KINESIOLOGY EXAM 3
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
4/17
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
bones of the hip/pelvis
pelvic bones (allium, ischium, pubis)
sacrum (contains five fused bones)
femur
joints of hip/pelvis
pubic symphysis (amphirarthrotic)
anterior articulation of hip bones
sacroiliac (si) joint (plane joint)
formed by hip bones and sacrum
hip joint (ball and socket joint/diathrotic)
formed by femur head, inserts into hip bone’s acetabulum
pelvic girdle movements
no joints w/in pelvis where movement is “normal”
si joints and pelvic bone joints are fused
pelvic motion is a result of combination of motion in the hip joint and vertebral column
pelvic girdle motions
anterior rotation
movement of upper pelvis anteriorly (iliac crest tilts forward - anterior tilt)
trunk extension and hip flexion
posterior rotation
movement of upper pelvis posteriorly (iliac crest tilts backwards - posterior tilt)
trunk flexion and hip extension
hip ligaments
iliofemoral ligament (y ligament)
pubofemoral ligament (limits hip abduction)
ischiofemoral ligament (limits medial rotation)
all of these limit hope hyperextension
hip joint movements
flexion and extension
abduction and adduction
medial and lateral rotation
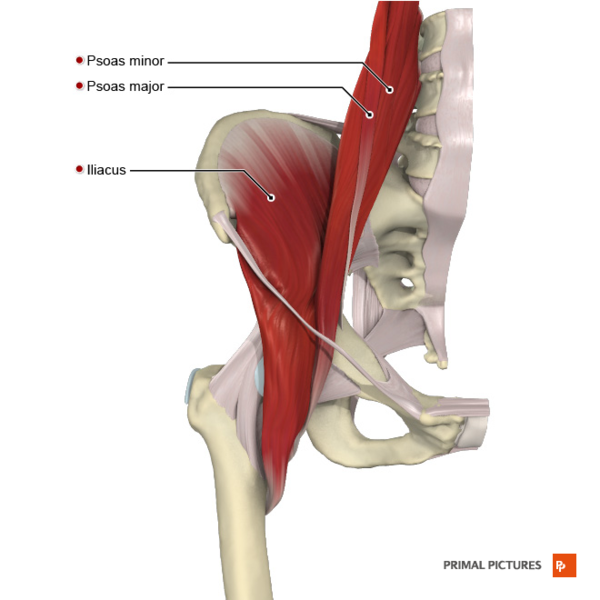
iliopsoas
combination of iliac and posts major
strongest hip flexor
ORIGIN: iliac fossa, anterior and lateral surfaces of T12 - L5
INSERTION: lesser trochanter of femur
ACTION: hip flexion and external rotation
NERVE: femoral nerve (iliacus) and lumbar nerves L1-L3 (psoas major)
exercises
supine leg raises
leg lifts from parallel bar
multi hip machine
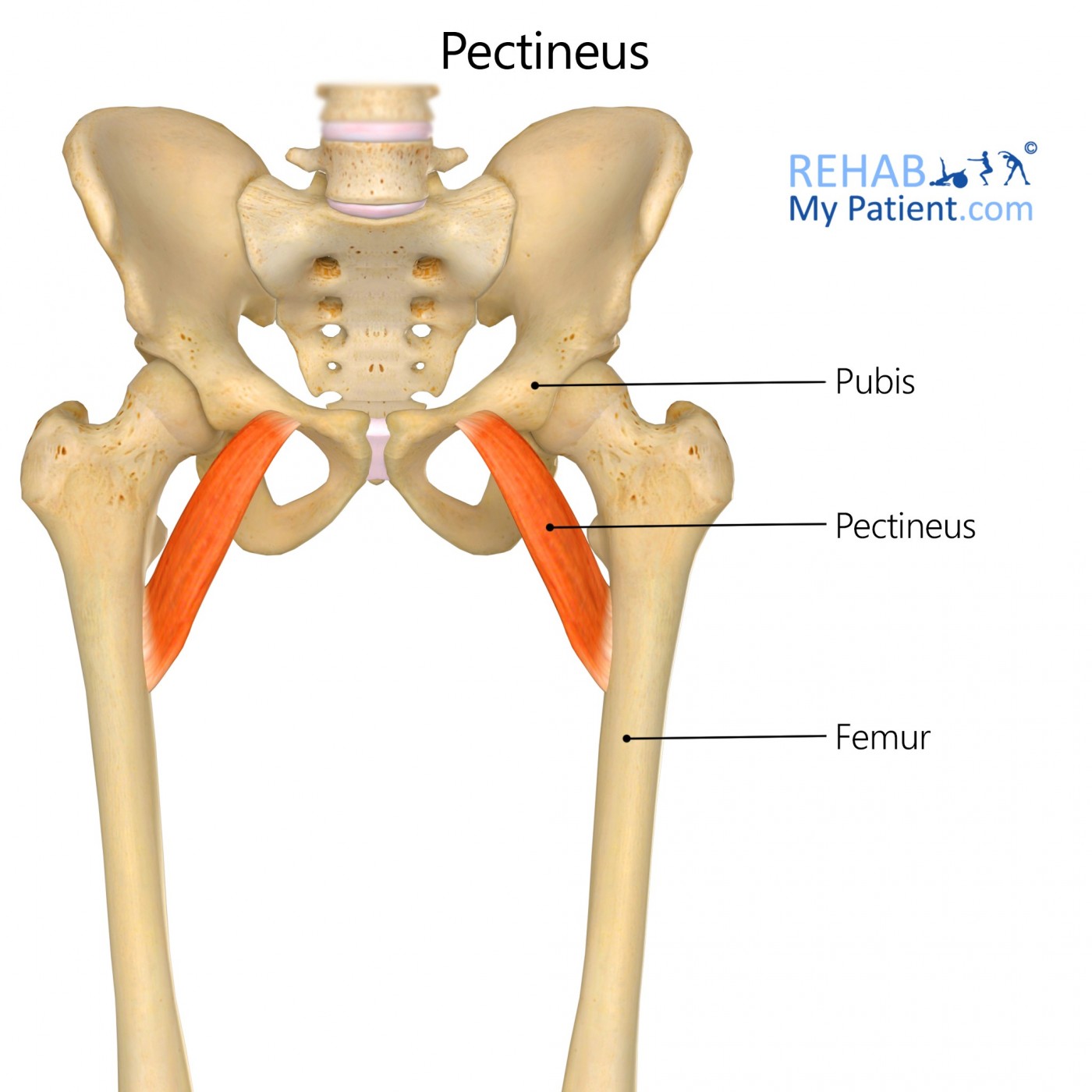
pectineus
uppermost of medial thigh muscles
sometimes considered an extension of iliopsoas
ORIGIN: superior ramus of pubis
INSERTION: pectineal line of femur
ACTION: hip flexion and adduction
NERVE: femoral nerve
exercises
supine leg rises
flexion and adduction against resistance
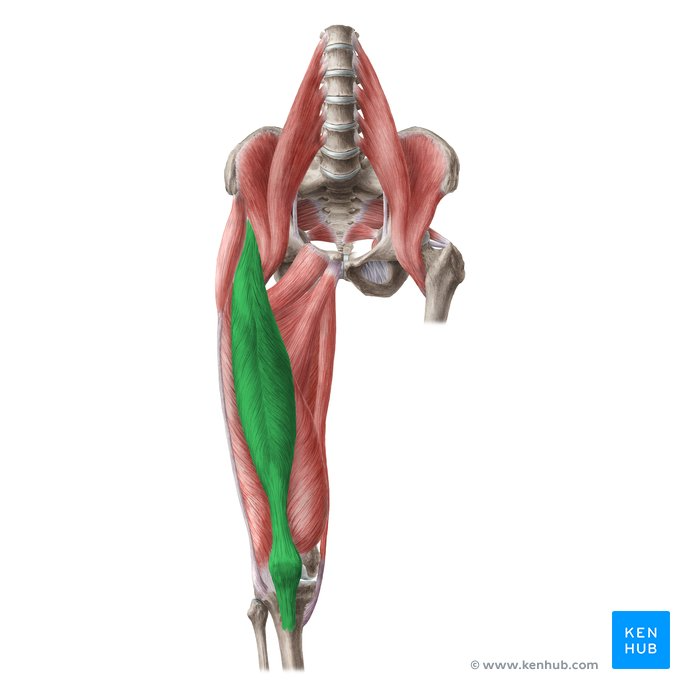
rectus femoris
part of the quadriceps group
only muscle that crosses knee and hip
combined action seen as leg swings forward while walking
ORIGIN: anterior inferior iliac spine
INSERTION: tibial tuberosity
