Pulmonary Exam 2: Physiology - Gas Exchange and Transport (Dr. Leavis)
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
Define the following:
The movement of gas between the environment and the blood
Gas exchange

What involves the following two steps:
1) transport between the atmosphere and the alveolus (breathing)
2) diffusion across the alveolar/capillary membranes into the blood
Gas exchange

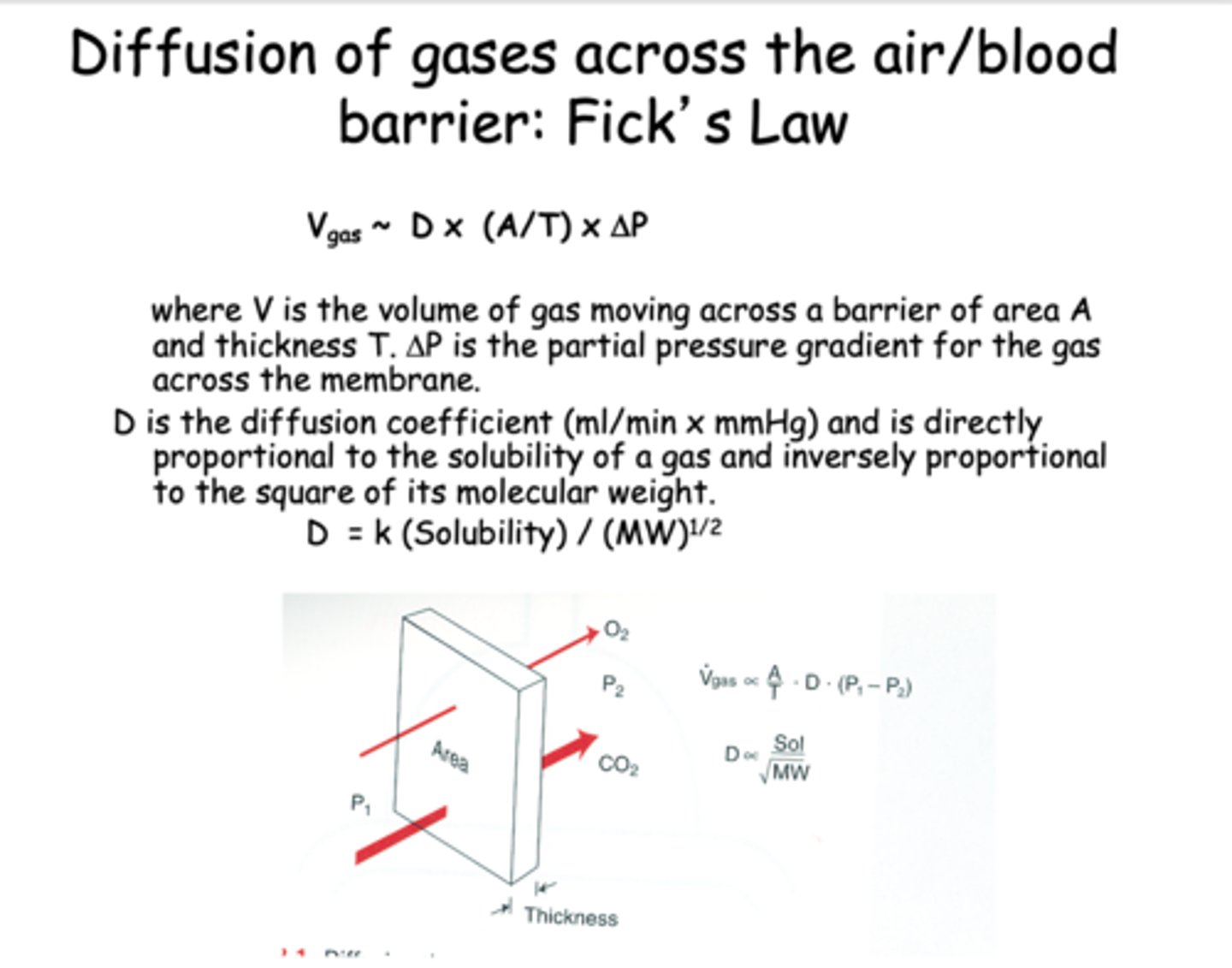
Diffusion of gases across the air/blood barrier: Fick's Law depends on what 4 things?
- Area
- Thickness
- Pressure gradient
- Diffusion coefficient
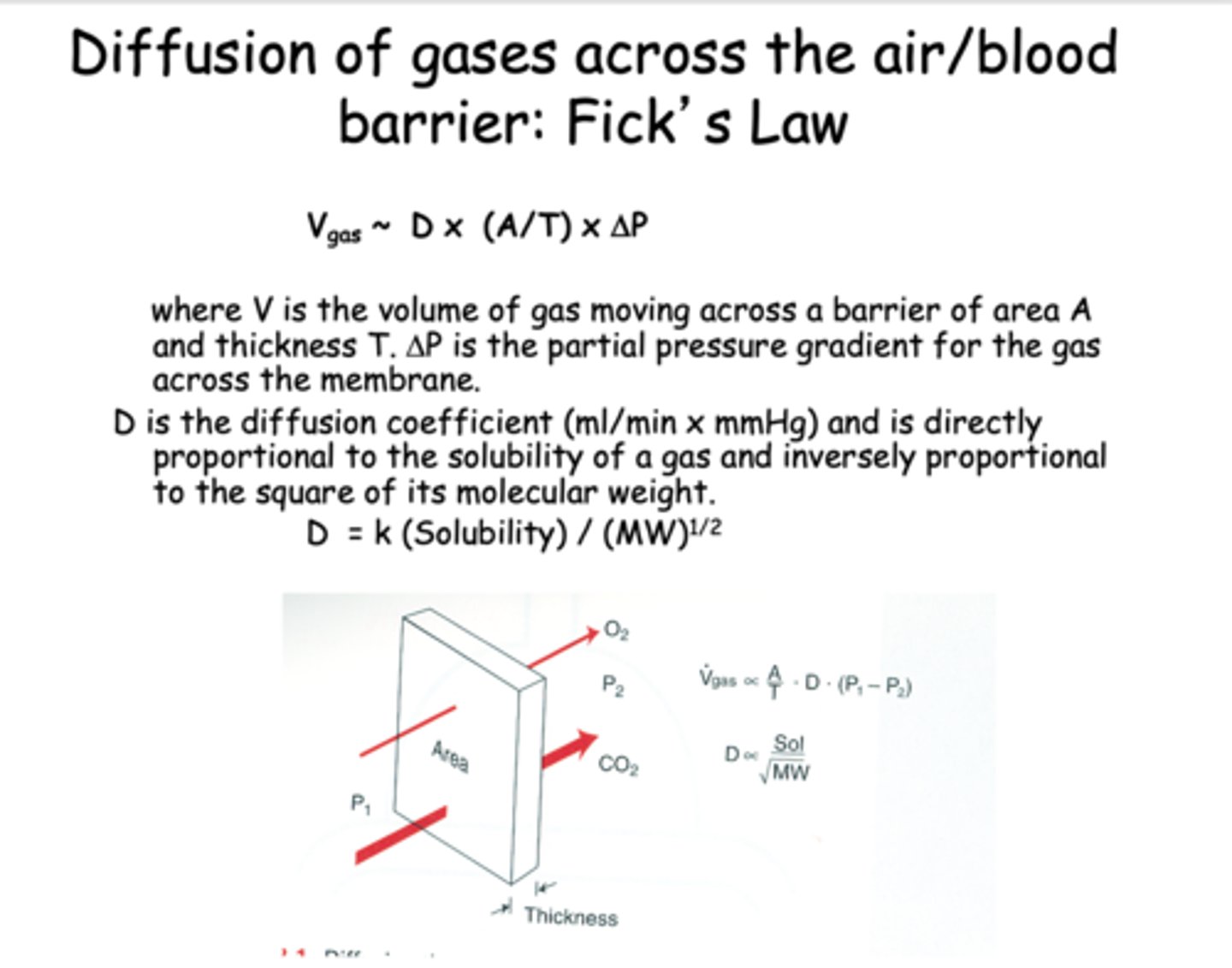
What equation is this?
Vgas ~ D x (A/T) x ΔP
Fick's law
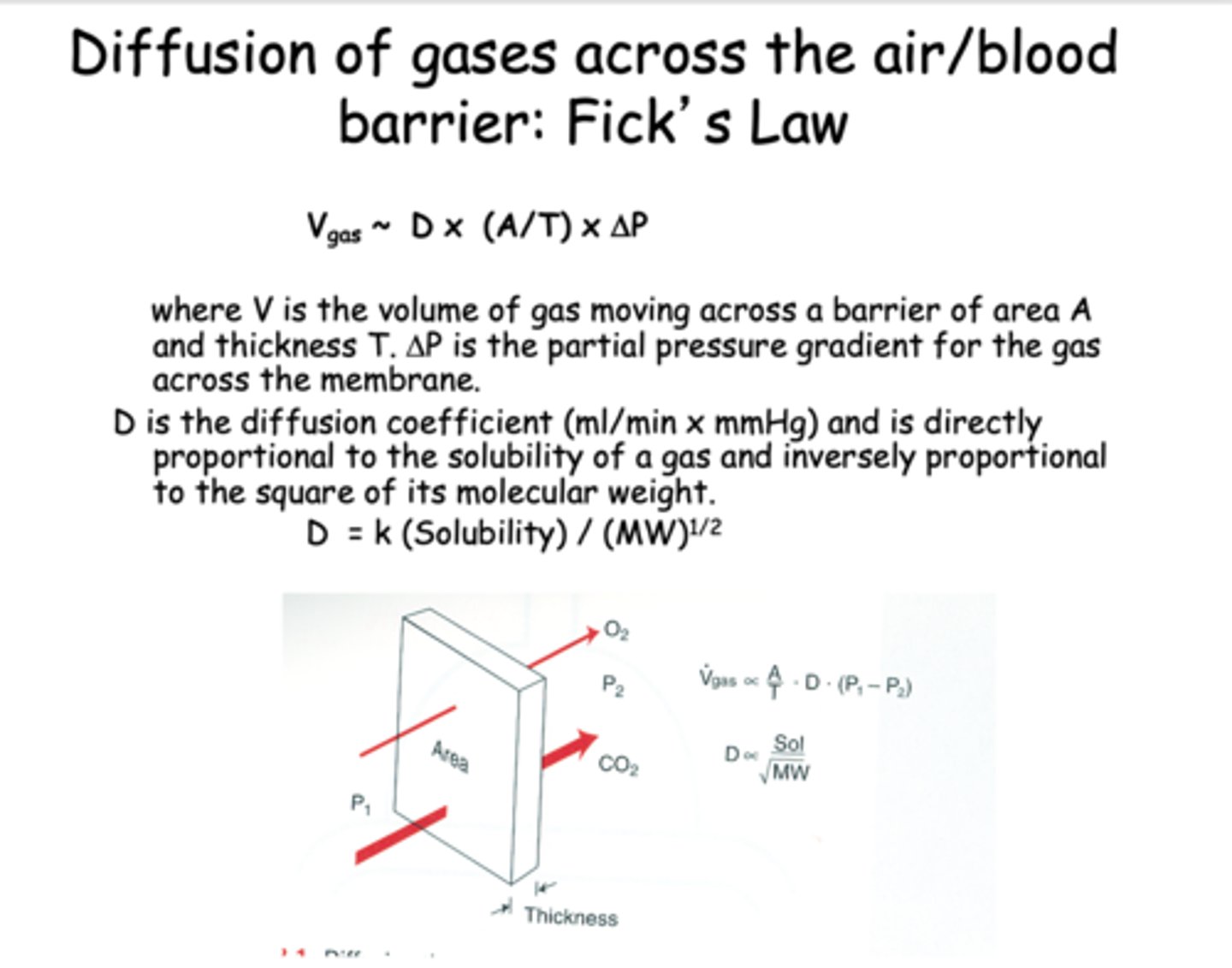
________________ is directly proportional to the solubility of a gas and inversely proportional to the square of its molecular weight
Diffusion coefficient
Define the following:
A gas will dissolve in a liquid in proportion to itspartial pressure over the liquid. The actual amount thatdissolves = the solubility coefficient X partial pressure
Henry's law

what is the dissolve constant for O2?
0.003 ml/dL/mmHg

what is the dissolve constant for CO2?
0.06 mlO2/dL/mmHg

which gas is more soluble & more readily dissolves into liquid/plasma: CO2 or O2?
CO2

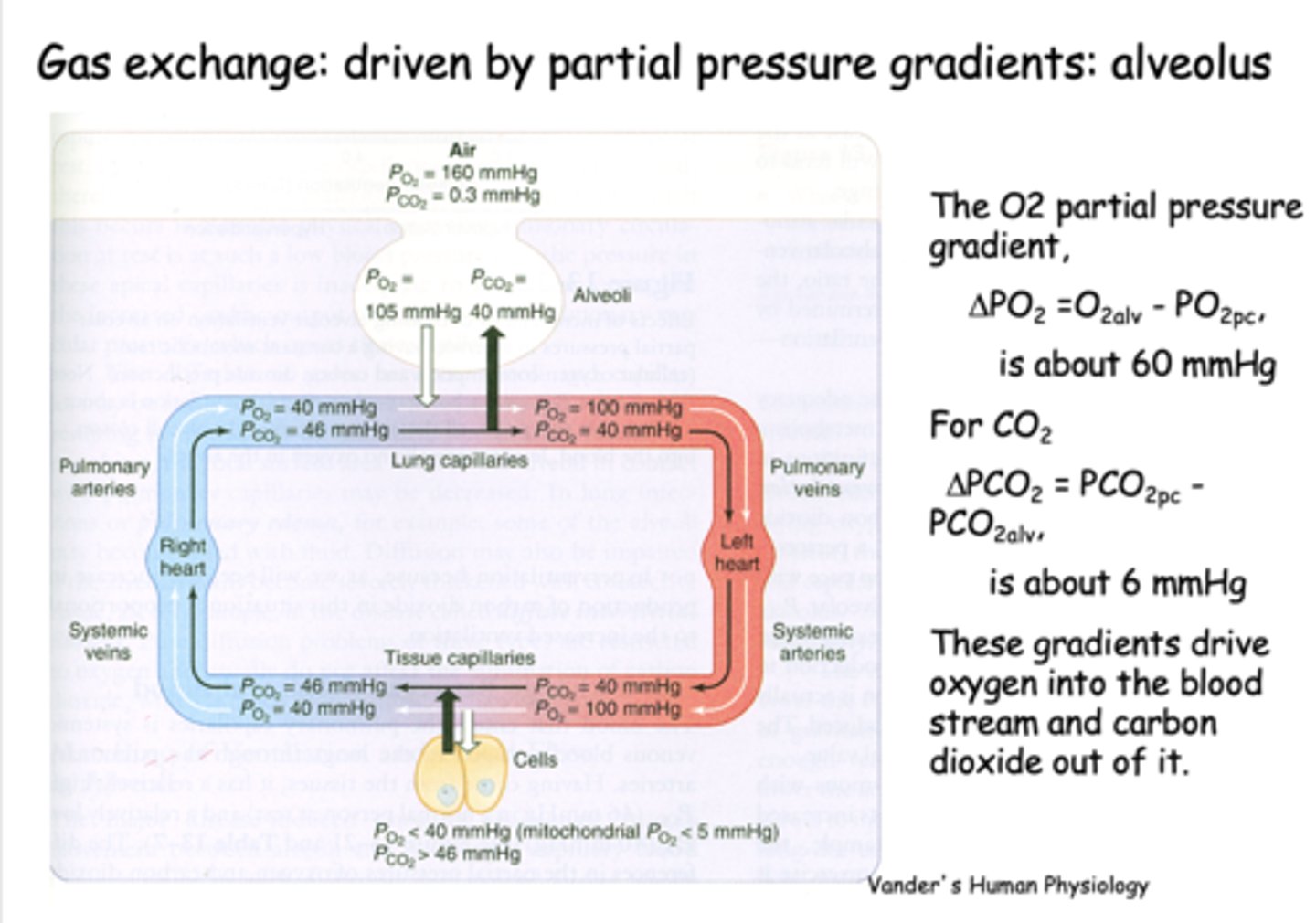
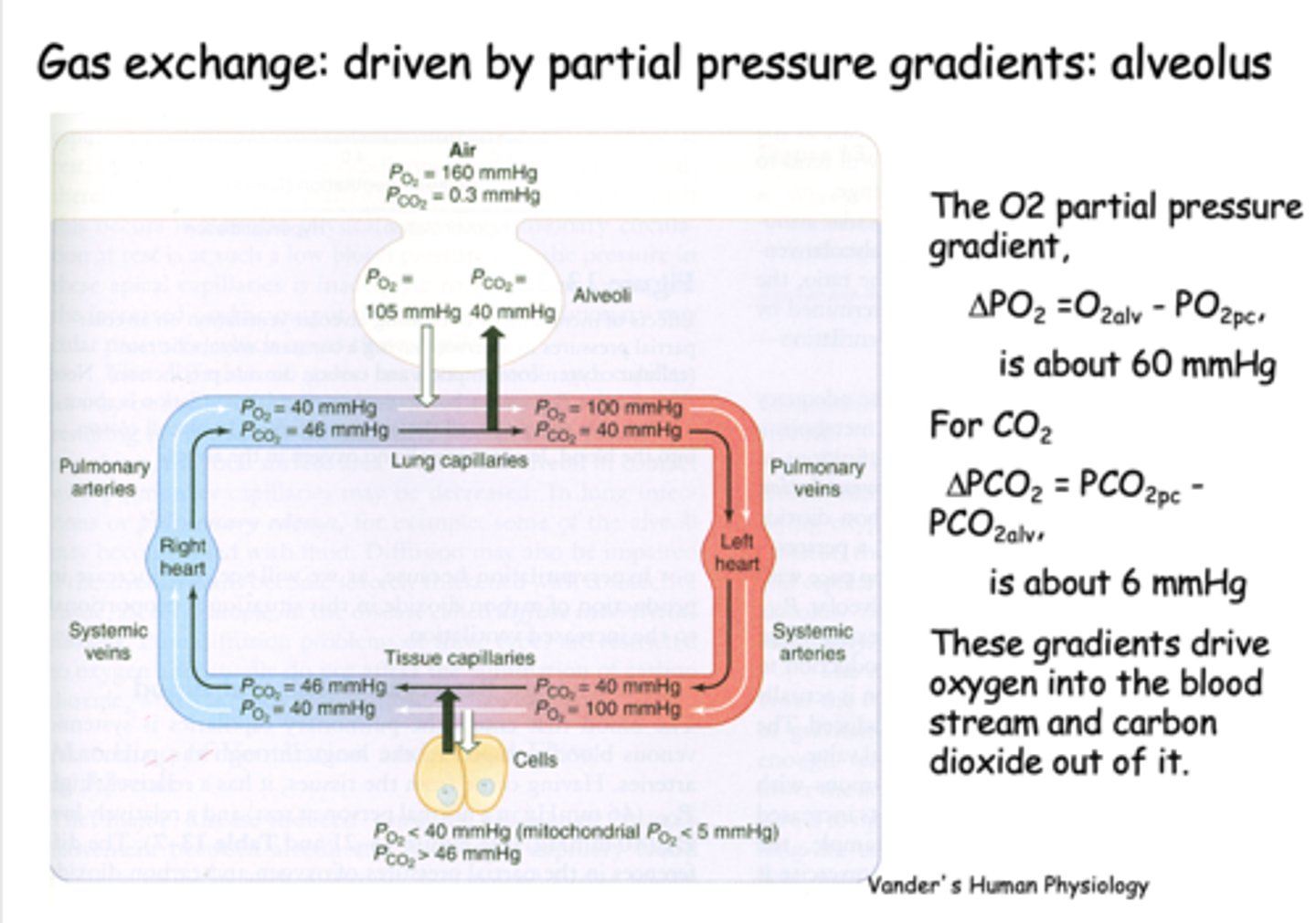
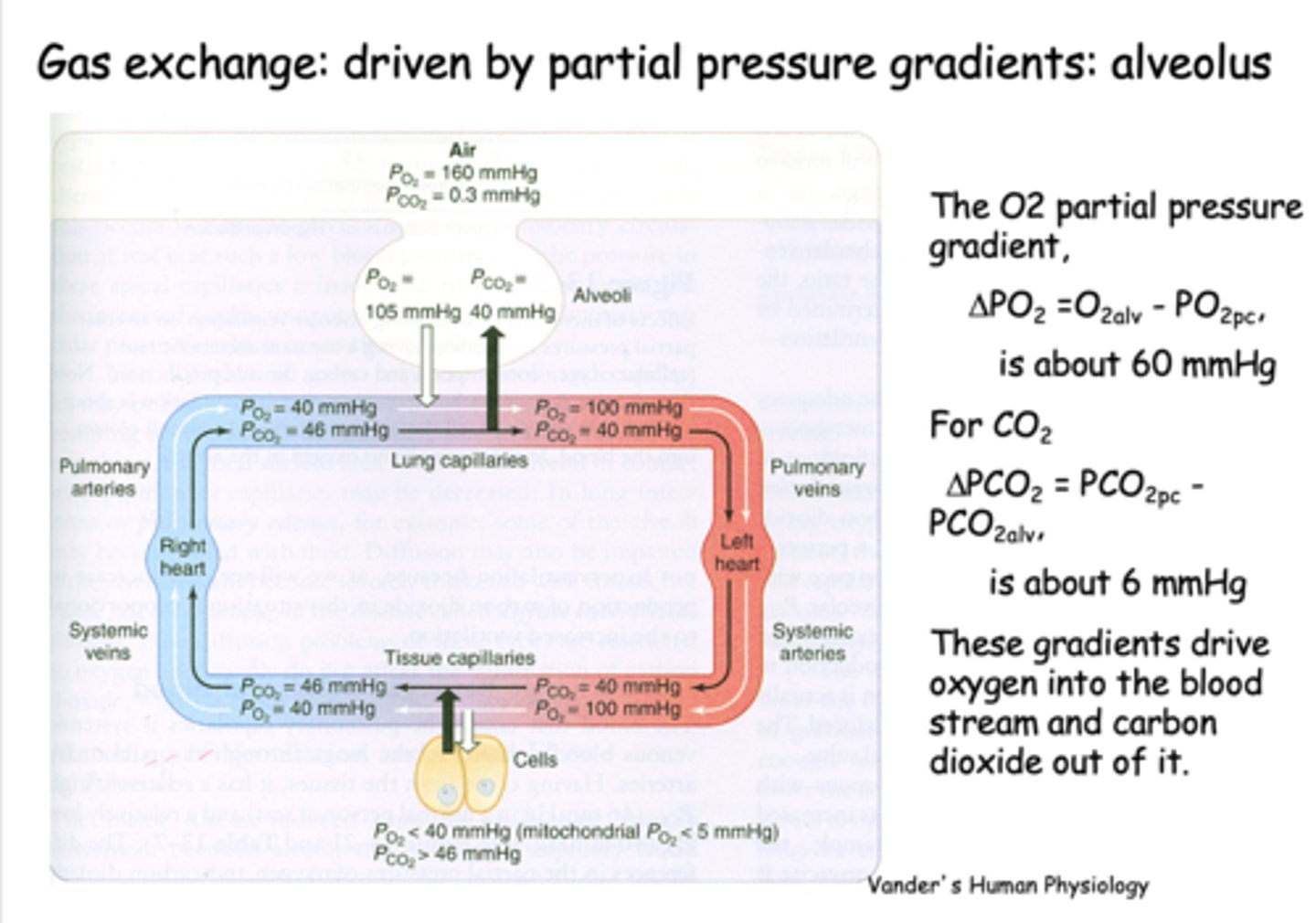
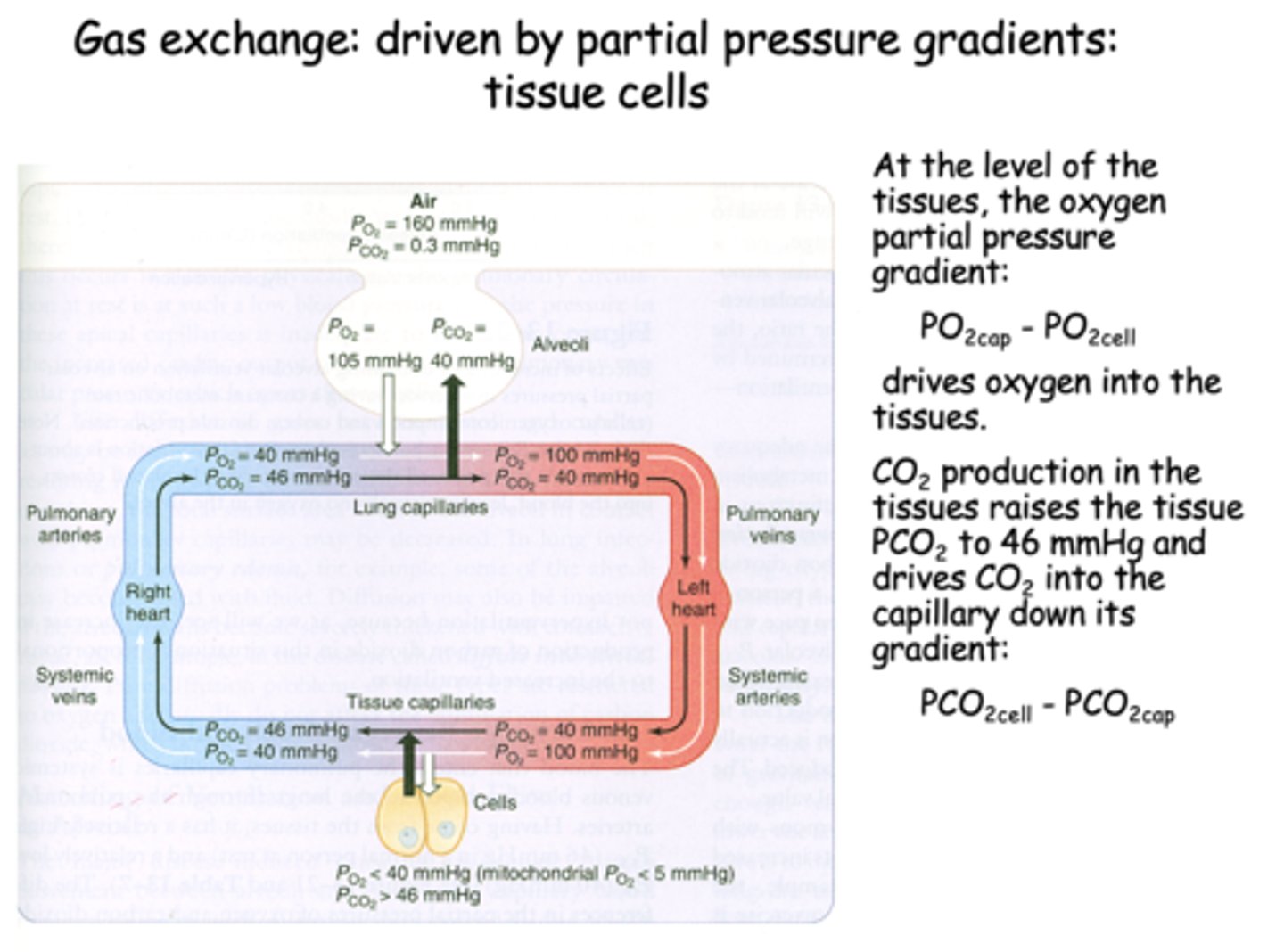
What is gas exchange at the alveolus is driven by?
