Biology - Chapter 19: Cell Junctions and Extracellular Matrix | Quizlet
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
extracellular matrix (ECM)
a complex network of proteins and polysaccharide chains that the cells secrete
connective tissues (bone, tendon)
formed from extracellular matrix produced by cells that are distributed sparsely in the matrix
epithelial tissues
cells form sheets called epithelia, ECM is less pronounced (basal lamina)
basal lamina (basement membrane)
thin extracellular layer that lies underneath epithelial cells and separates them from other tissues
anchoring junctions
link cytoskeleton to adjacent cells or ECM (adherens junctions, desmosomes, actin-linked cell-matrix junctions, hemidesmosomes)
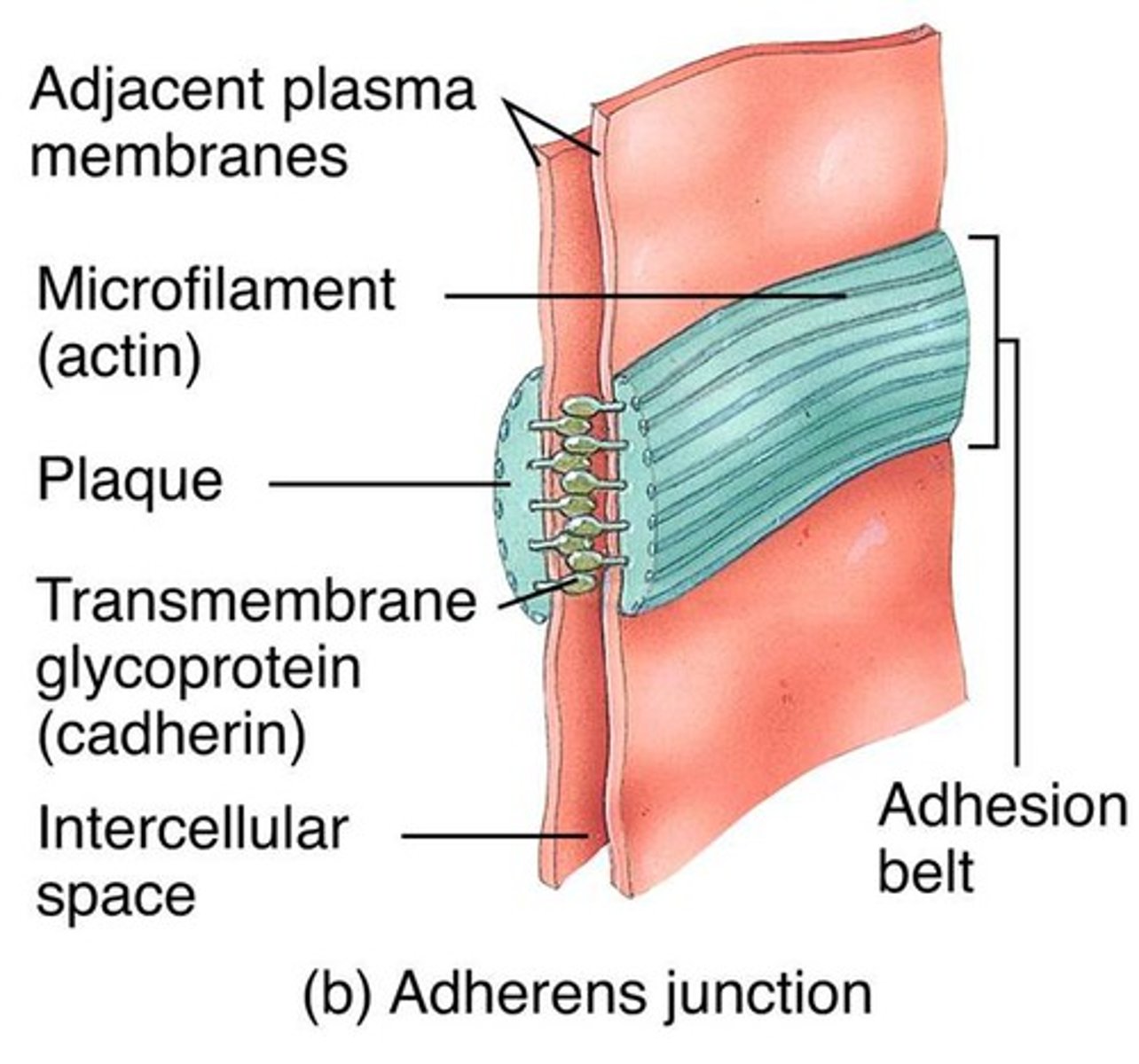
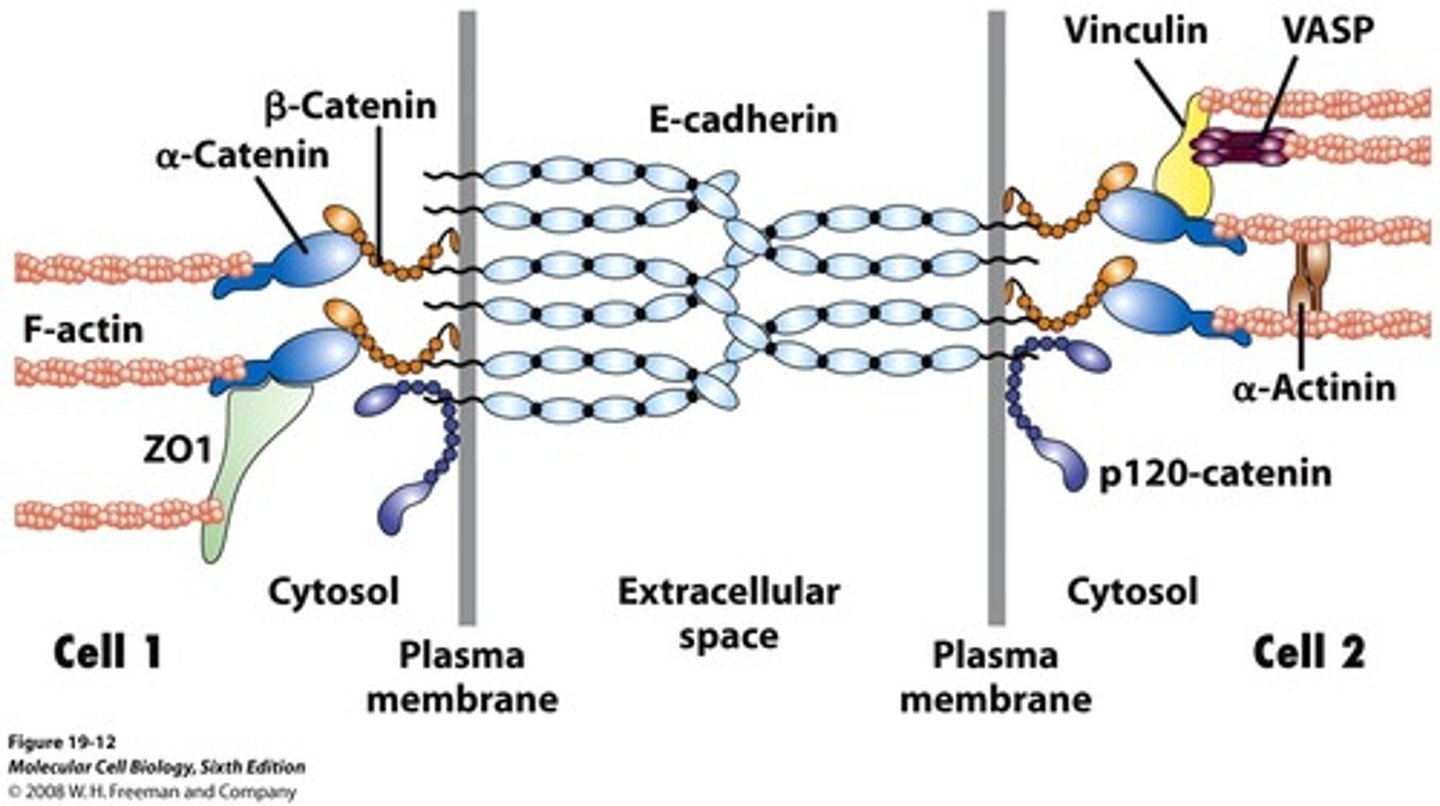
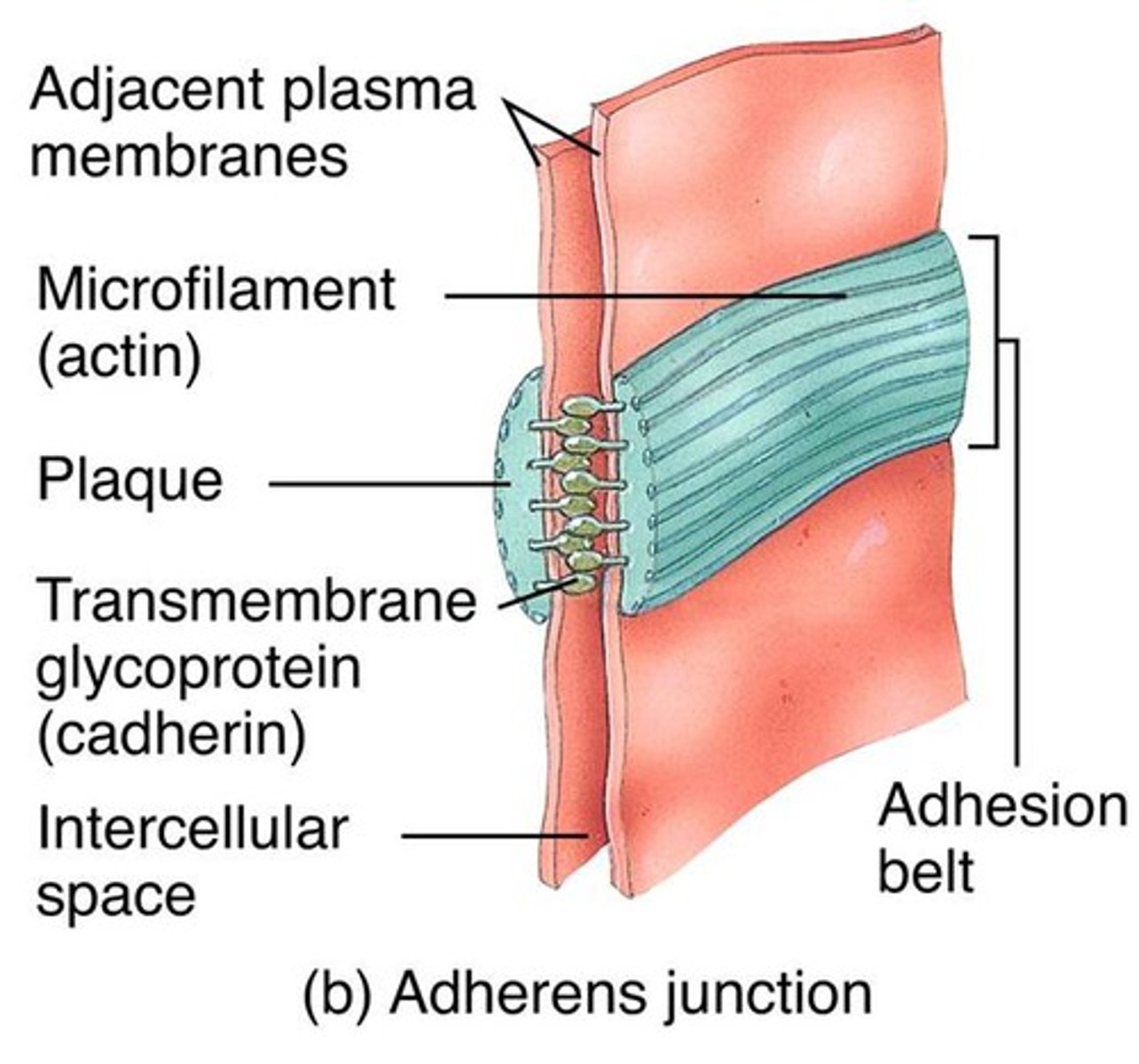
adherens junctions
anchorage sites for actin filaments
