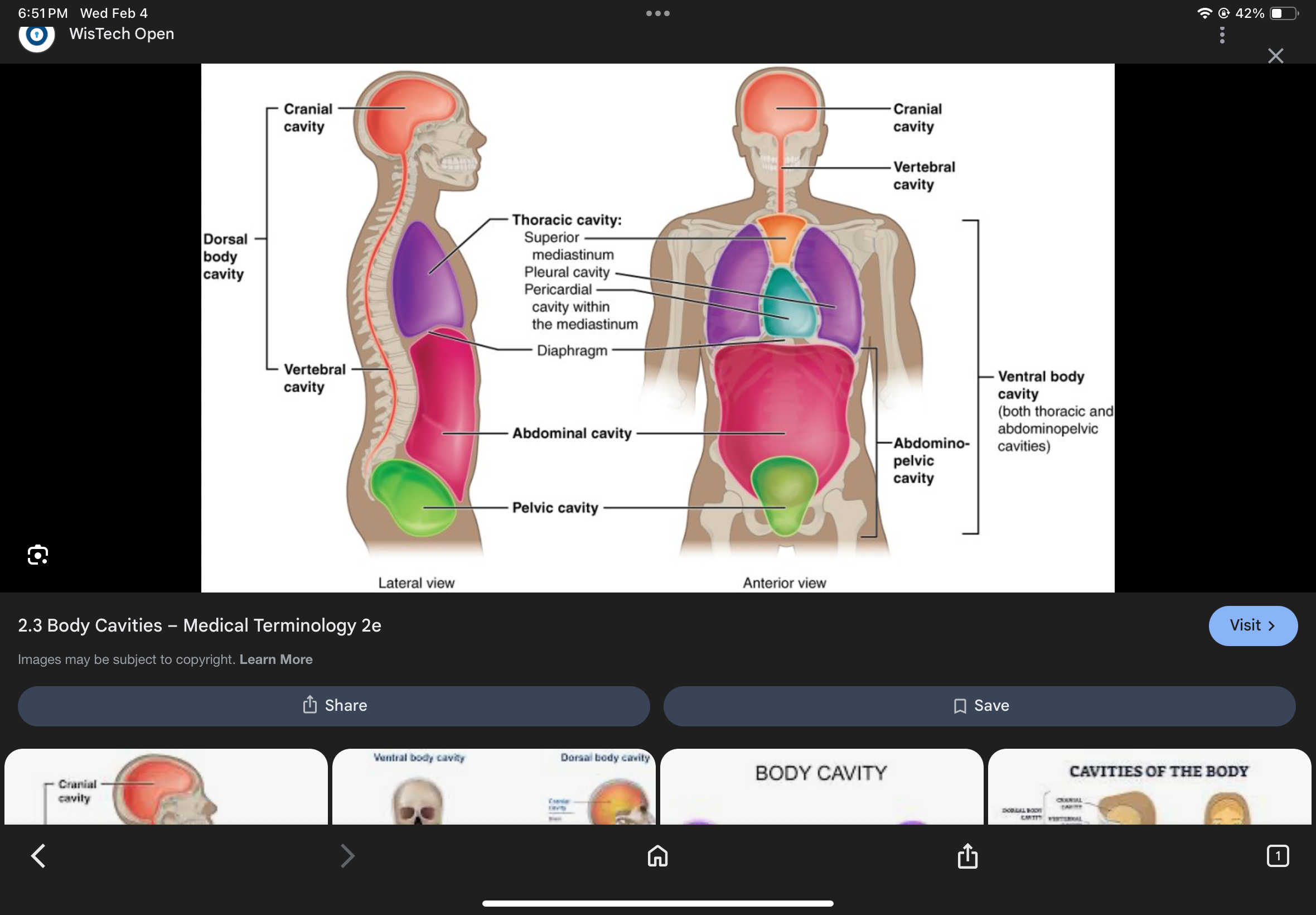
Mediastinum
The space between the lungs that contains the heart and great vessels.