ACTION: hip flexion and knee extension
NERVE: femoral nerve
exercises
leg raises
leg lifts
multi hip machine
leg extension
leg presses
squats
sartorius
longest muscle in the body
most superficial thigh muscle
forms lateral boarder of femoral triangle
not a powerful synergist
ORIGIN: anterior superior iliac spine
INSERTION: proximal medial tibia
ACTION: hip flexion, abduction and external rotation, WEAK knee flexion
NERVE: femoral nerve
exercises
leg lifts
leg raises
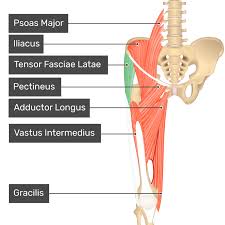
tensor fasciae latae
together with the gluteus maximus, it acts on the iliotibial band that inserts on the lateral side of the tibia
ORIGIN: anterior superior iliac spine
INSERTION: lateral condyle of tibia
ACTION: hip flexion, abduction, and internal rotation
NERVE: superior gluteal nerve
exercises
hip abduction
supine leg raises w femur internally rotated

gluteus maximus
mostly used for power - ring up stairs, rising from seated/squatting position, climbing, running (not used during walking)
ORIGIN: posterior ilium, sacrum and coccyx
INSERTION: gluteal tuberosity and iliotibial band
ACTION: hip extension, hyperextension, external rotation
NERVE: inferior gluteal nerve
exercises
squats
lunges
leg press
extensions on multi hip machine
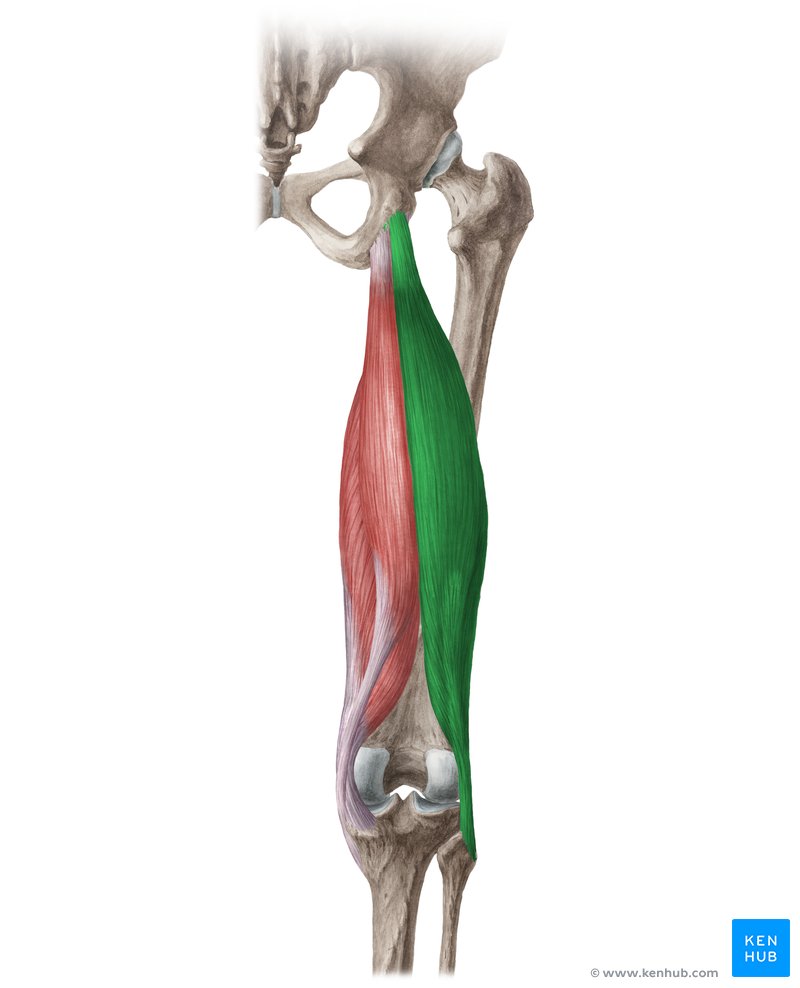
biceps femoris
one of three muscles forming the hamstring group
EXTERNALLY ROTATES HIP WHEN KNEE IS FLEXED
ORIGIN: ischial tuberosity (long head) and lines aspera (short head)
INSERTION: head of fibula
ACTION: extend hip and flex knee (long head); flex knee (short head)
NERVE: sciatic nerve
exercises
hamstring curls (prone or standing)
hip extension w extended knee
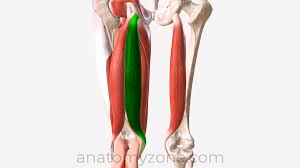
semitendonosis
middle of hamstring group
ORIGIN: ischial tuberosity
INSERTION: medial side of proximal tibia
ACTION: hip extension and internal rotation; knee flexion
NERVE: sciatic nerve
exercises
leg curls
hip extension

semimembranosus
third muscle in hamstring group
ORIGIN: ischial tubersoity
INSERTION: medial condyle of tibia
ACTION: hip extension and internal rotation; knee flexion
NERVE: sciatic nerve
exercises same as semitendinosus
deep lateral hip rotators
group of six muscles that we will consider as one
