2025 - pe unit 1 half of exam
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
cardiorespiratory
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
cardiovascular system
consists of heart, blood vessels, blood
cardiovascular system - pulmonary circuit
blood flow between heart and lungs
Pulmonary circulation is the blood that circulates between the heart and lungs. It starts in the right ventricles, where deoxygenated blood is pumped through the pulmonary arteries to the lungs. The lungs then oxygenate the blood (through respiratory system – pulmonary diffusion at alveoli-capillary interphase) and the lungs bring back oxygenated blood through the pulmonary veins into the left atria.
cardiovascular system - systematic circuit
blood flow between heart and body
Systematic circulation is the blood that circulates between the heart and the body. It starts in the left ventricle, where oxygenated blood is pumped through the aorta to the body. (The body uses the oxygen in the blood for cellular respiration, which creates co2). The body then brings back this deoxygenated blood to the right atrium.
cardiovascular system - functions of cardiovascular system
circulates blood
brings o2, water and nutrients to cells
removes co2 and other wastes from cells
thermoregulation + hydration
fight disease
blood clotting
cardiovascular system - heart structure
superior vena cava - vein that brings deoxygenated blood from upper body to right atrium
inferior vena cava - vein that brings deoxygenated blood from lower body to right atrium
right atrium - recieves deoxygenated blood from veins and pushes into right ventricle
tricuspid valve - valve between right atrium and right ventricle
right ventricle - recieves deoxygenated blood from atrium and pushes into pulmonary artery
pulmonic valve - valve between right ventricle and pulmonary artery
pulmonary artery - brings deoxygenated blood from right ventricle to lungs (there’s two because they need to go to each lung)
blood gets oxygenated and loses carbon dioxide in lungs
pulmonary veins - receives oxygenated blood from lungs (there’s two because they come from each lung)
bicuspid/mitral valve -
left ventricle -
aortic valve -
aorta -
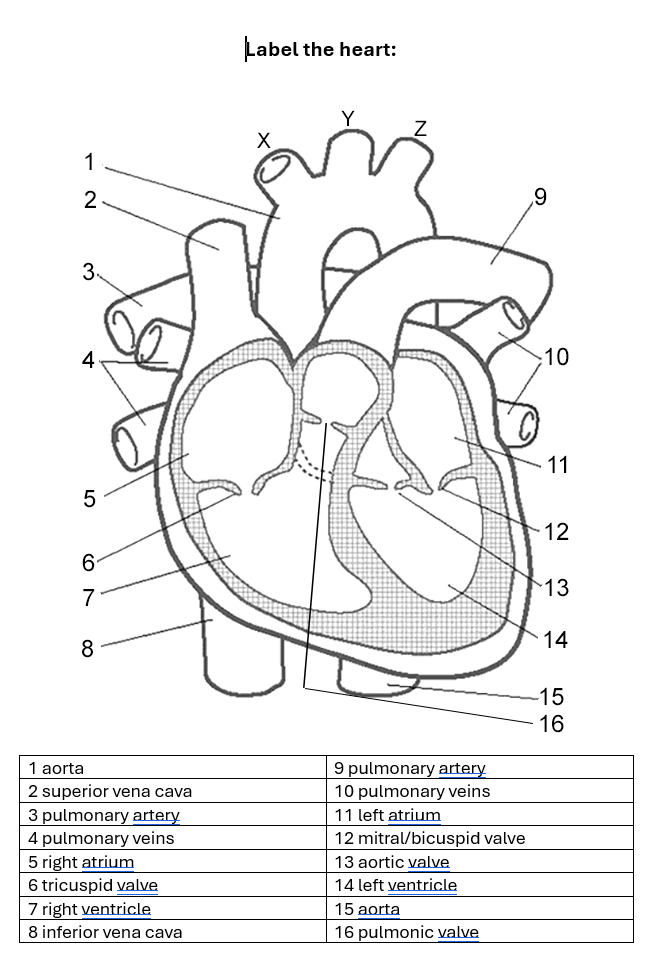
cardiovascular system - valves
prevent backflow
cardiovascular system - viscosity
low viscosity = water
high viscosity = syrup
cardiovascular system - stroke volume, heart rate + cardiac output
heart rate - measured in bpm
stroke volume - the volume of blood pumped from the left ventricle per beat
cardiac output - represents how much blood the heart pumps per minute
cardiac output increases during excercise to deliver more required oxygen to working muscles. this is because both heart rate and stroke volume increase.