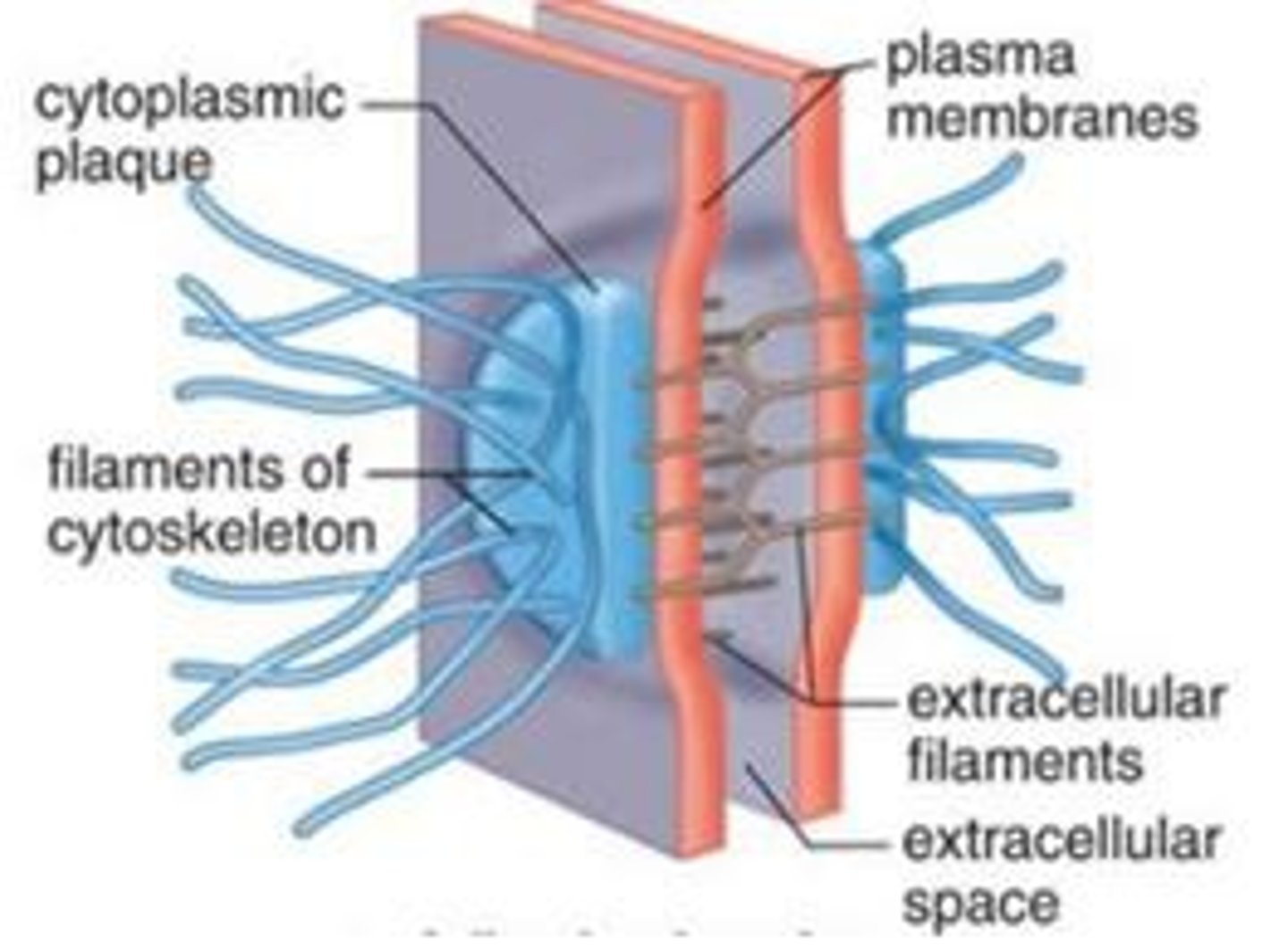
desmosomes
anchorage sites for intermediate filaments
transmembrane adhesion proteins
mediate anchoring junctions; include cadherins (to other cells) and integrins (to ECM)
classical cadherins
E-cadherin, N-cadherin, P-cadherin
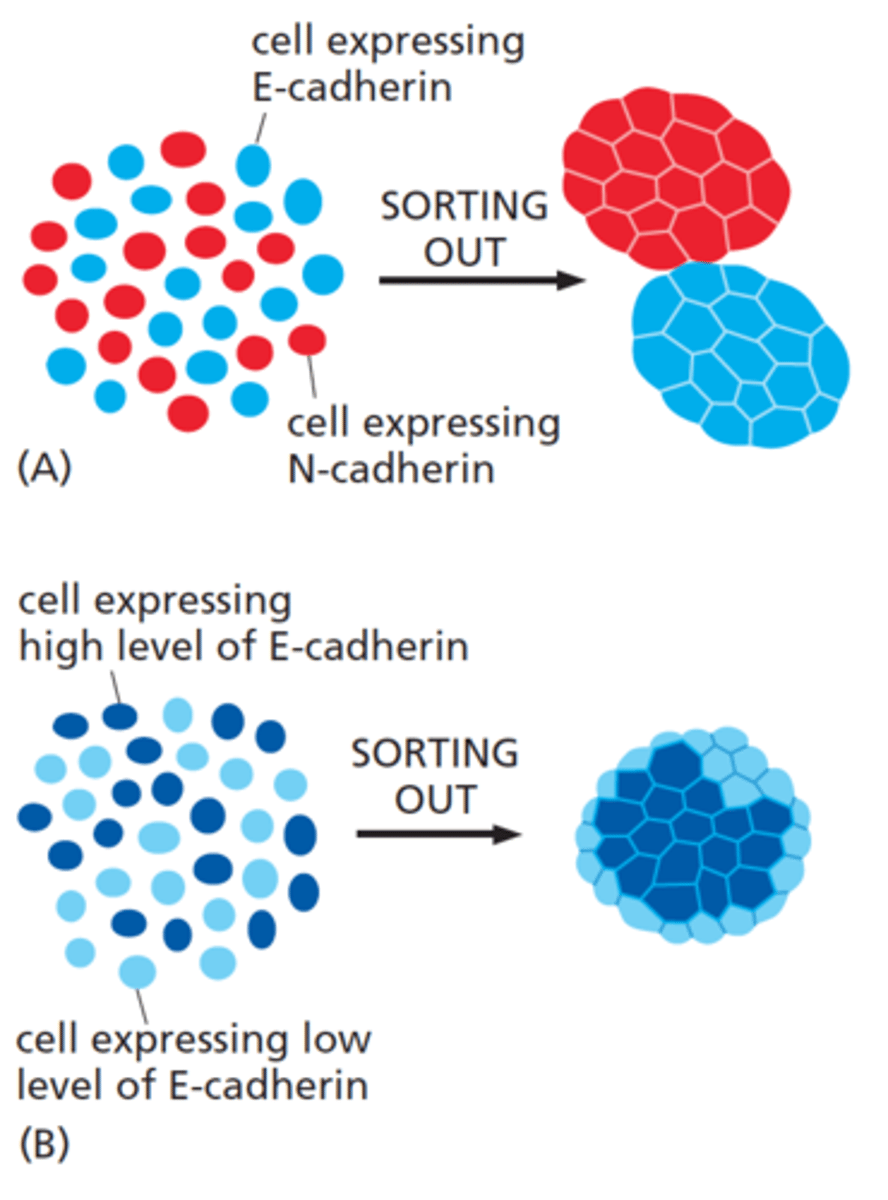
binding of cadherins is
homophilic
high selectivity of cadherins
important for cadherin-dependent cell sorting
mesenchymal cells
Stem cells that differentiate into fibroblasts, macrophages, etc.
epithelial-mesenchymal transitions
epithelial cells change their character, disassemble, and migrate away from their parent epithelium as separate cells
epithelial-mesenchymal transition is regulated by transcription proteins:
Slug, Snail and Twist
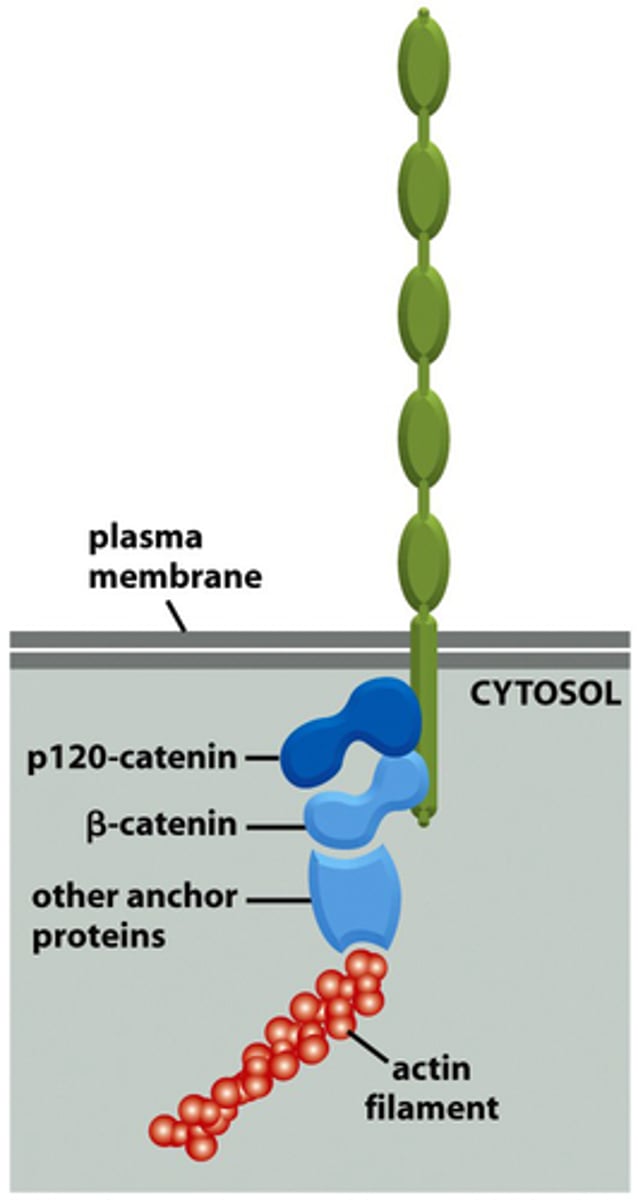
p120-catenin
(adherens junction) binds to cytoplasmic tail of cadherin
β-catenin
adaptor protein binding alongside p120 onto the actin filament
