Computer Fundamentals: Hardware, Types, and Network Components
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
Computer
Machine that uses electronic components and instructions to perform calculations and repetitive and complex procedures, process texts, and manipulate data and signals.
Computer Hardware
All of the physical components of the machine itself.
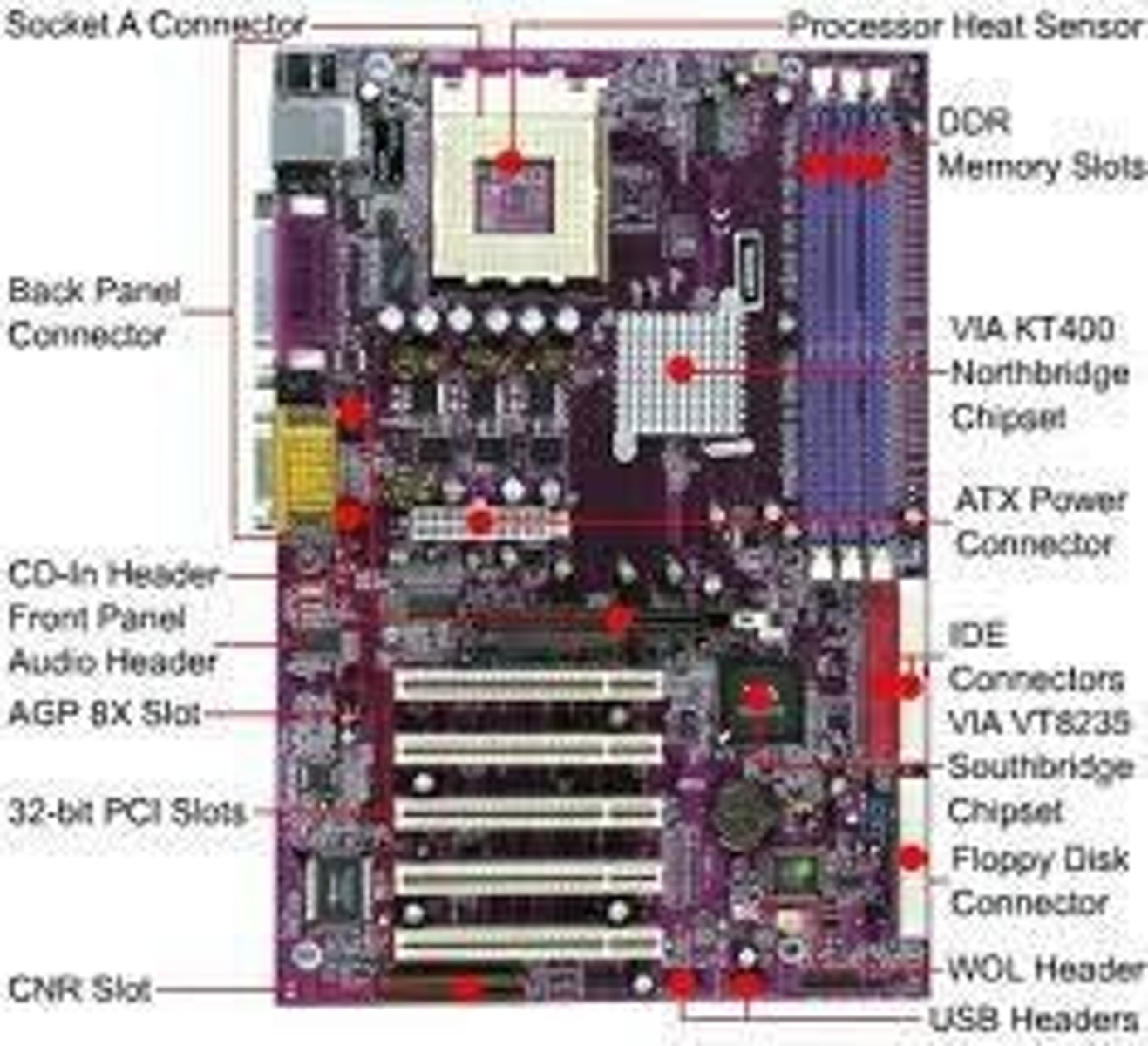
Motherboard
Thin, flat sheet made of a firm, non-conducting material on which the internal components (printed circuits, chips, slots, etc.) of the computer is mounted.
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
Brains of the computer, consisting of at least one arithmetic and logic unit, a control unit, and memory.
Arithmetic and Logic Unit
Controls mathematic functions and functions that test logic conditions.
Control Unit
Carries out the machine language functions called fetch, execute, decode, and store.
Memory
Includes the locations of computer's internal and main working storage.
Read Only Memory (ROM)
Permanent storage where data and programs can only be read by the computer and cannot be erased or altered.
Random Access Memory (RAM)
Working memory that is changeable and temporary, can be accessed, used, changed and written on repeatedly.
Input Device
Allow the computer to receive information from the outside world.
Mouse
Hand controlled mechanical device that electronically instructs the cursor to move across the video display screen.