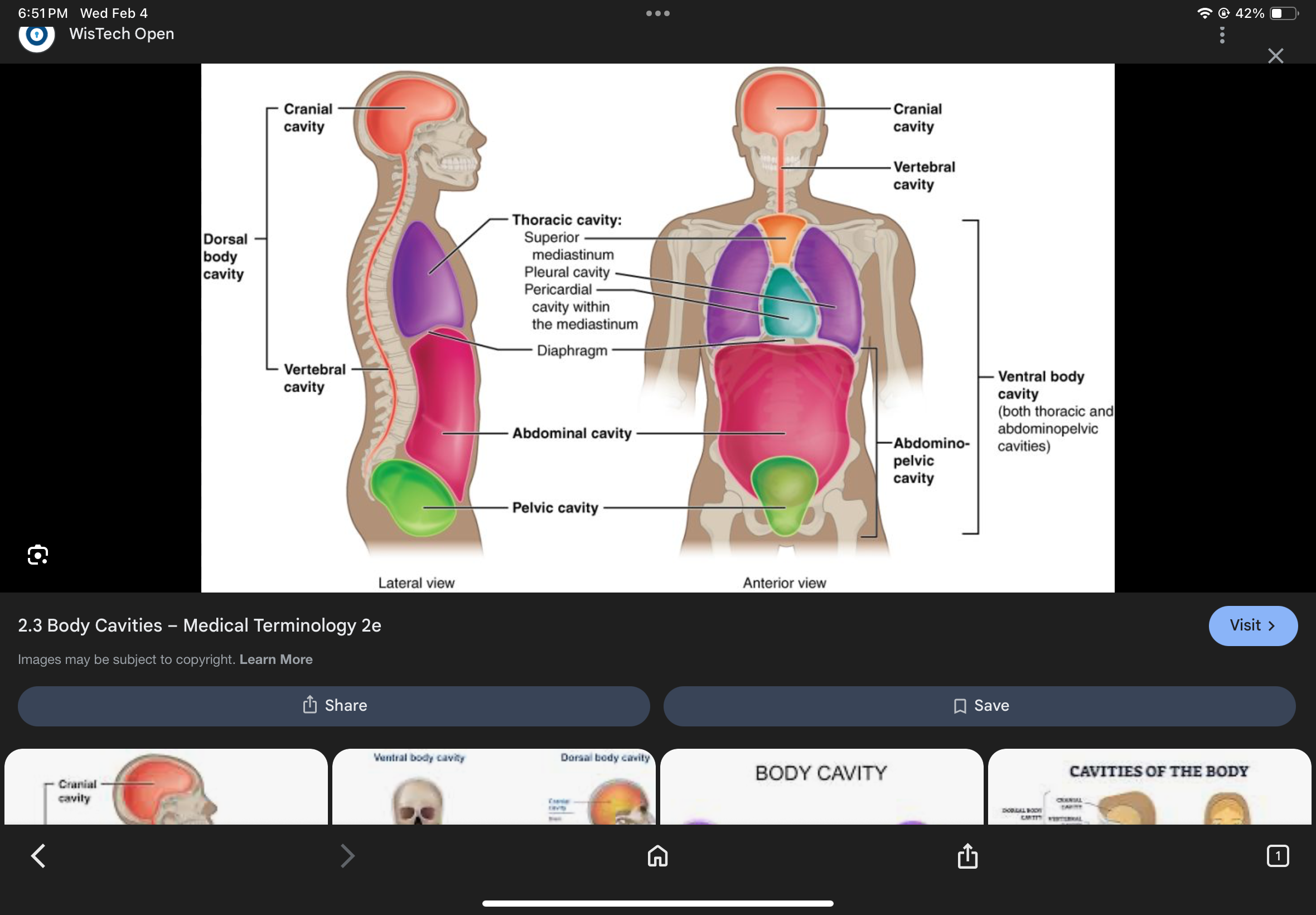
Abdominal Cavity
The cavity that contains digestive organs.
