Session 4: The Pelvis and Hip Joint
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
The pelvic girdle is a ring of bone that is partly formed by the axial skeleton.
What are its functions?
- It provides rigid connection with axial skeleton
- Allows for medium range hip motion (medium stability)
- Distributes weight of axial body to lower limbs
- Enables locomotion & standing
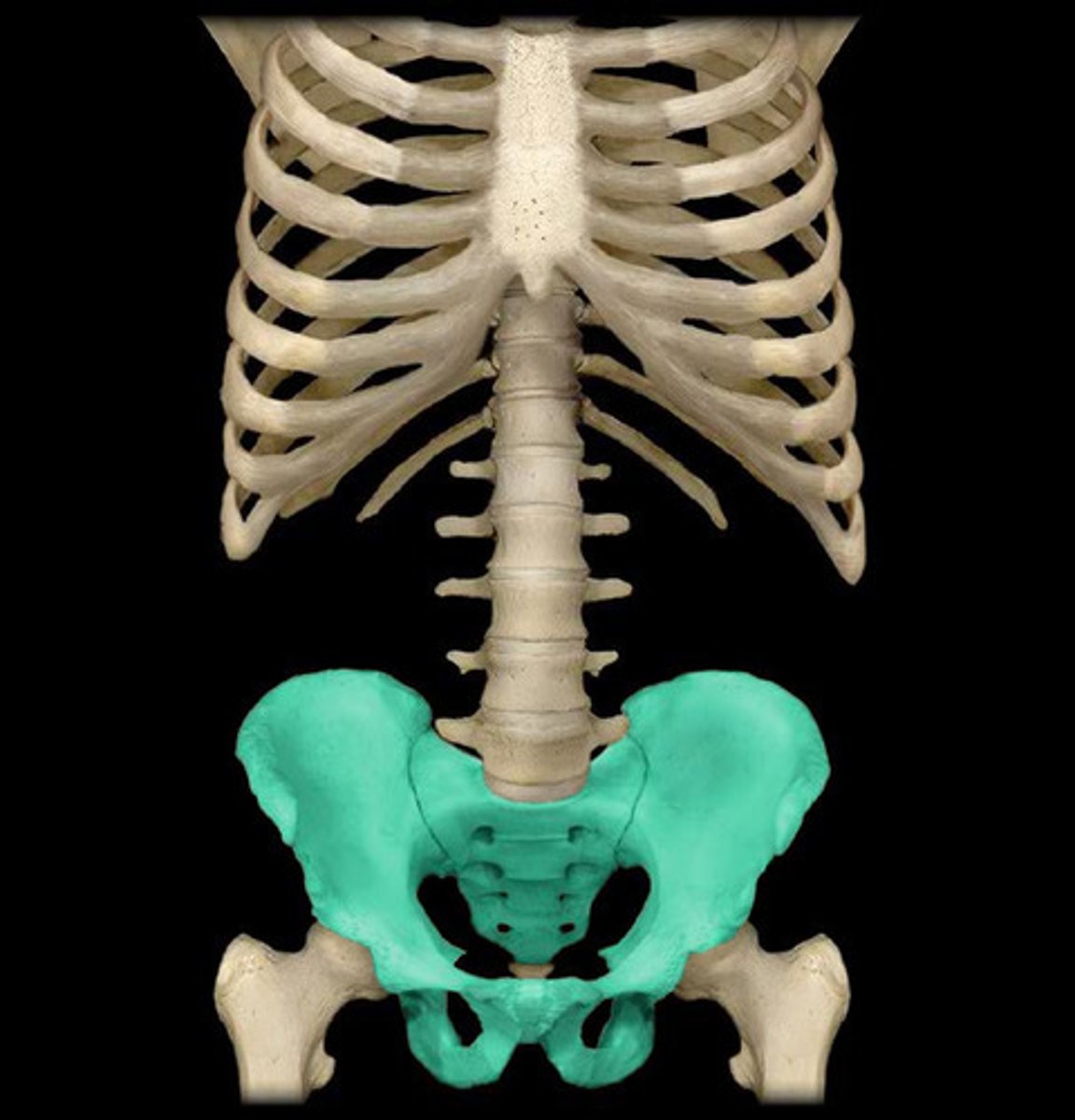
The hip bone is made up of what 3 bones?
Ilium
Ischium
Pubis
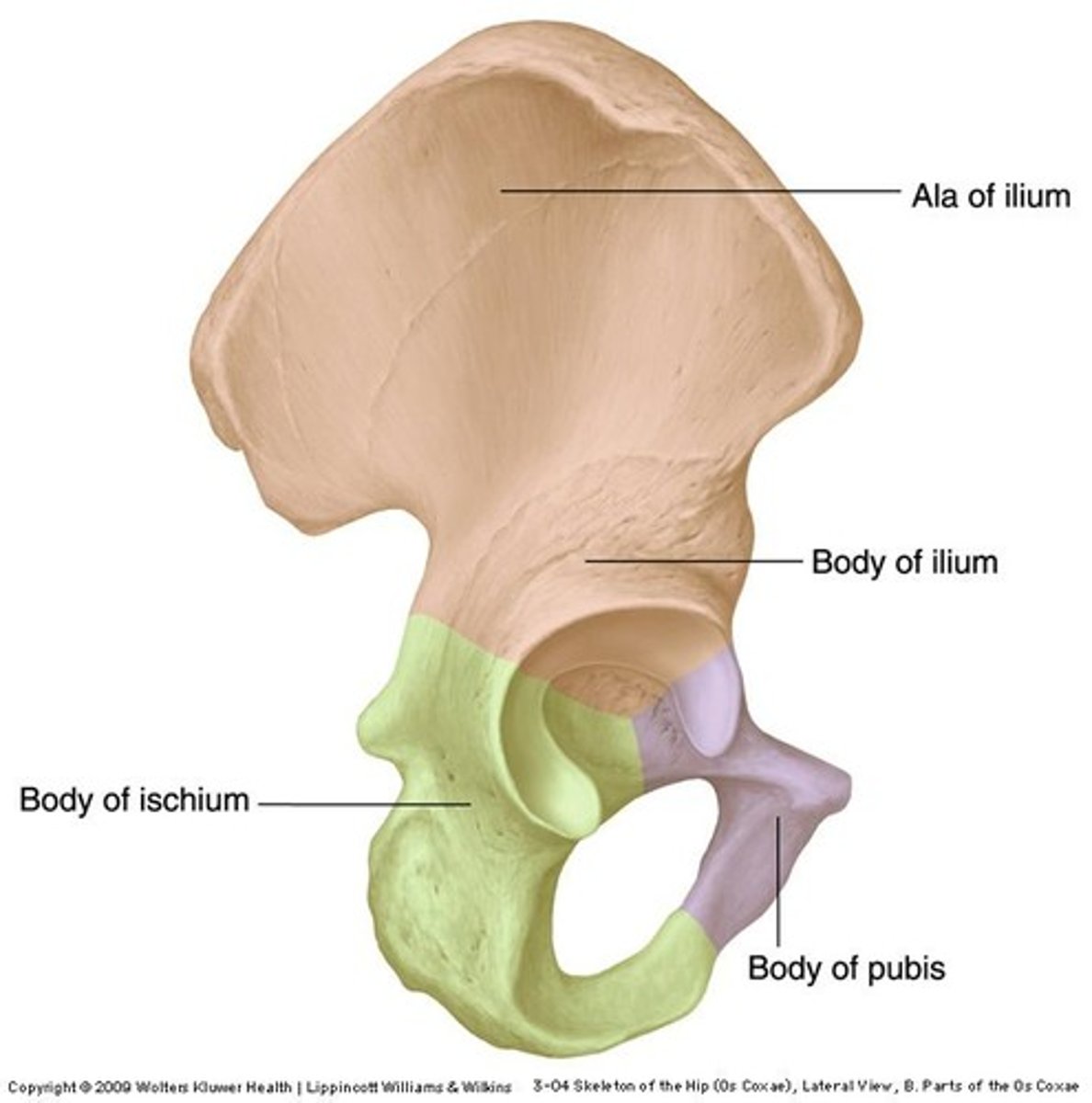
There are significant differences between the female and male bony pelvis.
Name these differences...
Female Gynecoid Pelvis
- Circular pelvic inlet
- Wider & broader
- Less prominent ischial spines
- Shorter sacrum
- Wider sub-pubic arch
Male Android Pelvis
- Heart-shaped pelvic inlet
- Less broad/wide
- More prominent ischial spines
- Longer sacrum
- More narrow sub-pubic arch
The pelvic girdle has three joints
What are they?
1) Lumbo-sacral joint (L5-S1)
2) Sacroiliac joint
3) Pubic symphysis
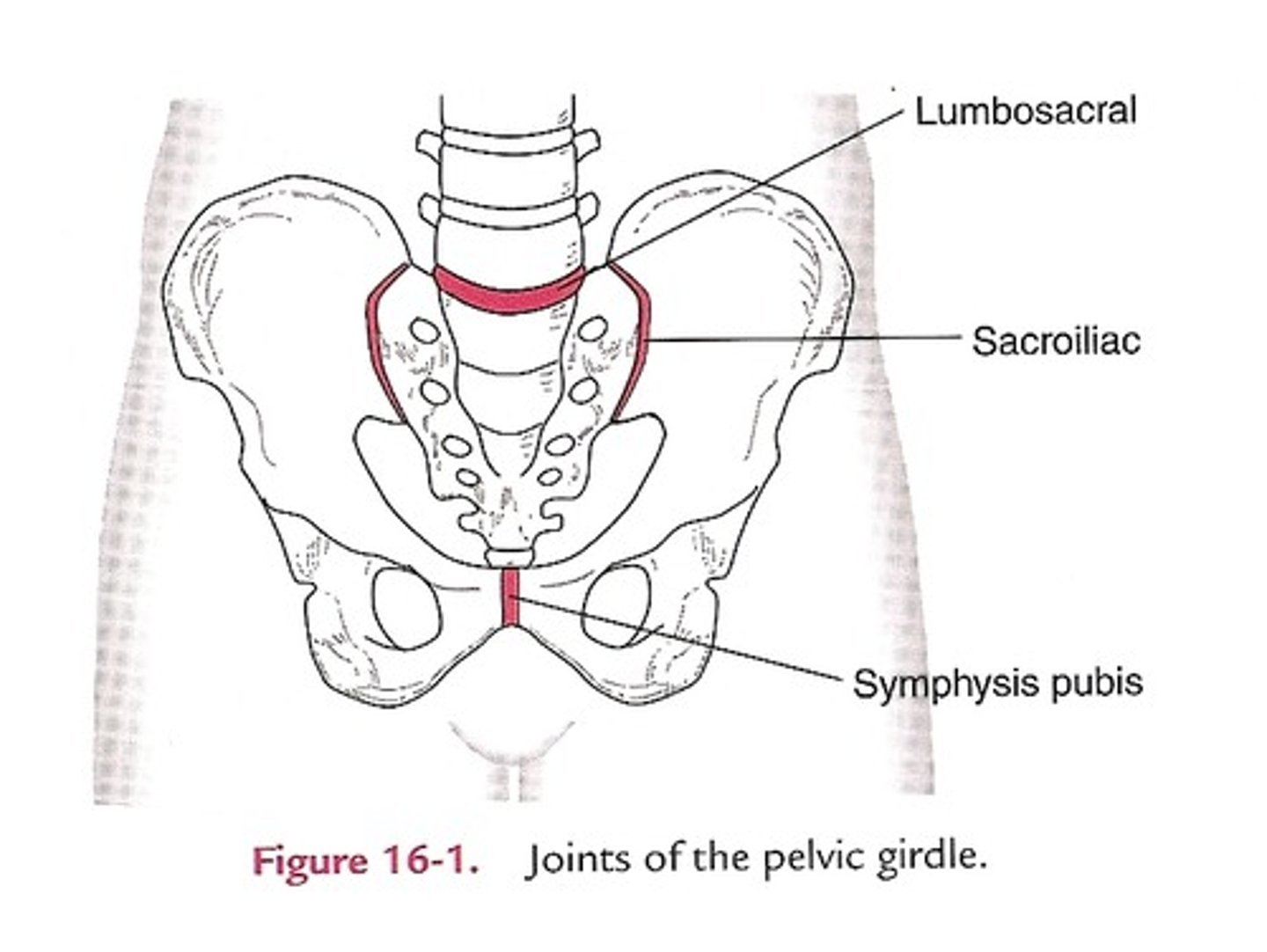
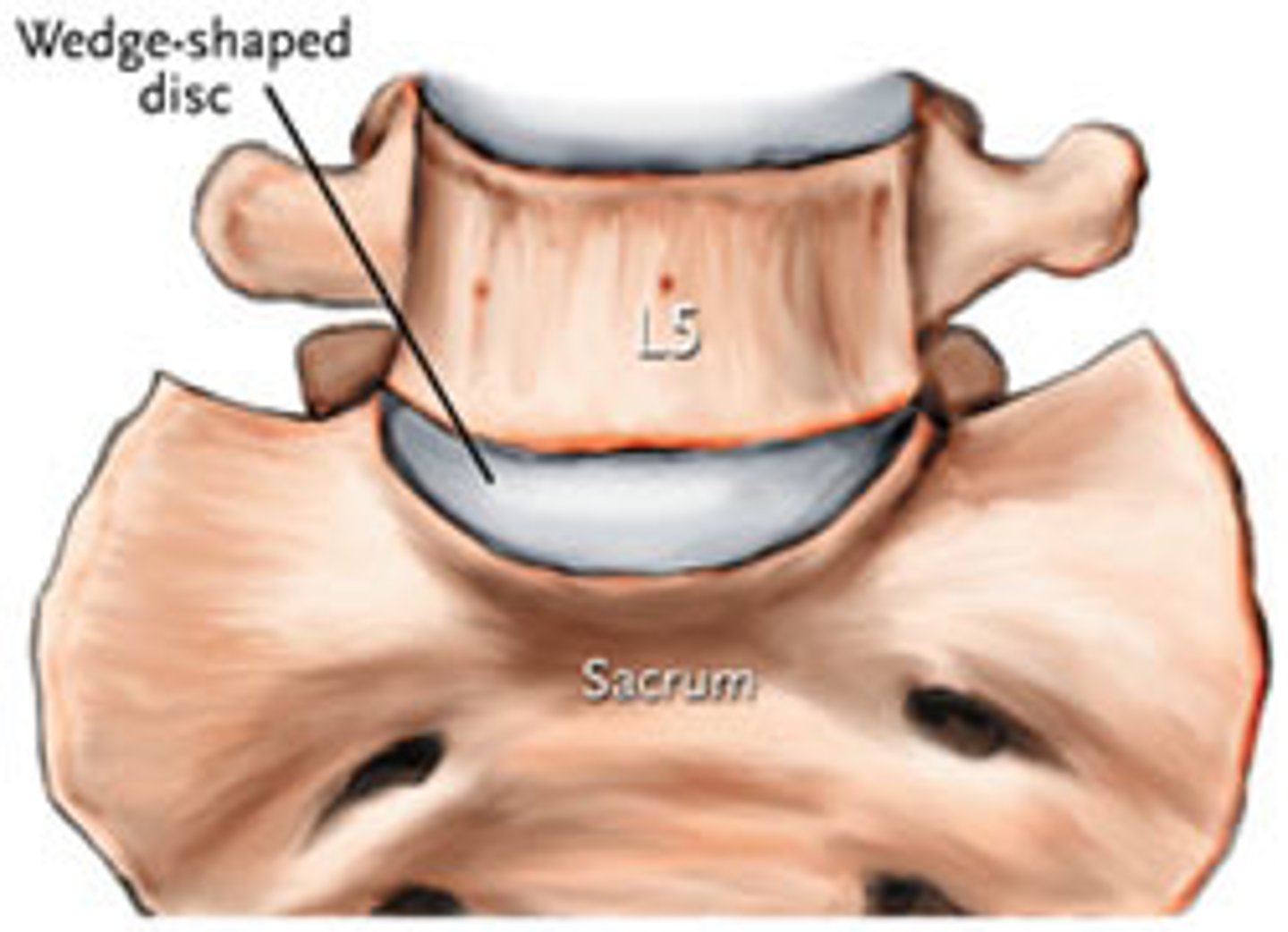
Lumbosacral joint (L5-S1)
Found between 5th lumbar vertebra and sacrum
Allows the pelvis to move relative to the trunk
- Weak joint
- Anterio IV joint is a symphysis
- Posterior facet joints are synovial plane joints
Sacroiliac joint
The joint between the sacrum and the ilium bones of the pelvis
- Synovial plane joint
- Strong ligaments
- Sacral surface covered in hyaline cartilage
- Iliac surface covered in fibrocartilage/syndesmosis
Pubic symphysis joint
Between pubic bones
- Symphysis
- Shows laxity in late pregnancy
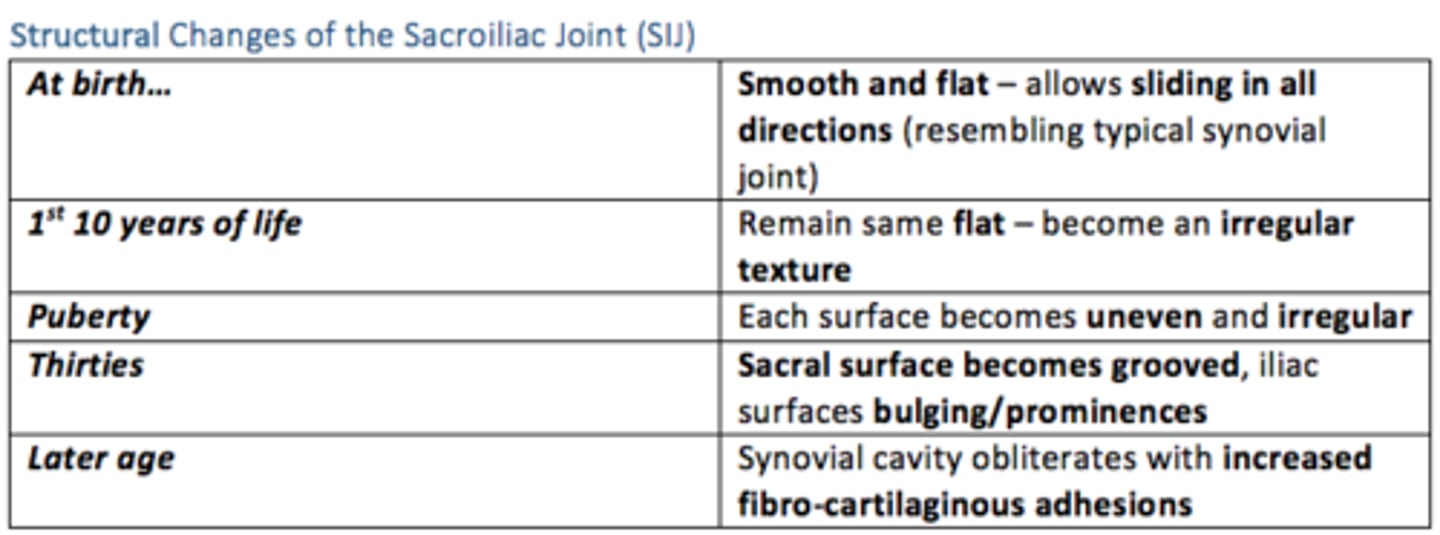
Structural changes of the sacroiliac joint (SIJ) over time
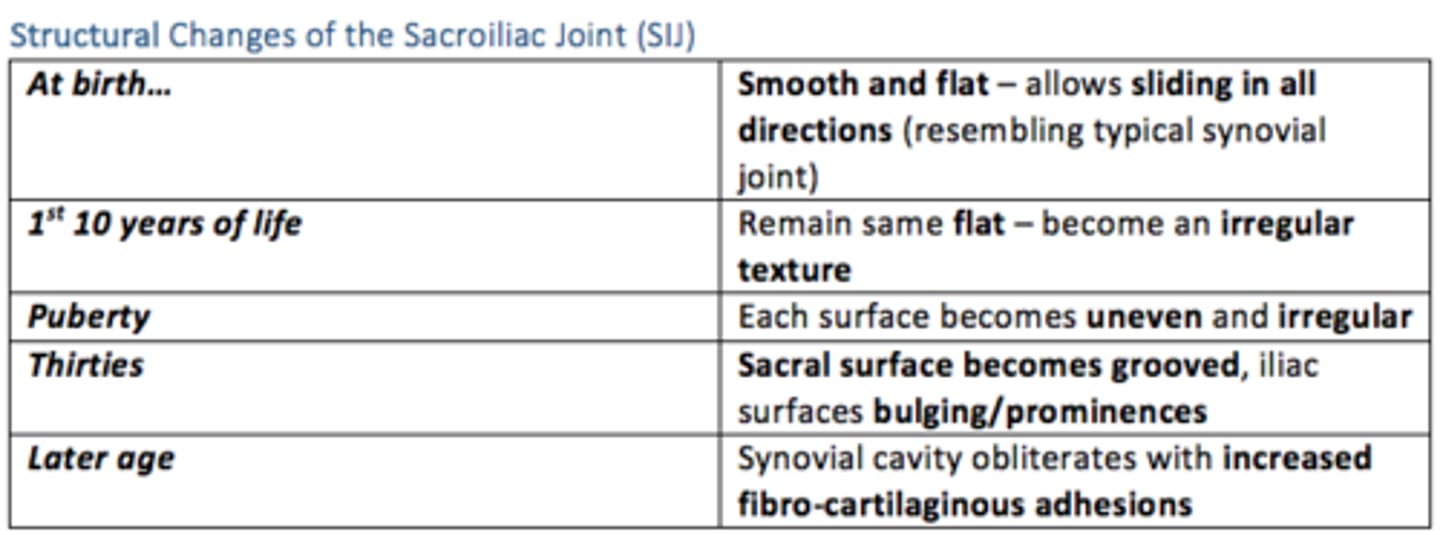
Pubic symphysis diastasis
Occurs after traumatic delivery or during pregnancy
Separation of the joint, without fracture
Presents:
Radiating suprapubic pain that is exacerbated by ambulation or weight bearing
ex: difficulty walking the day after delivery
Tx: supportive care
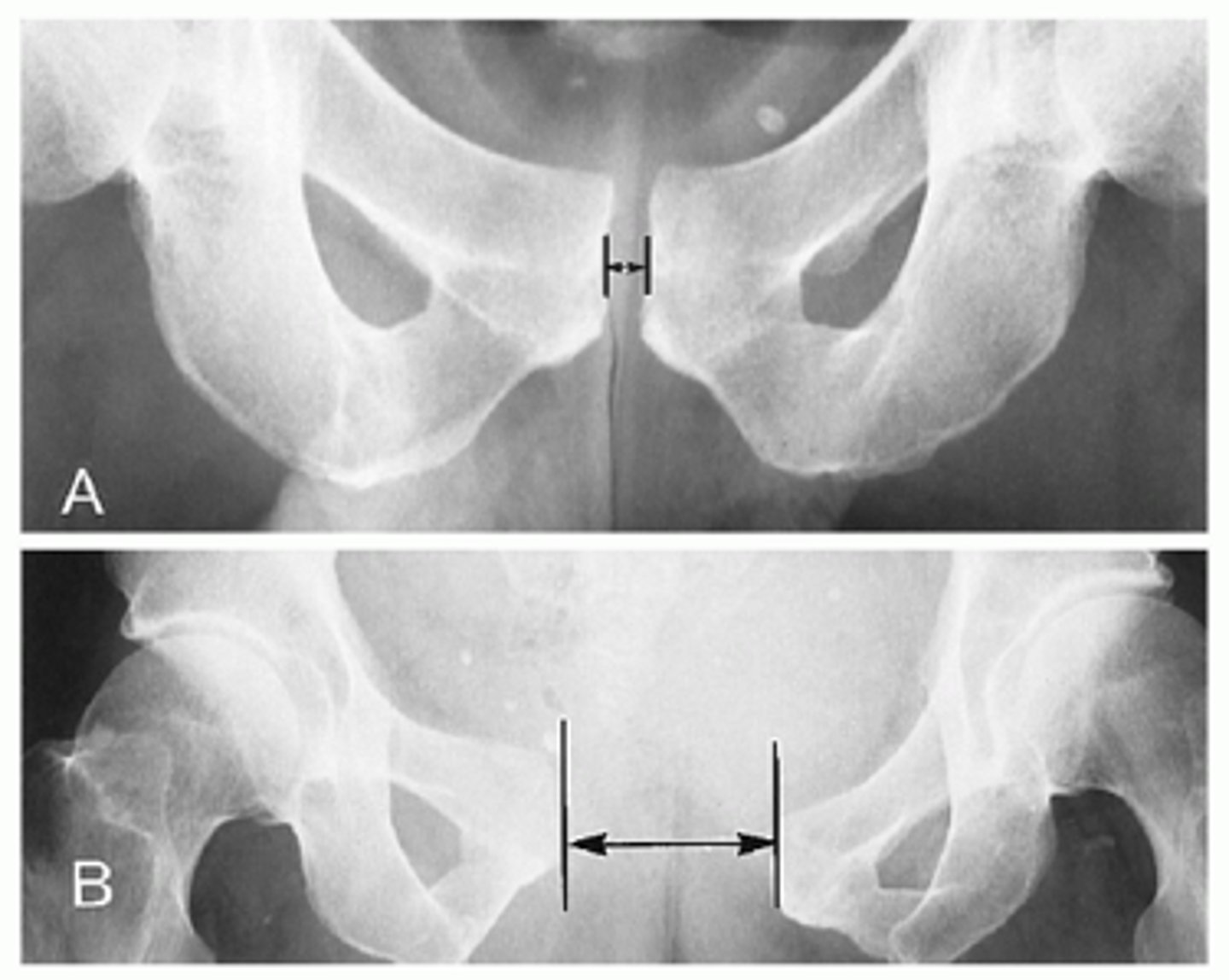
Pelvic fractures can be variable. They can be ___ or ___, ___ or ___ and they often occur on both sides of the pelvic ring (bilaterally). They are usually caused by high-energy major trauma but may also be caused by deficiency (e.g., osteoporosis) or pathology.