Partial pressure gradients
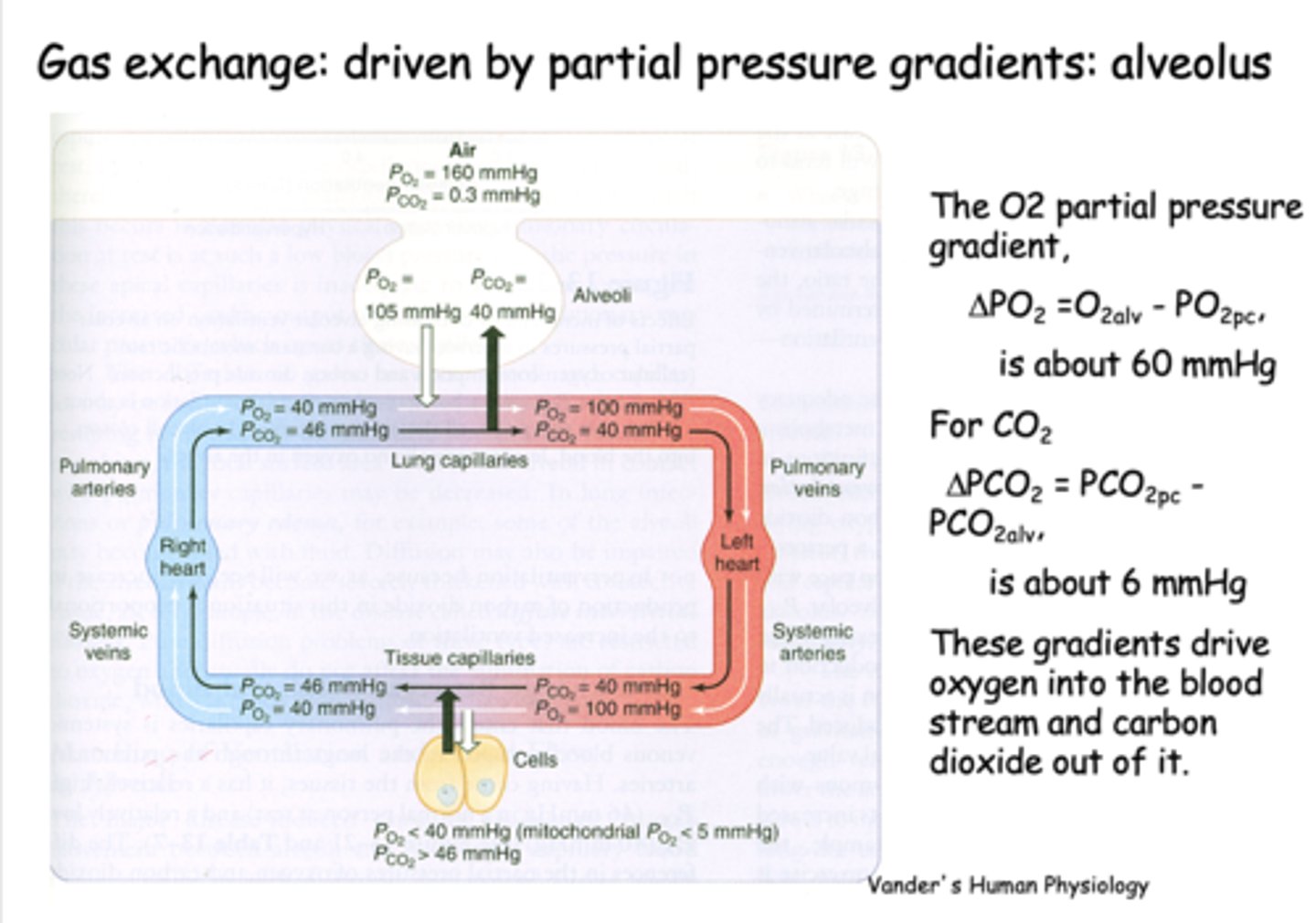
the partial pressure difference between alveolar PO2 and venous PO2 is about _____
60 mmHg
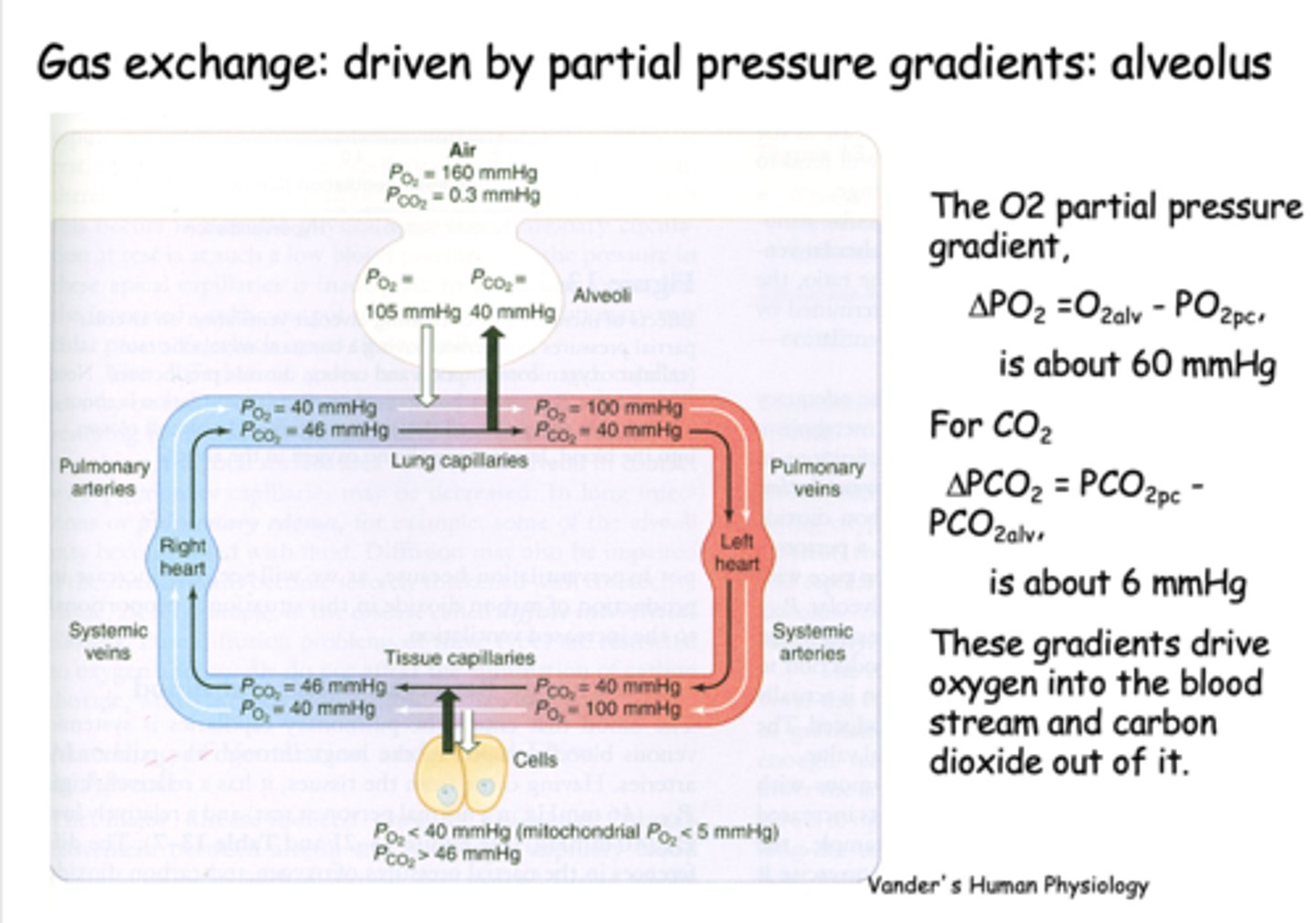
the partial pressure difference between alveolar PCO2 and venous PCO2 is about _____
6 mmHg
the partial pressure of O2 in the alveoli is ___________ than it is in the pulmonary arteries, driving O2 into the capillaries
higher
the partial pressure of CO2 in the alveoli is ___________ than it is in the pulmonary arteries, driving CO2 into the alveoli
lower
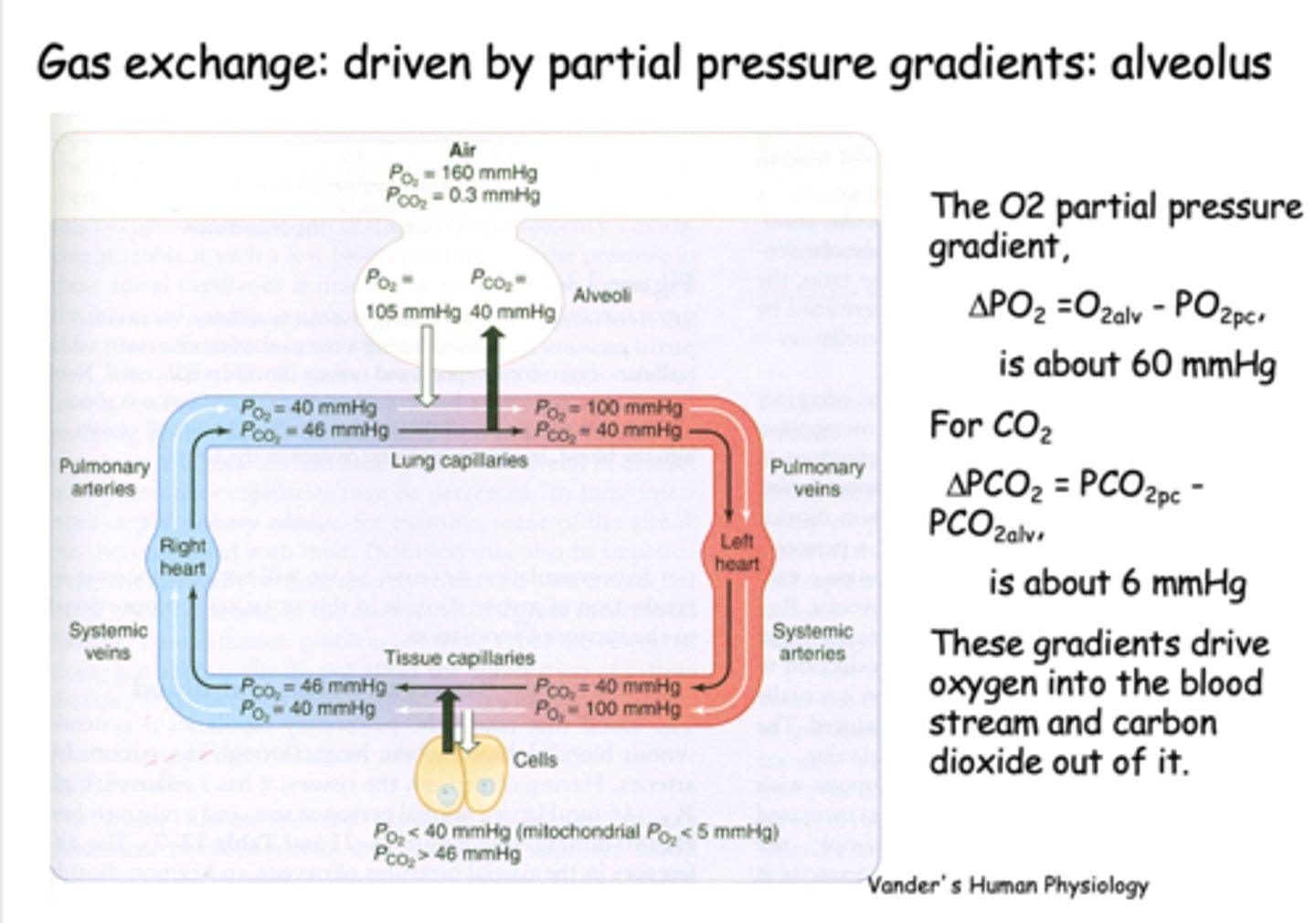
what is PO2 for freshly oxygenated arterial blood?
100 mmHg
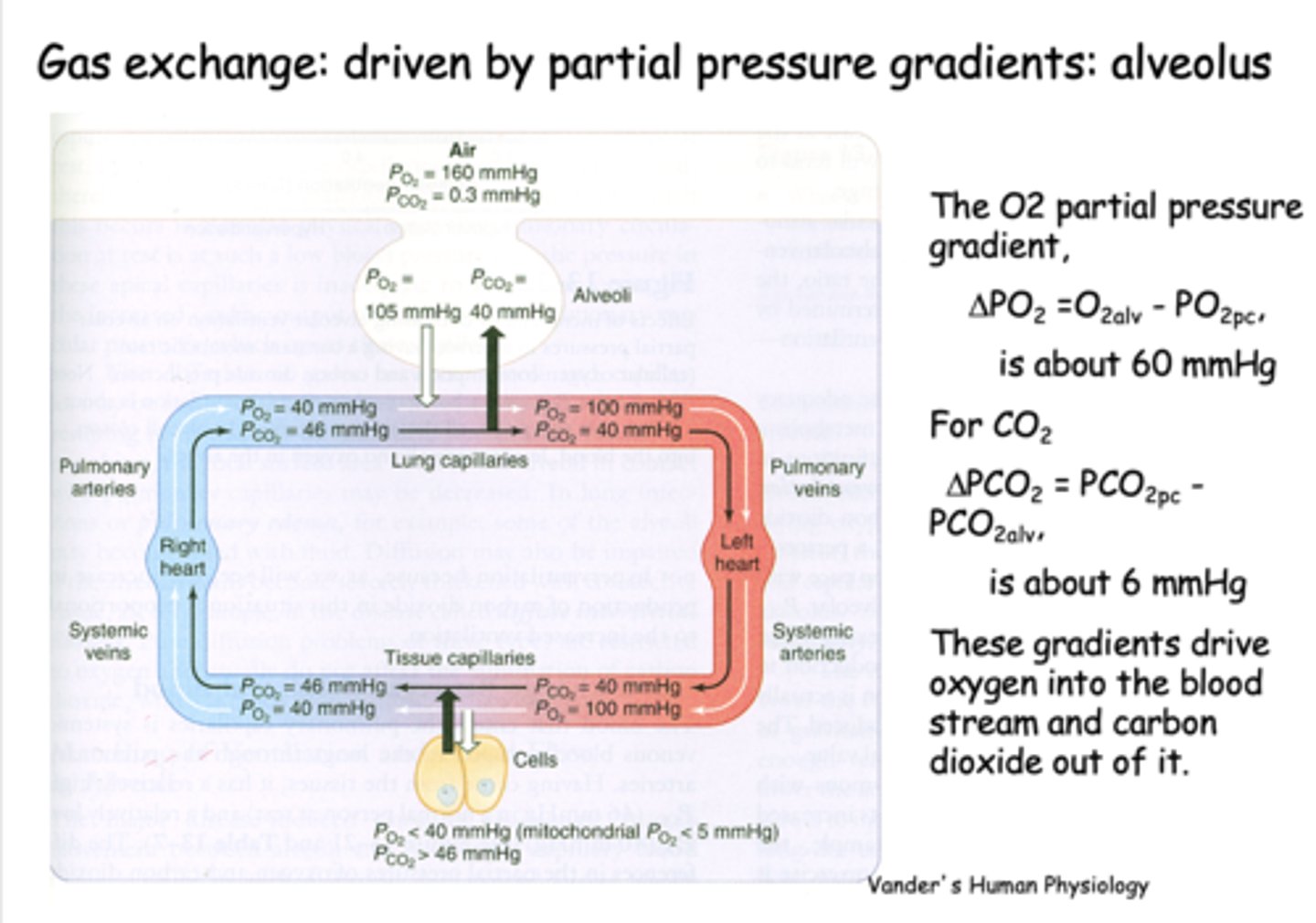
what is PCO2 for freshly oxygenated arterial blood?
40 mmHg
At the level of the tissues, the oxygen pressure gradient drives oxygen into the _______
tissues
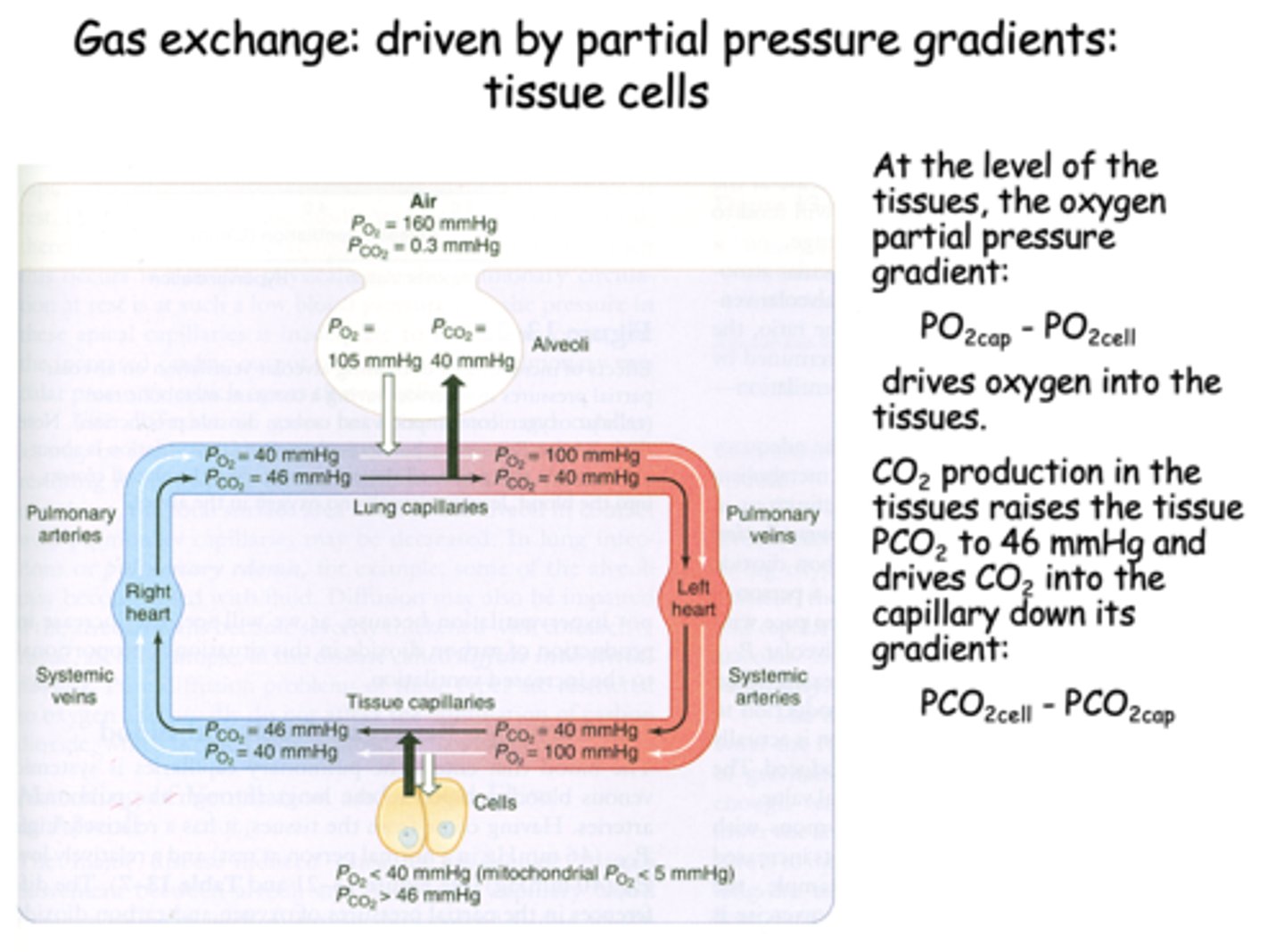
t/f: At the level of tissues, the CO2 production in the tissues raises the tissue PCO2 to 46mmHg and drives CO2 into the capillary down its gradient
true
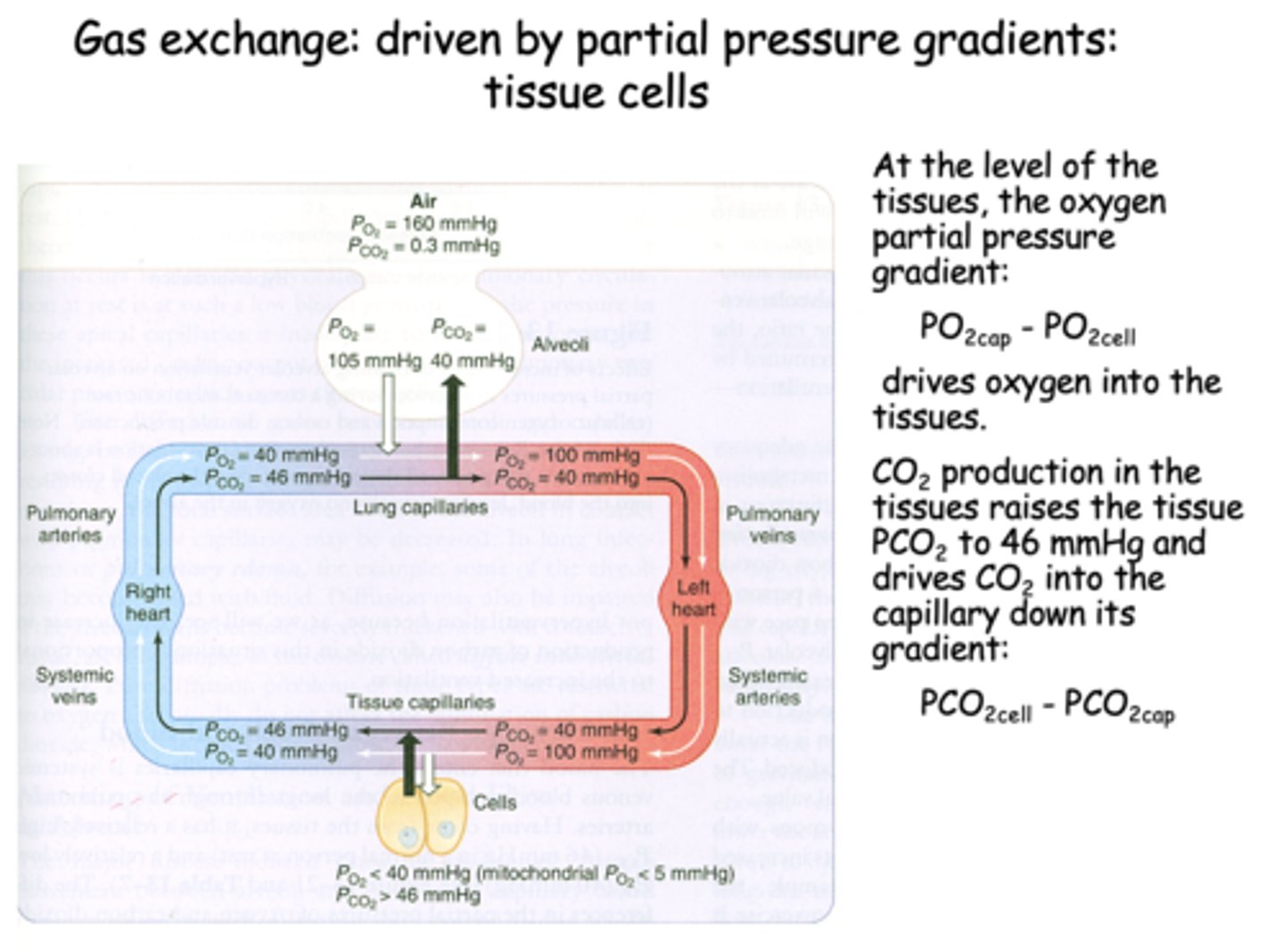
CO2 production in the tissues raises the tissue PCO2 to _______ and drives CO2 into the capillary down its gradient
46 mmHg
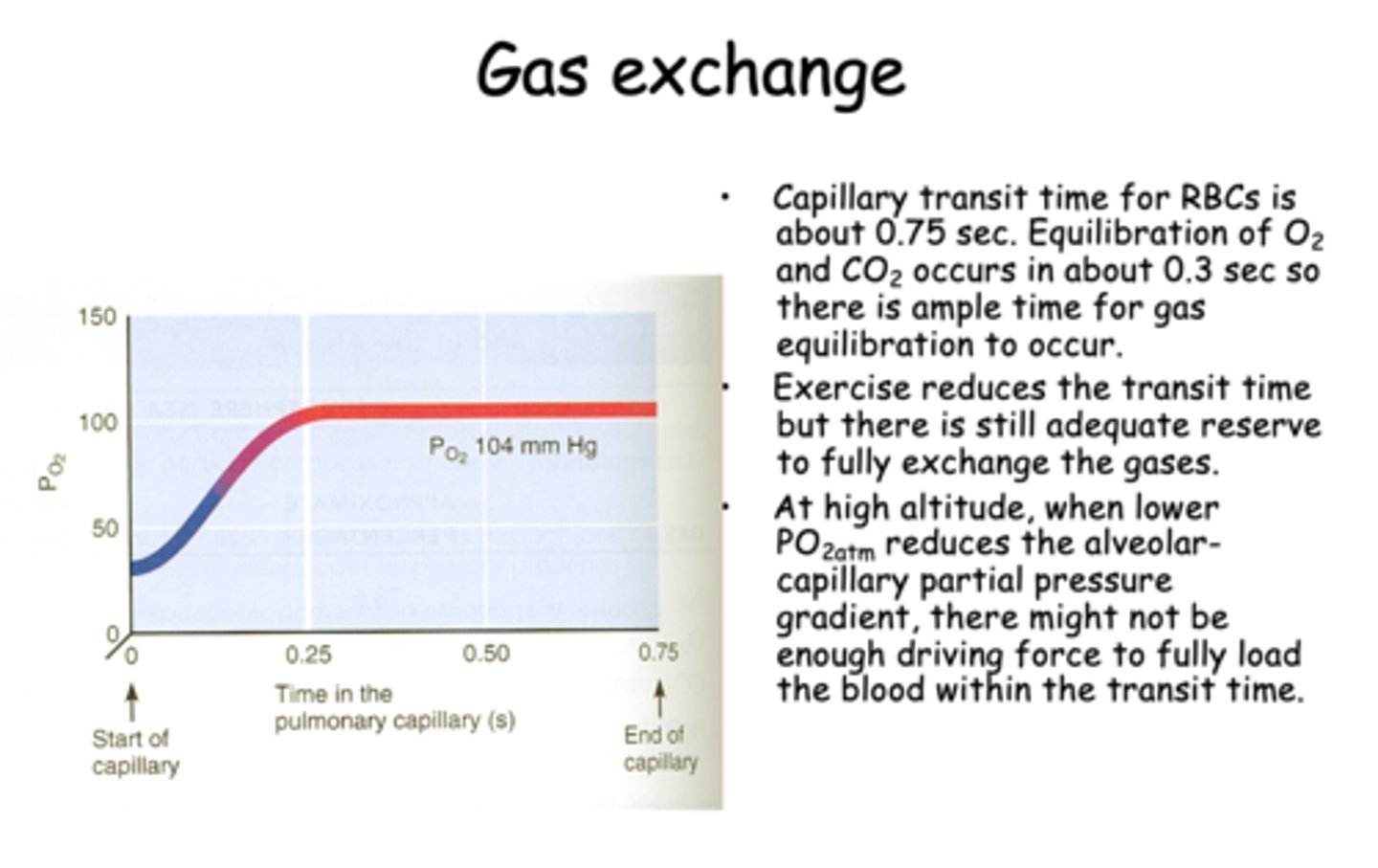
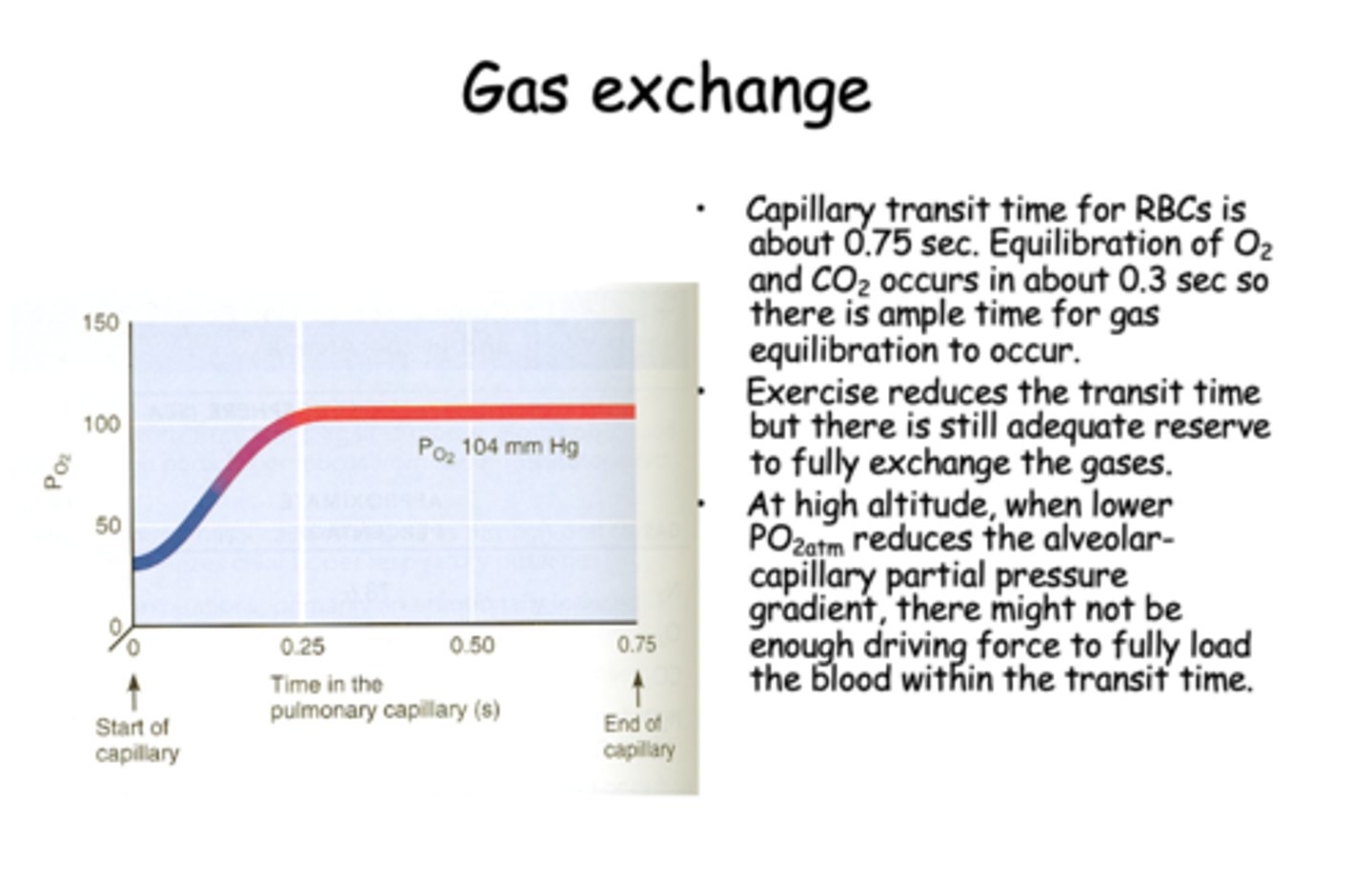
during gas exchange, capillary transit time for RBCs is about _____ seconds
0.75
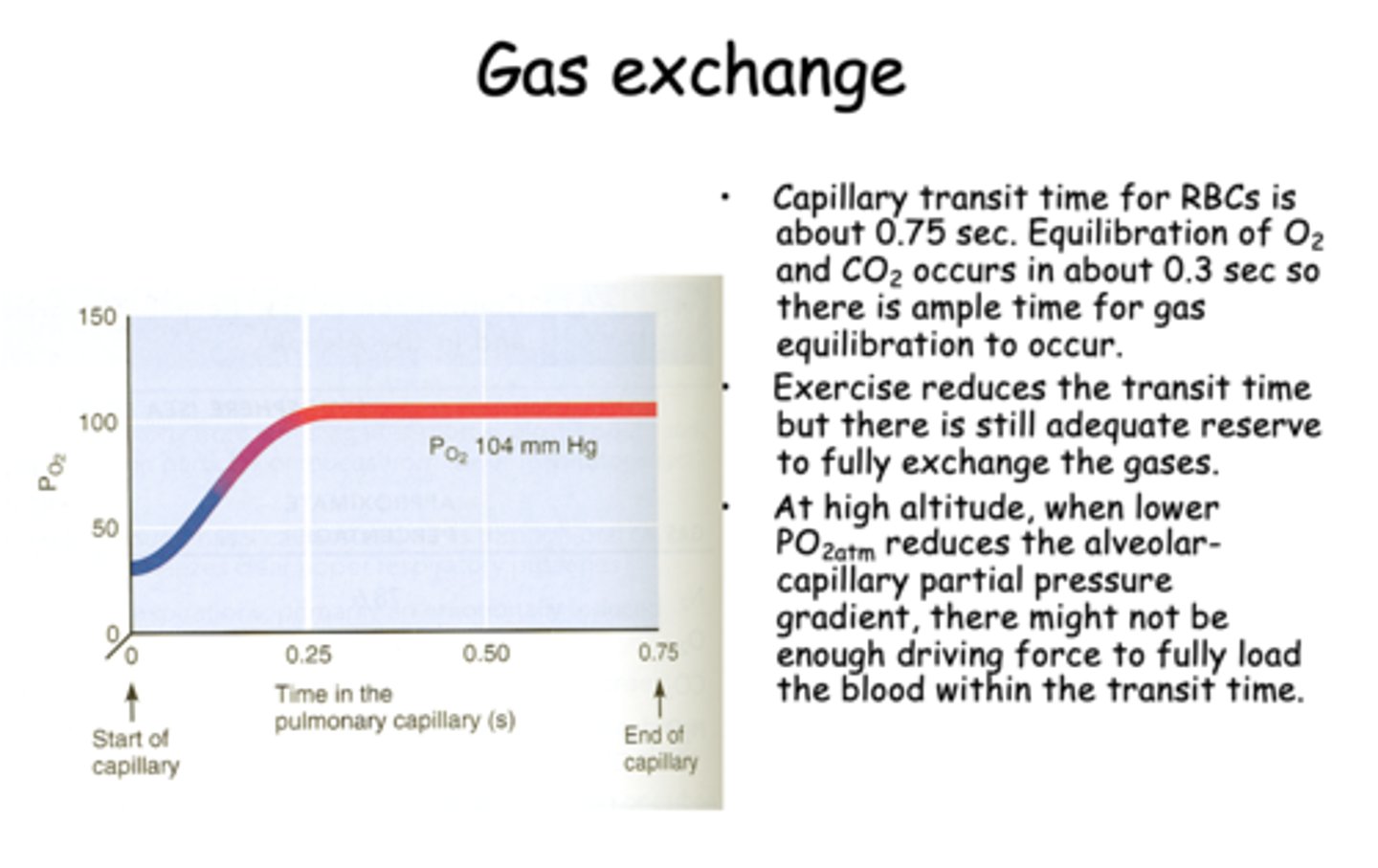
Equilibration of O2 and CO2 during gas exchange occurs in about _____ seconds
0.3
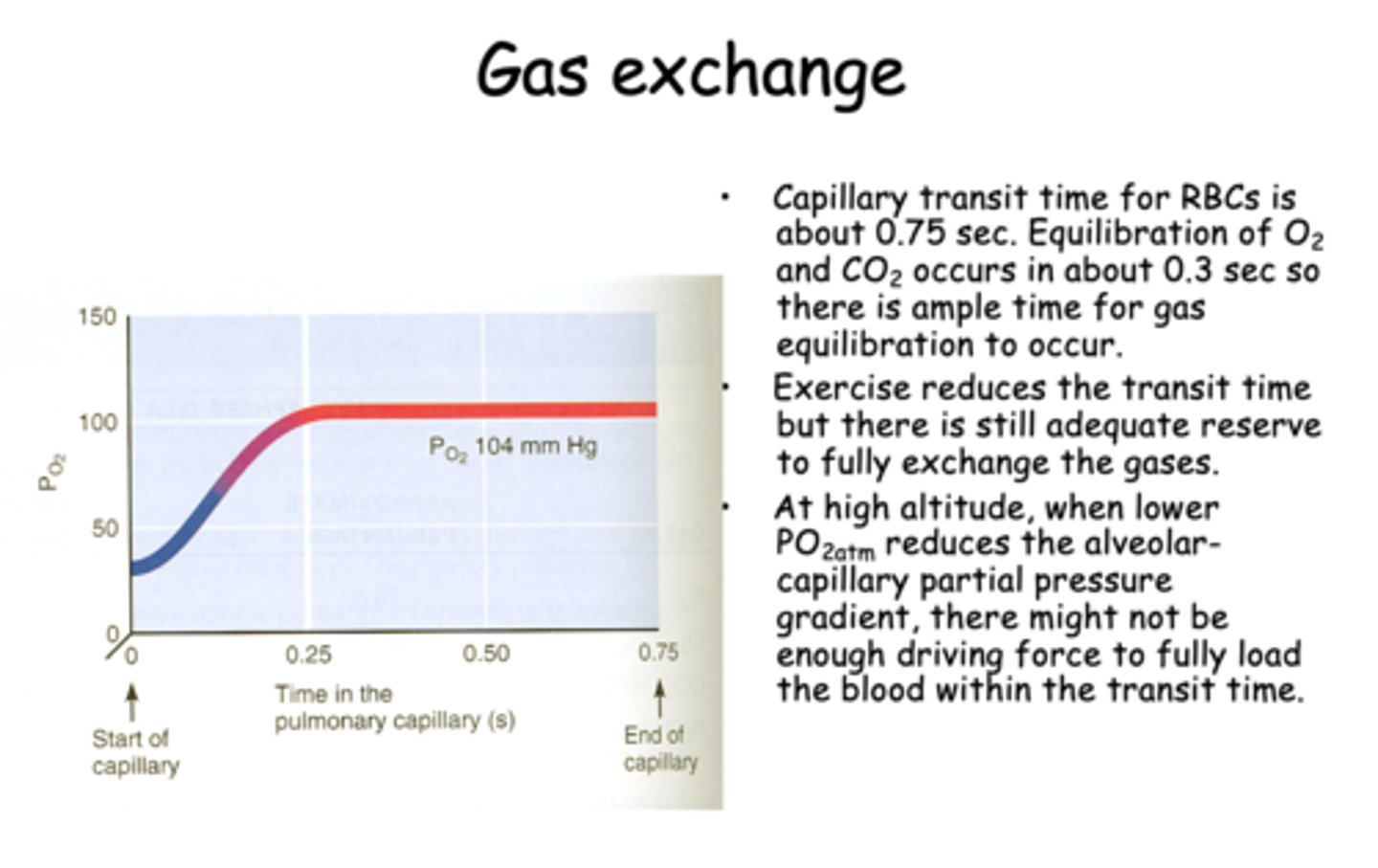
during exercise, the RBC transit time will _____________ but there is still adequate reserve to fully exchange the gases
decrease
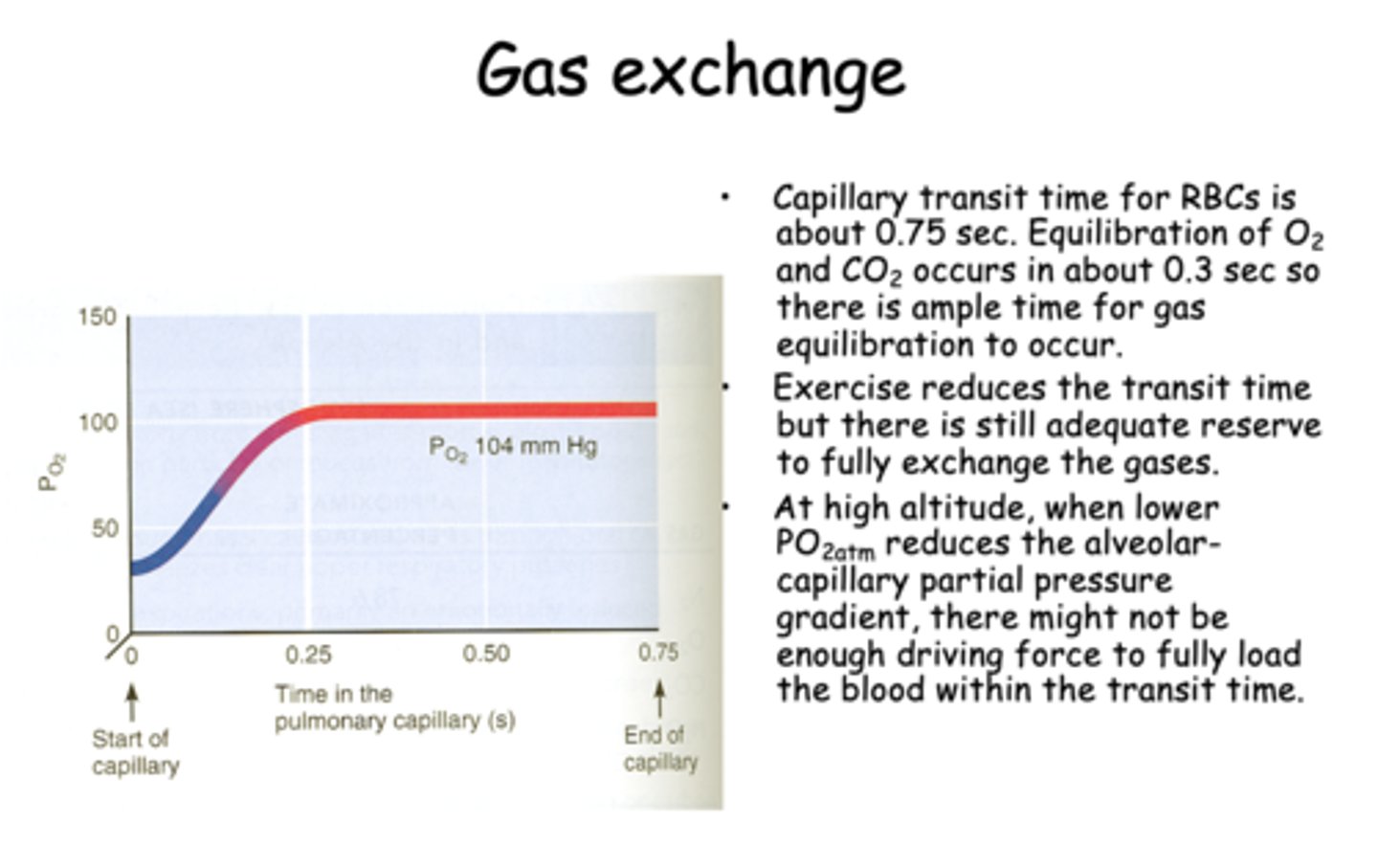
t/f: At low altitude, when lower PO2atm reduces the alveolar-capillary partial pressuregradient, there might not beenough driving force to fully loadthe blood within the transit time.