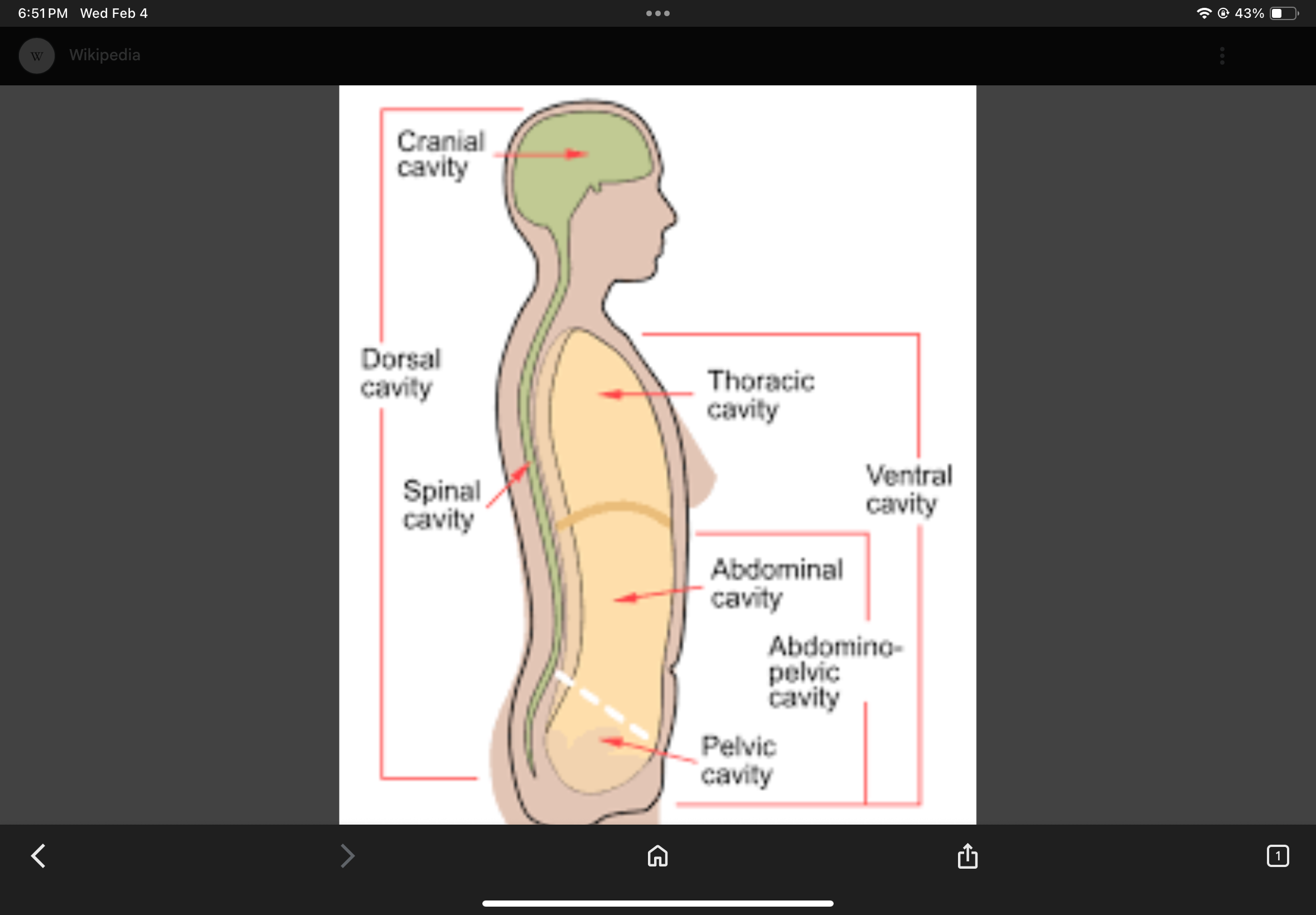
Pelvic Cavity
The cavity that contains reproductive organs.
Peritoneal Cavity
The cavity that surrounds the abdominal organs.
Serous Membranes
Double-layered membranes that line body cavities and secrete serous fluid.
Serous Fluid
A lubricating fluid found in serous membranes that reduces friction.