Keyboard
Most common input device, similar to keyboard of typewriter.

Touch Screen
Involves use of a special filter on a monitor screen that allows the screen to sense the pressure of the user's finger on a particular position on the screen.
Light Pen
Photosensitive device that responds to light images when placed against a monitor screen.
Optical Character Recognition
Specialized computer input medium that allows data to be read directly from a form or document.
Voice/Speech Synthesizer
Allows user to input data into the computer by speaking into a connected microphone.
Output Device
Allow the computer to report its result to the external world.
Monitor
Display screen component of a terminal that allows the user to see images, programs, commands the user sends to the computer, and results of computer's work.
Printer
Most important output device that converts information produced by the computer system into printed form.
Storage Media
Includes the main memory but also the external devices on which the programs and data are stored.
Hard Drive
Peripheral that has a very high speed and high density, a very fast means of storing and retrieving data.

Diskettes
Allows input and output from a diskette, which is a round magnetic disk encased in a flexible or rigid case.
CD ROM
A rigid disk that holds a much higher density of information than a diskette and has a much higher speed.
USB Disk
Form of a small, removable hard drive that is inserted into the port of the computer.
First Generation Computers
First true digital computer (Colossus Mark I) was made in 1943.
Second Generation Computer
Introduced in the late 1950s, included IBM 1401 and 1620, used transistors instead of vacuum tubes.
Third Generation Computer
Introduced in mid 1960s, used micro-miniature solid state components.
Fourth Generation Computers
Introduced by IBM, IBM 370, first mainframe family that had printed circuits.
Analog Computer
Operates on continuous physical or electronic magnitudes, measuring ongoing continuous analog quantities such as voltage, current, temperature, and pressure.
Digital Computer
Operates on discrete discontinuous numerical digits using the binary system.
Hybrid Computer
Contains features of both analog and digital computers.
Supercomputers
Largest type of computer, specifically designed for scientific applications requiring gigantic amounts of calculations.
Mainframes
Fastest, largest, and most expensive type of computer used in corporate America for processing, storing, and retrieving data.
Microcomputer (Personal Computer / PC)
Used for a number of independent applications as well as serving as a desktop link to the programs of the mainframe.
Handheld Computers
Small, special function computers.
Network
A set of cooperative interconnected computers for the purpose of information interchange.
LAN
Usually supports the interconnected computer needs of a single company or agency.
WAN
Supports geographically dispersed facilities.
Network Hardware
Provide interconnection between computers.
Network adapter or Network interface card
Computer circuit or card that is installed in a computer so that it will be connected to a network.
Communication Medium (Cabling)
Means by which actual transfer of data from one site to another takes place.
ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network)
Used to carry communications across phone lines.
Bandwidth
Controls how fast the signals can be transmitted across phone lines.
DS0
The first digital standard that transmitted at 64 kilobytes per second.
T-Lines
Replace DS0 and are used to handle the high speed transmission needed for network communications.
Servers
Computer program that provides services to other computer programs in the same computer or in other networks.
Client-server approach
One computer is the core or server computer that receives requests from the client computer and fulfills those requests.
Architecture
Refers to overall physical structure, peripherals, interconnections within the computer, and its software system.
Five fundamental components (Computer Subsystem)
Input/Output, Storage, Communication, Control, Processing.
Broadcast
Communication is done by transmitting the same information to all computers in the network.
Point-to-Point
Used in dial up networking.
Topology
Defines how the network computers in LAN are interconnected within a physical area.
Bus
Network topology or circuit arrangement in which all the node computers are directly attached to a line.
Star
Centralized structure where all computers are connected through a central computer (server).
Ring
Connection with wires or cables that directly connects computers together.
Hub
Consists of backbone or main circuit attached to outgoing lines.
Arcnet
Token bus system for managing line sharing among all users on the network.