L9: ELISA principles
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
What does ELISA stand for?
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay.
What is the main principle of ELISA?
It relies on the specificity of antibodies for antigens, detected through enzyme-linked antibodies that generate a measurable colour change proportional to antigen concentration.
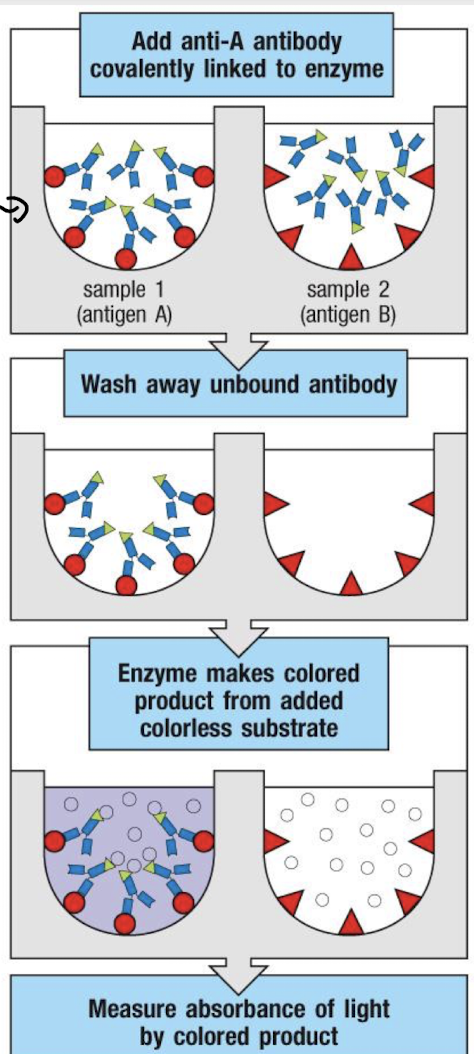
What are the main ELISA formats?
Direct and Indirect
Sandwich
Competitive (Inhibition)
What does the colour change in ELISA indicate?
The amount of antigen present—colour intensity is proportional to antigen concentration.
Why are antibodies ideal for diagnostic assays?
They are highly specific for their target antigens:
i.e. Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC-Ag)
Zika virus (IgM)
Which isotype is produced earliest in infection?
IgM is the earliest isotype produced during an infection, providing initial immune response.
What is affinity maturation?
The process that increases the binding strength of antibodies for their antigen through somatic hypermutation and selection.
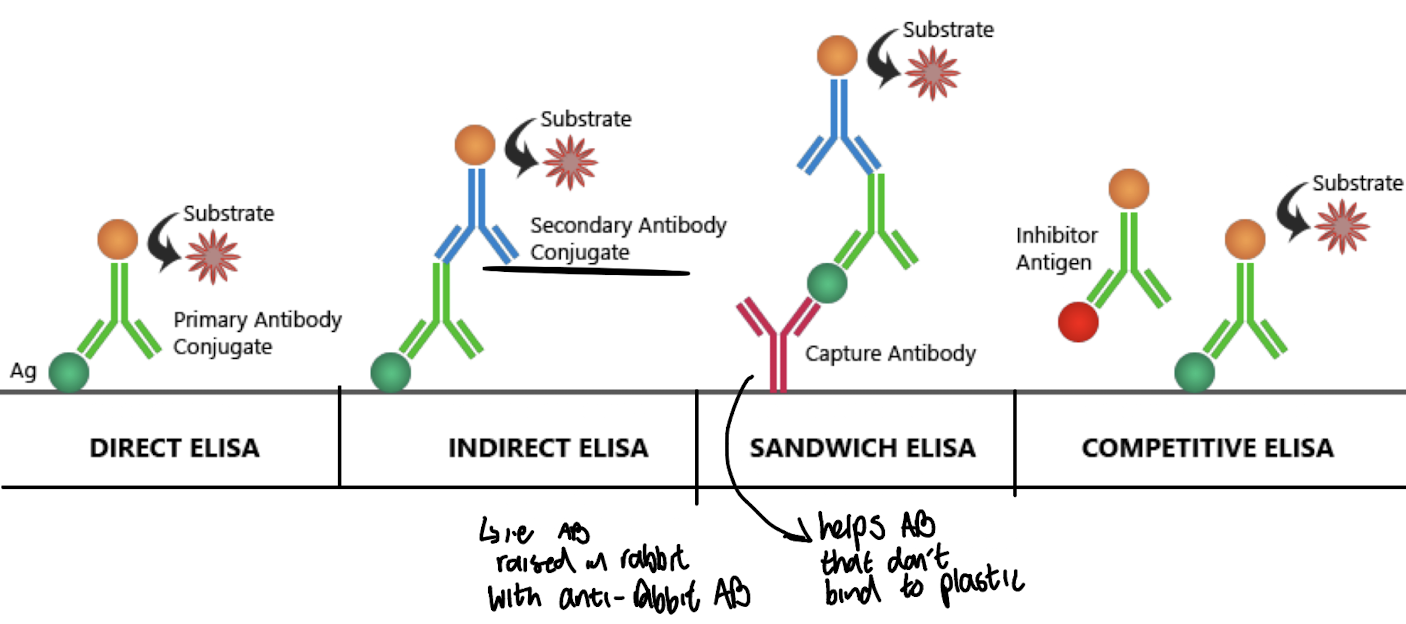
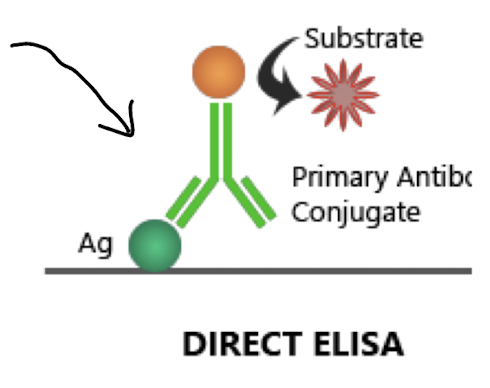
What is the key feature of a Direct ELISA?