false, HIGH ALTITUDE
what is the alveolar gas equation?
PAO2 = PIO2 - (PaCO2/0.8)

what is the respiratory exchange ratio (the volume of CO2 expired per volume of O2 inspired in a normal diet)?
0.8

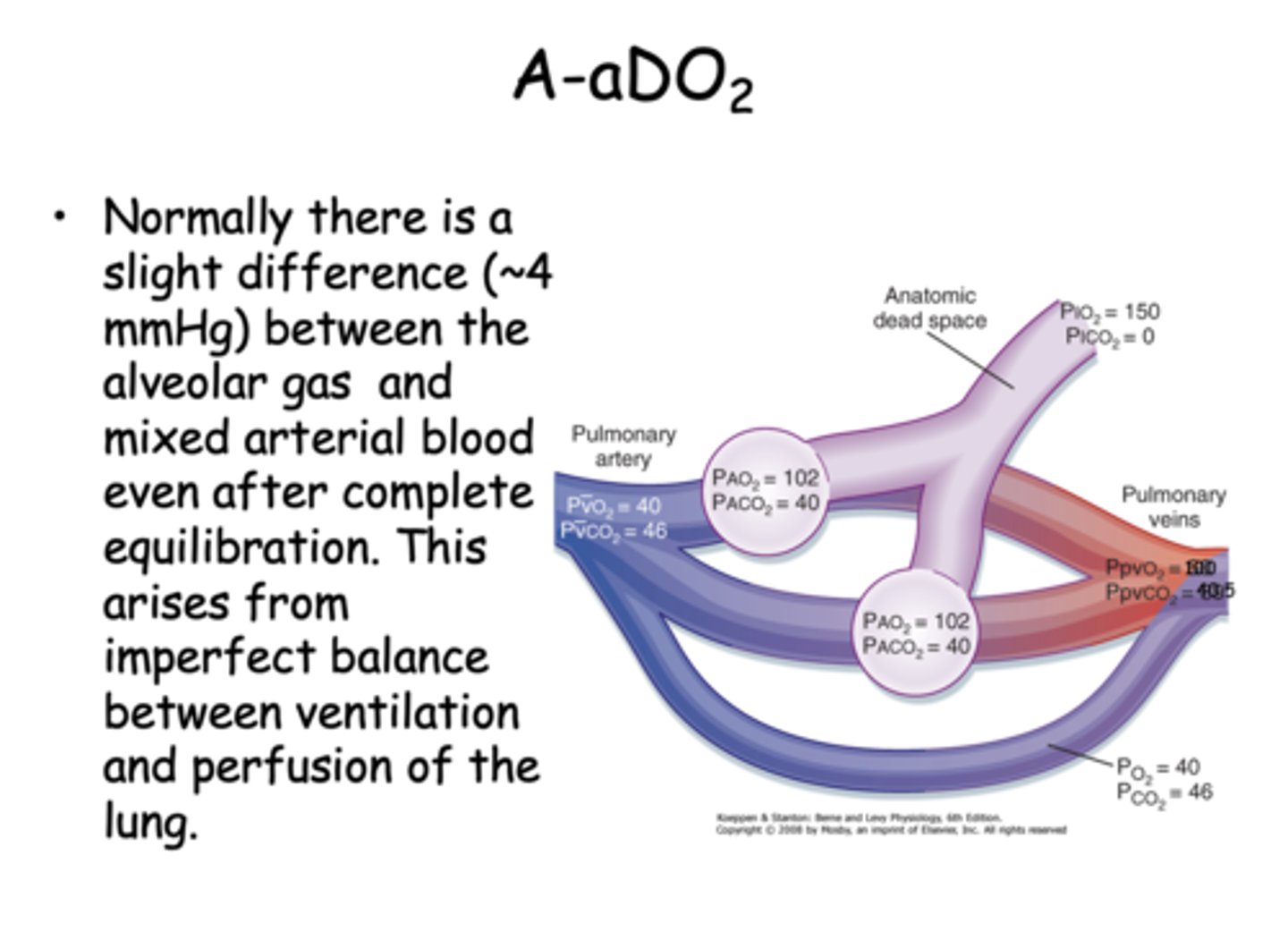
Normally there is a slight difference between the alveolar gas and mixed arterial blood even after complete equilibration. What is the pressure difference?
4 mmHg
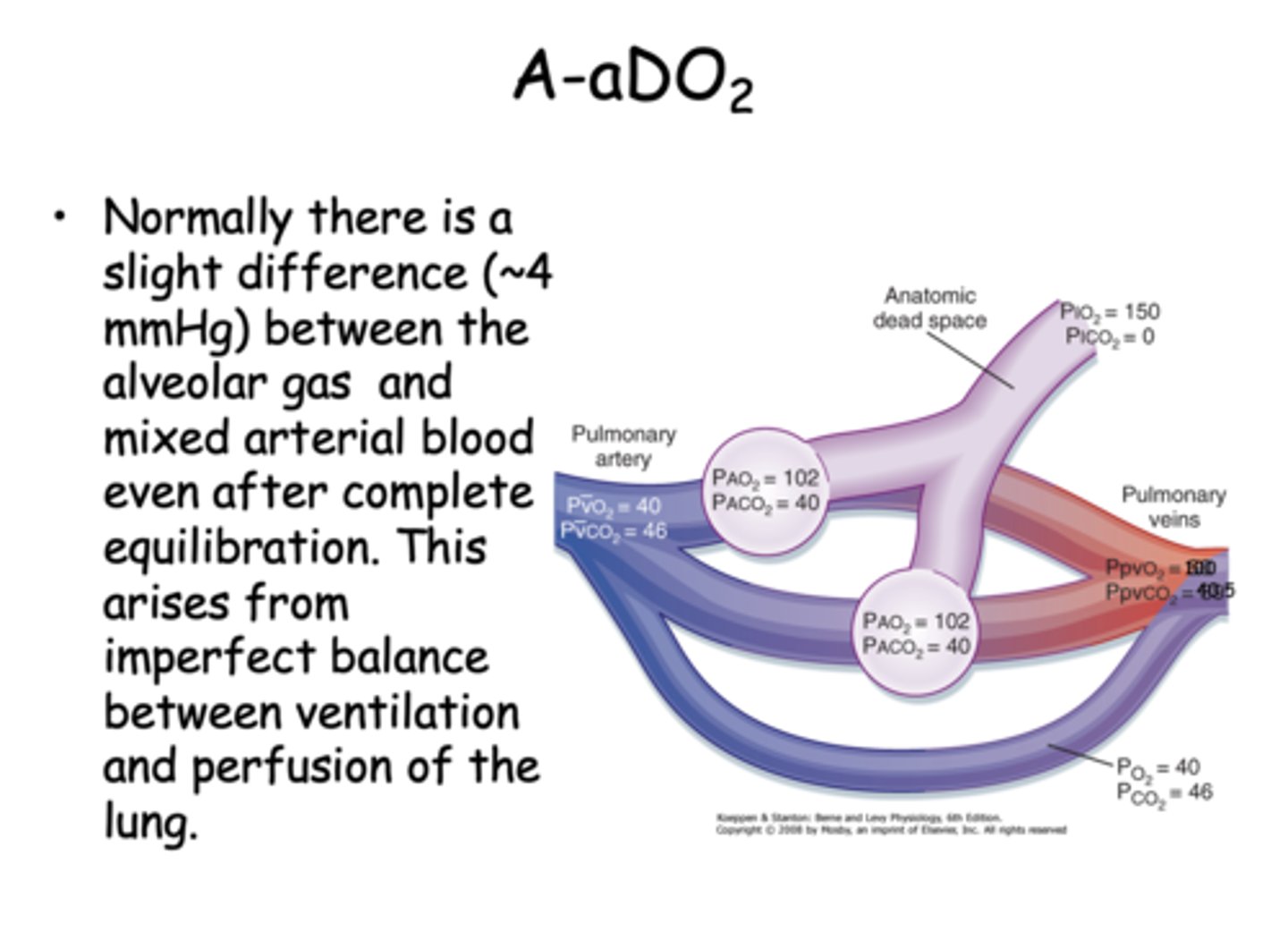
what causes the slight difference between the alveolar gas and mixed arterial blood even after complete equilibration?
imperfect balance between ventilation and perfusion of the lung
A-aDO2 (alveolar arterial difference) in normal subjects will ________ with age and loss of lung compliance
increase

how do you calculate A-aDO2 for patients ages 30 and over?
age x 0.3
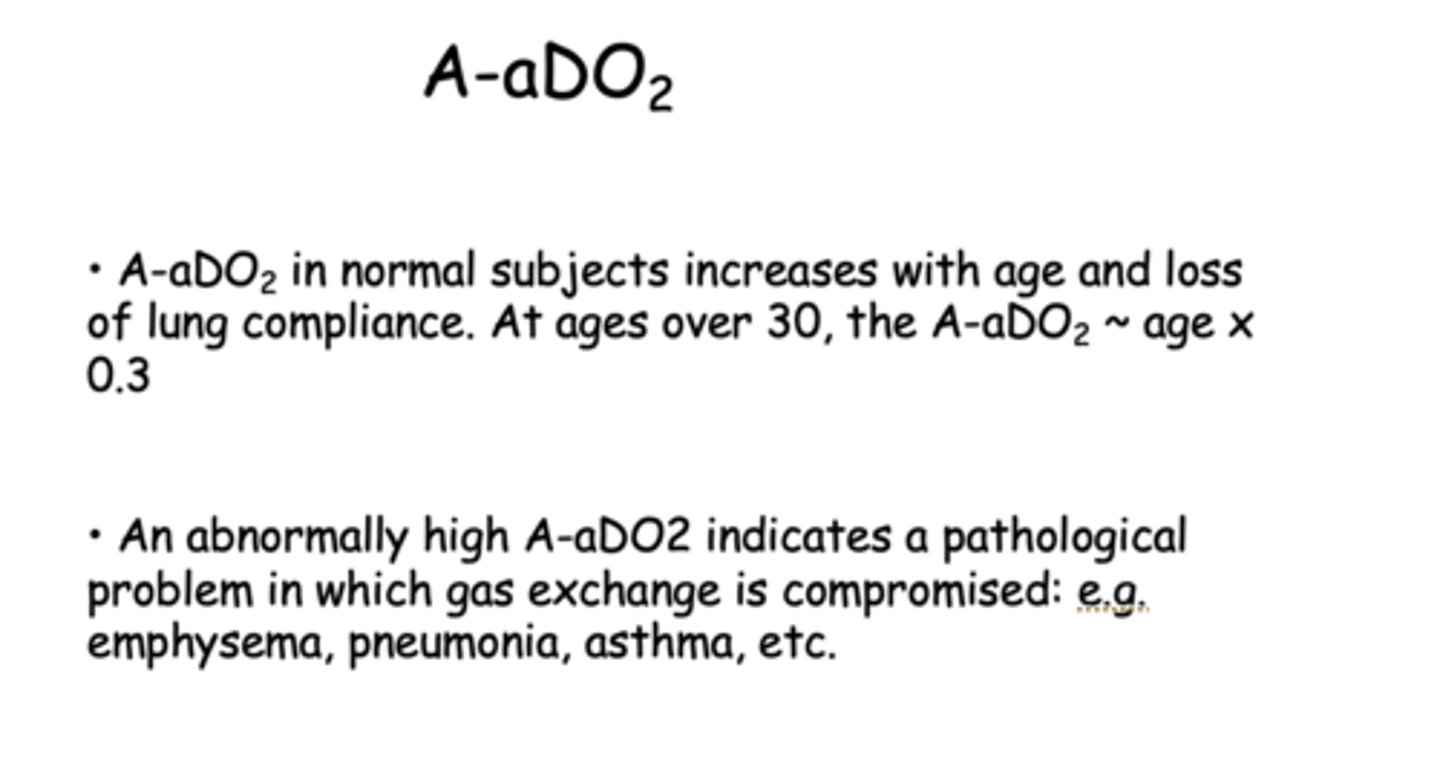
An abnormally _______ A-aDO2 indicates a pathological problem in which gas exchange is compromised i.e. emphysema, pneumonia, asthma
higher
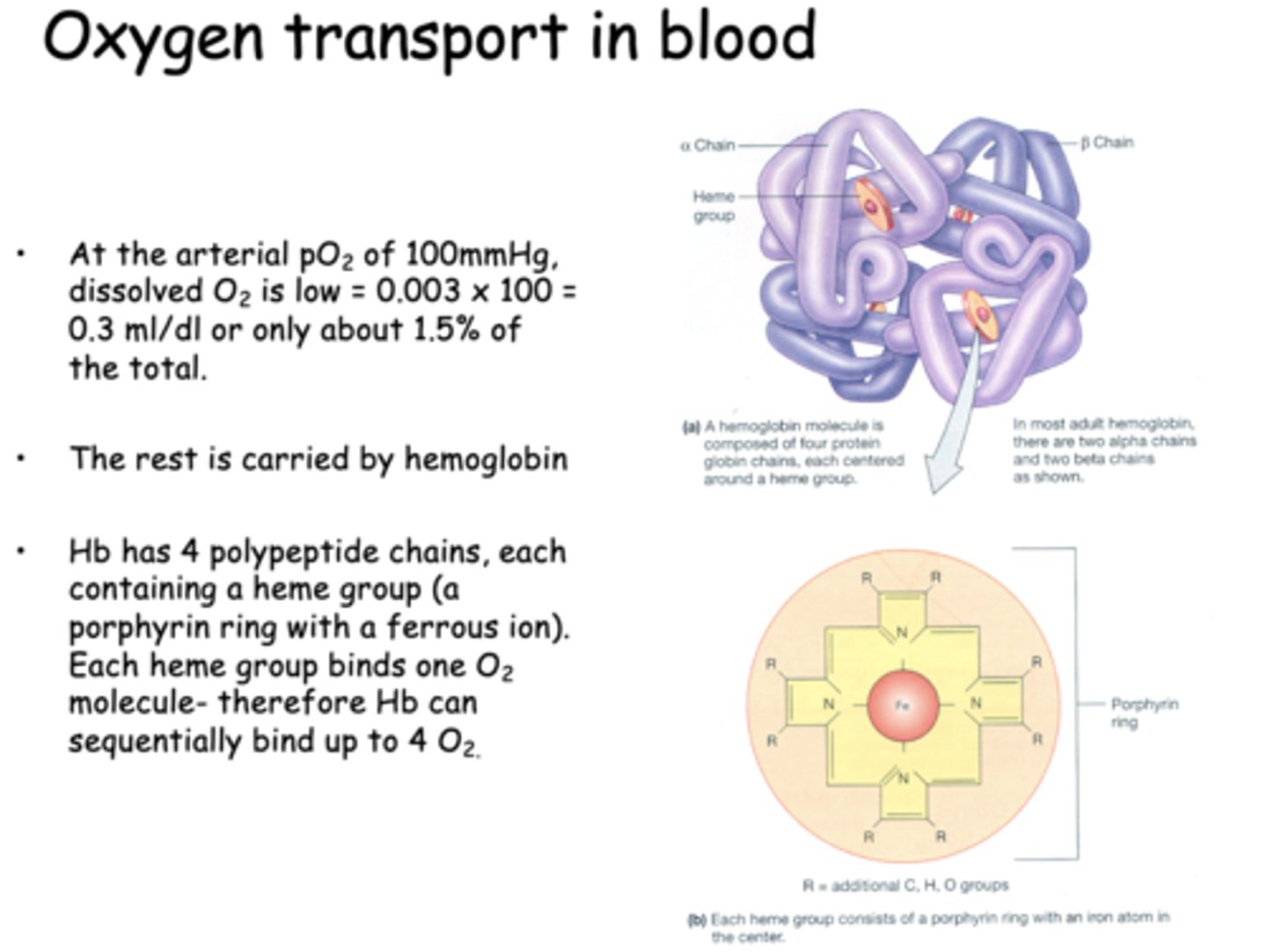
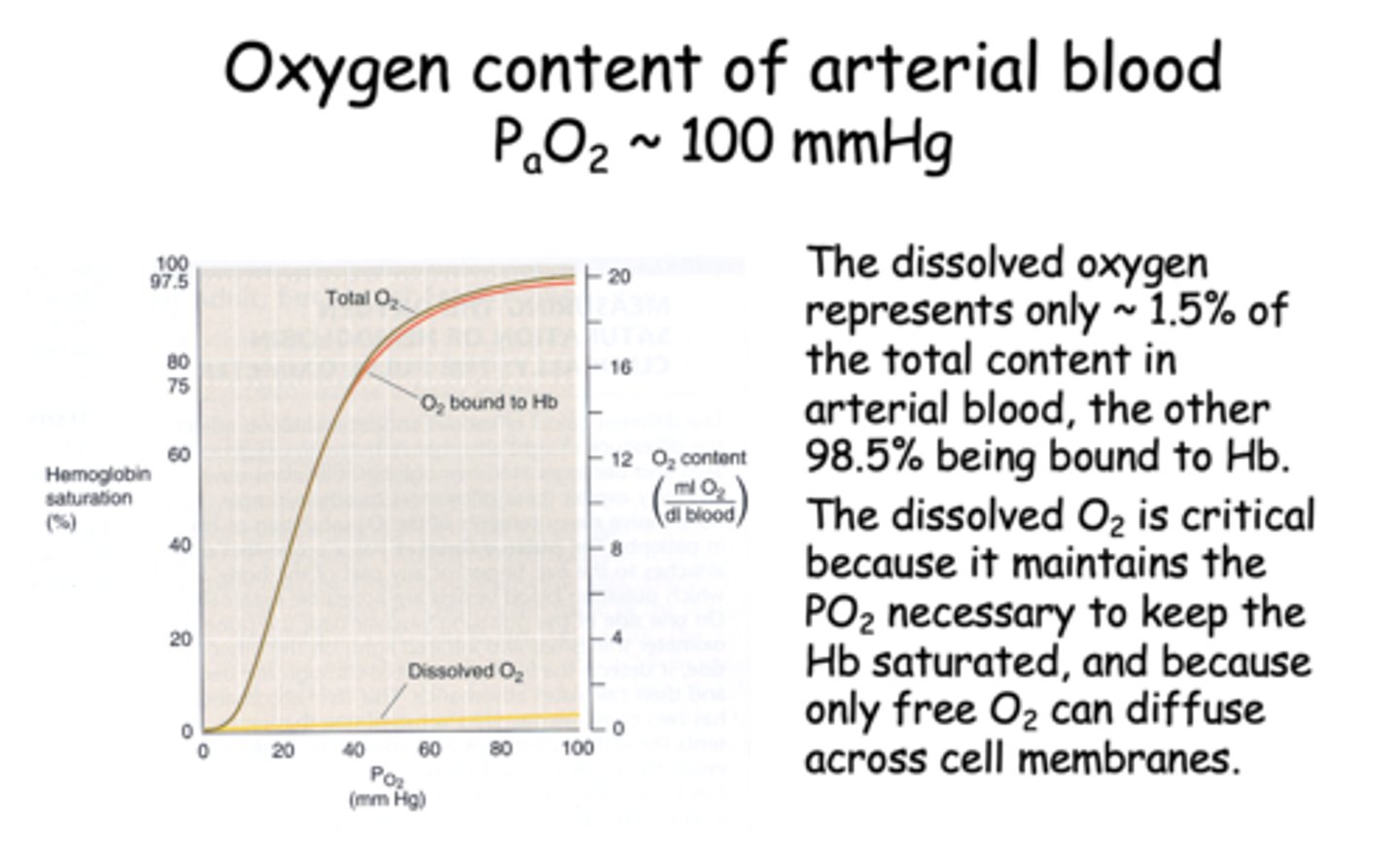
At the arterial pO2 of 100mmHg, dissolved O2 is low __________ ml/dl or only about 1.5% of the total.