Pelvic fractures can be variable. They can be stable or unstable, simple or complex and they often occur on both sides of the pelvic ring (bilaterally). They are usually caused by high-energy major trauma but may also be caused by deficiency (e.g., osteoporosis) or pathology.
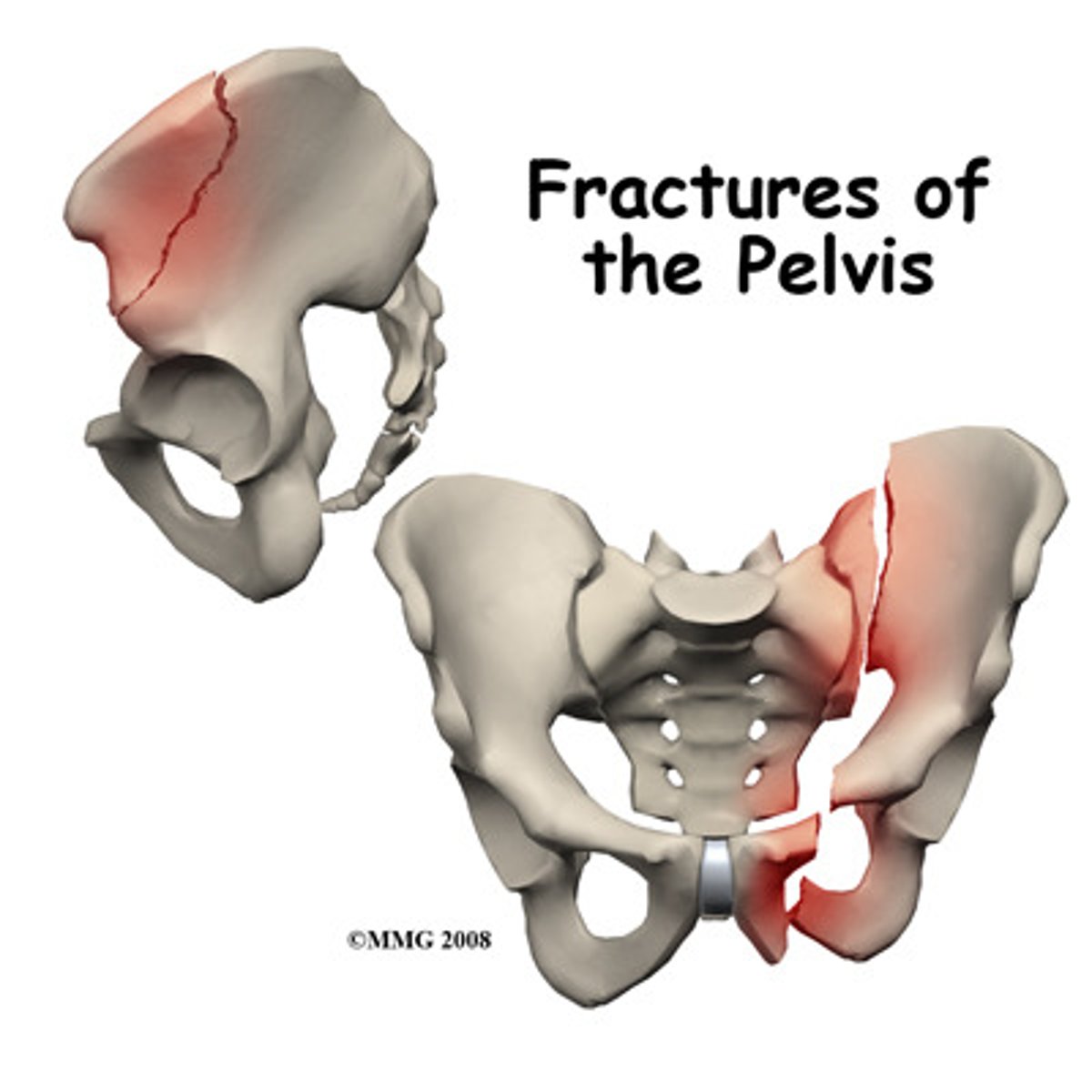
What type of joint is the hip?
Ball and socket joint (synovial)
This joint is formed by the head of the femur and the cup-shaped acetabulum of the pelvic bone.
Name three ways in which stability of the hip joint is achieved
1) Deep insertion of femoral head into acetabulum
2) Dense joint capsule
3) Strong ligaments/muscles that pass over the joint to insert a distance below the head of the femur.
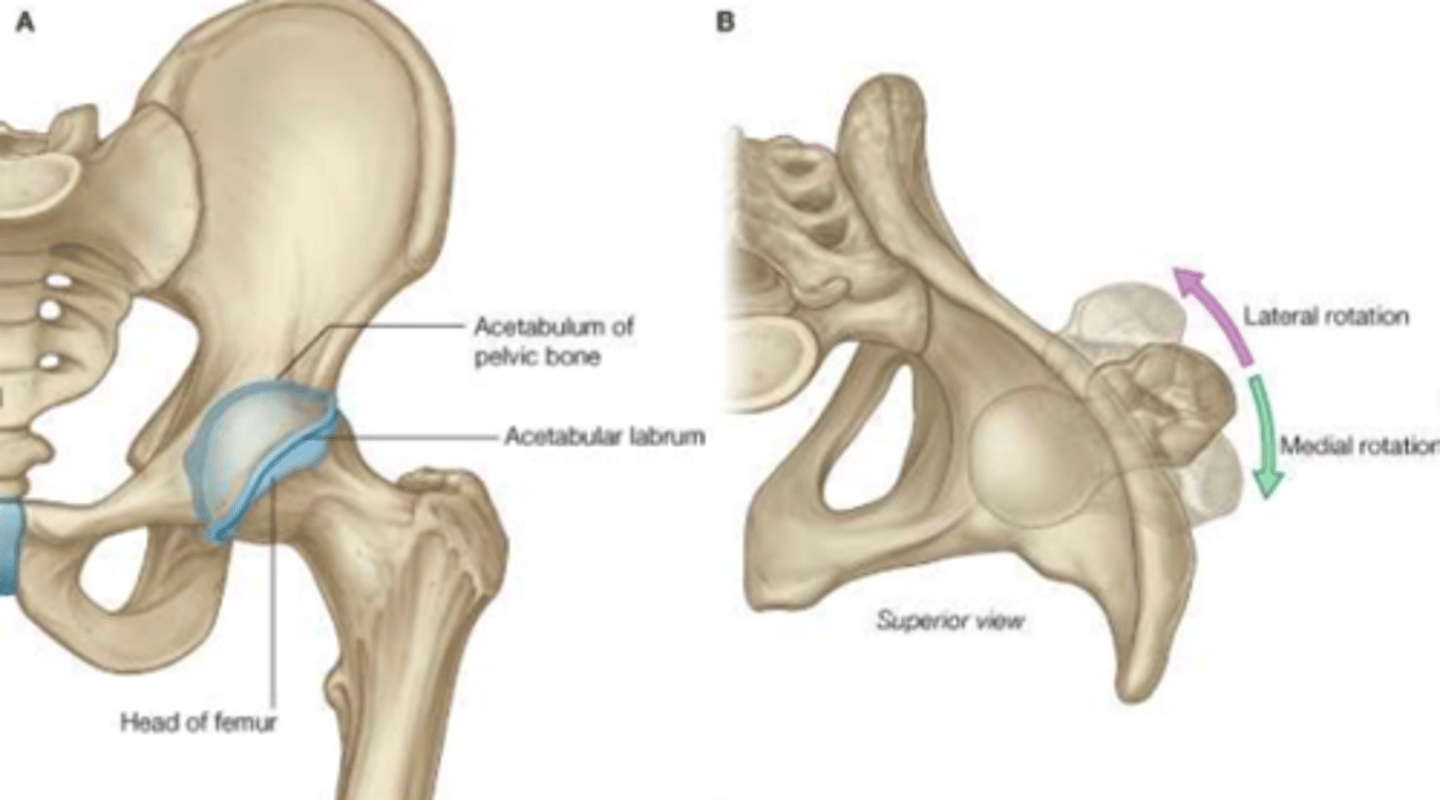
Femur
Found in the thigh
- Largest, longest & strongest bone in body
- Receives lots of stress
- Proximally: articulates with acetabulum
- Distally: articulates with tibia/patella
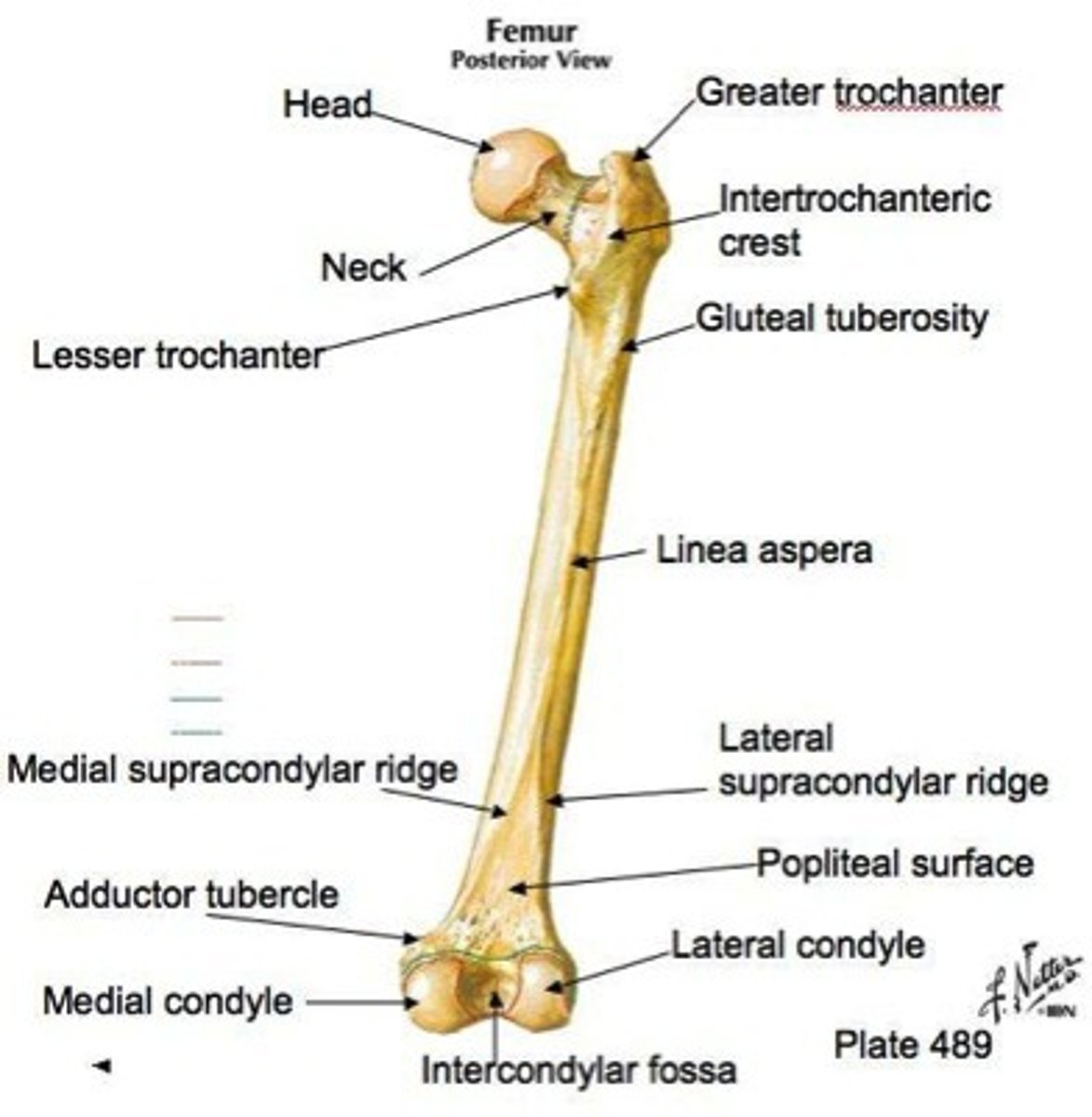
Acetabular labrum
Tough incomplete fibro-cartilaginous ring that surrounds the acetabulum of the hip
- Deepens the acetabulum
- Increases stability
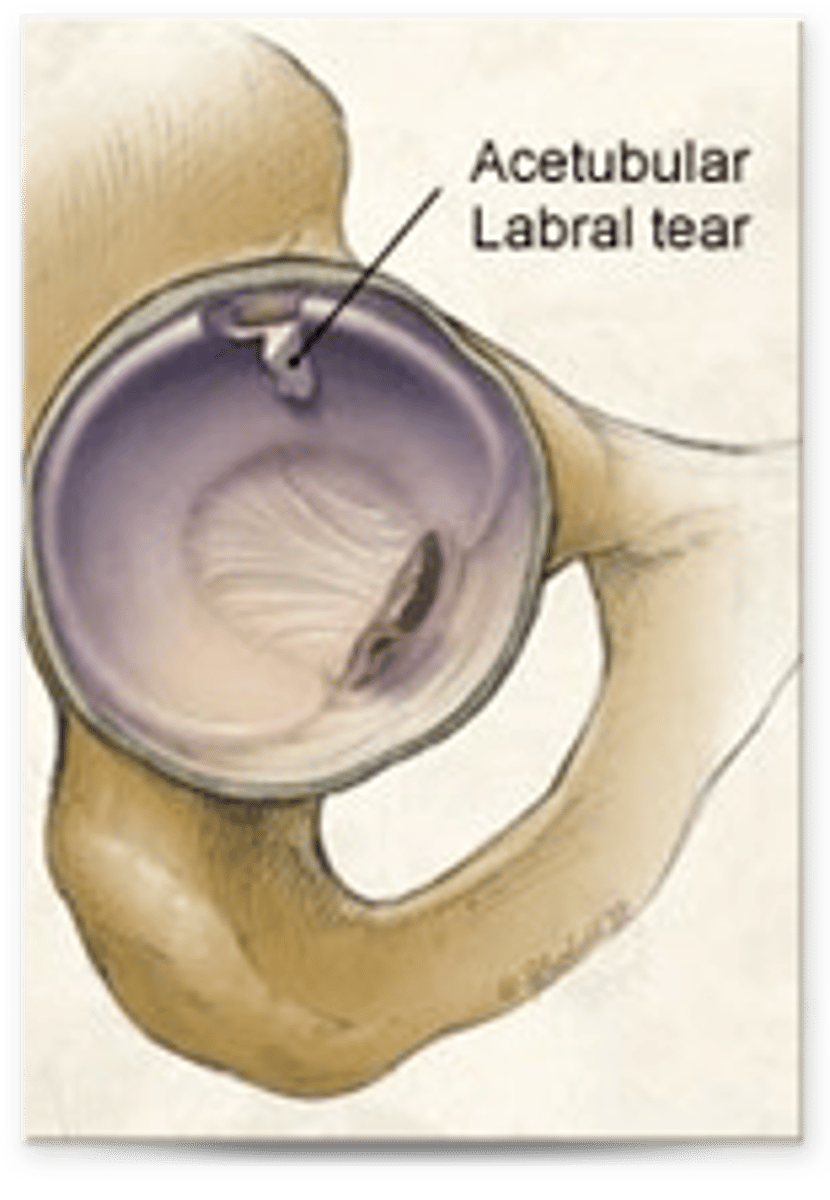
What type of injury is the acetabular labrum prone to?
Labral tears
What are the three strong ligaments found at the hip capsule and what do they prevent?