The antigen is bound to a solid surface and detected directly by an enzyme-labeled antibody.
Advantages of Direct ELISA?
Quick, fewer steps, reduced potential for error.
Disadvantages of Direct ELISA?
Less flexible, higher background noise, no signal amplification, and antisera / antibodies raised against different antigens need labelling
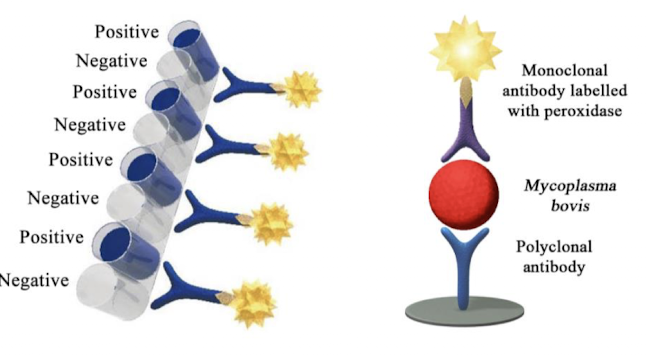
Example of Direct ELISA and what is its antigen?
Detection of Mycoplasma bovis (mastitis in dairy herds) using P48 antigen (lipoprotein on surface of M. bovis.
Enables rapid surveillance in herds, as assay is quick and easy to carry out by farmers
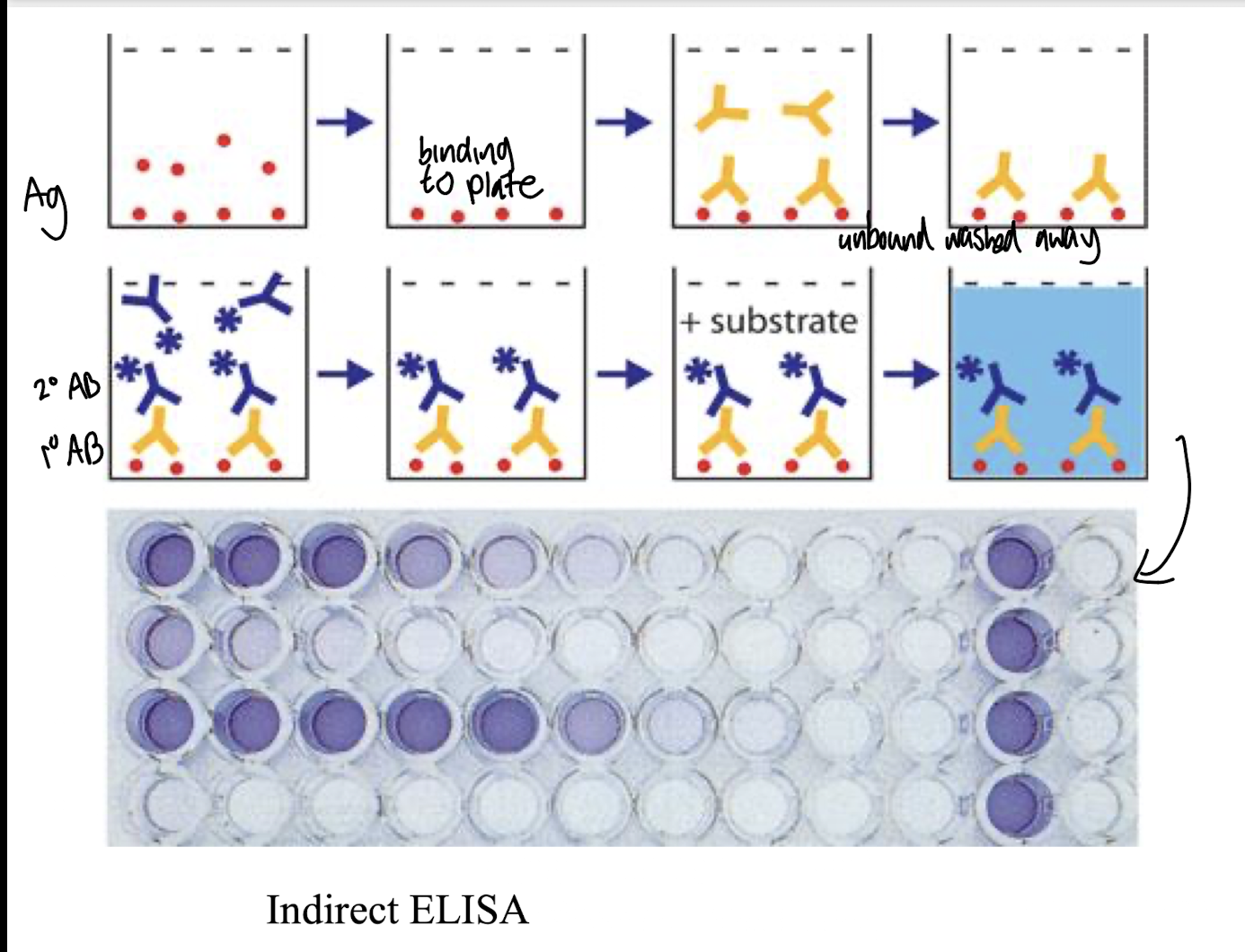
