PA week 1 and week 2
1/239
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
240 Terms
Preaucilar lymph node location
before the ear
Posterior auricular location
Behind the ear
Occiptial lymph node
Behind head
Tonsilsar lymph node
end of jawline behind it
Submental lymph node
Underneath the chin
Submandibular lymph node location
Underneath the jaw
PMH of head
Headaches, head injury, surgery on head
PMH of neck
Neck injury, neck cancer, thyroid issues, thyroid nodules
FMH for head AND neck
Family history of head and neck cancers
Physical exam for head includes
Inspect and palpate skull, scalp, hair
Physical exam for face includes (nerves)
Cranial nerve 7 and 5, temporal arteries, and temporomandibular joint.
When inspecting head, note the..
Size and shape
Normocephalic
Normal head size and shape
Macroceophalic/macrocephaly
Big head size and shape, abnormal
Microcephalic/microcephaly
Head is small in size and shape
Use fingertips to palpate the skull for..
Lumps
Inspect the scalp for any…
Lesions, redness, scaling
Inspect the face for..
Facial expressions, symmetry, involuntary movements, abnormal facial structures
Acromegaly (head abnormalities)
Body makes too much growth hormone and causes body parts to get bigger over time
Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (head abnormalities)
Microcephaly, thin upper lip,
Exophthalmos(head abnormalities)
Eyeballs stick out more than usual, common sign of hyperthyroidism
Cushing sydrome (head abnormalities)
Body has too much cortisol and causes face swelling
Testing cranial nerve 7 includes these actions
Raise eyebrows, close eyes tightly, smile, frown, puff out cheeks
When testing cranial nerve 7, all expressions should be
Symmetrical
Bells palsy is when…
cranial nerve 7 is affected and entire side of face does not move
Cranial nerve 5 controls
Sensory and motor
Cranial nerve 7 controls
Facial movement
How to test cranial nerve 5 for sensory
putting cotton wisp to each of the 3 divisions of the nerve and ask pt to say now when touch is felt
Be sure to test both sides of cranial nerve 5 for
Symmetry
Three divisions of the trigeminal nerve, nerve 5
Opthamalic, maxillary, mandibular
How to assess motor in cranial nerve 5
Palpate temporal and masseter muscles bilaterally as pt opens their mouth and clenches their teeth
for cranial nerve 5, muscles should feel..
Equally strong on both sides
Temporal arteritis
Tenderness and hard band with palpation, abnormal
Pulstations for temporal artery
Pulsations should be +2 bilaterally
TMJ normal findings
Movements should be smooth, no pain/tenderness
Physical assessment components for neck include
Palpate and ausculate carotids, lymph nodes and trachea, test cranial nerve XI, palpate thyroid gland
Inspect neck for…
Lumps, measels, pulsations, symmetry, JVD
JVD is
vein in neck is big and sticks out
Palpate trachea during…
Neck assessment
Tracheal deviation (abnormality)
Unequal deviation results from unequal intrathoracic pressure and is most often clinical emergency
Test cranival nerve 11 by..
Assessing trapezii and sternocleiodmastoid
Test trapezii by…
Placing one hand on each shoulder and ask pt to shrug upwards against pressure
Normal findings of trapezii include…
Strentgh and contractions are equal
How to test sternocleioidmastoid
Pt turn their head against your hand on each side
Nirmal findings of sternocleoidmastoid includes..
Strength and contractions should be equal bilaterally
Palpating thyroid steps include
pt bend head slightly forward to the right, push trachea to the right, use fingers to feel trachea and muscle, ask pt to swallow, thyroid should move up under your finger with trachea and larynx
if thyroid is enlarged…
Use the bell of stethoscope to listen for bruits
Goiter (neck abnormality)
Enlarged neck
TMJ should be without…
Pain and crepitus
Documentation of cranial nerve assessment will..
Go under neuro
Documentation of JVD will go under…
Cardiovascular
PMH of hair includes
Hair disorders
PMH of nails includes..
Nail diseases or abnormalities
Equipment needed to examine skin
Good lighting, pen light, gloves, cm ruler
Pallor
Paleness of the skin
Pallor in melanated skin shows…
Yellow/brown to ashen color
Pallor can be observed in..
Lips, nail beds, mucus membranes
Erythema
Intense redness of skin due to excess bloood in dilated superficial capillaries
Hypoxia
low oxygen in tissues and organs
Hypoxemia
Low oxyen in blood
Cyanosis
Bluish color of skin that signifies hypoxemia
cyanosis occurs when..