1) Iliofemoral ligament = prevent hyperextension
2) Ischiofemoral ligament = prevent hyperextension
3) Pubofemoral ligament = prevent hyperabduction
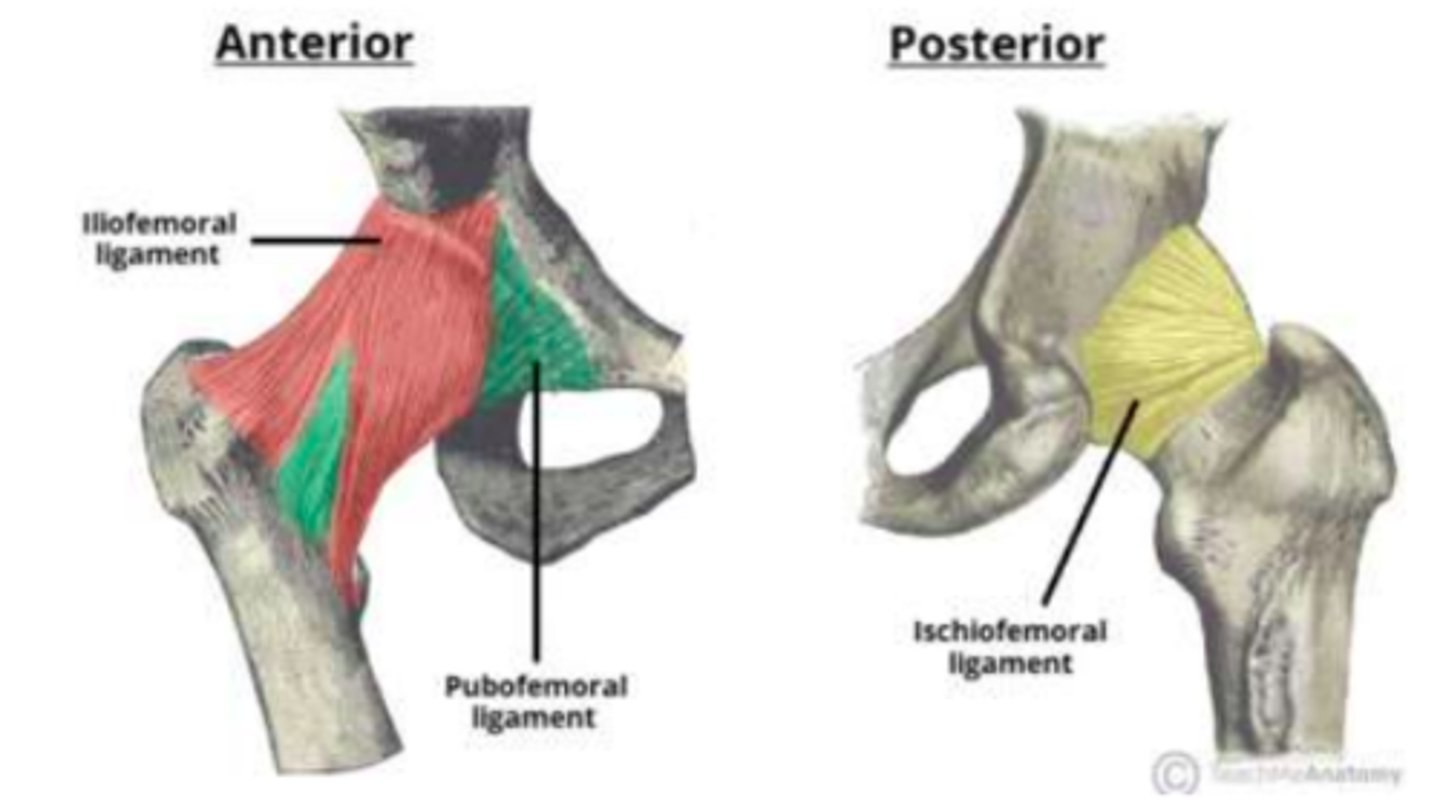
Which ligament of the hip is the strongest?
Iliofemoral ligament is the strongest. It is located anterior to the hip-joint and is triangular-shaped.
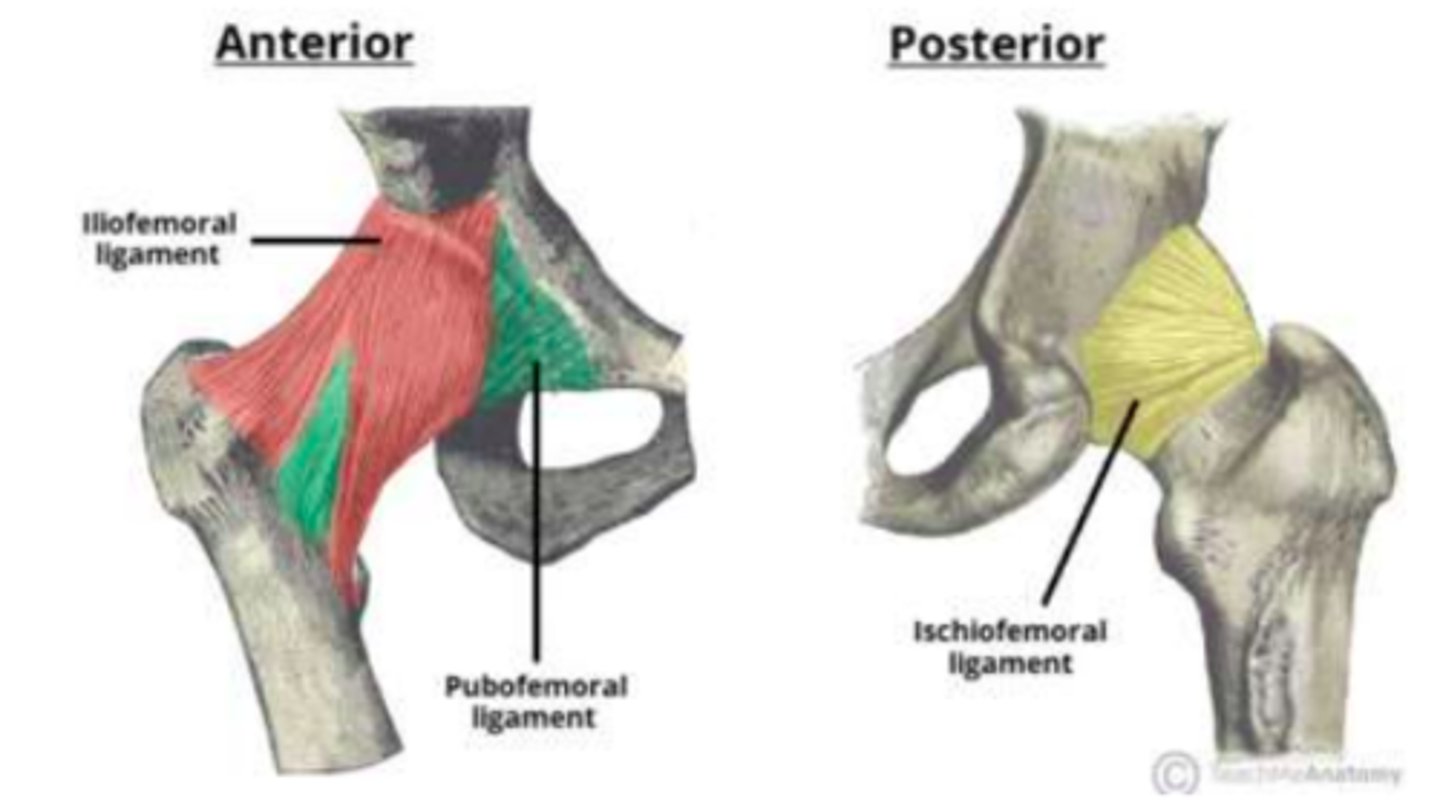
Intracapsular ligament of the hip
Ligament of the head of the femur
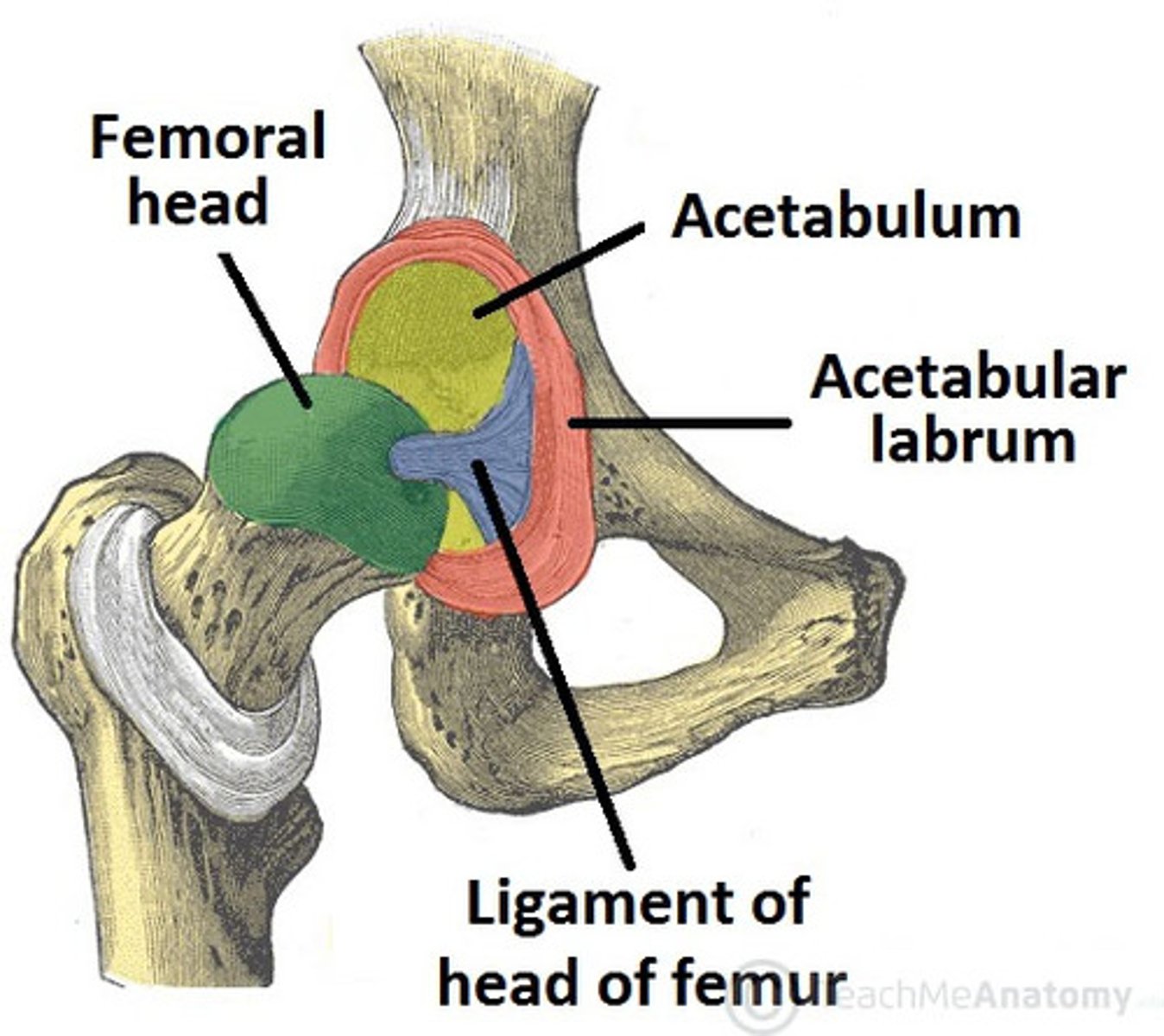
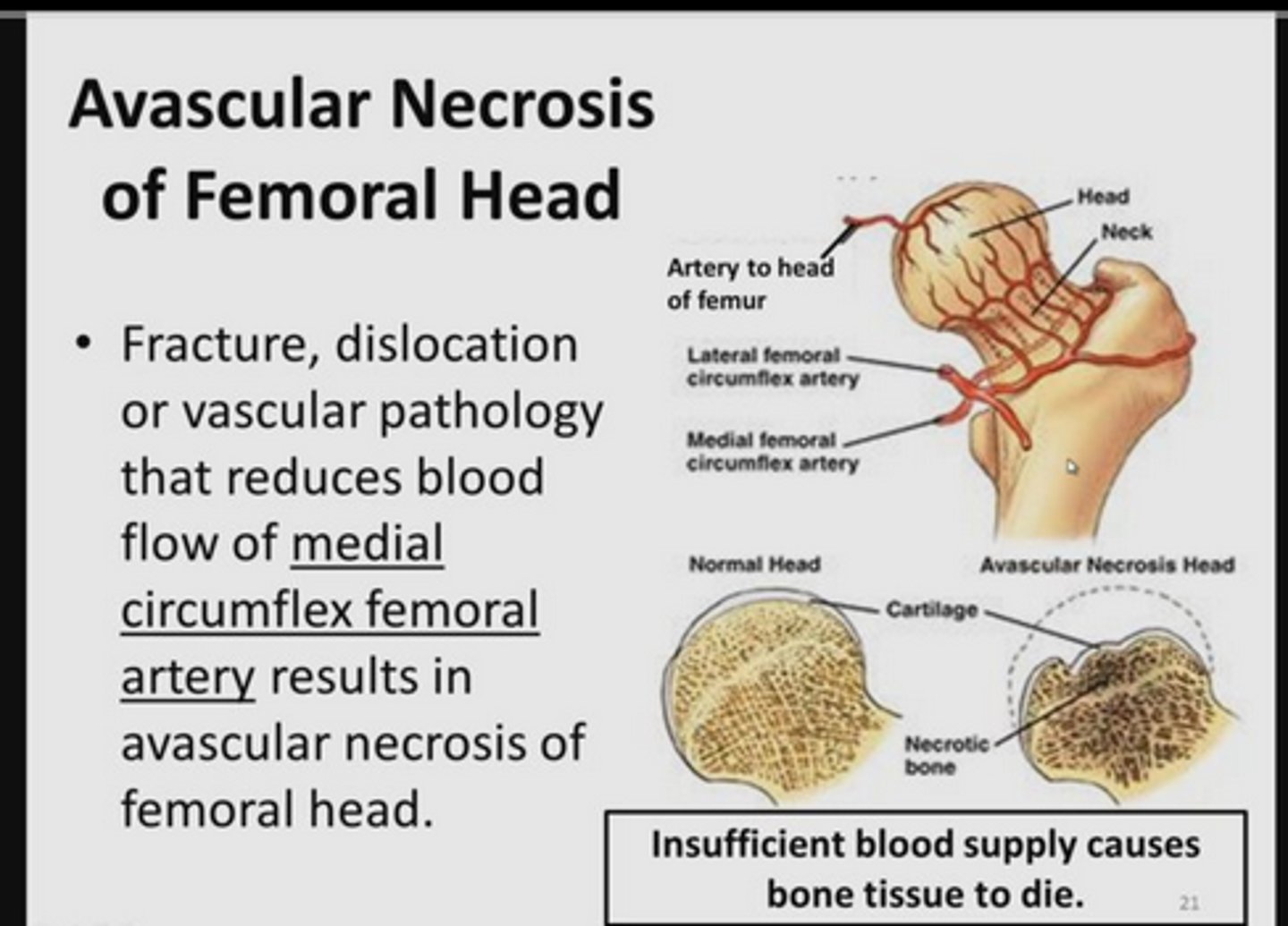
Blood supply to the femoral head
Femoral head = branch of obturator artery
Femoral neck = deep femoral (profundal-femoris) artery and its branches (the medial and lateral circumflex arteries)
Additional supply = branches of obturator artery and superior and inferior gluteal arteries.
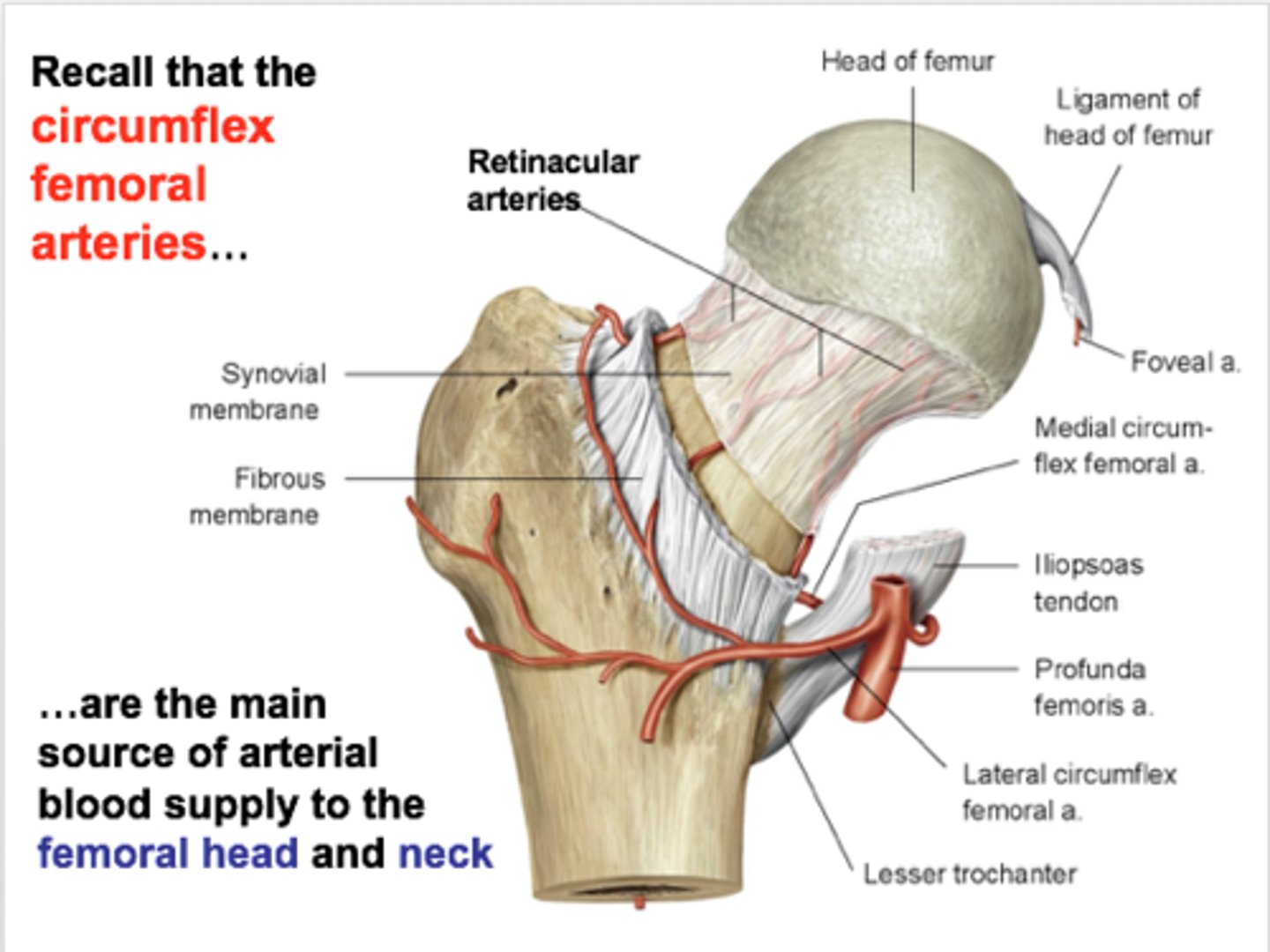
The articular branches of the vessels in the hip form a network around the joint. This is known as the ___ ___
Trochanteric anastamosis
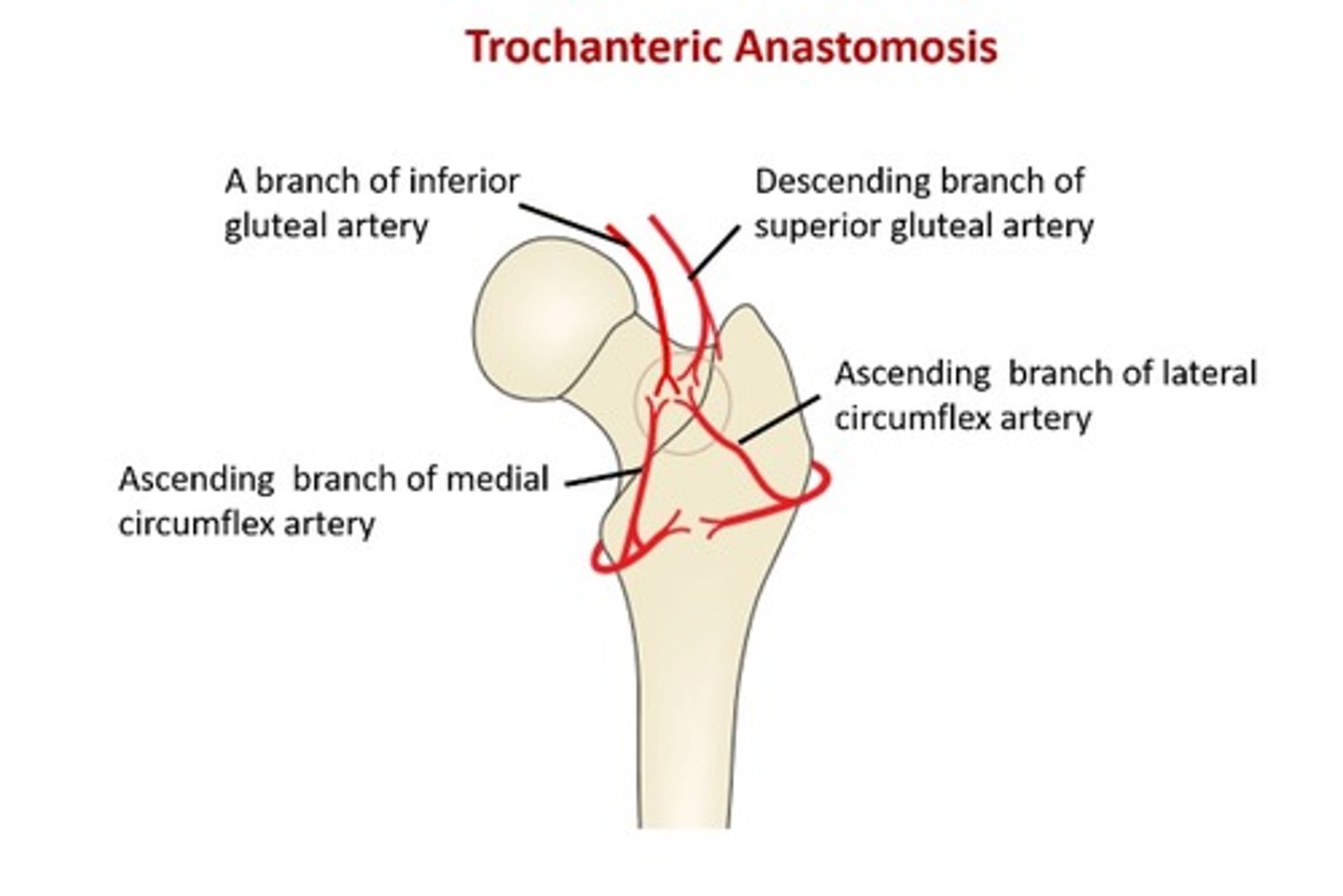
An intracapsular fracture of the hip can lead to a condition known as ___ ___
An intracapsular fracture of the hip can lead to a condition known as avascular necrosis - this is because an intracapsular fracture may cut off the blood supply to the head of the femur
