B2.1 supplying the cell
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
define active transport
the movement of particles from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration, against the concentration gradient. this requires energy
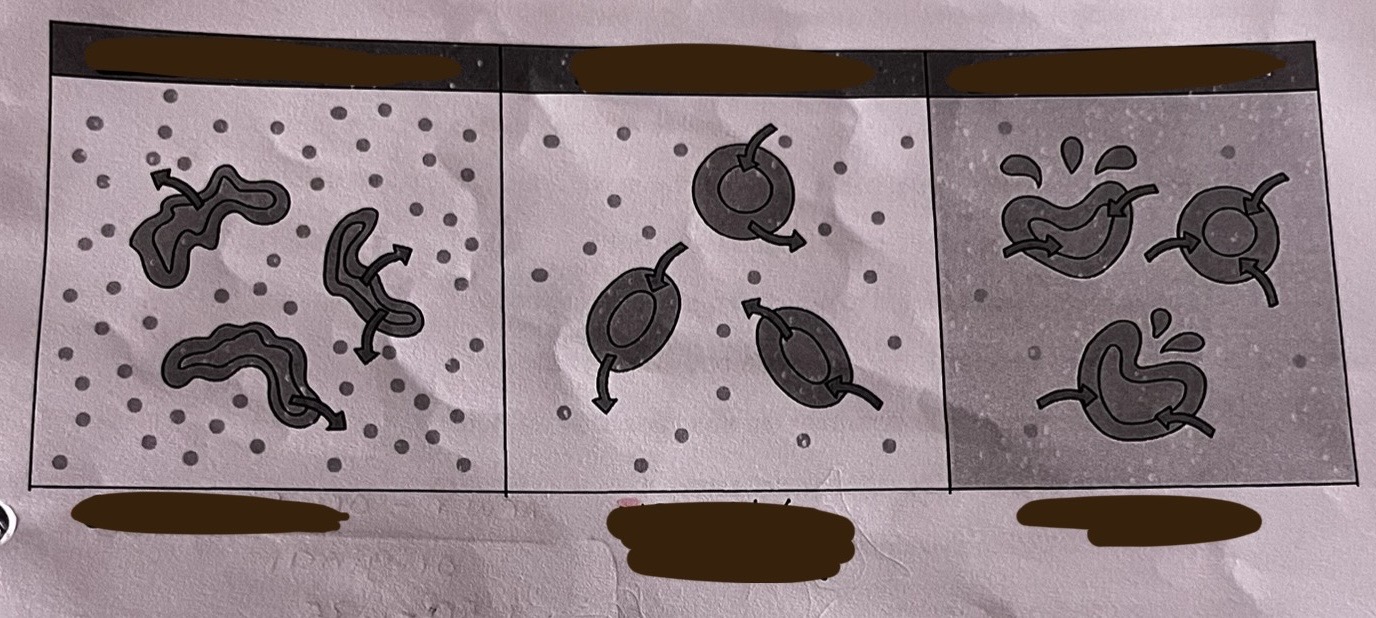
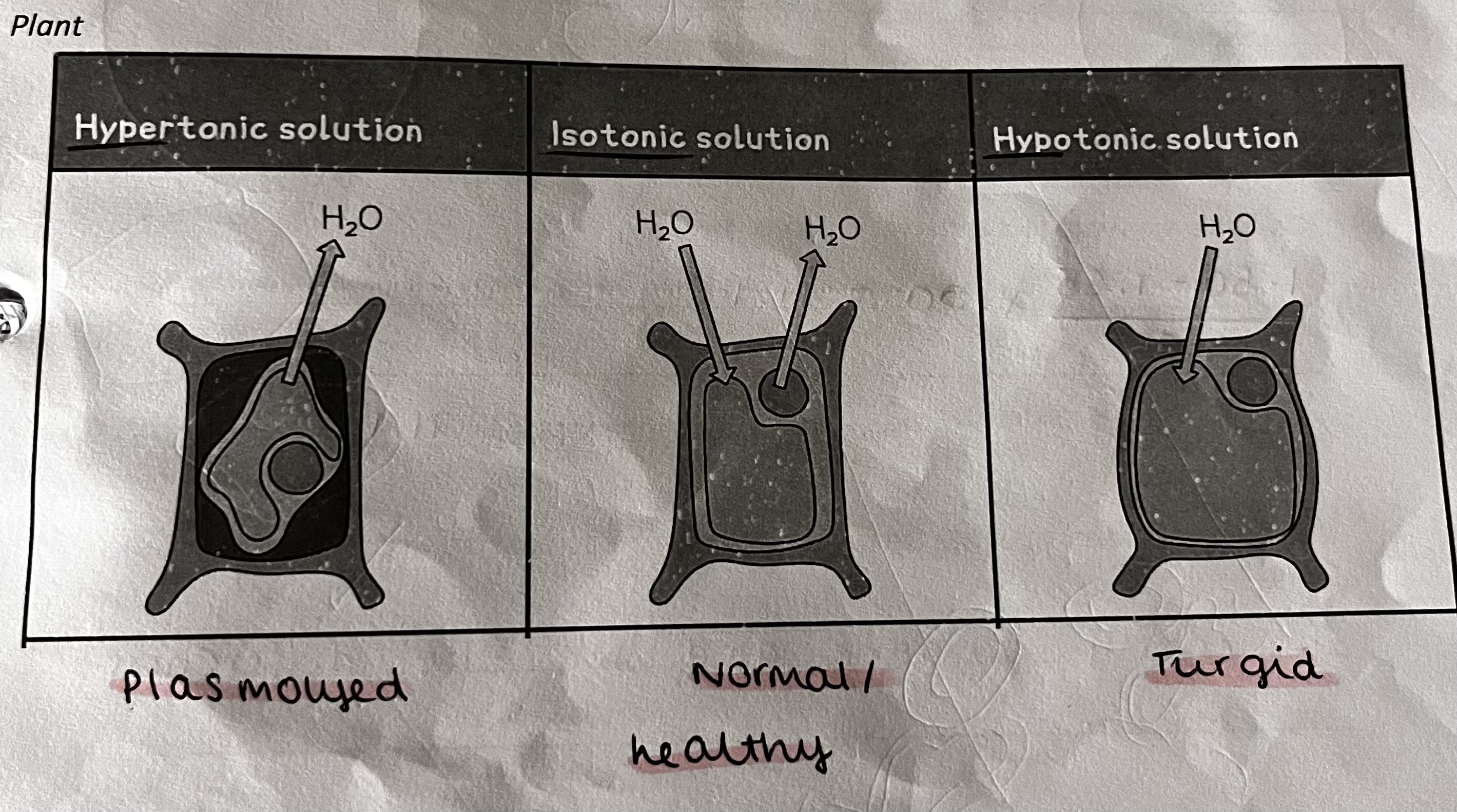
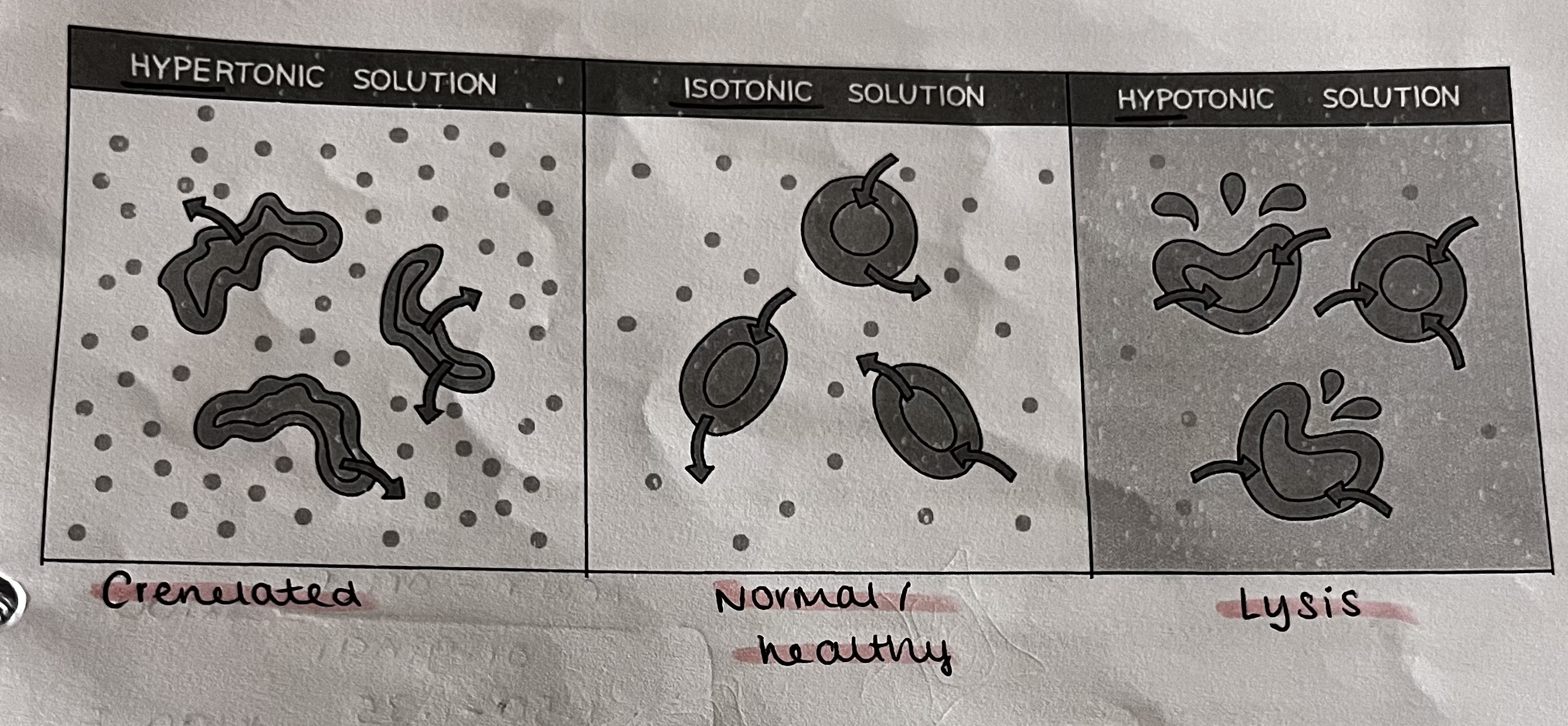
what is a hypotonic solution
the net movement of water INTO the cell via osmosis
hypOtonic - Outside
what is a hypertonic solution
the net movement of water OUT of the cell via osmosis
whats the difference between solute and solvent
solute - dissolves
solvent - dissolves something
in what state must particles be if they are going to be able to diffuse
liquid
gas
in solution
how does the following factor affect the rate of diffusion?
the difference in concentrations
higher concentration means a faster diffusion
how does the following factor affect the rate of diffusion?
larger surface area
the bigger the SA, the faster the rate of diffusion
how does the following factor affect the rate of diffusion?
shorter distance
diffusion is faster as there is less space to fill
how does the following factor affect the rate of diffusion?
higher temperatures
until a point, the higher the temperature, the faster the rate of diffusion
how does the following factor affect the rate of diffusion?