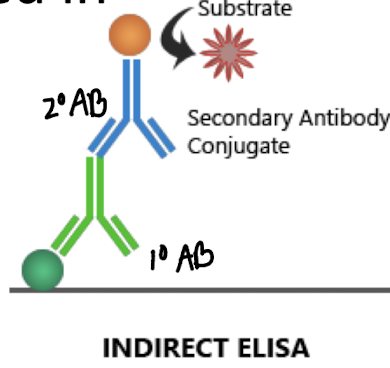
What is the main feature of an Indirect ELISA?
Uses a specific primary antibody which detects the antigen bound to a solid surface and a secondary enzyme-labeled Ab for detection, specific to the primary Ab.
Advantages of Indirect ELISA?
More specific (two Ab used) and flexible as the same labeled secondary antibody can detect multiple antigens.
Disadvantages of Indirect ELISA?
Slower—more incubation and washing steps.
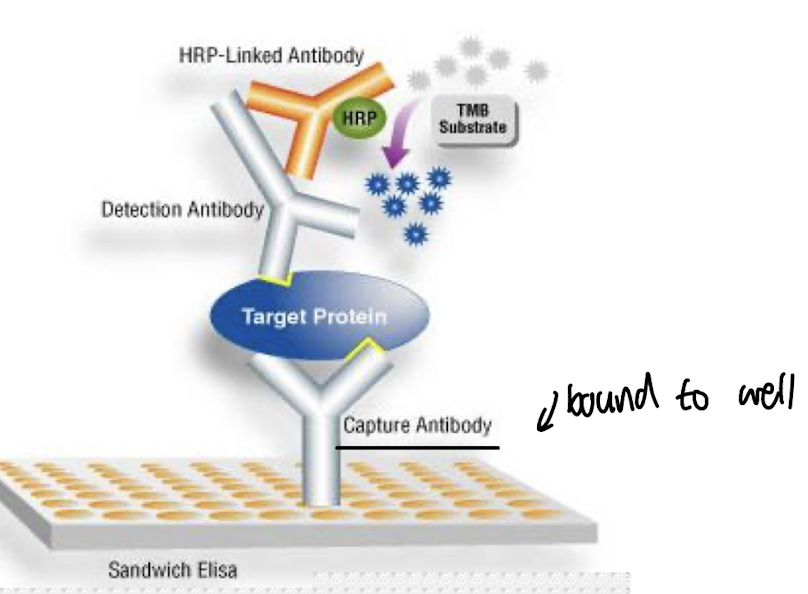
What is unique about a Sandwich ELISA?
It uses a constant dilution of capture antibody to immobilise the antigen, then detects it with a 2nd Ab.
