Esters and acid chlorides and the hydrolysis of these compounds
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
How can esters be formed?
From reacting carboxylic acids with alcohols.
Water is also formed.
What reagents / conditions are used when reacting carboxylic acids with alcohols to form esters?
Concentrated sulfuric acid catalyst.
The reaction is heated under reflux.
How are esters named?
The name of an ester is derived from the names of the two reactants from which it formed.
The first part of the name always relates to the alcohol.
The second part of the name relates to the carboxylic acid.
Esters can be converted back to carboxylic acids and alcohols in what type of reaction?
Hydrolysis- water is added.
Describe what happens in the acid hydrolysis of esters.
Reagents: concentrated sulfuric acid catalyst
Conditions: heated under reflux
The original carboxylic acid and alcohol is formed.
Describe what happens in the alkaline hydrolysis of esters.
Reagents: NaOH
Conditions: heated under reflux
The salt of the carboxylic acid and alcohol is formed.
The salt would have to be reacted with a dilute acid to cause it to reprotonate to give the carboxylic acid.
How are acid chlorides formed?
By reacting carboxylic acids with PCl3, PCl5 or SOCl2.
Why are acid chlorides suspectible to nucleophilic attack?
Acid chlorides are highly reactive and susceptible to nucleophilic attack due to the carbonyl carbon being electron deficient (δ+) as it is bonded to the electronegative oxygen and chlorine atoms.
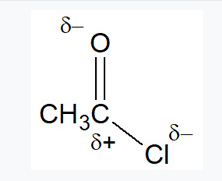
Acid chlorides react with water to form?
Carboxylic acids + HCl
Acid chlorides react with alcohols to form?
Esters + HCl.
Acid chlorides react with ammonia to form what?
Amides + HCl