α-catenin
(adherens junctions) binding to β-catenin and actin filament
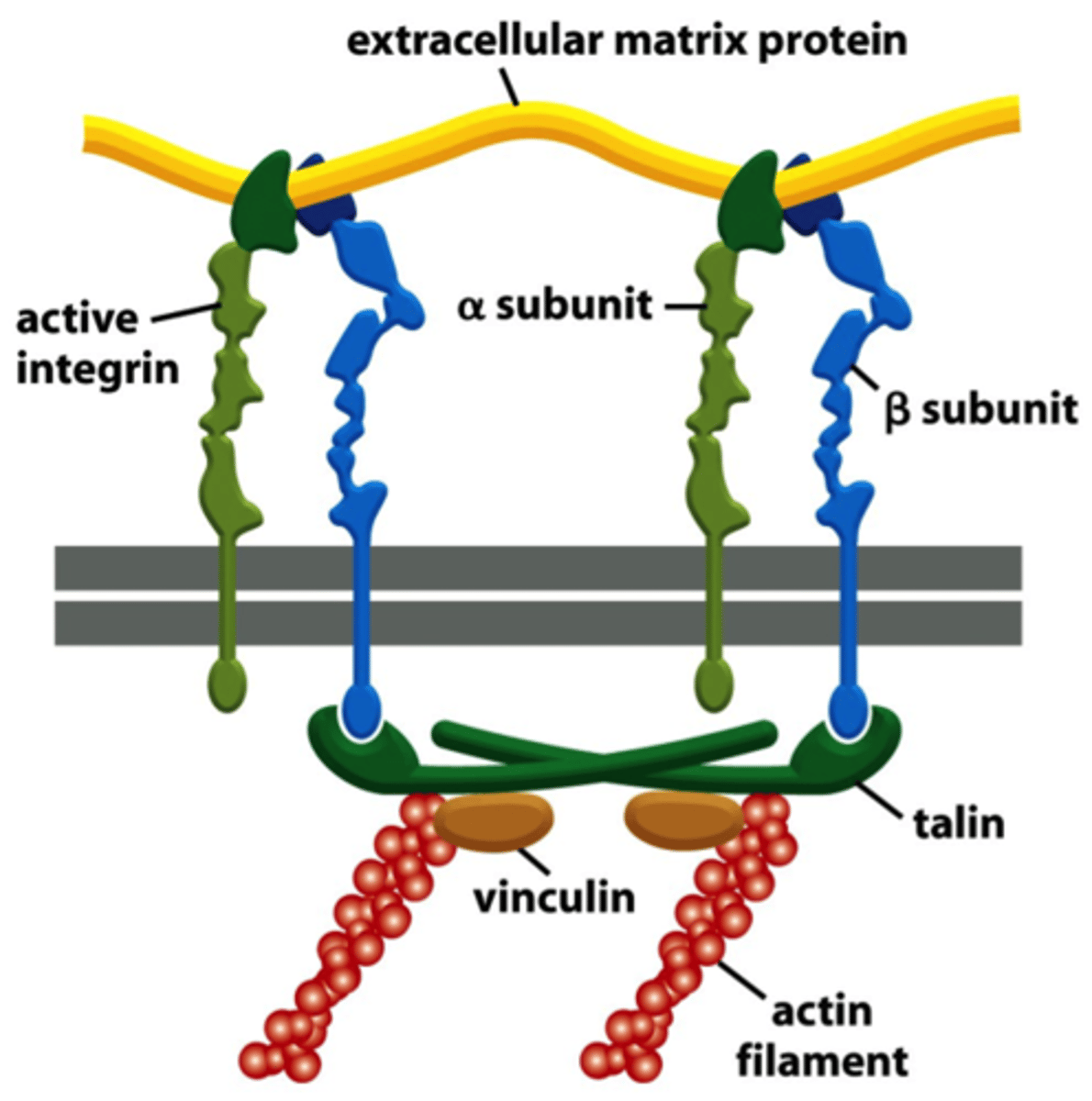
vinculin
connects actin filament to α-catenin
plankoglobin
adaptor protein connecting intermediate filaments and cadherins
Adhesion belts (in adherens junction)
continuous band of membrane proteins
intercalation
loss of adherens junctions to allow new cells to be inserted
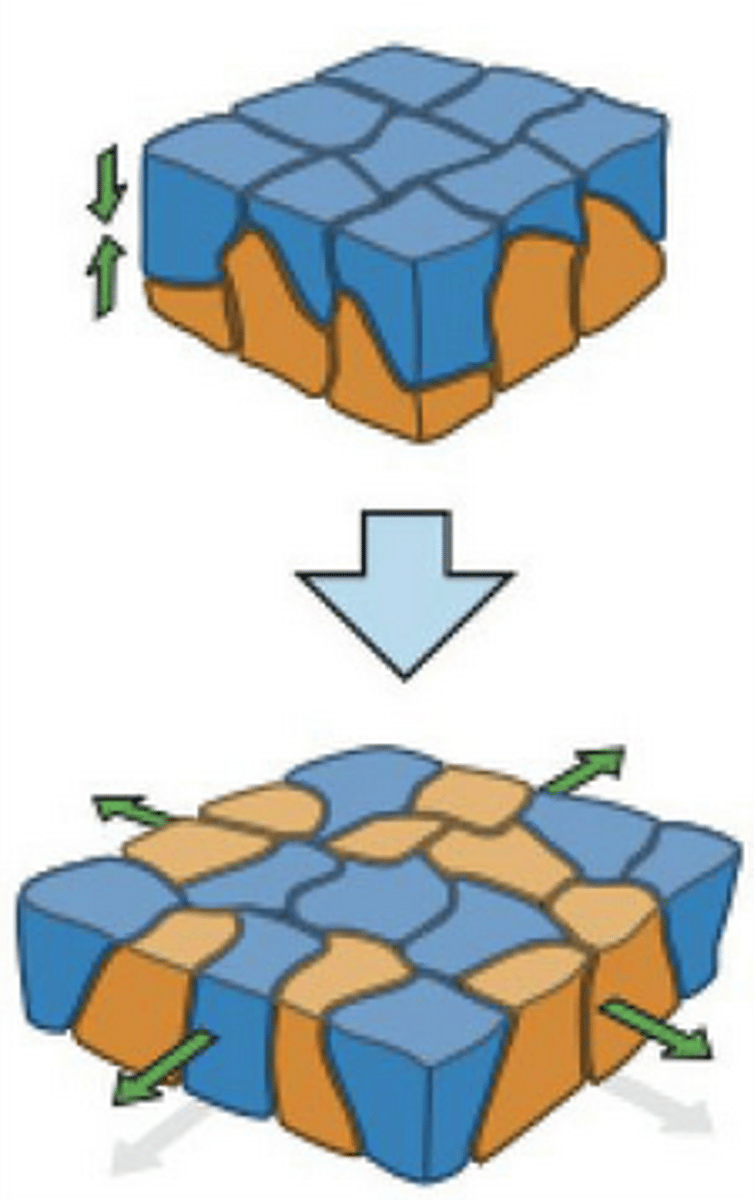
tight junctions
prevent leakage of extracellular fluid across a layer of epithelial cells
transmembrane proteins forming tight junctions
claudin (essential), occludin, tricellulin, JAM
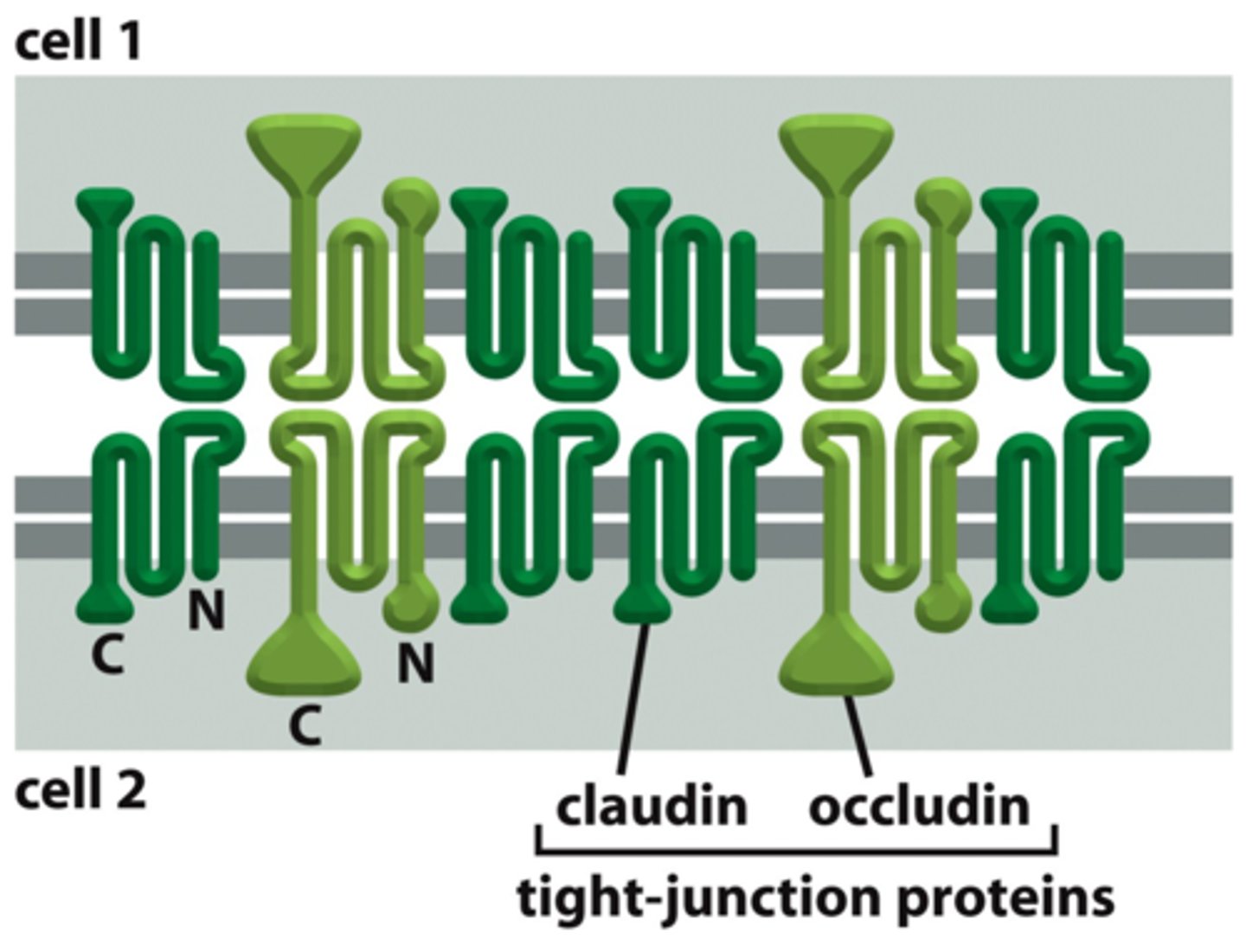
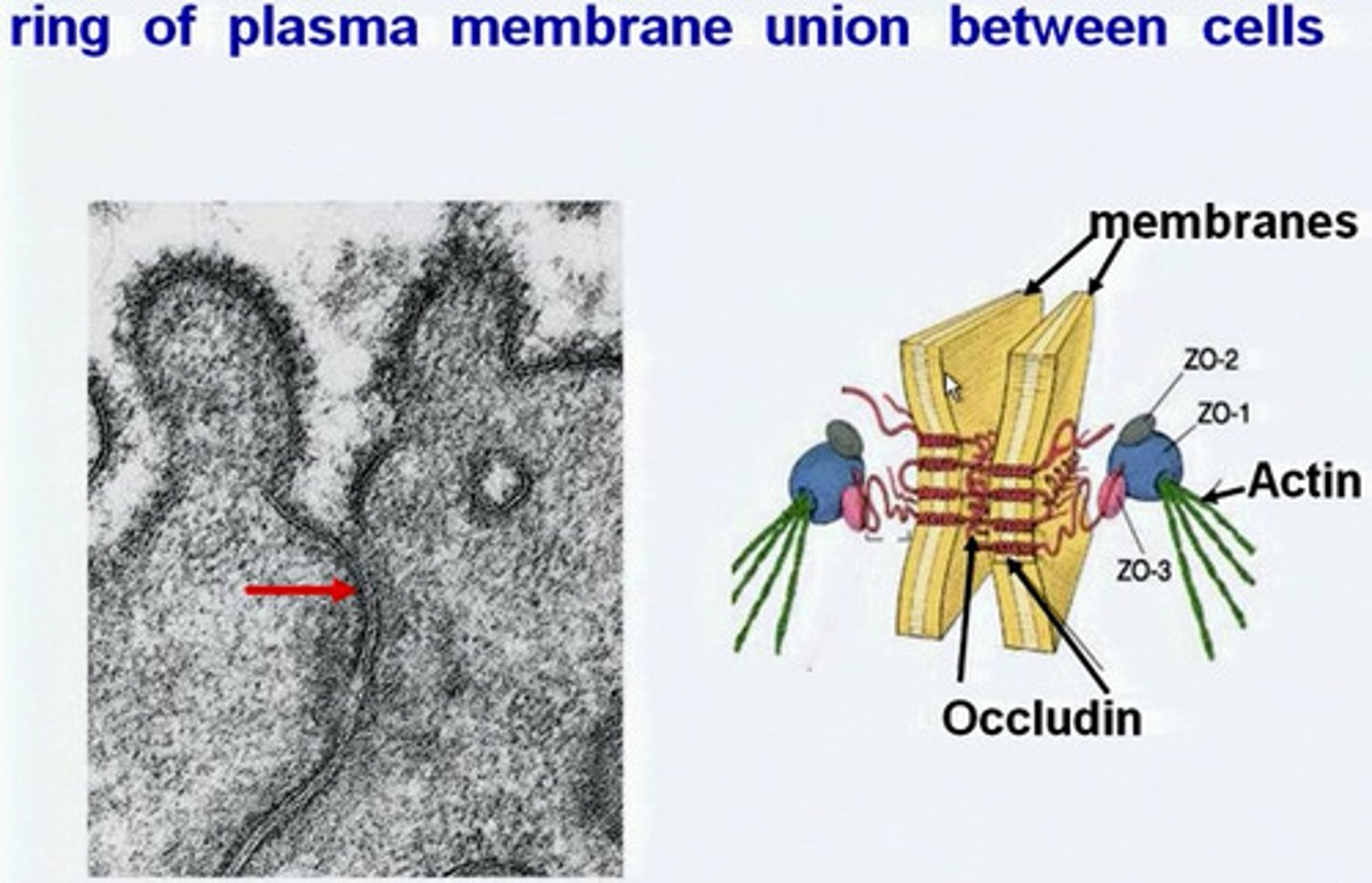
key organizational proteins at tight junctions
zonula occludens (ZO) - scaffold proteins with PDZ domains
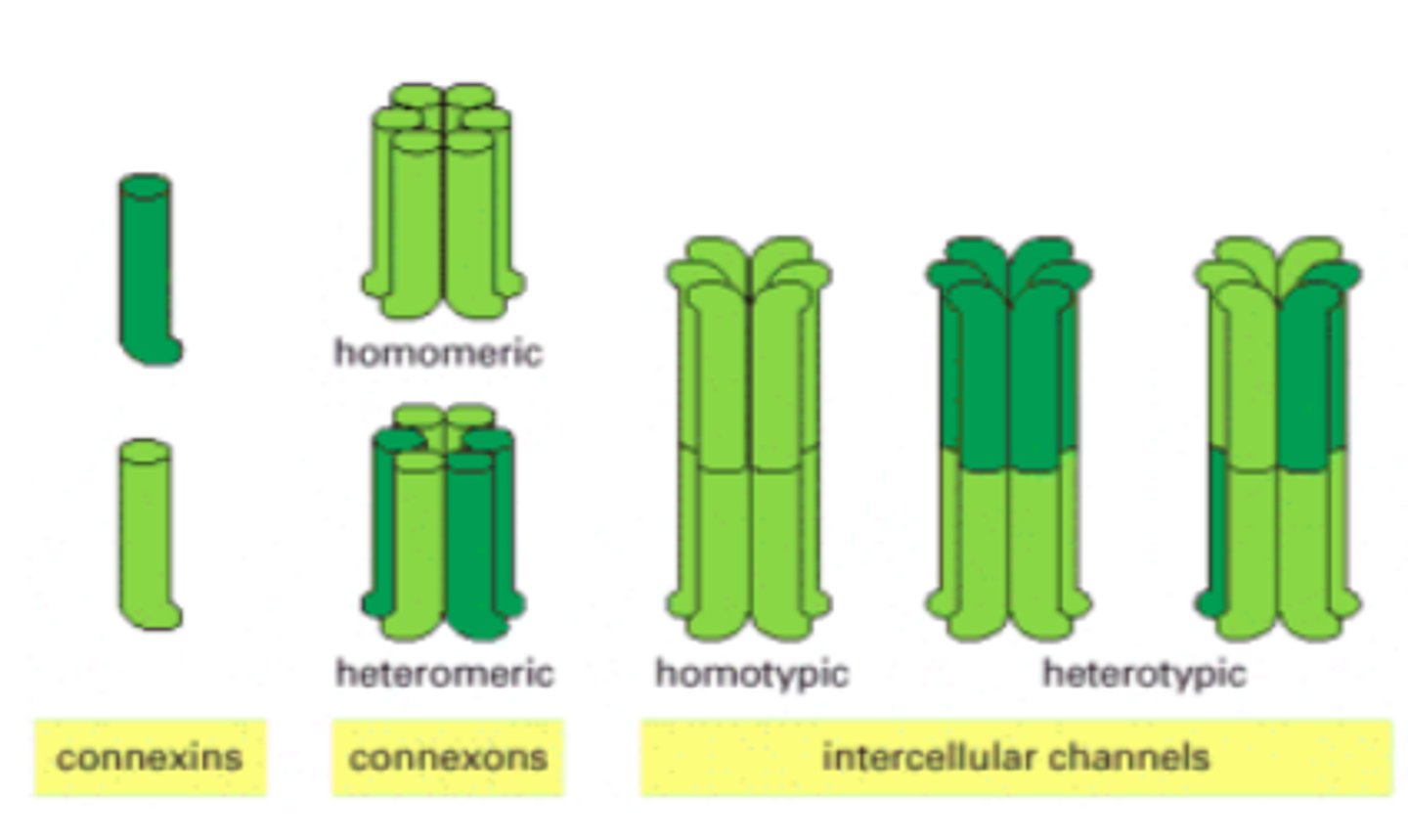
gap junctions
provide cytoplasmic channels between adjacent animal cells