0.3 ml/dl
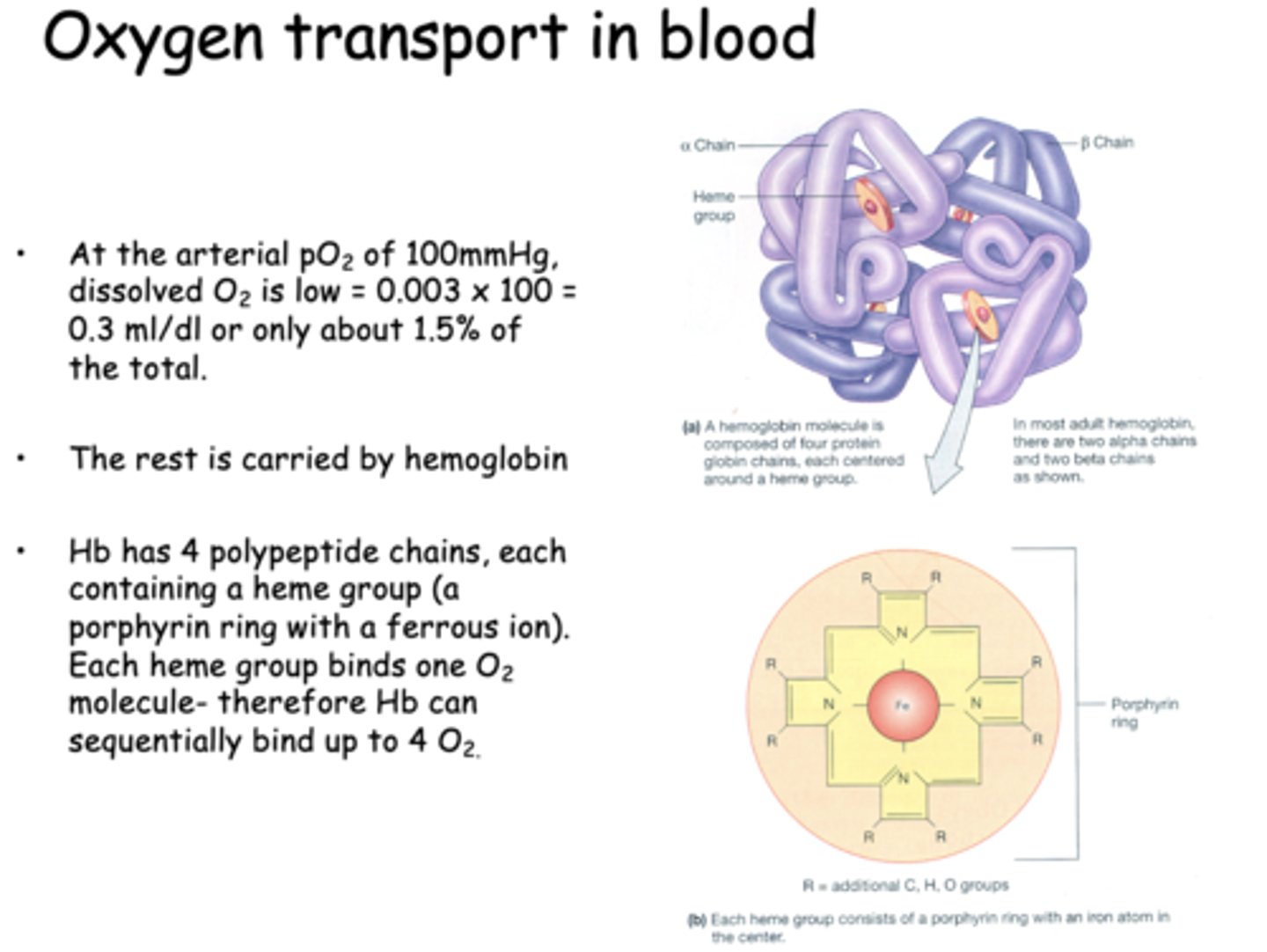
At the arterial pO2 of 100mmHg, dissolved O2 is low = 0.003 x 100 = 0.3 ml/dl or only about 1.5% of the total. The rest is carried by _____________
hemoglobin
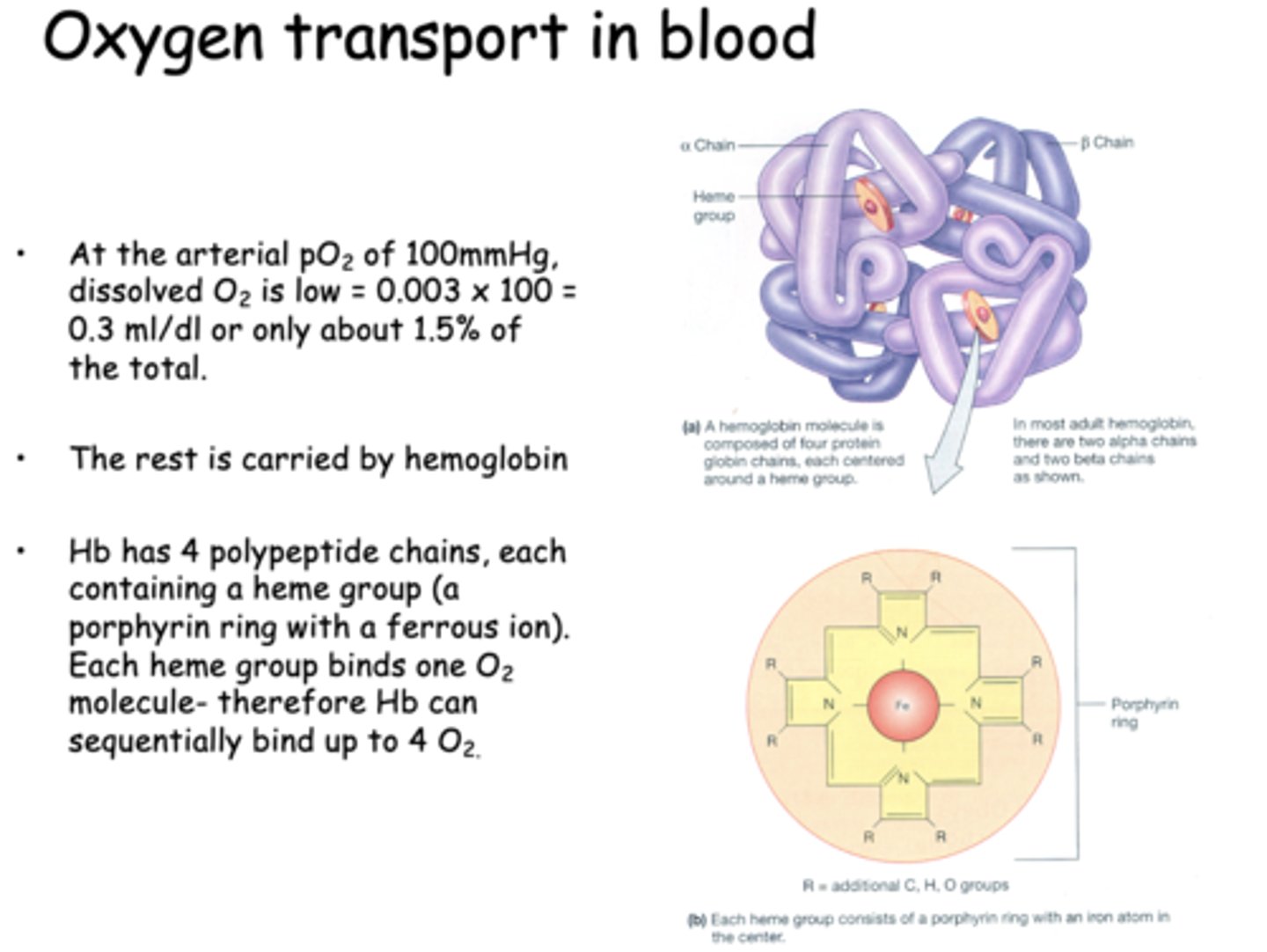
Hb can bind sequentially bind up to _____ due to its polypeptide chains which each carry 1 heme group
4 O2
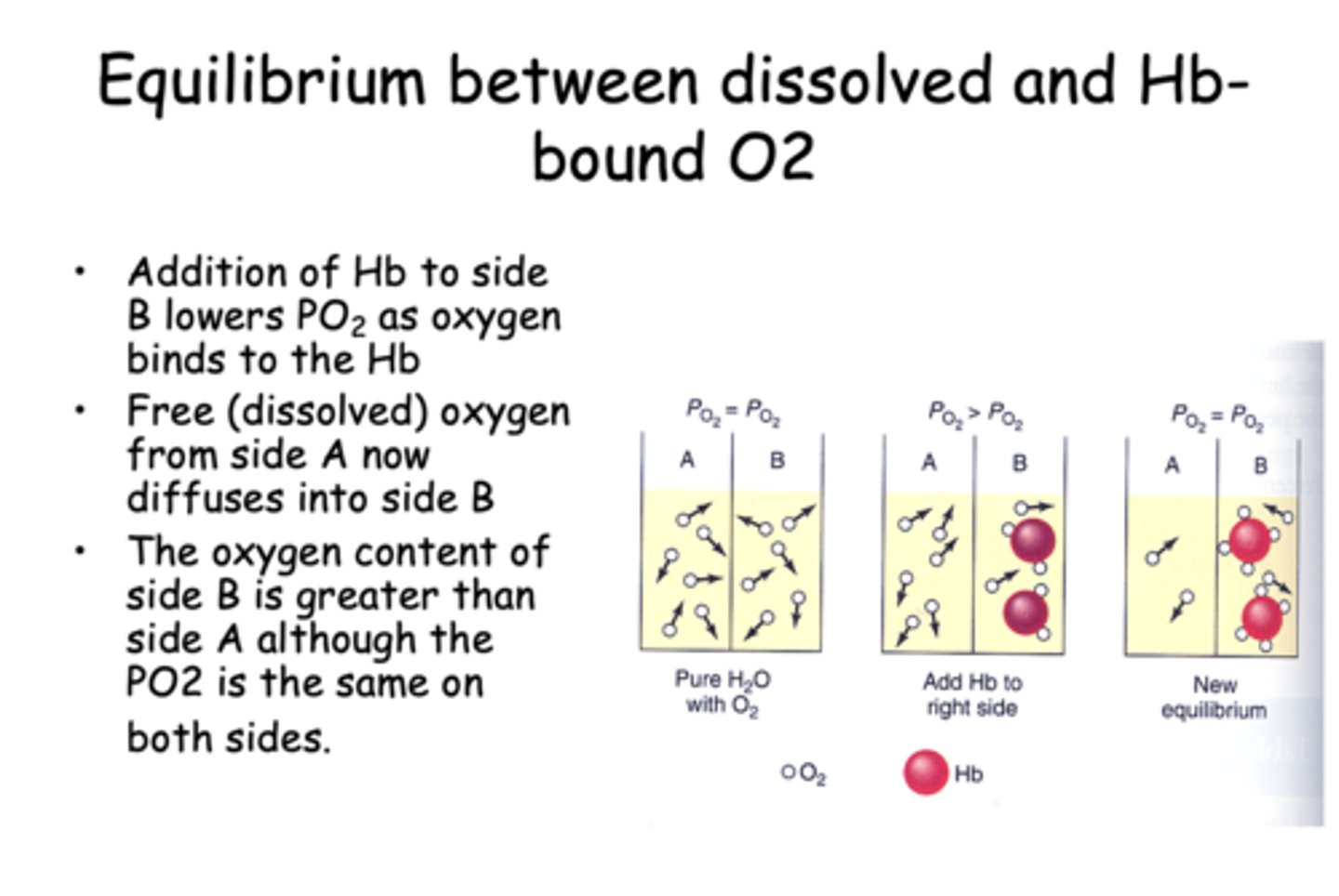
When hemoglobin (Hb) is added to one side of a system containing dissolved oxygen, the partial pressure of oxygen (PO₂) on that side initially decreases. Over time, PO₂ equalizes between both sides, but the total oxygen content remains higher on the side with Hb. What best explains this phenomenon?
Hemoglobin binds dissolved oxygen, lowering free O₂ and allowing more to diffuse in.
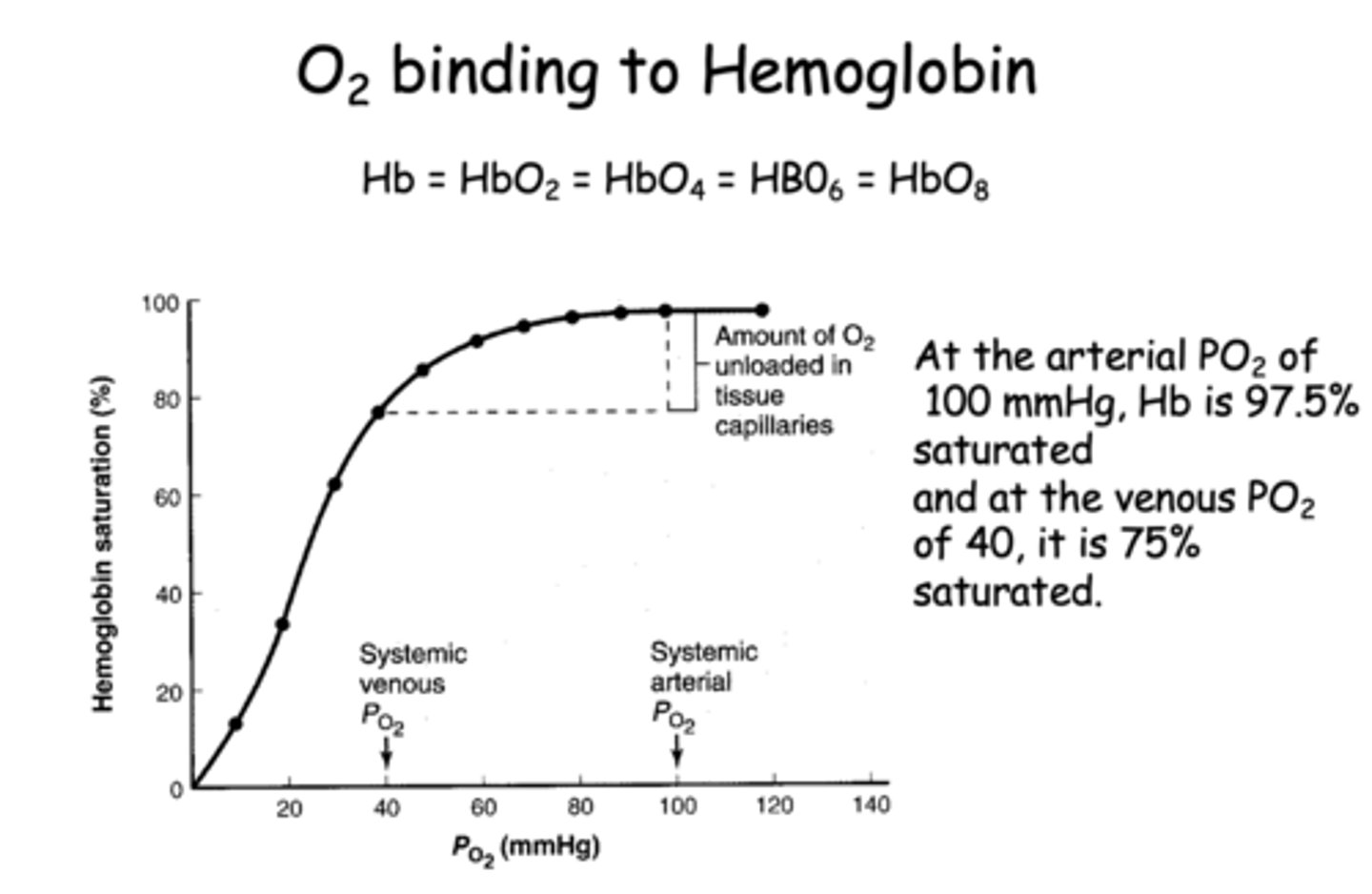
At the arterial PO2 of 100 mmHg, Hb is __________% saturated
97.5%
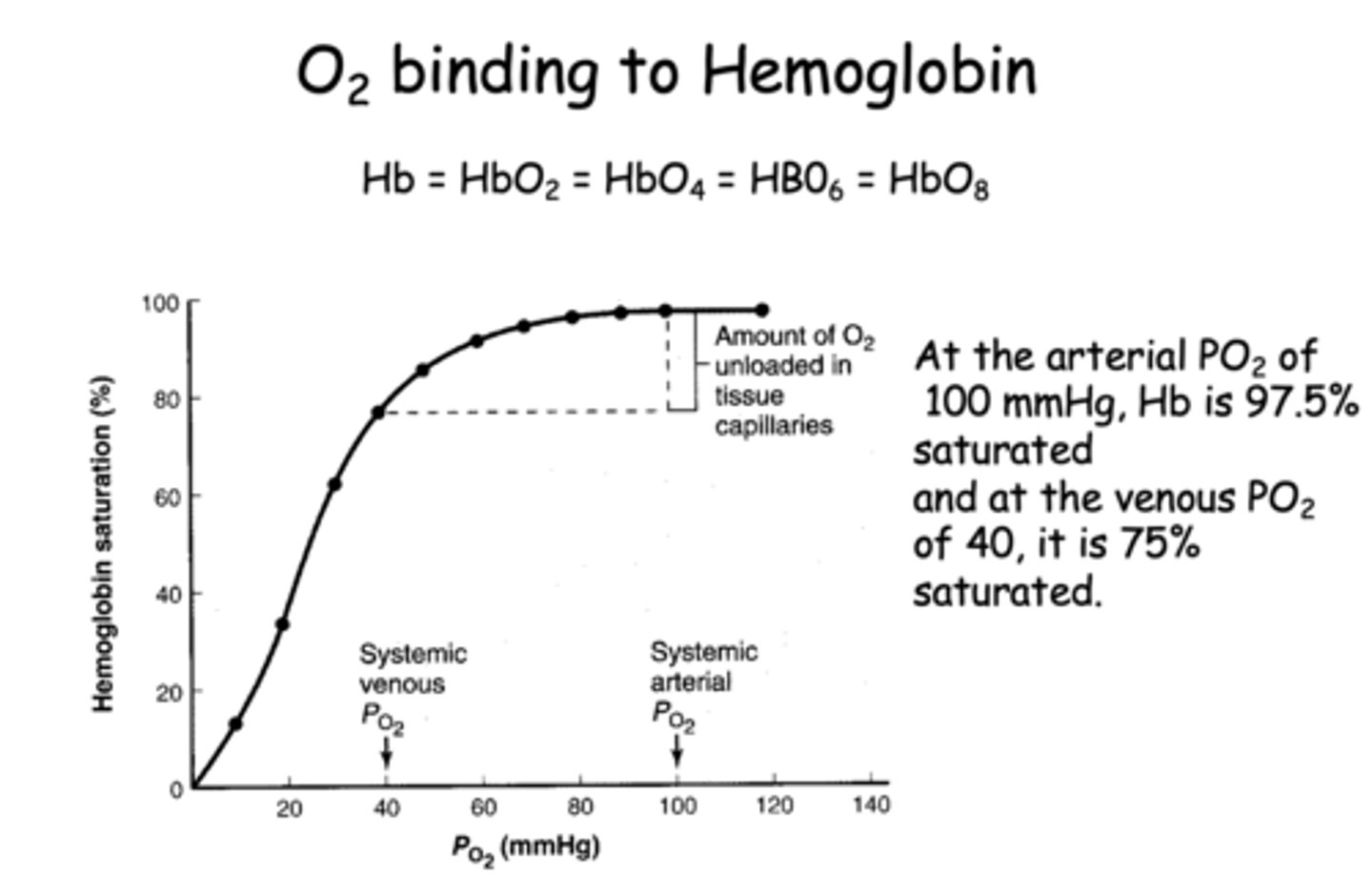
At the venous PO2 of 40, Hb is __________% saturated
75%
T/F: The binding of O2 to hemoglobin is known as positive cooperative binding
True
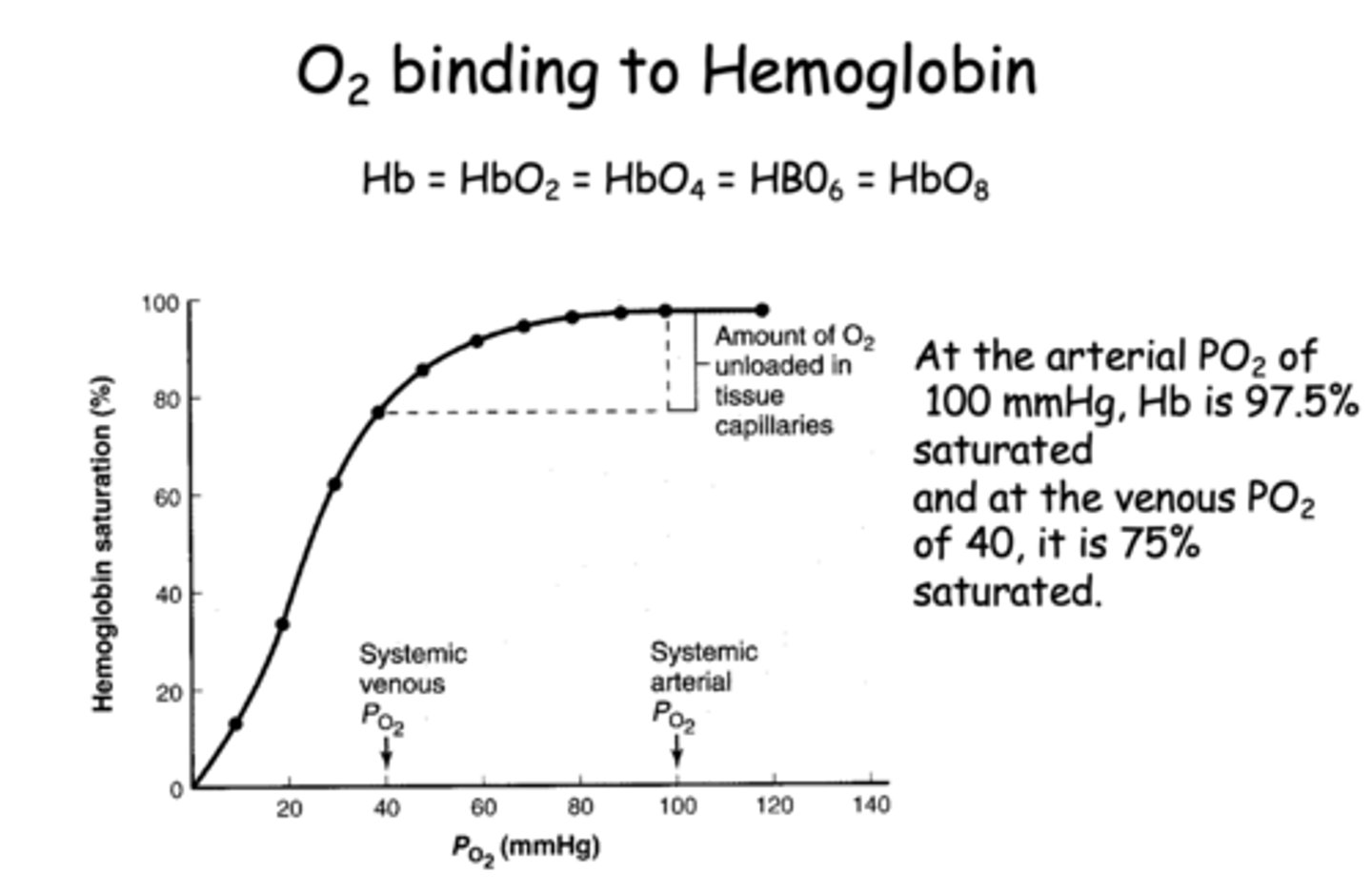
In normal resting conditions, how many oxygen molecules are typically released by hemoglobin to the tissues?
1
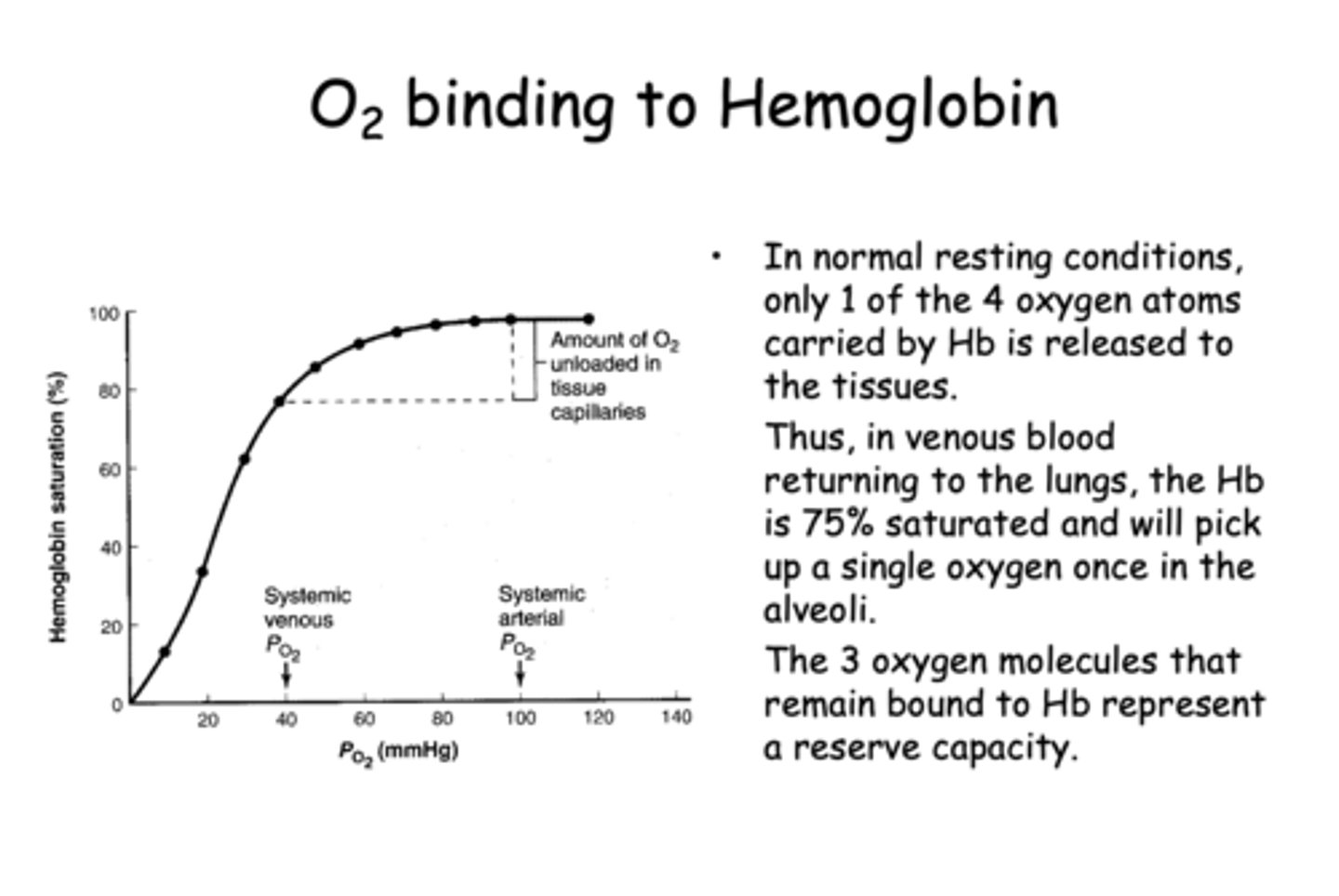
What is the approximate hemoglobin saturation in venous blood returning to the lungs under normal conditions?
75%
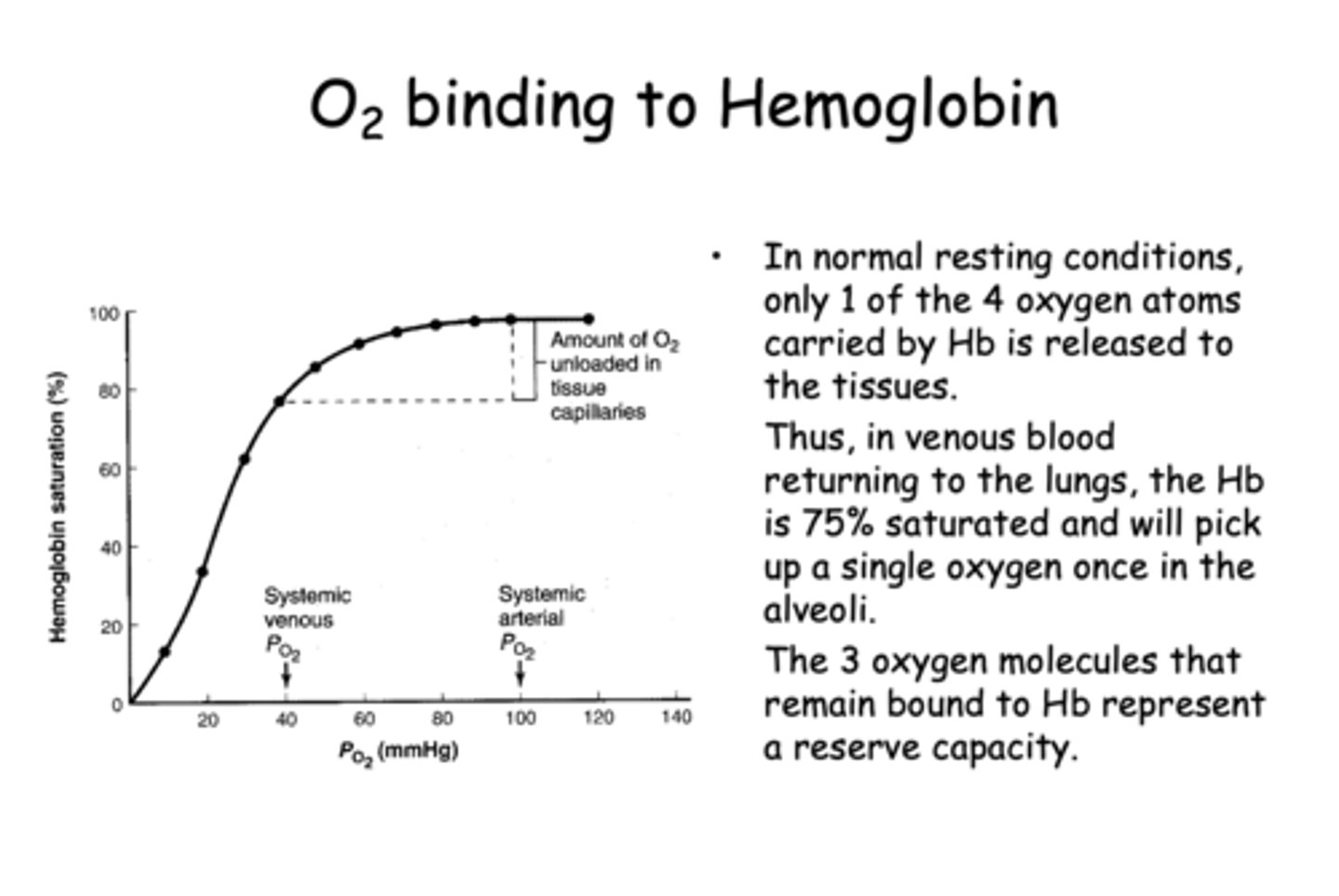
What is the physiological significance of the 3 oxygen molecules that remain bound to hemoglobin in venous blood?
They represent a reserve capacity for increased oxygen demand
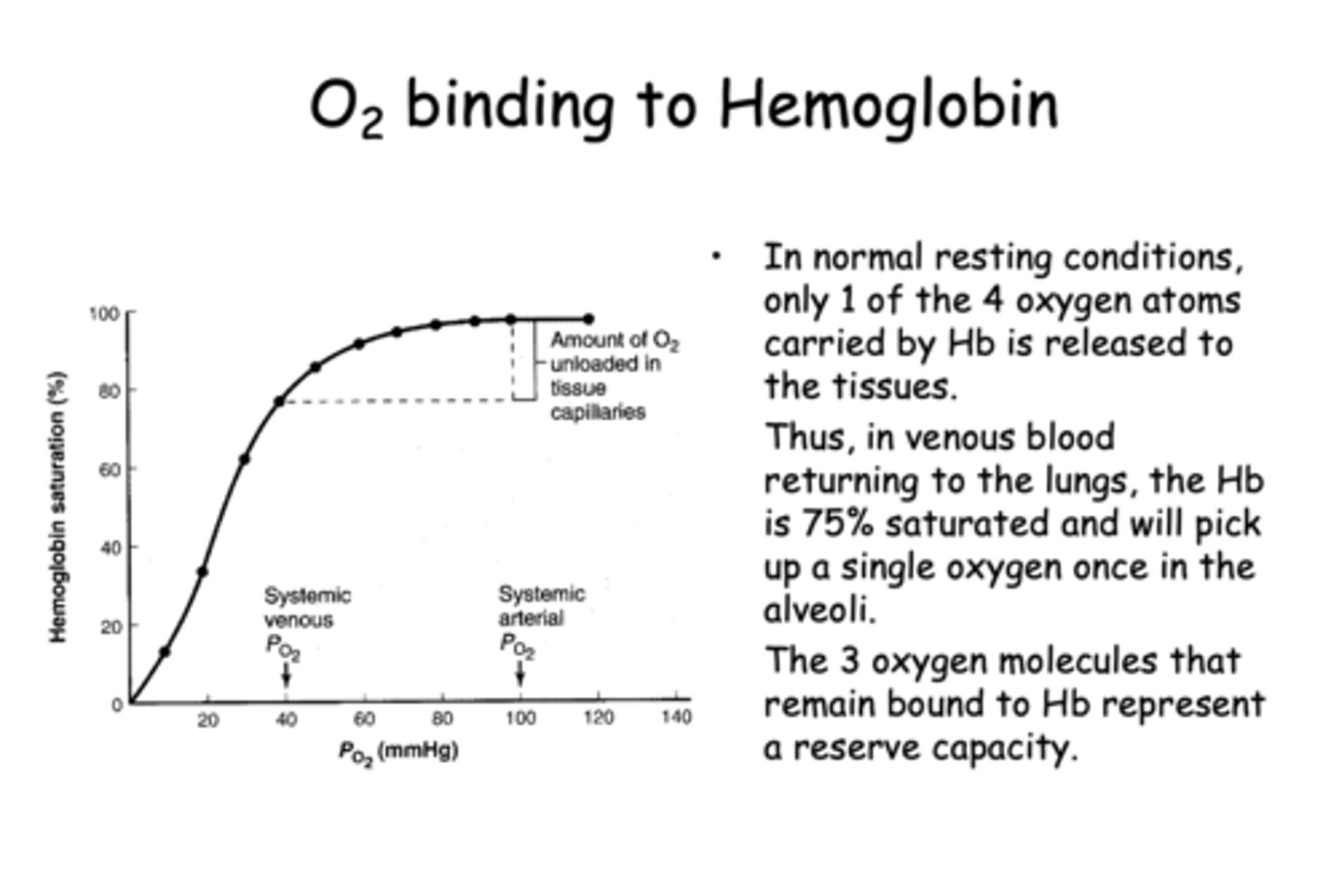
what is arterial PCO2?