Shock, heart failure, cardiac arrest, chronic bronchitis
Central cyanosis
Associated with arterial desaturation and involves the lips, tongue, mouth
Peripheral cyanosis
Affects fingers/toes due to poor circulation
Jaundice
Yellowing of skin due to high levels of bilirubin
Vitilgo
Decreased pigmentation
Acanthosis nigricans
Increased pigmentation
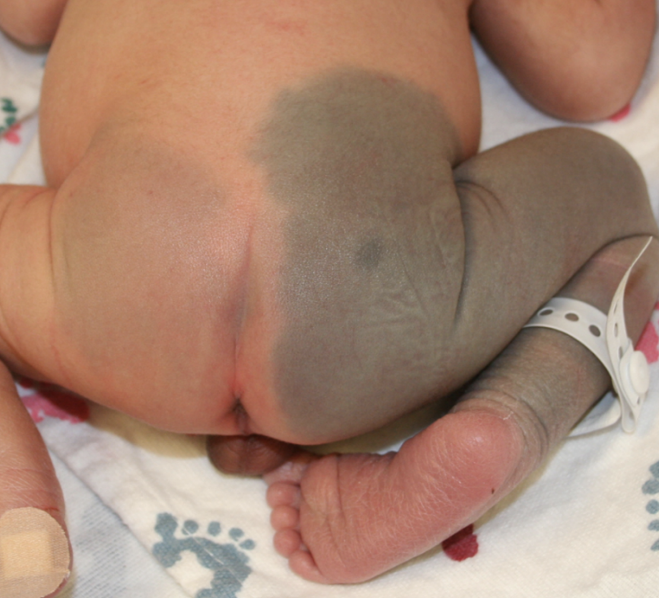
what developmental condition is this?
Congenital dermal melanocytosis. Blueish spot on butt
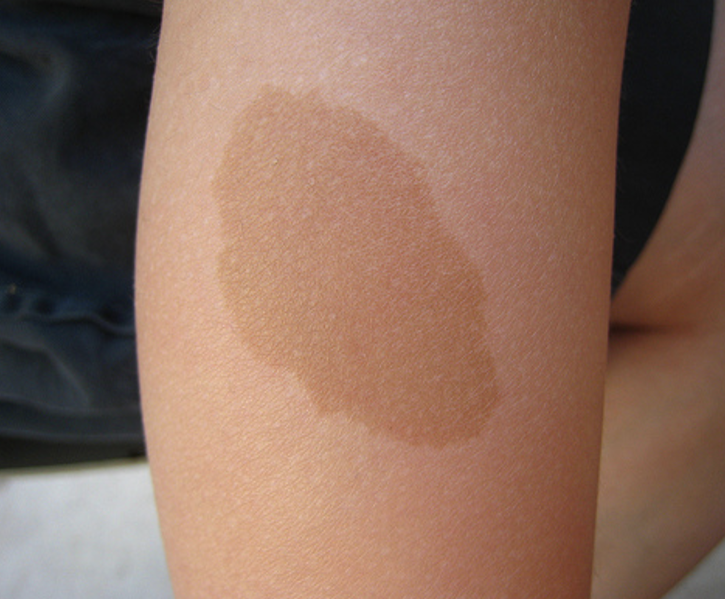
what is this?
Cafe au lait spot. Large round patch of pigment
Numerous Cafe au lait spot means….
Nerocutaneous disease
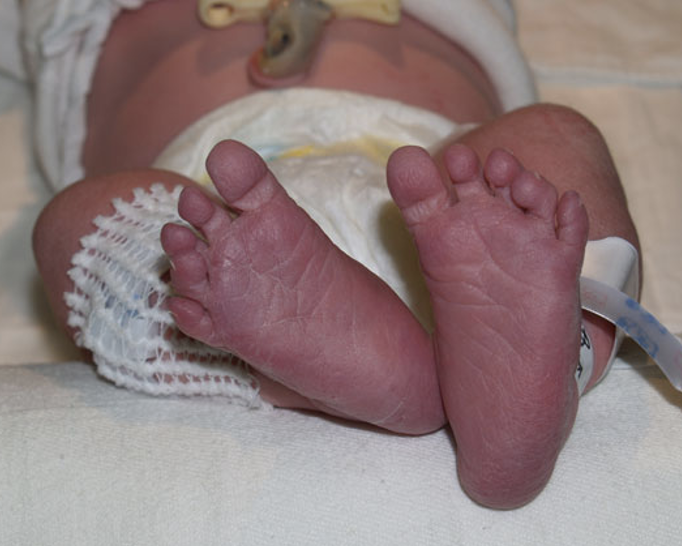
What condition?