ORIGIN: posterior sacrum, ischium, pubis
INSERTION: greater trochanter area
ACTION: externally rotates extended hip
NERVE: various nerves
exercises
external rotation against resistance
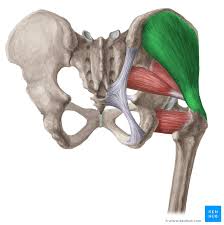
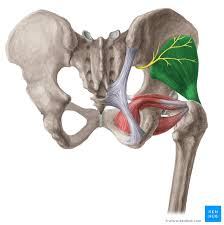
gluteus medius
when standing on one foot this muscles contracts on that side to keep pelvis from tilting to the unsupported side
ORIGIN: outer surface of ilium
INSERTION: lateral surface of greater trochanter
ACTION: hip abduction
NERVE: superior gluteal nerve
exercises
side lying leg raises
multi hip machine
ANTERIOR FIBERS CONTRIBUTE TO HIP FLEXION AND INTERNAL ROTATION
POSTERIOR FIBERS CONTRIBUTE TO HIP EXTENSION AND EXTERNAL ROTATION
gluteus minimus
deepest of the three gluteal muscles
works w gluteus medius
ORIGIN: lateral ilium
INSERTION: anterior surface of greater trochanter
ACTION: hip abduction and internal rotation
NERVE: superior gluteal nerve
exercises
similar to gluteus medius
trendelenburg gait
dysfunction of the gluteus medius and/or minimus resulting in abnormal gait
pelvis tilts toward unsupported side in walking
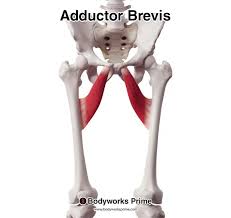
adductor brevis
deep to adductor longus
smallest adductor muscle
ORIGIN: pubis
INSERTION: proximal linea aspera of femur
ACTION: hip adduction
NERVE: obturator nerve
exercises
medial leg raises from a side lying position
multi hip machine
thigh master
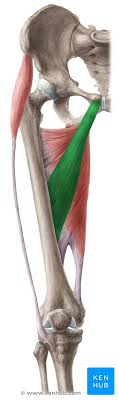
adductor longus
ORIGIN: pubis
INSERTION: middle line aspera of femur
ACTION: hip adduction
NERVE: obturator nerve
exercises
same as adductor brevis
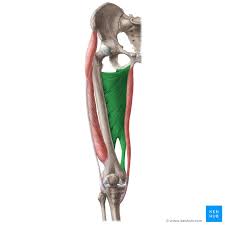
adductor magnus
longest and deepest adductor muscle
ORIGIN: ischium and pubis
INSERTION: entire lines aspera and adductor tubercle of femur
ACTION: hip adduction
NERVE: obturator nerve
exercises
same as other adductors
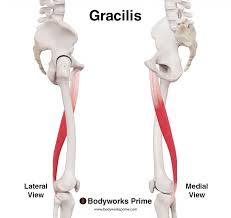
gracilis
most superficial adductor
forms letter V w shaft of femur
ORIGIN: pubis
INSERTION: proximal tibia (medial side)
ACTION: hip adduction
NERVE: obturator nerve
exercises
same as other adductors
hip contusions
usually a result from direct blow to a body part such as the quads (charley horse) or pelvic area (hip pointer)