barrier is permeable to a substance
the more permeable a barrier is, the faster the rate of diffusion


where does energy come from in plants
mitochondria release energy in the form of ATP
produced during respiration
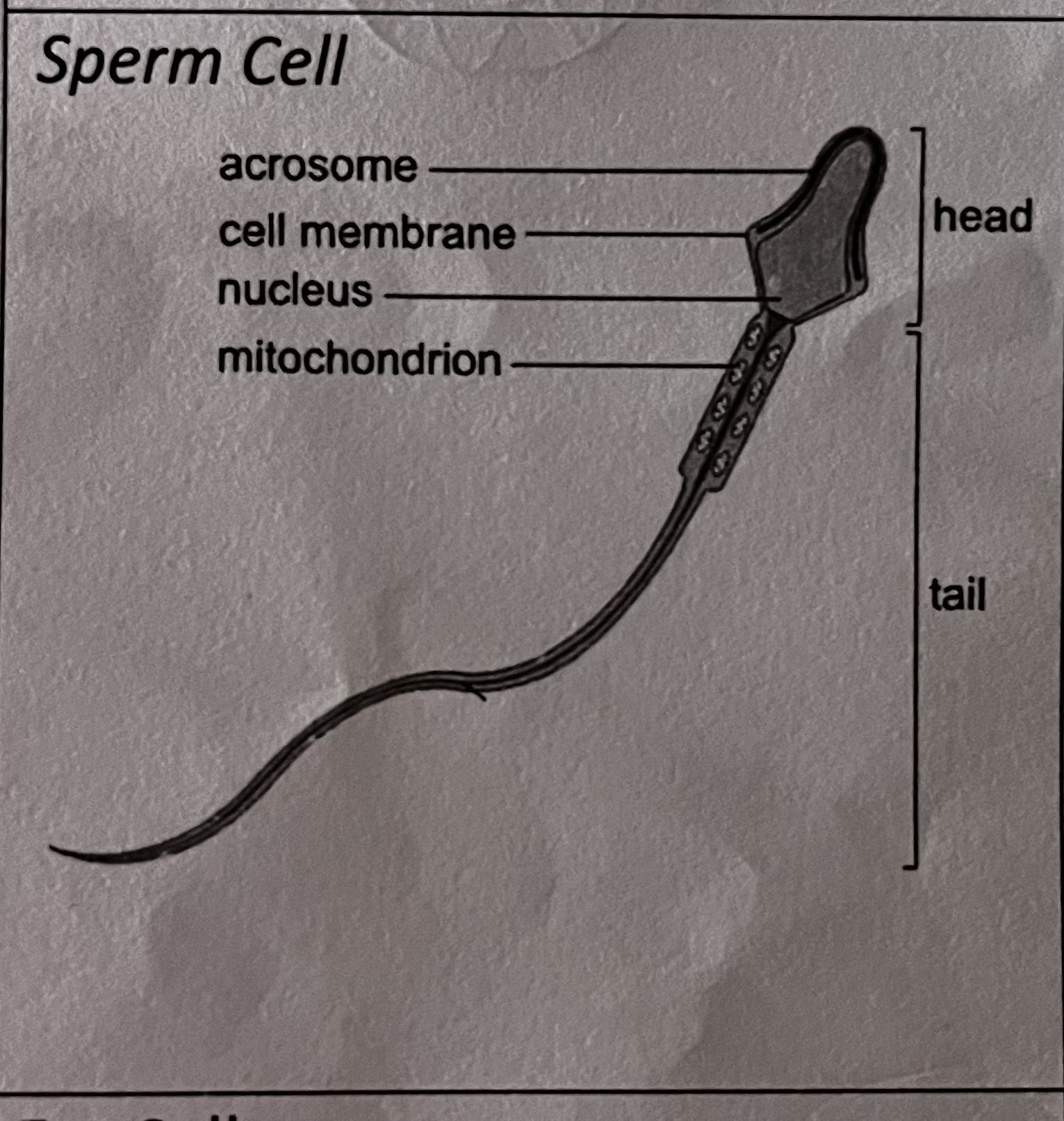
What is the role of the sperm cell
transfer genetic material from the male to the ovum
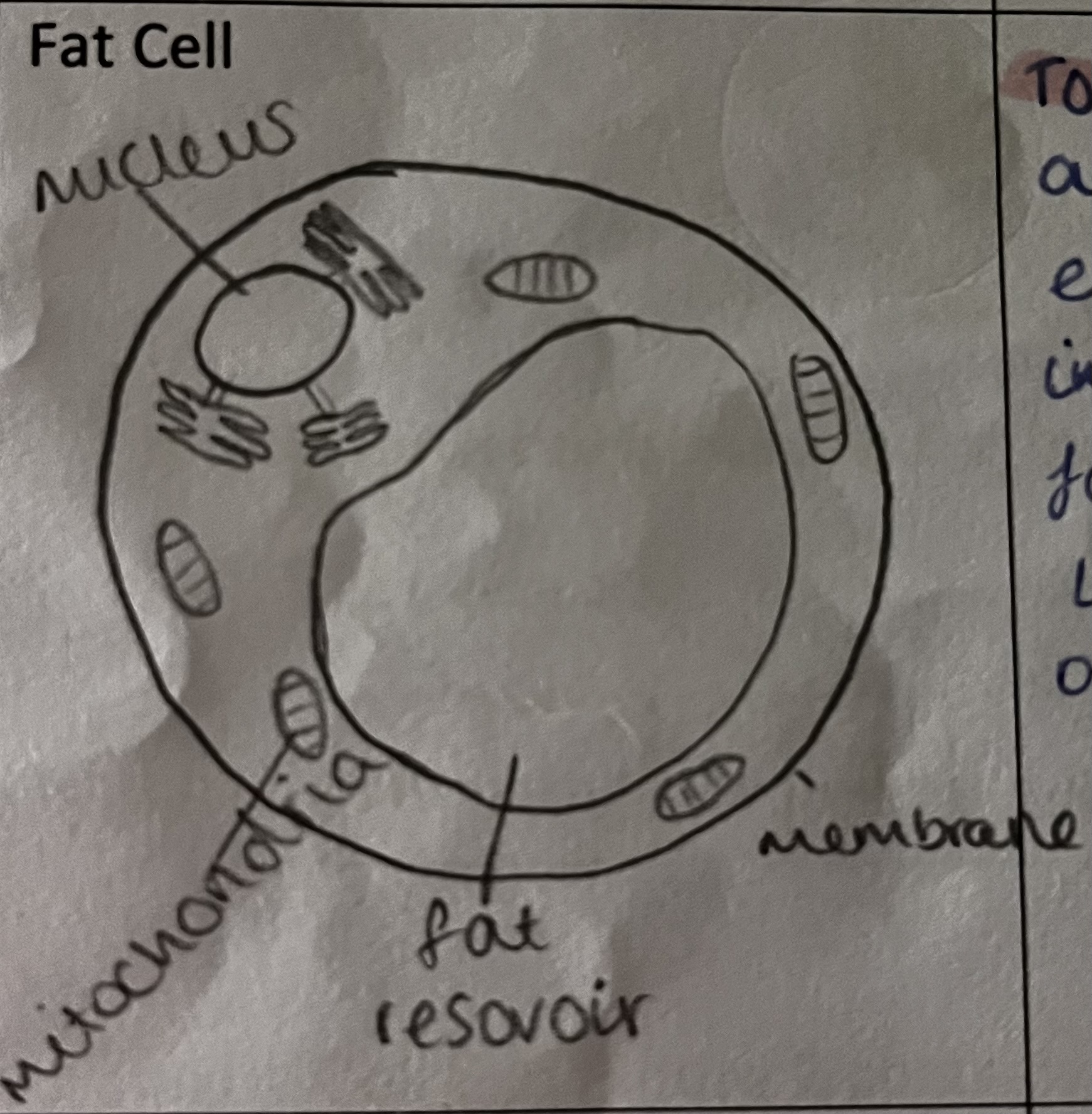
What is the role of the fat cell
store fat, used as a source of energy.
