Unit 05 - Electrons in Atoms
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
the test being tomorrow the day I come back is crazy
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
Electromagnetic Radiation
Form of energy that exhibits wavelike behaviour as it travels through space
Radiant Energy
Energy that travels in the form of waves; both electrical and magnetic properties
EM Spectrum
Whole range of EM radiation
Frequency
The number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time
Wavelength
The distance over which the wave's shape repeats
3.00 × 108 m/s
Speed of light (c) = ___
wavelength
The lower the frequency, the higher the ___.
frequency
The lower the wavelength, the higher the ___.
1km-1cm
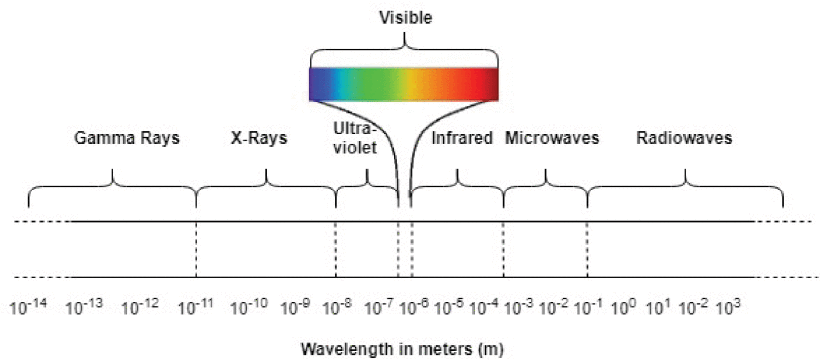
Radio Waves
0.1cm-1mm
Microwaves
1mm-1hm
Infrared (IR) Waves
1hm-100nm
Visible Waves
100nm-10nm
Ultraviolet (UV) Waves
10nm-0.001nm
X-Rays
0.001nm-0.00001nm
Gamma (y) Rays
E = hv
Energy equation for finding photons in waves
6.626 × 10^-34 J*s
Planck’s constant (h)
Niels Bohr
Proposed that electrons must have enough energy to keep them in constant motion around the nucleus
Planetary Model
All + charge and mass in nucleus
Electrons circle the nucleus in circular paths
Orbitals
__ are circular paths around atoms. They are defined with the quantum number n and can only be whole numbers and start at 1. They are regions of space in which electrons can move freely about the nucleus of an atom. More Specific.
n=1
<=2 electrons
n=2
<=8 electrons
n=3
<=18 electrons
Ground State
When electrons are in their lowest energy orbitals
Excited State
When energy is added to electrons, and they absorb it & jump to the next energy orbital
Emission
Excited → Ground. Energy released. e.g: visible light
emission spectrum
Range of light released from excited atoms of an element is called the __ of that element
Energy Levels
Fixed distances around the nucleus where an electron is likely to be found.
Electron Clouds
Space around the nucleus where electrons are most-likely found. More Broad.
speed of light (3.00 × 10^8 m/s)
Electrons move at the __ (__).
Aufbau Principle
Electrons occupy the lowest energy orbitals available
Pauli Exclusion Principle
A maximum of two electrons can occupy a single atomic orbital; electrons spin opposite directions.
Hund’s Rule
Single electrons with the same spin must occupy each equal-energy orbital before more electrons with opposite spins can occupy the same orbitals that these electrons are on; basically, all electrons in one orbital must have the same spin before other electrons with opposite spin can join in that orbital.
Valence electrons
Electrons in the outmost energy levels
Groups
Columns in the periodic table
Periods
Rows in the periodic table
G3-G12
Groups with 0 valence electrons
Electron Dot Diagram; 1 electron; 1 energy level; 1 orbital; 1 valence electrons; 1 possible bond
Diagram name; # of electrons; # of energy levels; # of orbitals; # of valence electrons; # of possible bonds