Capture Ab coated on the solid phase
Unabsorbed Ab is washed away
*Capture Ab and 2nd Ab shouldn’t recognise the same site
Sensitive detection of Ag is attributed to an avidin- streptavidin HRP (horse-radish peroxidase) complex, which binds to the biotin conjugated to the enzyme-labelled Ab, allowing for a coloured peroxidase substrate to be generated from HRP, which is detectable using a spectrophotometer
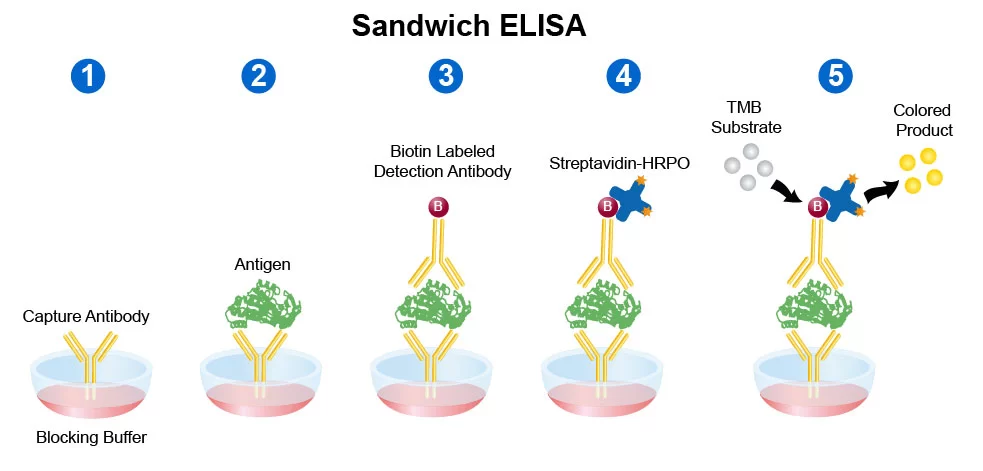
In Sandwich ELISA, the second Ab can be:
Produced in the same or different species
Why is Sandwich ELISA the most sensitive format?
It captures and detects antigen at two different epitopes, reducing background noise and increasing signal.
Disadvantages of Sandwich ELISA?
Requires large amounts of pure Ab and careful optimisation to avoid both Ab binding the same epitope.
What principle underlies Competitive ELISA?
Competition between a fixed amount of labelled and unlabelled (standard or test) antigen (or Ab) for limited binding sites.
This method reduces the amount of detectable signal as more unlabelled antigen increases, making it suitable for quantifying antigens in samples.
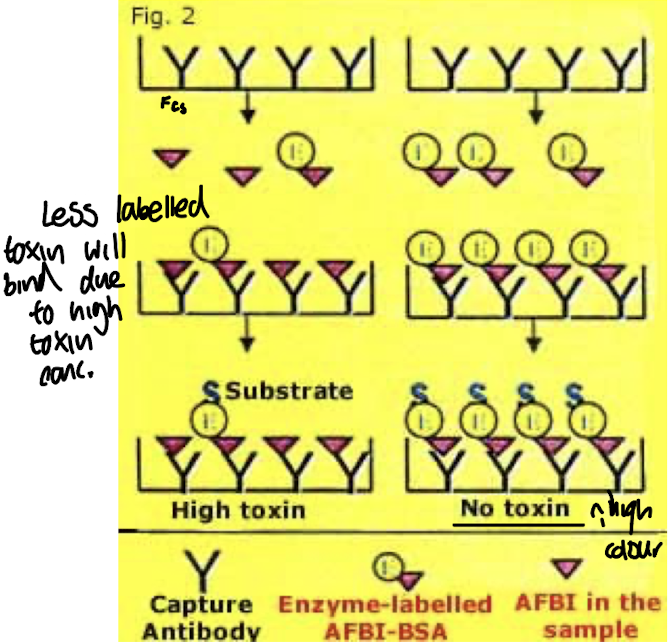
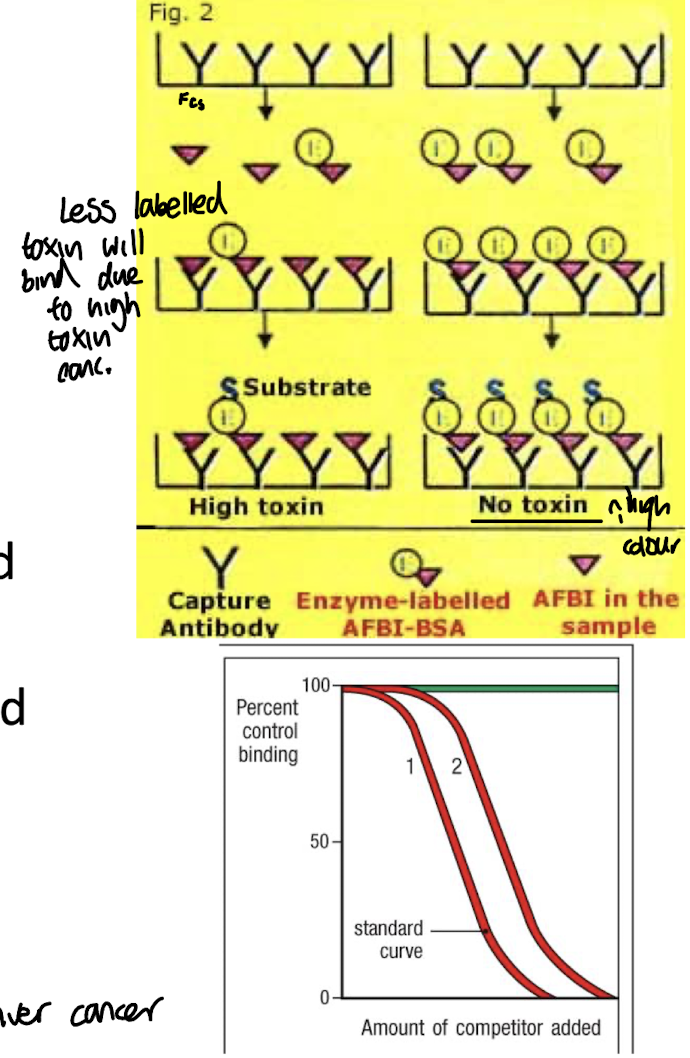
How is competitive ELISA used to detect Aspergillus contamination in grain stores?