40 mmHg
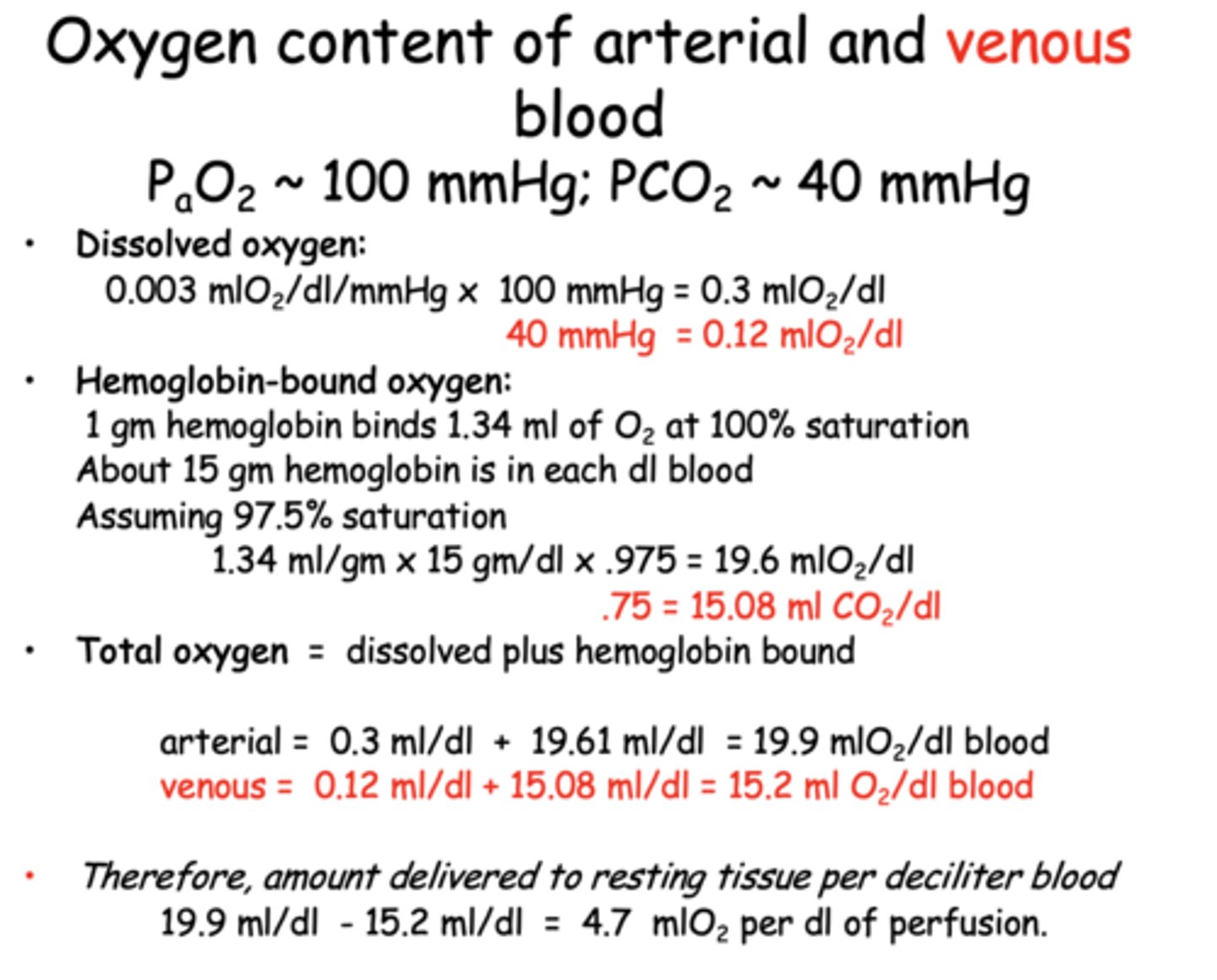
How much oxygen is dissolved in venous blood?
0.12 mL O₂/dL
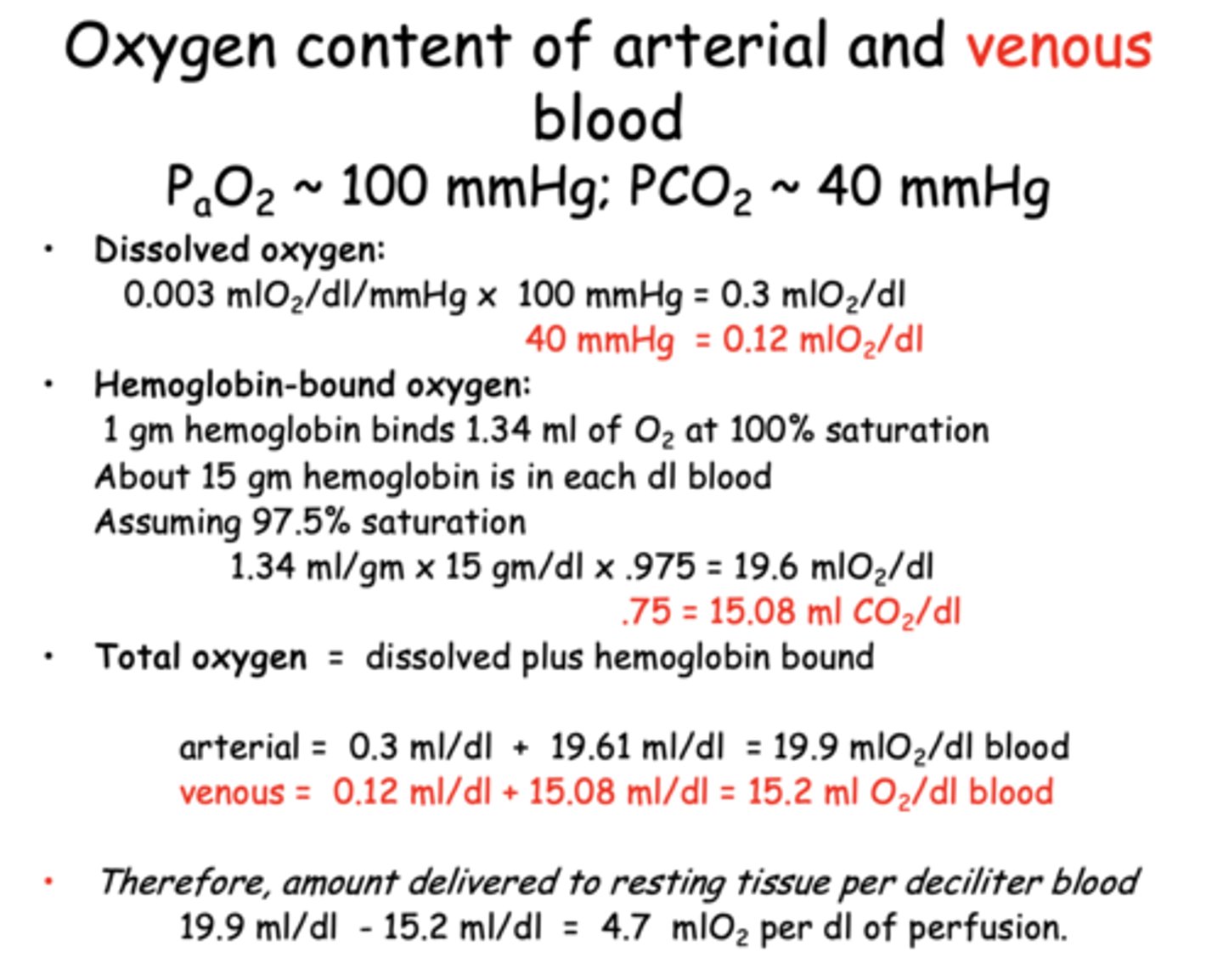
1 gm hemoglobin binds _________ml of O2 at 100% saturation
1.34
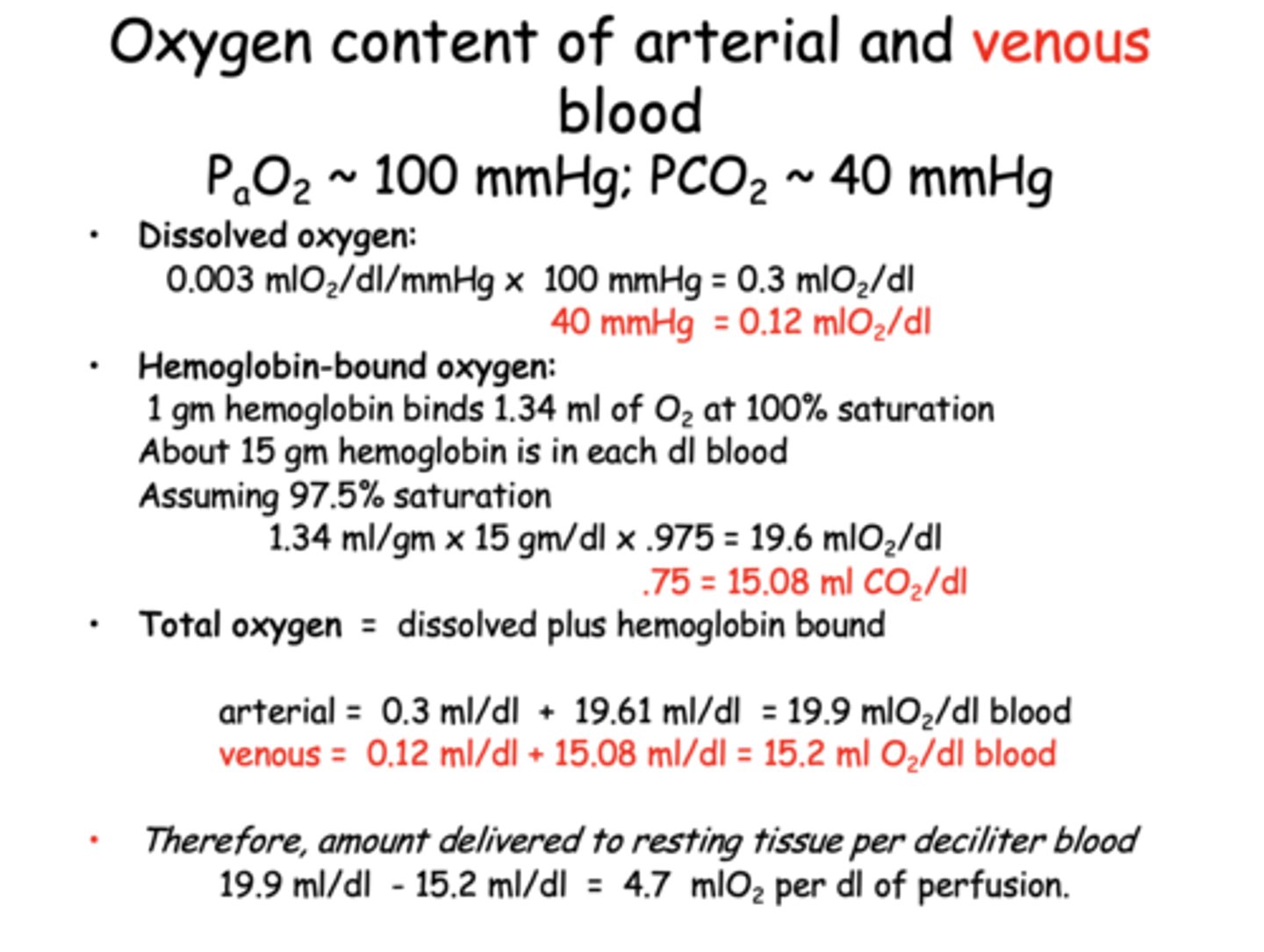
How much oxygen is dissolved in arterial blood (PaO₂ ≈ 100 mmHg)?
0.3 mL O₂/dL
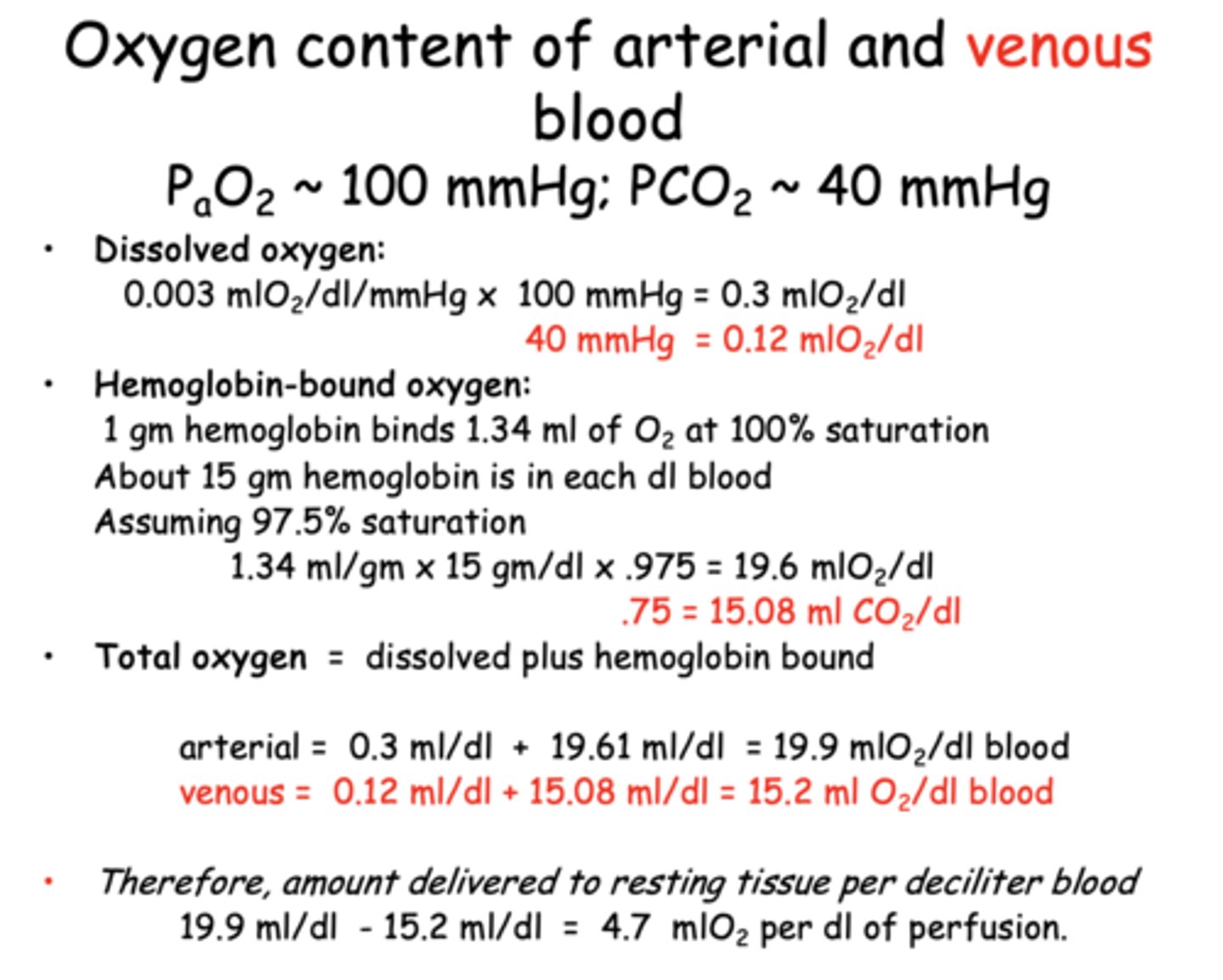
Approximately how much oxygen is bound to hemoglobin in venous blood?
15.08 mL O₂/dL
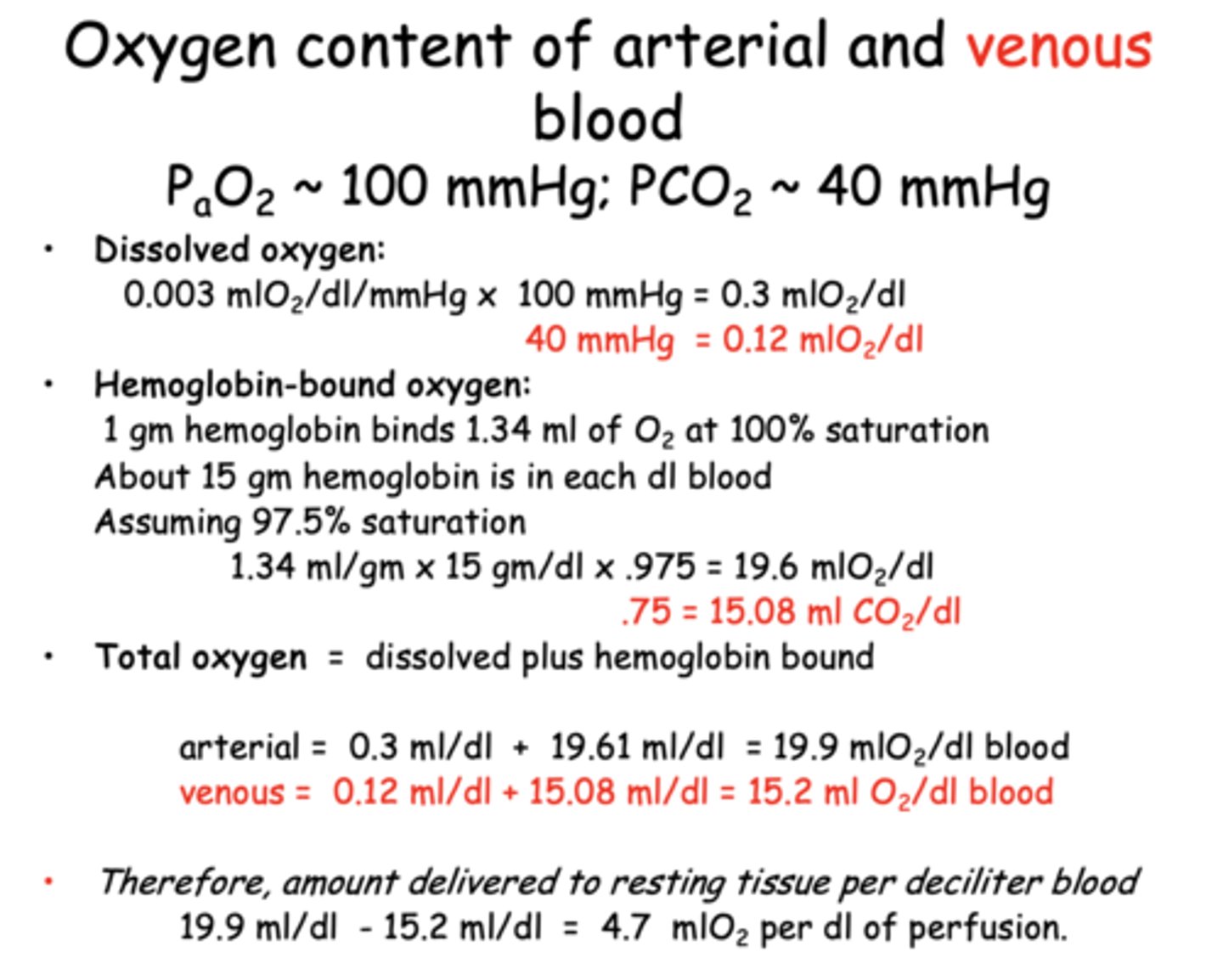
What is the total oxygen content of arterial blood per deciliter?
19.9 mL O₂/dL
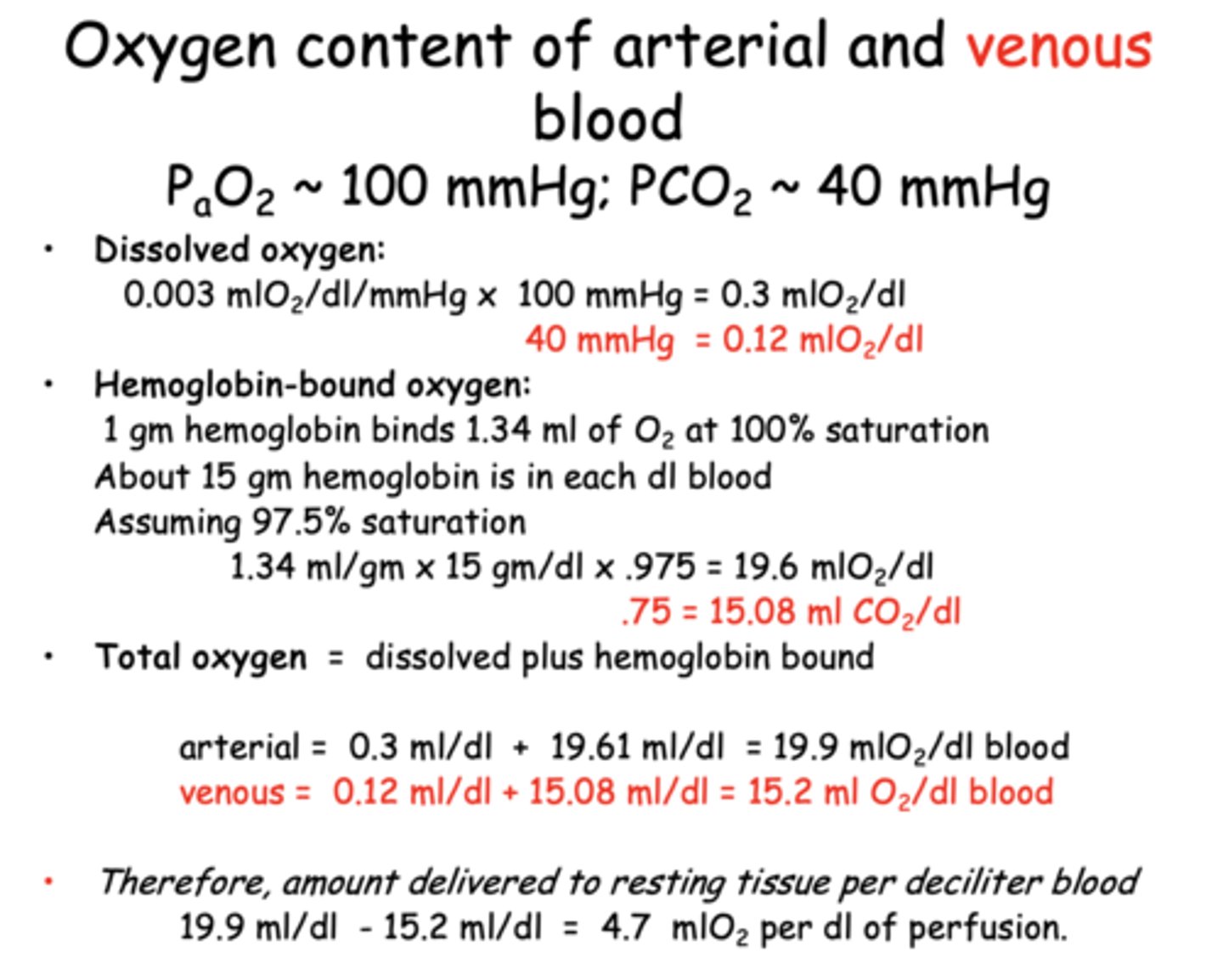
What is the total oxygen content of venous blood per deciliter?
15.2 mL O₂/dL
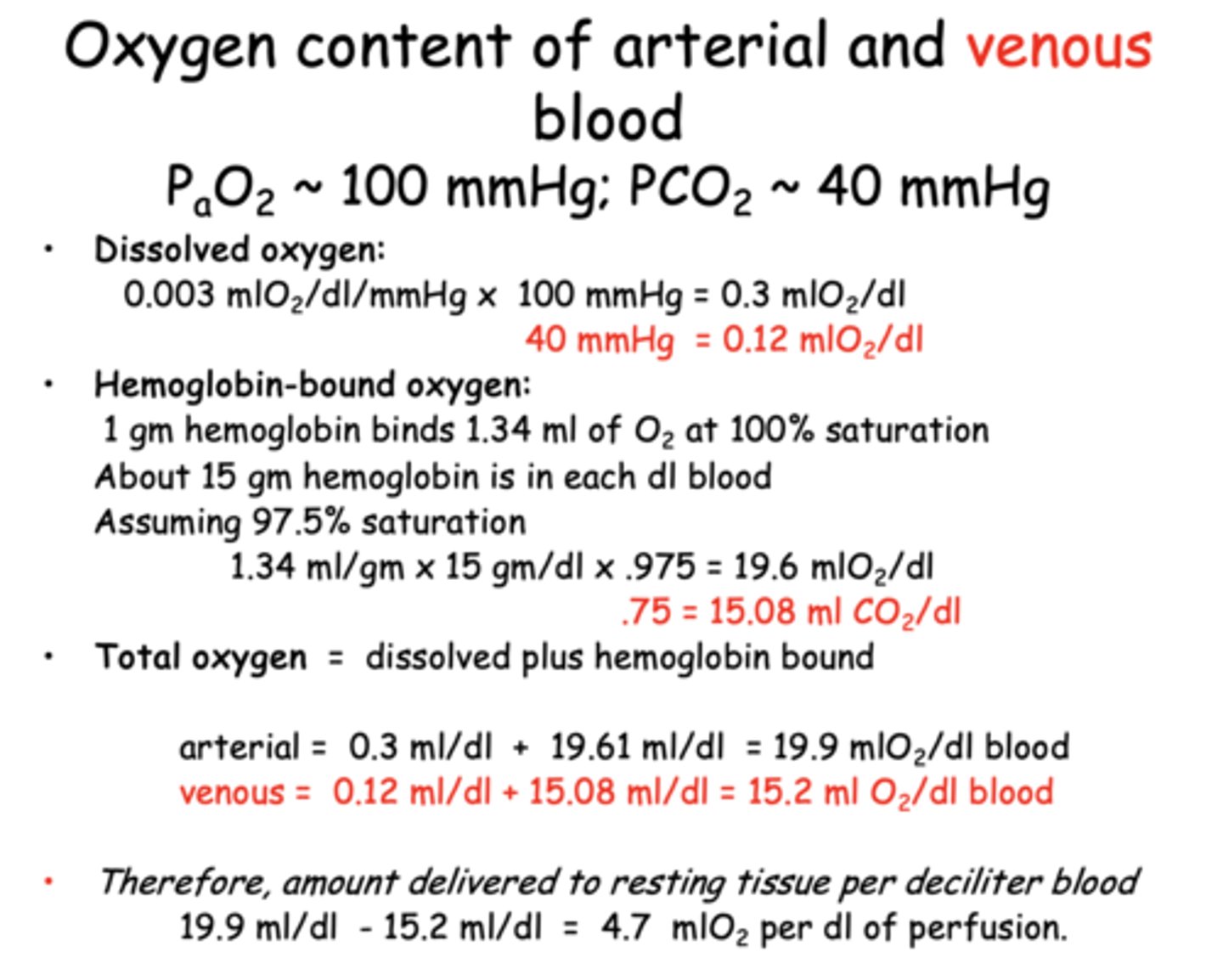
What is the oxygen delivery to resting tissue per deciliter of blood perfused?