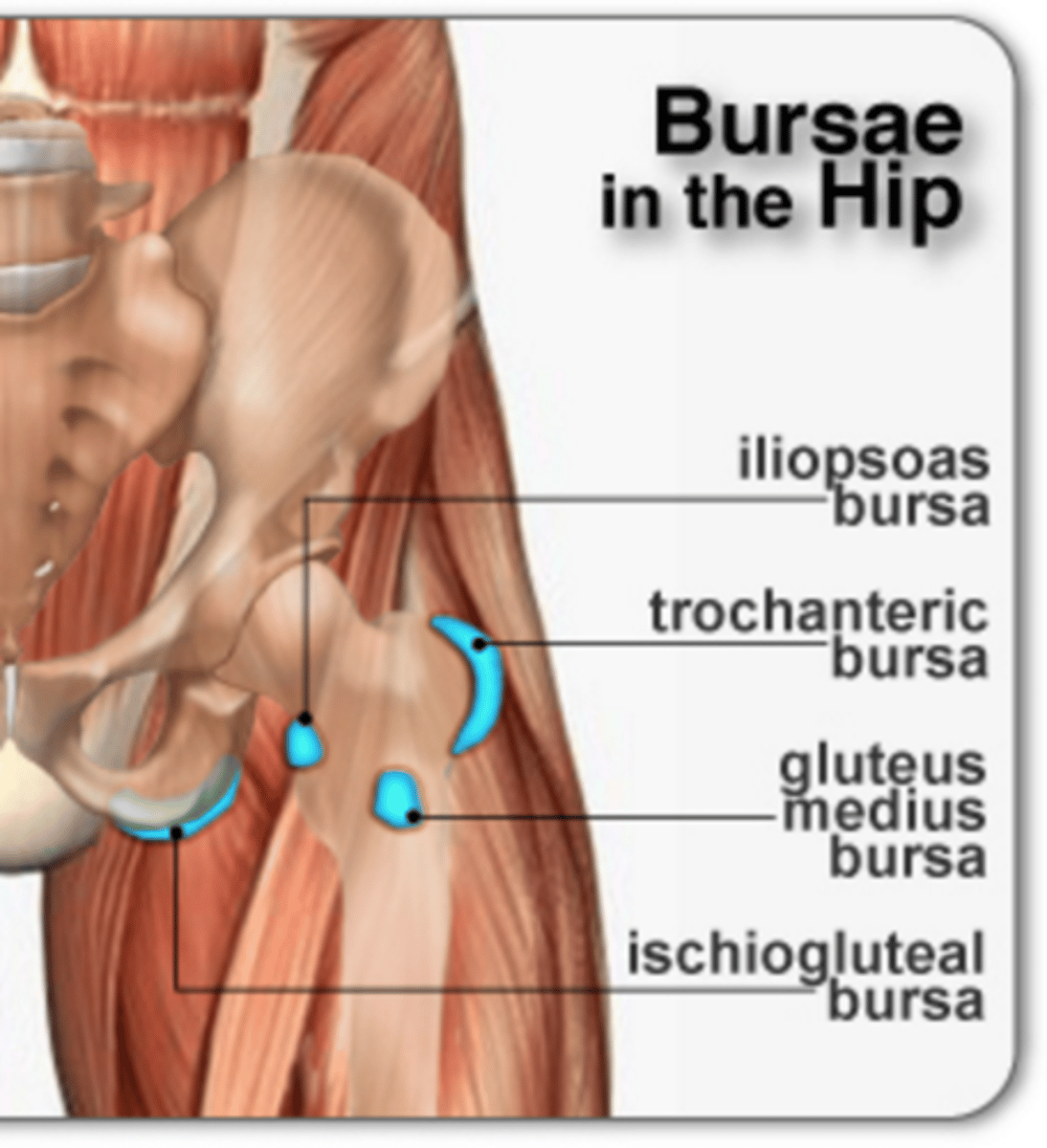
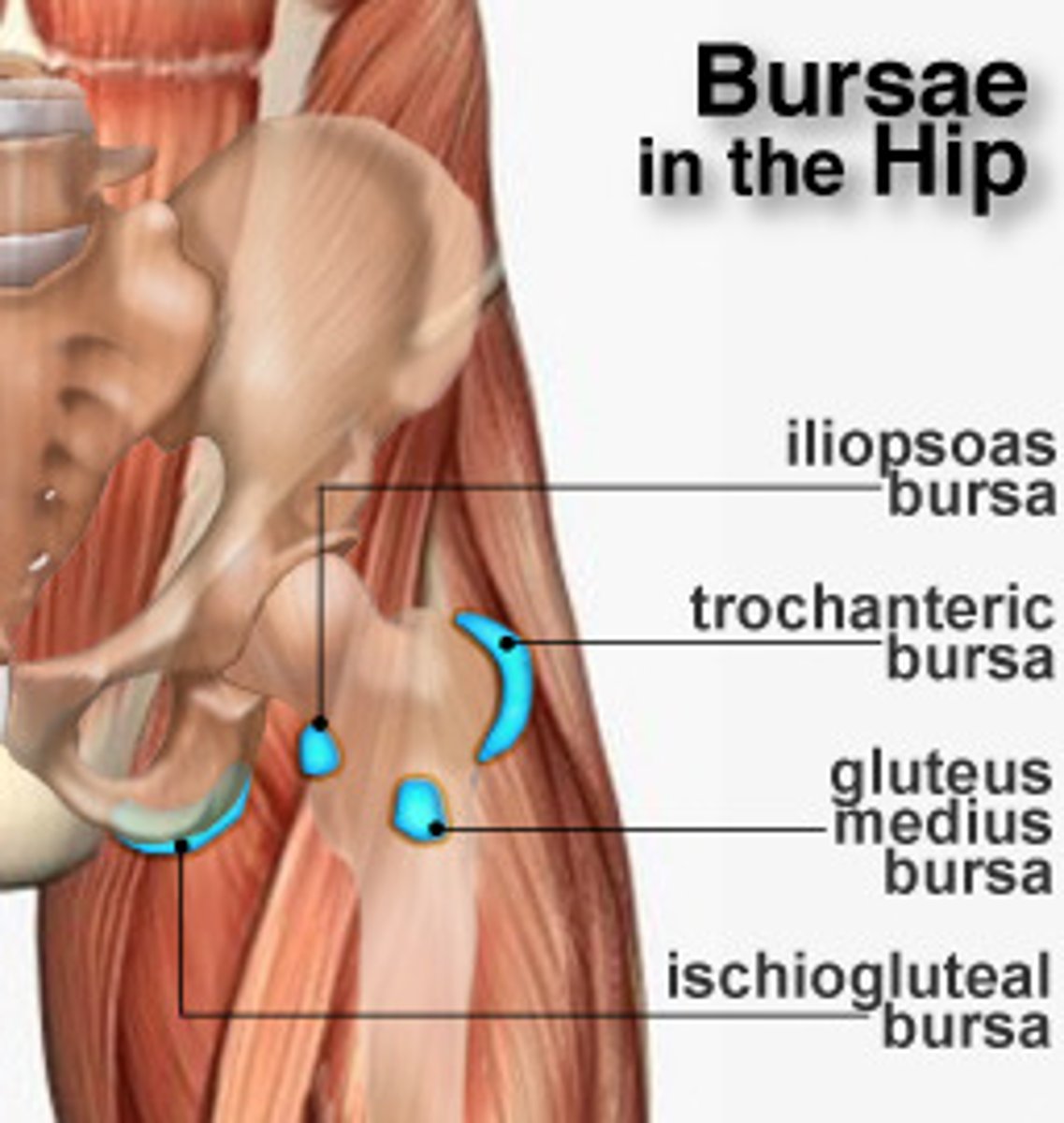
The hip has four bursae. What are they?
Trochanteric bursa
Iliopsoas bursa
Gluteus medius bursa
Ischiogluteal bursa
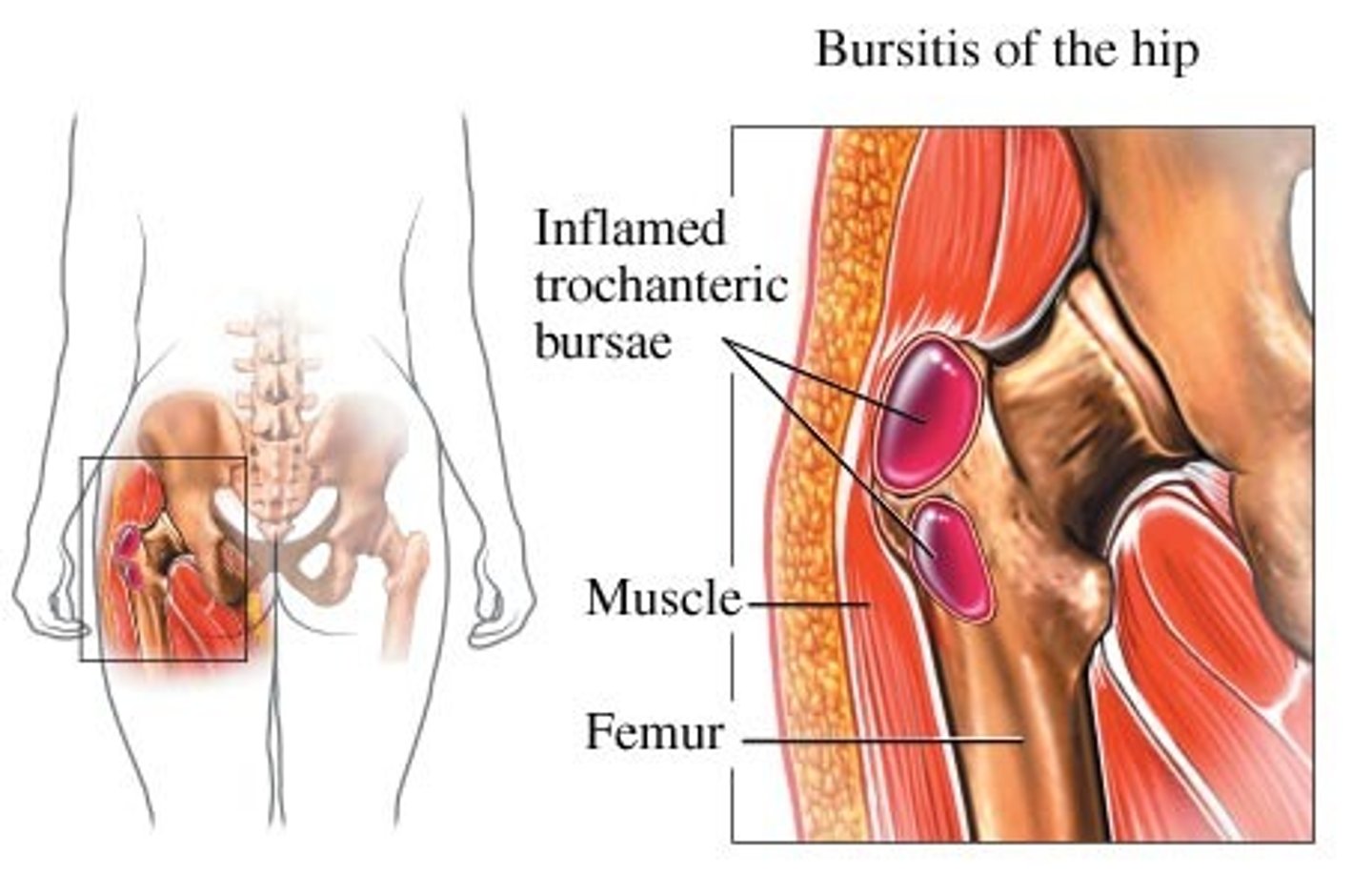
Condition that is caused by inflammation of trochanteric bursa
Trochanteric bursitis
Common cause of hip pain in middle-aged women
An ischiogluteal bursa can become inflamed due to...
Excessive friction from riding a bicycle or a horse
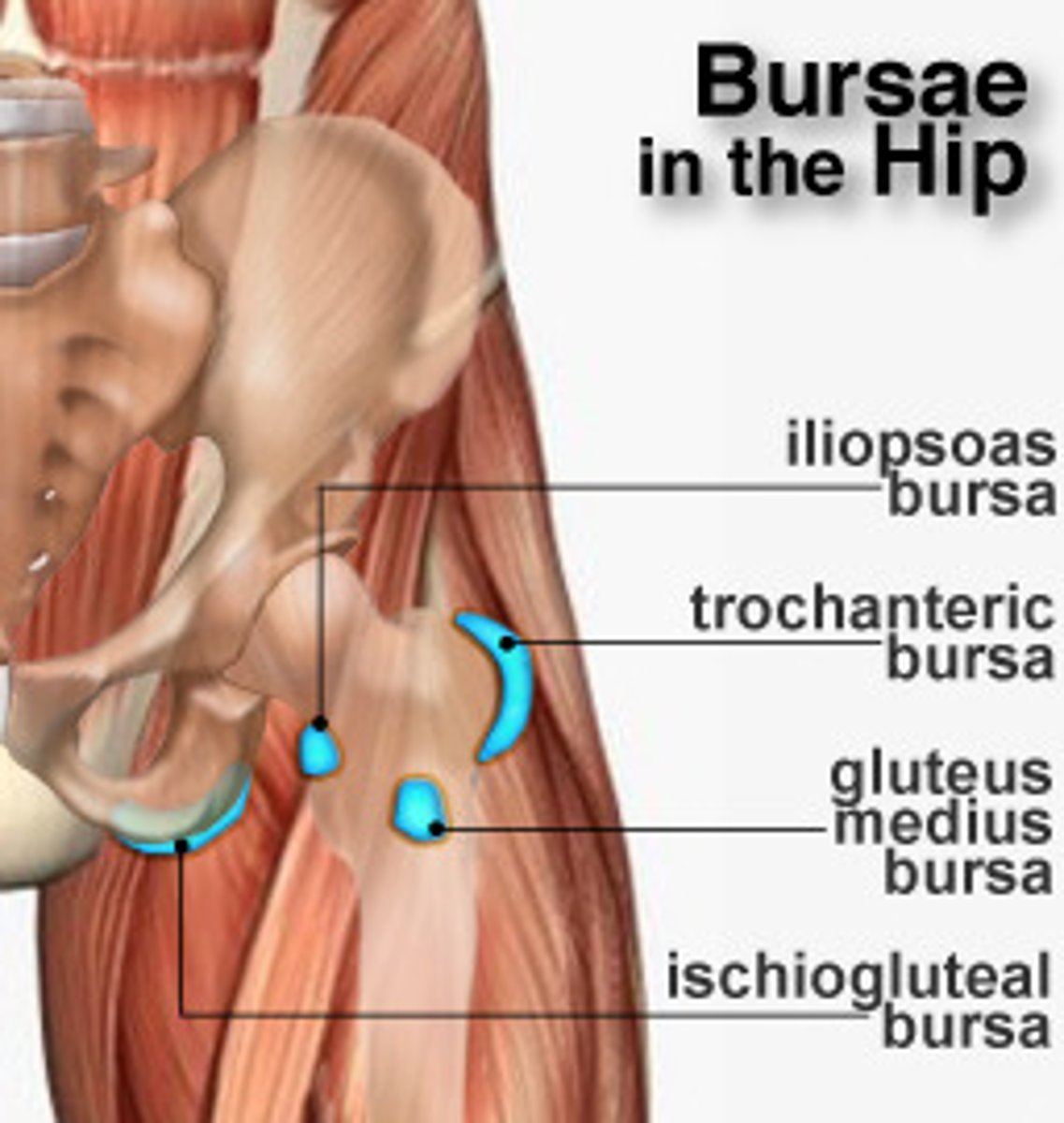
Largest bursa of the hip
Trochanteric bursa
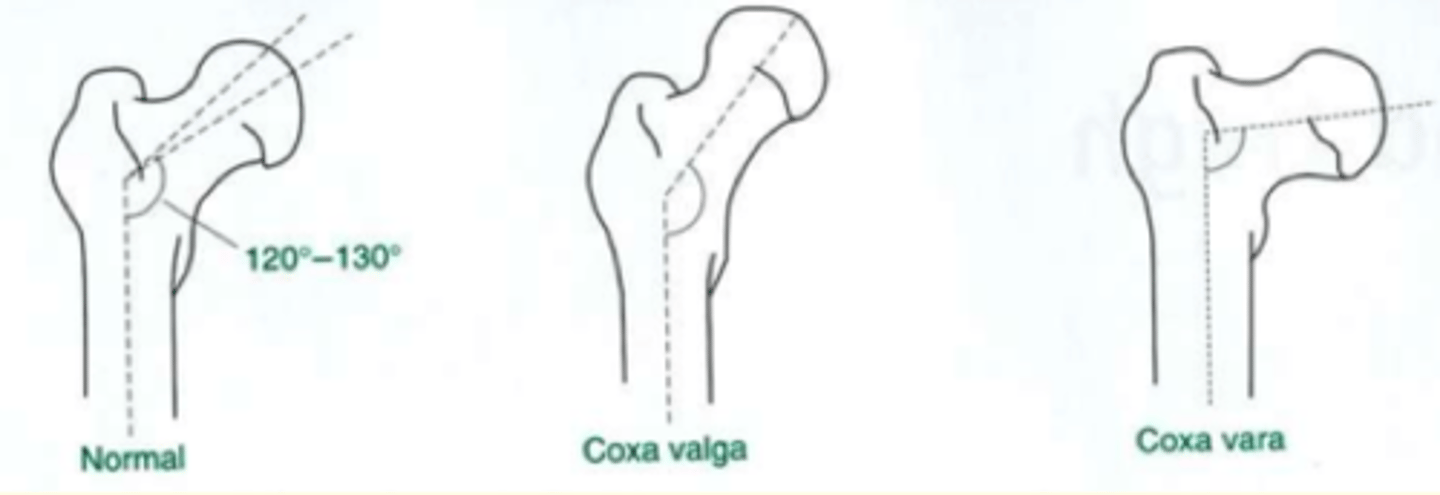
Deformity of the joints of the hip
1) Valgus
2) Varus
Valgus deformity of the hip
Distal part of the bone is directed away from the midline
In the hip this is called the Coxa Valga
The angle between the femoral neck & shaft is larger than normal
Knock-kneed
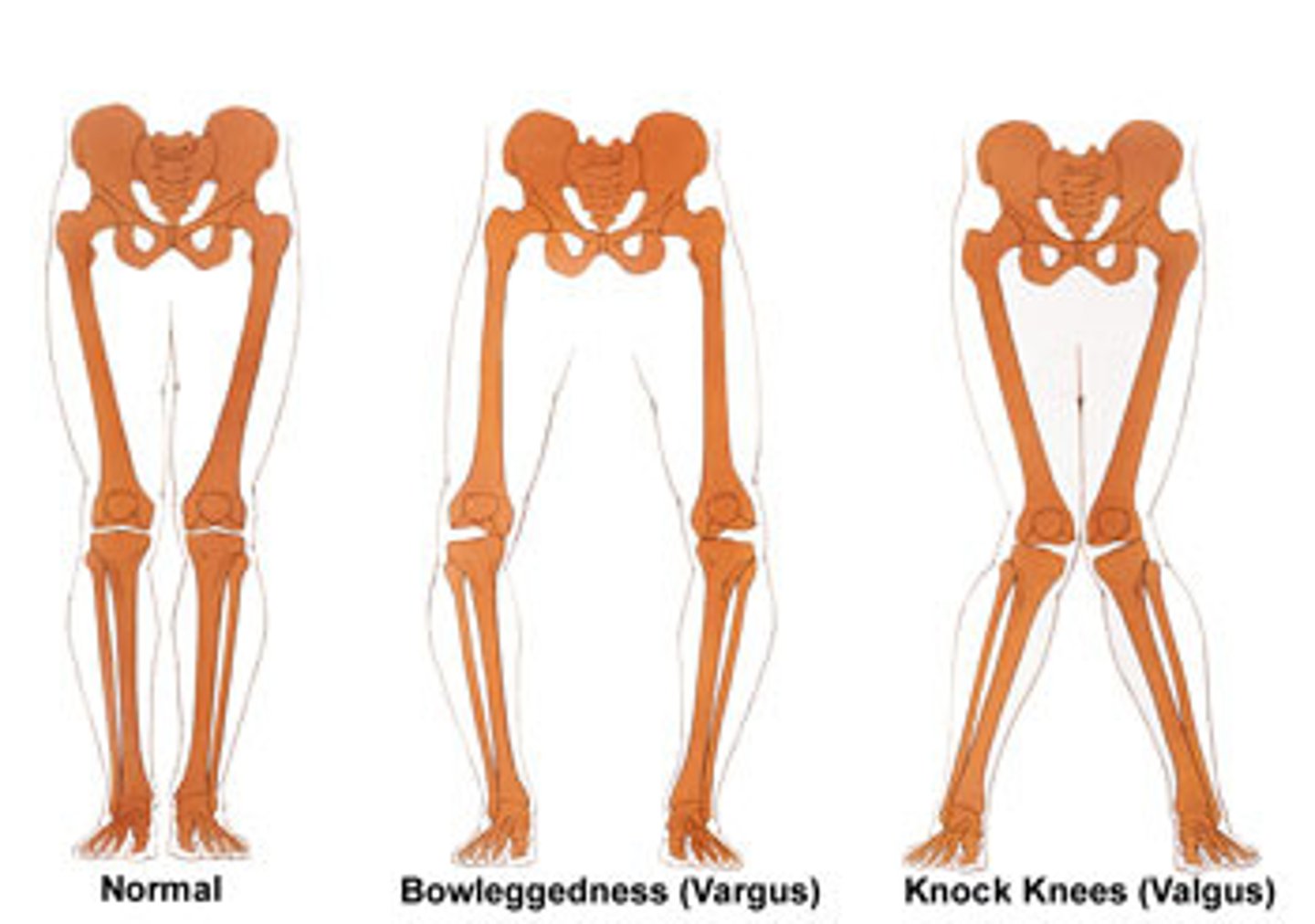
Varus (think: rustic bow) deformity of the hip
Distal part of the bone is directed towards the midline
In the hip this is called the Coxa Vara
The angle between the femoral neck & shaft is smaller than normal
Bow-legged
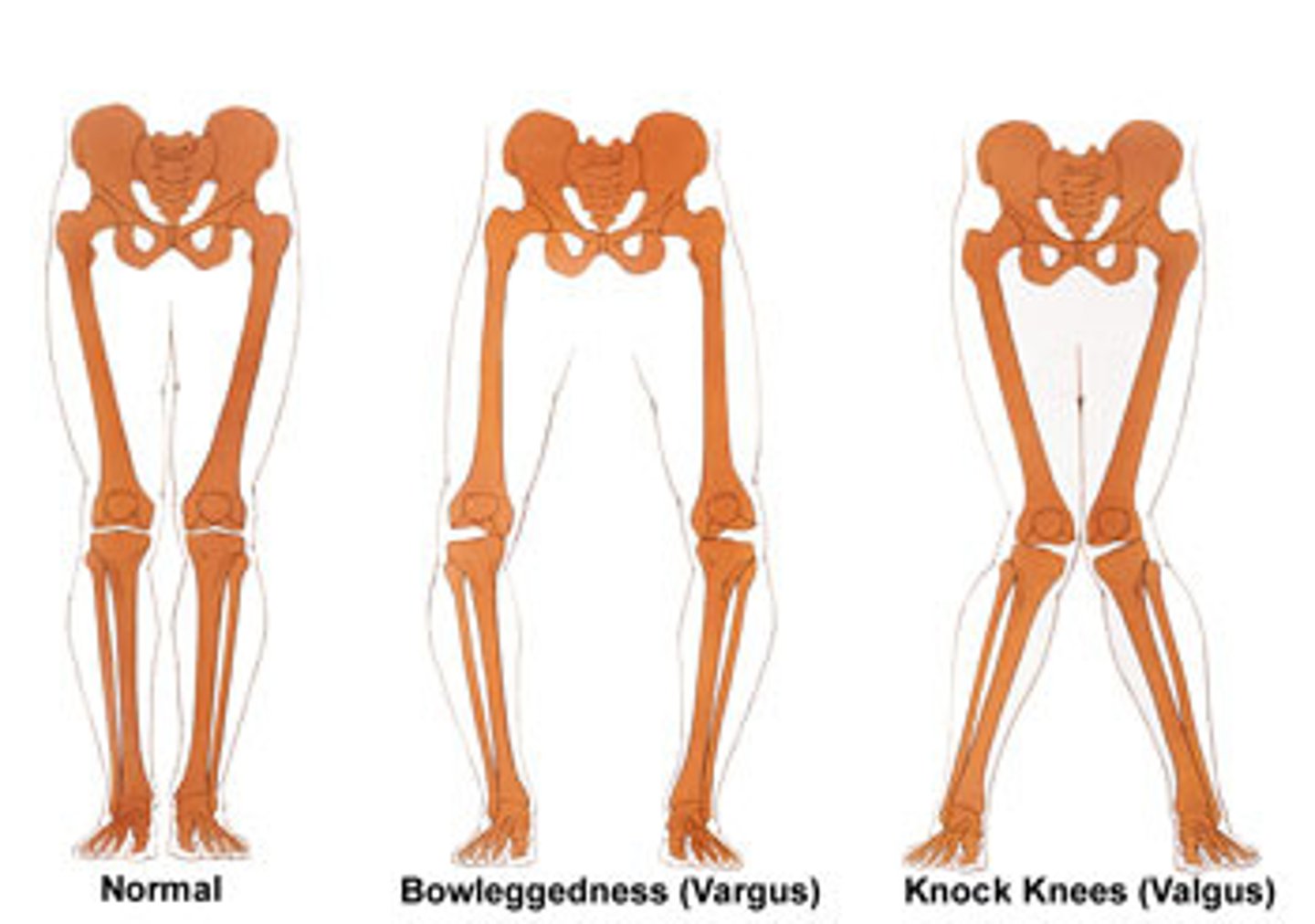
Normal angle between the femoral neck & shaft in a healthy/normal person is...