provide insulation and form protective layer around organs

What is the role of the red blood cell
delivers oxygen to body and removes co2
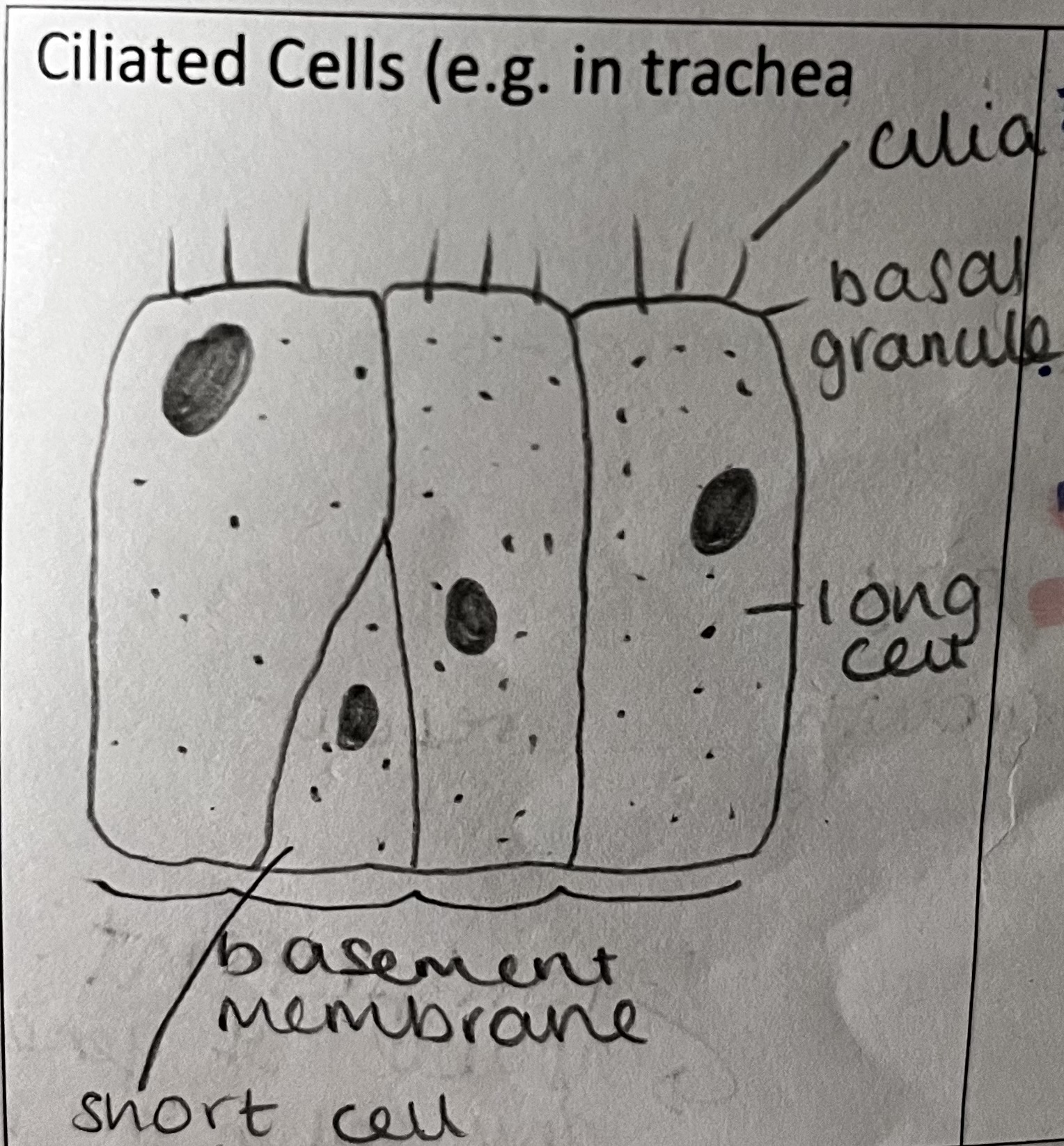
What is the role of the ciliated cell (eg in trachea)
hair like projections that move
job is to move mucus / liquid past the cells
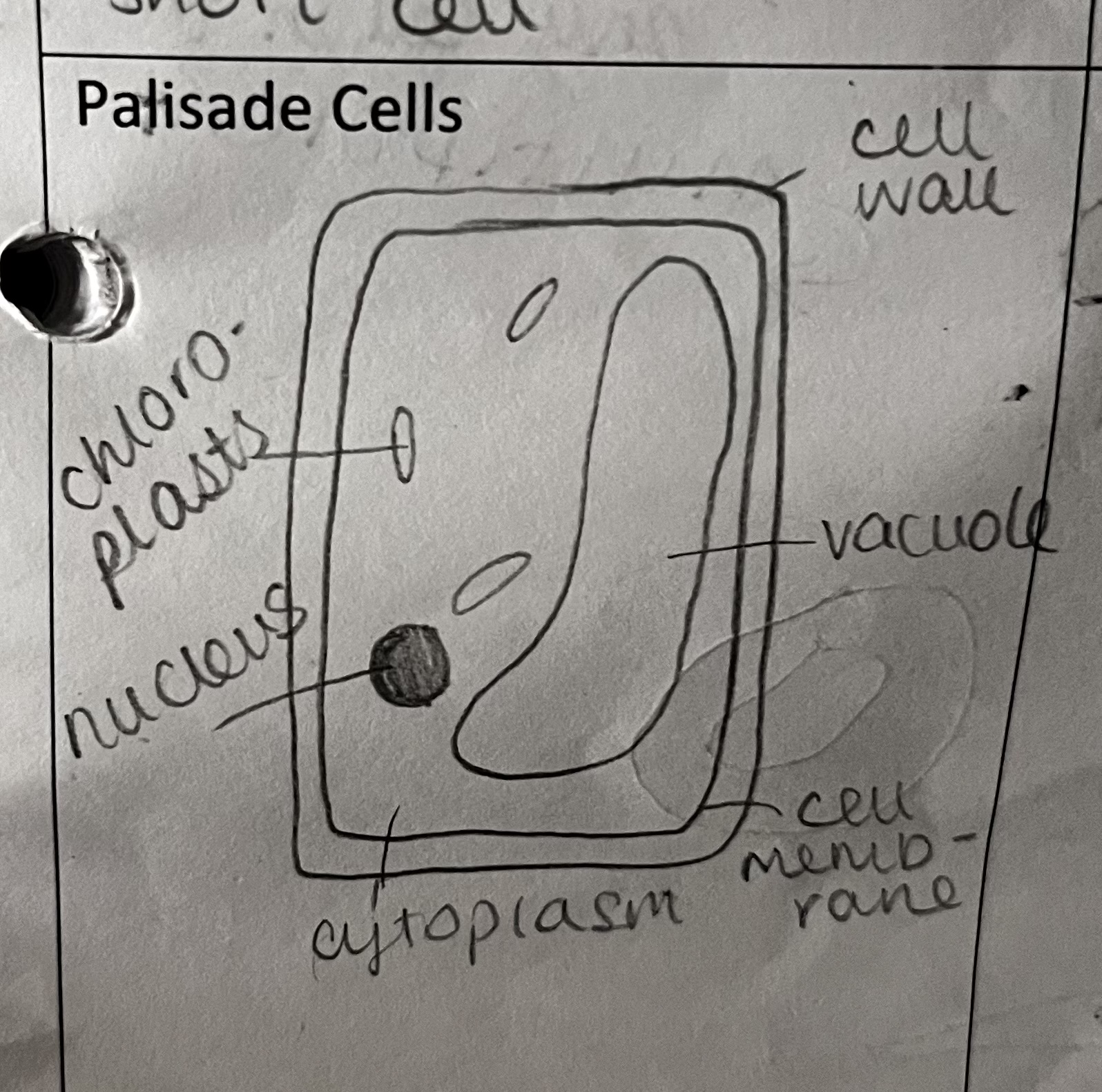
What is the role of the palisade cells
carry out photosynthesis
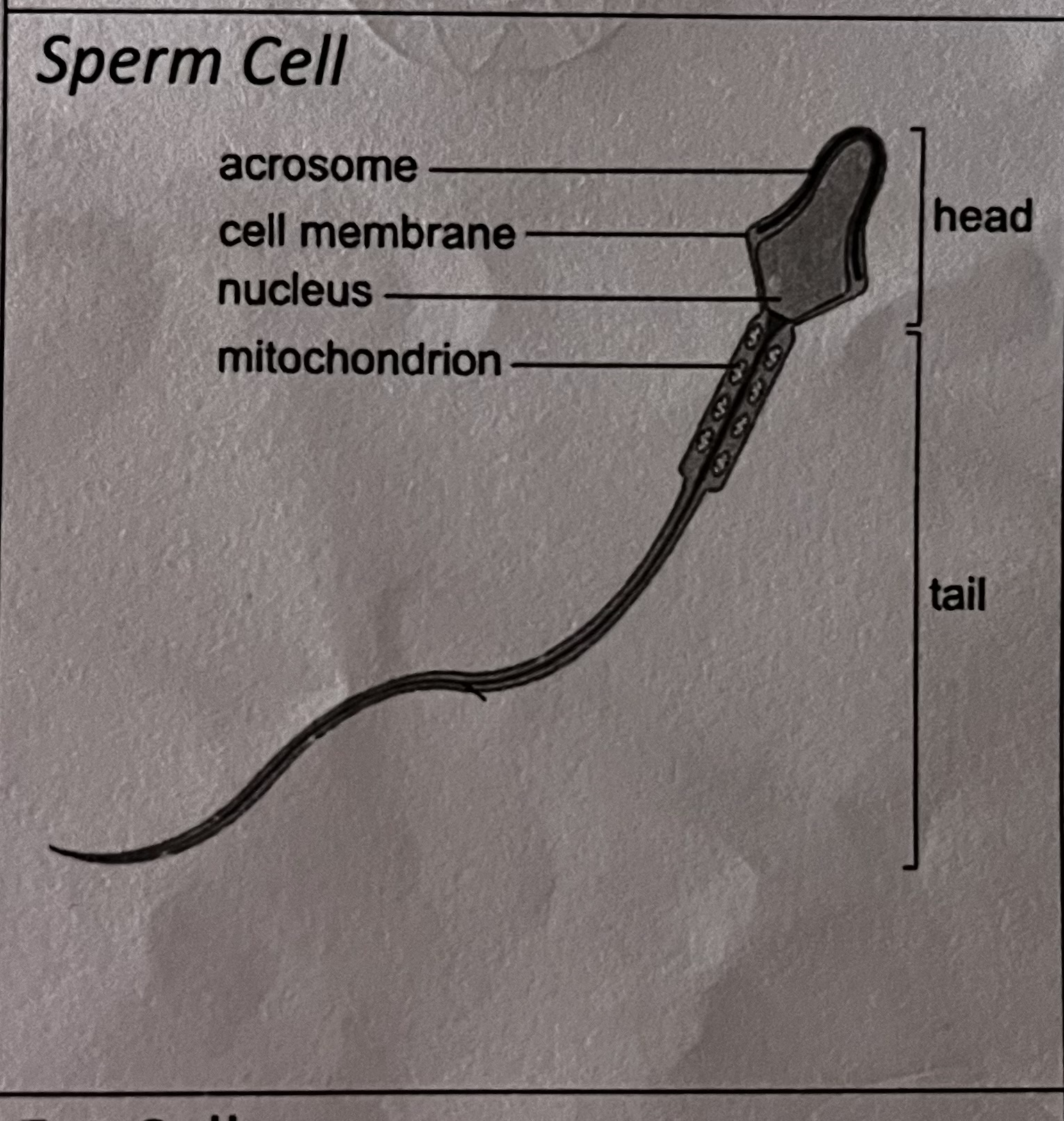
how is this specialised cell adapted to its role
has a flagellum