By measuring the amount of antigen in the test samples, using a known quantity of labeled antigen to compete with the contaminant. A
As the conc. of Aspergillus antigen increases, it reduces the signal from the labeled antigen, allowing for quantification.
When is Competitive ELISA typically used?
When antigen is small or has a single epitope (e.g., hormones, drugs).
What materials are used to immobilize antigens or antibodies?
Plastic carriers such as polystyrene or PVC microtitre plates.
How do proteins attach to polystyrene plates?
Through hydrophobic interactions between non-polar protein substructures and a non-polar plastic matrix(passive adsorption).
What is the purpose of blocking in ELISA?
To fill unoccupied binding sites and prevent nonspecific binding
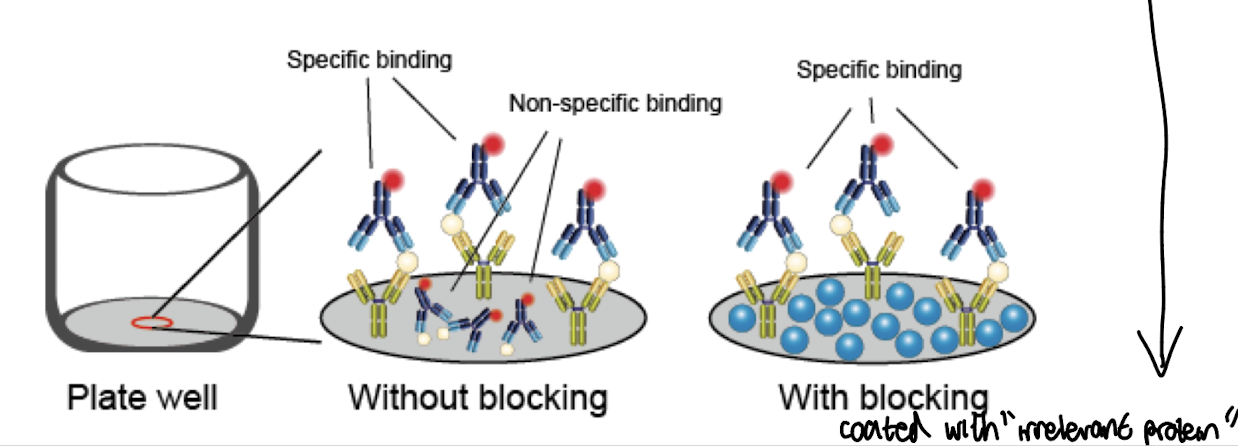
What is non-specific binding and how is it minimised?
Refers to enzyme labelled Ag or Ab binding specifically to the immobilised antigen but ALSO non-specifically to surfaces i.e microtitre plate that don’t involve specific interactions with target antigens or antibodies.
Minimised through blocking agents i.e non-ionic detergent like Triton X-100 / Tween 20 that occupy unbound sites on the solid phase.
Give examples of blocking agents.
BSA, casein, normal serum, gelatin, non-fat milk powder, Tween 20, Triton X-100.
“Irrelevant proteins that occupy nonspecific binding sites.”
Why are detergents used in washing steps?
To remove unbound reagents and minimise nonspecific binding without disrupting specific antigen-antibody interactions.
List four major diagnostic uses of ELISA.
Detection of tumour markers in serum
Infectious diseases
Hormones
Inflammatory markers.
What are examples of 2 approaches of using ELISA to diagnose infectious diseases?