120-130 degrees
Hip movements are...
Flexion/extension
Abduction/adduction
Medial (internal)/lateral (external) rotation
Circumduction
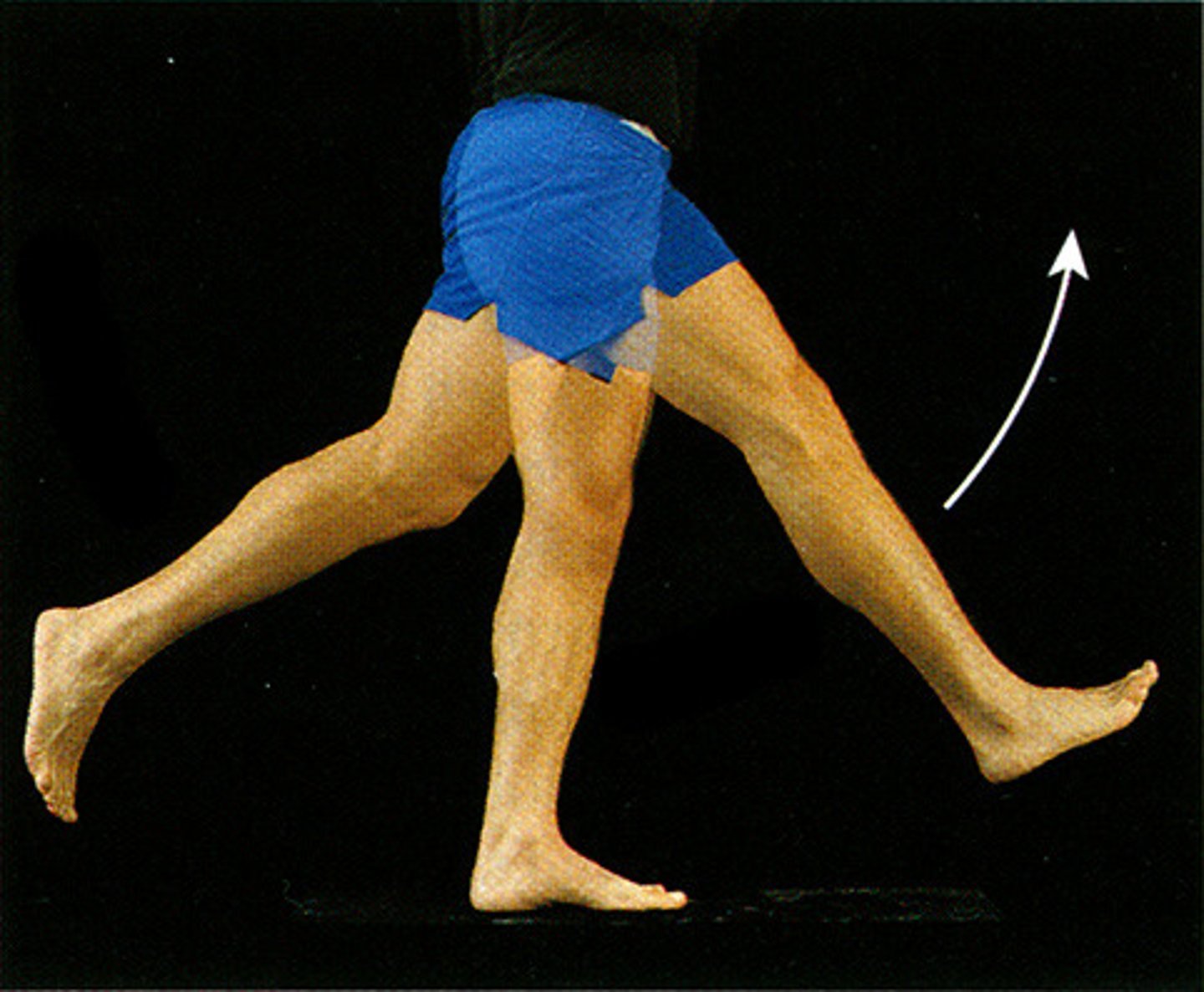
Hip movements
What movement is shown here?
Flexion of hip
Hip movements
What movement is shown here?
Extension of hip
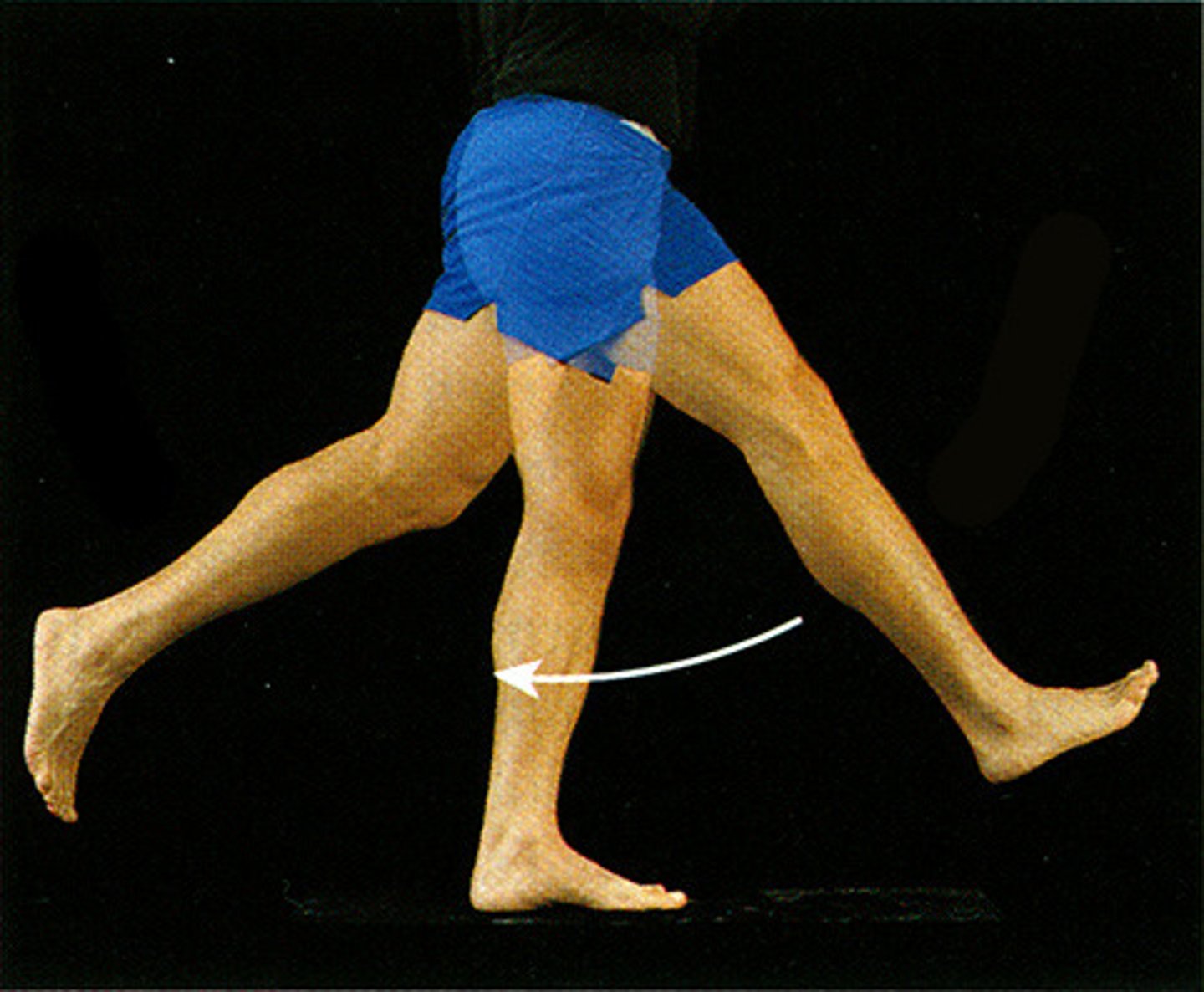
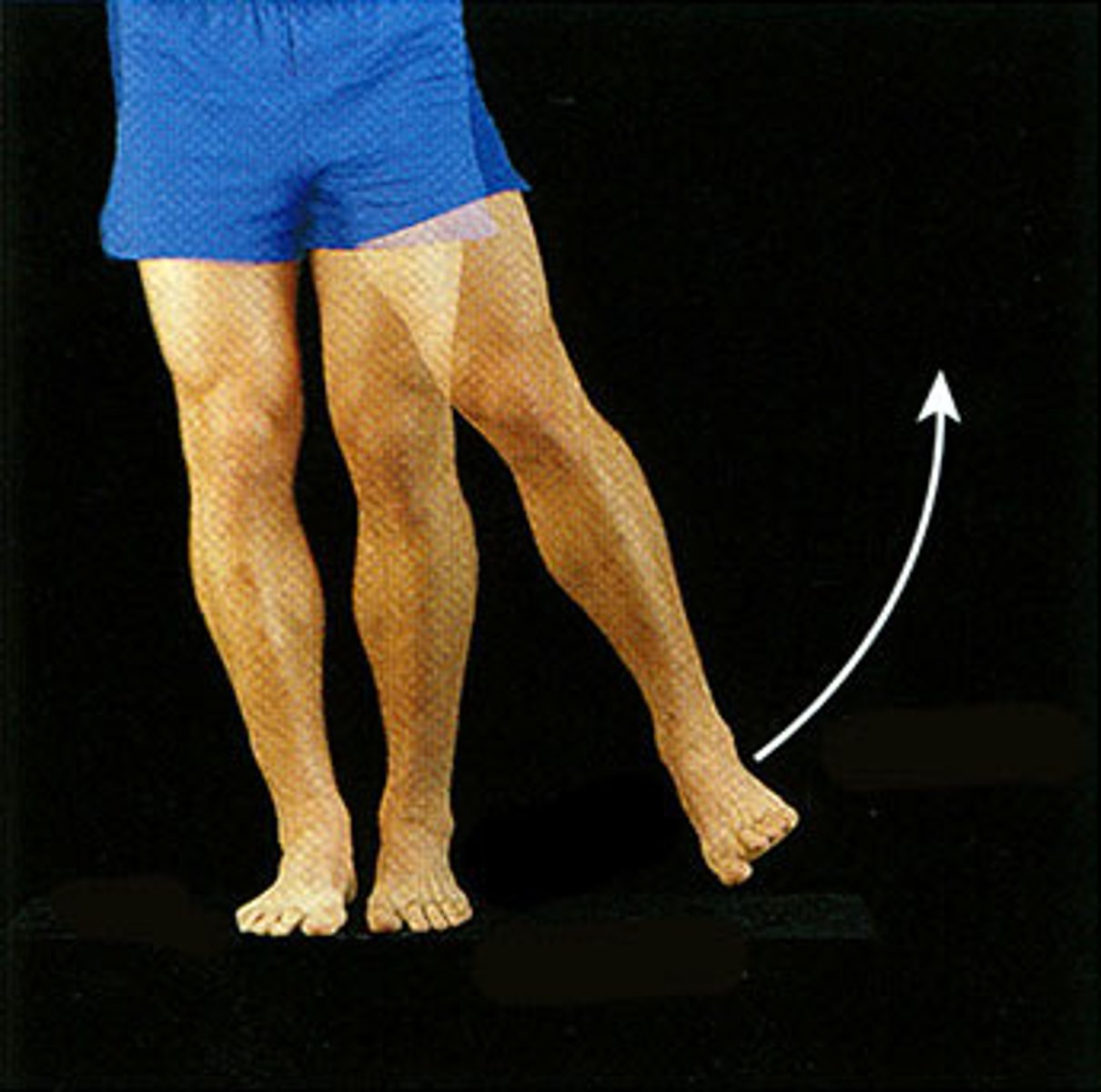
Hip movements
What movement is shown here?
Abduction of hip
Hip movements
What movement is shown here?
Adduction of hip
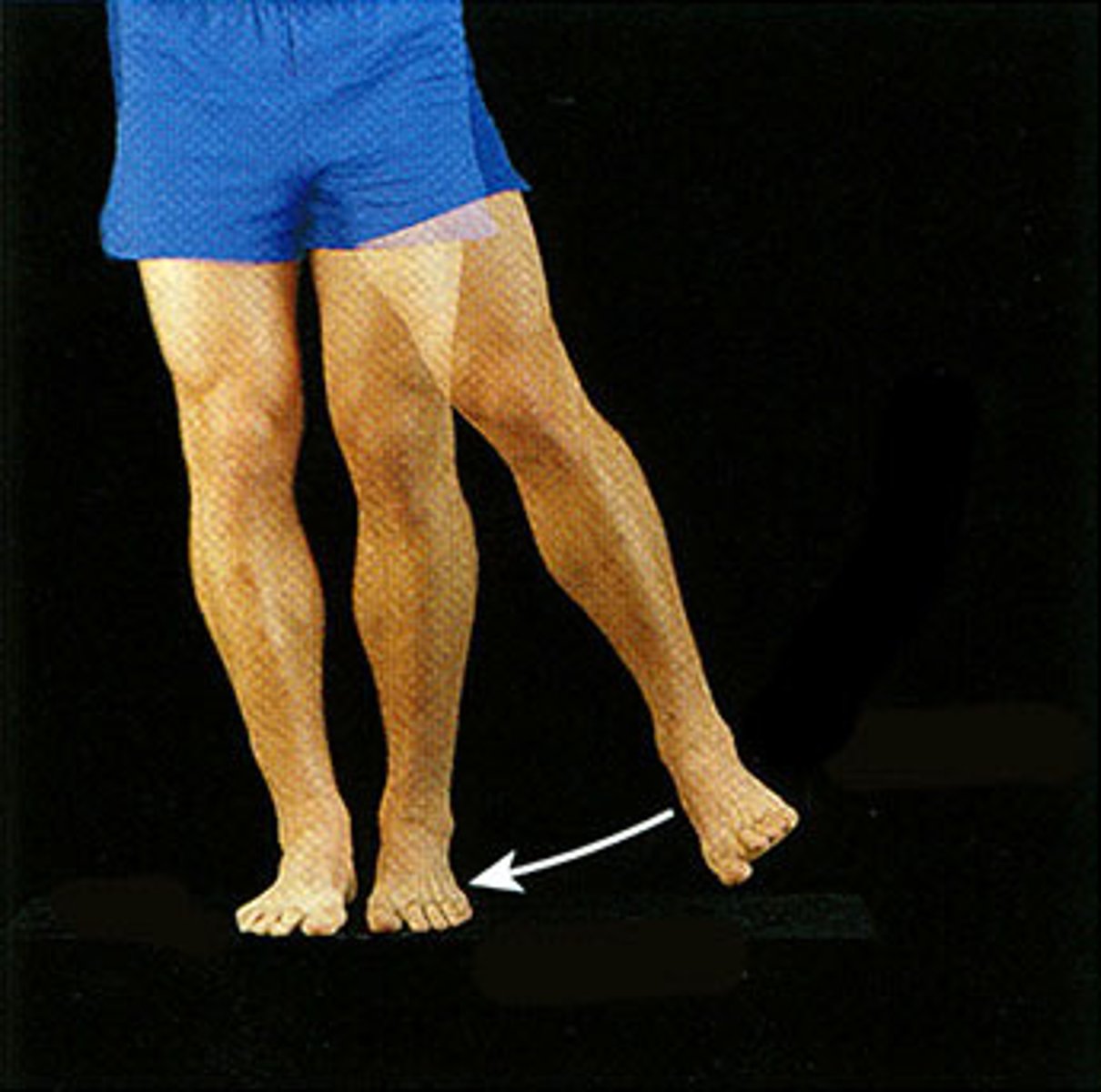
Hip movements
What movement is shown here?