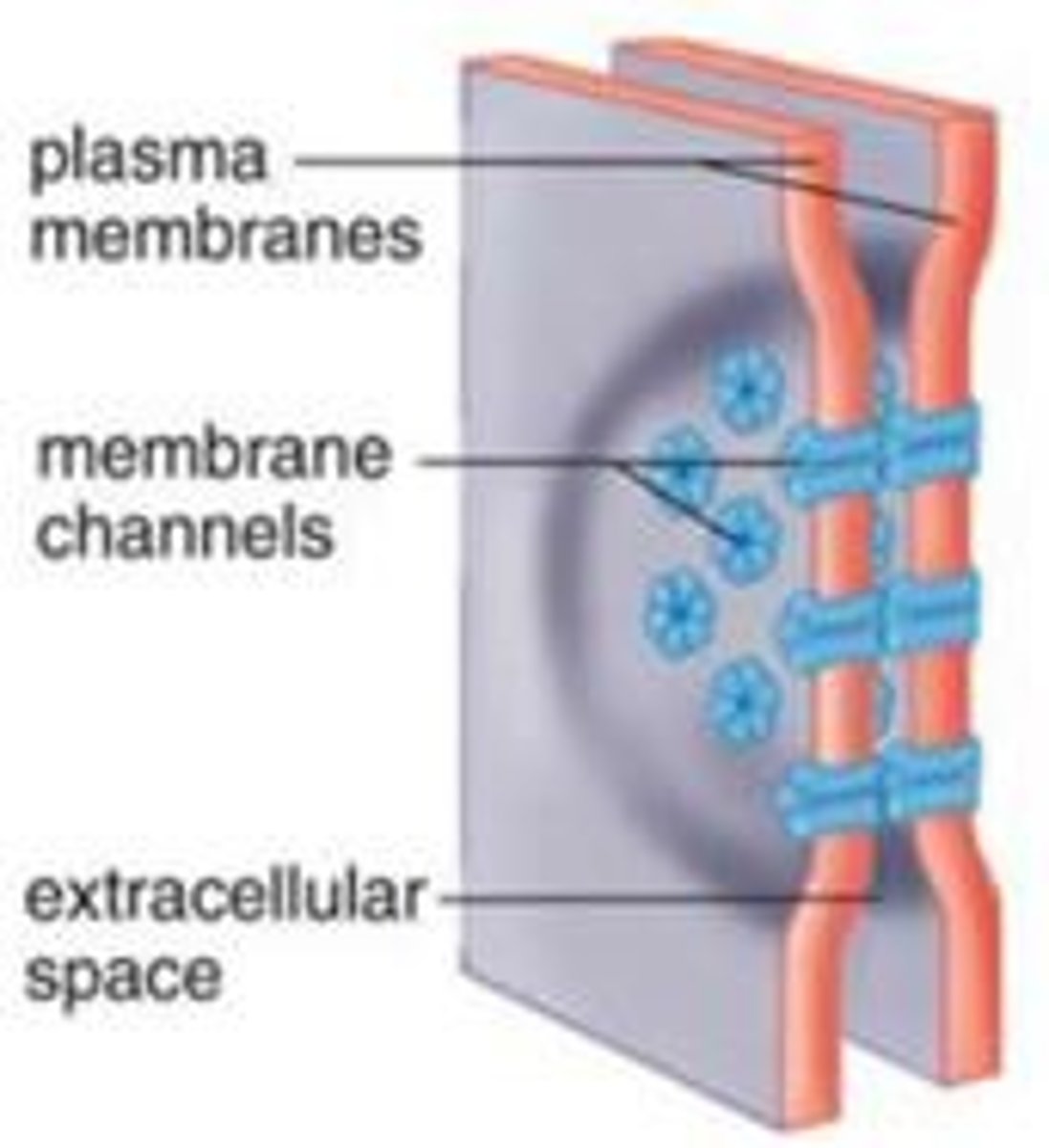
channel-forming proteins
connexins and innexins
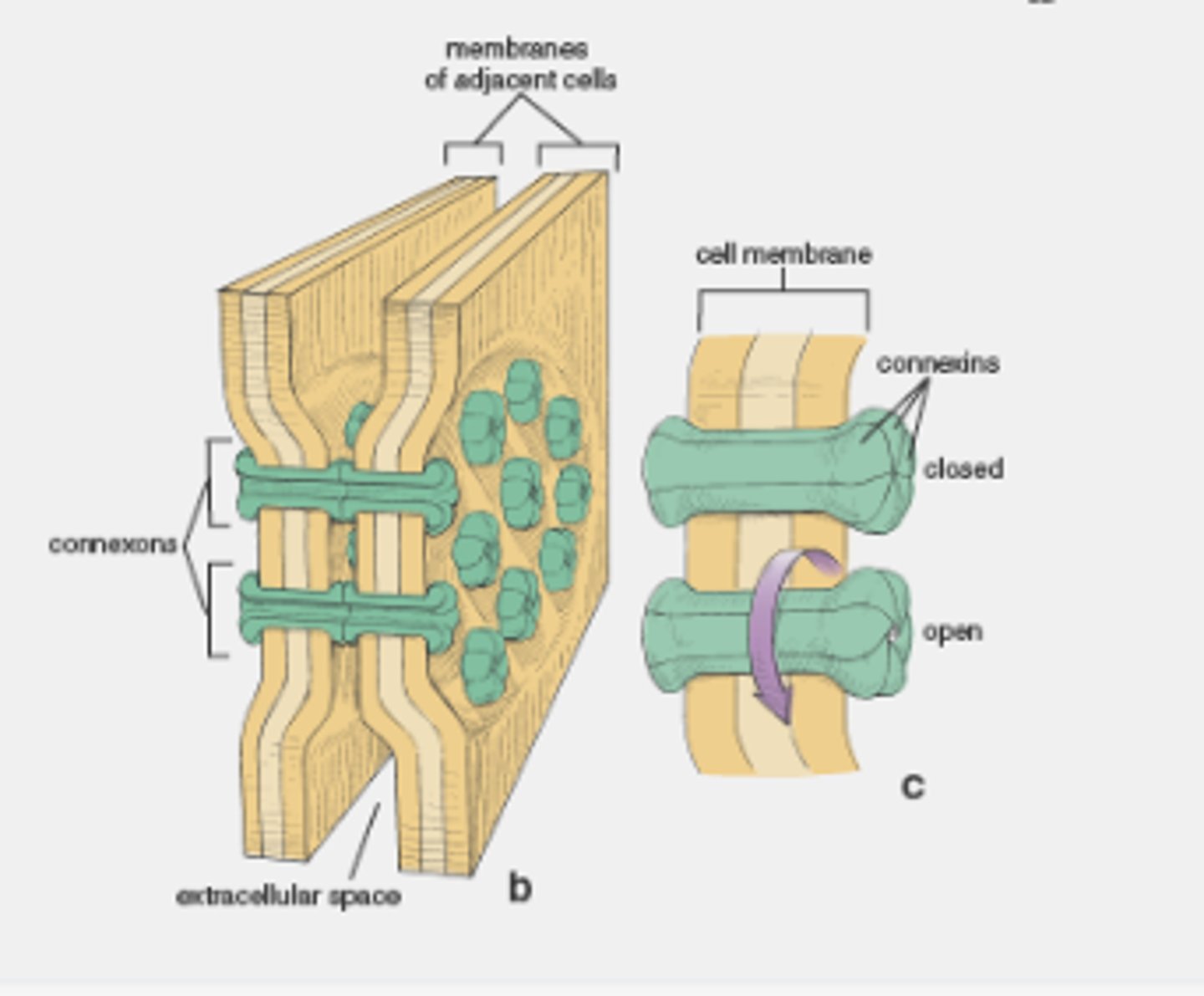
Gap junctions have a pore size of about 1.4 nm, which allows the exchange of
inorganic ions and small water-soluble molecules
connexon
six connexins combined
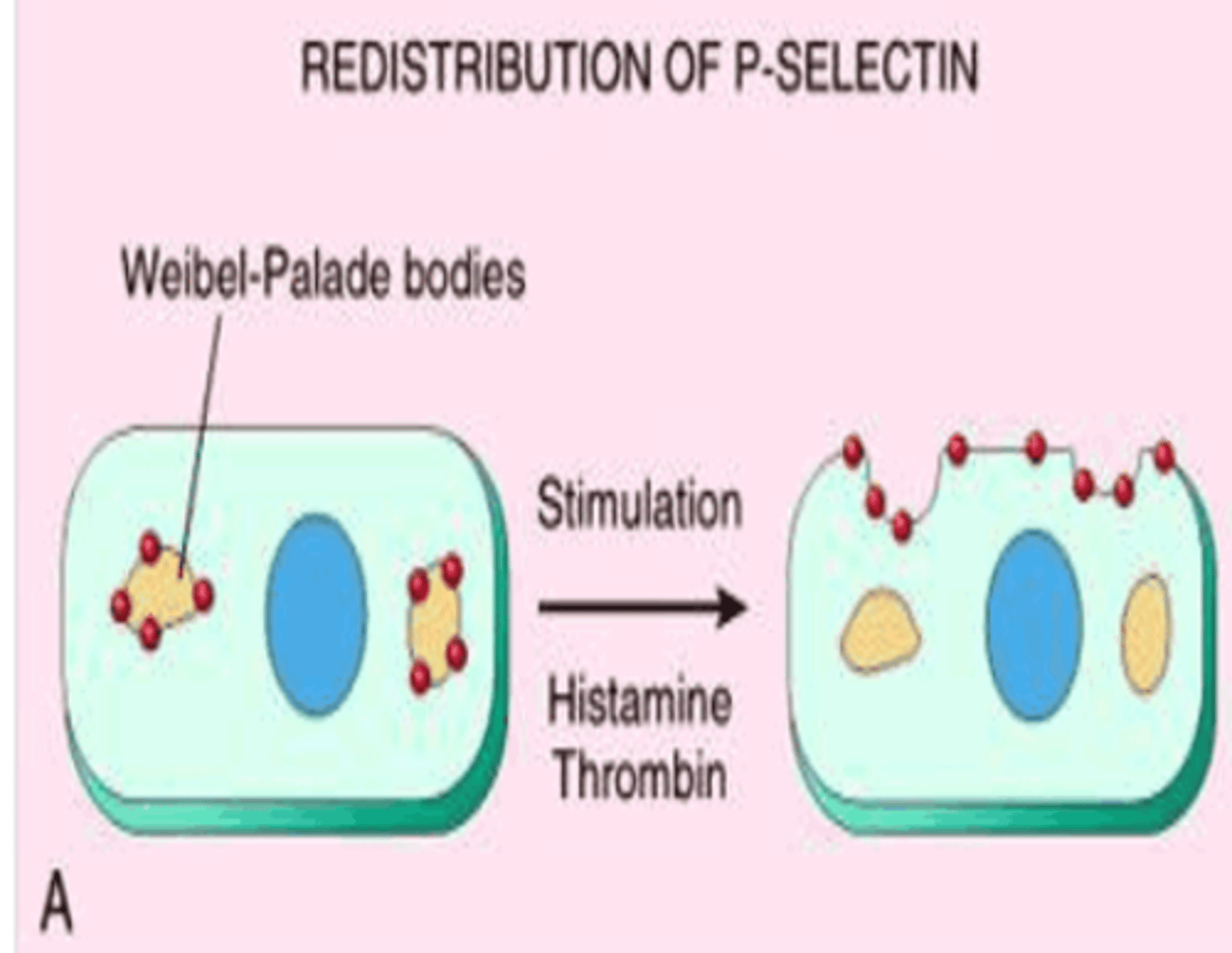
selectins
cell-surface carbohydrate-binding proteins (lectins) that mediate a variety of momentary cell-cell adhesion interactions in the bloodstream
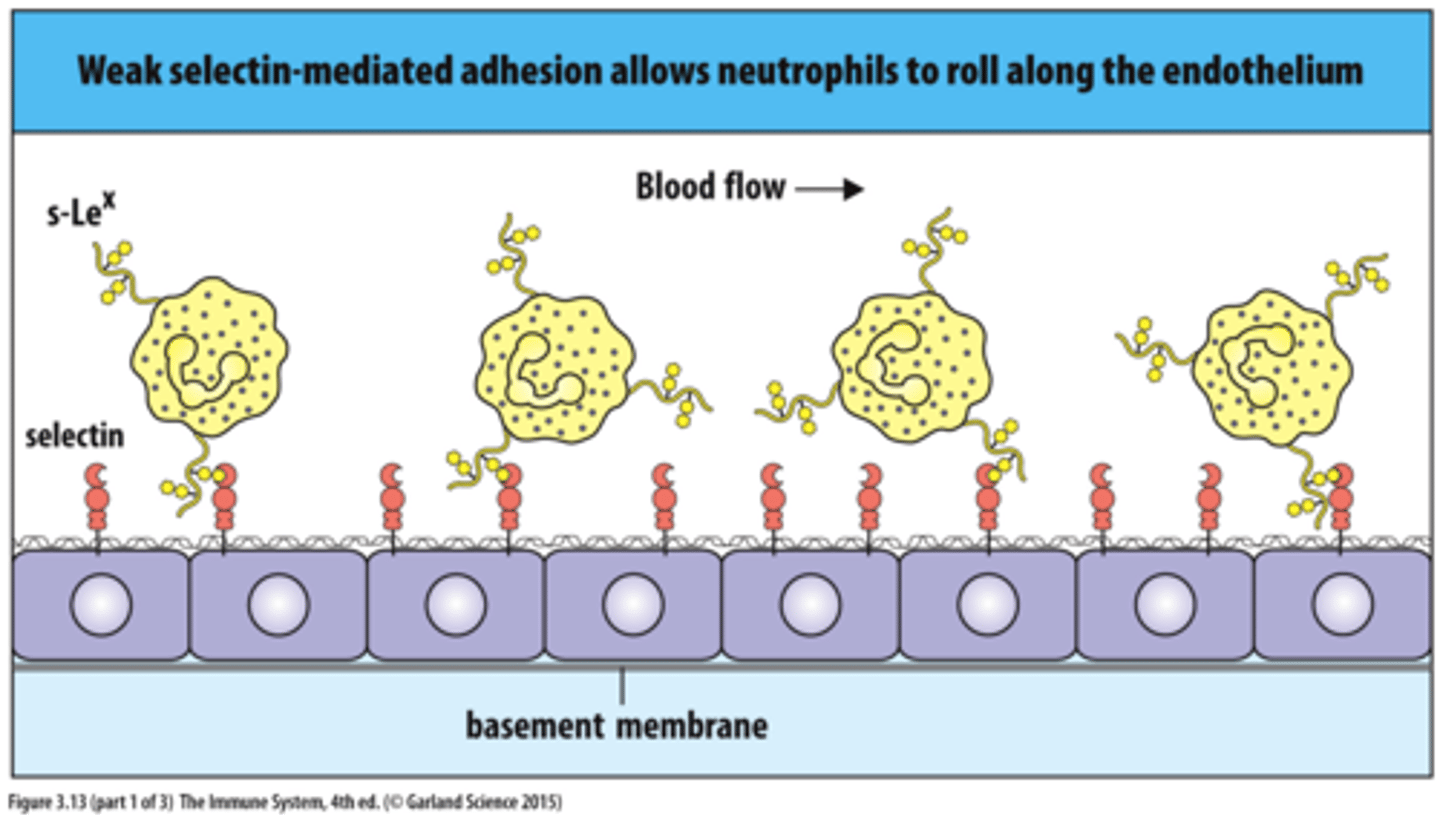
types of selectin
L-selectin (on white blood cells), P-selectin (on thrombocytes), E-selectin (on activated endothelial cells)
cell adhesion molecules (CAMs)
members of Ig superfamily that are recognized by the white blood cell integrins
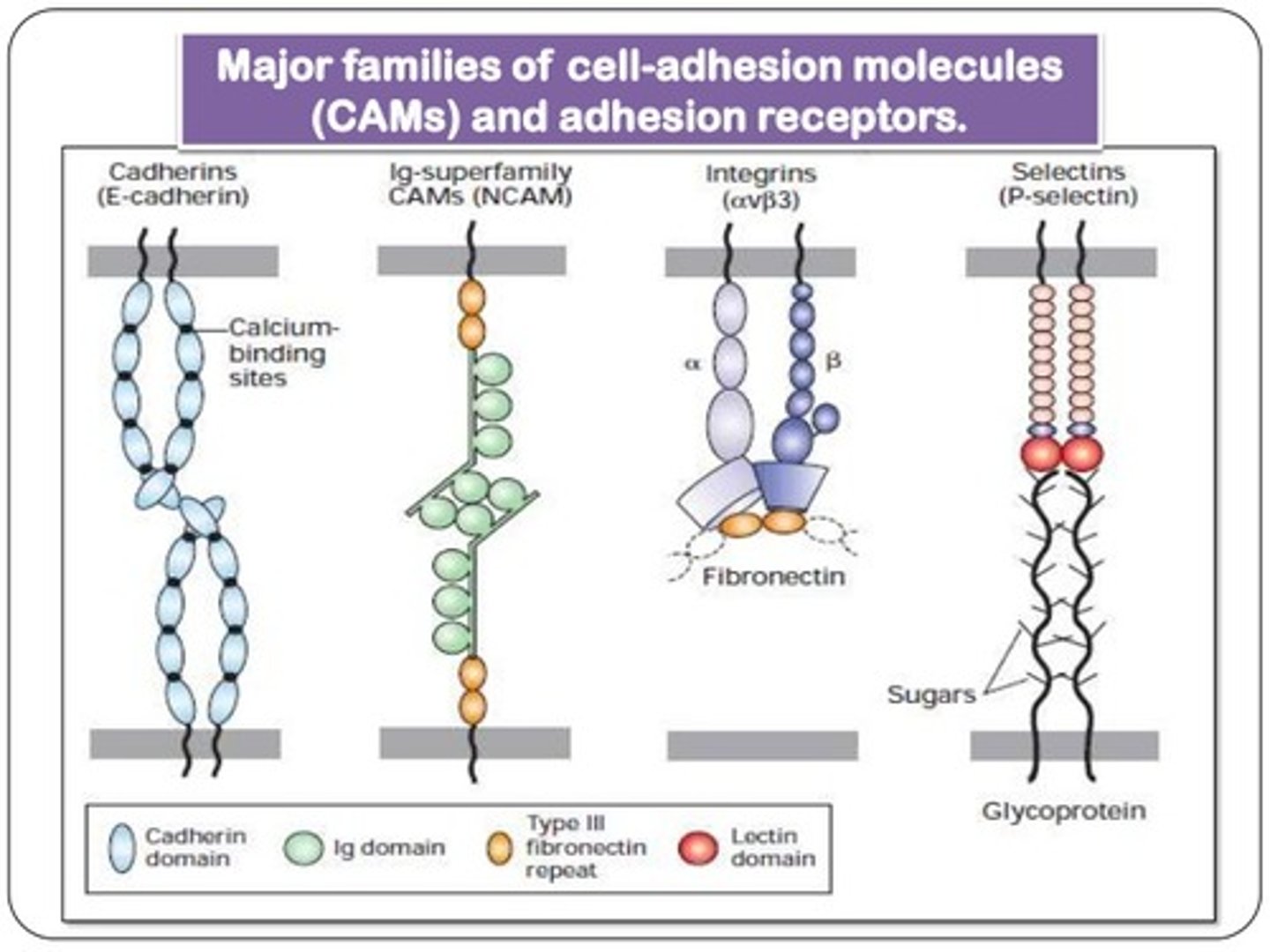
ICAM
intercellular adhesion molecule; heterophilic adhesion to integrins
VCAM
vascular cell adhesion molecule; heterophilic adhesion to integrins