Measure Ab to the pathogen, serology
Measure pathogen proteins in body fluids
Give examples of hormones detected by ELISA.
Steroid hormones i.e. cortisol
Protein (peptide based) i.e. FSH
Tyr derivatives i.e. thyroxine
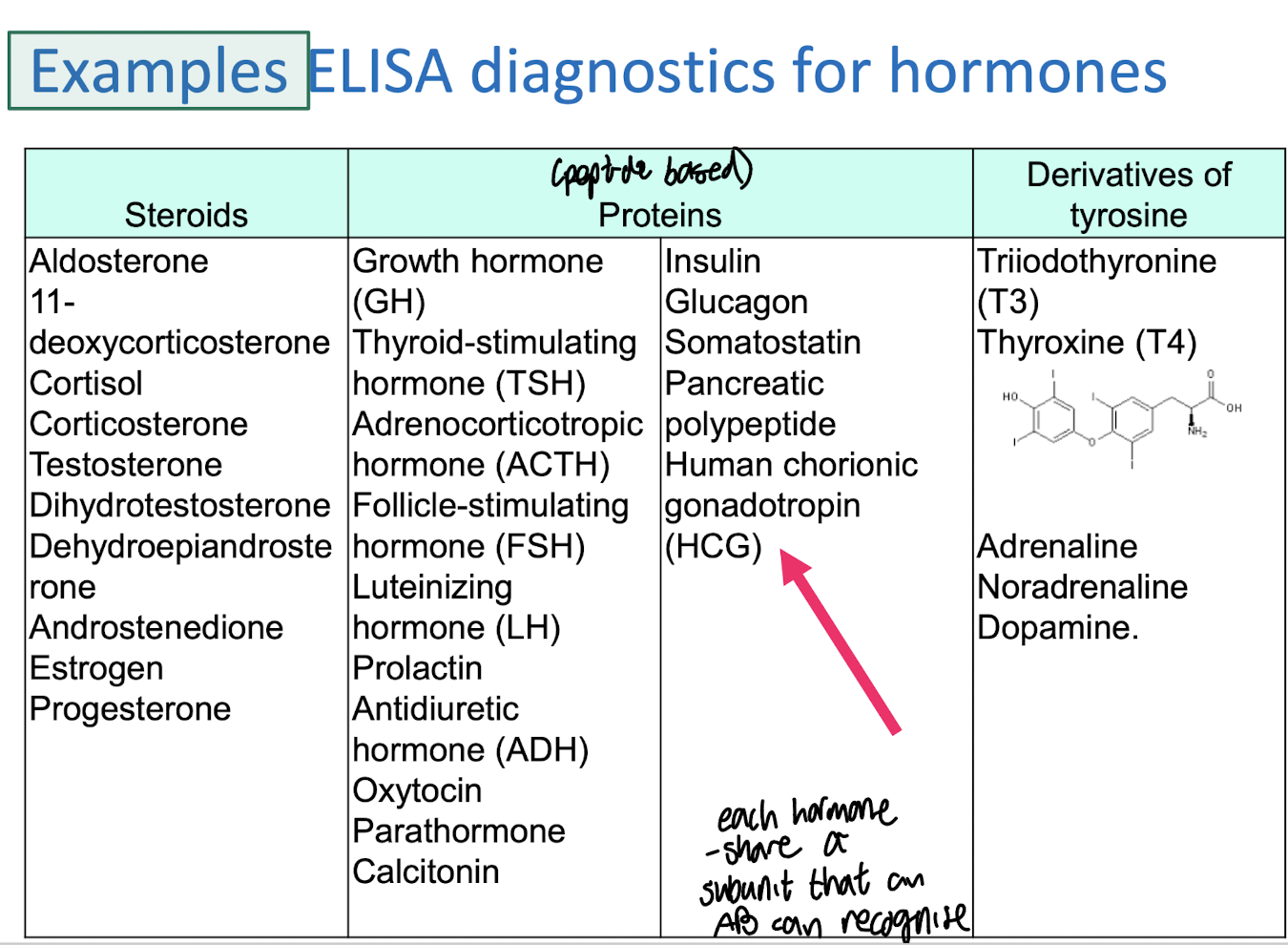
How can we distinguish between pituitary hormones like TSH and LH?
If the hormones are the same they will share the same ⍺ subunit but differ in their beta subunits, allowing for specific identification.