Internal (medial) rotation of hip
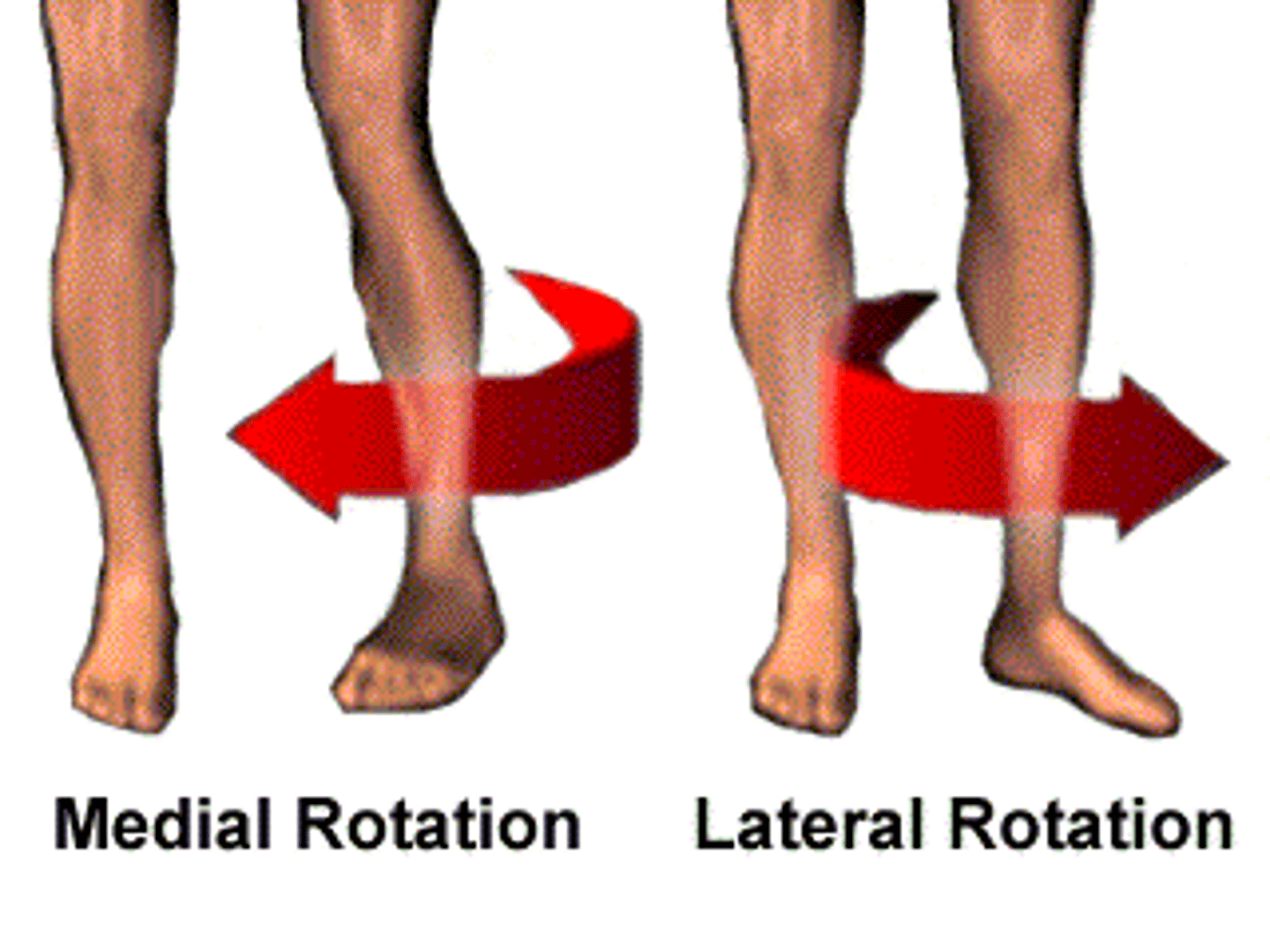
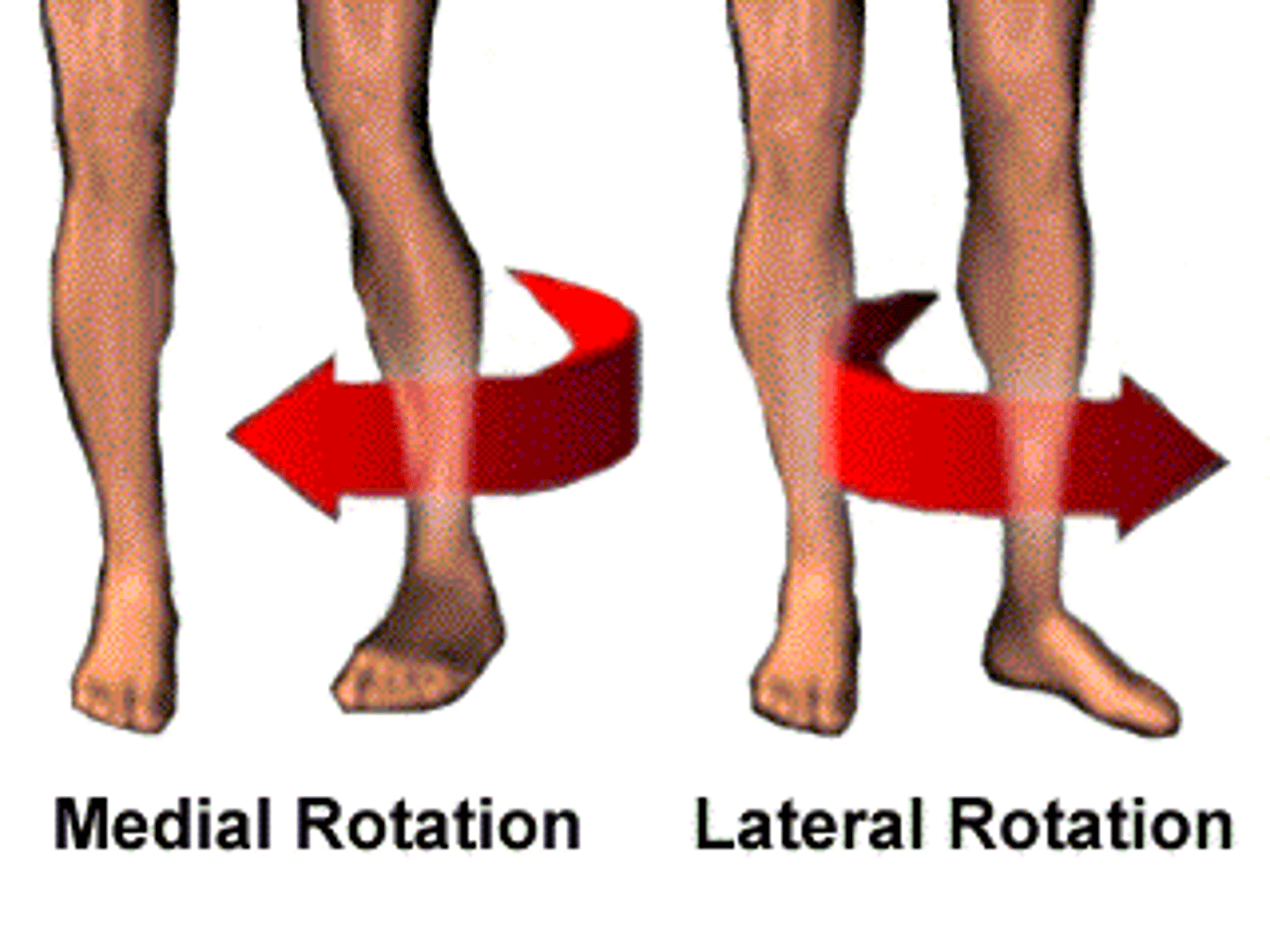
Hip movements
What movement is shown here?
External (lateral) rotation of hip
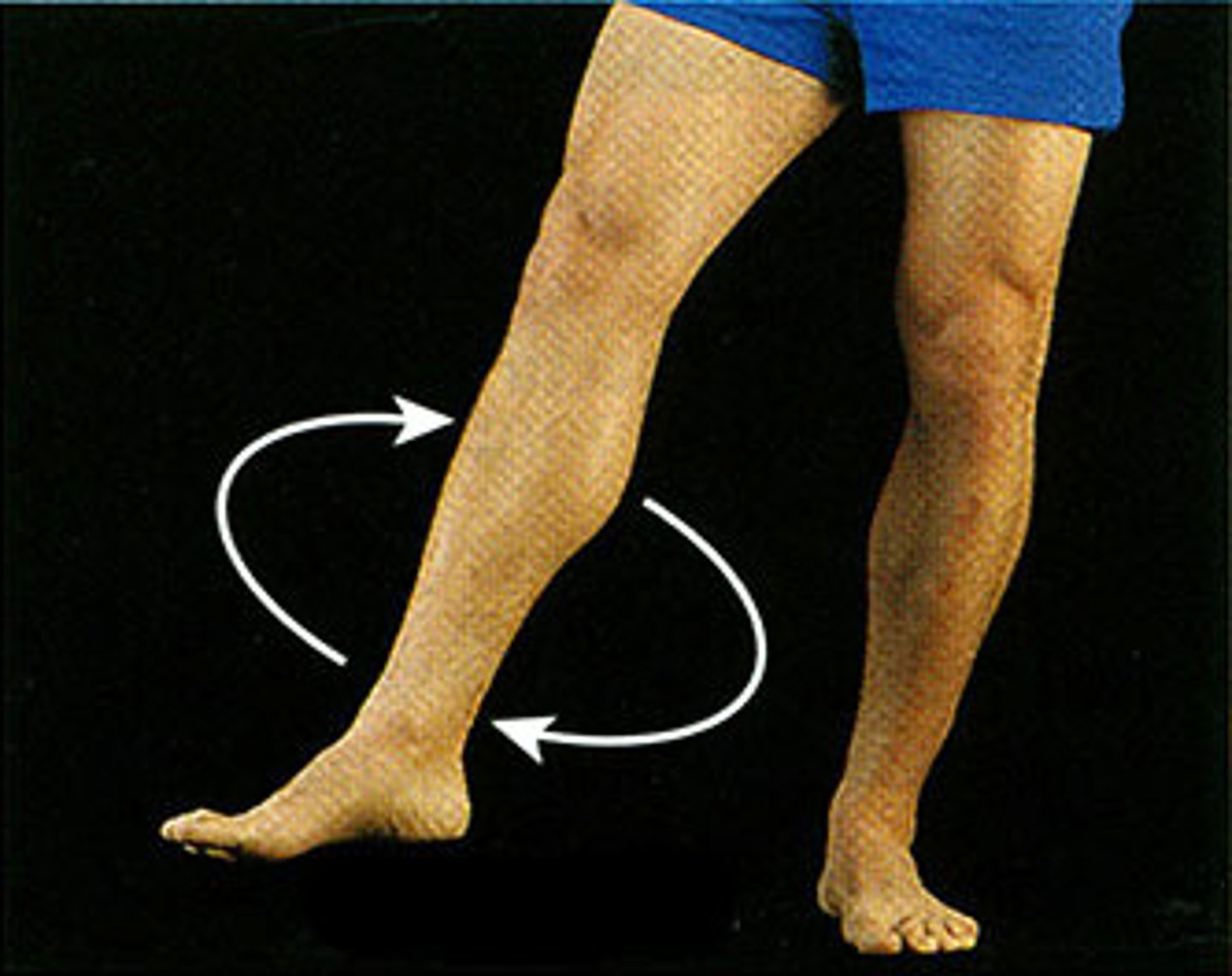
Hip movements
What movement is shown here?
Circumduction of hip
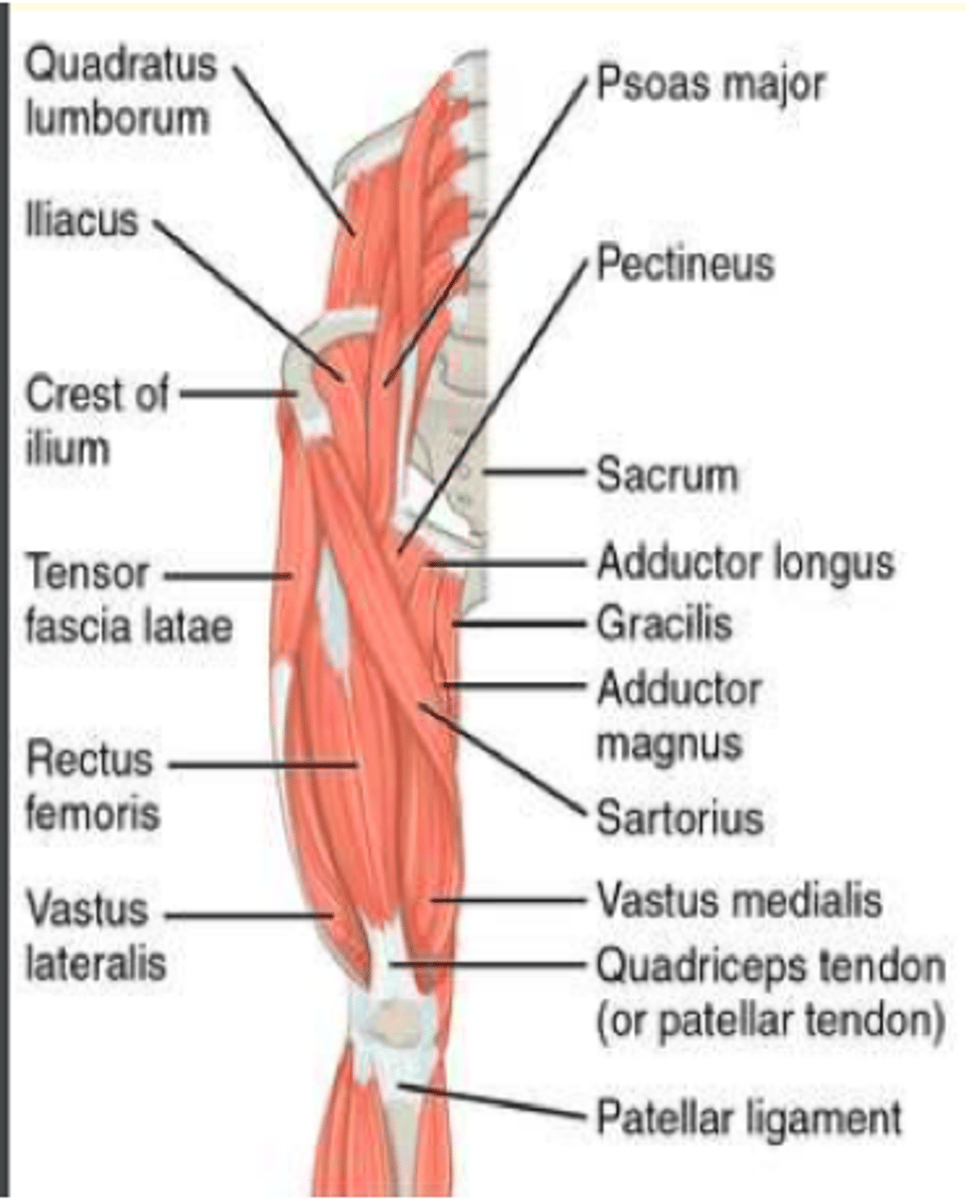
Tensor Fascia Latae (TFL)
Origin, insertion, action, innervation
Origin = iliac crest & anterior iliac spine
Insertion = iliotibial tract
Action = flex the thigh, abduct the thigh, medial rotation
Innervation = superior gluteal nerve
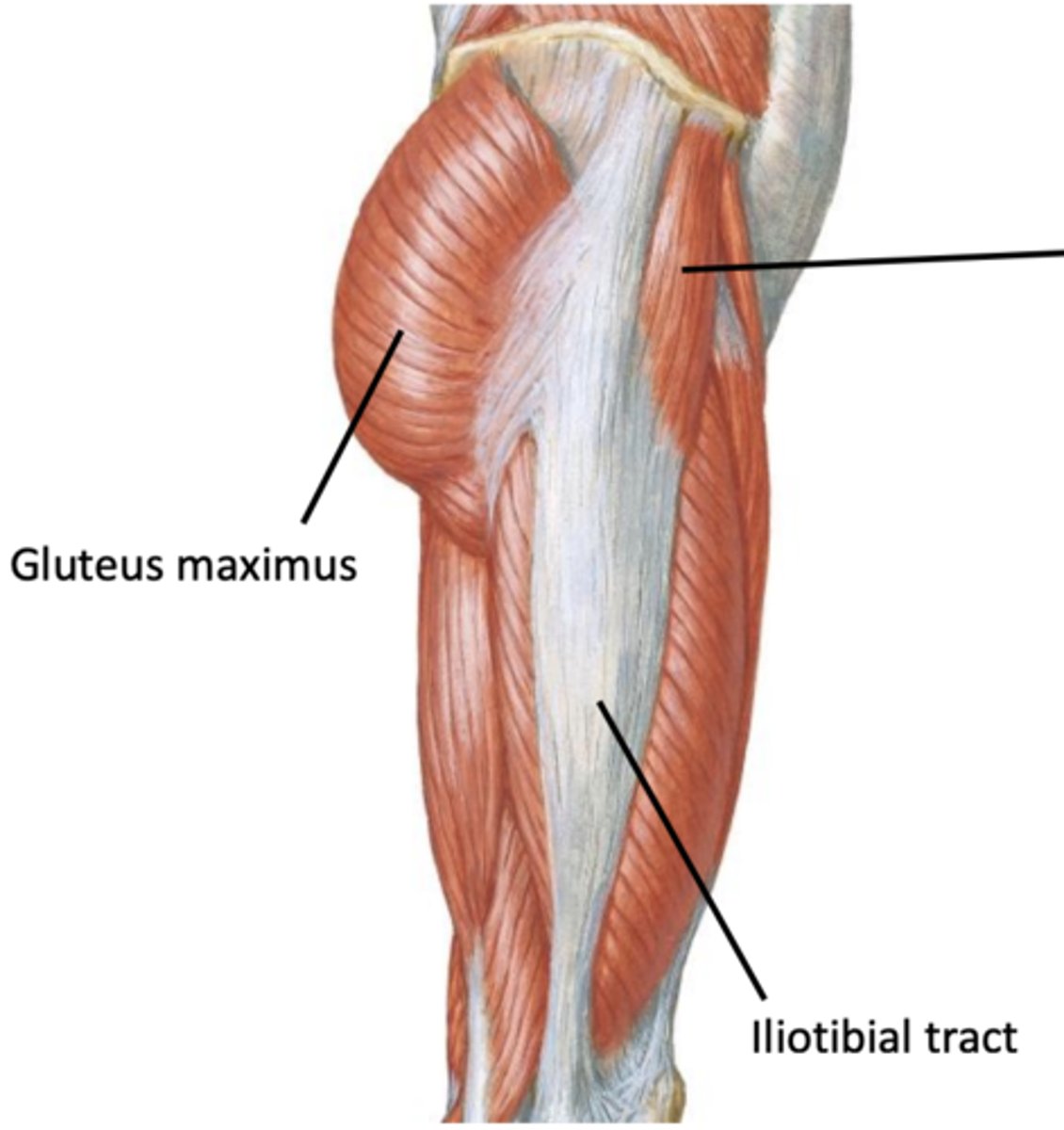
Muscles of lower limb
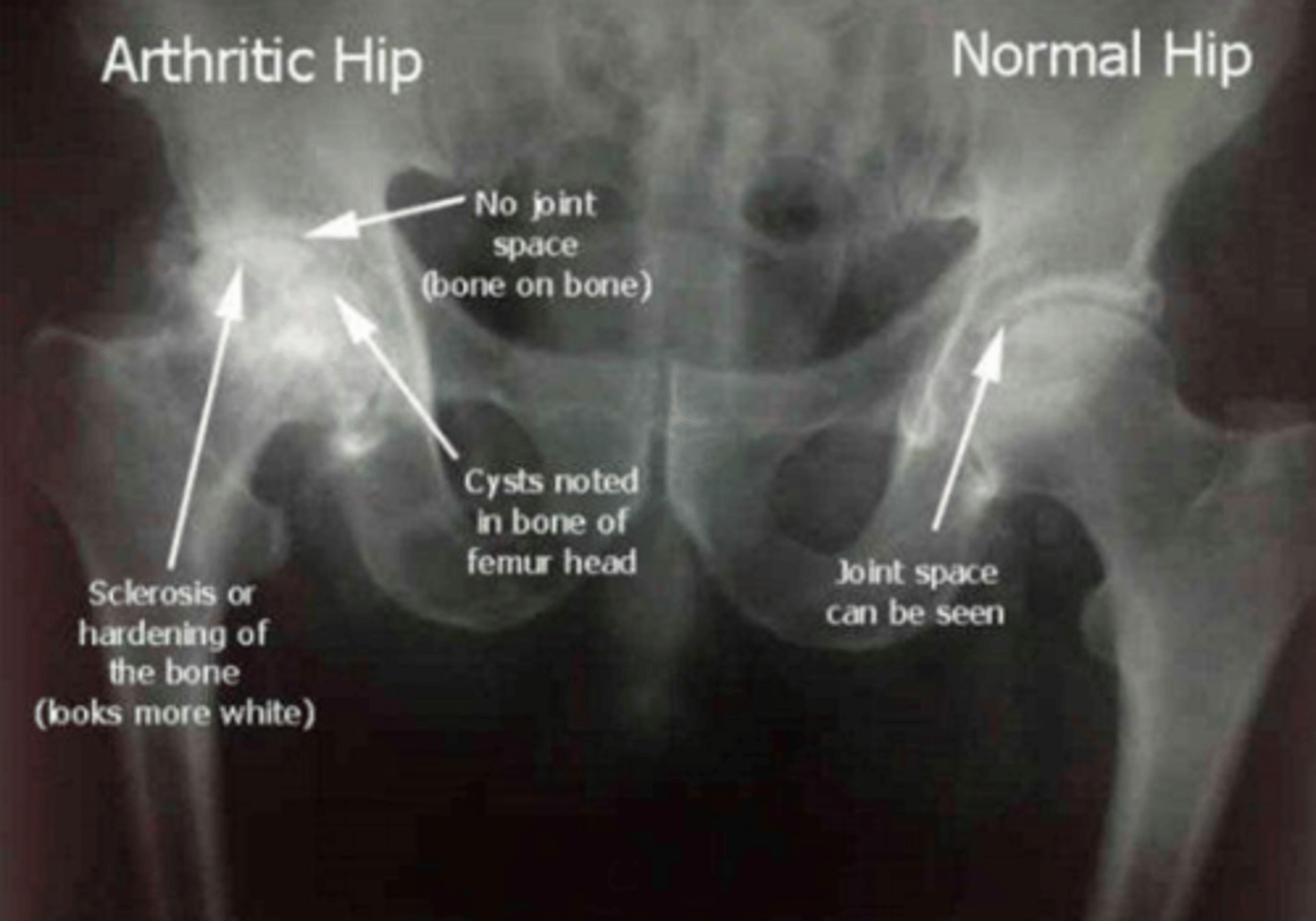
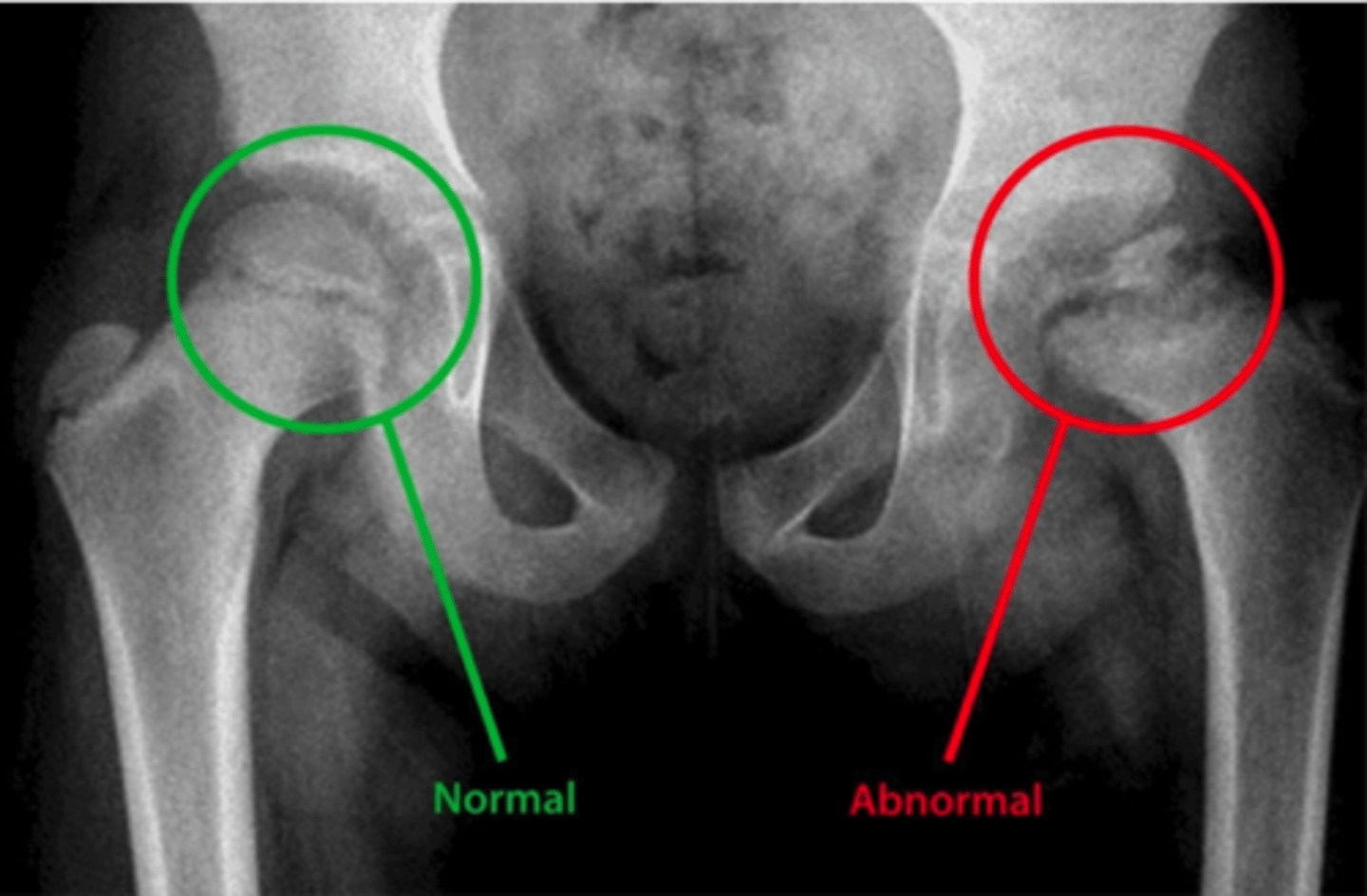
This x-ray shows characteristic signs of...