4.7 mL O₂/dL
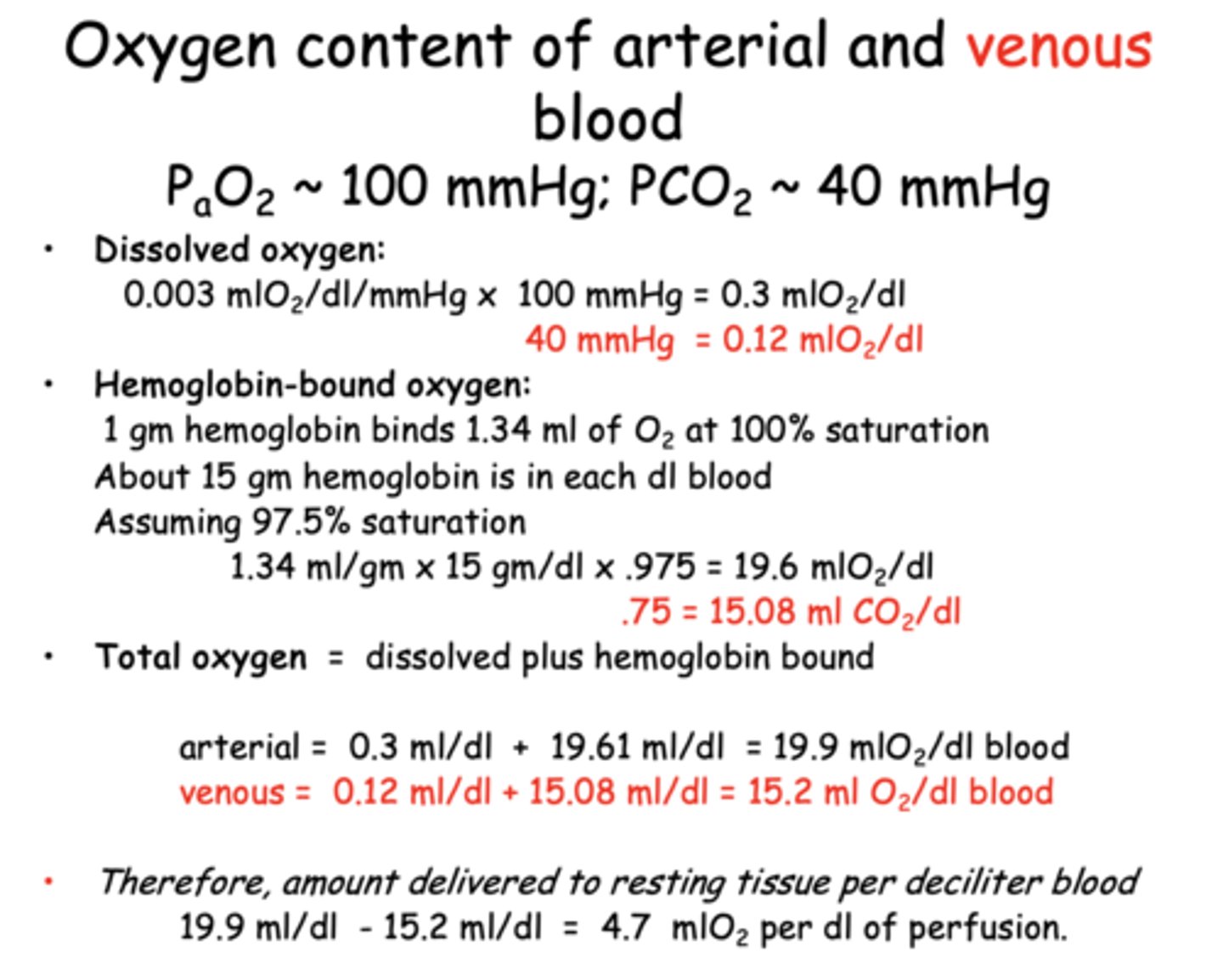
The _______________ is critical because it maintains the PO2 necessary to keep the Hb saturated, and because only free O2 can diffuse across cell membranes.
dissolved O2
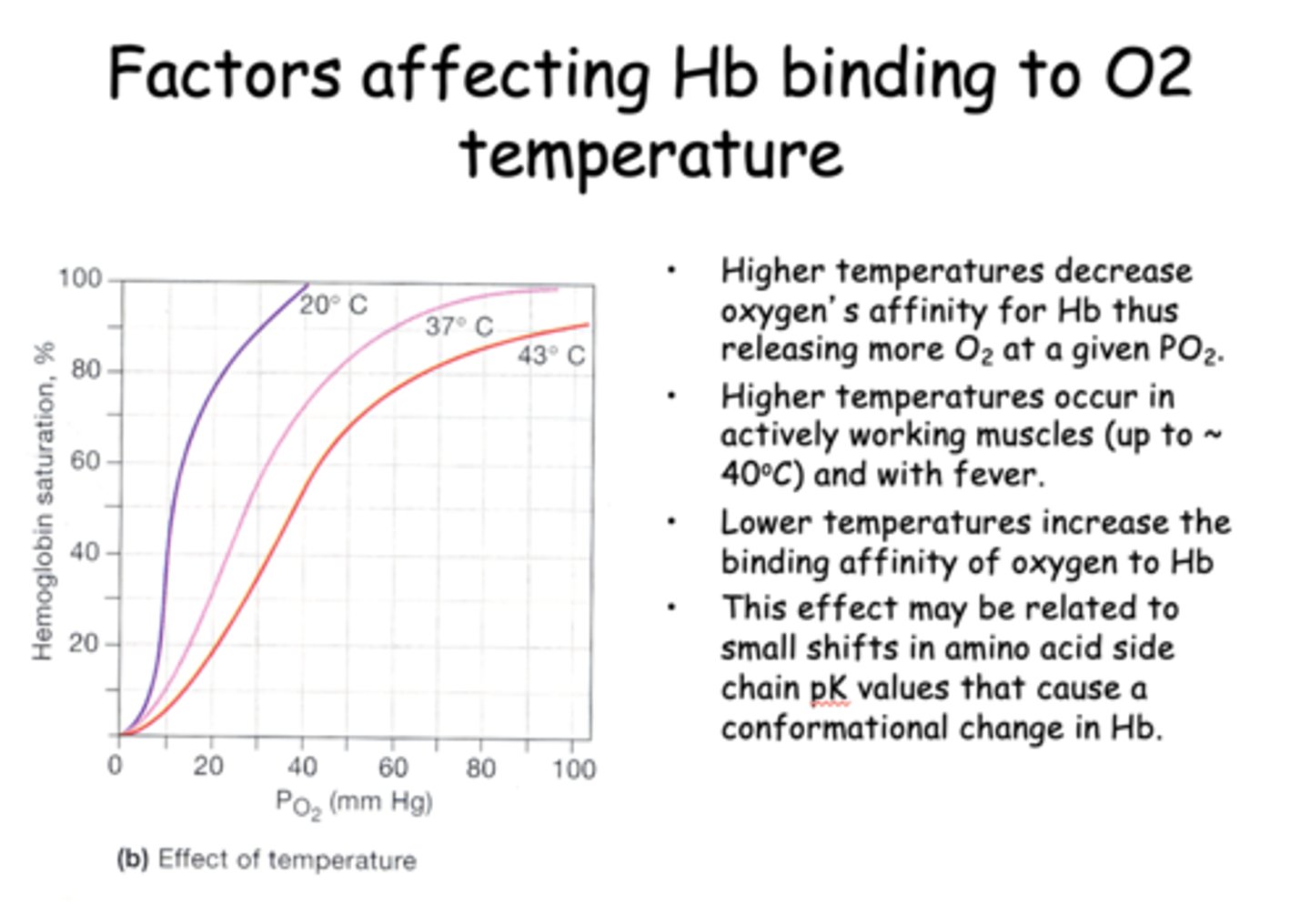
Higher temperatures ____________ oxygen's affinity for Hb thus releasing more O2 at a given PO2.
decrease
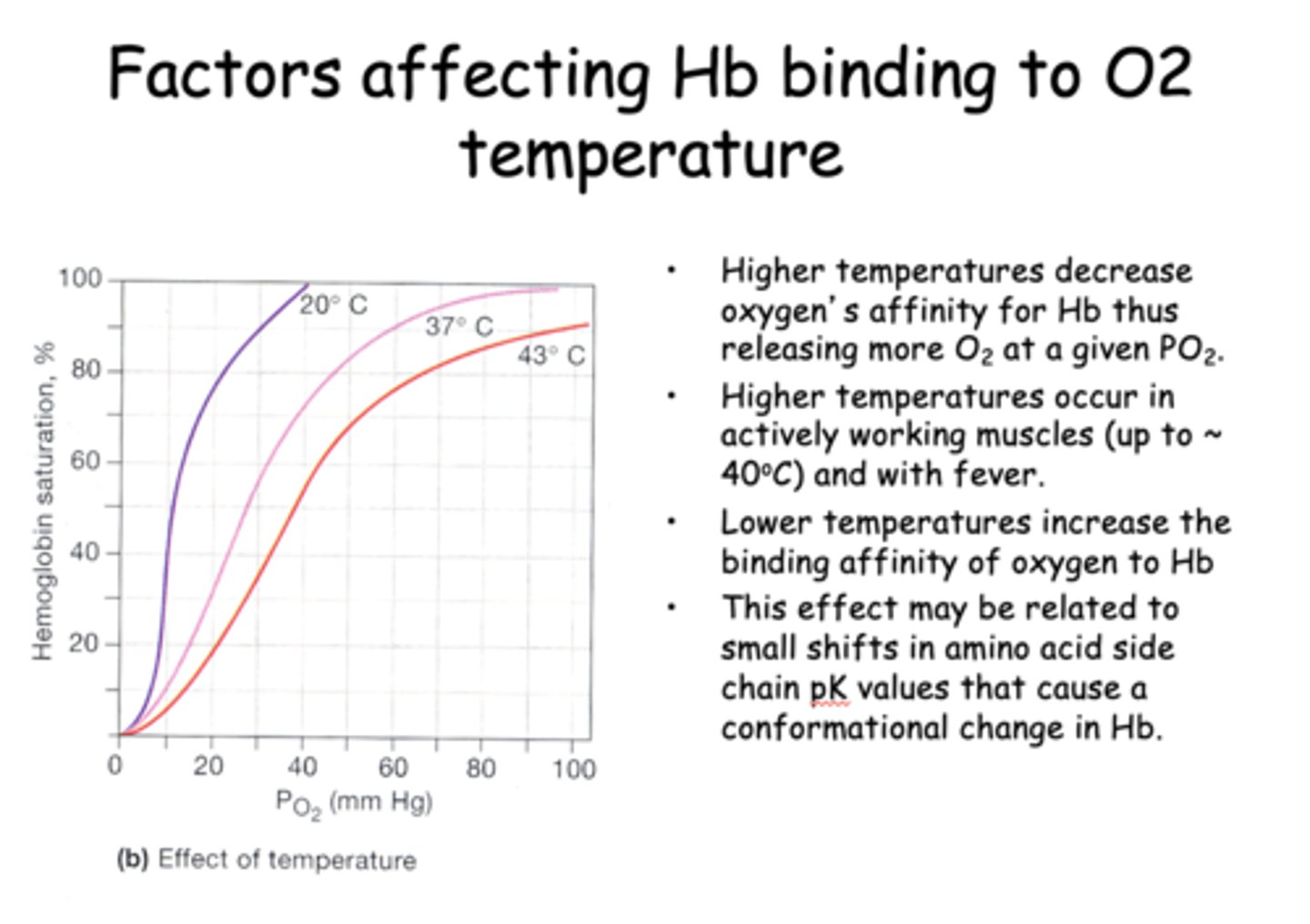
____________ temperatures increase the binding affinity of oxygen to Hb
Lower
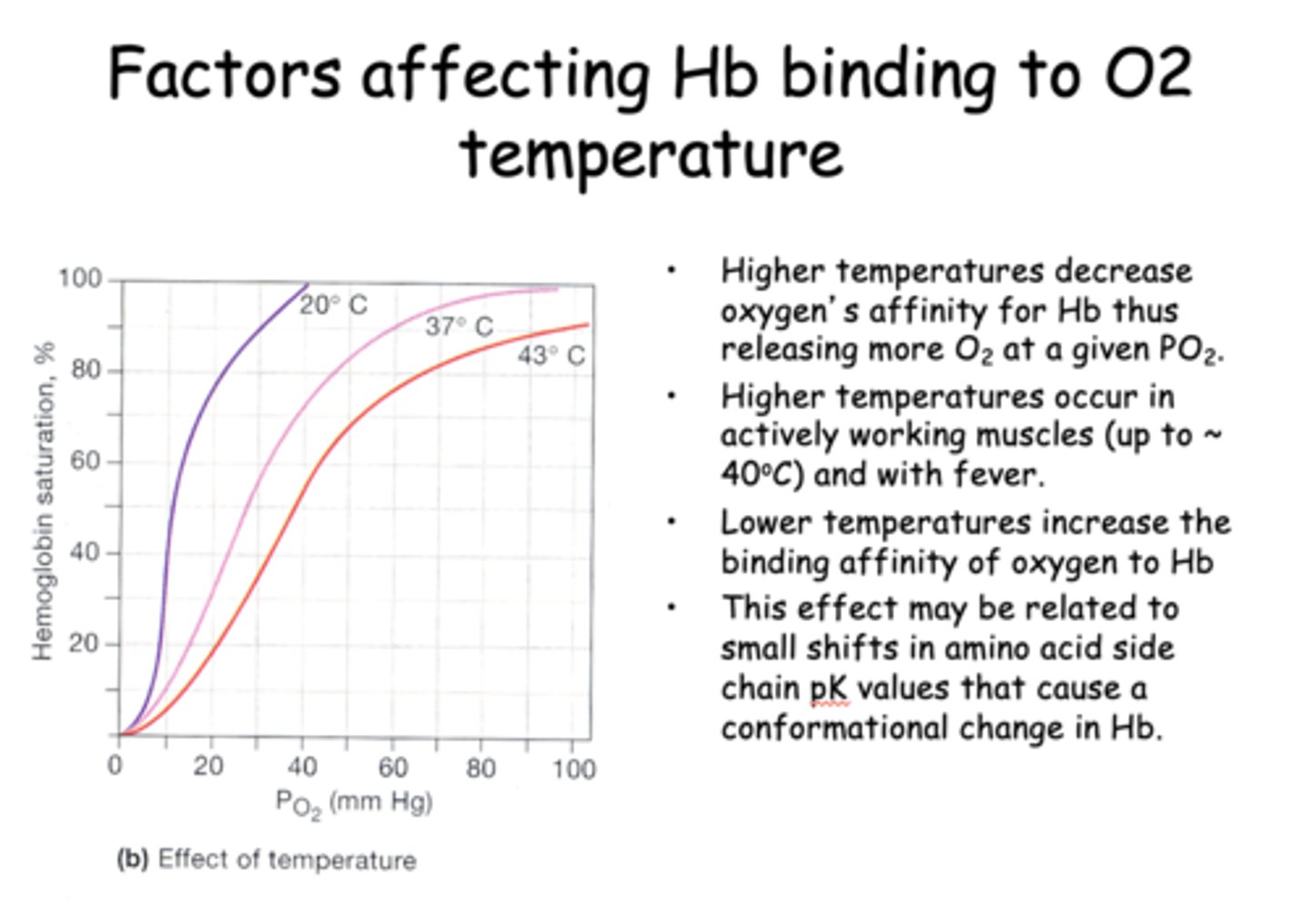
_____________ affect may be related to small shifts in amino acid side chain pK values that cause a conformational change in Hb.
Temperatures
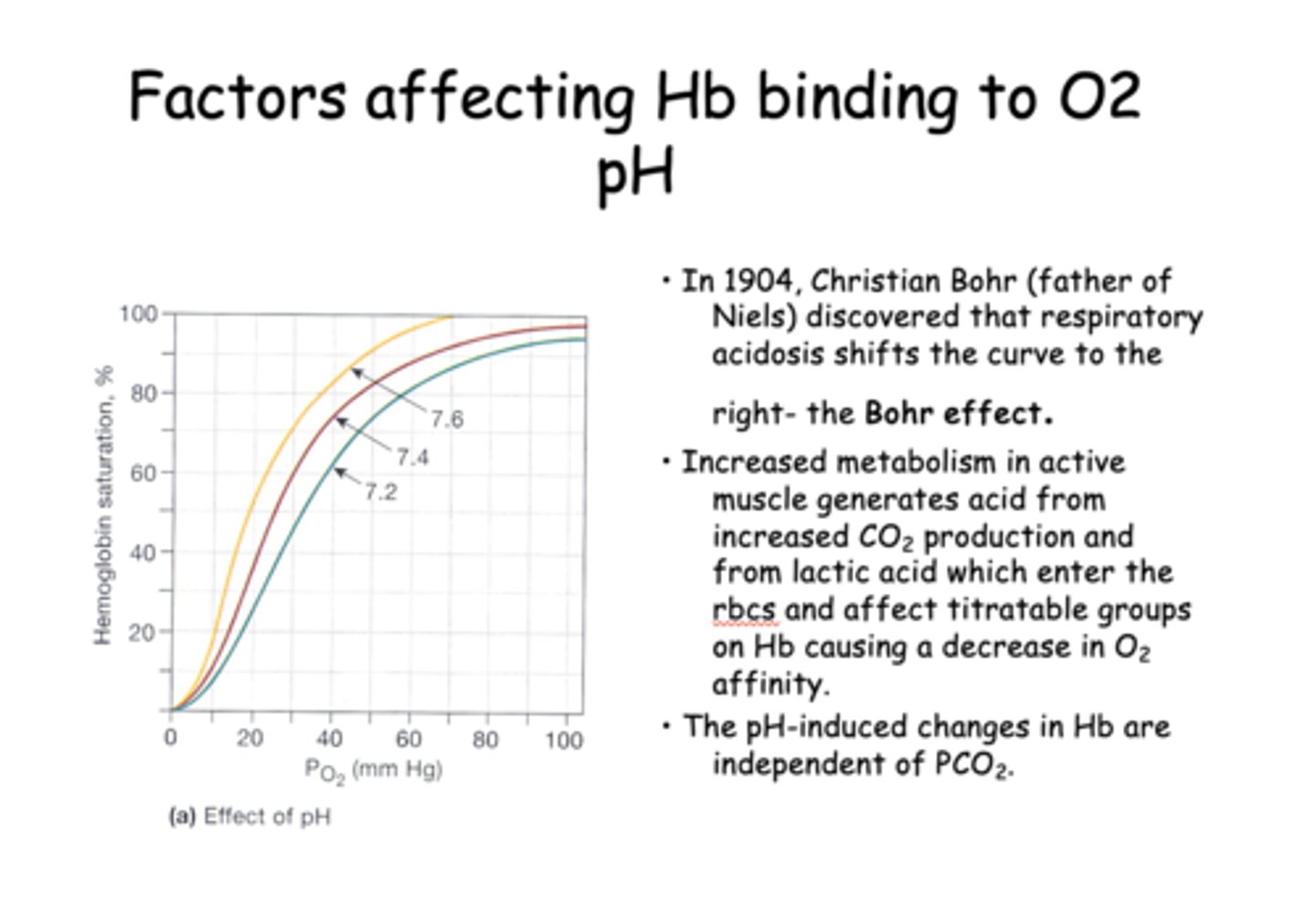
The respiratory acidosis shifts the curve to the right, which as known as the...
Bohr effect
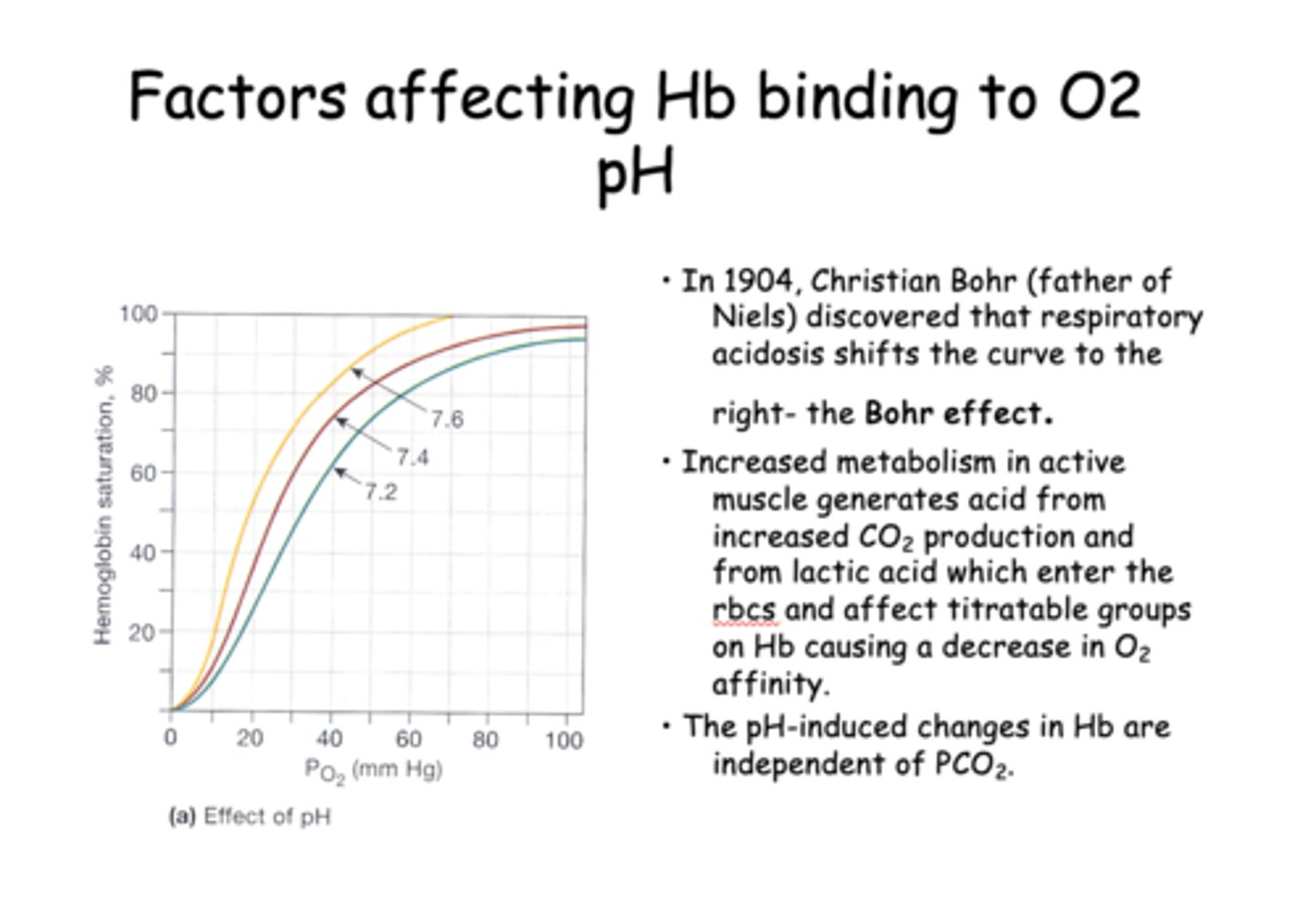
____________ metabolism in active muscle generates acid from increased CO2 production and from lactic acid which enter the rbcs and affect titratable groups on Hb causing a decrease in O2 affinity.
Increased
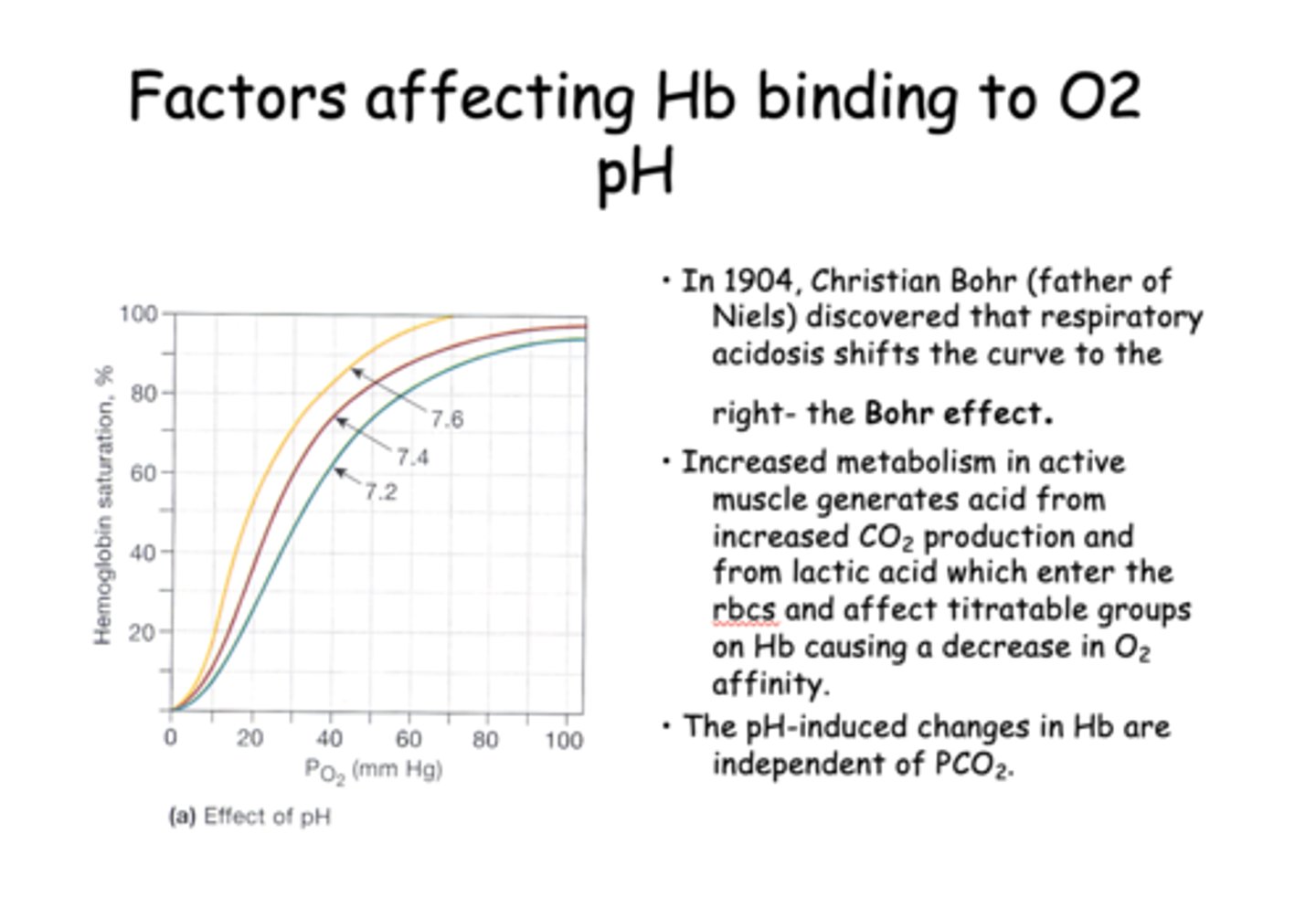
T/F: The pH-induced changes in Hb are independent of PCO2
True
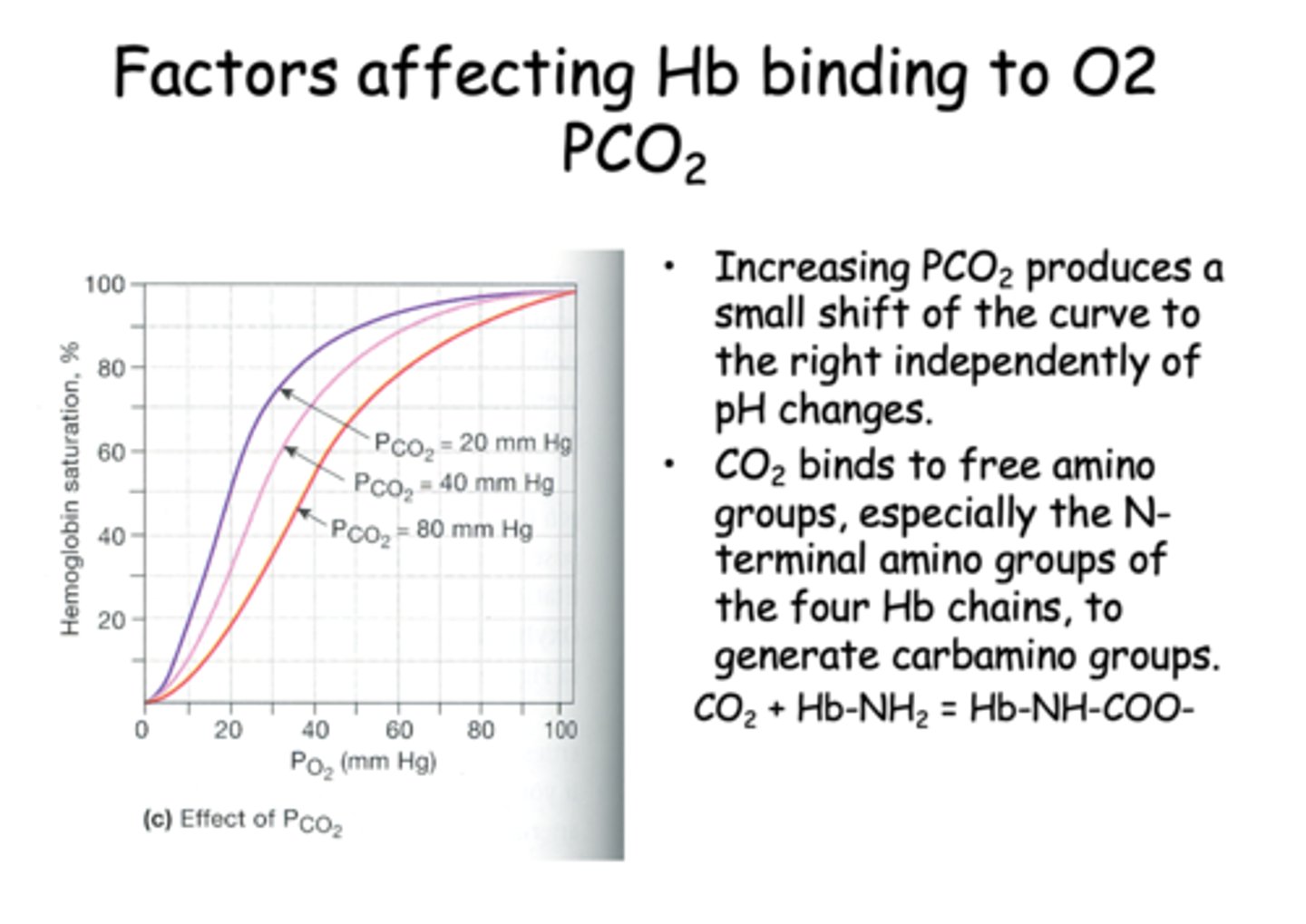
Increasing PCO2 produces a small shift of the curve to the ________ independently of pH changes.
right
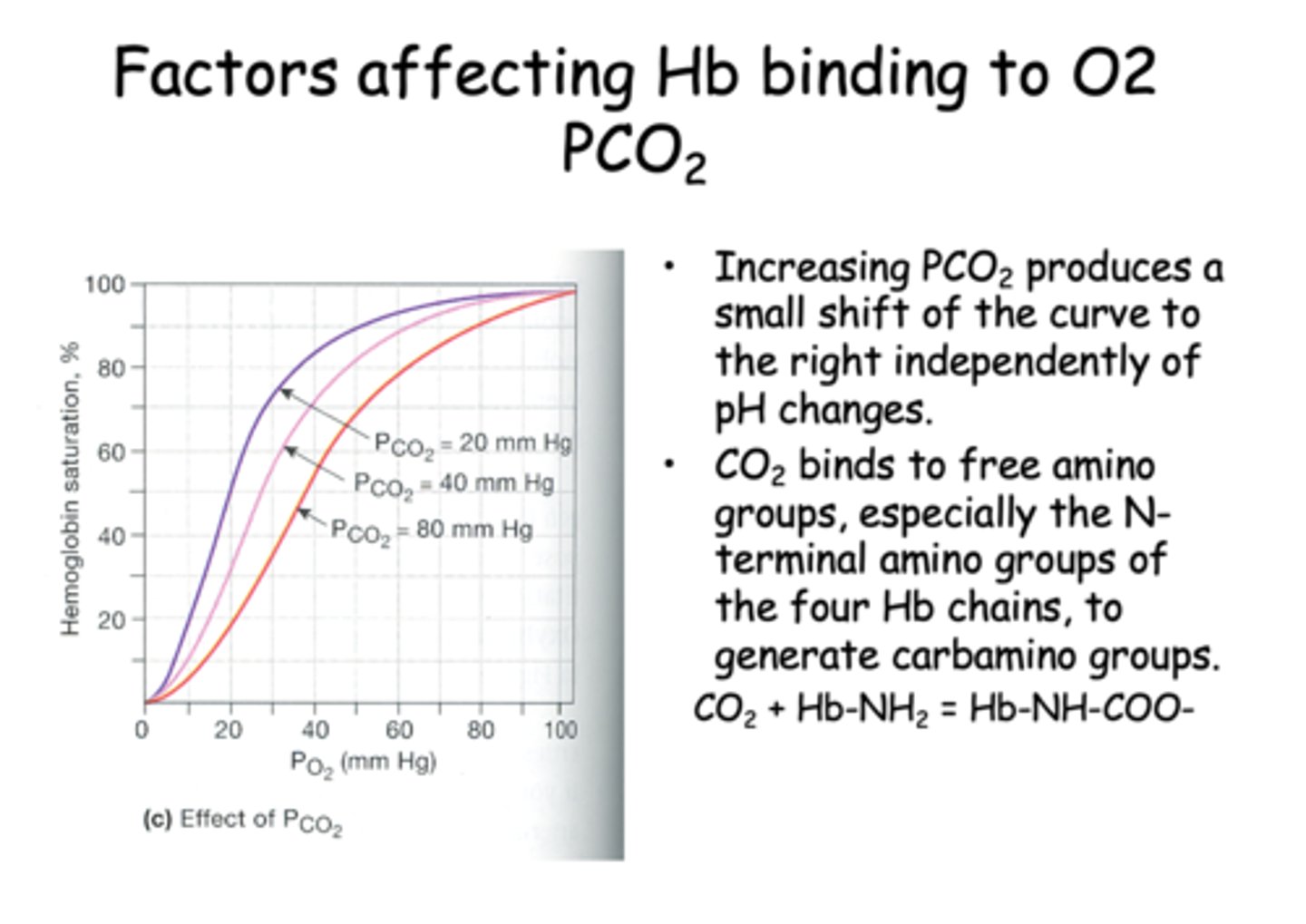
___________ binds to free amino groups, especially the N-terminal amino groups of the four Hb chains, to generate carbamino groups.