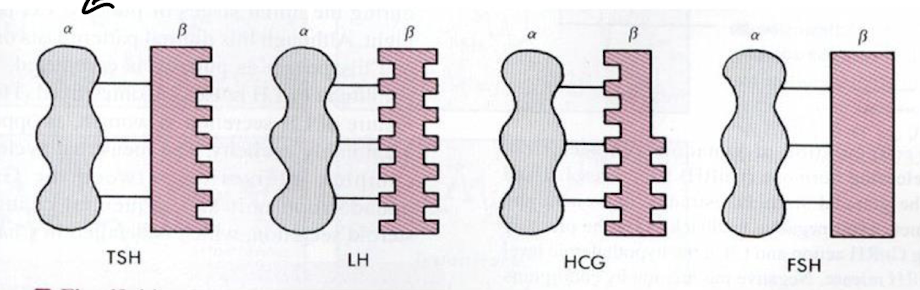
What is the role of ELISA in prostate cancer diagnosis?
Measuring PSA (tumour marker) levels to monitor disease progression and treatment response.
Serum levels correlate with tumour mass which can indicate stable or progressive disease
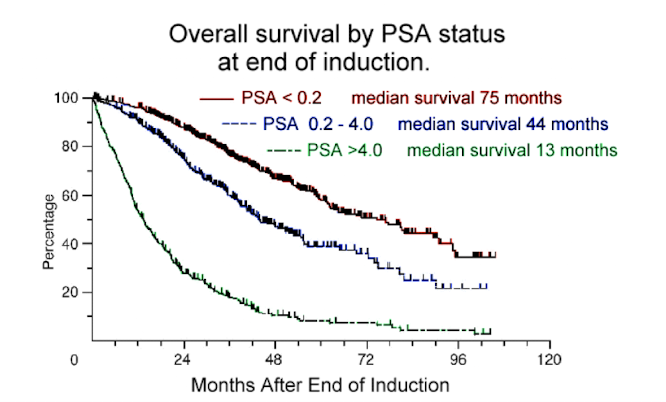
How is HIV diagnosed by ELISA?
Detection of viral-specific antibodies after the window period using recombinant envelope antigens to measure specific Ab
Used often to screen blood donations
In the case of HIV Ab screening, why are the assays configured to give more false positives over a few false negatives?
This is because it is crucial to identify all potential cases of HIV to provide timely treatment and prevent transmission, as any false negatives could lead to serious health risks.
What hormone is detected in pregnancy tests using ELISA principles?
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG).
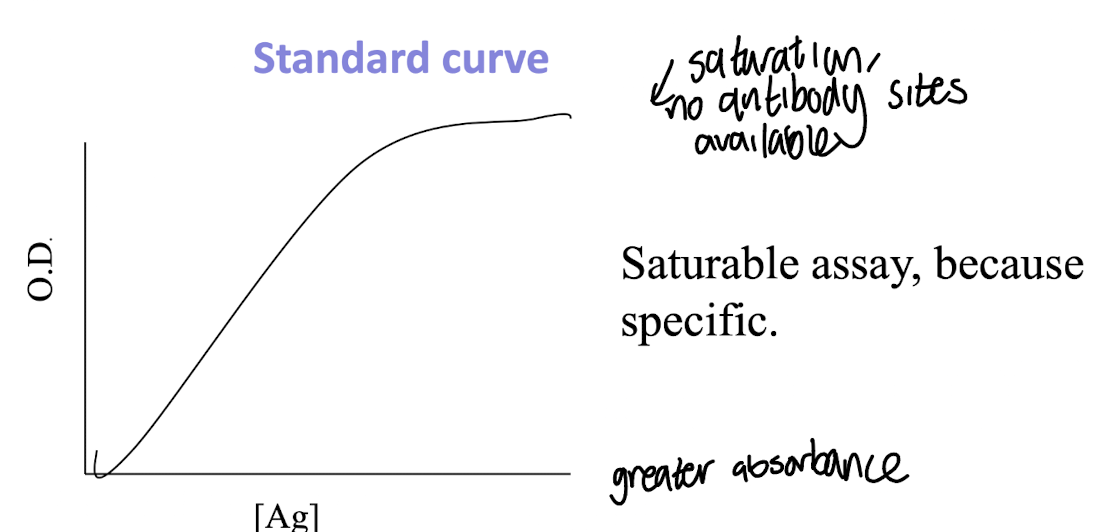
Why is a standard curve important in ELISA?
It allows quantitative determination of unknown antigen concentrations based on absorbance readings.