Hip disease (osteoarthritis)
Femoral neck fractures are commonly seen in?
Elderly women with osteoporosis
Femoral neck fracture classification
Intracapsular
Extracapsular
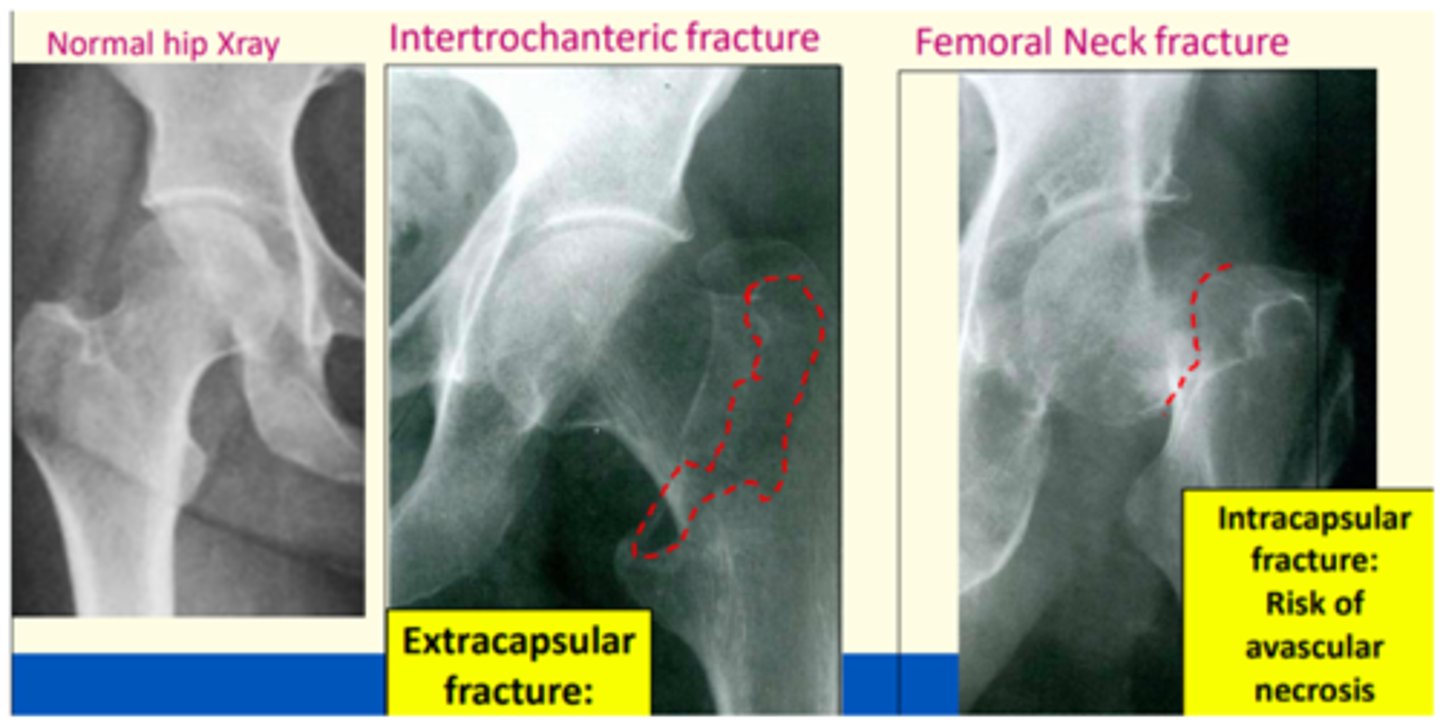
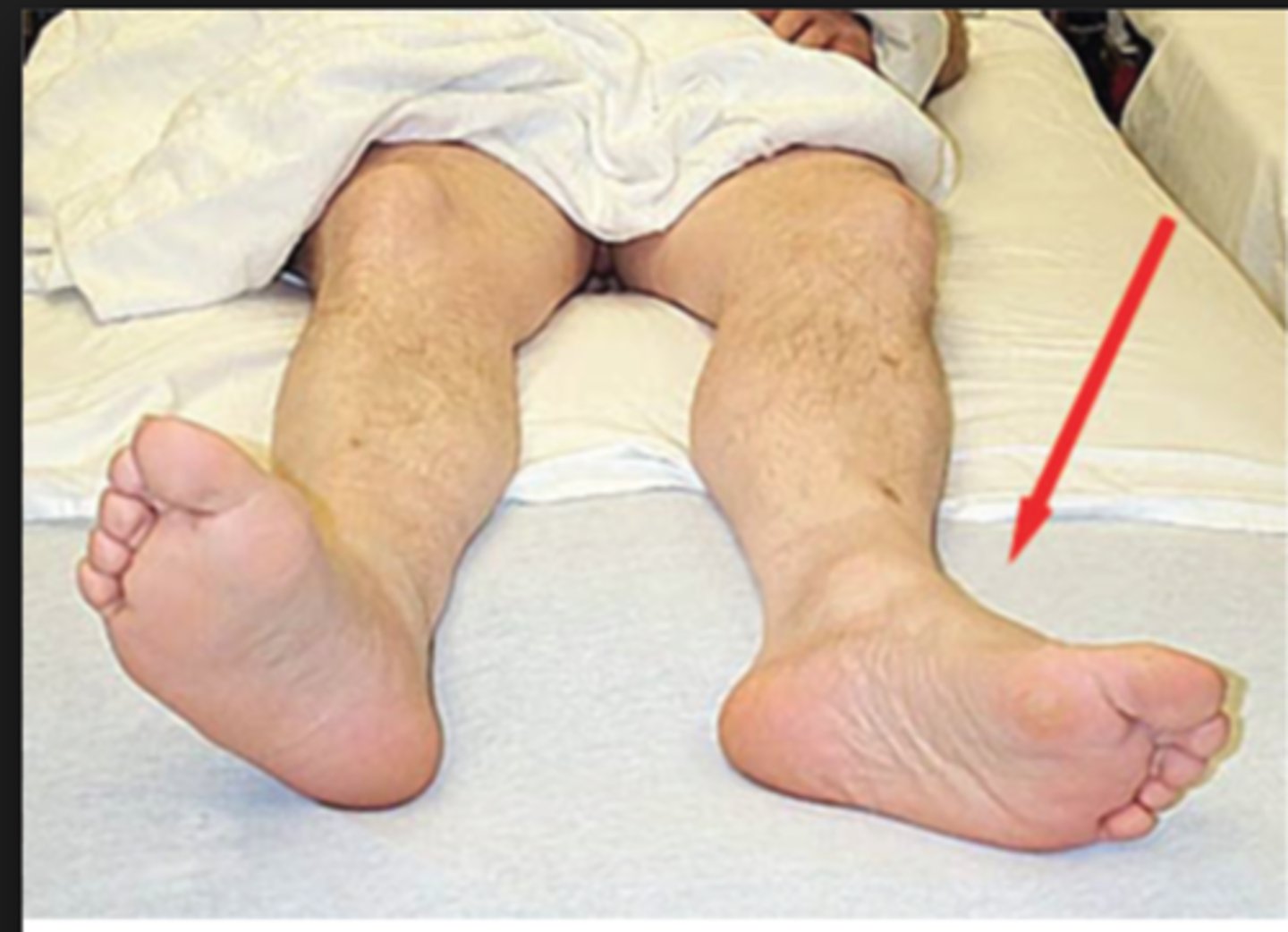
Presentation of femoral neck fractures
Affected limb will be shortened and laterally (externally) rotated
In ___ femoral neck fractures, there is a greater risk that the femoral head will be deprived of blood supply, leading to avascular necrosis and if this happens, the patient will require a hip replacement.
In intravascular femoral neck fractures, there is a greater risk that the femoral head will be deprived of blood supply, leading to avascular necrosis and if this happens, the patient will require a hip replacement.
This is due to the fact that an intracapsular femoral neck fracture may cause disruption to the blood supply to the head of the femur, cutting off blood supply to the proximal portion of the femoral head. This is because the fracture can disrupt the circumflex arteries.
Extra-capsular femoral neck fractures treament
Plates, screws
Intra-capsular femoral neck fractures treatment
Hemi-arthroplasty (replacement of femoral head) or total hip replacement
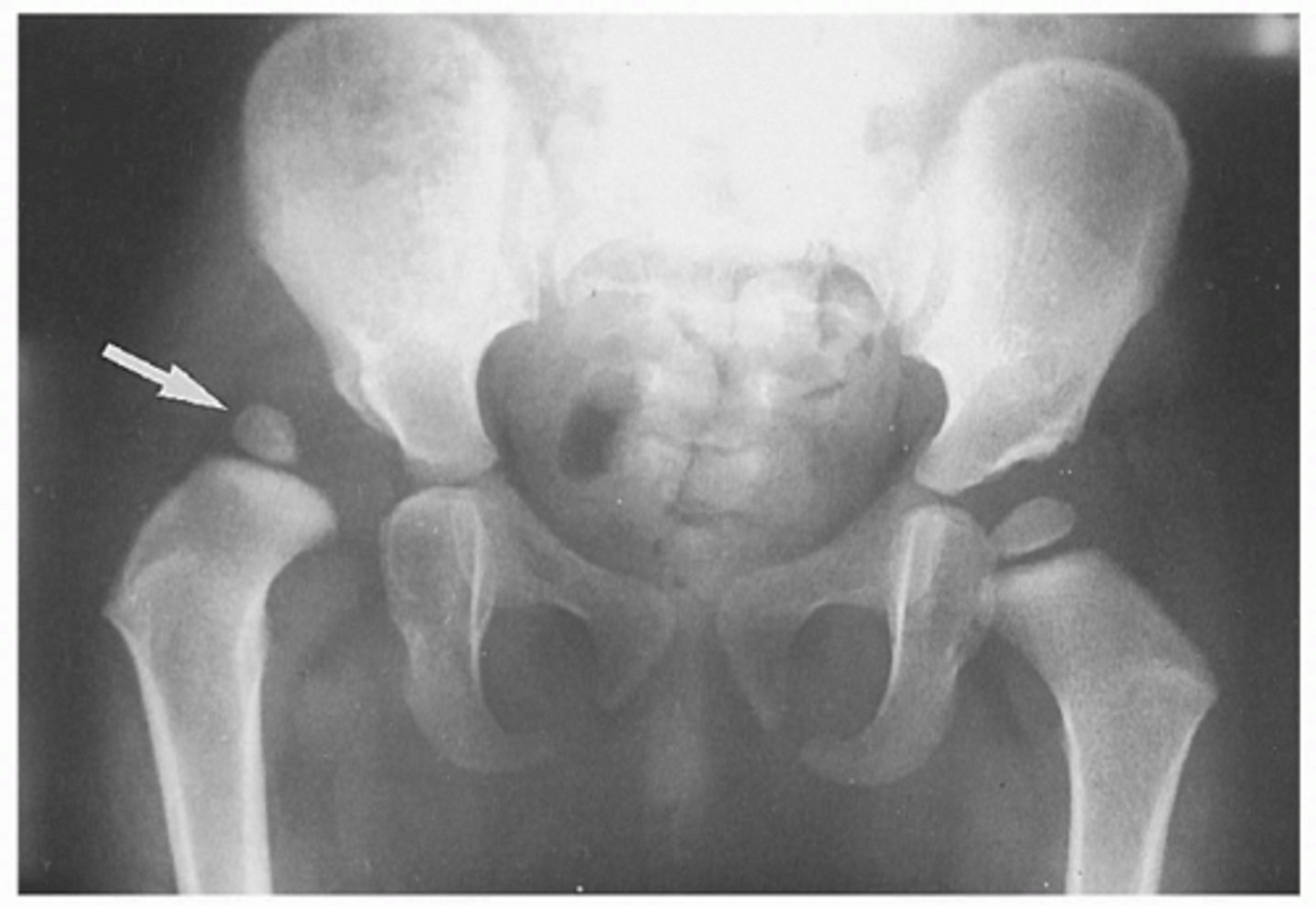
Congenital (from birth) dislocation of the hip
Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH) is an abnormality in the hip joint, usually present from birth.
There is an abnormality in either the shape of the head of the femur, the shape of the acetabulum, or supporting structures around them.
As a result, the acetabulum & femur are not in close contact as they should be.
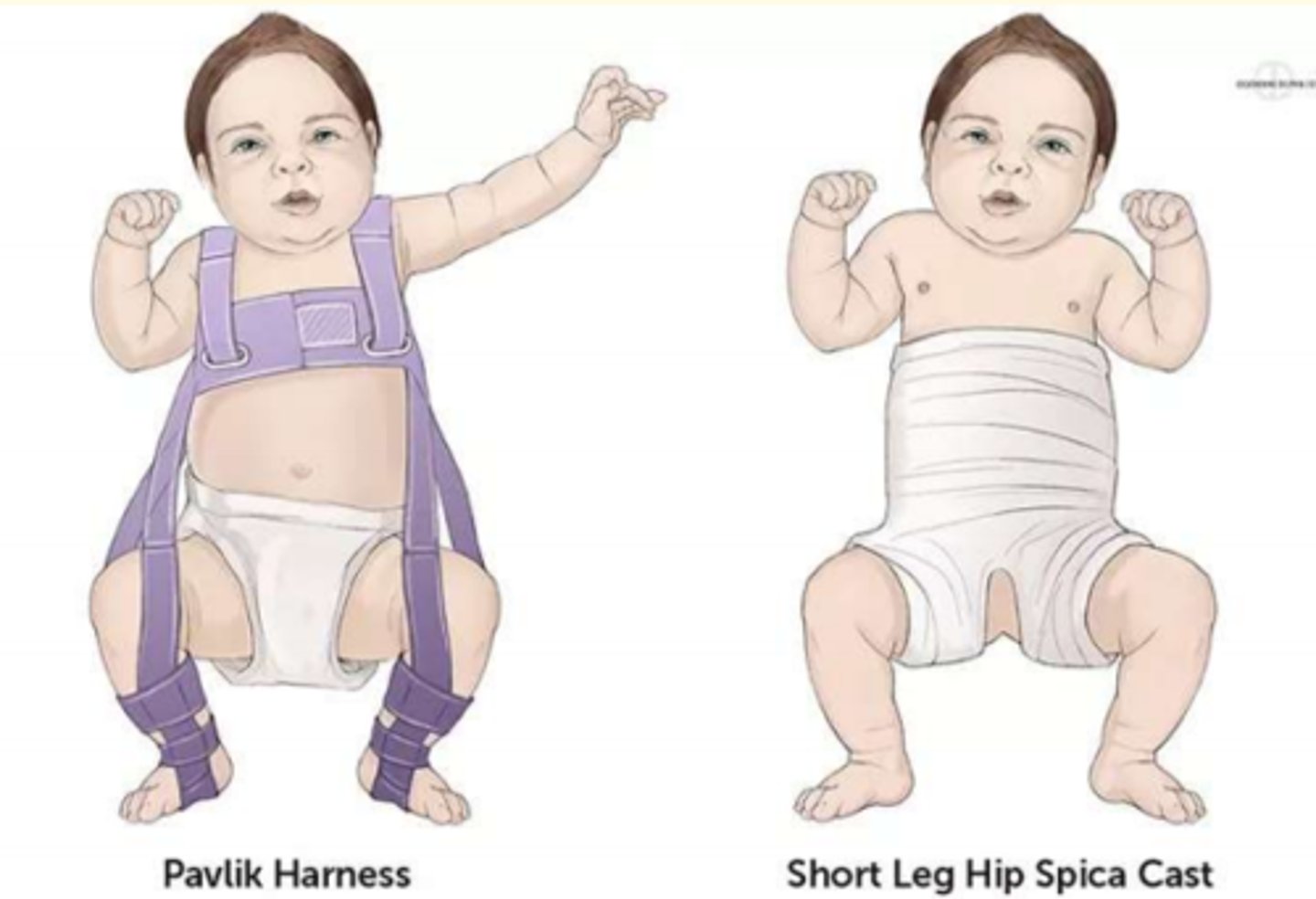
Treatment of Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH) in babies
Pavlik harness = this treatment holds the femoral head inside the acetabular fossa and promotes normal fevelopment of the hip joint.