lots of mitochondria to transfer energy from chemical stores so flagellum can move
acrosome - stores digestive enzymes to break down the outer layer of the ovum to allow the sperm to transfer and incorporate its genetic material
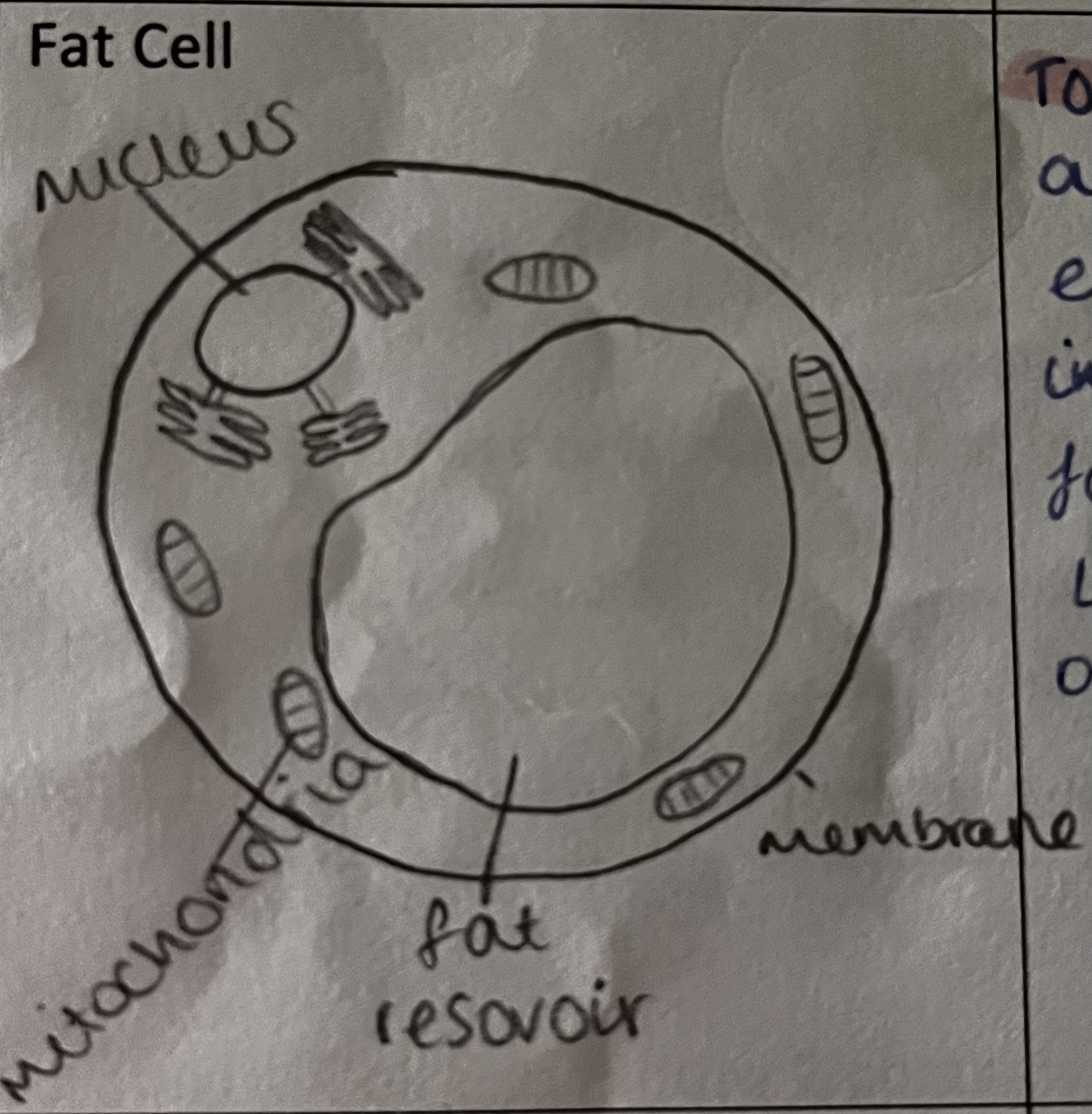
how is this specialised cell adapted to its role
small layer of cytoplasm surrounding a fat reservoir
can expand up to 1000x their original size as they fill with fat

how is this specialised cell adapted to its role
no nucleus / nucleoid region, more space for haemoglobin
Hb joins to oxygen
iron = red colour