cardiac output (Q) = heart rate x stroke volume
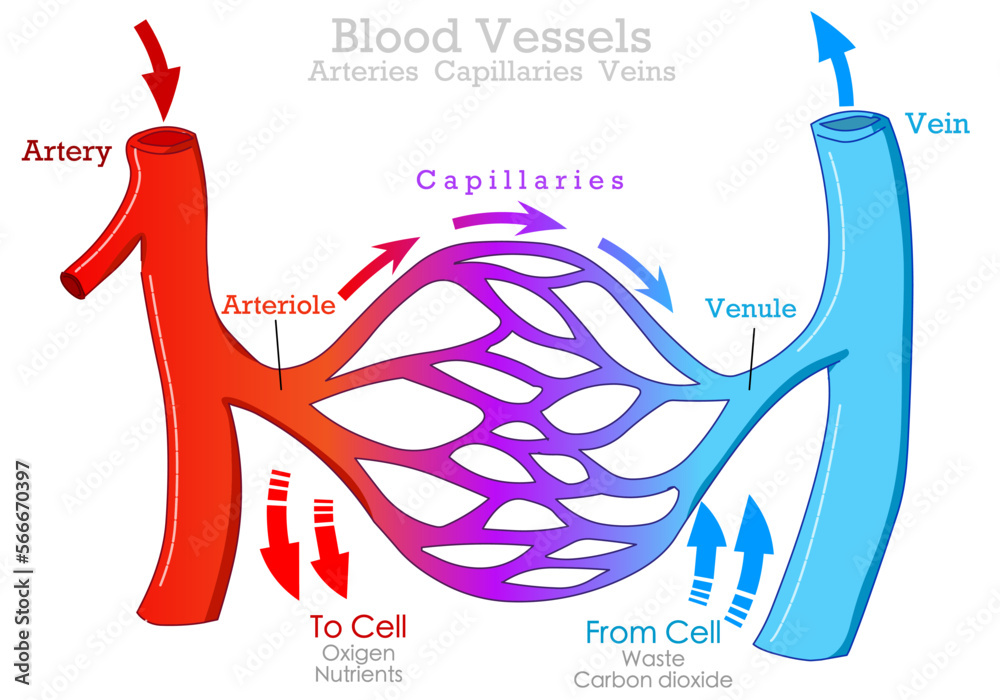
cardiovascular system - blood vessels
arteries - carry oxygen rich blood away from the heart (except for pulmonary arteries). have large, thick elastic walls
veins - carry oxygen poor blood back to the heart (except for pulmonary veins)
capillaries - smallest blood vessels that are the site of gaseous they connect arterioles and venules
cardiovascular system - max heart rate
220 - age
cardiovascular system - redistribution of blood flow
during excercise, blood flow is redistributed through vasodilation (widening of blood vessels to working muslces) and vasoconstriction (narrowing to non-essential organs such as the digestive system
(expand more on this in acute responses)
blood components - red blood cells
function - carry oxygen
blood components - white blood cells
function - fight infection
blood components - platelets
function - clot blood
blood components - plasma
function - transport nutrients/waste
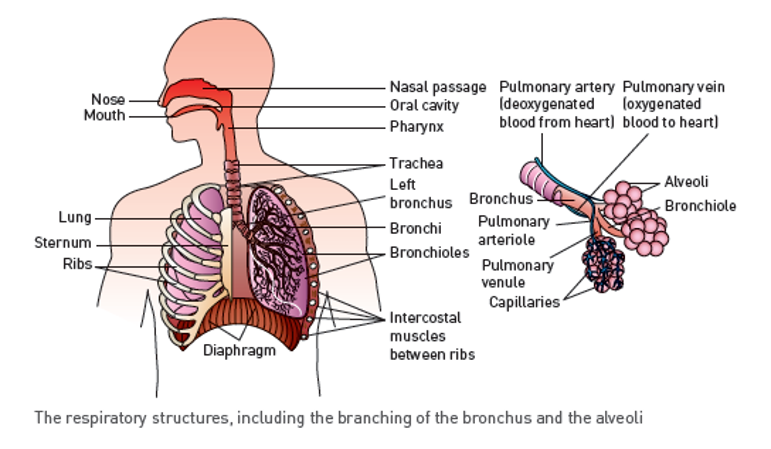
respiratory system
mouth / nose + nasal passage → oral cavity → larynx → pharynx → trachea → left/right bronchus → bronchioles → alveoli → capillaries → pulmonary venules
also includes diaphragm, intercostal muscles, ribs, lungs
respiratory system - inspiration
respiratory system - expiration
respiratory system - gaseous exchange
respiratory system - respiratory rate, tidal volume, ventillation/minute ventilation
respiratory rate -
tidal volume - the amount of air inhaled and exhaled per breath
minute ventilation - represents the total air breathed per minute
minute ventilation (VE) = respiratory rate x tidal volume
acute responses to excercise - how do the cardiovascular and respiratory systems work together to transport oxygen around the body during excercise
acute responses to excercise - how do heart rate, stroke volume and cardiac output change during excercise
submaximal intensties
maximal intensities
muscle fibre types
slow twitch (type I) - low force, high endurance. marathon runners
fast twitch (type II) - high force, low endurance. sprinters