If this fails, surgery is indicated.
Risk factor for developing DDH in babies
Incorrect swaddling can increase hip dysplasia risk
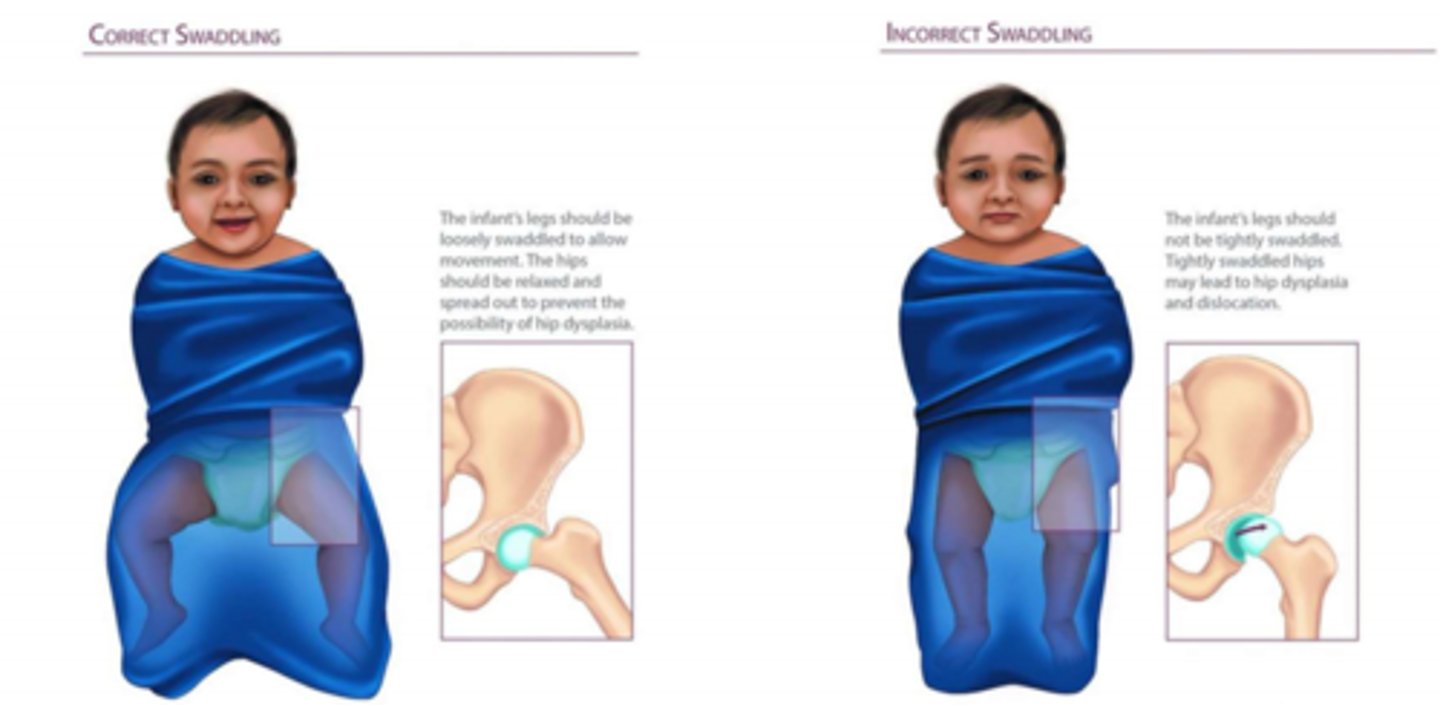
Acquired dislocation of the hip
- Uncommon
- Caused by major trauma or complication of total hip replacement surgery or hemiarthroplasty
1) Posterior dislocation (90% cases) = risk to sciatic nerve
2) Anterior dislocation
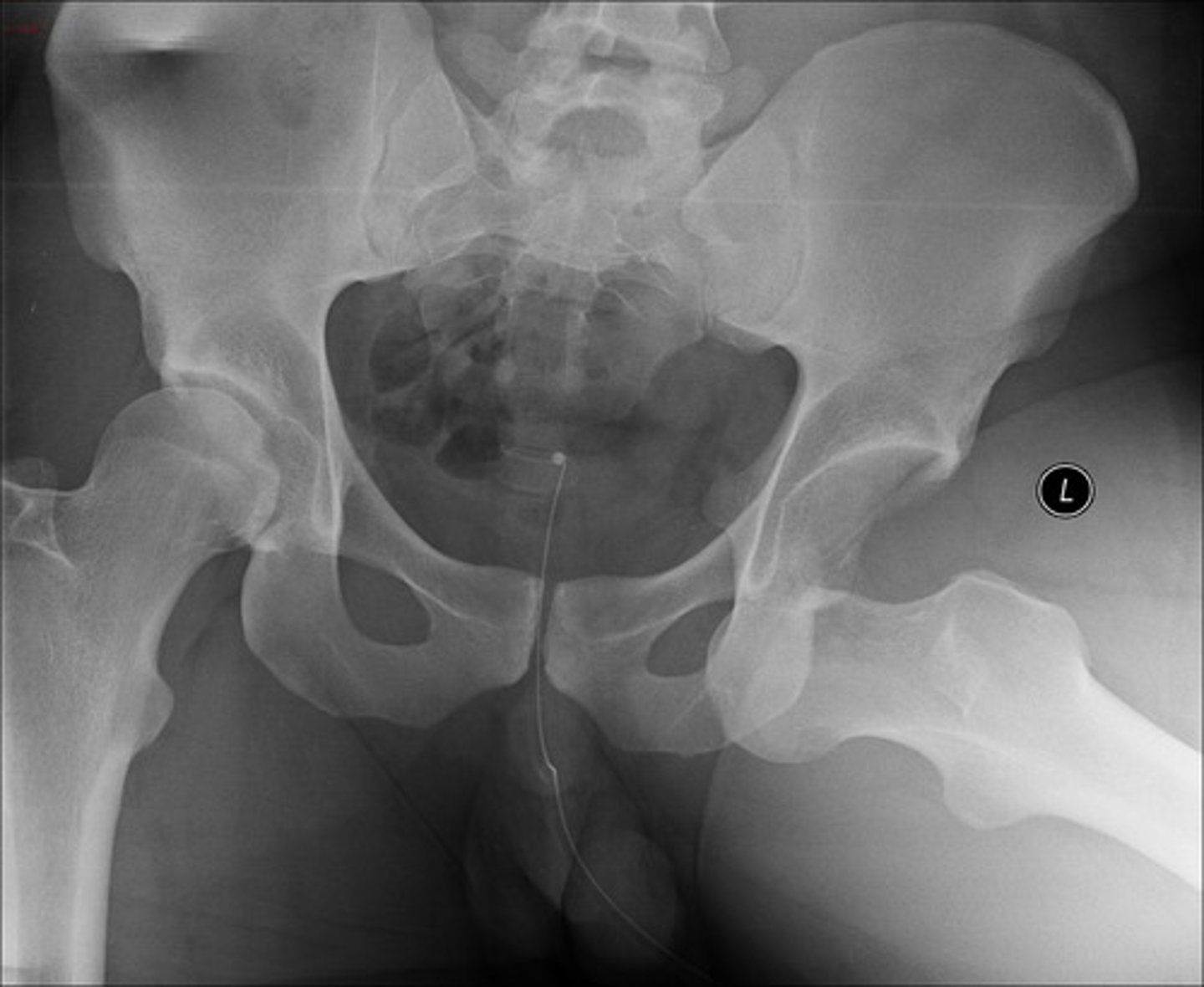
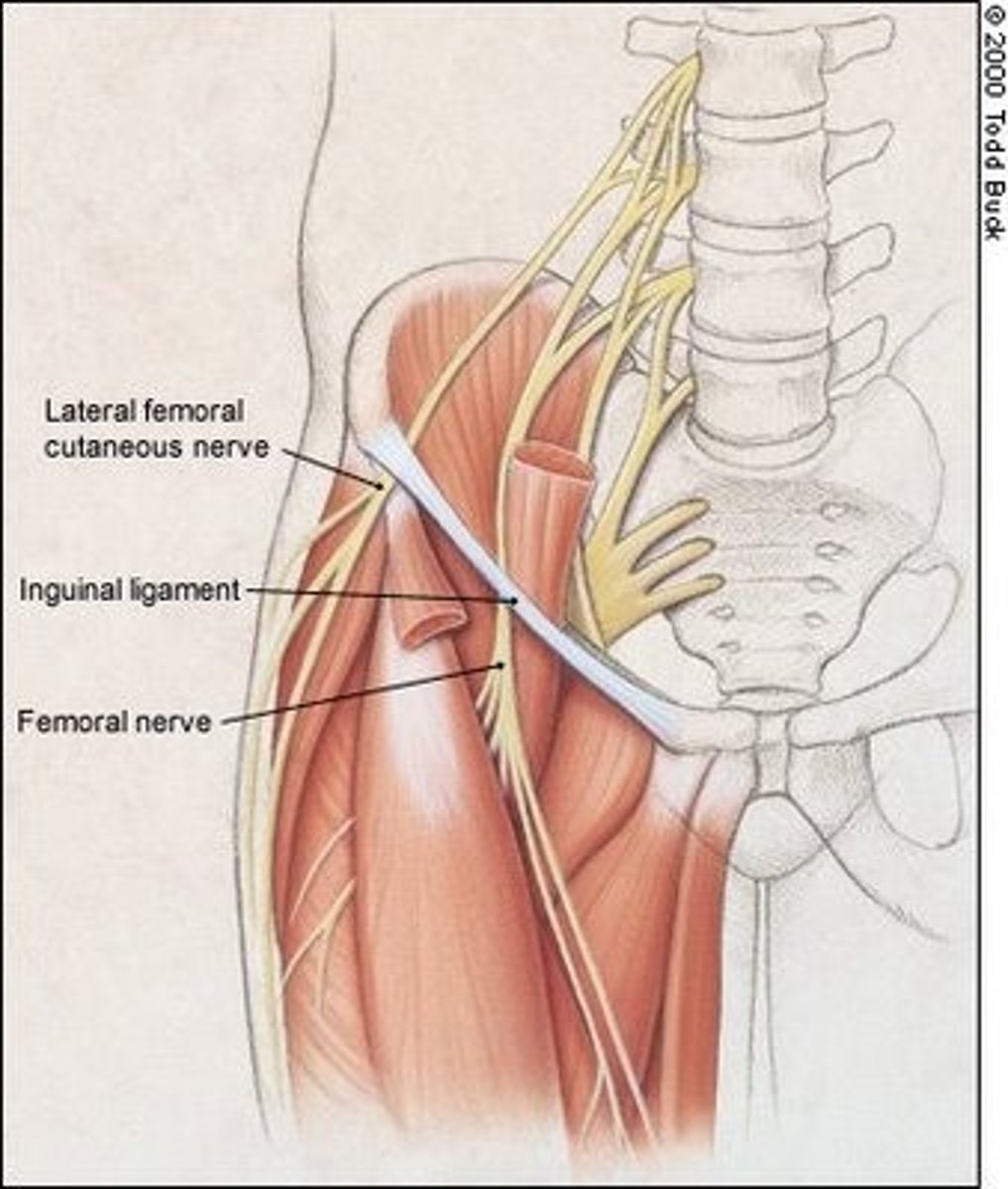
Which nerve emerges superficial to the sartorius muscle and if compressed can result in Meralgia Paresthetica AND how might this compression present in a patient?
A) Femoral nerve - numbness of the thigh
B) Obturator nerve - numbness of the middle thigh
C) Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh - numbness of lateral thigh
D) Sciatic nerve - numbness of the posterior leg
C) Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh - numbness of the lateral thigh
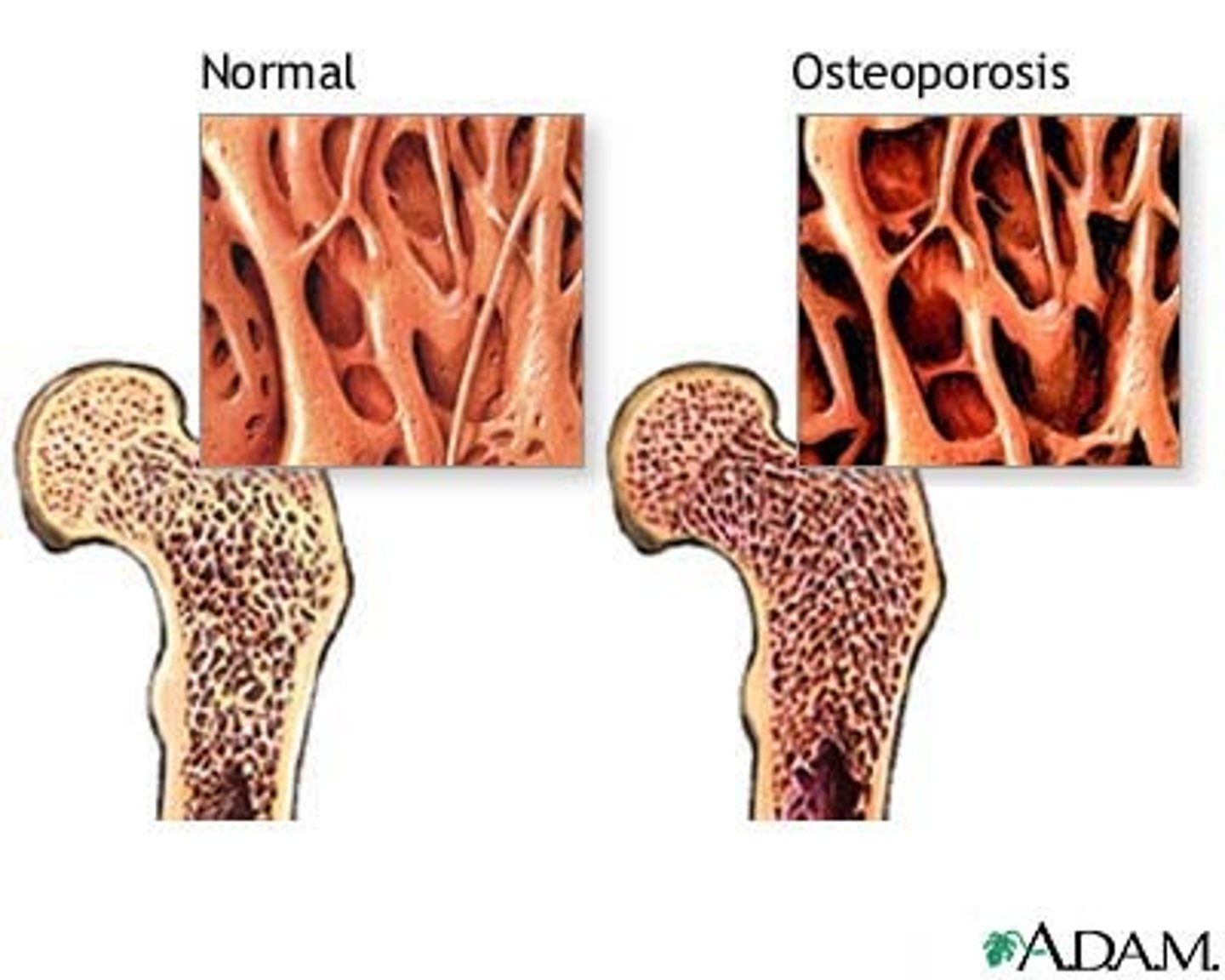
What is the pathophysiological explanation for osteoporosis?
When bone resorption exceeds bone formation
You are looking at the guidelines for the management of osteoporosis. According to WHO (World Health Organisation), at what age is a person classified as ‘old age’?
A) >85 years
B) >70 years
C) >65 years
D) >45 years
C) >65 years
Which of the following is a likely risk factor for Osteoporosis?
A) Having regular menstrual periods
B) BMI <19
C) Young age
D) High bone mass
B) BMI <19
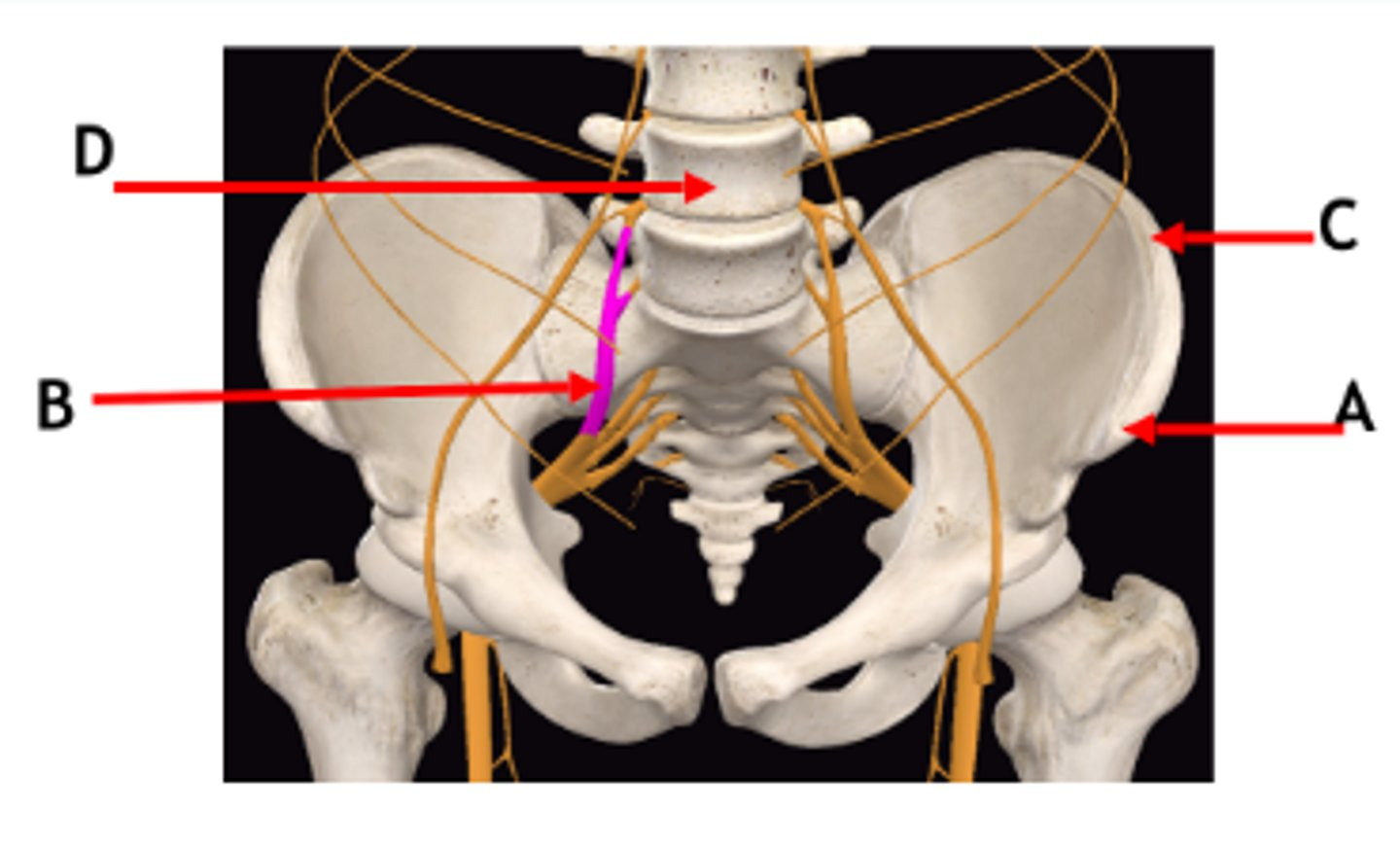
Identify labels A-D
A = Anterior superior iliac spine
B = Lumbosacral trunk
C = Iliac crest
D = Lumbar vertebra
Which one of the following is not a characteristic of the sacroiliac joint (SIJ)?
a) Architectural changes with age result in SIJ dysfunction
b) It resembles a typical synovial joint in an adult
c) It plays a role in supporting and transferring the body weight
d) It develops increased range of movement during late pregnancy
e) The mechanics of this joint is typically disturbed by lifting heavy objects without bending the knees
b) It resembles a typical synovial joint in an adult