very painful and potentially debilitating
if not treated properly, can lead to myositis ossifications
myositis ossifications
conditions in which calcification develops repeated trauma
can be caused by poor treatment such as vigorous massage, or returning from injury too soon
bones of the knee
femur
longest bone in body
tibia
medial bone of lower leg; weight bearing
fibula
lateral bone of lower leg; not weight bearing
does not articulate w femur/patella
provides attachment sites for knee joint structure/muscles
patella
sesamoid bone embedded in patellar tendon
protects structures beneath and change angle of pull to create greater rotary force
knee joint
hinge joint
not entirely accurate bc it allows some rotation
complex, and somewhat unstable
often injured in athletics
menisci
cartilage discs attached to tibia allowing enhanced stability and a deeper tibial plateu
both thicker on outside border, taper to very thin on inside border
collateral ligaments
medial collateral ligament (MCL)
protects knee from valves forces
often injured by blows to lateral side of knee
lateral collateral ligament (LCL)
protects knee from virusforces
injured by blows to medial side of knee
anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)
prevents tibia from moving forward
attaches to the tibia anteriorly and the femur posteriorly
helps maintain rotary stability
posterior cruciate ligament (PCL)
prevents the tibia from moving posteriorly
attaches anteriorly to the femur and posteriorly to the tibia
knee motions
flexion
extension
external rotation
internal rotation
vastus lateralis
most lateral muscle of the quadriceps group
ORIGIN: linea aspera of femur
INSERTION: tibial tuberosity (via patellar tendon)
ACTION: knee extension
NERVE: femoral nerve
exercises
seated knee extension
seated leg press
hip sled
squats
lunges
vastus intermedius
middle of the three vests muscles
deep to the rectus femoris
ORIGIN: anterior femur
everything else is same as vastus lateralis
vastus medialis
most medial of vastus muscles
often the target for biopsies when the quadriceps muscle is studied
same OIAN and exercises as vastus lateralis
popliteus
“the key that unblocks the knee”