NCAM
neural cell adhesion molecule; homophilic binding
fibroblasts
produces proteins and polysaccharides composing the ECM
three major classes of macromolecules composing ECM
1. glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)
2. fibrous proteins (primarily members of collagen family)
3. noncollagen glycoproteins
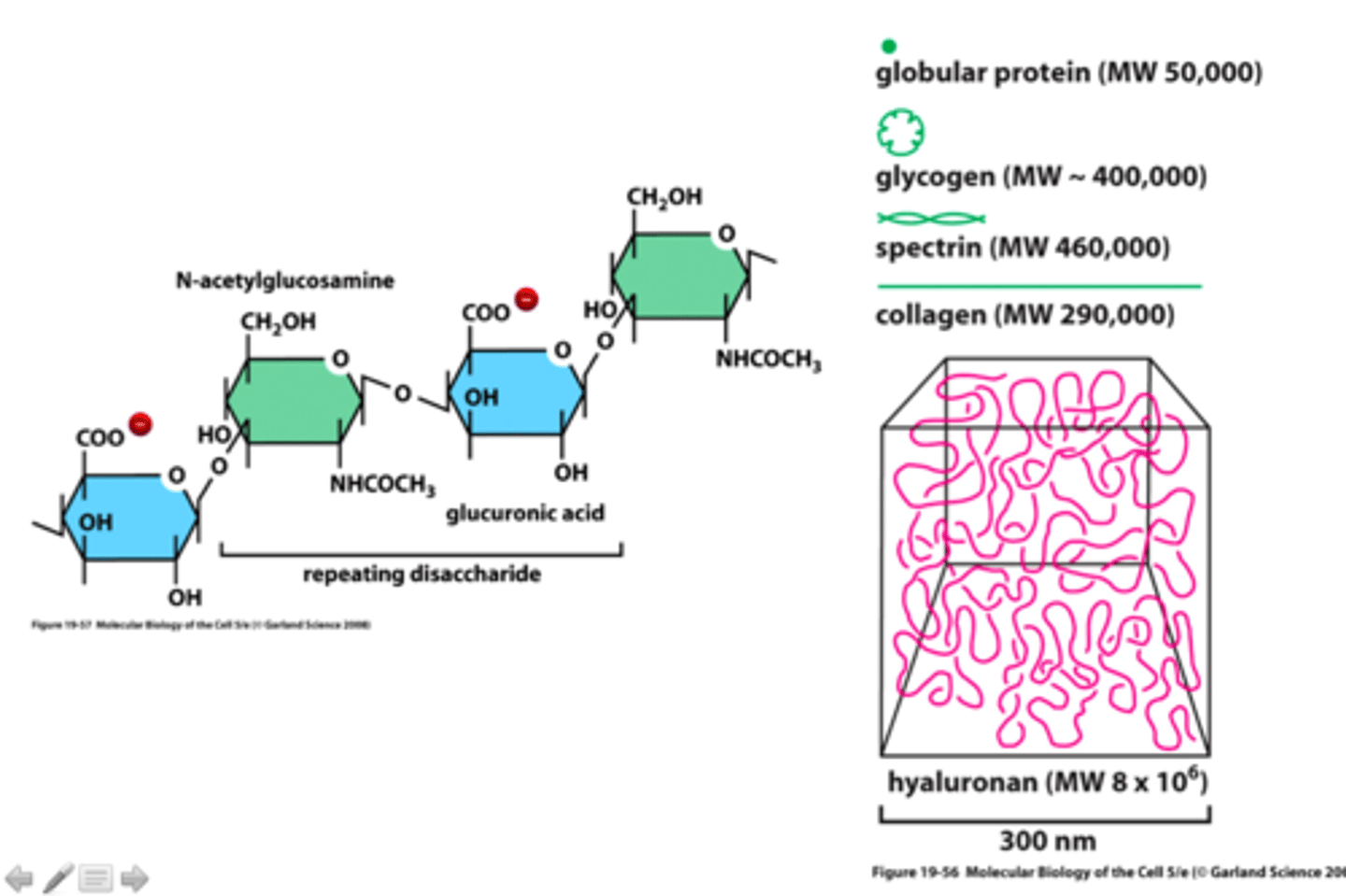
GAGs (glycosaminoglycans)
unbranched polysaccharide chains composed of repeating disaccharide units (usually N-sugar + uronic acid)
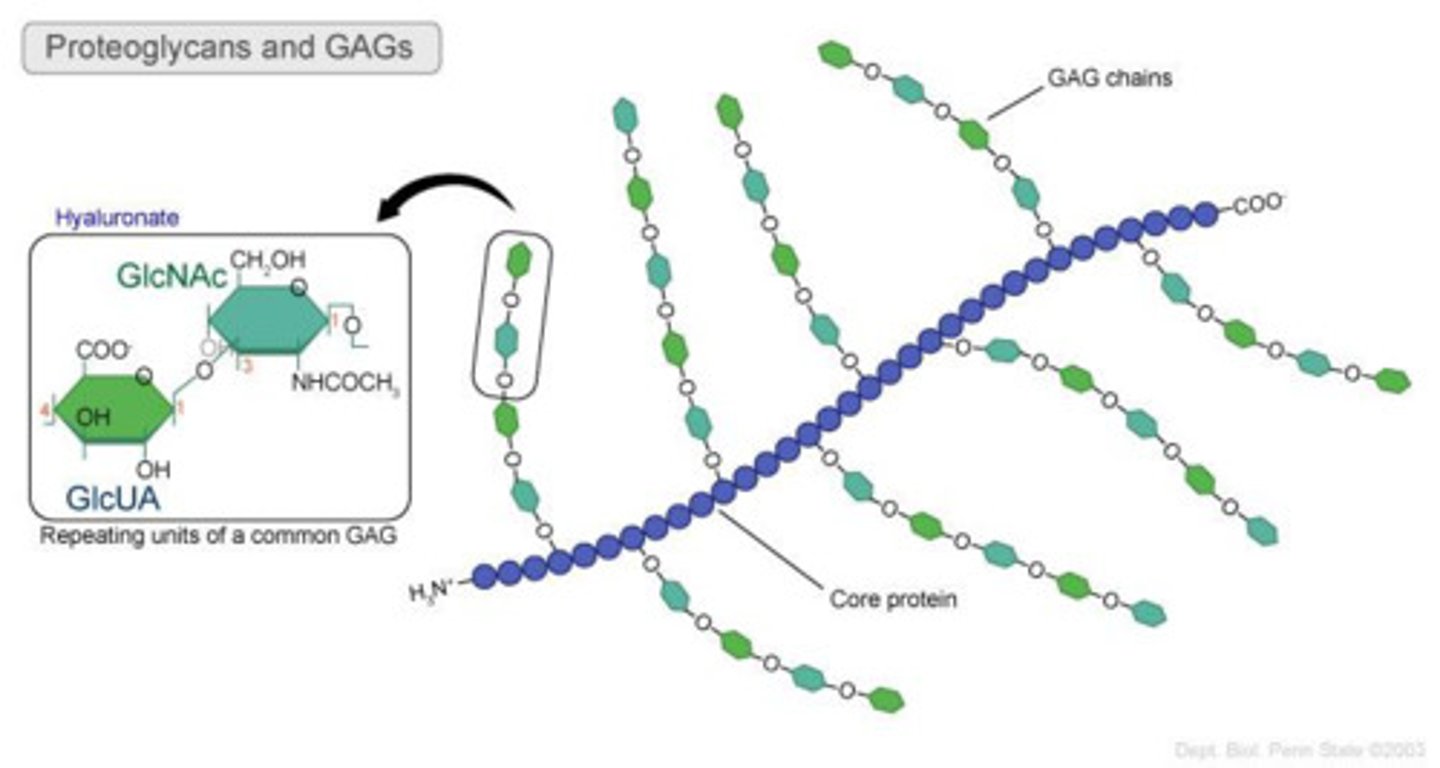
properties of GAGs
strongly hydrophilic, high density of negative charges (attracts osmotically active Na+)
four main groups of GAGs
1. hyaluronan
2. chondroitin sulfate
3. dermatan sulfate
4. keratan sulfate
hyaluronan
simplest of the GAGs, has a role in resisting compressive forces in tissues and joints, a space filler during embryonic development
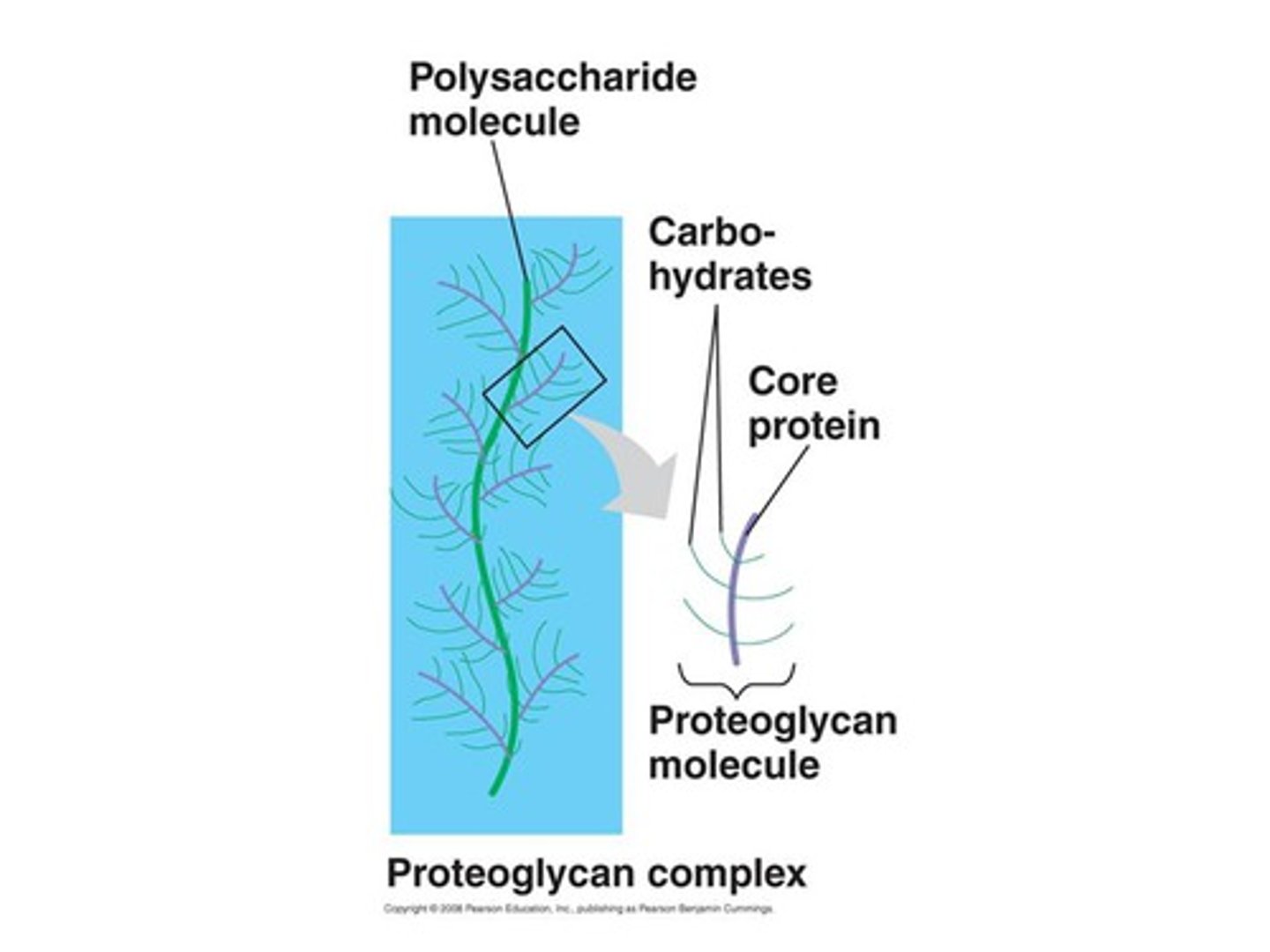