replaced every three months
large sa from the biconcave shape to maximise diffusion of CO2 and O2
shape = flexible to go through capillaries
found in the circulatory system
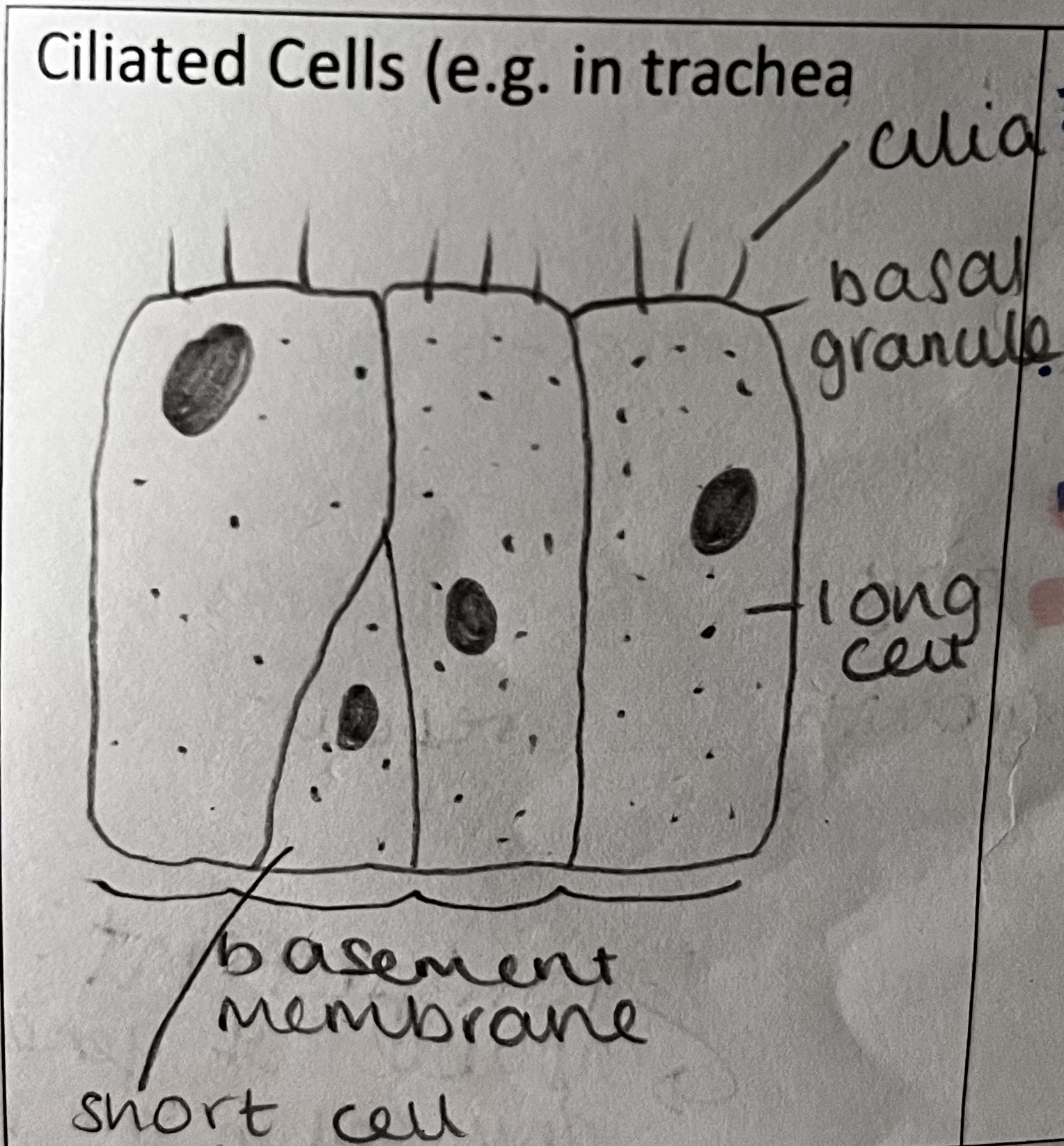
how is this specialised cell adapted to its role
lots of mitochondria to provide energy from respiration for cilia to move
found in the lining of airways and fallopian tubes
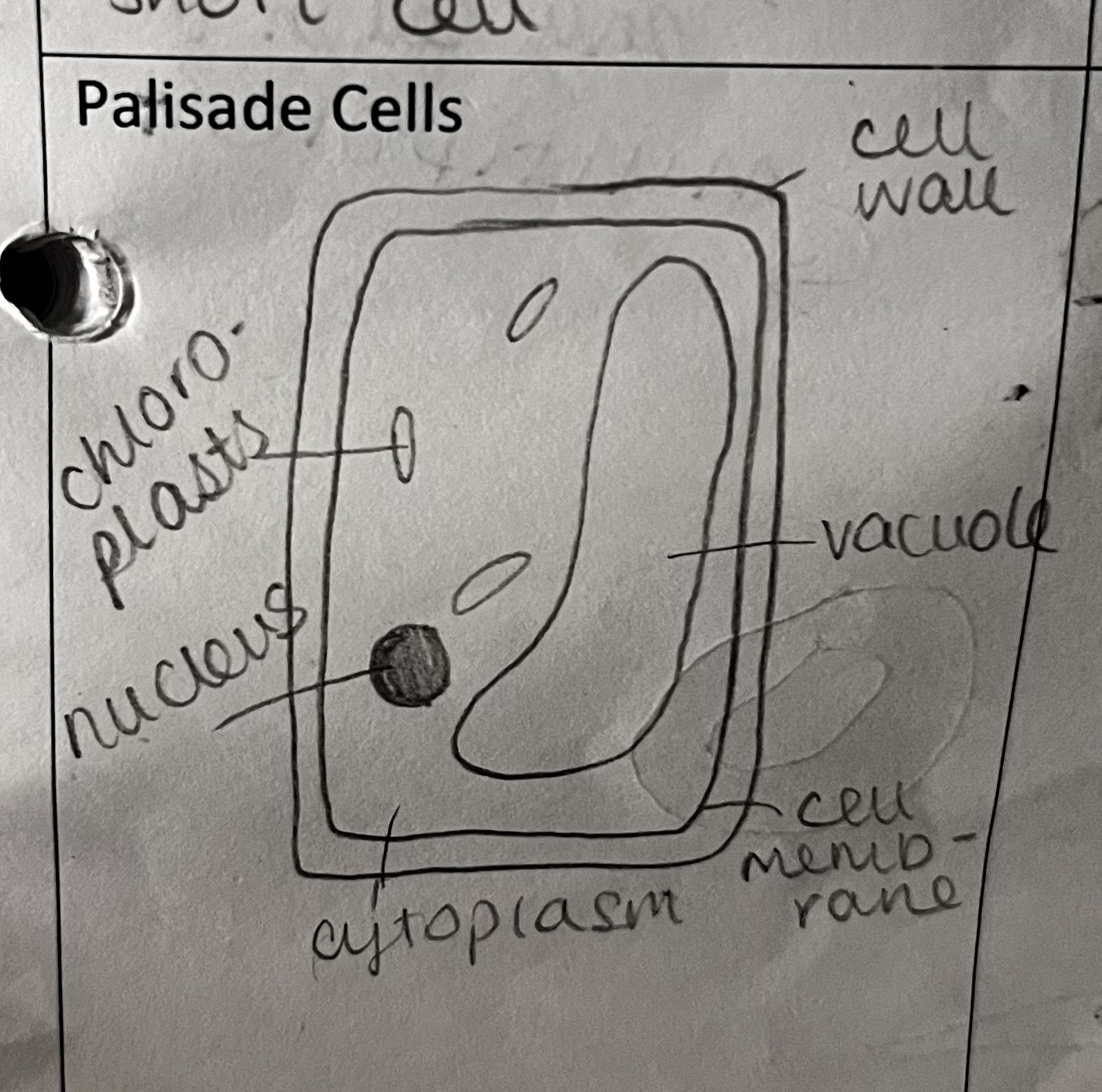
how is this specialised cell adapted to its role
found in the top of the leaf, closer to the sunlight
lots of tightly packed chloroplasts