deepest muscle of the posterior knee
ORIGIN: lateral condyle of femur
INSERTION: posterior proximal tibia
ACTION: initiate knee flexion
NERVE: tibial nerve
exercises
leg curls
knee flexion w internal rotation
knee flexion assisters
sartorius
gracialis
both flex and internally rotate knee
gastrocnemius
flexes knee
plantaris
assists with knee flexion; missing in some people
ACL Injury
many sports apply external and internal forces to the knee
ACL is the most commonly damaged ligament of the knee
often caused by cutting, twisting, and/or hyperextension
due to poor vascularity, a torn ACL does not have the capacity to heal
once injured, it does not reconstitute as a functional entity
ACL Injury and Gender
ACL injury rates are 4-8 times higher in female athletes who partake in soccer, basketball, track, and softball (compared to baseball) than male athletes
sagital plane landing mechanisms may play less of a role in gender-related ACL injury than frontal and transverse plane mechanisms
effect of fatigue on knee valves and internal rotation may have more of a consequence in females than males
ACL Injuries and Gender Theories
women have a wider pelvis, increasing the “Q” angle of knee
the place where the ACL passes through the knee is smaller in females
hormones
women in preovulatory phase have more ACL injuries; presumably due to laxity - more compliance means more instability
Collateral Ligament Injury
one of the most frequent knee injuries
usually cause by blow to lateral knee
deep fibers of the MCL attach to the medial meniscus which could disrupt the meniscus too
meniscus tear
frequency caused by planting foot during weight bearing while body undergoes rotation
symptoms include pain accompanied by locking or buckling of the knee
chondromalacia
affects the articulating cartilage on the interior surface of the patella
possibly caused by incongruence between patella and femur
symptoms include pain, swelling, and grating sensation
osgood schlatter disease
usually affects children
inflammation of the patellar tendon at the tibial tuberosity caused by repeated usage of knee extensors
symptoms include pain, swelling, hemorrhage
severe overuse may result in tearing or avulsion of patellar tendon