proteoglycans
proteins to which GAGs covalently bind (all except hyaluronan)
collagens
fibrous glycoproteins found only in the ECM
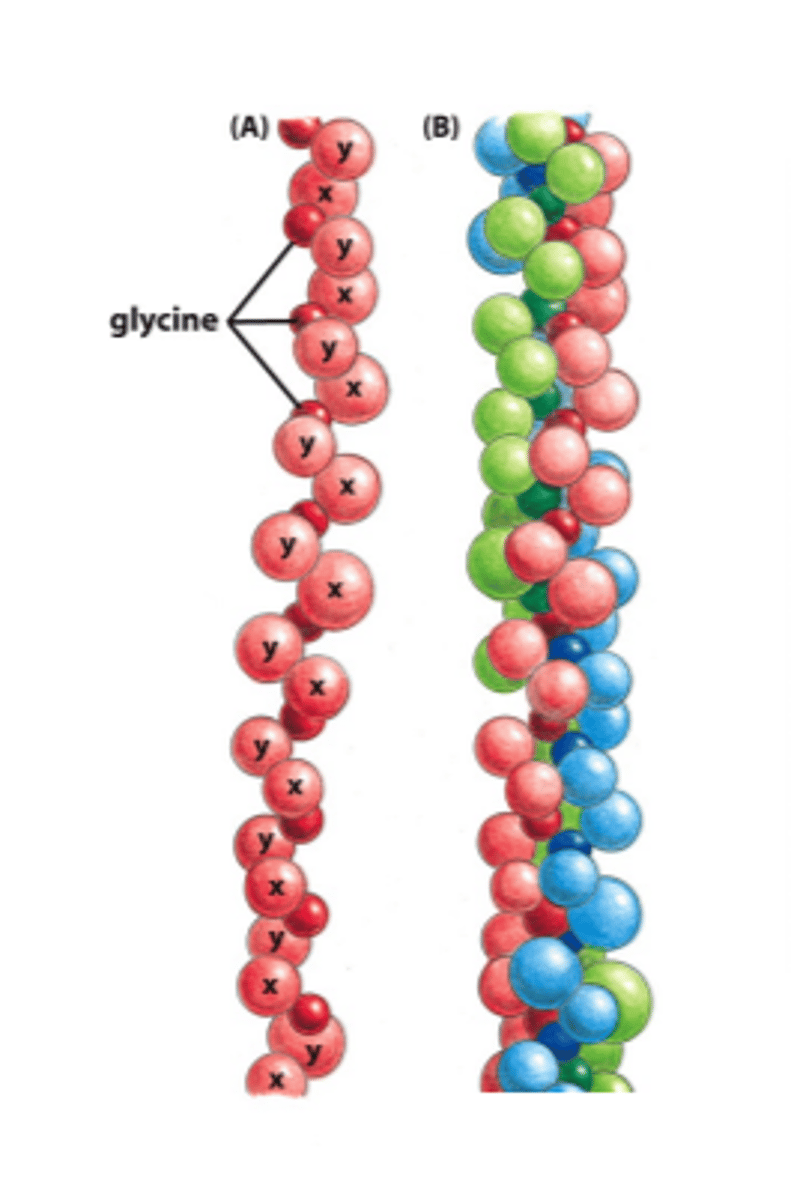
types of collagen
fibril-forming collagens, fibril-associated, network-forming, transmembrane, proteoglycan core protein
fibril-associated collagens
IX, important in organizing collagen fibrils
fibrillar collagens
I, II, III, V, XI
elastin
protein base similar to collagen (but not glycosilated) that forms elastic tissue
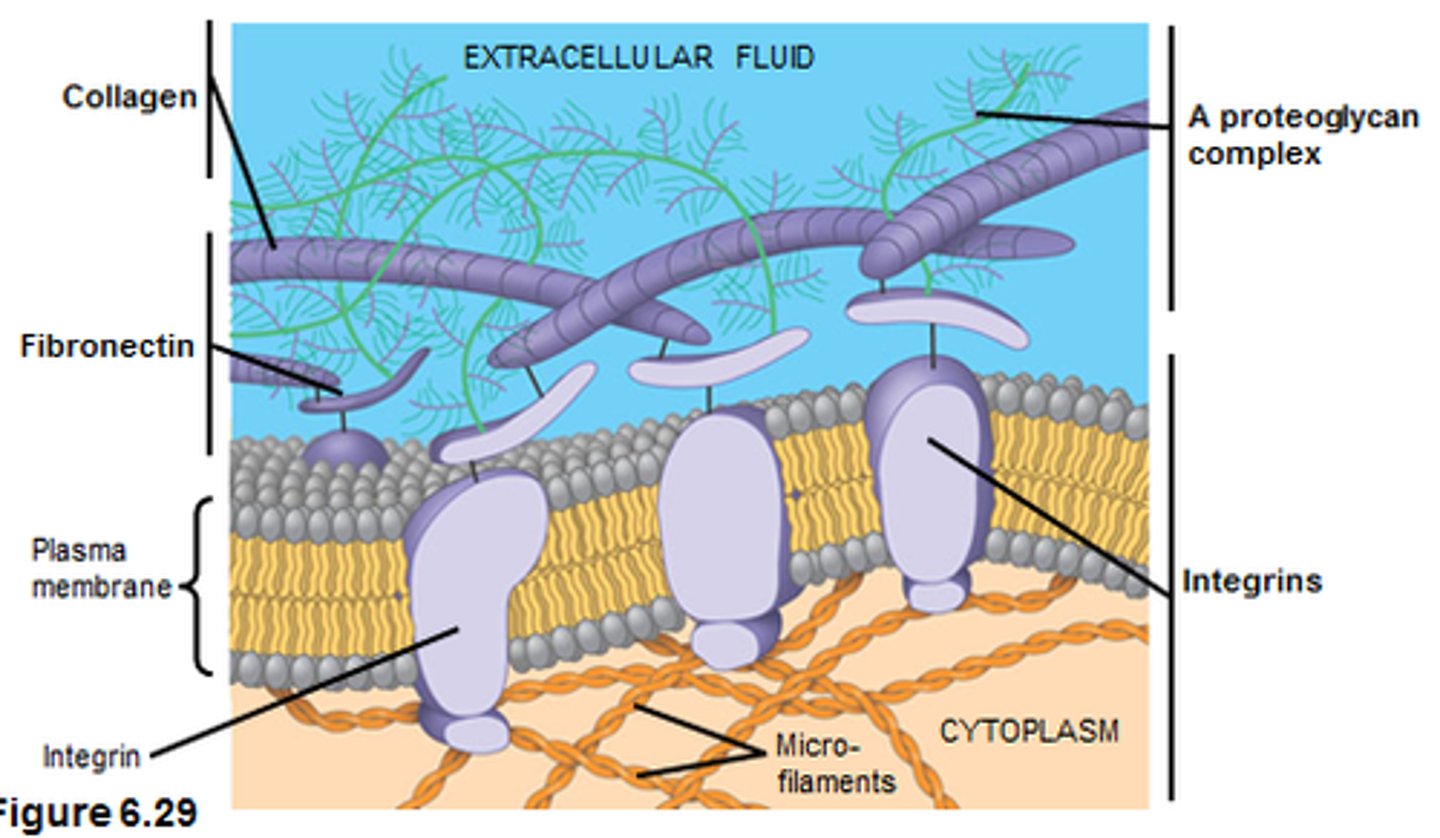
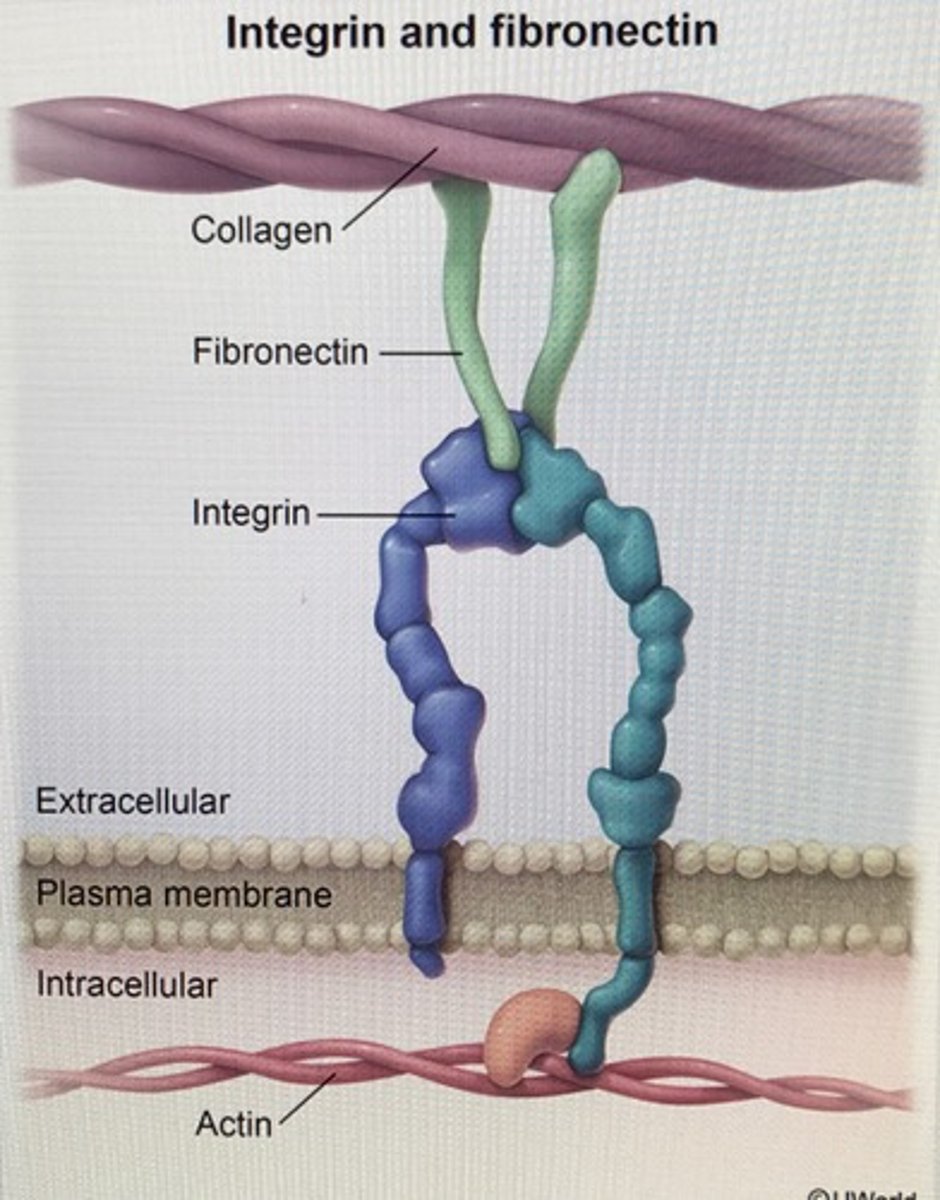
fibronectin
a noncollagen glycoprotein with many binding sites that helps organize the ECM
type III fibronectin repeat
the major repeat domain in fibronectin, which is 90 AA long and occurs at least 15 times in each subunit
RGD sequence
Arg-Gly-Asp
peptides containing RGD sequence can compete with ____ for the binding site on cell (anti-clotting drugs)