CO2
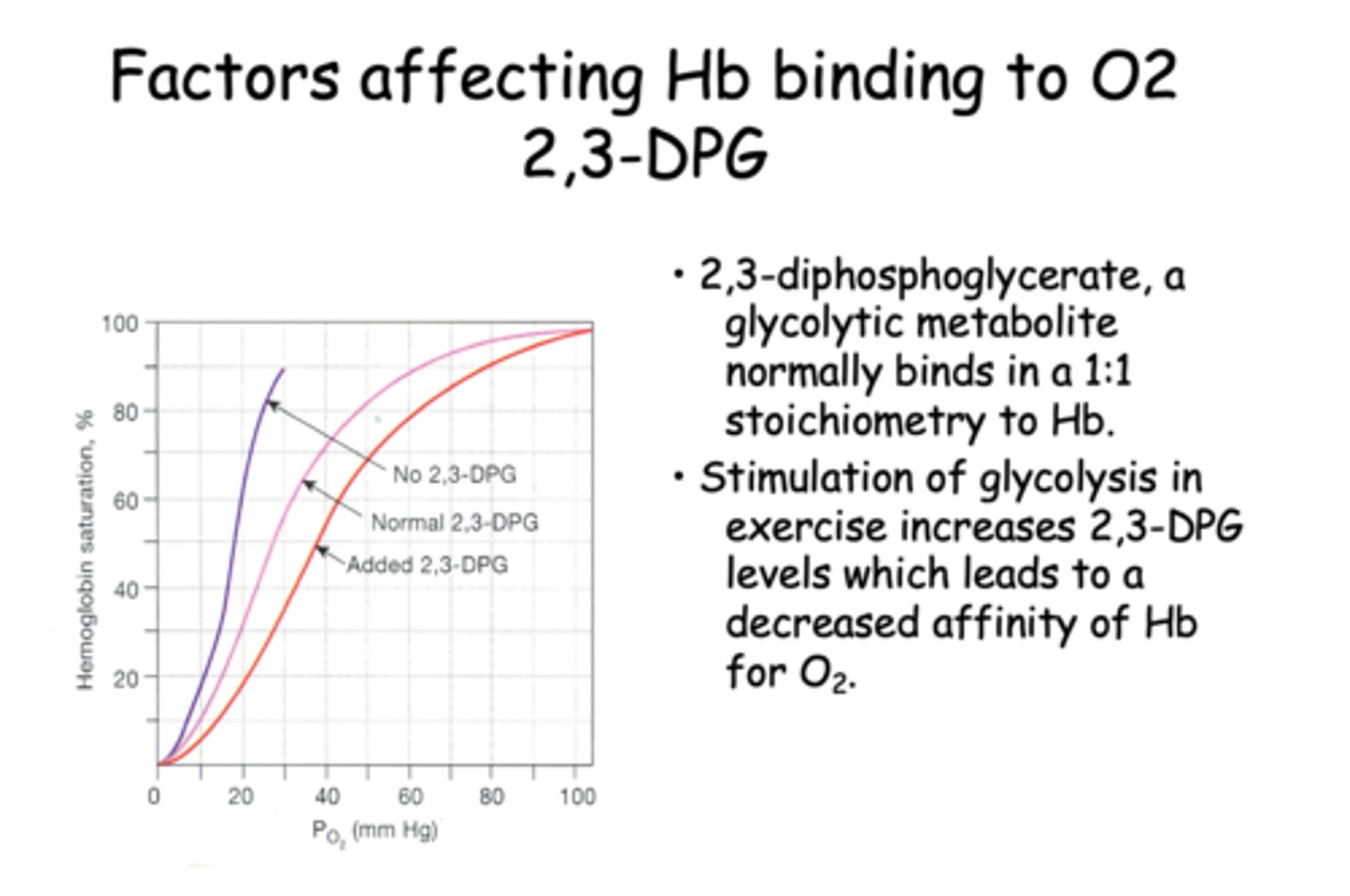
Stimulation of glycolysis in exercise increases 2,3-DPG levels which leads to a ____________ affinity of Hb for O2.
decreased
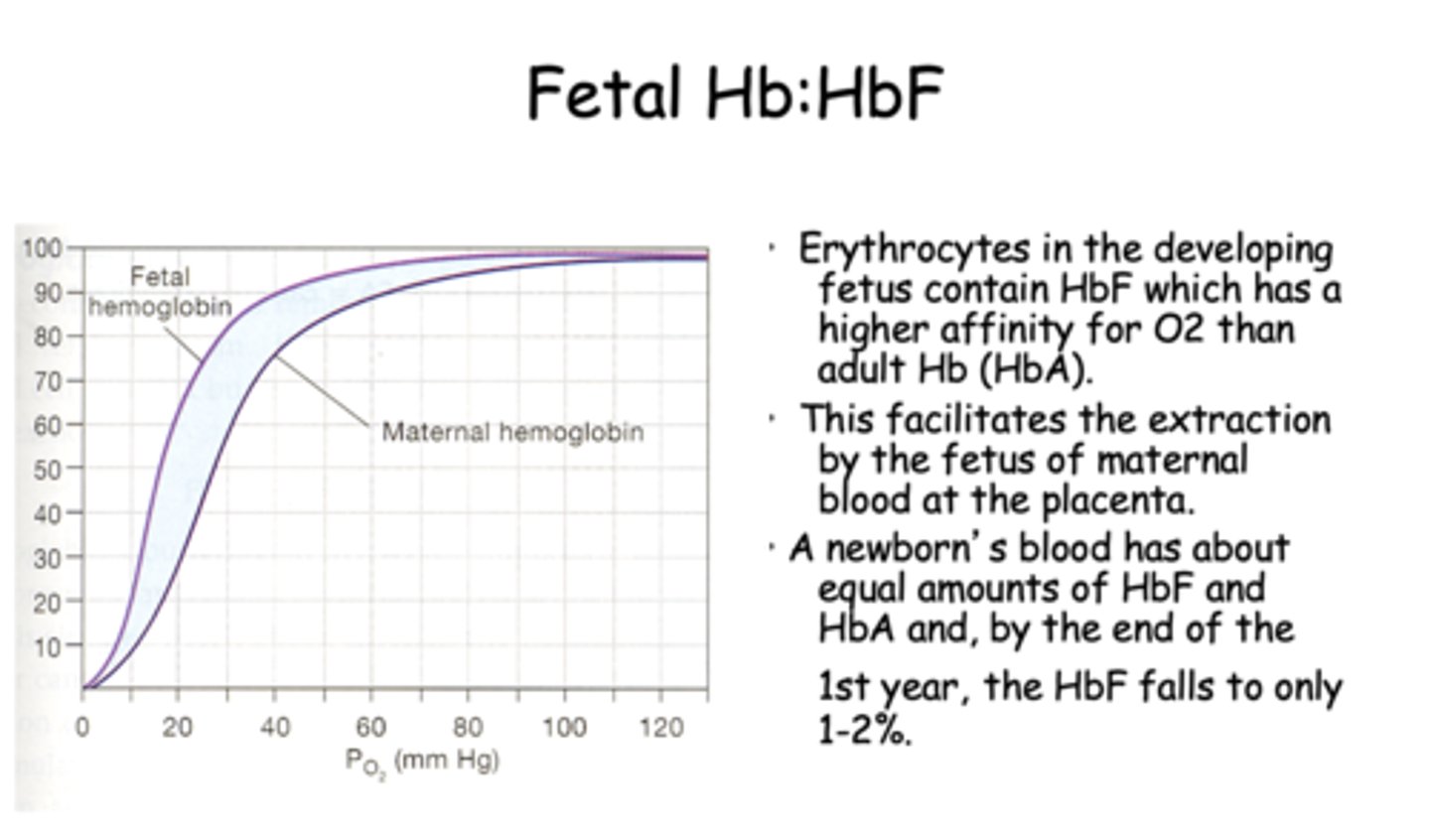
Erythrocytes in the developing fetus contain HbF which has a _________ affinity for O2 than adult Hb (HbA).
higher
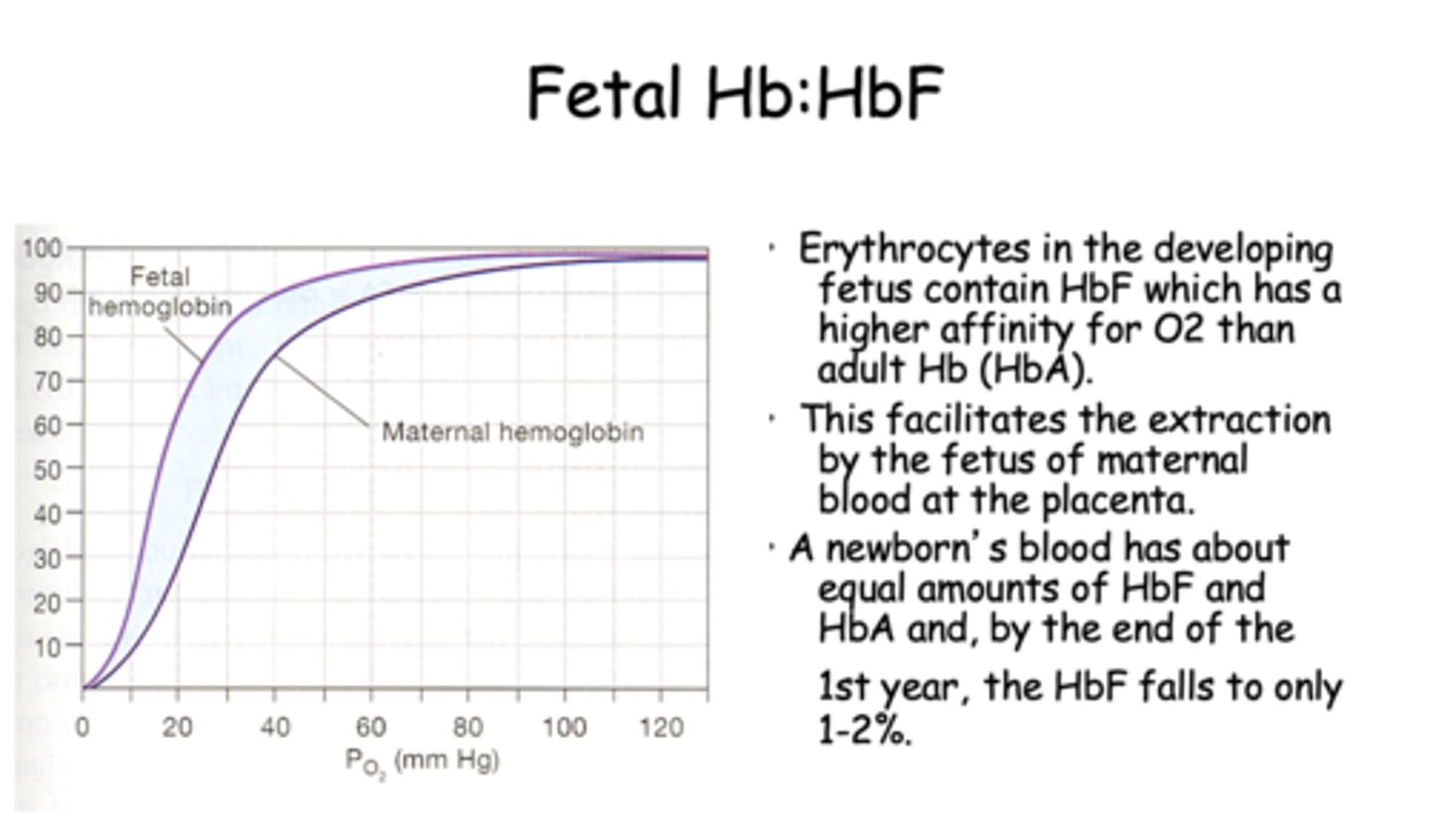
Erythrocytes in the developing fetus contain HbF which has a higher affinity for O2 than adult Hb (HbA). This facilitates the extraction by the fetus of maternal blood at the ____________.
placenta
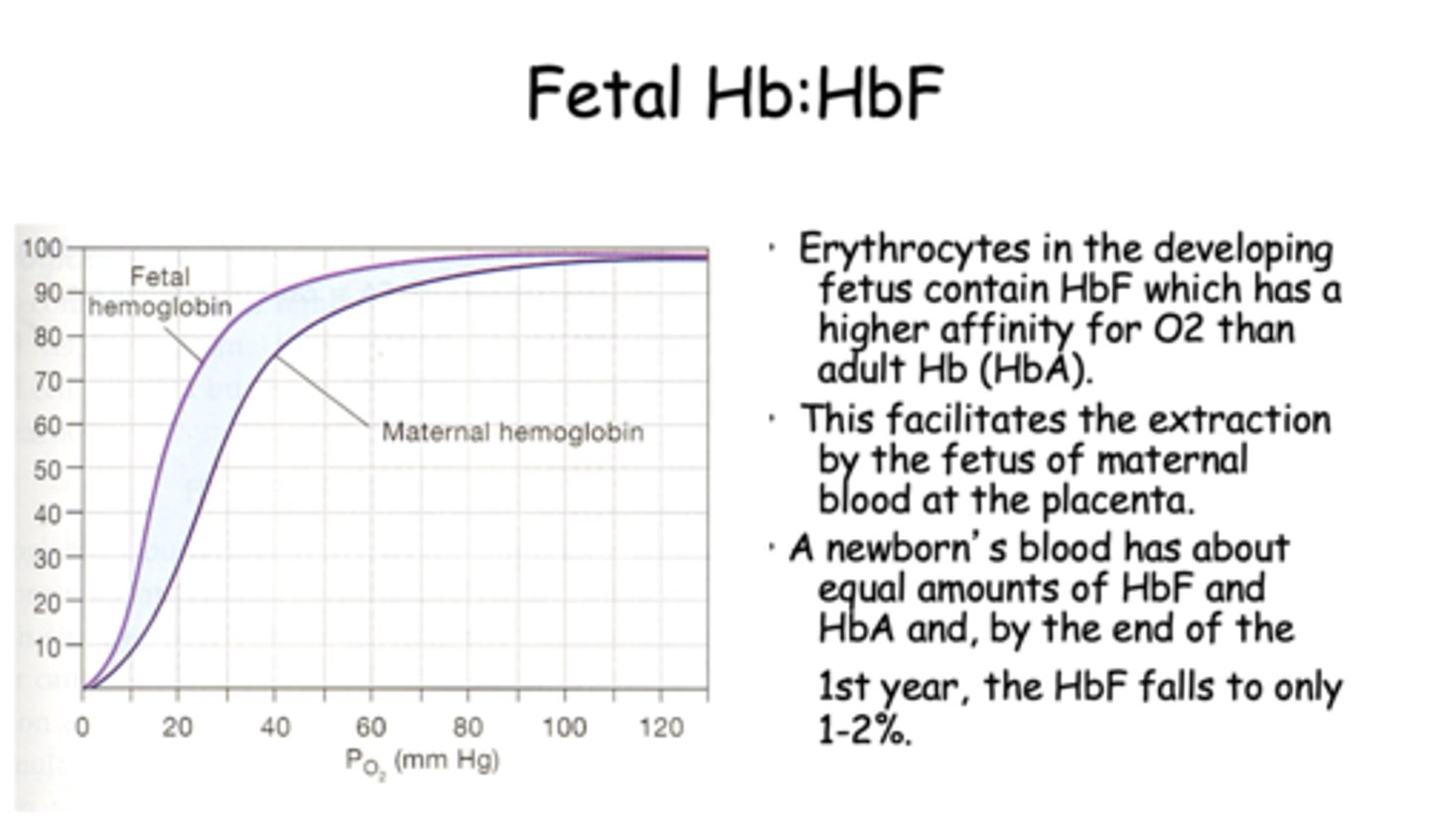
T/F: A newborn's blood has about equal amounts of HbF and HbA and, by the end of the 1st year, the HbF falls to only 1-2%.
True
Normal Hb can have its ferrous ion (Fe++) oxidized into a ____________ ion by various drugs or chemicals (e.g. nitrites, sulfonamides).
Ferric (Fe+++)

Normal Hb can have its ferrous ion (Fe++) oxidized into a ferric (Fe+++) ion by various drugs or chemicals (e.g. nitrites, sulfonamides). The resulting molecule is ______________ which cannot bind O2.
Methemoglobin (Met-Hb)

What are three forms of CO2 transport in the blood?
- Dissolved CO2
- Bicarbonate
- Carbamino compounds
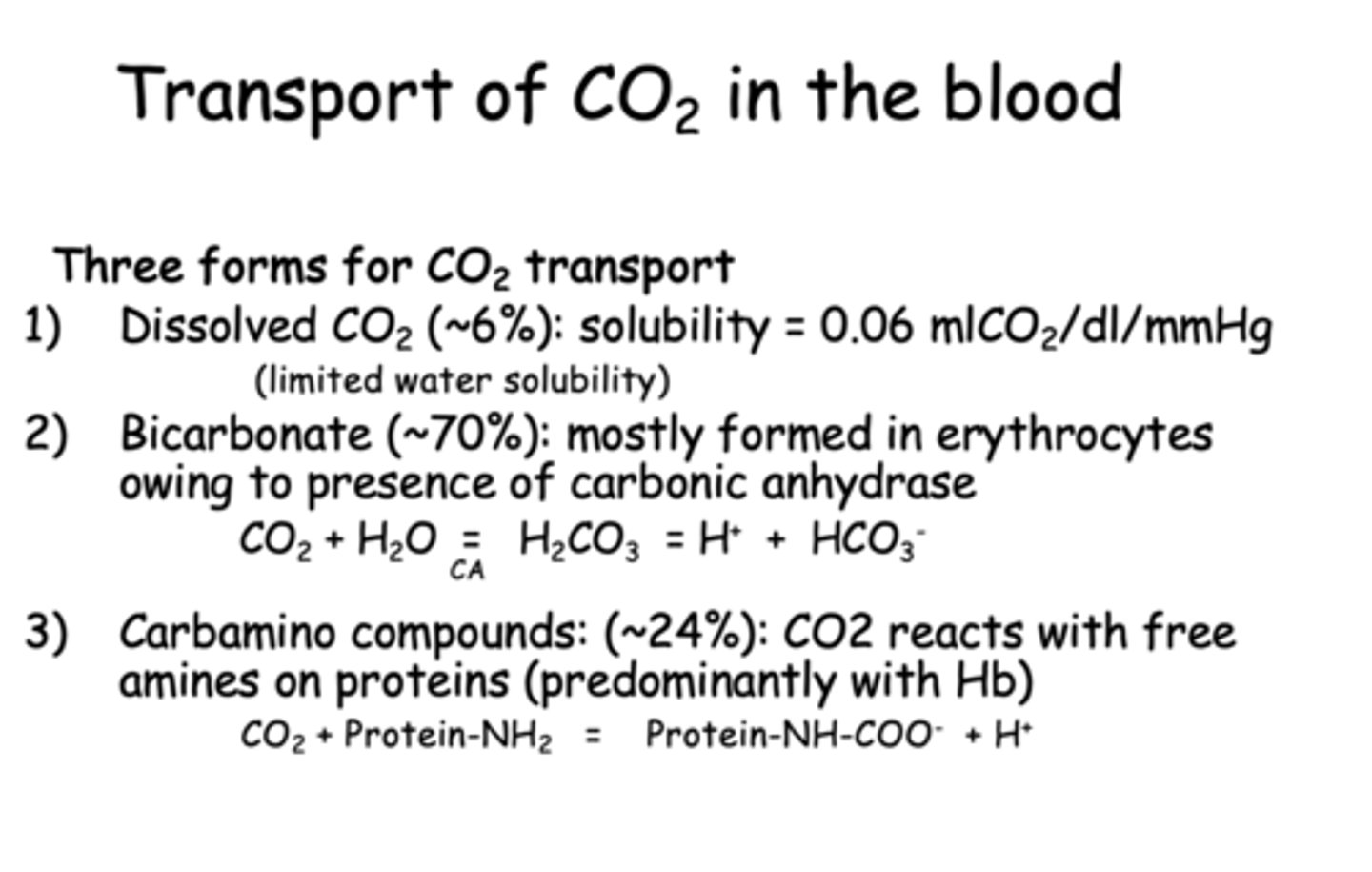
__________ is mostly formed in erythrocytes owing to presence of carbonic anhydrase
Bicarbonate
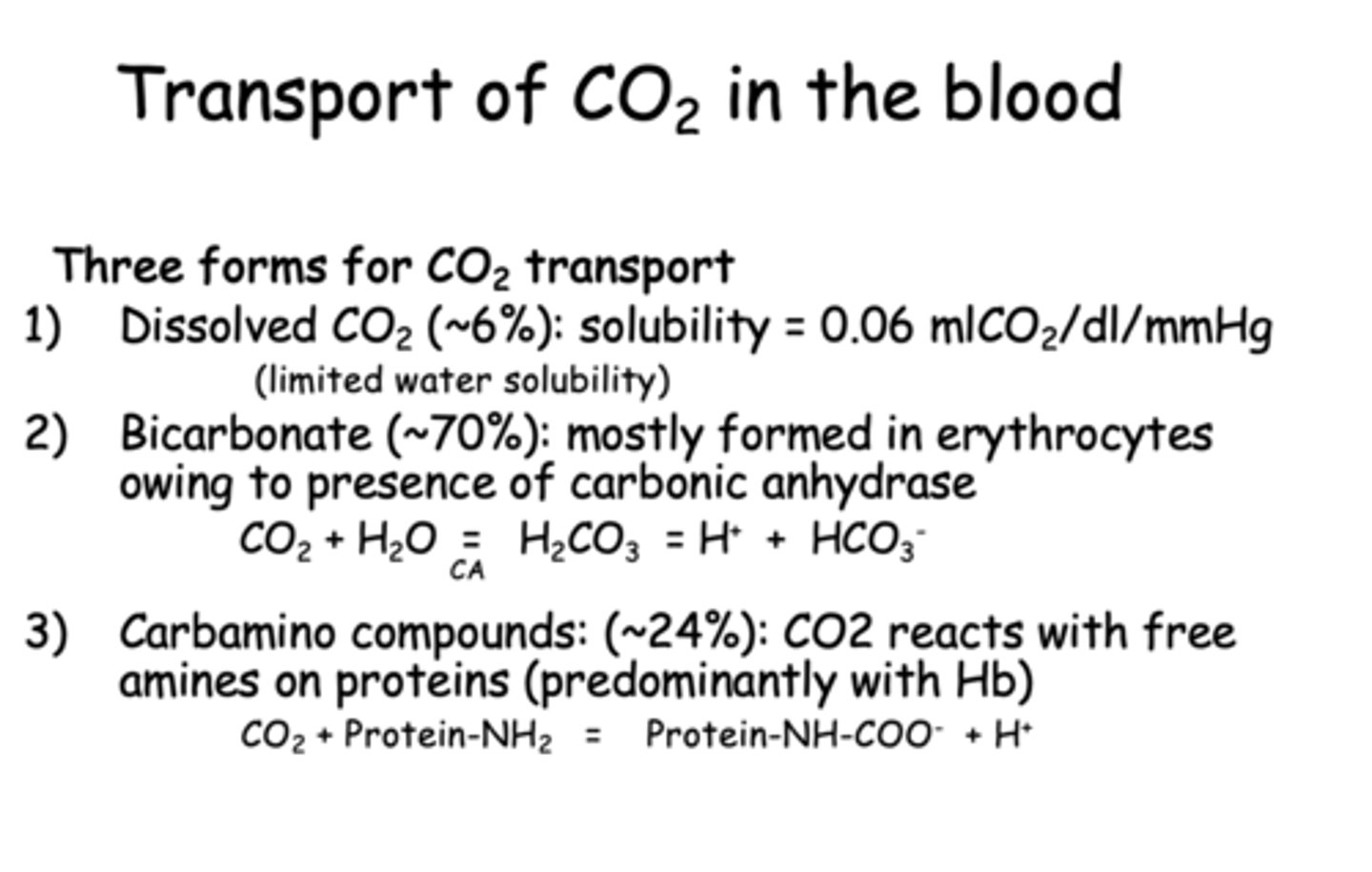
___________ can bind O2, CO2, and is a great buffer
Hemoglobin
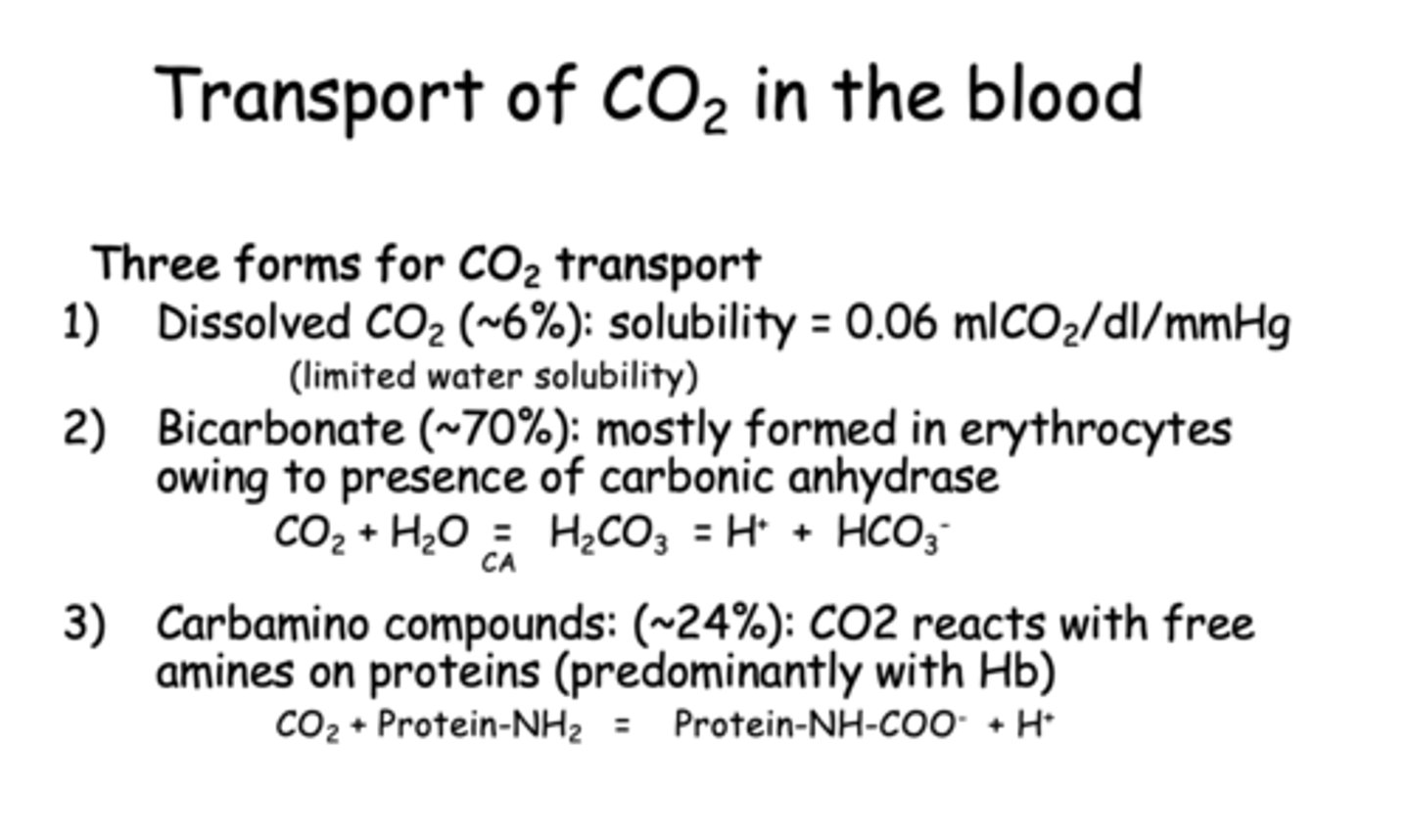
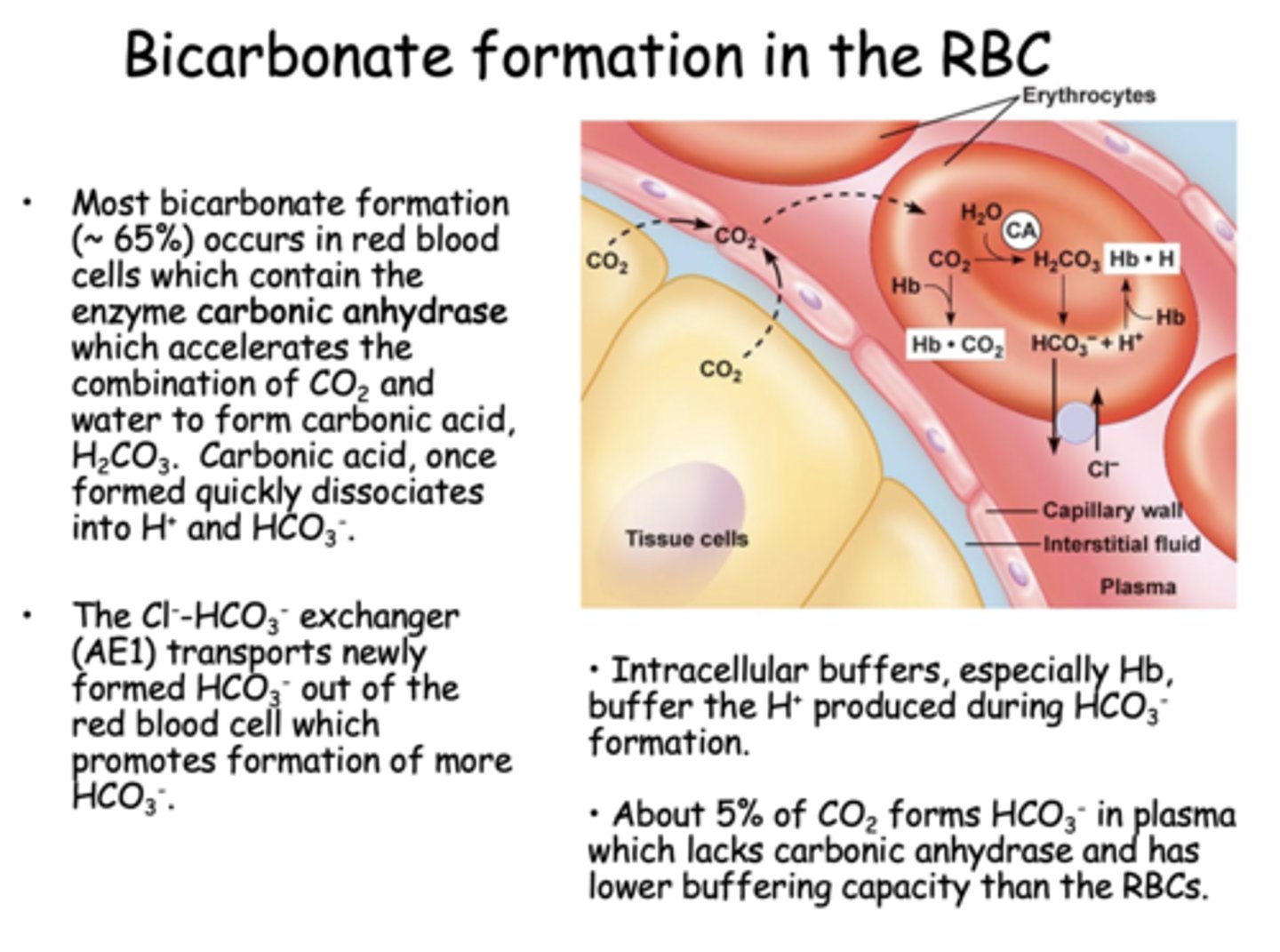
Where is most bicarbonate formed?
