BU3: Acoustics Module 5 - Sound Waves
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
sound wave
a PRESSURE DISTURBANCE that travels through a MEDIUM by means of particle-to-particle interaction
Velocity
- Speed in a given direction
- rate of change of displacement
Speed
- rate of change of position of an object in any direction
- rate of change of distance
Frequency
the number of complete wavelengths that pass a point in a given time
wavelength and frequency
The velocity of a wave is equal to the product of its __________ and _____________ (number of vibrations per second) and is independent of its intensity.
0.33 km/s or 0.2 mile/s
Sound has a velocity of about ____________ in air
1.5 km/s
Sound has a velocity of ______________ in water
5 km/s
Sound has a velocity of _________________ in steel
Air
All soundwave travel with the same speed in ______ regardless of their frequency
False
True or False
When an object moves outward, it pushes air molecules which create an area of low pressure. When the object moves inward, it creates an area of high pressure.
speed of sound
the distance travelled per unit time by a sound wave
1. Elasticity of Solid
2. Density of the Medium
3. Temperature
Factors Affecting Speed of Sound Wave
Faster
Faster or Slower?
The more elastic the medium, the ________ is the speed of sound.
Clue: Rigid materials such as steel are considered to have a high elasticity.

Slower
Faster or Slower?
The greater the density of the medium, the less responsive they will be to the interactions between particles and the ________ that the wave will be.
Helium
A sound wave will travel nearly three times faster in _______ than it will in air.
Sound propagation
travel of sound from the sound source to the surrounding medium.
343m/s
average speed of sound
Wavelength
The distance travelled by the pressure wave during one cycle
Simply the distance from the crest of one wave to the next nearest crest
Crest
Highest point of a wave
Trough
Lowest point of a wave
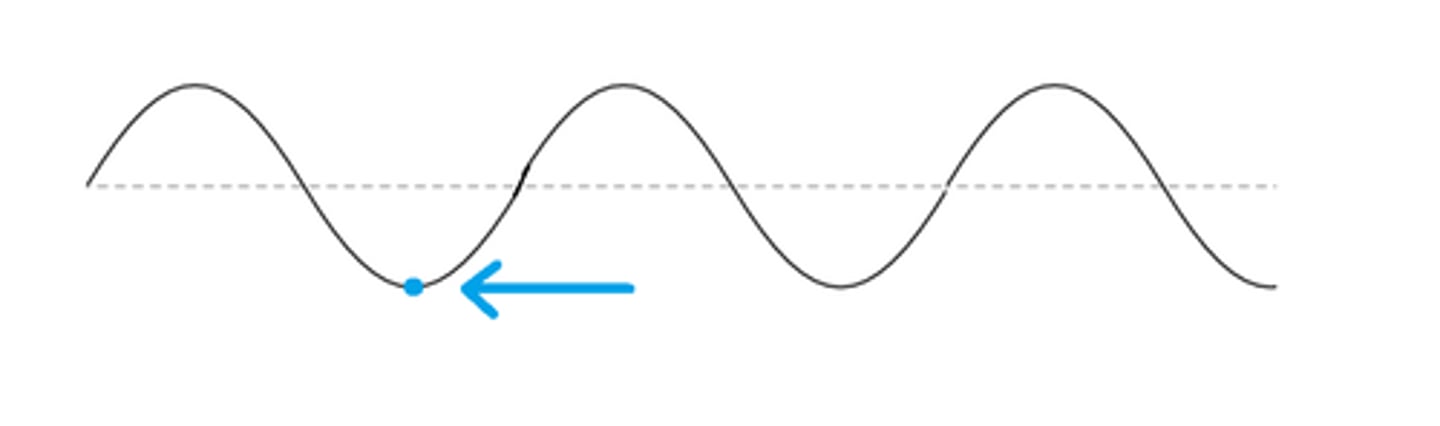
Amplitude
Height of a wave
Sound Intensity