fibronectins
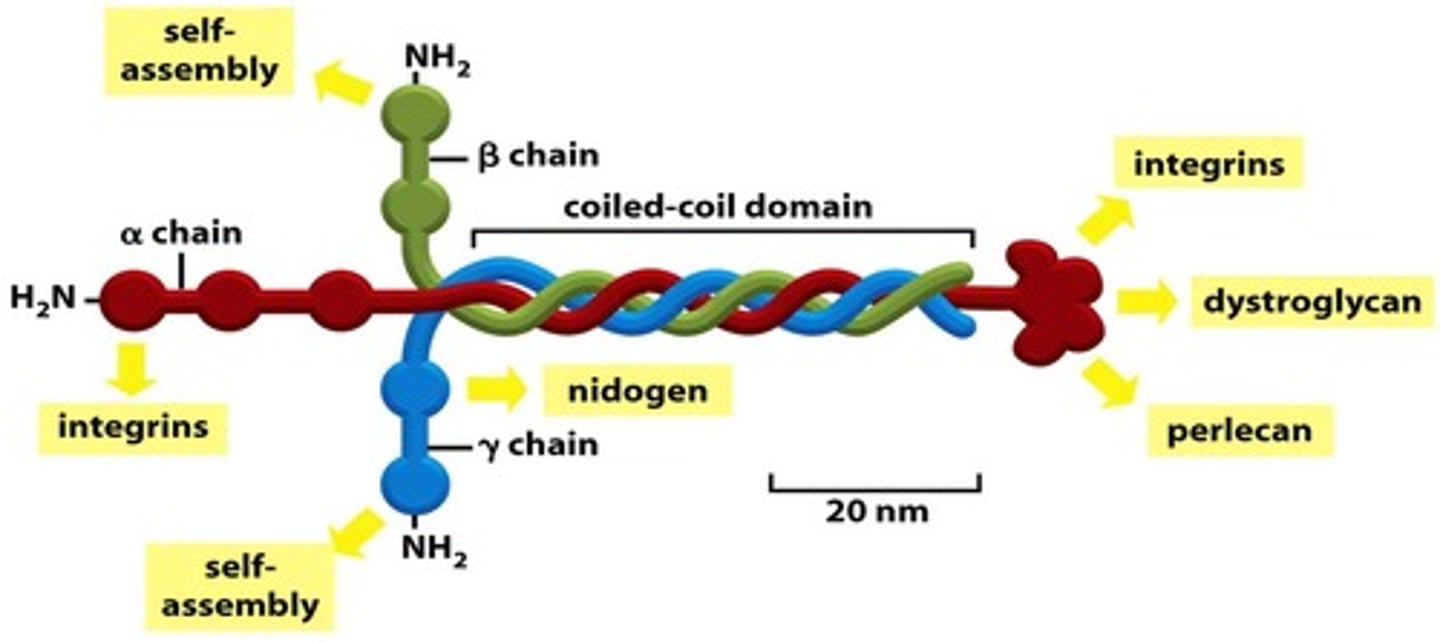
structure of basal lamina
laminin, type IV collagen and nidogen with proteoglycan perlecan
laminin
is the protein found in the basement membrane to which integrins from cells attach
degradation of ECM
division of cells, travelling through ECM
proteolytic enzymes degrading ECM
matrix metalloproteases and serine proteases
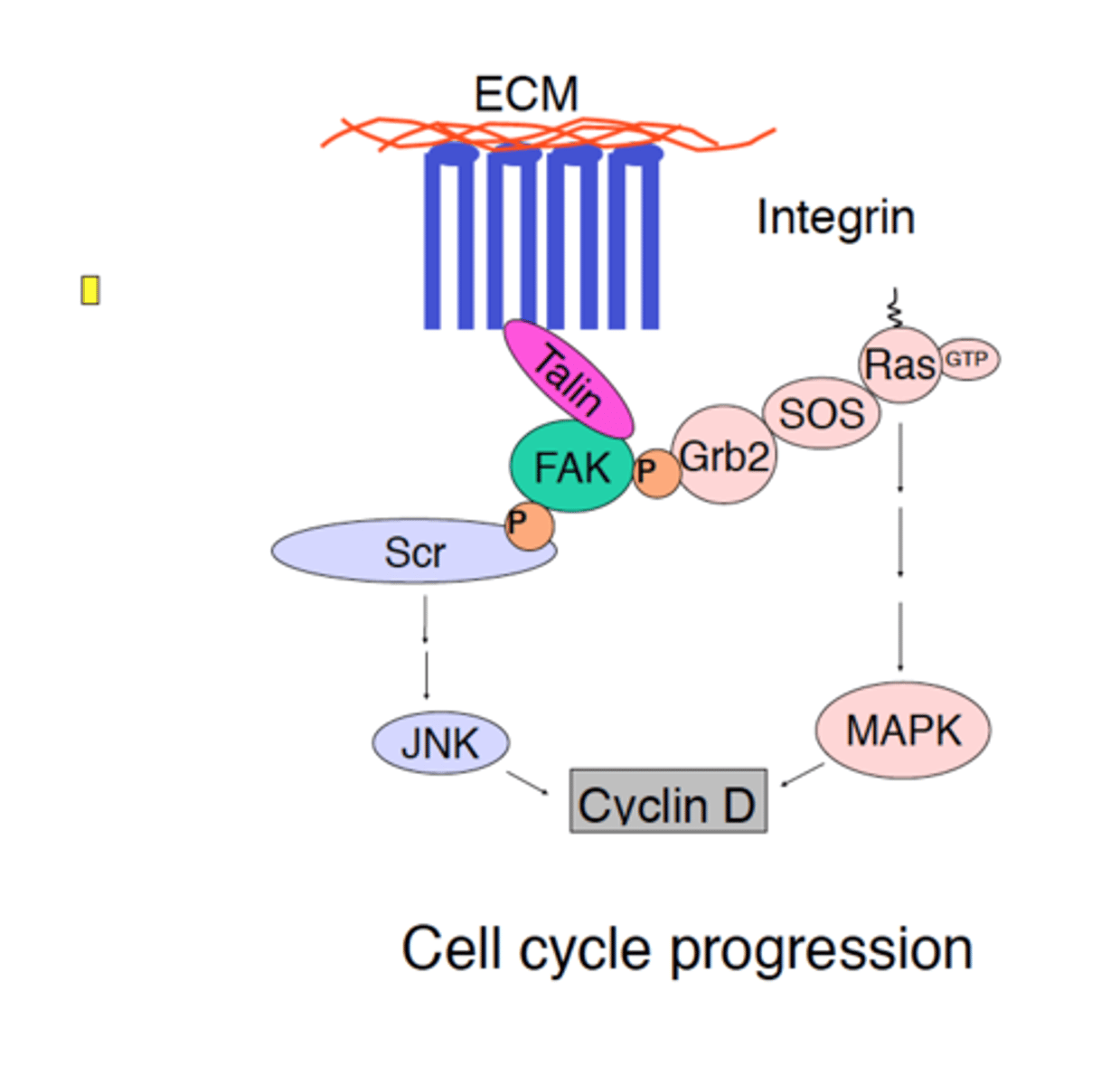
integrins
membrane proteins that transmit signals between the ECM and cytoskeleton
structure of integrins
two noncovalently associated glycoprotein subunits α and β; short C-terminal tails and large N-terminal extracellular domains
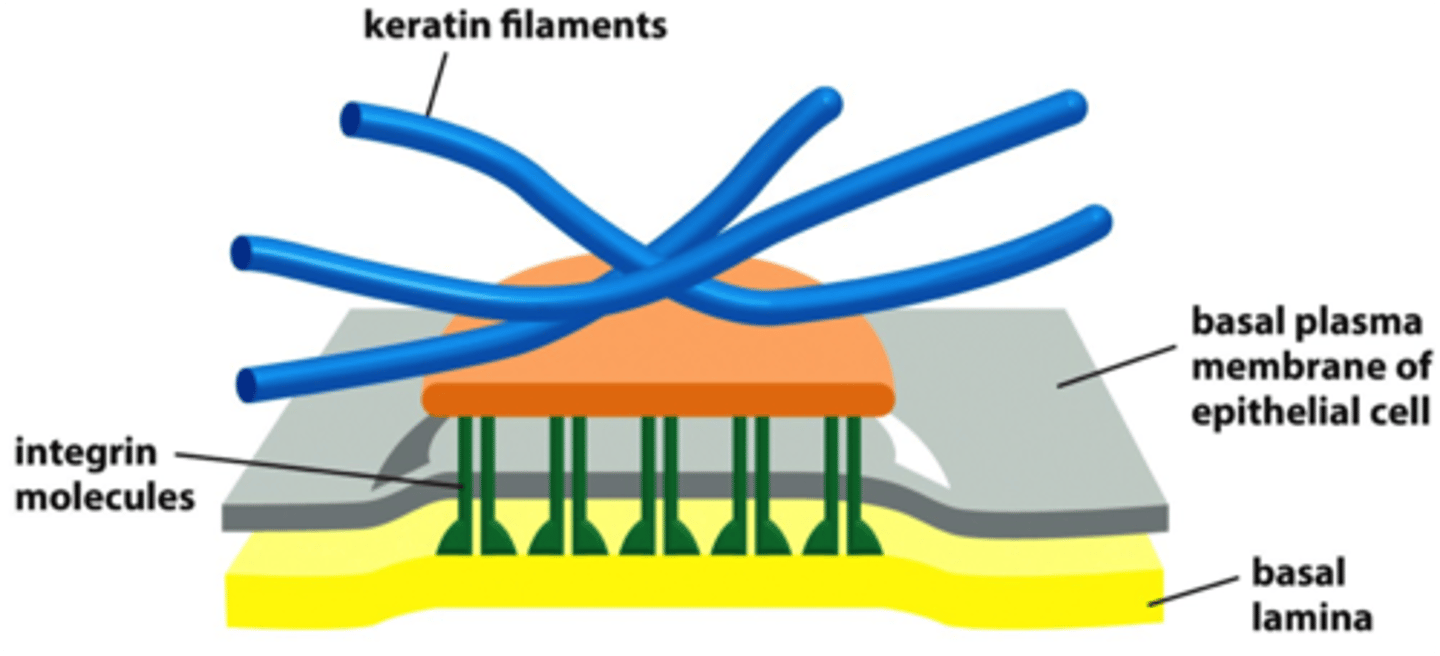
hemidesmosomes
integrins anchor the cell to laminin in basal lamina and to keratin intermediate filament in a cell via adaptor proteins plectin and BP230
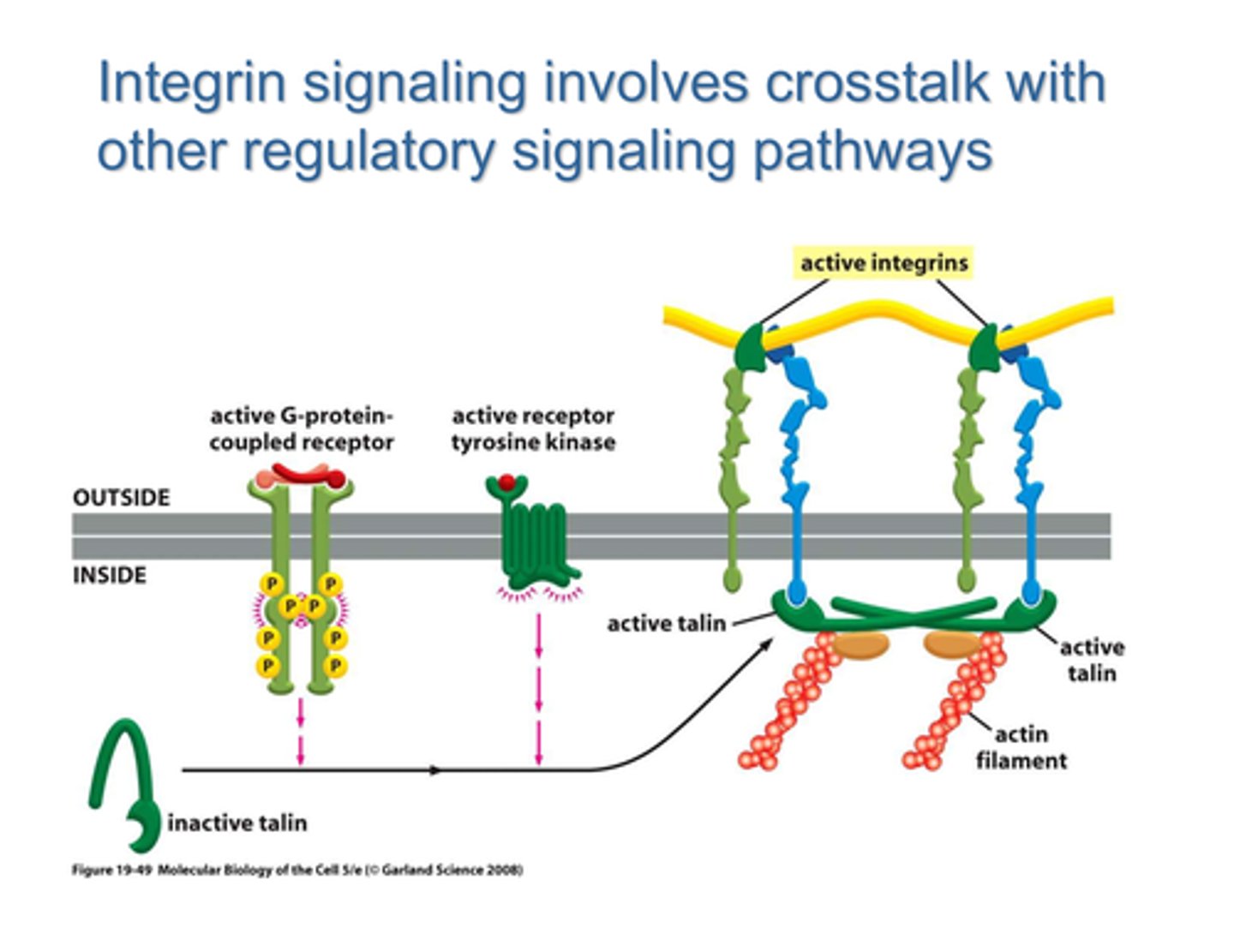
active integrin conformation