Acrocyanosis. Benign condition of bluish hands and feet in infants
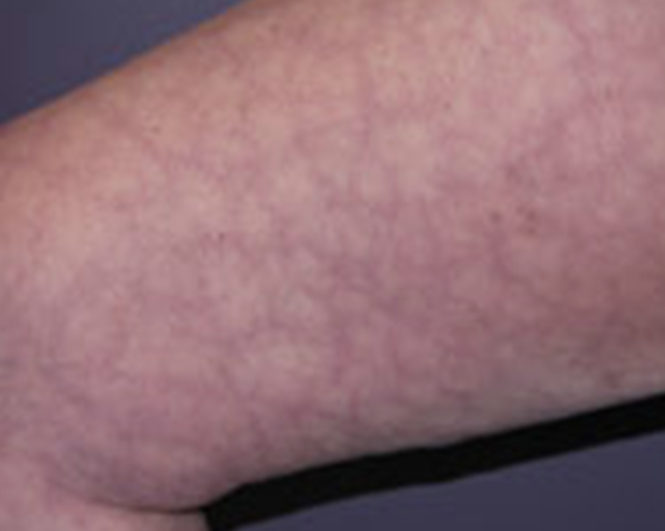
what condition is this?
Cutis marmorata. Marbeled pattern on skin, normal
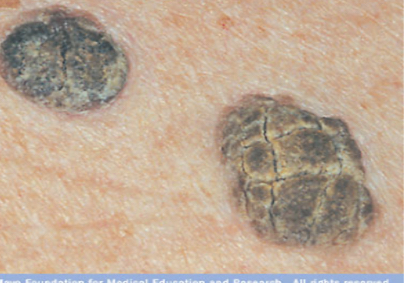
Seborrheic keratosis. Non cancerous skin growth, raised, thickened pigmentation
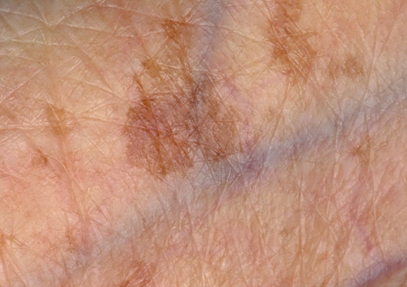
Senile lentigines. Common, non cancerous skin spot, clusters of melanocytes after skin exposure
Perspiration appears normally in response to activity, warm environment, or anxiety, on the…
Face, hands, axillae, skin folds
Dehydration may be apparent by
Dry lips, dry or cracked mucous membranes
Xerosis
Dry skin
Developmental considerations for older adults for moisture…
Sebeacous glands decrease causing dry skin
Diaphoresis
Excessive sweating
Hyperthermia
Increased temperature
Hypothermia
Low temperature
Atrophic skin
Thin and shiny, occurs with arterial insufficiency
Edema
Fluid accumulating in the interstitial spaces
Rebounds immediately
Grade 1 edema
<15 sec rebound
Grade 2 edema
60 second rebound
Grade. 3 edema
2-3 min rebound
Grade 4 edema
Anasarca
Generalized edema, usually bc of kidney failure
Turgor
Ability for skin to to return back to place
Normal turgor
Skin goes back to place quickly
Tenting
Abnormal finding when testing skin turgor
Tenting may be normal in older adults because..
As they age their skin loses elasticity
Mobility
Skins ease of rising
Normal mobility
Skin rises easily
Abnormal mobility
Unable to lift
Primary skin lesions include..
Macule, patch, plaque, pustule, nodule, vesicle, bullae, wheals, urticaria
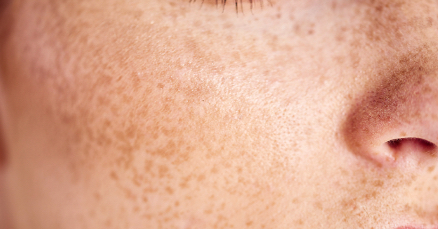
Macule, primary lesion. freckles, flat, moles, what type of lesion is this and class
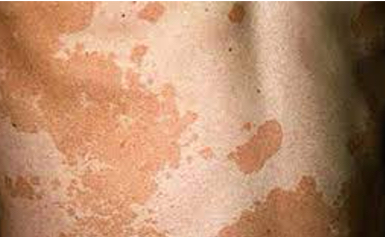
Identify class and type
Patch, primary lesion. Flat, vitiligo, cafe au lait, irregular borders
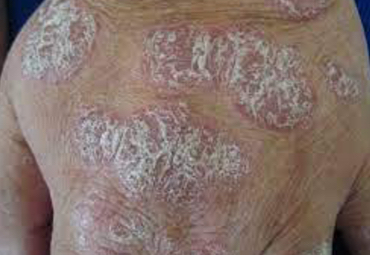
Identify class and type and features
Plaque, primary lesion. Palpable, psoriasis.
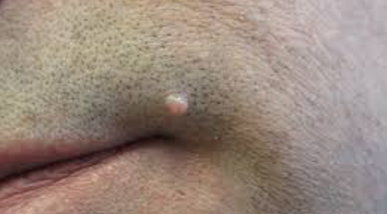
Identify class and type
Papule, primary lesion. Raised, insect bites, common wart.