Also known as Acoustic Intensity
Defined as the MEAN value of the acoustic energy which crosses a unit area perpendicular to the direction of propagation in unit time
Sound wave intensity
The AMOUNT OF ENERGY that is transported past a given area of the medium per unit of time.
watts/m^2
Typical units for expressing the intensity of a sound wave are
Sound intensity level (SIL)
the level of the intensity of a sound relative to a reference value
Inverse Square Law
States that a specified physical quantity is inversely proportional to the square of that physical quantity.
In acoustics the sound pressure of a spherical wave front radiating from point sources decreases by 50% as the distance r is doubled.
Intensity Decrease = Density Increase
Sound Field
- any area where sound waves are present
- within given boundaries (walls, floors, ceiling)
1. Free Field
2. Diffuse Field
3. Near Field
4. Far Field
Types of Sound Field
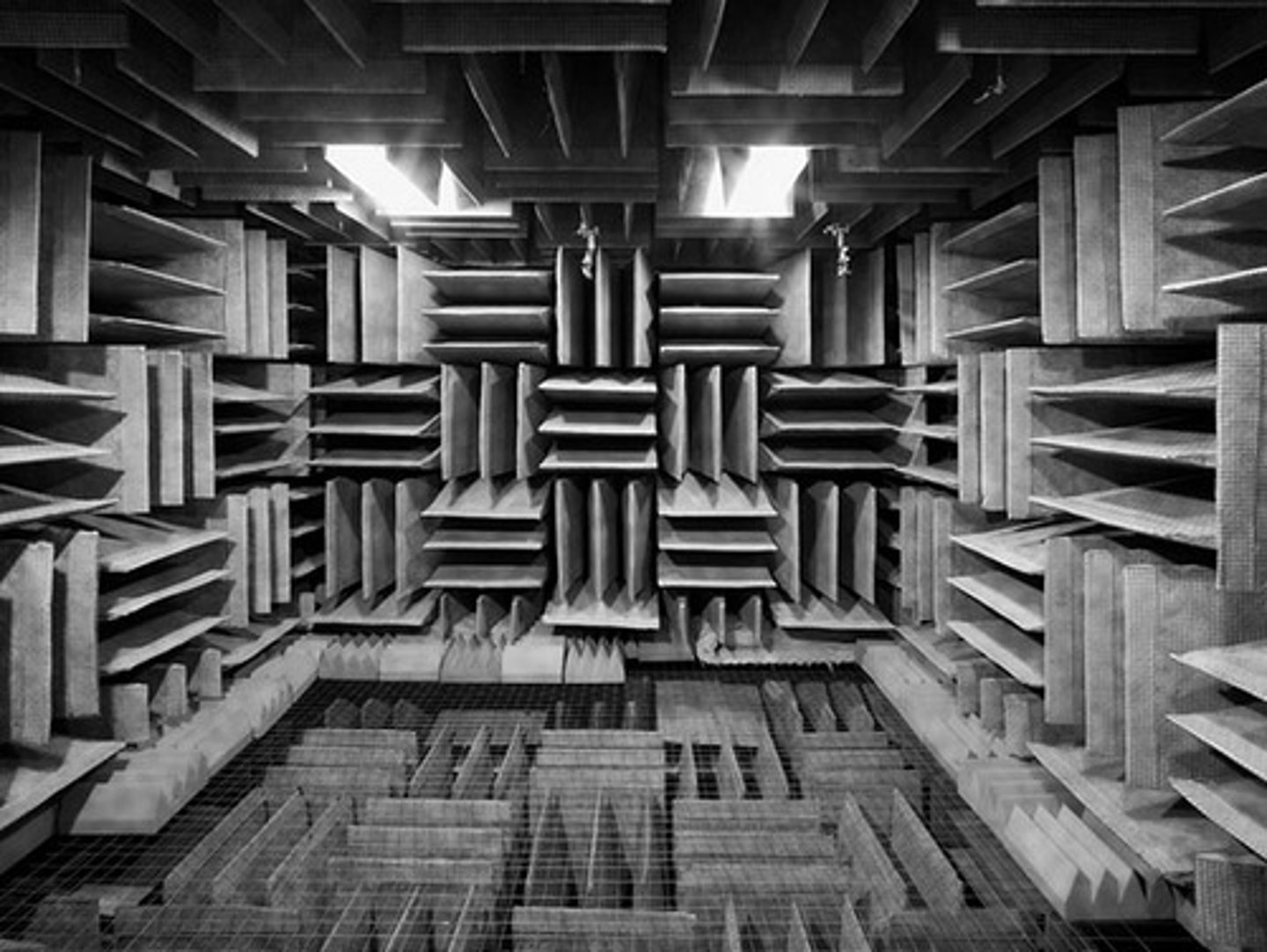
Free Field
a sound field without any obstructions (reflections)
anechoic chamber
a sealed room in which all the surfaces are designed to completely absorb all sound produced in the room
Example of Free Field

Diffuse Field
Sound is reflected from many surfaces
Near Field
the part of a sound field that is close to a sound source

evanescent waves.
Very close to the source, the sound energy circulates back and forth with the vibrating surface of the source, never escaping or propagating away.
Far Field
the part of the sound field that is far from a sound source
The wavefront is deemed as a plane wave and will decay at a rate of 6 dB per distance doubled from the source.
begins approximately at a distance of 1 wavelength, and extends outward to infinity
Sound Pressure
- the pressure caused by the vibration of the sound source
- the force of sound (N) on a surface perpendicular to the direction of sound
- ultimately what our ears hear (loudness)
- the most commonly used indicator of the acoustic wave strength
Pa or N/m2
The SI-unit for sound pressure
Sound Power
ENERGY of sound per unit of time (J/s or W)