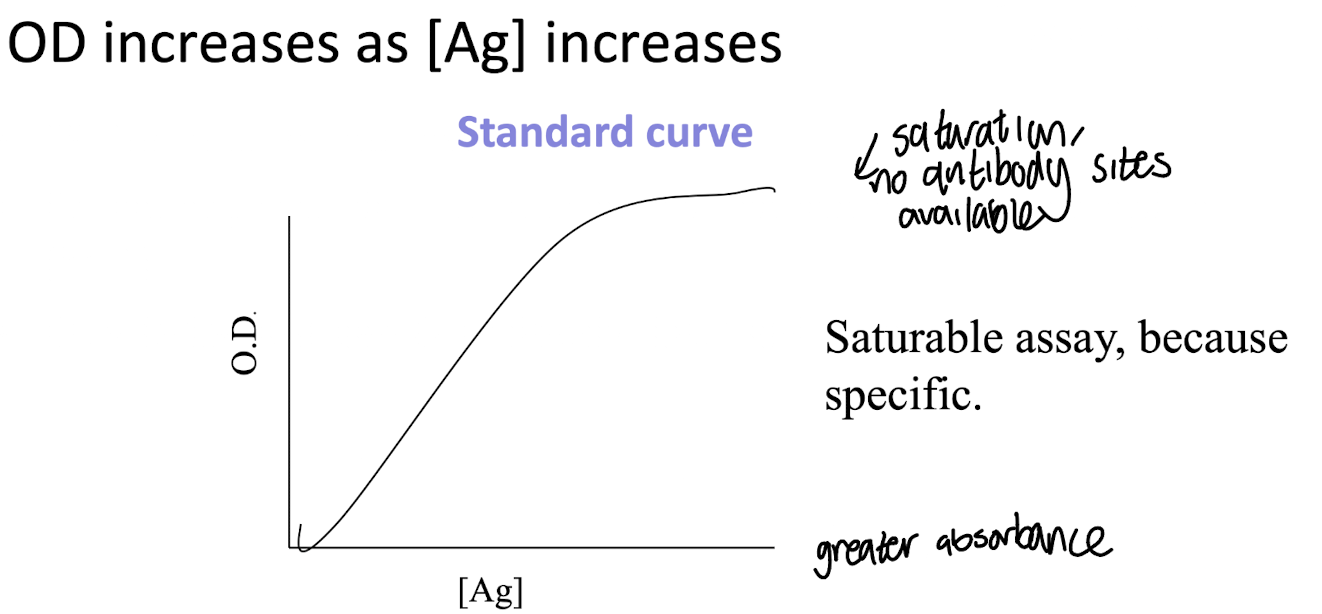
How does the standard curve in ELISA show that it is a saturable assay?
The standard curve demonstrates that, at high concentrations of the antigen, increasing the amount of antigen does not significantly change the signal, indicating that the assay reaches saturation.
In a sandwich ELISA, if no colour develops, what could be the cause?
Absence of antigen, degraded enzyme conjugate, or missing secondary antibody.
What happens if washing is insufficient?
Non-specific binding increases, leading to false positives.
Define sensitivity in diagnostic testing.
The ability of a test to correctly identify true positives.
Define specificity in diagnostic testing.
The ability of a test to correctly identify true negatives.
What is the relationship between sensitivity and false negatives?
Higher sensitivity reduces false negatives.
What is the relationship between specificity and false positives?
Higher specificity reduces false positives.
What are point-of-care (POC) antibody tests?
Rapid diagnostic kits used outside the lab, e.g., pregnancy or COVID-19 tests.
How do COVID-19 antigen tests detect infection?
By using antibodies that bind to SARS-CoV-2 nucleoprotein antigen.
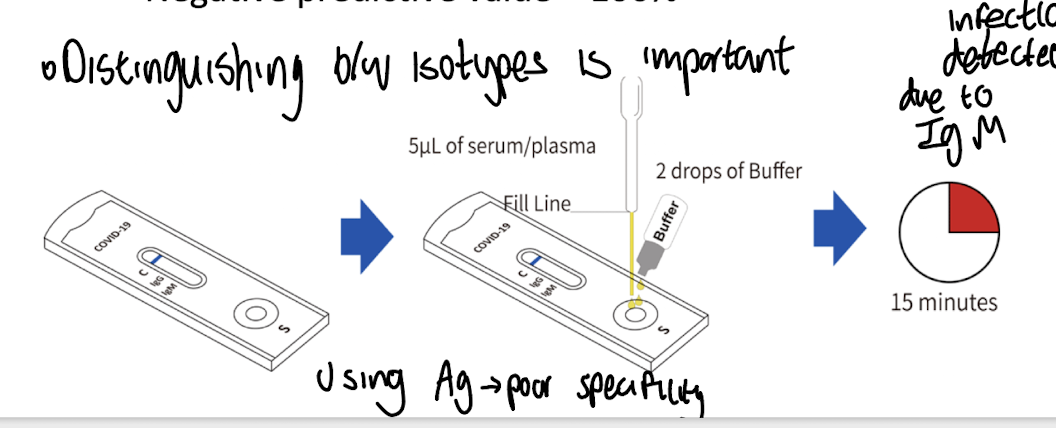
What do the 'C' and 'T' lines represent in a COVID test?
'C' is the control line (valid test), 'T' indicates presence of target antigen.
What are multiplex ELISAs?
Assays that detect multiple analytes in one sample using color-coded or bead-based systems.