unhooked, exposing intracellular binding sites, external segments unfold
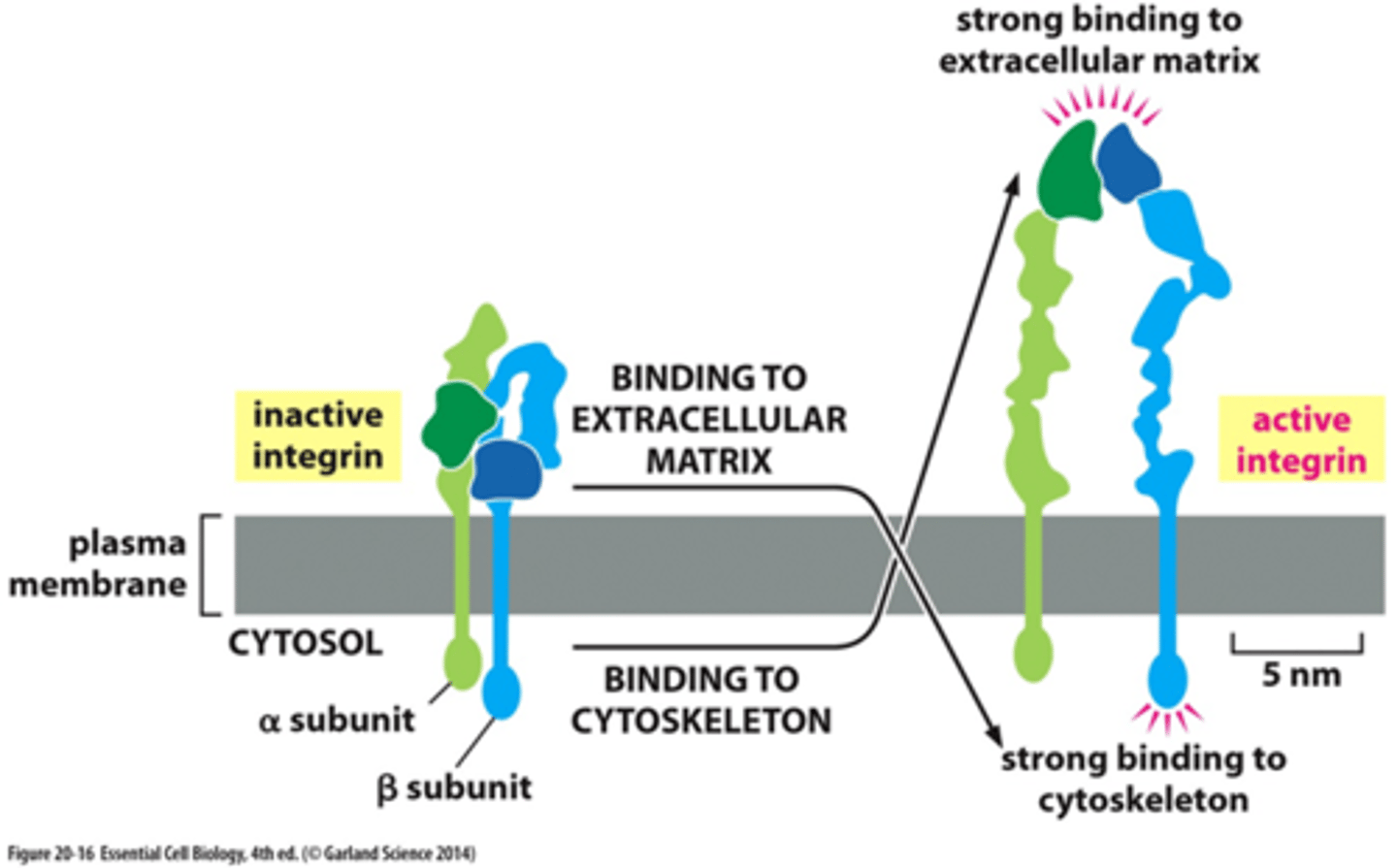
inactive integrin conformation
intracellular segments are hooked, extracellular segments are folded
outside-in mechanism for integrin activation
binding of an external matrix protein, such as the RGD sequence of fibronectin
inside-out integrin activation
depends on intracellular regulatory signals that stimulate the ability of talin and other proteins to interact with the β chain of the integrin
talin
adaptor protein which competes with the α-subunit of integrin for a binding site on the β-subunit; it mediates the interaction of integrin with actin filaments
anchorage dependence
dependence of cell growth, proliferation and cell survival on attachment to a substratum (mainly mediated by integrins)
FAK (focal adhesion kinase)
a nonreceptor tyrosine kinase that plays a key role in integrin signaling