RBCs
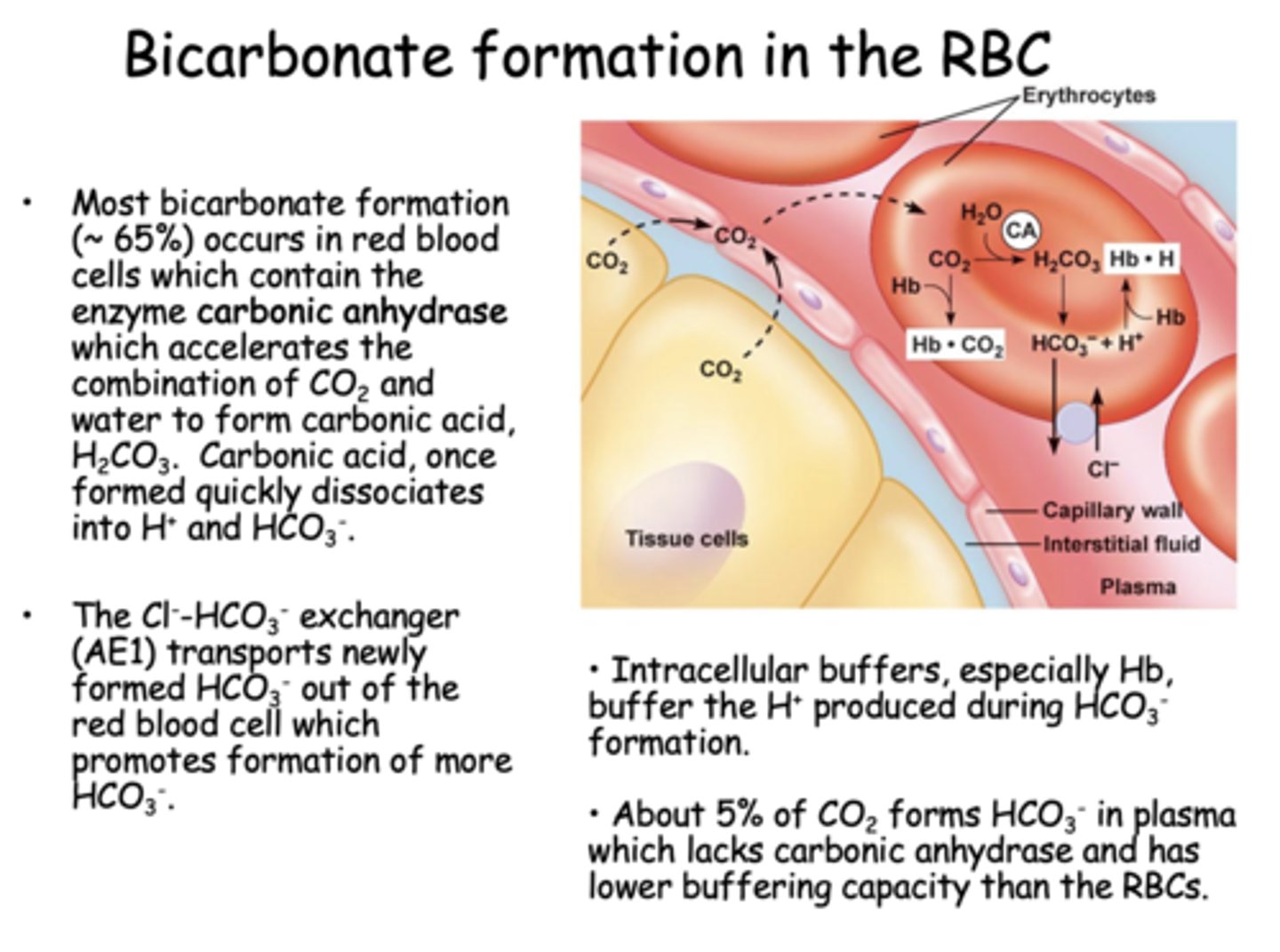
Most bicarbonate formation (~ 65%) occurs in red blood cells which contain the enzyme ____________ which accelerates the combination of CO2 and water to form carbonic acid, H2CO3.
carbonic anhydrase
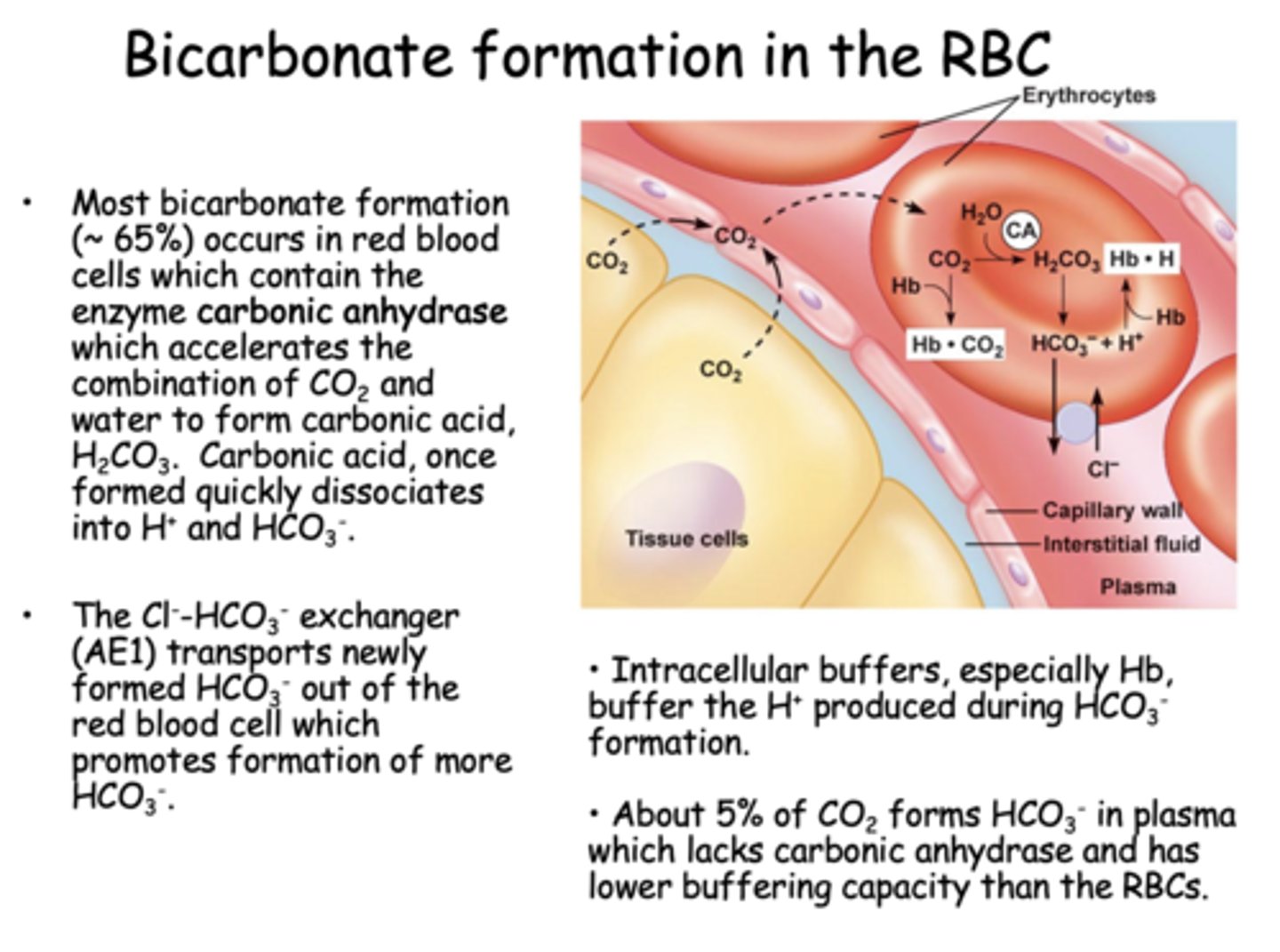
The Cl--HCO3- exchanger (AE1) transports newly formed HCO3- out of the red blood cell which promotes formation of more ________
HCO3-
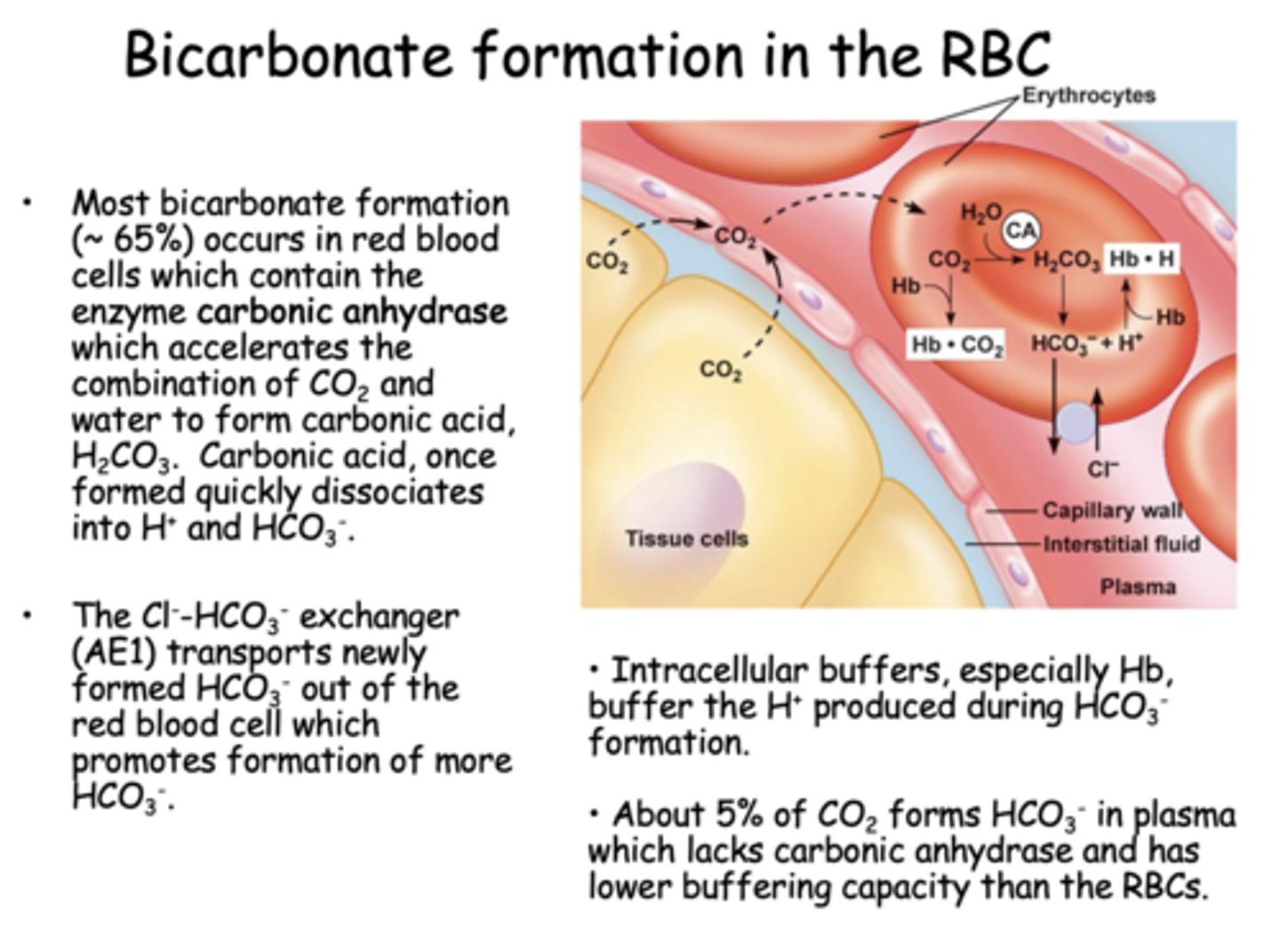
About ______% of CO2 forms HCO3- in plasma which lacks carbonic anhydrase and has lower buffering capacity than the RBCs
5%
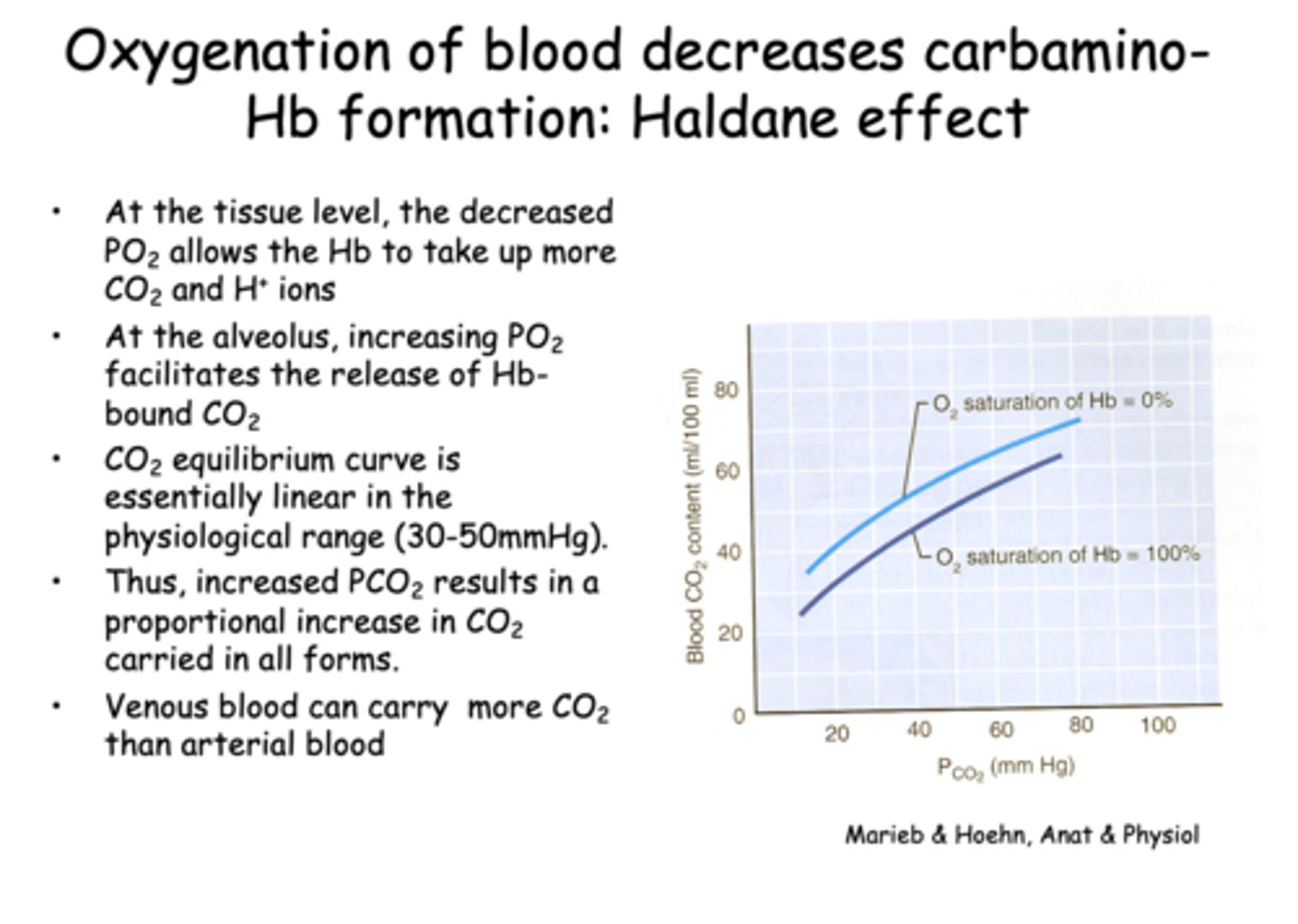
Oxygenation of blood decreases carbamino-Hb formation, known as the...
Haldane effect
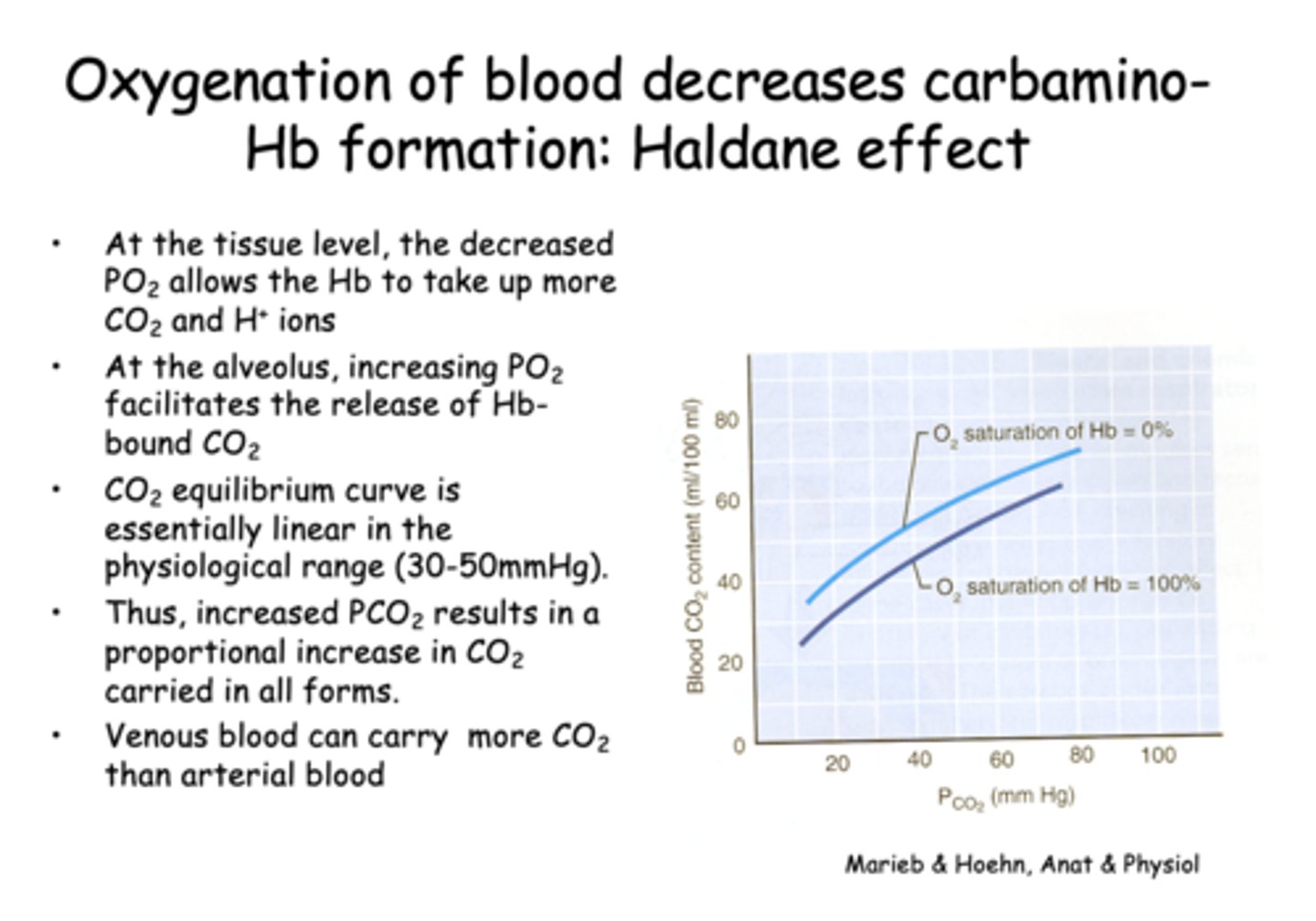
What does the Haldane effect describe?
The ability of deoxygenated hemoglobin to carry more CO2 and H⁺
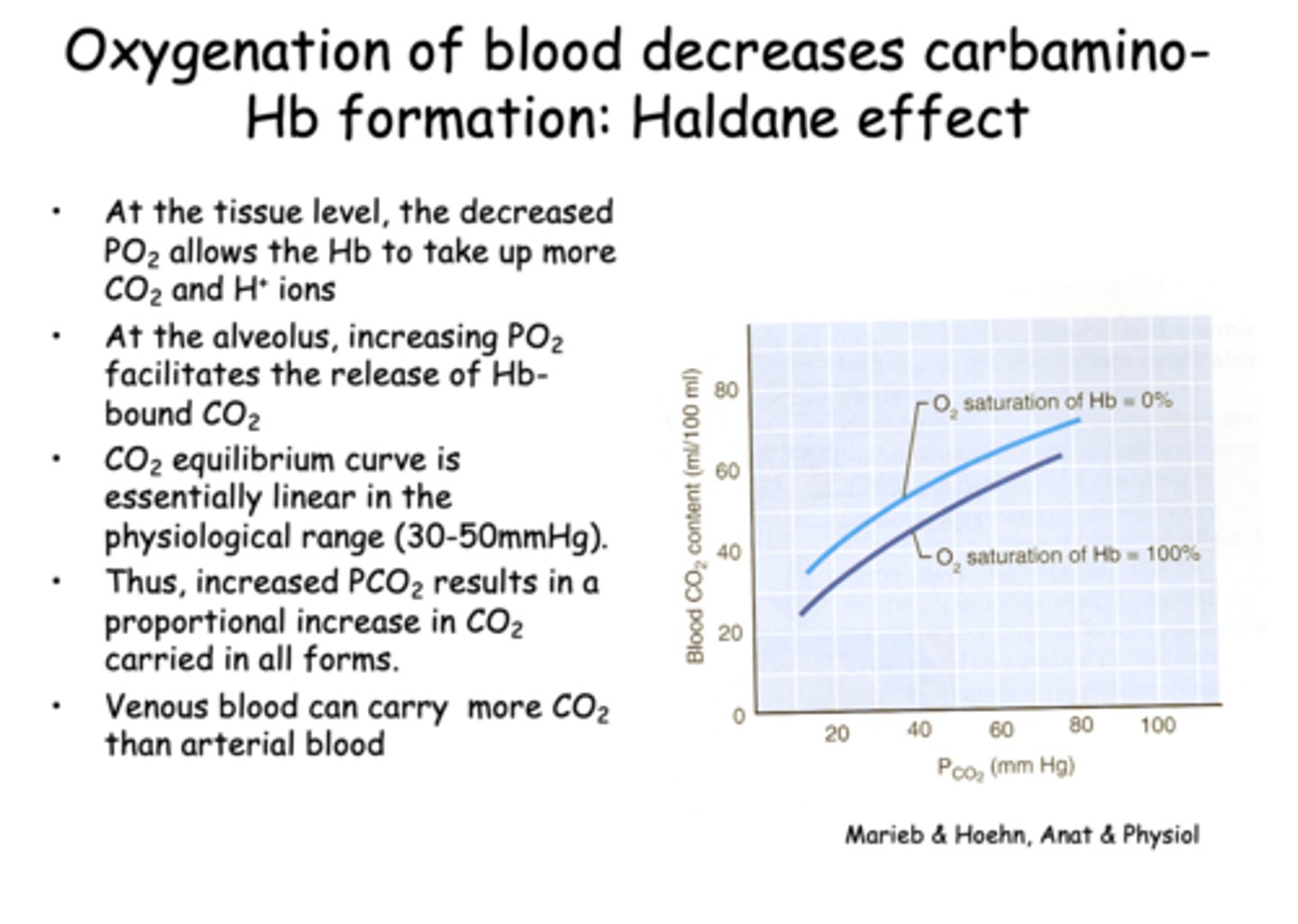
At the alveolar level, what happens as PO₂ increases?
releases more CO2
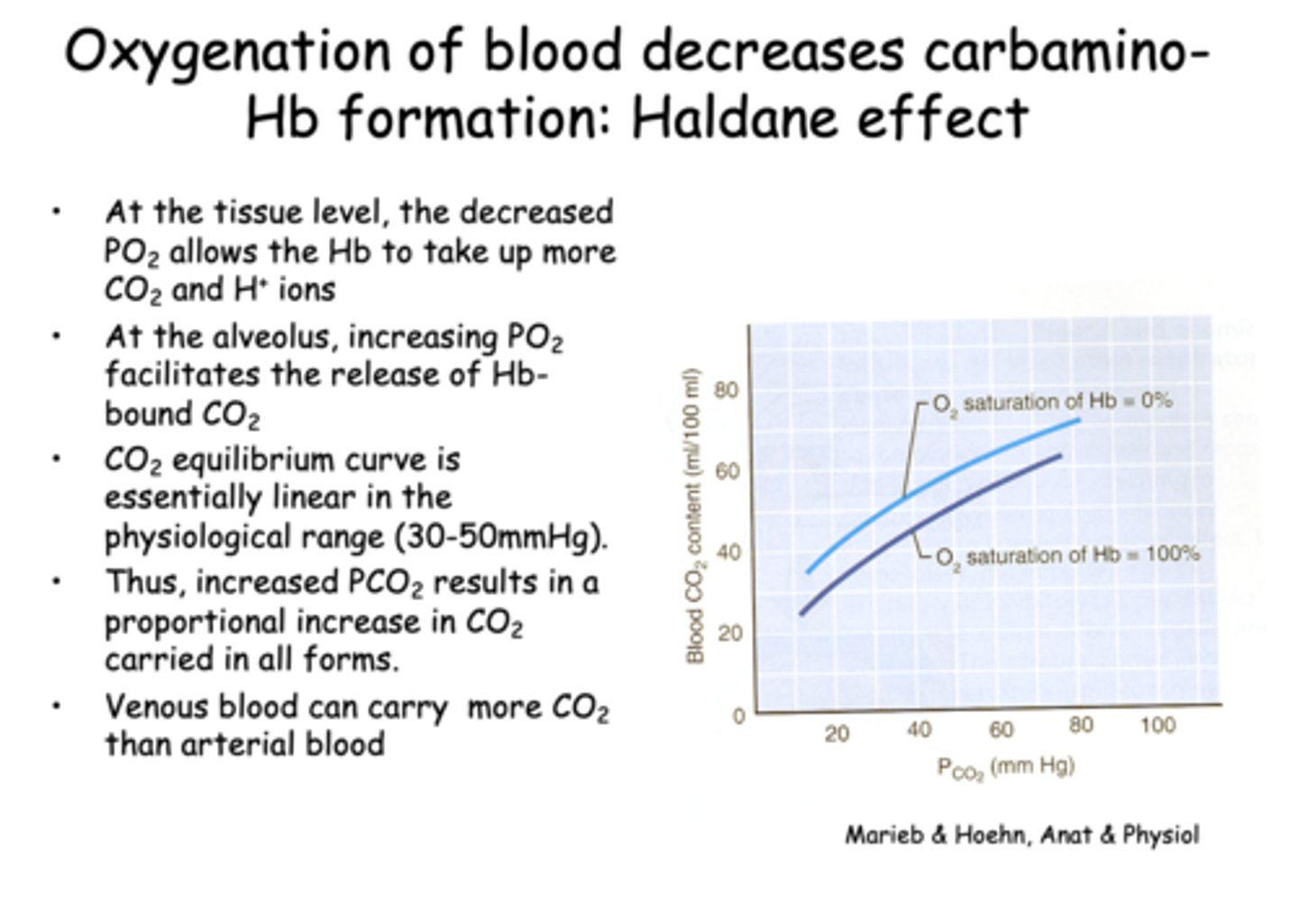
Which of the following best explains why venous blood can carry more CO2 than arterial blood?
Deoxygenated hemoglobin binds CO2 more readily
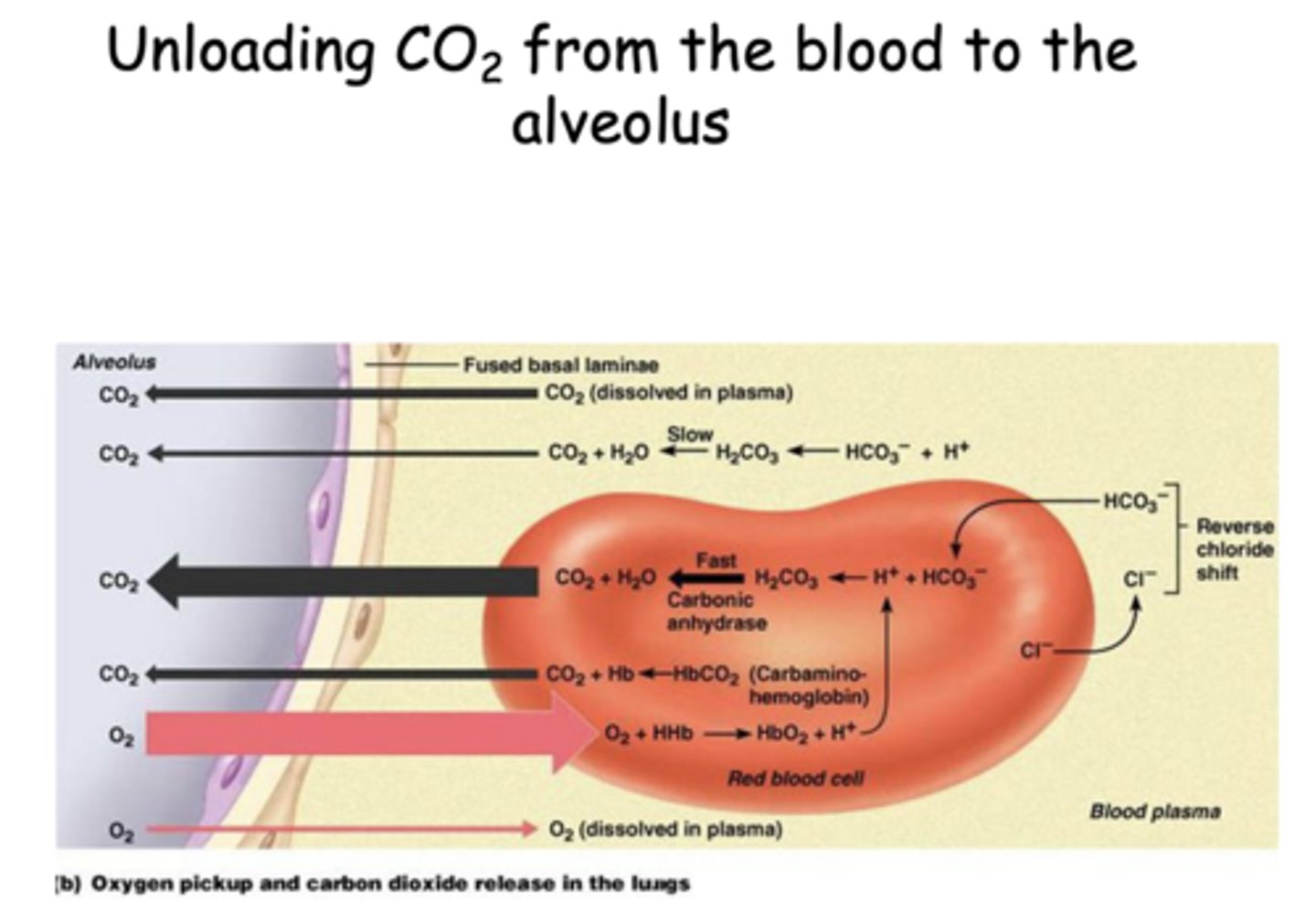
Which enzyme accelerates the conversion of H2CO3 into CO2 and H2O in red blood cells?
Carbonic anhydrase
t/f: At high altitude, when lower PO2atm reduces the alveolar-capillary partial pressure gradient, there might not be enough driving force to fully load the blood within the transit time.
true
In pulmonary diseases with increased thickening of the alveolar-capillary walls such as COPD & fibrosis, the diffusion coefficient _______ and the PO2 at the end of the capillary may be below the PAO2
decreases
what is the PO2 of inspired air?
160 mmHg