regular shaped, closely packed cells form a continuous layer for efficient and maximum absorption of sunlight
what are 6 kinds of stem cells
neurons
egg cells
muscle cells
red blood cells
epithelial cells
fat cells (adipocyte)
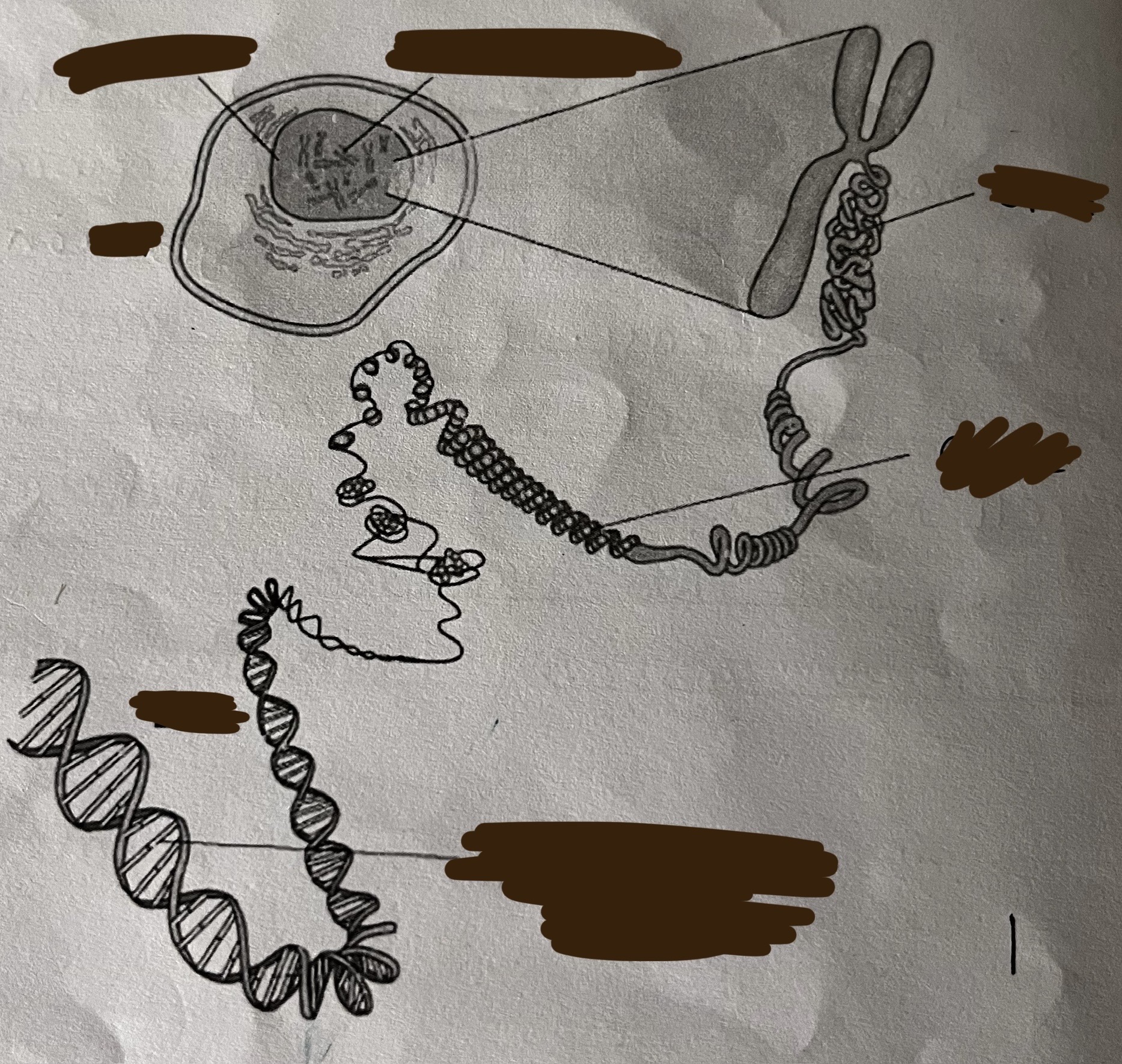
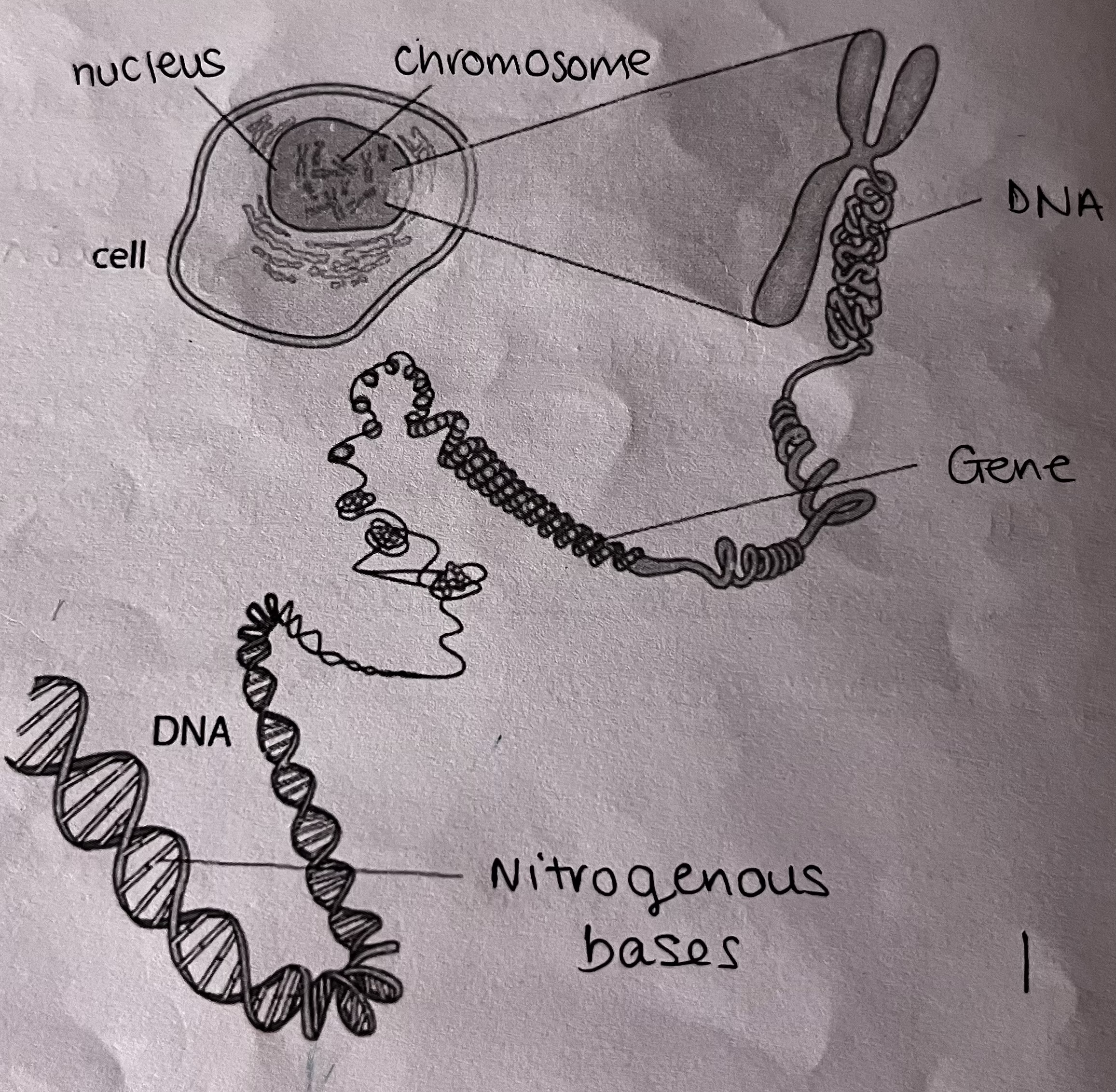
What is a stem cell?
an _ cell
a cell that divides by _ forming cells which can _ and become _
a cell which can develop into any type of specialised cell
used by the body during _ , _ and _
undifferentiated
mitosis
differentiate
specialised
growth
repair
development
What is interphase
when the chromosomes replicate so it contains two identical chromatids
What is prophase
chromosomes becomes visible by shortening and thickening
What is metaphase
chromosomes align at the centre of the parent cell, moved by spindle fibres
What is anaphase
the two chromatids in each chromosomes are pulled apart by spindle fibres to the opposite poles of the cell
What is telophase
there are now two nuclei
What is cytokinesis
the cells split in two to produce two daughter cells, each containing the same chromosomes